Abstract
Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 of the genus Gerbera is of importance in Chinese ethnic medicine. In this research, the whole genome DNA of G. piloselloides was extracted and sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq platform, its chloroplast genome was assembled and annotated, and its sequence characteristics were analyzed using bioinformatic methods. The results showed that its chloroplast genome has a length of 151,871 bp and contains 133 annotated genes, consisting of 88 protein-coding genes, 8 rRNA genes, and 37 tRNA genes. In total, 202 simple sequence repeat sites and 43 long repeats were detected in G. piloselloides, mainly consisting of mono-nucleotide and tri-nucleotide repeats, with A/T as the major base composition. The chloroplast genome of G. piloselloides contains 22,772 codons, with leucine-coding codons being the most abundant. Comparative genomics showed that the genome structure, composition and variation were basically the same in the Asteraceae family. The phylogenetic tree analysis indicated a close relationship between the genus Atractylodes and Gerbera, consistent with the morphological classification. The research of the G. piloselloides chloroplast genome will lay a foundation for species discrimination, genetic evolution analysis, and DNA barcode construction in Gerbera plants.
1 Introduction
The chloroplast is a plant cell organelle enclosed by a double membrane that contains chlorophyll and can complete photosynthesis, which plays an important regulatory role in plant growth [1]. The chloroplast genome usually exists in the form of double stranded circular molecules, and most higher plants have a tetrad structure, which determines the conservatism of higher plants in gene expression, species formation, and other aspects [2,3]. The widespread application of high-throughput sequencing has resulted in an increasing number of plant chloroplast genome sequences [4]. To date, more than 55,351 plastid genome sequences have been uploaded to NCBI (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/home, up to November 15, 2024). Compared to the nuclear genome, the chloroplast genome is more conserved in genome structure, length, GC content, gene sequence, and gene quantity [5,6]. Chloroplast genome studies demonstrated that the chloroplast genome has a wide range of applications in species identification, systematic evolution, and population genetics research. Sheng [7] carried out the molecular marker development and discriminated the plant of Asparagus cochinchinensis with chloroplast genome. He et al. [8] conducted research on the chloroplast genome sequencing analysis of Cucurbita ficifolia in the family Cucurbitaceae. Song et al. [9] provided the chloroplast genome sequence of eight Delphinium species, and performed a comparative analysis of this genus. Wang et al. [10] obtained molecular markers of pan-chloroplast genome sequences from the maize germplasm resources. He et al. [11] conducted research on the chloroplast genome of Taraxacum and developed molecular markers to distinguish their weedy relatives. Moreover, the chloroplast genome provides more molecular markers to accurately identify and distinguish different species and it is, therefore, known as the “super barcode” for species identification [12]. Gerbera piloselloides Cass. is a plant of the genus Gerbera, belonging to the Asteraceae family. There are approximately 80 species of this genus worldwide, mainly distributed in Africa, followed by East Asia [13]. There are approximately 20 species in China, mainly distributed in southwestern provinces, such as Guizhou, Yunnan, and Guangxi. G. piloselloides is a commonly used medicinal plant among ethnic minorities in China, promoting lung function, relieving sweating, cough, and promoting diuresis, Qi and blood circulation. But the variety of Gerbera plants used for medicinal purposes in various regions is not standardized [14]. This not only hinders the implementation of unified drug management nationwide but also poses great risks to drug safety. And research on G. piloselloides has mainly focused on its chemical composition [15,16,17]. Little research was concentrated on chloroplast genomes in plants of the genus Gerbera, and only 36 single nucleotide sequences have been obtained from NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/?term=Gerbera%20piloselloides). The only chloroplast genome of Gerbera jamesonii (NC:046760.1) was registered in this genus. In this research, the complete chloroplast genome sequence of G. piloselloides was successfully obtained. And my primary objectives are to (1) investigate the plastome structure and sequence divergence of G. piloselloides; (2) identify simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and divergence hotspots of G. piloselloides; and (3) preliminarily elucidate the phylogenetic relationships among the Chinese group of medicinal species and related taxa within Asteraceae.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sampling, DNA extraction, and sequencing
G. piloselloidis was sampled from the campus of Guizhou University in July, 2023 (26°25′39.62″N, 106°40′5.81″E). Fresh leaves (100 mg) were ground, and whole-genome DNA was extracted using the CTAB method [18]. The sampled DNA with a concentration greater than 200 ng/µL and an A260/A280 value between 1.8 and 2.0 was sent to Nanjing Genepioneer Biotechnologies Co., Ltd for quality inspection. Qualified DNA was used for library construction, and Illumina double-end sequencing was performed in Illumina NovaSeq platform of Genepioneer Biotechnologies Co. [19].
2.2 De novo assembly, gap filling, and gene annotation
The raw data were filtered and obtained with adapters for subsequent assembly. The chloroplast genome sequences were assembled using CLC Microbial Genomics Module 24.1.1 (https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/clc-microbial-genomics-module-latest- improvements/) and Perl scripts to run NOVOPlasty v4.2 with default parameters [20]. BLAST (https://blast.Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) was performed to determine the sequence of contigs splicing (similarity index great than 90%), referring to NCBI’s published G. jamesonii (NC:046760.1). Then, the Geneious Prime 2024.0 software was used for splicing to obtain the final circular chloroplast genome and perform manual calibration (https://www. geneious.com/download-previous-versions). The resulting genome was annotated using online annotation software Annotation of Organellar Genomes [21] (https://chlorobox.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/geseq.html) and GetOrganelle [22] running Perl scripts (https://github.com/Kinggerm/GetOrganelle). The online servers version 2.0 (http://lowelab.ucsc.edu/tRNAscan-SE/) [23] were used to identify the tRNA gene, and the annotated sequence was uploaded to NCBI to register the sequence number. The OGDRAW version 1.3.1 visualization tool for chloroplast genome circle diagram was used to draw its genome map [24].
2.3 Repetitive sequence analysis
Repetitive sequences are important molecular sequences used for species identification, genetic diversity, population evolution, and other research [8]. The Tandem Repeats Finder v4.09 (https://tandem.bu.edu/trf/trf.html) was used to discriminate tandem repeat sequences [25]; the parameters were set as Match 2, Mismatch and Delta 7, PM 80, PI 10, Minscore 50, MaxPeriod 500. Then, the SSR Hunter v1.3 [26] was used to assess simple repeats of sequences with default parameters.
2.4 Analysis of codon preference
The protein-coding sequences were obtained from the chloroplast genes of the experimental materials using Geneious software (https://www.geneious.com/) and saved in FASTA format. The CodonW (https://codonw.sourceforge.net/) script was used to calculate the relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of protein-coding sequences. Codons with RSCU > 1 were considered preferred [27].
2.5 Chloroplast genome variation analysis
The G. piloselloidis chloroplast genome was compared and analyzed with published chloroplast genomes of the main Chinese representative medicinal plants from the Asteraceae family (Atractylodes macrocephala: NC_044671.1; Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium: NC_057202.1; Artemisia annua: NC_034683.1; Taraxacum officinale: NC_030772.1; Arctium lappa: NC_042724.1; Xanthium Strumarium: NC_042232.1; Helianthus annuus: NC_ 007977.1). The IRscope website (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/irapp/) was utilized to visualize the expansion and contraction of large single-copy (LSC), inverted repeat (IR), and small single-copy (SSC) regions in the chloroplast genomes of representative groups from the Asteraceae family.
Collinearity analysis of chloroplast genome was performed using the Geneious software (https://www.geneious.com/). Chloroplast genome alignment was conducted using the MAFFT version 7 software [28], and we manually proofread the alignment sequences using the BioLign 4.0.6 version software (https://www.softpedia.com/get/Science-CAD/BioLign.shtml), calculated chloroplast genome sequence nucleotide polymorphism (Pi) using the DnaSP version 6 software, set a search window length of 600 bp, step size of 200 bp, and plotted using the R program [29].
2.6 Phylogenetic analysis
To explore the phylogenetic relationship of the chloroplast genome of G. Piloselloidis and determine its taxonomic position, the online sequence alignment tool MAFFT v7 (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/) was used. The chloroplast genome sequence data of 31 Chinese medicinal plants were aligned and a sequence matrix was constructed using an alignment/server index. The principles for selecting these genera are common genera in the family, including the genus Cirsium, Atractylodes, Chrysanthemum, Artemisia, Carthamus, Rhaponticum, Taraxacum, Inula, Arctium, Xanthium, Aster, Senecio, Lactuca, Dahlia, Eclipta, Gerbera, Bidens, Erigeron, Youngia, Ageratina, Mikania, Silybum, Saussurea, Ligularia, Stevia, and Helianthus. The basis for species selection is the most common traditional Chinese medicine plant in the Asteraceae family in China, and Platycodon grandiflorus (Jacq.) A. DC. (KX352464.1) from the Campanulaceae family was also selected for the external group. Using maximum likelihood (ML) for phylogenetic analysis, a ML tree was generated with the integrated plugin IQ-TREE v2 [30]. Using IQ-TREE software’s ModelFinder to filter the most optimal model, set the self-expansion value to 1,000 to construct ML tree. And the ML tree was visualized and beautified using the Figtree v1.4.4 software (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/).
3 Results
3.1 Basic characteristics
As shown in Table 1, the complete length of the chloroplast genome sequence of G. piloselloidis was 151,871 bp (GenBank accession number: PP473789), and has a typical four-segment structure. The lengths of the LSC region, the two IR regions, and SSC region were 83,468, 50,172, and 18,231 bp, respectively, and the GC content was 37.75%. There were 133 annotated genes in the chloroplast genome of G. piloselloidis, with 84 (63.15%), 36 (27.06%), and 13 genes (9.77%) in the LSC, IR, and SSC regions, respectively. There were 88 protein-coding genes, accounting for 66.16% of the total gene number; the number of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) was 8, accounting for 6.02%; and the number of transport RNA (tRNAs) was 37, accounting for 27.82%. As shown in Figure 1, four rRNA genes (4.5S, 5S, 16S, and 23S), seven tRNA genes (trnV-GAC, trnI-GAU, trnI-CAU, trnL-CAA, trnA-UGC, trnN-GUU, and trnR-ACG), and seven protein-coding genes (rpl2, rpl23, rps12, ycf2, ndhB, ycf15, and rps7) are located in the IR region. All 18 genes had two copies in the chloroplast genome.
Basic characteristics of chloroplast genome in Gerbera piloselloides
| Feature | Numerical value |
|---|---|
| GC content (%) | 37.75 |
| LSC length (bp) | 83,468 |
| SSC length (bp) | 18,231 |
| IR length (bp) | 25,086 |
| Gene number | 133 |
| Gene number in LSC regions | 84 |
| Gene number in SSC regions | 13 |
| Gene number in IR regions | 36 |
| Protein-coding gene number | 88 |
| Protein-coding gene percentage (%) | 61.16 |
| rRNA gene number | 8 |
| rRNA percentage (%) | 6.02 |
| tRNA gene number | 37 |
| tRNA percentage (%) | 27.82 |
| Length (bp) | 151,871 |
Note: LSC: large single-copy; IR: inverted repeat; SSC: small single-copy; bp: base pair.
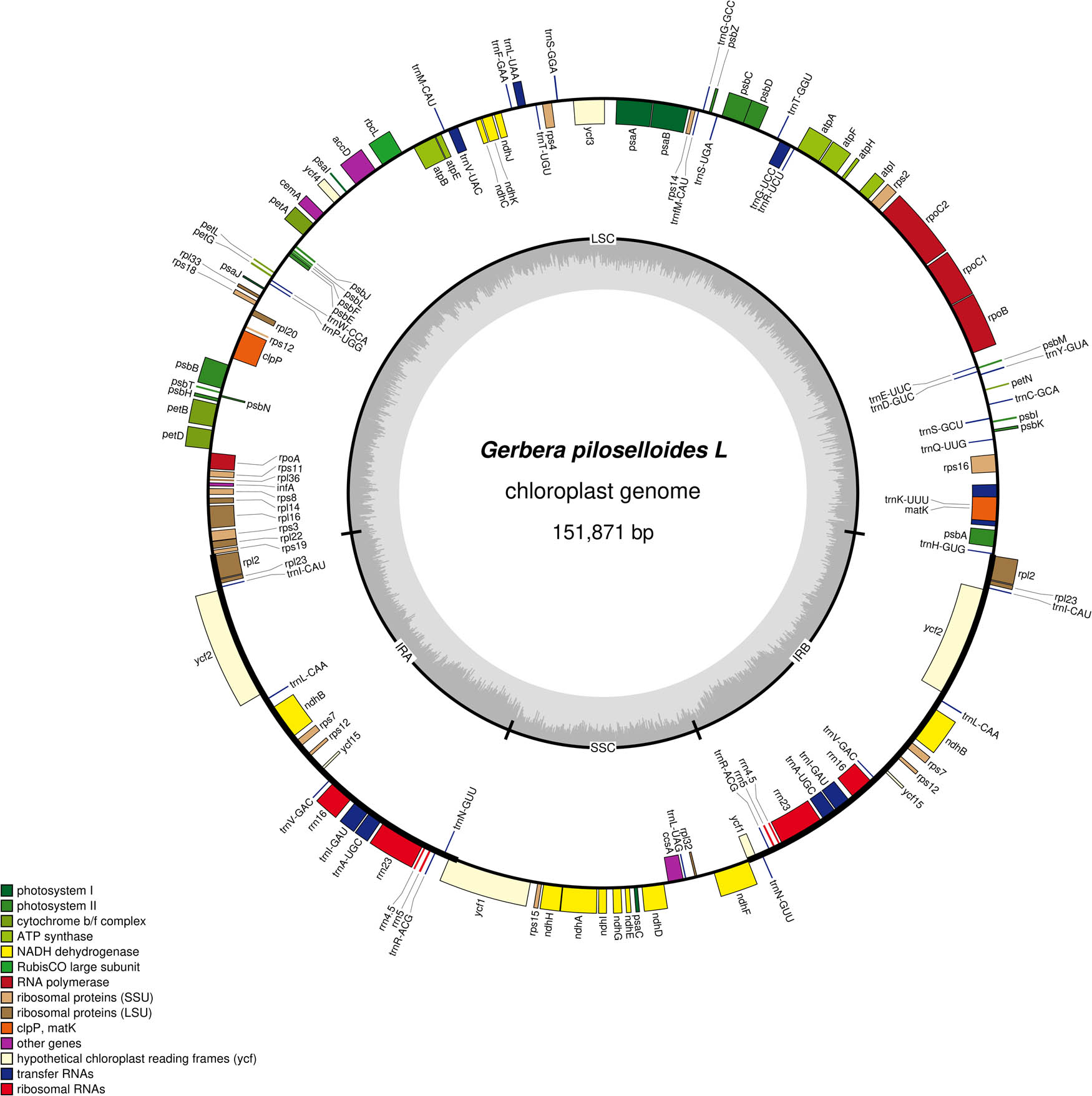
Chloroplast genome map of Gerbera piloselloides.
Based on the classification of all gene functions, most genes associated with photosynthesis and self-replication were found in the chloroplast genes of G. piloselloides (Table S1). Photosynthesis-related genes involves six major subunits: NADH dehydrogenase, ATP synthase, cytochrome b/f complex, photosystem I, photosystem II, and ribose diphosphate oxygenase/carboxylase genes. And the number of genes related to photosystem II subunits was the highest, with a total of 15 genes. But only one gene (rbcL) was associated with the ribose diphosphate oxygenase/carboxylase subunit. There are five categories of self-replication-related genes: large subunits of ribosomes, DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, small subunits of ribosomes, rRNA genes, and tRNA genes. The tRNA gene family contained the highest number of genes (30), whereas the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase class had the lowest number of genes, with only four (rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, and rpoC2). Further analysis of the chloroplast genes of G. piloselloidis showed that most genes did not have introns (Table S2). In the present study, only 23 genes in the chloroplast genome of G. piloselloidis had introns. Except for two introns in ycf3 and clpP, all other genes contained one intron. The intron of trnK-UUU was the longest, reaching 2,526 bp, and the intron of trnL-UAA was the smallest (431 bp).
3.2 Condon usage bias
In the G. piloselloidis chloroplast genome, 61.16% of the sequences were made up of gene-coding regions. Statistical analysis of the codons from all protein-coding genes showed that 2,416 (10.61%) codons encoded leucine (Leu), which has the highest coding rate, and only 251 (1.1%) codons encoded cysteine (Cys), which has the lowest coding rate. In the protein-coding region, the AT contents in the first, second, and third codons were 55.47, 62.88, and 71.63%, respectively (Figure 2). This codon-encoding preference, with high AT content in the third position, is extremely common in the chloroplast genomes of other higher plants [5].

Codon usage in chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloidis.
3.3 Repetitive sequence analysis
In total, 43 tandem repeats (T), including 18 forward repeats (F), 23 palindromic repeats (P), and two reverse repeats (R), were identified through repeat sequence analysis of G. piloselloidis, but no complementary repeats (C) were discovered (Figure 3, Table S3). In total, 202 information loci were excavated in the chloroplast genome of G. Piloselloidis, containing 128 single nucleotides, six dinucleotides, 63 trinucleotides, and 5 tetranucleotides (Figure 4). Only 15 of them were in the coding area.

The long fragment repeats of Gerbera piloselloidis. Note: F: forward repeats; P: palindromic repeats; R: reverse repeats; and C: complementary repeats.

The SSR type and length of Gerbera piloselloidis.
3.4 Chloroplast genome comparative analysis and boundary position difference
To compare the differences in chloroplast genomes between G. piloselloidis and its closely related species, we compared the basic information on chloroplast genomes between G. piloselloidis and a representative group of Chinese medicinal plants in Asteraceae (Table 2). The chloroplast genomes of G. Piloselloidis and its seven closely related species were highly similar, with a total length ranging from 150,952 bp (Artemisia annua) to 153,256 bp (Atractylodes macrocephala), all of which are typical tetrad structures, and the GC content was also very close (37.5–37.7%). The gene compositions and quantities in these species were similar.
Comparison of eight representative chloroplast genomes in Asteraceae medicinal species
| Genome structure | Gerbera piloselloides PP473789 | Atractylodes macrocephala NC_044671.1 | Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium NC_057202.1 | Artemisia annua NC_034683.1 | Taraxacum officinale NC_030772.1 | Arctium lappa NC_042724.1 | Xanthium strumarium NC_042232.1 | Helianthus annuus NC_007977.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size/bp | 151,871 | 153,256 | 151,085 | 150,952 | 151,324 | 152,708 | 151,897 | 151,104 |
| LSC length/bp | 83,468 | 84,290 | 83,034 | 82,772 | 83,895 | 83,764 | 83,846 | 83,530 |
| SSC length/bp | 18,231 | 18,674 | 18,279 | 18,268 | 18,567 | 18,582 | 17,900 | 18,308 |
| IR length/bp | 25,086 | 25,146 | 24,886 | 24,956 | 24,431 | 25,181 | 24,905 | 24,633 |
| GC content (%) | 37.7 | 37.7 | 37.5 | 37.5 | 37.7 | 37.7 | 37.5 | 37.6 |
| Number of genes | 133 | 125 | 131/132 | 133 | 133 | 132 | 132/133 | 136/137 |
| Protein-coding gene | 88 | 88 | 88 + 1pseudogene | 88 | 88 | 87 | 87 + 1pseudogene | 85 + 1pseudogene |
| rRNA | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| tRNA | 37 | 29 | 35 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 37 | 43 |
The boundary positions of the eight Asteraceae species were compared and analyzed using IRscope (https://irscope.shinyapps.io/IRplus/). Among the four regions of the chloroplast genomes, the IR region was relatively conserved, with sequence sizes ranging from 24,431 to 25,181 bp. As shown in Figure 5, the IR boundary of G. Piloselloidis chloroplast genome is similar to those of the other seven species. The LSC/IRb, IRb/SSC, and SSC/IRa boundaries were located within the rps19, ycf1, and trnH gene, respectively. At the LSC/IRb boundary, rps19 for Arctium lappa which was 69 bp away from this locus, and this gene in other seven Asteraceae species spanned this locus. At the IRb/SSC and SSC/IRa loci, ycf1 spanned these two loci, with 462–583 bp. At the IRa/LSC locus, trnH was located far away from the locus from Xanthium strumarium to Atractylodes macrocephala, with sizes ranging from 1 to 16 bp. However, in Helianthus annuus, trnH spanned the locus by 1 bp.

Boundary comparison of chloroplast genome in the Asteraceae.
3.5 Genomic structure and molecular sequence variations
The rearrangement and collinearity of the Asteraceae chloroplast genomes were analyzed using the Geneious software (Figure 6). And the chloroplast genome structures of the eight Asteraceae species were highly similar, with consistent numbers and arrangements of all genes, and no gene rearrangement or inversion events were found. Nucleotide polymorphisms in the chloroplast genome sequence of Asteraceae species were analyzed using the DnaSP software (Figure 7). In total, 10,879 polymorphic sites were determined in the eight genomes, accounting for 7.16% of the total sequence length. Nucleotide polymorphism values (P i) ranged from 0 to 0.25536, with an average value of 0.02738. The average P i in the LSC, SSC, and IR regions were 0.01736, 0.0293, and 0.00463, respectively. Seven highly variable regions (P i > 0.1) were detected, most of which were intergenic region. And four sequence fragments (petN-trnY, trnY-trnD, trnE-rpoB, and psbM) were located in the LSC region, and one sequence (ycf1) was located in the SSC region. The highest polymorphic site P i value (psbM) in the LSC region was 0.25536, indicating higher nucleotide polymorphisms in the SSC and LSC than in the IR region.

Alignment of eight representative chloroplast genomes structure of Asteraceae species.

The P i value of eight representative chloroplast genome sequences of Asteraceae species.
3.6 Phylogenetic analysis
To distinguish the phylogenetic position of G. piloselloidis, a reference was made to the chloroplast sequences of 31 other Chinese herbal medicinal plants in Asteraceae already published by NCBI, and the whole genome sequences were selected for phylogenetic analysis. The results were as follows: the support rate for clustering was high, with a test score of 100% for 24 nodes, indicating a high reliability of the clustering results. As shown in Figure 8, the 32 plants can be divided into two main categories. The first category includes 13 plant species, containing the genera Lactuca, Taraxacum, Youngia, Gerbera, Atractylodes, Cirsium, Silybum, Rhaponticum, Carthamus, Saussurea, and Arctium. The second category includes 18 plant species from the genera Mikania, Stevia, Ageratina, Eclipta, Xanthium, Helianthus, Bidens, Dahlia, Inula, Ligularia, Senecio, Aster, Erigeron, Chrysanthemum, and Artemisia. According to the cluster diagram, the closest phylogenetic relationship was observed between G. piloselloidis and Gerbera jamesonii of the same genus, Gerbera, followed by Atractylodes macrocephala and Atractylodes chinensis of the genus Atractylodes. Gerbera and Atractylodes belong to the Carduoideae subfamily, and the above results are consistent with traditional taxonomy.
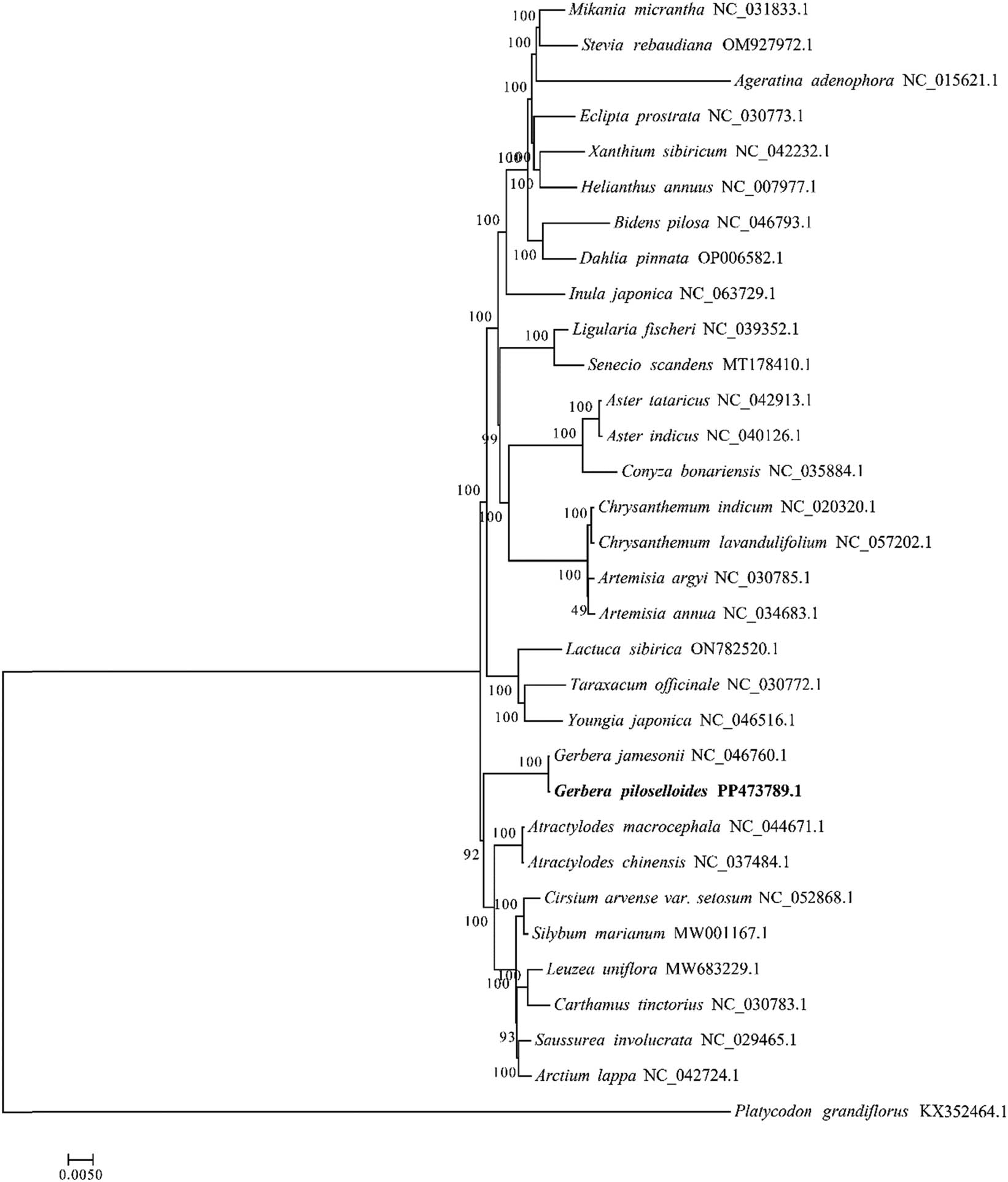
Phylogenetic trees based on the whole-genome sequences of chloroplast genomes of 31 Asteraceae medicinal species.
4 Discussion
Chloroplasts are semi-autonomous organelles within plant cells that are the main sites of photosynthesis, and this organelle plays an important role in plant growth. Sequencing of the chloroplast genome provides a basis for further understanding chloroplast gene expression, photosynthesis, cytoplasmic interactions, and other related research [1,31]. Herein, we reported the assembly and annotation of the high-quality G. Piloselloidis chloroplast genome. The chloroplast genome size of G. piloselloidis was 151,871 bp, and the length of the IR region was 25,086 bp. Within the range of 120–180 kb and 20–30 kb in angiosperms [4,32], it had a typical circular tetrad structure of the angiosperm chloroplast genome. The GC content was 37.7%, and it comprised 133 genes. Among these genes, 21 genes (trnK-UUU, rps16, rpoC1, atpF, trnG-UCC, trnL-UAA, petB, petD, trnV-UAC, rps12, rpl16, rpl2, ndhB, trnA-UGC, ndhA, rps12, trnI-GAU, trnI-GAU, trnA-UGC, ndhB, and rpl2) contained a single intron, and two genes (clpP and ycf3) contained two introns.
In total, 202 SSR loci were determined, including 36 repeating units. Among them, the highest number of mononucleotide repeats were found, with a total of 128, accounting for 63.37% of the total SSR number; trinucleotide repeats, totaling 63, accounting for 31.18% of all SSRs; and once again, there were 6 dinucleotide repeats and 4 tetranucleotide repeats, without pentanucleotide and hexanucleotide repeats. A large number of SSRs with dinucleotide motifs are also relatively rare in other species [33], which may be due to different screening criteria. AG, AT, AAG, AGG, and AGC were the main types of repetitive motifs, which is consistent with previous reports [34]. The A/T and AT/AT repeat units accounted for 66.9% of all SSR sites, and polyA or polyT is an important reason for the high AT content in chloroplast genomes. Most perfect SSR sequences are based on short sequences of 6–8 bp in length, which are related to a large number of trinucleotide-based SSRs [35].
This highly variable region of the chloroplast genome sequence could serve as a molecular marker for plant species identification [36]. Size differences and nucleotide variations in the single-copy regions between the chloroplast genomes of Gerbera species were greater than those in the IR region. Among the five nucleotide hypervariable regions with P i > 0.1 identified in this study, three (petN-trnY, trnY-trnD, and trnE-rpoB) were located in the intergenic region, and two were located on psbM and ycf1 gene, which is consistent with the results for the genus Artemisia [37]. The chloroplast ycf1 is crucial for plant environmental adaptability, and nucleotide sequence polymorphisms reflect the adaptation of plants to different environments [4]. These polymorphic regions can be made to develop powerful candidate sites for taxonomic research and genetic diversity analysis of Gerbera species.
Codon preference refers to the uneven use of synonymous codons and it has an important role in the evolution of biological genomes. This is usually reflected in the frequency of the RSCU values [38]. RSCU analysis showed that the codons with the highest and lowest RSCU values were AGA (2.10) and CGA (0.47), respectively, both of which encode Arginine. Among the codons, 31 had RSCU values greater than 1, of which 27 ended in A/U, indicating that the chloroplast genome of G. piloselloidis prefers codons ending in A/U. The codons with A/T as the first base accounted for 55.47% of the total codon count, the second for 62.88%, and the third for 71.63% in G. piloselloidis. Furthermore, this codon-encoding preference with high AT content in the third position is extremely common in the chloroplast genomes of other higher plants [39].
G. piloselloidis is often used as an ornamental plant abroad; however, little research has been conducted on its use. However, it is widely used in ethnic medicine in Southwestern China. Studying the chemical composition and pharmacological activity of G. piloselloidis can promote the standardization of related medicinal materials, provide theoretical guidance, and facilitate further research and development of this ethnic medicine [40]. And special SSR motifs and divergent hotspot regions identified from G. piloselloidis chloroplast provided reference for subsequent identification investigations. In order to more accurately identify G. piloselloidis in the Asteraceae family, it is necessary to conduct further research on these systematic relationships. Each variety is strictly distinguished based on its molecular sequence, and its identification is crucial to achieve the goal of authentic and safe drug use. A systematic evolutionary analysis of the complete genome sequence in the chloroplasts of 31 other published medicinal plants showed that G. piloselloidis has the closest phylogenetic relationship with Gerbera jamesonii, followed by Atractylodes macrocephala and Atractylodes chinensis of the genus Atractylodes, and the evolutionary analysis results are consistent with traditional taxonomy (https://www.iplant.cn/info/Asteraceae). The plastome-based phylogeny provided preliminary insights into the relationships among the Chinese group of medicinal species and related taxa within Asteraceae.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, the G. piloselloidis chloroplast genome was sequenced and assembled in this research. The chloroplast genome structure, repeat sequences, codon preferences, and phylogenetic relationships of G. piloselloidis might provide a theoretical basis for phylogenetic analysis of plants in the genus Gerbera, and serve as important references for taxonomic research and phylogenetic analysis within the Asteraceae family. Overall, this study offers a wealth of informative genetic resources pertinent to G. piloselloidis, thereby enhancing our understanding of its evolution and laying a foundation for species identification, assessment of genetic population diversity, as well as the exploration and conservation of germplasm resources in Asteraceae.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the Education Reform Program of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (JXJG-22-23-3, JXJG-23-23-5), and Education Reform Program of Nanchang Normal University (NSJG-21-25).
-
Author contribution: The author confirms the sole responsibility for the conception of the study, presented results and manuscript preparation.
-
Conflict of interest: Author states no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wang J, Kan SL, Liao XZ, Zhou JW, Tembrock LR, Daniell H, et al. Plant organellar genomes: much done, much more to do. Trends Plant Sci. 2024;29(7):754–69. 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.12.014.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Sloan DB, Triant DA, Forrester NJ, Bergner LM, Wu M, Taylor DR. A recurring syndrome of accelerated plastid genome evolution in the angiosperm tribe Sileneae (Caryophyllaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;72:82–9.10.1016/j.ympev.2013.12.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Daniell H, Jin S, Zhu XG, Gitzendanner MA, Soltis DE, Soltis PS. Green giant-a tiny chloroplast genome with mighty power to produce high-value proteins: history and phylogeny. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021;19:430–47.10.1111/pbi.13556Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Dobrogojski J, Adamiec M, Luciński R. The chloroplast genome: a review. Acta Physiol Plant. 2020;42:98.10.1007/s11738-020-03089-xSearch in Google Scholar
[5] Daniell H, Lin CS, Yu M, Chang WJ. Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016;17(1):134.10.1186/s13059-016-1004-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Wu ZQ, Liao XZ, Zhang XN, Tembrock LR, Broz A. Genomic architectural variation of plant mitochondria-A review of multichromosomal structuring. J Syst Evol. 2022;60(1):160–8.10.1111/jse.12655Search in Google Scholar
[7] Sheng WT. The entire chloroplast genome sequence of Asparagus cochinchinensis and genetic comparison to Asparagus species. Open Life Sci. 2022;17(1):893–906. 10.1515/biol-2022-0098.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] He SL, Xu B, Chen SY, Li GY, Zhang J, Xu JQ, et al. Sequence characteristics, genetic diversity and phylogenetic analysis of the Cucurbita ficifolia (Cucurbitaceae) chloroplasts genome. BMC Genomics. 2024;25:384. 10.1186/s12864-024-09996-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Song CF, Zhu JW, Li HM. Complete chloroplast genomes of eight Delphinium taxa (Ranunculaceae) endemic to Xinjiang, China: insights into genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Plant Biol. 2024;24:600. 10.1186/s12870-024-05279-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Wang R, Yang Y, Tian H, Yi H, Xu L, Lv Y, et al. A scalable and robust chloroplast genotyping solution: Development and application of SNP and InDel markers in the maize chloroplast genome. Genes. 2024;15:293. 10.3390/genes15030293.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] He M, Han X, Qin X, Bao JJ, Li HB, Xie QL, et al. Comparative chloroplast genome analyses provide new insights into phylogeny of Taraxacum and molecular markers for distinguish rubber producing dandelions from their weedy relatives in China. Ind Crop Prod. 2024;207:117712. 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.117712.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Li XW, Yang Y, Henry RJ, Rossetto M, Wang YT, Chen SL. Plant DNA barcoding: from gene to genome. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2015;90(1):157–66.10.1111/brv.12104Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] The Editorial Committee of Flora of China. Chinese Academy of Sciences. Vol. 79, 1st edn. Beijing, Flora of China: Science Press; 1996. p. 73, (in Chinese).Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhang BX, Wang JJ, Lei QY, Zhou JJ, Liu SZ, Long CL. Advance in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Gerbera piloselloides. J Nanjing Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2019;35(3):351–5, (in Chinese).Search in Google Scholar
[15] Zhao C, Li J, Hu Y, Li L, Yu M, Huang Y, et al. 1(+)/(−)-Gerbeloid A, a pair of unprecedented coumarin-based polycyclic meroterpenoid enantiomers from Gerbera piloselloides: Structural elucidation, semi-synthesis, and lipid-lowering activity. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(6):2657–68. 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.03.035.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Liu C, Fu C, Lu Y, Sun J, Liu T, Wang Y, et al. Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics to reveal the mechanism of Gerberae piloselloidis herba in alleviating bronchial asthma. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;325:117852. 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117852.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Zhou K, Lu D, You J, Liu T, Sun J, Lu Y, et al. Integrated plasma pharmaco chemistry and network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of Gerberae Piloselloidis Herba in treatment of allergic asthma. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;298:115624. 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115624.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Chen LY, Song MS, Zha HG, Li ZM. A modified protocol for plant genome DNA extraction. Plant Diversity Resour. 2014;36(3):375–80. 10.7677/ynzwyj201413156.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Sewe SO, Silva G, Sicat P, Seal SE, Visendi P. Trimming and validation of Illumina short reads using trimoraic, trinity assembly, and assessment of RNA-Seq data. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2443:211–32.10.1007/978-1-0716-2067-0_11Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Dierckxsens N, Mardulyn P, Smits G. NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(4):e18. 10.1093/nar/gkw955.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Tillich M, Lehwark P, Pellizzer T, Ulbricht-Jones ES, Fischer A, Bock R, et al. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(1):W6–W11. 10.1093/nar/gkx391.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Jin JJ, Yu WB, Yang JB, Song Y, DePamphilis CW, Yi TS, et al. GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020;21:1–31.10.1186/s13059-020-02154-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Chan PP, Owelt M. tRNAscan-SE: Searching for tRNA genes in genomic sequences. Methods Mol Biol. 1962;2019:1–14.10.1007/978-1-4939-9173-0_1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Greiner S, Lehwark P, Bock R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:W59–64.10.1093/nar/gkz238Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Gary B. Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;2:573–80.10.1093/nar/27.2.573Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Li Q, Wan JM. SSRHunter: Development of a local searching software for SSR sites. Heredity. 2005;27(5):3.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Sharpl PM, Li WH. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15(3):1281–95.10.1093/nar/15.3.1281Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(4):772–80.10.1093/molbev/mst010Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sanchez-Delbarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, et al. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(12):3299–2.10.1093/molbev/msx248Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Minh BQ, Schmidt HA, Chernomor O, Schrempf D, Woodhams MD, Haeseler AV, et al. IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol Biol evol. 2020;37(5):1530–4.10.1093/molbev/msaa015Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Arimura S, Nakazato I. Genome editing of plant mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024;65(4):477–83. 10.1093/pcp/pcad162.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Li DM, Pan YG, Liu HL, Yu B, Huang D, Zhu GF. Thirteen complete chloroplast genomes of the costaceae family: insights into genome structure, selective pressure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genomics. 2024;25(1):68.10.1186/s12864-024-09996-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Liu YM, Zhan JL, Li JJ, Lian MJ, Li JC, Xia CJ, et al. Characterization of the DNA accessibility of chloroplast genomes in grasses. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):760.10.1038/s42003-024-06374-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Tyagi S, Jung JA, Kim JS, Won SY. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of mainland Aster spathulifolius and other Aster species. Plants. 2020;9:568. 10.3390/plants9050568.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Chen H, Li TY, Chen XY, Qu TM, Zheng XY, Luo JJ, et al. Insights into comparative genomics, structural features, and phylogenetic relationship of species from Eurasian Aster and its related genera (Asteraceae: Astereae) based on complete chloroplast genome. Front Plant Sci. 2024;15:1367132. 10.3389/fpls.2024.1367132.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Liao XF, Luo JJ, Chen H, Li TY, Qu TM, Tang M, et al. Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genomes of Synotis species (Asteraceae, Senecioneae) for identification and phylogenetic analysis. BMC Genomics. 2024;25:769. 10.1186/s12864-024-10663-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Liu C, Lv YQ, Shi ZL, Mao R, Han LH. Characteristics of chloroplast genomes and phylogenetic analysis of Artemisia species. J Northwest For Univ. 2023;38(3):78–86, (in Chinese).Search in Google Scholar
[38] Cackett L, Luginbuehl LH, Schreier TB, Lopez-Juez E, Hibberd JM. Chloroplast development in green plant tissues: the interplay between light, hormone, and transcriptional regulation. New Phytol. 2022;233:2000–16. 10.1111/nph.17839.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Lubna AS, Jan R, Asif S, Bilal S, Khan AL, Al-Rawahi AN, et al. The complete plastome sequences of invasive weed Parthenium hysterophorus: genome organization, evolutionary significance, structural features, and comparative analysis. Sci Rep. 2024;14:4006. 10.1038/s41598-024-54503-0.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] You JR, Sun J, Lan YY, Li YJ, Wang YL, Liu CH. Simultaneous determination of six constituents in Gerbera piloselloides by UHPLC-PDA. Chin Tradit Pat Med. 2021;4(1):111–6.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

