Abstract
Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer (UCCRC) represents a significant complication of ulcerative colitis. CEBPB has been shown to promote the invasion of colon cancer cells. In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of CEBPB in the progression of cancers associated with colitis. The wild-type (WT) mice, transfected with a vector expressing CEBPB and siRNA targeting CEBPB, along with their littermate controls, were subjected to a challenge using azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate to establish a model of UCCRC. Colon tissues and blood samples were collected for analysis through hematoxylin and eosin staining and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Immunohistochemical staining was employed to assess protein expression. In the UCCRC model, mice transfected with vectors expressing CEBPB exhibited a reduction in weight loss and colorectal stenosis, as well as disordered colonic gland structure. Additionally, these mice demonstrated an increased number and size of tumors compared to WT controls. Furthermore, transfection with CEBPB resulted in a decrease in both the quantity and dimensions of tumors. NF-κB was found to enhance the phosphorylation level of STAT3 based on Western blot assay. The activation of NF-κB and STAT3 subsequently promoted the proliferation, invasion, and migration of colon cancer cells by clone formation assays, transwell assays, and scratch-wound assays. Moreover, rescue experiments indicated that CEBPB induced UCCRC through the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway. CEBPB mediated colonic injury in UCCRC mice by activating the NF-κB/STAT3 pathway. This finding reveals a previously unrecognized link between CEBPB and colitis-related tumorigenesis and provides new insight into UCCRC pathogenesis.
1 Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily impacts the mucosal and submucosal layers of the large intestine. It is characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain, hematochezia, and diarrhea [1]. The severity of UC can vary and may recur over time. Unfortunately, there is currently no universally accepted standard for the diagnosis of UC. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive approach that includes clinical presentation, biochemical analysis, fecal examination, endoscopy, imaging studies, and pathological findings [2]. Patients with UC face an increased risk of developing colon cancer, which represents a significant complication and a leading cause of mortality in cases of ulcerative colitis [3]. Furthermore, the severity of colon inflammation serves as an independent risk factor for the emergence of colon neoplasms in individuals with chronic UC.
Currently, various signaling pathways and pivotal molecular nodes are associated with colitis and colon cancer. Research has demonstrated that oxidative stress induced by nitrogen and oxygen compounds within the inflammatory microenvironment, coupled with the activation of NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways by inflammatory mediators, plays a crucial role in the progression from colitis to colon cancer [4,5]. Persistent activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway can result in DNA damage to intestinal epithelial cells and expedite the development of intestinal adenomas [6,7]. Mutant p53 has the capacity to prolong this activation, leading to chronic inflammation and contributing to the emergence of inflammation-related colorectal cancer [8,9]. Additionally, the activation of the interleukin (IL)-6-STAT3 signaling pathway can facilitate the progression of colonic inflammation to cancer [10].
CEBPB is a member of the CCAAT family of element-binding proteins, consisting of six basic leucine zipper DNA-binding proteins. It functions as a homodimer to specifically bind to regulatory regions within DNA [10,11]. CEBPB plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory genes and facilitating mitosis across various cell types. It was found that CEBPB is upregulated in samples of ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer (UCCRC) and constitutes part of an NF-κB-related gene signature [12]. Additionally, CEBPB regulates gene transcription in response to the expression of IL-1 and IL-6 by activating the NF-κB and STAT pathways [13]. This modulation can exacerbate the inflammatory microenvironment, which is critical to the cancer microenvironment. Chronic inflammation has been associated with malignant cell transformation and the onset of cancer. Therefore, this study aims to investigate how the expression of CEBPB may regulate the occurrence and progression of UCCRC.
2 Methods
2.1 Mice and UCCRC model
About 90 male wild-type C57BL/6 mice was obtained from Heyuan Biotechnology Co., LTD (SYXK(HU)2017-0003), which were 8–10 weeks old and weighed 20 ± 1.2 g. To ensure their health and safety, they were kept in a specific pathogen-free (SPF) environment. All in vivo procedures were conducted in compliance with the Animal Experiment Administration Committee of the university. To induce UCCRC, which was previously described in a study, mice were injected with azoxymethane (AOM) (12 mg/kg) intraperitoneally. After 7 days, they were administered 2% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) dissolved in drinking water for 7 consecutive days, followed by 14 days of regular drinking water for recovery. This cycle was repeated twice, followed by regular drinking water until day 84 when the mice were euthanized. Littermate controls were injected with normal saline (NS, 12 mg/kg) intraperitoneally, and the procedure was the same as mentioned earlier. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 9 (rAAV9) expressing a siRNA targeting CEBPB (siCEBPB), full-length CEBPB cDNA (CEBPB), and scramble control (NC) were generated by Biowit Technologies Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. In the CEBPB-treated groups, CEBPB or siCEBPB was tail vein-injected at a dose of 1 × 1011 vg on days 1, 3, and 5 during DSS treatment. In IkappaB kinase-2 (IKK2) inhibitor 2-[(aminocarbonyl)amino]-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-thiophenecarboxamide (TPCA-1)-treated groups, TPCA-1 (10 mg/mL; Tocris Bioscience, Ellisville, Missouri) was intraperitoneally injected from days 1 to 56 during DSS treatment. The colons were collected and cut open longitudinally to measure the tumor numbers and sizes. Simultaneously, the body weight and disease activity index (DAI) of the mice were recorded. Eventually, the mice were euthanized, placed in a plexiglass chamber with 5% isoflurane for 5 min, and decapitated when sufficiently sedated. Colorectal length and associated indicators were measured, and the colon tissues were either frozen in liquid nitrogen or fixed with formaldehyde (4%) and embedded in paraffin for downstream assays.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals, and has been approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Experiments of Hubei University of Arts and Science.
2.2 Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining for mice’s colon tissues
After the paraffin-embedded colon tissues of mice were cut into sections, they underwent a series of treatments to prepare them for observation under a light microscope. Xylene and ethanol were used to remove any remaining wax from the tissue samples, ensuring that they were clean and ready for staining. The Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining Kit (Beyotime Biotechnology Co., LTD, Shanghai, China) was then applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions, which allowed for clear visualization of the colon tissues. This process is essential in order to accurately analyze any changes or abnormalities present in the tissue samples. By observing these tissues under a microscope, researchers can gain valuable insights into various diseases and conditions affecting the colon.
2.3 Determination of the concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-6, and IL-1β
After the harvest of mice’s blood, the sera were carefully separated to ensure accurate results. The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits from Beyotime were used to determine the serum concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. This method is widely recognized as a reliable way to measure cytokine levels in biological samples.
The absorbance at a wavelength of 450 nm was measured according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Beyotime). This allowed for precise quantification of each cytokine present in the serum samples. These measurements are important because they provide insight into how different immune cells respond during an inflammatory response.
2.4 Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis
After the initial preparation steps of deparaffinization and rehydration, the sections underwent antigen retrieval with 1% sodium citrate to enhance the detection of specific proteins. To prevent interference from endogenous catalase, a 3% H2O2 solution was applied for 30 min to block its activity. The next step involved treating the sections with a 3% bovine serum albumin solution (Beyotime) to minimize non-specific binding of antibodies. Primary antibodies against E-catenin and Ki67 were then added and allowed to incubate overnight at 4°C. This process is crucial in identifying cellular markers that can provide insight into various biological processes such as cell proliferation and adhesion. By carefully following these procedures, researchers can obtain reliable results that contribute to our understanding of complex biological systems. After being washed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) thrice to remove any residual debris or contaminants, the sections were carefully incubated with HRP (horseradish peroxidase; Beyotime)-conjugated secondary antibody for 1 h at room temperature (RT). This step is crucial in order to ensure that the primary antibody has bound specifically to its target antigen. The use of a conjugated secondary antibody allows for easy detection and visualization of the primary antibody–antigen complex.
Once the sections have been incubated with the secondary antibody, they are developed using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB; Beyotime) chromogenic solution. DAB reacts with HRP to produce a brown precipitate at sites where the primary antibody has bound to its target antigen. This reaction can be monitored under a light microscope and provides valuable information about protein expression patterns within tissues. To counterstain the nuclei and provide contrast against the brown precipitate, hematoxylin is applied after development. Hematoxylin stains DNA-rich regions blue-purple, allowing for clear visualization of cell nuclei within tissue sections.
Finally, coverslips are added using mounting medium in order to protect and preserve the stained tissue sections. The slides can then be visualized under a light microscope at various magnifications depending on experimental needs. Overall, this protocol provides an effective method for detecting specific proteins within tissue samples through immunohistochemistry techniques. The immunoreactive score (IRS) is a widely used method for evaluating the expression of proteins in tissue samples. It takes into account both the percentage of cells that are positive for a particular protein and the intensity of staining. This allows researchers to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of how much of a given protein is present in different tissues or under different conditions.
The IRS system uses a scale from 0 to 4 to rate the percentage of positive cells, with higher scores indicating greater levels of expression. Similarly, staining intensity is rated on a scale from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating stronger staining.
By combining these two scores, researchers can generate an overall score that reflects both the amount and strength of protein expression in each sample. This information can be used to compare different tissues or experimental conditions and identify patterns or trends that may be relevant to disease processes or other biological phenomena.
2.5 Cell culture and treatment
The human CC line SW480 was procured from Icell Bioscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All cell lines were maintained in Dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 mg/mL streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2. To treat SW480 cells, 20 nM phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA, Sigma, St Louis, USA) or Colivelin TFA (Proteintech, Wuhan, China) in DMEM medium for 12 h was used.
2.6 Clone formation assay
For the clone formation assay, 4 × 10² SW480 cells were cultured in 2 mL of complete medium in 6-well plates for 7 days, with regular observations. The culture was terminated upon visible clone appearance. Cells were fixed with 2 mL of 4% paraformaldehyde for 10 min and stained with 2 mL of 5% crystal violet for 8 min. Petri dishes were inverted, and a transparent grid film was used to count clones visually, which were then recorded. The clone formation rate was calculated as follows: number of clones/number of inoculated cells × 100.
2.7 Transwell assays
Migration and invasion were assessed using a Boyden chamber assay (8-μm pore). CRC cells (1 × 105) were resuspended in 200 μL FBS-free medium and placed in the top chamber (BD, USA), while the lower chamber contained medium with 10% FBS. After 24 h, the cells were fixed, stained, and counted in six randomly selected fields under a microscope. The invasion assay was performed similarly using a modified Boyden chamber coated with Matrigel (BD Bioscience, USA).
2.8 Wound healing assay
Cells (1 × 105) were cultured in 6-well plates. After 16 h, the complete medium was replaced with low serum fresh medium (2%). Wounds were created using a 10 μL pipette tip once cells reached 90% confluence. The cells were washed twice with PBS to remove loose ones, and serum-free medium was added. To ensure comparability of wound areas, positioning marks were made at the center of each denuded surface. Scratch zones were photographed by inverted microscopy at 0 and 24 h. Image J software measured the migrating ability of cancer cells. Data presented were from three independent experiments.
2.9 RNA extraction and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) analysis
After killing the mice, their brains were quickly removed and dissected to isolate the cortex tissues. The tissues were then homogenized using a tissue grinder to break down cell membranes and release RNA. The Invitrogen TRIzol reagent (ThermoFisher) was used for RNA isolation, which involves adding chloroform to separate the aqueous phase containing RNA from other cellular components. After centrifugation, the RNA was collected from the upper layer and purified further.
To prepare cDNA for gene expression analysis, reverse transcription was performed using BeyoRT™ III cDNA transcriptase kit (Beyotime) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This involved annealing primers specific to target genes with extracted RNA templates in a thermal cycler machine at appropriate temperatures and durations.
The sequences of these primers were carefully designed based on known gene sequences or predicted mRNA transcripts using bioinformatics tools such as BLAST or Primer3 software. They are critical for amplifying specific regions of interest during PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reactions that follow reverse transcription step. The sequences of these primers were as follows: TNF-α, 5′-AGGAGGGAGAACAGCAACTC-3′ (forward) and 5′-TGTATGAGAGGGACGGAACC-3′ (reverse); IL-1β, 5′-TCTCCAGTCAGGCTTCCTTG-3′ (forward) and 5′-ATCTGGACAGCCCAAGTCAA-3′(reverse); IL-6, 5′-CCACTGCCTTCCCTACTTCA-3′ (forward) and 5′-ACAGTGCATCATCGCTGTTC-3′ (reverse); Ki67, 5′-CAAAGCAGGAAGCAACAGGT-3′ (forward) and 5′-TGCTAATGTGCTCCTCCACA-3′ (reverse); E-cadherin, 5′-ATCGCCTACACCATCCTCAG-3′ (forward) and 5′-CAGCCTGAACCACCAGAGTA-3′ (reverse); N-cadherin, 5′-GGCAATCAAGTGGAGAACCC-3′ (forward) and 5′-CCCTCTGGAACAGACCCATT-3′ (reverse); vimentin, 5′-GAAAGTGTGGCTGCCAAGAA-3′ (forward) and 5′-GTTTGACTCCTGCTTTGCCT-3′ (reverse); GAPDH, 5′-GCCCTGACTGGAGATGAAGT-3′ (forward) and 5′-AAGCGACCCTTGGTGTCATA-3′ (reverse). Subsequently, RT-qPCR analyses were performed using the SYBR premix EX Taq™ (Takara, Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s protocol in a Light Cycler 480 System (Roche Diagnostics, Grenzacherstrasse, Basel, Switzerland). The DNA amplification process is a crucial step in genetic research and analysis. In this study, the amplification was carried out using a specific protocol that involved maintaining the first cycle at 95°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles consisting of denaturation, annealing, and extension. The denaturation step involves separating the double-stranded DNA into single strands by heating it to high temperatures (95°C), while annealing allows primers to bind to complementary sequences on each strand of DNA. Extension then occurs when Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to the growing chain.
After amplification, gene expression levels were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCt method. This method involves comparing the expression level of an unknown sample against a calibrated sample with known gene expression levels. By calculating differences in threshold cycle values (Ct) between target genes and reference genes, researchers can determine relative changes in gene expression.
2.10 Western blot analysis
Protein extraction is a crucial step in many biological experiments, and the radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) used in this study is a commonly used reagent for this purpose. The addition of 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and protease/phosphatase inhibitors helps to prevent protein degradation during the extraction process. After solubilization, the proteins (30 µg) were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, which uses an electric field to separate proteins based on their size and charge. The separating gel has a higher concentration of acrylamide than the stacking gel, allowing for better resolution of smaller proteins. Finally, transferring gel to a PVDF membrane (Roche) allows for the detection of specific target proteins using antibodies. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-ki67, anti-E-cadherin, anti-N-cadherin, anti-vimentin, anti-p65, and anti-phospho-STAT3 (dilution of 1:800; Beyotime).
After washing, the membranes were carefully incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Pierce) to ensure optimal binding and detection of the target proteins. The use of a high-quality secondary antibody is crucial for obtaining accurate and reliable results in Western blot experiments. Following incubation, protein bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence Plus Western blot detection kit (Amersham Biosciences), which provides sensitive and consistent detection of even low-abundance proteins. The manufacturer’s instructions were followed precisely to ensure reproducibility across multiple experiments.
2.11 Data analysis
The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a statistical method used to compare the means of three or more groups. In this study, SPSS19.0 software was used to perform ANOVA on our data and calculate the mean ± S.D. (standard deviation). The results showed that there was a statistically significant difference between the groups with a two-sided value of P < 0.05, indicating that our hypothesis was supported by the data.
It is important to note that P < 0.01 was considered extremely statistically significant in this study, which suggests an even stronger level of evidence supporting our findings. This highlights the importance of using appropriate statistical methods and setting clear significance levels when analyzing research data.
3 Results
3.1 CEBPB affects the progression of UCCRC mice
To investigate the role of CEBPB in UCCRC, a mouse model was established using azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate (AOM/DSS) induction. The mice were meticulously selected and injected with AOM, followed by three cycles of DSS treatment as detailed in the Methods section and illustrated in Figure 1a. Subsequently, it was observed that the injection of CEBPB exacerbated the shortening of the colorectum and loss of colon weight induced by AOM/DSS (Figure 1b–d). Furthermore, there was a significant decrease in survival rates among UCCRC mice treated with CEBPB (Figure 1e). Concurrently, symptoms associated with UCCRC in these mice – including reduced activity, low energy levels, diminished responsiveness, and lacklusterness – were aggravated by CEBPB administration, as evidenced by decreased body weight (Figure 1d). Histological examination via HE staining revealed that CEBPB treatment led to more severe pathological alterations in UCCRC-affected mice (Figure 2a). Conversely, treatment with siCEBPB mitigated AOM/DSS-induced pathological changes in these animals. To further elucidate the influence of CEBPB on inflammatory responses within UCCRC mice, serum levels of pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β along with their expression within colon tissues were measured (Figure 2b–d). The results indicated that CEBPB significantly affected the levels of inflammatory cytokines associated with UCCRC progression. Specifically, it was found that CEBPB upregulated both serum concentrations and tissue expression levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, all critical mediators involved in inflammatory responses (Figure 2e–g).
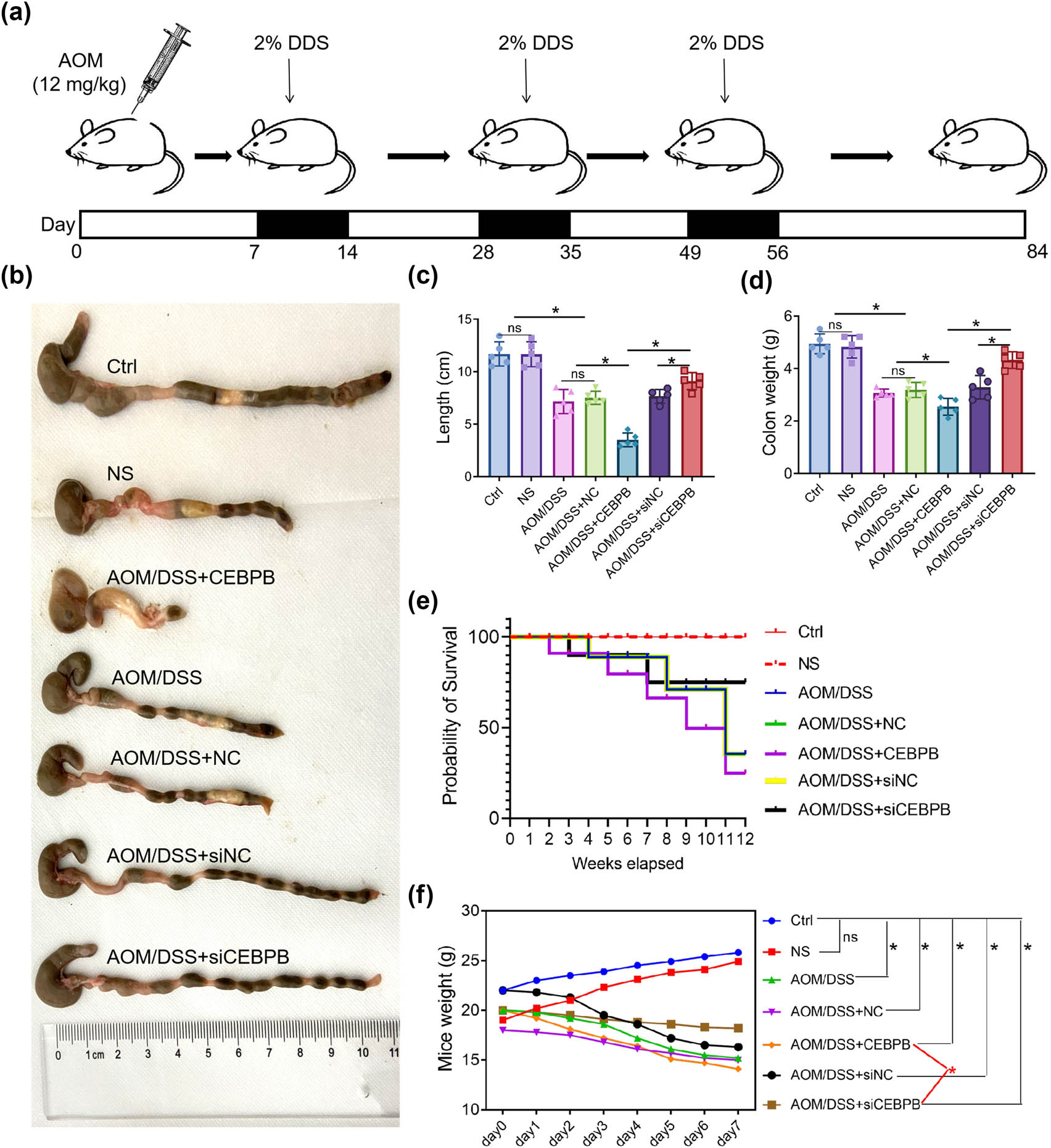
CEBPB affects the progression of UCCRC mice: (a) the modeling method of AOM/DSS-induced UCCRC in mice and treatment regimens, (b) representative photographs of AOM/DSS-induced UCCRC in mice, (c) colorectal length of mice, (d) colon weight of mice, (e) survival rate of mice, and (f) body weight of mice. N = 10, *P < 0.05.

CEBPB affects the pathogenic alterations and inflammatory response in UCCRC mice, and representative images of H&E-stained colorectal tissues of mice. The scale bar is 200 μm (a); the concentrations of TNF-α (b), IL-6 (c), and IL-1β (d) in mice’s sera were determined with ELISA kits; the expression of TNF-α (e), IL-6 (f), and IL-1β (g) in colon tissues was determined with RT-qPCR assay, as per the manufacturer’s protocol. *P < 0.05. The red arrows represent the pathological changes.
These findings suggest that CEBPB may play a pivotal role in promoting inflammation within UCCRC, which could contribute to disease progression. Further studies are warranted to comprehensively understand the underlying mechanisms driving these effects.
CEBPB alters the expression of the related proteins and the activation of NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Given that CEBPB accelerated the carcinogenesis of AOM/DSS-induced UCCRC in mice, we speculated whether CEBPB contributes to proliferation and metastasis in UCCRC. Intriguingly, IHC analysis revealed that AOM/DSS treatment increased Ki67 protein expression while decreasing E-cadherin protein levels in the colon tissues of mice (Figure 3a and b), which was consistent with the results obtained from Western blotting. Specifically, CEBPB led to a reduction in E-cadherin protein levels alongside an elevation of N-cadherin and vimentin protein levels in AOM/DSS-treated mice (Figure 3c–g). Furthermore, these findings were corroborated by RT-qPCR analysis (Figure 3h–k). Given that Ki67 is a pro-proliferation gene and E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin are associated with epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), it can be inferred that CEBPB potentially induces proliferation and metastasis in UCCRC, thereby facilitating its progression.

CEBPB alters the expression of the related proteins and the activation of NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway, IHC analysis of the protein expression of E-cadherin (a) and Ki67 (b) in the UCCRC tissues of mice. The scale bar is 50 μm and 100 μm. (c)–(g) Western blot analysis of the protein expression of Ki67, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimtein in the UCCRC tissues of mice. RT-qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of Ki67 (h), E-cadherin (i), N-cadherin (j), and vimentin (k) in UCCRC tissues of mice. (l) Western blot analysis of p-STAT3 and NF-κB-p65 expression UCCRC tissues of mice. (m) Western blot analysis of p-STAT3 expression in SW480 cells treatment with PMA. After PMA or Colivelin TFA treats SW480 cells, clone formation, transwell, and scratch-wound assay were used to detect cell proliferation (n), invasion (o), and migration (p). N = 3, *P < 0.05. PMA, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate; the red arrows represent the pathological changes.
Subsequently, significant activation of STAT3 phosphorylation and NF-κB-p65 expression in AOM/DSS-treated mice were observed. Notably, overexpression of CEBPB further activated the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway within this context. Conversely, silencing CEBPB inhibited the activation of the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway in AOM/DSS-treated mice (Figure 3l).
NF-κB enhances the phosphorylation of STAT3, thereby activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway in colon cancer.
After treatment with NF-κB’s activator (PMA) on colon cell lines (SW480), there is a significant upregulation in the phosphorylation of STAT3 (Figure 3m). Furthermore, both PMA and colivelin TFA, an activator of STAT3, enhance proliferation, invasion, and migration in SW480 cells (Figure 3n–p).
CEBPB activates the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway in UCCRC mice.
The NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway has been extensively investigated in relation to colon cancer, and it is widely acknowledged that this pathway plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of the disease. However, the precise mechanisms through which these transcription factors facilitate tumor progression remain inadequately understood. To illuminate this issue, researchers have focused their attention on CEBPB, a transcription factor that has been demonstrated to promote the advancement of colorectal cancer.
To investigate the influence of CEBPB on the activity of the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway, researchers assessed its effects on two critical markers: NF-κB-p65 and STAT3. P65 serves as a crucial transcription factor within the NF-κB signaling cascade, while STAT3 is an essential component of the STAT3 signaling pathway. By analyzing alterations in the levels of these proteins following modifications to CEBPB expression or activity, researchers aim to elucidate how CEBPB facilitates tumor growth and metastasis.
It was revealed that the expression of the protein p65 and the phosphorylation level of STAT3 in colon tissues of UCCRC mice were significantly upregulated by CEBPB, as evidenced by Western blot analysis (Figure 4a). Furthermore, TPCA-1, a dual inhibitor of STAT3 and NF-κB signaling, was employed to inhibit the activation of NF-κB/STAT3 signaling in AOM/DSS-induced UCCRC mice. Our results indicated that CEBPB counteracted the effects of TPCA-1 on colon length; specifically, the colon length in the AOM/DSS group was markedly reduced compared to that observed in the normal control group. Following treatment with TPCA-1, there was a partial restoration of colon length; however, it remained lower than that seen in the normal control group. Notably, CEBPB transfection effectively negated the beneficial effects of TPCA-1 on improving colon length (Figure 4b–d). Additionally, TPCA-1 treatment enhanced survival rates among UCCRC mice, while CEBPB abolished this effect (Figure 4e).

CEBPB activates the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway in UCCRC mice: (a) Western blot analysis of the protein expression of NF-κB-p65 and p-STAT3 in the UCCRC tissues of mice. (b) Representative photographs of the different groups in mice and (c) the colon weight of mice, (d) colorectal length of mice, and (e) the survival rate of mice. (f) Representative images of H&E-stained colorectal tissues of mice. The scale bar is 200 μm. (g) The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in mice’s sera were determined with ELISA kits. (h) The expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in colon tissues was determined with RT-qPCR assay, as per the manufacturer’s protocol. *P < 0.05. The red arrows represent the pathological changes.
Subsequently, TPCA-1 ameliorated pathological changes in colon tissue induced by AOM/DSS; however, CEBPB inhibited these effects on colonic tissue within UCCRC mice (Figure 4f). It was found that CEBPB significantly elevated serum concentrations and expressions of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β when compared to those in the AOM/DSS + TPCA-1 group (Figure 4g and h). Moreover, IHC and Western blot analyses demonstrated that TPCA-1 impeded protein expression levels associated with proliferation and EMT, including Ki67, N-cadherin, and vimentin (Figure 5a and b), while increasing E-cadherin expression levels. Importantly, CEBPB nullified these effects exerted by TPCA-1 in UCCRC mice.

CEBPB regulates the expression of proteins via activating NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway, IHC analysis of the protein expression of E-cadherin and Ki67 in the UCCRC tissues of mice. The scale bar is 50 μm. (b) Western blot analysis of the protein expression of Ki67, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in the UCCRC tissues of mice. (c) Real-time RT-qPCR analysis of the mRNA expression of Ki67, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in colon tissues of mice. N = 3, *P < 0.05. The red arrows represent the pathological changes.
Additionally, RT-qPCR analysis supported these findings regarding CEBPB’s influence on protein levels mentioned earlier (Figure 5c), demonstrating that CEPBP activated NF-kB/STAT3 signaling pathways within UCCRC mice.
4 Discussion
Intracellular inflammation is closely linked to colon cancer; however, the mechanisms underlying the transition from inflammation to malignancy remain to be fully elucidated [14]. Research has demonstrated that a critical state exists within the tumor microenvironment, specifically referred to as the tumor inflammatory microenvironment [15]. Previous research has indicated that inflammation-related factors may significantly contribute to the development of cancer metastases. As a crucial regulator of the inflammatory response, the nuclear transcription factors NF-κB and STAT3 play significant roles in modulating this process [16]. A detrimental cycle of “inflammation-tumor” is present within the tumor microenvironment. Once a tumor is established in the human body, the inflammatory environment created by tumor cells can activate the NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways [17]. This activation leads to an increased expression of various inflammatory cytokines within the tumor microenvironment, including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and other cytokines. The activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway enhances the secretion of the cytokine IL-6 [18]. Furthermore, in vivo expression of tumor suppressor genes P53 and P65 is influenced by IL-6 secretion, which subsequently induces cellular carcinogenesis and facilitates the differentiation of tumor cells [19]. Additionally, TNF-α secretion can also promote the occurrence of inflammatory responses in vivo. The secretion of the cytokine IL-6 can also activate the STAT3 signaling pathway, thereby influencing the entire process of tumor initiation and progression [20].
It has been reported that the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway can stimulate the release of inflammatory factors, thereby triggering an inflammatory response that enhances the immune response [21]. NF-κB plays a crucial role in conveying information by modulating tissue repair processes and engaging in tumor-associated inflammation. This involvement ultimately contributes to the maintenance of tumor growth and invasion. It has been demonstrated that the STAT3 signaling pathway significantly influences tumor cell growth, reproduction, metastasis, and apoptosis [22,23]. Furthermore, it plays a crucial role in tumor formation and development. It have demonstrated that CEBPB functions as a transcription factor, potentially playing a significant role in the inflammatory state [24]. Blocking CEBPB using siRNA significantly diminishes the production of IL-6 and IL-8 induced by tunicamycin. Endoplasmic reticulum stress can modulate the inflammatory response and extracellular matrix degradation through the activation of CEBPB expression. STAT3, CEBPB, and NF-κB are recognized as significant biomarkers in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and may serve as potential drug targets for its treatment [25]. Further research has established a connection between CEBPB and the enhanced nuclear expression of phosphorylated STAT3 [26]. Consequently, CEBPB may play a pivotal role in the “inflammation-cancer” nexus by modulating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway. In this study, CEBPB was utilized as a focal point to explore the mechanisms underlying UCCRC development.
In the present study, CEBPB was found to enhance the secretion and expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β), exacerbate AOM/DSS-induced pathological loss of colon tissue, and upregulate the expression of oncogenes. The inhibition of CEBPB mitigated the inflammation-driven carcinogenic effects associated with AOM/DSS, indicating that CEBPB facilitates the progression from colitis to colon cancer. Subsequently, we observed that CEBPB increased the expression levels of markers related to the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway (p65 and STAT3) induced by AOM/DSS. Treatment with a CEBPB blocker in AOM/DSS mice significantly reduced p65 and STAT3 expression. These findings suggest that CEBPB may promote the activation of NF-κB/STAT3 signaling.
To further validate this observation, an NF-κB/STAT3 signaling inhibitor (TPCA-1) was administered to AOM/DSS mice in order to assess both inflammatory responses and pathological damage within the colon tissue. Our results indicated that CEBPB obstructed TPCA-1’s therapeutic efficacy on UCCRC. Notably, our data demonstrated the activation of the NF-κB/STAT3 pathway in UCCRC mice alongside evidence that activated NF-κB stimulated STAT3 signaling. The activated NF-κB/STAT3 pathway was shown to facilitate the proliferation, invasion, and migration of colon cells. This underscores the significant role played by the NF-κB/STAT3 pathway in UCCRC development while highlighting how NF-κB can regulate STAT3 activation.
This study has validated the role of CEBPB in UCCRC mice at the animal level; however, the transition from colitis to colorectal cancer is a protracted process that involves epithelial phenotype switching. Future investigations will concentrate on the transformation of colon epithelial cells and tumor cells to gain a deeper understanding of how CEBPB functions in UCCRC.
Collectively, our findings indicate that CEBPB exacerbates pathological tissue damage in the colon and activates inflammatory responses. NF-κB enhances the phosphorylation levels of STAT3. The NF-κB/STAT3 pathway is activated in the colon tissues of UCCRC mice. This activation promotes the proliferation, invasion, and migration of colon cancer cells. In summary, our results suggest that CEBPB facilitates the progression of UCCRC by activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling cascade, thereby contributing to a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying the progression from colitis to colon cancer.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by Science and Technology Project of Health Commission of Hubei Province (WJ2021F066).
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and consented to its submission to the journal, reviewed all the results, and approved the final version of the manuscript. Shan Gao collected data and drafted the manuscript. Wei Wang and Ai-Xia Tian collected data. Xu-Dong Tong and Dao-Rong Wang analyzed and interpreted the data and performed the statistical analysis. Wei Yang and Jin-Min Chen concepted and designed the research, revised the drafted manuscript for important intellectual content, and received funding supports.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Le Berre C, Honap S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2023;402(10401):571–84.10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00966-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Kaenkumchorn T, Wahbeh G. Ulcerative colitis: making the diagnosis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2020;49(4):655–69. Epub 2020/10/31.10.1016/j.gtc.2020.07.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Segal JP, LeBlanc JF, Hart AL. Ulcerative colitis: an update. Clin Med. 2021;21(2):135–9. Epub 2021/03/26.10.7861/clinmed.2021-0080Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Elhefnawy EA, Zaki HF, El Maraghy NN, Ahmed KA, Abd El-Haleim EA. Genistein and/or sulfasalazine ameliorate acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulating INF-γ/JAK1/STAT1/IRF-1, TLR-4/NF-κB/IL-6, and JAK2/STAT3/COX-2 crosstalk. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;214:115673. Epub 2023/07/07.10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115673Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Zhang N, Liu C, Jin L, Zhang R, Wang T, Wang Q, et al. Ketogenic diet elicits antitumor properties through inducing oxidative stress, inhibiting MMP-9 expression, and rebalancing M1/M2 tumor-associated macrophage phenotype in a mouse model of colon cancer. J Agric Food Chem. 2020;68(40):11182–96. Epub 2020/08/14.10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04041Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Li B, Du P, Du Y, Zhao D, Cai Y, Yang Q, et al. Luteolin alleviates inflammation and modulates gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis rats. Life Sci. 2021;269:119008. Epub 2021/01/13.10.1016/j.lfs.2020.119008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Liuu S, Nepelska M, Pfister H, Gamelas Magalhaes J, Chevalier G, Strozzi F, et al. Identification of a muropeptide precursor transporter from gut microbiota and its role in preventing intestinal inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(52):e2306863120. Epub 2023/12/21.10.1073/pnas.2306863120Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] He W, Tang M, Gu R, Wu X, Mu X, Nie X. The role of p53 in regulating chronic inflammation and panoptosis in diabetic wounds. Aging Dis. 2024;16(1):373–93. Epub 2024/02/20.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Watanabe S, Hibiya S, Katsukura N, Kitagawa S, Sato A, Okamoto R, et al. Influence of chronic inflammation on the malignant phenotypes and the plasticity of colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021;26:101031. Epub 2021/06/08.10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101031Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Kim SL, Shin MW, Seo SY, Kim SW. Lipocalin 2 potentially contributes to tumorigenesis from colitis via IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2022;42(5):BSR20212418. Epub 2022/04/27.10.1042/BSR20212418Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Zhou Z, Shu Y, Bao H, Han S, Liu Z, Zhao N, et al. Stress-induced epinephrine promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness of CRC through the CEBPB/TRIM2/P53 axis. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):262. Epub 2022/06/08.10.1186/s12967-022-03467-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Ge CY, Wei LY, Tian Y, Wang HH. A seven-NF-κB-related gene signature may distinguish patients with ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2020;13:707–18. Epub 2020/12/11.10.2147/PGPM.S274258Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Horváth G, Horváth A, Reichert G, Böszörményi A, Sipos K, Pandur E. Three chemotypes of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L.) essential oil and their main compounds affect differently the IL-6 and TNFα cytokine secretions of BV-2 microglia by modulating the NF-κB and C/EBPβ signalling pathways. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):148. Epub 2021/05/24.10.1186/s12906-021-03319-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Parker BJ, Wearsch PA, Veloo ACM, Rodriguez-Palacios A. The genus alistipes: gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front Immunol. 2020;11:906. Epub 2020/06/26.10.3389/fimmu.2020.00906Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Tomkins-Netzer O, Niederer R, Greenwood J, Fabian ID, Serlin Y, Friedman A, et al. Mechanisms of blood-retinal barrier disruption related to intraocular inflammation and malignancy. Prog Retinal Eye Res. 2024;99:101245. Epub 2024/01/20.10.1016/j.preteyeres.2024.101245Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Malki A, ElRuz RA, Gupta I, Allouch A, Vranic S, Al Moustafa AE. Molecular mechanisms of colon cancer progression and metastasis: recent insights and advancements. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):130. Epub 2020/12/31.10.3390/ijms22010130Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Zhang Z, Du J, Xu Q, Xing C, Li Y, Zhou S, et al. Adiponectin suppresses metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through blocking the activation of NF-κB and STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):12729. Epub 2022/11/12.10.3390/ijms232112729Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Zhang Y, Wang S, Dai X, Liu T, Liu Y, Shi H, et al. Simiao San alleviates hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and JAK2/STAT3 signaling in hyperuricemia mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;312:116530. Epub 2023/04/26.10.1016/j.jep.2023.116530Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Hirano T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int Immunol. 2021;33(3):127–48. Epub 2020/12/19.10.1093/intimm/dxaa078Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Ren Q, Tao S, Guo F, Wang B, Yang L, Ma L, et al. Natural flavonol fisetin attenuated hyperuricemic nephropathy via inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling. Phytomedicine. 2021;87:153552. Epub 2021/05/18.10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153552Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Mukherjee T, Kumar N, Chawla M, Philpott DJ, Basak S. The NF-κB signaling system in the immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Sci Signal. 2024;17(818):eadh1641. Epub 2024/01/09.10.1126/scisignal.adh1641Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Ouyang S, Li H, Lou L, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Mo J, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Redox Biol. 2022;52:102317. Epub 2022/04/29.10.1016/j.redox.2022.102317Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Zou S, Tong Q, Liu B, Huang W, Tian Y, Fu X. Targeting STAT3 in cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):145. Epub 2020/09/26.10.1186/s12943-020-01258-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Westin ER, Khodadadi-Jamayran A, Pham LK, Tung ML, Goldman FD. CRISPR screen identifies CEBPB as contributor to dyskeratosis congenita fibroblast senescence via augmented inflammatory gene response. G3 (Bethesda). 2023;13(11):jkad207. Epub 2023/09/17.10.1093/g3journal/jkad207Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Berendsen S, van Bodegraven E, Seute T, Spliet WGM, Geurts M, Hendrikse J, et al. Adverse prognosis of glioblastoma contacting the subventricular zone: Biological correlates. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0222717. Epub 2019/10/12.10.1371/journal.pone.0222717Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Han JH, Jang KW, Myung CS. Garcinia cambogia attenuates adipogenesis by affecting CEBPB and SQSTM1/p62-mediated selective autophagic degradation of KLF3 through RPS6KA1 and STAT3 suppression. Autophagy. 2022;18(3):518–39. Epub 2021/06/09.10.1080/15548627.2021.1936356Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

