Abstract
Pectin has bad effects on the sensory quality of cigarettes. In order to reduce the pectin content in tobacco leaves, polygalacturonase (PG) gene was extracted from Aspergillus niger sw06, and recombinant plasmid pPICZαA was constructed and transformed into Pichia pastoris X33 to build an engineered strain X33/pPICZαA-PG. Transformant genomic fragment was 1,608 bp. The genomic fragment was amplified and recovered, and sequencing indicated that PG gene expression have been successfully inserted into P. pastoris expression vector. Positive clones were detected by SDS protein with a molecular weight of about 60 kDa. The enzyme production cycle of the recombinant strain was 36 h, and crude enzyme activity was 2872.91 U/mL. The fusion protein was purified by nickel Sepharose affinity chromatography. A clear band was detected and the concentration of recombinant protein was 8.1 μg/μL. It showed a good effect on degrading pectin after addition of the PG crude enzyme produced by recombinant yeast on the tobacco pulp. The optimized addition amount on process product line was 0.8%, which could reduce tobacco pulp pectin from 3.65 to 3.01% and achieve a degradation rate of 17.53%. Sensory evaluation showed that the effect was better when the addition amount of pulping was 0.4%.
1 Introduction
Pectin, a major structural component of plant cell walls, including tobacco [1], is a polysaccharide primarily composed of α-1,4-linked galacturonic acid residues [2]. During cigarette combustion, pectin affects the sensory quality and produces methanol that can be oxidized into formaldehyde and formic acid. In addition, 1–1.5% acetic acid is generated by pectin in fermentation process, which increases the spiciness and irritation of smoke and stimulate choking [3]. Furthermore, due to its hydrophilic nature, pectin exhibits strong hygroscopicity, adversely affecting tobacco combustibility. Elevated pectin levels in cigarette products have been correlated with increased tar generation [4]. Therefore, pectin is a negative factor for smoking safety.
With the development of biotechnology, the study on pectinase to degrade pectin in tobacco is increasing year by year [5]. Pectinase is a general term for a class of enzymes capable of degrading pectin molecules, with various types including polygalacturonase (PG), pectinesterase and pectinate lyase [6]. Sources of pectinase include animals, plants, and microorganisms, among which microorganisms are widely applied because of their wide variety, high yields, and high efficiency in the production of pectinase [7]. Research on the application of pectinase in tobacco processing has made significant progress in recent years, primarily focusing on efficient pectin degradation to improve tobacco quality, reduce the formation of harmful substances, and develop new enzymatic hydrolysis technologies. A penicillin-based method was used to degrade pectin content in reconstituted tobacco leaves, achieving pectinase activity as high as 3,000 U/mL and a pectin degradation rate of 28.6%. Subsequent evaluation of the treated tobacco samples for cigarette applications showed enhanced overall sensory quality, although a slight reduction in strength was observed [8]. Fan et al. [9] studied the changes in volatile aromatic components of tobacco stems after pectinase treatment, finding that the degradation products of carotenoids, phenylalanine, and neopentadiene in tobacco stems were increased to varying degrees, while the Maillard reaction products and phenylalanine degradation products also showed a certain degree of increase. Dai et al. [10] isolated high-yield pectinase-producing microorganisms from the surface of high-quality flue-cured tobacco leaves and applied them to inferior tobacco leaves to improve their usability. Yu et al. [11] sprayed a solution of pectinase onto tobacco leaves, effectively reducing the pectin content in the leaves and increasing the total amount of neutral aromatic substances.
In particular, fungi such as Penicillius sp., Aspergillus sp., Mucor sp., and Rhizopus sp. have high yields of pectinase [12]. However, natural strains often exhibit inherent limitations, including insufficient enzymatic activity and limited productivity. To address these challenges, physical, chemical, and genetic engineering approaches have been employed to develop high-performance industrial pectinase-producing strains [13]. The structural gene pelA of alkaline pectinase of Bacillus licheniformis DG-3 was obtained and amplified by PCR, which was successfully expressed in Escherichia coli [13]. An engineering strain E. coli BL21(pET29a-pelA) producing alkaline pectinate lyase was constructed. The endogenous poly arabinose AbnC gene was cloned from the genome of strain Penicillium sp. Y702 by overlapping PCR, and expressed it in Pichia Pastoris GS115, which increased the AbnC enzyme activity threefold [14]. The PG gene contained in Aspergillus oryzae PO strain was cloned and expressed it in Pichia pastoris GS115, which expressed enzyme activity 558 times higher than that of wild bacteria [15]. Genetically engineered strains (such as Pichia pastoris) have advantages such as short fermentation cycles and easy purification of enzyme products. Compared with the fermentation processes of natural fungi such as Penicillium, they are easier to scale up and can reduce the amount and cost of enzyme preparations in industrial production [16]. At the same time, microbial-derived recombinant pectinase can replace chemical pectin removal agents, reducing the risk of chemical residues in tobacco processing and complying with the development trend of green production [17].
Based on this, the current study used tobacco pulp from the production line of Henan Tobacco Leaf Processing Co., Ltd as the research material. The PG gene isolated from A. niger sw06 was cloned into a vector, and a pectinase genetically engineered strain was constructed. Through screening for high-yield strains, the optimized strain demonstrated effective pectin degradation in tobacco leaves, ultimately contributing to enhanced tobacco leaf quality.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Fungal strain
The Aspergillus niger strain sw06 was isolated and screened from tobacco field soil in Yunnan Province. This strain was identified by Shanghai Sanen Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China) using a 575 bp sequence length, and its sequence was found to be completely identical (100% homology) to that of the Aspergillus niger strain KHSMF44, thereby confirming it as Aspergillus niger. The Pichia pastoris strain X33 was provided by Shanghai Health Industry Co., Ltd. The identification of this Fugal strain was primarily based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region of the ribosomal RNA gene, specifically including partial sequences of ITS1, the complete sequence of the 5.8S rRNA gene, and the complete sequence of ITS2, combined with partial sequences of the 28S rRNA gene. The gene sequence of this fungus has been submitted to NCBI, with the accession number KP159438.1 GI:76881007.
2.2 Kits, enzymes, vectors, and reagents
Total RNA extraction was performed using the Total RNA Extractor Kit from Shanghai Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd (Shanghai Sangon Biotech); the cDNA synthesis kit, primers, and Pfu high-temperature polymerase were also purchased from the same company; the cloning vector pGAPZaA was provided by Shanghai Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. Culture media included YPD-Genomycin agar plates for strain screening, BMGY and BMMY media for bacterial culture and induction, and super optimal broth (SOB) medium for preparing competent cells. Additionally, the reagents used in the experiment included sorbitol, chloroform, isopropanol, and 75% ethanol (prepared with RNAse-free ddH₂O), while the substrate polygalacturonic acid was purchased from Sigma.
2.3 Instrument
Vertical high-speed centrifuge (Japan HITACHI), conversion instrument (Bio-Rad), analysis balance, pH meter (METTER TOLEDO), constant temperature water bath (Jintan Huafeng), centrifuge (Shanghai Anting), 722 spectrophotometer (Shanghai Yidian), magnetic agitator (Gongyi Yuhua), and electroporator (Thermofisher) were used for this research.
2.4 Extraction of total RNA from Aspergillus niger sw06
The mycelium of Aspergillus Niger cultured overnight was fully ground in liquid nitrogen until it was powdered, and RNA was extracted by Trizol method.
2.4.1 RNA extraction
Grind overnight-cultured Aspergillus niger mycelium thoroughly in liquid nitrogen until it becomes powder, then extract RNA using the Trizol method. 50–100 mg of mycelium powder was placed in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and homogenized with 1 mL of TRIzol reagent by thorough mixing, followed by 5 min incubation at room temperature. Subsequently, 0.2 mL of chloroform was added, the mixture was vortexed vigorously for 15 s and allowed to stand for 2 min before centrifugation at 12,000 g for 15 min at 4°C to separate phases. The aqueous supernatant was transferred to a new tube, mixed with 0.5 mL of isopropanol by gentle inversion, and incubated at room temperature for 10 min to precipitate RNA. After centrifugation at 12,000 g for 10 min at 4°C, the supernatant was discarded and the RNA pellet was washed with 1 mL of 75% ethanol, followed by centrifugation at 7,500 g for 5 min at 4°C. Finally, the air-dried RNA pellet was dissolved in an appropriate amount of DEPC-treated H₂O (promote dissolution at 65°C for 10–15 min).
2.4.2 RNA detection
RNA has its maximum absorption peak at 260 nm. Therefore, RNA concentration can be determined by spectrophotometry at 260 nm, with an optical density (OD) value of 1 corresponding to approximately 40 μg/mL of single-stranded RNA [18]. When performing spectrophotometric quantification using a 1 cm pathlength cuvette, the DNA sample should be diluted n-fold with ddH2O, using ddH2O as the blank control. The concentration of the sample before dilution can be calculated based on the OD260 value read at this point.
The OD260/OD280 ratio for pure RNA is 2.0, so the purity of RNA can be estimated based on the OD260/OD280 ratio. A low ratio indicates the presence of residual proteins; a high ratio suggests RNA degradation.
2.5 Construction of expression vectors
Synthesis of the first strand cDNA. According to the measured concentration of Total RNA of samples, 1 µL solution was accurately removed for reverse transcription to obtain 20 μL cDNA (RT product). The following reagents were added to the RNase-free tubes: Oligo-(dT) (0.5 µg/μL), 1 μL; Total RNA, X (1 µg) μL; RNase-free H2O, constant volume to 12 μL.
The procedure was performed according to the operating instructions of the first cDNA synthesis kit (Dalian Baogong): centrifuge for 5 s after mixing, bathe at 65°C for 5 min, then cool and centrifuge for 5 s. The tube in ice bath was added with the following reagents: 5× Reaction Bμffer, 4 μL; RNase Inhibitor (20 μ/μL), 1 μL; dNTP Mix (10 mmol/L), 2 μL; AMV RT (10 μ/μL), 2 μL. The above reagents were mixed and centrifuged for 5 s. RT-PCR was carried out at 42°C for 60 min and then heating at 85°C for 5 min, and the obtained reverse transcription products were stored at −20°C for later use.
Amplification of target cDNA. Two specific primers were designed according to the start codon and stop codon of galacturonase gene from A. niger sw06, the upstream primer: A7488MJ1FN (GACGAATTCCATCATCATCATCATCATGCTCCTTCTCGCGTCTCCGA) and downstream primer: A7488MJ1RN (GACTGCGGCCGCTTAGCAAGAAGCACCGGAAGG). Using the gene sequence of strain sw06 as the template for PCR amplification, the product segment was about 1,079 bp. The amplification system: the total volume of PCR was 50 μL, the first strand cDNA as the template, and the following reagent were added into the sterile microcentrifuge tube [19]: A7488MJ1FN, 2 μL; A7488MJ1RN, 2 μL; Template, 1 μL; dNTP, 1 μL (25 mM each); 10 × pfμ Buffer, 5 μL; Pfμ, 0.4 μL (5 µ/μL), then replenish with ddH2O to 50 μL. The procedure reacts at 95°C for 3 min, (95°C 30 s, 50°C 30 s, 72°C 70 s), with 22 cycles, at 72°C for 8 min and then the reaction products were stored at 4°C.
After PCR, 15 μL of amplified products were identified by agarose gel electrophoresis and the obtained images were analyzed. The DNA fragments were recovered according to the operation instructions on the centrifuge column agarose gel DNA recovery kit (UNIQ-10, Shanghai Sheng gong), and purified according to the instructions of the PCR purification kit.
Transformation of link vectors and screening of positive clones. The receptive cells were prepared by selecting strain X33 from plate YPD and inoculating it into medium YPD (20 mL). The recovered PCR product was mixed with pμC57 vector, and the reaction condition was at 16°C for 2 h, and then stored at 4°C [20]. The reaction system: PG, 4 μL; pμC57 Vector, 1 μL; Solution Ⅰ, 1 μL.
All the conjugated products (10 μL) were added into Pichia pastoris X33 receptive cells (100 μL) and gently mixed in ice bath for 30 min. After heating shock treatment at 42°C for 90 s, standing tube was cooled in ice bath for 5 min. Then, 900 μL SOB medium was added, which was oscillating incubated with 150 rpm at 37°C for 1 h.
One hundred μL positive clone DH5α was removed and coated, then incubated at 37°C for 12 h to form a single colony. Restriction endonuclease system: plasmid, 37 μL; EcoRI, 1 μL (10 μ/μL); NotI, 1 μL (10 μ/μL); 10× Bμffer BamHI, 10 μL. The enzyme digestion system of the new vector was as follows: pPICZαA, 1 μg; EcoRI, 1 μL (10 μL/μL); NotI, 1 μL (10 μL/μL); 10× Bμffer BamHI, 10 μL. The enzyme digestion of new vector was performed from the correctly sequenced plasmid, reaction sustained 3 h at 37℃. Then, the target gene was bound to the treated new vector. The binding systems of target gene and new vector were as follows: enzyme cut fragment, 10 μL (100 ng); enzyme digestion vector, 3 μL (100 ng); 10× T4 DNAligase Bμffer, 2 μL; T4 DNAligase, 1 μL (5 μ/μL); replenish with ddH2O to 20 μL.
According to the method described by Yu et al. [20], 20 μL of linearized monocopy plasmid was mixed with 80 μL of X33 competent cells. The mixture was then spread onto selective plates containing 0.5 mg/mL zeocin (200 μL per plate). Positive clones grown on the selection plates were subsequently isolated, and their plasmids were extracted for electrophoretic verification.
2.6 Measured enzyme activity expression and growth curve of X33/pPICZαA-PG
The activity of enzymes was measured according to the method established by Miller [21]. The protocol is as follows:
0.4 mL of 1% pectin solution and 1.0 mL of 0.04 mol/L Na2HPO4-0.02 mol/L citric acid buffer (pH 5.0) was pre-incubated in a water bath at 45°C for 5 min. Subsequently, 0.1 mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution (0.5 mg/mL) was added to initiate the reaction, which proceeded at 45°C for 30 min (with heat-inactivated enzyme solution serving as the blank control). The reaction was terminated by adding 3.0 mL of DNS (1% w/v) reagent, followed by boiling for 5 min to develop color. After cooling to room temperature, the reaction mixture was diluted to a final volume of 15 mL. The absorbance was measured at 540 nm wavelength by spectrophotometer, and galacturonic acid was quantified.
Enzyme activity calculation formula:
where N is the dilution ratio of enzyme solution, V T is the total volume of reaction, V E is the total volume of enzyme fluid, and t is the time.
A standard curve was prepared using a 1.0 mg/mL galacturonic acid solution. 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 mL of the standard solution were transferred into separate test tubes, and the volume in each tube was adjusted to 1.0 mL with deionized water. Subsequently, 3.0 mL of DNS reagent was added to each tube, followed by thorough mixing. The mixtures were then incubated in a boiling water bath for 7 min. After cooling to room temperature, the final volume was brought to 15 mL. Absorbance was measured at 540 nm using a UV spectrophotometer.
X33/pPICZαA-PG constructed with YPD liquid culture was inoculated into 120 mL BMGY medium at 4% inoculated volume, fermented for 24 h, inoculated into 3 L BMMY medium for culture, and then induced to express for 54 h. Methanol was added every 12 h at the induced concentration of 0.5%. Samples were taken every 6 h and the dry weight, pH and enzyme activity of the bacteria were photographed and measured at a fermentation temperature of 28℃ (220 rpm) to determine the optimum time for enzyme production. The supernatant after centrifugation was the PG solution expressed by X33, and the enzyme activity was measured. SDS-PAGE detection was performed using sample with volume 10 μL.
2.7 Purification and identification of recombinant proteins
The induced expression system of the step of measured enzyme activity expression and growth curve of X33/pPICZαA-PG was used for culture, and the protein expression level was about 0.2 mg/mL. The supernatant after centrifugation was collected and dialyzed into 50 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, and pH = 8.0 buffer solution. The supernatant was dialyzed at 4℃ for 12 h, centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 30 min, and then passed through the membrane for nickel agarose affinity chromatography.
Ten mL Ni-NTA was added into column, then the column was cleaned and balanced at a flow rate of 5 mL/min with binding buffer (50 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 0.1%TritonX-100, pH = 8.0). The volume of binding buffer was ten times that of the column volume. After the supernatant and column packing were mixed evenly, the sample was added into the column at a flow rate of 2 mL/min to collect penetrating liquid. Wash Buffer (50 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 10/20 mM imidazole, pH = 8.0) was used for eluting and collection at a flow rate of 5 mL/min. Elution collection was then performed with Elution Buffer (50 mM Tris, 300 mM NaCl, 500 mM imidazole, pH = 8.0) at 2 mL/min.
Following SDS-PAGE analysis, the 500 mM imidazole eluent was dialyzed against a dialysis buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.4), filtered, aliquoted, and stored at –80°C for further use.
The purified protein was determined by a non-interfering protein concentration assay kit (Shanghai Sangon Biotech SK3071). The concentration of BSA was 2 mg/mL and the volume of recombinant protein was 4 μL.
2.8 Application of tobacco sheet preparation
The recombinant yeast was induced and cultured by BMMY medium, centrifuged after fermentation for 36 h, and the supernatant liquid was frozen and dried to produce crude enzyme powder. Tobacco stem (4.34% pectin content) and tobacco fines (4.59% pectin content) were evenly mixed at a 5:4 mass ratio. The mixture was combined with water at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 9:20 (w/v) and thoroughly blended to produce tobacco pulp. Mechanical extrusion was employed to separate the pulp into an extract and filter residue. The residue was subsequently repulped, formed into paper sheets, and dried to yield a substrate with a final moisture content of 10% (w/w). The concentrate solution was reduced to 1/8 of the original volume and coated onto the prepared substrate at a 1:4 (w/w) concentrate-to-substrate ratio. The coated substrate was then dried to produce tobacco sheets with a final moisture content of 12% (w/w), yielding the reconstituted tobacco product. The pectinase was added to tobacco pulp at the dosage of 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8%, respectively, with a temperature of 40°C for 3 h. The pectin content in paper-making reconstituted tobacco was identified by carbazole colorimetry from experimental samples [22]. R: Degradation rate of pectin, Ca: Pectin content of concentrated solution before enzymatic hydrolysis, and Cb: Pectin content of concentrated solution after enzymatic hydrolysis.
Recycled tobacco leaves are cut into small pieces and processed into individual tobacco leaf pieces. These are then further processed into reconstituted tobacco strands. The tobacco leaf pieces are stored in a constant temperature and humidity chamber (relative humidity: (60 ± 5)%, temperature: (22 ± 2)°C) for 48 h before use, and are manually rolled into cigarettes. The experimental group consisted of cigarettes treated with enzymatic hydrolysis, while the control group consisted of cigarettes treated with inactivated enzyme solution. The samples were rolled according to the standard of 0.80 g ± 0.01 g per cigarette, in compliance with national standard [23], and balanced for 24 h in a constant temperature and humidity chamber at (22 ± 2)°C and (60 ± 5)% relative humidity. According to the current national standard for the evaluation of finished cigarettes GB5606.4-2005, the quality of cigarettes before and after enzymatic hydrolysis was assessed and evaluated from three aspects: aroma characteristics, smoke characteristics, and taste characteristics.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Total RNA quality identification and cDNA amplification
Total RNA extracted from A. niger sw06 was identified by agarose-gel electrophoresis with 1.5% mass fraction, and the results are shown in Figure 1. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the high-quality RNA was suitable for subsequent experiments. After the first strand cDNA of A. niger sw06 was synthesized by reverse transcription, the A. niger PG gene was amplified by PCR, and the electrophoretic diagram is shown in Figure 2. The sequencing analysis showed that the total length of the gene was 1,079 bp. Subsequent sequence analysis using the NCBI database revealed a 97% similarity between the obtained nucleotide sequence and that of Aspergillus niger. Based on this high sequence homology, the nucleotide sequence was identified as the PG from A. niger sw06. The total gene sequence of PG of A. niger and its encoded amino acid sequence are shown in Figure 3. Then, the expression vector pGAPZaA-PG was constructed by homologous recombination. The recombinant vector pPICZαA-PG, which contains the 1,079 bp PG gene insert, has a molecular weight of approximately 4.7 kb, which is approximately 1.1 kb larger than that of the empty vector pPICZαA (approximately 3.6 kb), consistent with theoretical calculations.
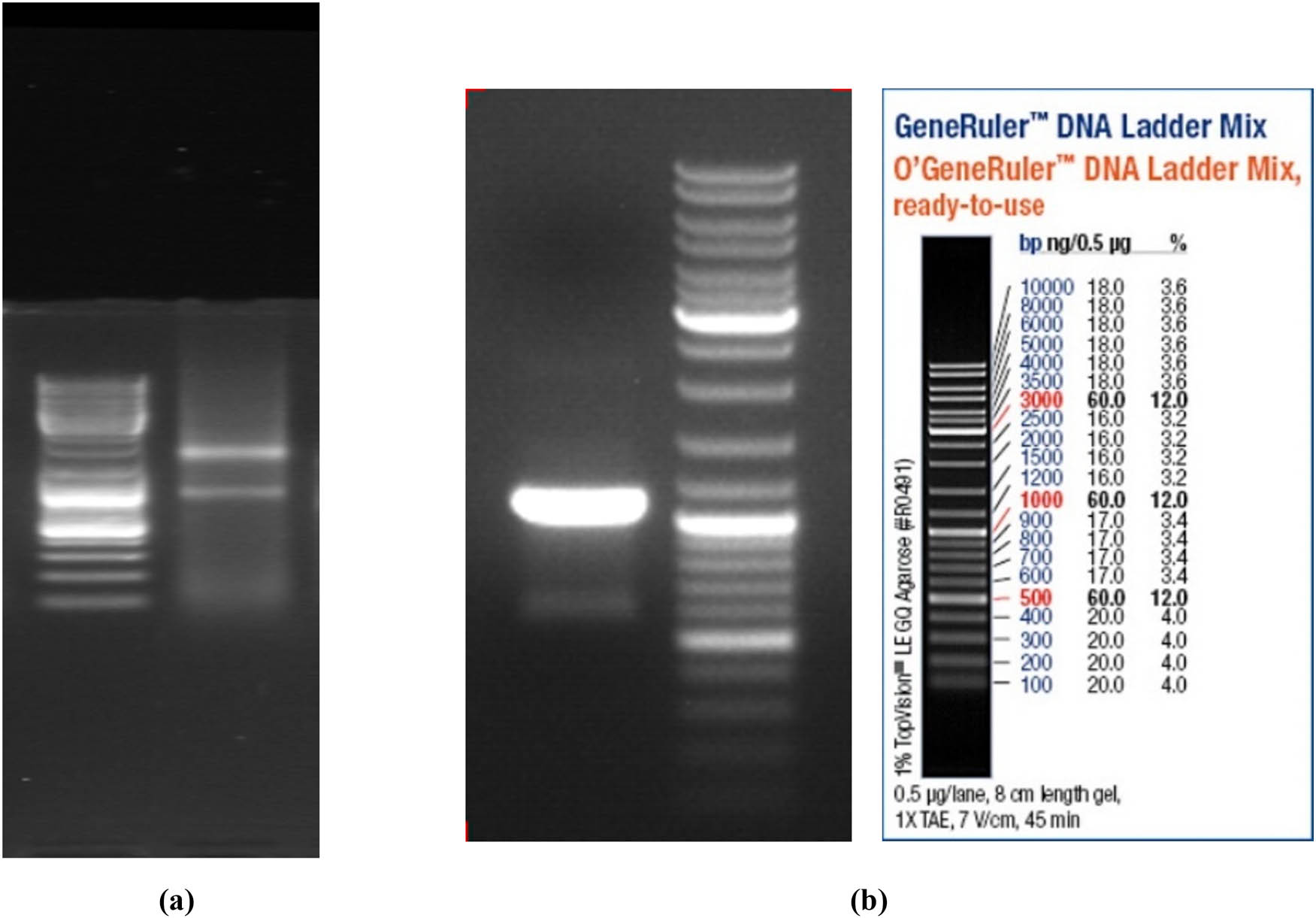
Total RNA detection of A. niger (a) and electrophoresis of PCR amplification products of the cDNA (b).

The gene sequence and amino acid sequence of PG from A. niger sw06.

Electrophoresis of the positive clones carrying expression vector X33/pPICZαA-PG by PCR amplification. Annotation: Lane M: DNA molecular weight standard; Lane N: Negative control; Lanes P1–P12: PCR products of positive clones.
3.2 PCR identification of positive cloning vector
The electrophoresis diagram in Figure 4 revealed that two bands were amplified in the transformed sub-genome. The blue arrow in the figure showed the AOX gene in the genome, about 2,200 bp. The other was a vector containing the target gene (about 1,079 bp), about 1,608 bp. Yeast genome (labor number SK8228) was extracted and annealed at 55℃, 30 cycles, using carrier universal primer AOX. The X33/pPICZαA-PG plasmid served as the positive control template. The recombinant strains generated via transformation—designated as X33/pPICZαA-PG < P1–P12 >, corresponding to 12 individual transformant clones—were used as test samples for PCR verification.

The growth curve of positive clone strain X33/pPICZαA-PG. Annotation:  Enzyme activity (U/mL),
Enzyme activity (U/mL),  Dry weighrt(g/L),
Dry weighrt(g/L),  pH.
pH.
3.3 Enzyme activity expression and growth cycle identification of positive clone X33/pPICZαA-PG
The positive clone X33/pPICZαA-PG was cultured in fermenter for 54 h, and the growth curve of X33/pPICZαA-PG was obtained by measuring the changes in dry weight, pH, and enzyme activity. Figure 5 showed that the pH value remained stable between 5.3 and 5.5 during the culture period. The enzyme activity of PG increased gradually in the first 36 h, and then decreased after reaching the peak at 36 h. The maximum PG activity reached 2872.91 U/mL at 36 h, indicating that the optimal culture time was 36 h. As shown in Figure 6, microscopic observation of the positive clone strain X33/pPICZαA-PG revealed that Pichia pastoris began budding and differentiation at 12 h. In conjunction with Figure 5, the mycelial dry weight increased rapidly between 12 and 18 h, suggesting vigorous cellular growth during this period.

The microscopic structure of positive clone strain X33/pPICZαA-PG.

The SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of the target protein from positive clone strain X33/pPICZαA-PG. Annotation: M, Marker, 75 60 45 35 25 15 10 kDa; N, Negative, X33/pPICZαA; P1-P12, Positive, X33/pPICZαA-PG.
3.4 Expression of target proteins, purification of recombinant proteins, and determination of protein concentration after purification
SDS-PAGE electrophoresis of the target protein in Figure 7 showed that the molecular weight of the protein was about 60 kDa, which was close to the theoretical analysis of the protein segment of 64 kDa. As can be seen from the western blot identification diagram in Figure 8, the molecular weight of the protein was about 60 kDa, which was close to the theoretical analysis of the protein segment of 64 kDa.

Western blotting identification of the target protein from positive clones strain X33/pPICZαA-PG. Annotation: M, Marker, 75 60 45 35 25 15 10 kDa; N, Negative, X33/pPICZαA; P2, P4, P6, P8, P9, P10, positive, X33/pPICZαA-PG.

The pure detection of recombinant protein. Annotation: M, protein marker; 1, purified target protein.
As shown in Figure 8, the molecular weight of recombinant protein was 60 kDa, and it had a high concentration that may have contributed to some degree of diffusion during electrophoresis.
The standard curve of BSA was y = ‒0.0078x + 0.9486, and R 2 = 0.9916. After purification of recombinant protein, the protein concentration was 8.1 μg/μL identified by SK3071 kit, indicating a high expression.
Compared with previous studies, Ibrahim et al. [24] expressed the PehA gene encoding PG carotovorum in Escherichia coli, reporting a molecular weight of 41.5 kDa; Liu et al. [25] expressed the cohesive PG (pehA gene) in Pichia pastoris, with a molecular weight of 40 kDa, both of which are lower than the molecular weight of the recombinant protein in this study. This difference may be attributed to variations in the amino acid sequences of PG from different sources. The recombinant protein produced in this study through genetic engineering demonstrated a molecular weight and functional properties consistent with those of its natural counterpart, confirming successful cloning and expression of the target gene [26].
3.5 Laboratory experiment and sensory evaluation results
Table 1 revealed that tobacco pulp, concentrated solution, and extract solution had a high content of water, which were suitable for enzyme application. However, the content of pectin in concentrated solution and extract solution was very low, so tobacco pulp was selected as the enzyme addition point. The tobacco pulp had a water content of 96.83%. After enzymatic hydrolysis with recombinant PG at concentrations of 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8%, followed by sheet forming, the pectin content decreased (Table 2). The 0.8% enzyme dosage showed the most effective degradation, reducing the pectin content from 3.65 to 3.01%, achieving a degradation rate of 17.53%. This result confirms the degradation activity of the recombinant enzyme on tobacco pectin, which is consistent with the high expression characteristics of the recombinant enzyme (8.1 μg/μL) in previous fermentation experiments, indicating that the enzyme preparation produced by the engineered strain X33/pPICZαA-PG has practical application potential.
Pectin content and moisture content of each sample
| Tobacco stem | Tobacco fines | Tobacco pulp | Extract | Concentrated solution | Substrate | Product | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture content % | 10.1 | 11.6 | 96.83 | 88.25 | 55.35 | 9.45 | 9.9 |
| Dry weight pectin content % | 4.34 | 4.59 | 3.65 | 0.09 | 0.60 | 4.94 | 5.54 |
Pectin content prior to and after enzyme degradation in tobacco pulp
| Tobacco pulp | Pectin content | Degradation rate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pectin content | 0.4% after enzymatic hydrolysis | 0.6% after enzymatic hydrolysis | 0.8% after enzymatic hydrolysis | 0.4% | 0.6% | 0.8% | |
| Pectin content | 3.65 | 3.44 | 3.19 | 3.01 | 5.75 | 12.60 | 17.53 |
Compared with existing studies, although pectinase derived from Penicillium can achieve a higher degradation rate of 28.6% [8], the recombinant enzyme in this study was obtained through a Pichia pastoris expression system, which has advantages such as high product stability and a simple purification process, making it more suitable for the safety and controllability requirements of enzyme preparations in industrial production. Additionally, a degradation rate of 17.53% is sufficient to effectively reduce pectin residues in tobacco pulp, providing a material basis for flavor improvement.
Sensory evaluation results (Table 3) showed that different enzyme addition levels had varying effects on flavor. At 0.4% enzyme addition, the treated tobacco exhibited enhanced aroma and reduced impurities, though with a somewhat weak aftertaste. The 0.6% enzyme treatment produced finer smoke with pleasant taste characteristics, albeit with slightly low concentration. Notably, the 0.8% enzyme treatment made the smoke smooth, taste strong, and aftertaste improved. However, it might have led to excessive pectin degradation, potentially causing an imbalance in flavor compound release.
Results of sensory evaluation
| Sample | Fragrance | Taste | Miscellaneous gas | Burning sensation | Dry sensation | Vestigial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tobacco pulp | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 |
| 0.4% | 6.25 | 6.50 | 6.50 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 5.75 |
| 0.6% | 6.00 | 6.00 | 5.75 | 6.00 | 6.50 | 6.25 |
| 0.8% | 6.00 | 6.50 | 6.00 | 5.75 | 6.75 | 7.00 |
This phenomenon can be further explained by referring to the research by Fan et al. [9], who demonstrated that pectinase treatment promotes the accumulation of volatile aromatic components in tobacco pulp, such as carotenoid degradation products and phenylalanine metabolites. Moderate degradation (such as 0.4% enzyme addition rate) can optimize the release of flavor compounds by improving cellular structure, while excessive enzyme levels may disrupt the matrix’s ability to retain flavor components, leading to reduced flavor harmony. Therefore, it is recommended to add 0.4% enzyme in tobacco pulp.
4 Conclusion
This study cloned a 1,079 bp PG gene from the Aspergillus niger sw06 strain, which shares 97% sequence similarity with known Aspergillus niger PG genes. A recombinant vector pPICZαA-PG was constructed using EcoRⅠ and NotⅠ, and transformed into Pichia pastoris X33 to obtain the engineered strain. Sequencing confirmed the successful integration of the target gene (1,608 bp in the transformed genome). The crude enzyme activity reached a peak of 2,872.91 U/mL after 36 h of cultivation in the recombinant yeast. In tobacco pulp applications, 0.8% recombinant PG achieved a pectin degradation rate of 17.53%; the most significant improvement in tobacco flavor was observed at a 0.4% addition rate. This study provides genes, strains, and optimized parameters related to efficient enzyme preparations for pectin degradation in tobacco processing.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the reviewer’s valuable comments that improved the manuscript.
-
Funding information: This research work was funded by the 2023 Henan Province Major Science and Technology Special Project (231100310200).
-
Author contributions: Jiafeng Bai: investigation, resources, visualization, formal analysis, and writing original draft. Xiaoqin Peng: supervision; Yi Zhou: supervision, project administration, and writing – review and editing; Lili Qu: supervision, project administration, writing – review and editing; Zhizhong Hu: supervision; Changtong Lu: review; supervision, validation, and project administration; Chunping Xu: funding acquisition and writing – review and editing. All authors accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript. Changtong Lu and Xu Chunping are the corresponding authors. The contribution levels of the two authors are equal.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Espitia PJP, Du WX, Avena-Bustillos RDJ, Soares NFF, McHugh TH. Edible films from pectin: physical-mechanical and antimicrobial properties - a review. Food Hydrocoll. 2014;35:287–96.10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.06.005Search in Google Scholar
[2] Harholt J, Suttangkakul A, Vibe Scheller H. Biosynthesis of pectin. Plant Physiol. 2010;153:384–95.10.1104/pp.110.156588Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Zhou S, Xu Y, Wang C, Tian Z. Pyrolysis behavior of pectin under the conditions that simulate cigarette smoking. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2011;91:232–40.10.1016/j.jaap.2011.02.015Search in Google Scholar
[4] Zhu D, Lee C, Zhang A. Relationship between harmful components of smoke and chemical components of Tobacco Leaves. Tob Sci Technol. 1999;4:25–7.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Jayani R, Saxena S, Gupta R. Microbial pectinolytic enzymes: A review. Process Biochem. 2005;40(9):2931–44.10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.026Search in Google Scholar
[6] Sharma N, Rathore M, Sharma M. Microbial pectinase: sources, characterization and applications. Rev Environ Sci Biol Technol. 2013;12:45–60.10.1007/s11157-012-9276-9Search in Google Scholar
[7] Man Z, Jing L, Qi H, Ma K, Hu X, Wang G. The purification and characterization of a novel alkali-stable pectate lyase produced by Bacillus subtilis PB1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;33(10):190.10.1007/s11274-017-2357-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Xu CP, Qu LL, Jiang Y, Ma YP, Sun S, Wang XJ, et al. Study on the degradation of pectin in high-concentration mixed pulp of remanufactured tobacco leaves by Microcyan pectinase. J Light Ind. 2019;34(01):27–35.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Fan X, Zi WH, Ao JC, Li BY, Qiao JF, Wang Y, et al. Analysis and application evaluation of the flavour-precursor and volatile-aroma-component differences between waste tobacco stems. Heliyon. 2022;8:e10658.10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10658Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Dai TC, Fan JQ, Zheng HN. Identification and enzyme activity determination of pectinase-producing bacteria from tobacco leaves. Microbiol Bull. 2011;38(6):816–24.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Yu JJ, Ma HY, Yang HW, Dong GF. Study on the degradation of pectin in tobacco leaves using pectinase. J Jiangxi Agric Sci. 2009;21(3):136–8.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Lee L, Sun Z, Hao J. Progress in the production and industrial application of pectinase. Adv Biotechnol. 2022;12:549–58.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Kenfaoui J, Lahlali R, Laasli S-E, Lahmamsi H, Goura K, Radouane N, et al. Unlocking the potential of rhizobacteria in Moroccan vineyard soils: biocontrol of grapevine trunk diseases and plant growth promotion. Biol Control. 2023;186:105338.10.1016/j.biocontrol.2023.105338Search in Google Scholar
[14] Manjusha WA, Josphine JS, Deepa PK, Sujatha S, Ahil Raj S. Biosoftening of banana pseudostem fiber using cellulase and pectinase enzyme isolated from Aspergillus niger for textile industry. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2023;21:170.10.1186/s43141-023-00617-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Guan Y, Wang D, Lv C, Zhang Y, Gelbic I, Ye X. Archives of microbiology: screening of pectinase-producing bacteria from citrus peel and characterization of a recombinant pectate lyase with applied potential. Arch Microbiol. 2020;202:1005–13.10.1007/s00203-020-01807-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Alqahtani YS, More SS, Keerthana R, Shaikh IA, Anusha KJ, More VS, et al. Production and purification of pectinase from bacillus subtilis 15a-b92 and its biotechnological applications. molecules. 2022;27(13):134195.10.3390/molecules27134195Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Dou Y, Yufei Z, Zabed HM, Yun J, Li J, Qi X. Fine-tuning the pathway and fermentation conditions to explore Pichia pastoris for high-level d-arabitol production from glucose. Bioresour Technol. 2025;424:132256.10.1016/j.biortech.2025.132256Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Calvo H, Mendiara I, Arias E, Gracia AP, Blanco D, Venturini ME. Study on the antifungal activity of the volatile organic compounds produced by Bacillus velezensis strains against postharvest fungal pathogens. Postharvest Biol Technol. 2020;166:111208.10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111208Search in Google Scholar
[19] Huang D, Song Y, Liu Y, Qin Y. A new strain of Aspergillus tubingensis for high-activity pectinase production. Braz J Microbiol. 2019;50:53–65.10.1007/s42770-018-0032-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Yu P, Wang X, Ren Q, Huang X, Yan T. Genome shuffling for improving the activity of alkaline pectinase in Bacillus subtilis FS105 and its molecular mechanism. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;35:165.10.1007/s11274-019-2749-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Miller GL. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem. 1959;31:426–8.10.1021/ac60147a030Search in Google Scholar
[22] Zhao J, Ouyang S, Qi H, Ma K, Hu X, Wang G, et al. Metabolomics and transcriptomics uncover the pectin hydrolysis during tobacco stem fermentation by Aspergillus niger. J Clean Prod. 2024;442:141005.10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141005Search in Google Scholar
[23] Zhu DH, Li CX, Zhang AZ. Relationship between harmful components in tobacco smoke and chemical components in tobacco leaves. Tob Sci Technol. 1999;4:25–6.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Ibrahim E, Jones DK, Hosseny NE, Escudero J. Molecular cloning and expression of cellulase and polygalacturonase genes in E. coli as a promising application for biofuel production. J Pet Environ Biotechnol. 2013;4:147.10.4172/2157-7463.1000147Search in Google Scholar
[25] Liu M, Dai X, Bai L, Xu X. Cloning, expression of Aspergillus niger JL-15 endo-polygalacturonase A gene in Pichia pastoris and oligo-galacturonates production. Protein Expr Purif. 2014;94:53–9.10.1016/j.pep.2013.10.025Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Rafique N, Bashir S, Khan MZ, Hayat I, Orts W, Wong DWS. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus subtilis with an endopolygalacturonase gene isolated from Pectobacterium. Carotovorum; a plant pathogenic bacterial strain. PLoS ONE. 2021;16(12):e0256562.10.1371/journal.pone.0256562Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

