Abstract
Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Pran known as Flixweed is recognized as an ethnomedicinal plant in Chinese traditional medicine, offering numerous therapeutic benefits. Antioxidant chemicals found in this medicinal plant protect cellular integrity from various sources of damage and may help prevent cancer. In this study, we investigated copper/nickel nanoparticles (Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed) that were green-mediated following principles of green chemistry, utilizing the aqueous extract of D. sophia seeds for the treatment of lung carcinoma. The effectiveness of these Cu/Ni nanoparticles’ effectiveness was tested against three common human lung cancer cell lines. Methods such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy, and energy dispersive X-ray were used to analyze the Cu/Ni nanoparticles produced through environmentally friendly methods. The XRD pattern revealed that the crystalline structure of the generated NPs is seen in the XRD pattern. According to the FE-SEM results, the nanoparticles had an average size of 68.52 nm and a semi-spherical shape. The IC50 values of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed against HLC-1, LC-2/ad, and PC-14 cells were found to be 170, 98, and 57 μg/mL, respectively. The IC50 values of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed against 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl free radicals was 30 μg/mL. Recent research indicates that Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed may be a promising option to assist in the treatment various types of lung cancer.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Nanotechnology offers numerous benefits across various scientific disciplines. In this context, nanoparticles (NPs) are the fundamental components of nanotechnology [1–3]. Nanotechnology provides a wide range of advantages in different scientific fields. Within this framework, NPs serve as the essential building blocks of nanotechnology [4,5]. The ability to establish stable interactions with ligands, along with their diverse shapes and sizes, significant carrying capacity, and ease of binding to both hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances, make NPs ideal platforms for the controlled and targeted delivery of micro- and macromolecules in disease treatment [5–8]. NPs paired with therapeutic agents address challenges associated with traditional treatments. However, concerns regarding side effects and toxicity remain topics of discussion that should be carefully considered before their use in biological systems. Therefore, it is essential to understand the unique characteristics of therapeutic NPs and the methods used for their delivery [7–12]. Recent research has shown that NPs have beneficial therapeutic effects on various conditions, including cardiovascular issues, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, cancer, eye conditions, neurodegenerative diseases, and respiratory diseases [1,2,9–12]. Some research groups have investigated the anti-breast cancer and anti-gastric cancer effects of silver NPs using Sambucus ebulus rhizome and hull of Pistacia vera extracts and gold NPs green-mediated by P. vera extract, respectively [8,11]. Gaining insight into the properties of NPs and how they interact with biological systems will enable us to develop new approaches for treating, preventing, and diagnosing various diseases, especially those that are currently untreatable [1–4].
Bimetallic NPs are increasingly important in various fields due to their unique properties and enhanced functionalities compared to their monometallic counterparts. Composed of two different metals, bimetallic NPs can exhibit synergistic effects that improve their physical, chemical, and biological properties. These enhancements include increased catalytic activity, optical properties, and antimicrobial efficacy [13,14]. Bimetallic NPs have garnered attention for their antimicrobial properties, which outperform those of monometallic NPs. They have proven effective against a wide range of pathogens, making them promising candidates for medical applications, particularly in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. The dual metal composition allows for multiple mechanisms of action, decreasing the likelihood of microbial resistance [14,15]. In biomedicine, bimetallic NPs are utilized for drug delivery, imaging, and therapeutic agents. Their small size enables them to effectively penetrate biological barriers. Additionally, they can be engineered to release drugs in a controlled manner or enhance imaging contrast in diagnostic applications [15,16].
Because of their unique qualities and potential applications, nickel/copper bimetallic NPs, also known as Ni/Cu NPs, have recently garnered significant interest across various scientific fields. Ni/Cu NPs can be synthesized using different methods, such as chemical reduction and hydrothermal processes. The synthesis conditions, including the molar ratio of nickel to copper, can greatly impact the structural properties of the NPs [17–20]. One of the most noteworthy applications of Ni/Cu BMNPs is in catalysis. The bimetallic system often exhibits superior activity compared to its monometallic counterparts due to synergistic effects that enhance electron transfer rates and overall reaction efficiency [21]. Ni/Cu NPs have also been investigated for their antimicrobial properties. Studies have shown that these NPs can effectively inhibit the growth of various pathogenic microorganisms, surpassing individual nickel or copper NPs in terms of antibacterial efficacy. This is attributed to their unique physicochemical properties and mechanisms of action resulting from the bimetallic composition. They have demonstrated effectiveness against bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae, making them potential candidates for medical and environmental applications [22,23].
There is an increasing demand for straightforward, cost-effective, and scalable methods to produce NPs. Utilizing plant extracts aligns with these requirements, as they are easy to cultivate in large quantities, renewable, and environmentally sustainable [24]. In the process of synthesizing metallic NPs, phytochemicals serve dual functions: they act as both reducing agents and stabilizers for the NPs [24,25]. Bimetallic NPs synthesized using plant extracts exhibit enhanced stability and diversity in their shapes and sizes. Consequently, the presence of reducing agents in these extracts such as flavonoids, terpenoids, and phenolic acids is crucial for the successful synthesis of bimetallic NPs [26].
The Brassicaceae family, commonly known as the mustard family, consists of approximately 338 genera and around 3,700 species of flowering plants. This family is well known for its edible members, which are widely consumed as vegetables worldwide and are valued for their high content of bioactive phytochemicals. Notable vegetables from this family include Brussels sprouts, cabbage, broccoli, and kale, among others [27]. Descurainia sophia holds significant importance in traditional medicines globally, where it is highly regarded among practitioners of folk medicine for its extensive use in various remedies [28,29]. D. sophia is prevalent in northeastern China and has a long history of use in traditional folk medicine. This plant is notorious for being a broadleaf weed that infests winter wheat fields in the region. Notably, it has developed resistance to the acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicide tribenuron-methyl, posing a significant challenge for agricultural management in these areas [30]. The decoction made from the aerial parts of D. sophia is used to treat throat ailments and acts as an antipyretic in cases of measles and smallpox. This traditional application highlights the plant’s importance in herbal medicine, particularly in addressing fever and respiratory issues associated with these diseases [31]. There is substantial evidence highlighting the therapeutic properties of D. sophia for a variety of health issues, including asthma, cough, urinary tract disorders, pain, edema, cardiac conditions, constipation, fever, itching, intestinal parasites, and internal bleeding. Additionally, the seeds of D. sophia are utilized to address various pathological conditions such as gastrointestinal issues, inflammation, and cardiovascular diseases. The plant is also suggested as a treatment for vitamin C deficiency. D. sophia has been observed to exhibit significant cytotoxic effects against a variety of human cancer cell lines, indicating its potential as an anticancer agent. Studies have documented its efficacy in targeting cancer cells from the lung, liver, colon, prostate, ovary, skin, and stomach. Also, the D. sophia seeds ethanolic extract has shown the ability to suppress cancer cell growth and induce apoptosis, particularly in lung cancer cells, by regulating genes associated with cell growth signaling pathways. This suggests that D. sophia may serve as a promising candidate for the development of anticancer therapies [32–35]. D. sophia seed extract is known for its potent cytotoxic effects against lung cancer cells [36,37]. The diverse medicinal uses of D. sophia are attributed to the presence of various secondary metabolites, including phenolics, cardiac glycosides, flavonoids, and sulfur glycosides [31,36,38]. These compounds play a crucial role in the plant’s therapeutic effects, contributing to its efficacy in treating a range of health disorders. The phytochemical profile of D. sophia supports its traditional applications in medicine, highlighting its potential as a source of bioactive substances for future pharmacological development [36,38]. So far, silver and gold NPs have been synthesized using D. sophia extract. The gold NPs showed acceptable ability to treat ovalbumin-induced asthma [39]. The silver NPs were found to be active against lung cancer cell lines [40]. The NPs also exhibited antimicrobial and antifungal activity [41].
In recent years, the synthesis of metallic NPs using plant extracts has gained desirable attentions. This is primarily due to the green, eco-friendly, and cost-effective nature of this approach compared to conventional physical and chemical methods. Bimetallic NPs have shown promising potential for lung cancer treatment due to their unique properties and advantages. In this study, we focused on the green synthesis of bimetallic NPs of copper and nickel using the extract of the seeds of D. sophia as a reducing and stabilizing agent. This method provides a green, eco-friendly, and cost-effective alternative, avoiding toxic chemicals typically used in NP synthesis, and the resulting biocompatible NPs are safer for biomedical applications. By synthesizing Ni/Cu NPs using D. sophia seed extract, we leverage the plant’s natural anticancer compounds and the unique properties of metal NPs to create a green, stable, and effective therapeutic agent with enhanced cytotoxicity against lung cancer cells. The physio-chemical characteristics of the NPs were evaluated using analytical methods. Furthermore, the application of NPs in preventing lung cancer, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant properties was assessed. However, a major gap in the present study lies in the clinical evaluation of these specific NPs against lung cancer. Lung cancer is a complex disease, and the efficacy, targeting ability, and safety of these specific NPs for lung cancer treatment would require rigorous testing.
2 Experimental
2.1 Plant and chemical materials
The seed of D. Sophia was purchased from a medicinal plant store in Wuhan, China. The plant was identified by a botanist in the biology section of Wuhan University with a voucher specimen of WU1054. The plant seeds were washed and dried in a dark place at room temperature.
All chemicals for the present study were purchased from Sigma Aldrich with analytical grade.
2.2 Chemical characterization
The Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) spectra were recorded using a Shimadzu 8400 spectrophotometer with KBr disc ranging from 400 to 4,000 cm−1. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) diagram was obtained on the 2θ scale using a STOE PW2773.00 device with Cu Kα radiation at 45 kV and 40 mA. The field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) images and energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) data were obtained using a MIRA3TESCAN instrument.
2.3 Synthesis of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed
The synthesis was carried out according to a previous study with some modification [42]. First, 5 g of flixweed seeds were boiled in deionized water (200 mL) for 15 min. After reaching ambient temperature, the extract was filtered. To synthesize Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed, 15 mL of the extract was mixed with Ni(NO3)2·6H2O and Cu(SO4)·5H2O in a 1:1 ratio at a concentration of 0.05 M. The pH was adjusted to 9. The reaction mixture was refluxed at 75°C for 12 h. The residue was then centrifuged at 10,000 RPM for 10 min. The NPs were centrifuged with four water washes to eliminate unreacted components. Finally, dried for 6 h at 55°C in an oven before processing for characterization and biological tests. The synthesis of NPs was repeated five times.
2.4 Anti-lung cancer efficacy of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed
The cytotoxic effects of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed was evaluated on the PC-14 (origin source: human lung, accession number: CVCL_1640), LC-2/ad (origin source: human lung, accession number: CVCL_1373), and HLC-1 (origin source: human lung, accession number: CVCL_5529) purchased from Shenzhn Bike Biotechnology Company, China. Lung carcinoma cells were measured using the 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed were applied to the cells for 24 h at various dosages from 1 to 1,000 µg/mL. To each well 100 µL of 0.5 mg/mL MTT solution was added to replace the medium for cytotoxicity assessment. After 4 h of dark incubation at 37°C, the medium was removed and 0.1 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide was added to each well and mixed well for an additional 10 min. A microplate reader (Bio-Rad, CA, USA) was used to measure the absorbance at 570 nm. Cell viability was calculated using the following equation [43]:
The program GraphPad Prism version 9 was used to calculate the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values. Additionally, a digital camera-equipped phase-contrast inverted microscope (Olympus, Japan) was utilized to observe the cellular morphology of both untreated and treated cells.
2.5 Antioxidant efficacy of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed
The antioxidant activity of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed was examined using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical test, based on techniques from a previous study [43]. When a material capable of donating hydrogen atoms was added to the alcoholic DPPH solution, the DPPH decreased and turned pale yellow instead of purple. Two milliliters of a freshly made methanolic solution (0.1 Mm) of DPPH was mixed with 2 mL of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed solution (1–1,000 µg/mL). The test tubes were then placed in the dark for half an hour and absorbance was measured at 517 nm after incubation. Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) at concentrations ranging from 1 to 1,000 µg/mL was used as a reference or control. A reaction mixture showing lower absorbance indicates greater free radical scavenging activity [43]. Using BHT as a reference, equation (2) was used to calculate the antioxidant capabilities of the samples based on their DPPH radical scavenging abilities:
where SCV represents the DPPH radical scavenging effect, and AS and AC denote the absorbance of the sample and control, respectively.
2.6 Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism Version 9.0 was utilized for the graphical analysis of the data, presenting the results as mean ± standard deviation. The statistical significance was evaluated using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey–Kramer Multiple Comparison Test, with a p-value of ≤0.01 denoted by an asterisk.
3 Results and discussion
Scheme 1 presents the chemical process of the synthesis for bi-metallic NPs of copper and nickel using the aqueous extract of D. sophia (Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed). The reaction was optimized using different factors such as pH values of 7, 8, 9, and 10; temperatures of 45, 60, 75, and 90°C; and varying concentrations of metallic salts (0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07 M). A comparison of the yield percentages revealed the optimal conditions for the synthesis of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed to be pH 9, temperature 75°C, and metallic salt concentration 0.05 M.

Synthesis procedure of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed.
FT-IR is an effective technique for the characterization of metallic NPs. It offers important details on the functional groups and chemical makeup of the NPs, which are essential for understanding their characteristics and uses. The technique can be used to monitor any structural changes in metallic NPs upon exposure to various conditions (e.g., temperature, pH, or biological environments). Changes in peak positions or intensities in the FT-IR spectrum can indicate modifications in the chemical structure or bonding environment around the NPs [44,45]. Figure 1 presents the FT-IR spectra of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed and the plant extract. The obtained results authenticate the synthesis of copper/nickel bi-metallic NPs with a linkage of the organic compounds of Flixweed extract to the surface of NPs. The bands at 451 and 619 cm−1 correlate with Cu–O and Ni–O bonds. These results are in agreement with previous reports on the green synthesis of Cu/Ni BMNPs [46,47]. Other bands at various wavenumbers reveal the coating of the NPs surface by the secondary metabolites of Flixweed extract, with evidence provided by the bands related to different organic functional groups. The peaks for functional groups of O–H (3,434 cm−1), C–H (2,939 cm−1), C═C and C═O (1,379–1,616 cm−1), and C–O (1,095 cm−1) are reported in the FT-IR spectrum of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed. These signals closely match the bands of functional groups which were recorded for the plant extract, with slight shifts in peak positions. The results show bands at 3,417, 2,925, 1,407–1,611, 1,263, and 1,056 cm−1 for vibrational bands of O–H, C–H, C═C, C═O, and C–O.
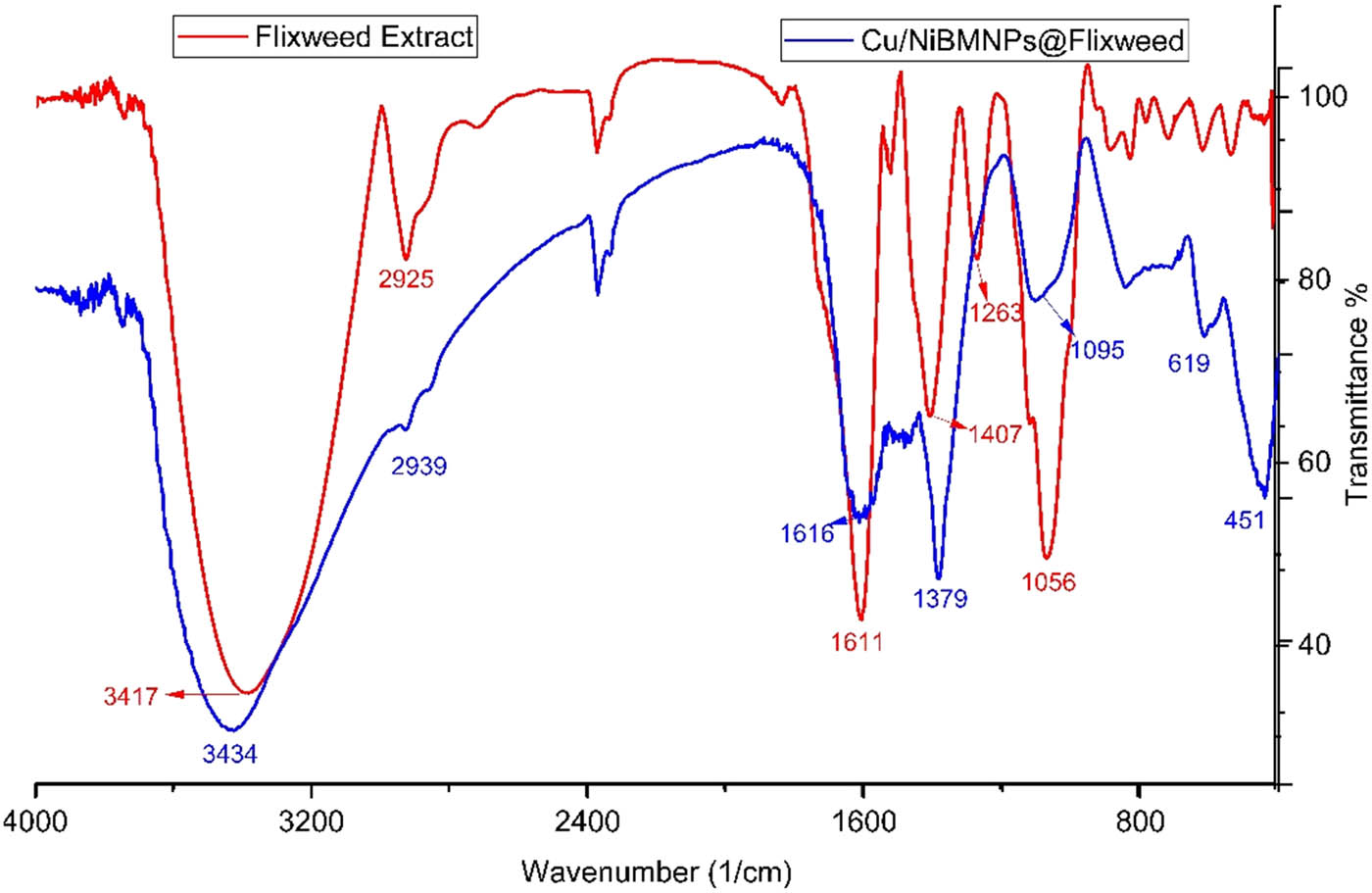
Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed FT-IR spectrum.
XRD is a widely used technique for the characterization of NPs, providing essential information about their structural properties. XRD is primarily employed to determine the crystalline structure of NPs. The technique helps to identify the phases present in a sample by comparing the observed diffraction peaks with standard reference patterns from databases. This phase identification is crucial for understanding the material properties and potential applications of the NPs [48]. Figure 2 shows the XRD diagram of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed. According to the results, the NPs were materialized in the crystalline structure. The signals at different positions match the standard data of copper oxide (CuO) and nickel oxide (NiO). However, due to the formation of bimetallic NPs, slight differences in the positions of signals are perceptible. The signals at 37.03 (111), 48.49 (−202), 61.03 (−113), 73.34 (311), 74.97 (004), and 79.07 (023) match the PDF card No. 04-012-7238 for CuO and the signals at 36.28 (111), 43.11 (200), 62.76 (220), and 77.02 (311) are compatible with the standard data of JCPDS No. 1313-991 for NiO. The obtained data are similar to previous reports for Cu/Ni NPs [46,47,49].

Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed XRD diagram.
EDX spectroscopy is an essential technique for the characterization of NPs, providing critical insights into their elemental composition and distribution. Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy allows for the determination of the elemental composition of NPs by analyzing the sample’s characteristic X-rays emitted when excited by an electron beam. Researchers can identify the types and relative abundances of elements present in the NPs, crucial for confirming the successful synthesis and composition of metallic NPs [50]. The EDX analysis results of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed are shown in Figure 3, indicating signals for copper (around 0.9 keV for Cu Lα, 7.5 keV for Cu Kα, and 9 keV for Cu Kβ) and nickel (around 0.8 keV for Ni Lα, 7.6 keV for Ni Kα, and 8.2 keV for Ni Kβ). Furthermore, signals for carbon or oxygen from organic compounds demonstrate the importance of flixweed secondary metabolites as the reducing and capping agent for the synthesis of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed. Compared to previous reports on the green synthesis of copper, nickel, and Cu/Ni, the results confirm the successful synthesis of Cu/Ni NPs [47,51,52]. EDX mapping is a powerful technique used in the characterization of NPs, allowing for the identification of the elemental composition of NPs crucial in understanding their properties and behavior. It also provides information on the spatial distribution of elements within the NPs [53]. The EDX diagram of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed is exhibited in Figure 4 showing the uniform distribution of copper, nickel, and oxygen elements in NPs.

Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed EDX diagram.

Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed EDX mapping.
FE-SEM is a tool used to characterize green-formulated metallic NPs. It provides high-resolution imaging that reveals important information about the morphology, size, and distribution of these NPs. FE-SEM allows for a detailed visualization of the shape and surface characteristics of green-synthesized metallic NPs, which is crucial for understanding how their morphology affects their properties and potential applications. For example, spherical, rod-shaped, or irregularly shaped NPs can exhibit different behaviors in biological or catalytic contexts [54,55]. The FE-SEM images of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed are shown in Figure 5, illustrating a semi-spherical morphology for Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed with an average size of 68.52 nm. The NPs display a tendency to aggregate, similar to other metallic NPs reported previously [56–59]. Aggregation typically occurs when the stabilizing agents such as organic compounds from the plant extract that prevent NPs from clumping are disrupted [60].

Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed FE-SEM images. (a) 500 nm; (b) 200 nm.
Recent gas chromatography and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of the volatile components in the aerial parts of D. sophia revealed that neoisomenthyl acetate, menthol, and cis-β-ocimene are the main components of the volatile oil [36]. Studies have shown that the seeds of D. sophia can inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells. Specifically, the viability of SF268, NCI-H460, and SGC-7901 cells was significantly reduced by n-butanol extract of the seeds [61,62]. Previous research has found that artabotryside A, a flavanol glycoside isolated from D. sophia seeds, halted the growth of U87 glioblastoma cells by inducing G2/M phase arrest and caspase-3-dependent cell death [36]. In A549 lung cancer cells, Kim et al. demonstrated that the ethanol extract from D. sophia seeds showed dose-dependent efficacy [36]. BGC-823 and MDA-MB-435 cells were both found to be cytotoxically affected by some of the antioxidant chemicals present in D. sophia seeds [63]. The hydrolyzed derivatives of glucosinolates, specifically isothiocyanates, have exhibited antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer, and chemoprotective properties. It has been consistently shown that consuming plants high in isothiocyanates can reduce the risk of developing cancer [64]. By aiding in detoxification, which reduces the activation of pro-carcinogens and enhances the removal of carcinogens, isothiocyanates may offer cancer prevention. A diet rich in cruciferous vegetables has also been shown to increase detoxifying enzymes. Additionally, isothiocyanates may reduce tumor development by blocking the CYP-dependent activation of pre-carcinogens promoting, or inhibiting the proliferation of cancer cells [65].
Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed significantly decreased the viability of cancer cells in this study (Figures 6–9). The viability of tumor cells decreases from 100 to 0% as the concentration of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed increased from 0 to 1,000 μg/mL. PC-14, LC-2/ad, and HLC-1 had respective IC50 values of 57, 98, and 170 μg/mL, respectively. Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed exhibit greater cytotoxicity toward cancer cell lines due to its superior stability and cellular absorption. Since Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed are smaller and have a larger surface area, they may enter cells more readily by endocytosis and circumvent the p-glycoprotein efflux mechanism [66]. Biosynthesized NPs have shown great promise in the fight against cancer cell lines, according to earlier studies [67,68]. Recent research by AshaRani et al. and Nagajyothi et al. suggests that environmentally friendly NPs may effectively stop the growth of MCF-7 cells, A549 cells, and human glioblastoma cells. The precise mechanism by which cancer cells function is yet unclear [69,70]. According to Xu et al. a hydrogel containing NPs damaged DNA and raised the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancer cells, which eventually led to cell death. Recent research suggests that NPs may have harmful effects on healthy cells. However, the level of cytotoxicity is influenced by variables such as particle size and concentration [71]. Larger particles are generally less dangerous than tiny ones, and higher concentrations are more likely to have adverse consequences. It is crucial to remember that dosage determines how harmful NPs are, and the quantities employed in research may not accurately reflect exposure levels seen in daily life. Additionally, the results may change based on the kind of normal cells examined since various cell types may respond to NPs differently [72]. So far, a few studies have focused on the anti-lung cancer activity of bi-metallic NPs. These materials show promising anti-lung cancer activities primarily through inducing cytotoxicity and affecting cancer cell survival pathways. They have been found to cause dose-dependent cytotoxic effects on non-small cell lung cancer cell lines reducing cell viability significantly. They induce oxidative stress and programmed cell death selectively in cancer cells, sparing healthy cells due to the enhanced permeability and retention effect that allows NPs to accumulate in tumor tissues. They also demonstrate antioxidant properties by reducing ROS and interfering with key cancer survival signaling pathways [73–76].

Activities of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed on the normal cell viability (%).

Activities of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed on the lung cancer HLC-1 viability (%).

Activities of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed on the lung cancer LC-2/ad viability (%).

Activities of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed on the lung cancer PC-14 viability (%).
A DPPH experiment was conducted to evaluate the antioxidant potential of BHT and NPs. Antioxidant properties varied significantly and increased in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 10). At the highest doses of 250, 500, and 1,000 μg/mL, the reported value of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed increased from 5.3% at the lowest concentration of 3 μg/mL to 100%. The antioxidant results are presented using IC50 values (Figure 10). The IC50 value of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed is 30 μg/mL. A lower IC50 indicates greater antioxidant capacity. Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed’s surface contains a variety of functional groups that may enhance its antioxidant properties. Based on these findings, Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed could potentially be used as a substitute antioxidant for treating illnesses caused by free radicals. The strong antioxidant properties of NPs have been demonstrated in several studies [38,60,61]. When free radicals obtain hydrogen from the proteins, phenols, alkaloids, and other compounds present in D. Sophia, stable phenoxyl radicals are generated [56–60].

Antioxidant activities of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed on DPPH inhibition (%).
4 Conclusion
Copper/nickel bimetallic NPs were prepared using a green chemistry approach with flixweed seed extract. The NPs were characterized using SEM, XRD, FT-IR, and EDX. Results indicated an interaction between the plant extract and metallic ions during synthesis, resulting in reduced NPs with a crystal structure, semi-spherical morphology, and an average size of 50.55 nm. Tests on Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed showed antioxidant efficacy against free radicals ranging from 5.3 to 100%. The effectiveness against lung cells decreased with increasing NP concentration, demonstrating the anti-lung cancer properties of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed. According to the findings of the in vitro study, several concentrations of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed had notable anti-lung cancer effects with low toxicity against normal cells suggesting potential in cancer treatment.
The anti-lung cancer and antioxidant properties of Cu/NiBMNPs@Flixweed suggest they be utilized as a supplementary treatment globally. However, thorough safety assessments are necessary due to the unique properties of bimetallic NPs. Understanding their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in living system (pharmacokinetics) and their effects on the body (pharmacodynamics) is crucial for clinical translation. This research highlights a promising path for future studies combining the benefits of flixweed with anti-cancer activity of Cu/Ni NPs.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: XZ and JH conceived the study; XZ analyzed the data; JC and JH wrote the manuscript; XZ, JC, and JH revised the data and obtained funding; and JH confirmed the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Sishu NK, Selvaraj CI. Bio-fabrication of Cichorium intybus L. root aqueous extract mediated ZnO nanoparticle (CIRAE-ZnO NP) for its promising therapeutic applications. Green Chem Lett Rev. 2025;18(1):2489461.10.1080/17518253.2025.2489461Search in Google Scholar
[2] Sishu NK, Selvaraj CI. Phytochemical profiling, bioactive potential and in silico analysis of Kydia calycina Roxb. leaf extracts. Chem Biodivers. 2025;22(7):e202403132.10.1002/cbdv.202403132Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Sishu NK, Karunakaran MK, Hadkar VM, Mohanty C, Sharmila A, Selvaraj CI, et al. Phyto-mediated synthesis of SnO2 nanoparticles using Croton malabaricus Bedd. for its antioxidant, antibacterial, hemocompatibility properties and photocatalytic activity. New J Chem. 2025;49(2):536–52.10.1039/D4NJ03958KSearch in Google Scholar
[4] Abadi EH, Amiri M, Ranaee M, Mortazavi-Derazkola S, Khademian A, Najafzadehvarzi H, et al. Plasmonic selenium nanoparticles biosynthesized from Crataegus monogyna fruit extract: a novel approach to mitigating chromium-induced toxicity. Plasmonics. 2024;20(6):3805–15.10.1007/s11468-024-02539-3Search in Google Scholar
[5] Barzegarparay F, Najafzadehvarzi H, Pourbagher R, Parsian H, Ghoreishi SM, Mortazavi-Derazkola S. Green synthesis of novel selenium nanoparticles using Crataegus monogyna extract (SeNPs@ CM) and investigation of its toxicity, antioxidant capacity, and anticancer activity against MCF-7 as a breast cancer cell line. Biomass Convers Biorefin. 2024;14(20):25369–78.10.1007/s13399-023-04604-zSearch in Google Scholar
[6] Ghoreishi SM, Derazkola SM. Eco-friendly synthesis of gold nanoparticles via tangerine peel extract: unveiling their multifaceted biological and catalytic potentials. Heliyon. 2025;11(1):e40104.10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40104Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Hashemi Z, Mizwari ZM, Alizadeh SR, Habibi M, Mohammadrezaee S, Ghoreishi SM, et al. Anticancer and antibacterial activity against clinical pathogenic multi-drug resistant bacteria using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles with Mentha pulegium and Crocus caspius extracts. Inorg Chem Commun. 2023;154:110982.10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110982Search in Google Scholar
[8] Hashemi Z, Mizwari ZM, Hosseini Z, Khosravi Z, Alizadeh SR, Shirzadi-Ahodashti M, et al. In-vitro anticancer and antibacterial activities and comparative of eco-friendly synthesized silver nanoparticles using hull of Pistacia vera and rhizome of Sambucus ebulus extracts. Inorg Chem Commun. 2023;154:110913.10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110913Search in Google Scholar
[9] Zare-Bidaki M, Aramjoo H, Mizwari ZM, Mohammadparast-Tabas P, Javanshir R, Mortazavi-Derazkola S. Cytotoxicity, antifungal, antioxidant, antibacterial and photodegradation potential of silver nanoparticles mediated via Medicago sativa extract. Arab J Chem. 2022;15(6):103842.10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103842Search in Google Scholar
[10] Shirzadi-Ahodashti M, Hashemi Z, Mortazavi Y, Khormali K, Mortazavi-Derazkola S, Ebrahimzadeh MA. Discovery of high antibacterial and catalytic activities against multi-drug resistant clinical bacteria and hazardous pollutants by biosynthesized of silver nanoparticles using Stachys inflata extract (AgNPs@ SI). Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 2021;617:126383.10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126383Search in Google Scholar
[11] Shirzadi-Ahodashti M, Mizwari ZM, Mohammadi-Aghdam S, Ahmadi S, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Mortazavi-Derazkola S. Optimization and evaluation of anticancer, antifungal, catalytic, and antibacterial activities: biosynthesis of spherical-shaped gold nanoparticles using Pistacia vera hull extract (AuNPs@ PV). Arab J Chem. 2023;16(1):104423.10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104423Search in Google Scholar
[12] Kiani Z, Aramjoo H, Chamani E, Siami-Aliabad M, Mortazavi-Derazkola S. In vitro cytotoxicity against K562 tumor cell line, antibacterial, antioxidant, antifungal and catalytic activities of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Sophora pachycarpa extract. Arab J Chem. 2022;15(3):103677.10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103677Search in Google Scholar
[13] Hadkar VM, Selvaraj CI. Characterization and investigating the potential therapeutic effects of phyto-assisted CuO and Zn-doped CuO nanoparticles from Calophyllum apetalum (Willd.) leaf extract. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2025;104:106530.10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106530Search in Google Scholar
[14] Bhargava V, Sishu NK, Mohanty C, Hadkar VM, Sharmila A, Nanda B, et al. Exploring Moringa concanensis nimmo mediated bio-preparation of Ag doped MgO nanoparticles for biological activity and chromium (VI) remediation. Chem Eng J. 2024;502:157386.10.1016/j.cej.2024.157386Search in Google Scholar
[15] Papitha R, Hadkar V, Sishu NK, Arunagiri S, Roopan SM, Selvaraj CI. Green synthesis of CuO/TiO2 and ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposites using Parkia timoriana bark extract: enhanced antioxidant and antidiabetic activities for biomedical applications. Ceram Int. 2024;50(20):39109–21.10.1016/j.ceramint.2024.07.277Search in Google Scholar
[16] Sharmila A, Roopan SM, Selvaraj CI. Natural carbon incorporated ZnO/C and ZnO: sustainable nanomaterials for antioxidant, toxicity and cytotoxicity investigations. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2024;96:105731.10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105731Search in Google Scholar
[17] Kumaran AV, Sharmila A, Hadkar VM, Sishu NK, Mohanty C, Roopan SM, et al. Sustainable production of ZnO/MgO nanocomposite for effective photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B and their other properties. Mater Sci Eng B. 2025;313:117866.10.1016/j.mseb.2024.117866Search in Google Scholar
[18] Ivanova NM, Muldakhmetov ZM, Soboleva YA, Vissurkhanova YA, Beisenbekova ME. Preparation and electrocatalytic activity of bimetallic Ni–Cu micro-and nanoparticles. Catalysts. 2023;13(8):1166.10.3390/catal13081166Search in Google Scholar
[19] Phinjaroenpha R, Boonserm K, Rattanasuporn S. Preparation and characterization of bimetallic Cu–Ni and/or Ni–Cu core-shell nanoparticles with high photocatalytic activity. Naresuan Univ J Sci Technol. 2020;29(2):54–63.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Hu H, Zhang D, Yu W, Sugawara K, Guo T. Monodisperse and 1D cross-linked multi-branched Cu@ Ni core–shell particles synthesized by chemical reduction. J Electron Mater. 2014;43:2548–52.10.1007/s11664-014-3201-7Search in Google Scholar
[21] Chaudhary J, Tailor G, Yadav BL, Michael O. Synthesis and biological function of nickel and copper nanoparticles. Heliyon. 2019;5(6):e01878.10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01878Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Argueta-Figueroa L, Morales-Luckie RA, Scougall-Vilchis RJ, Olea-Mejía OF. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of copper, nickel and bimetallic Cu–Ni nanoparticles for potential use in dental materials. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int. 2014;24(4):321–8.10.1016/j.pnsc.2014.07.002Search in Google Scholar
[23] Lee HJ, Song JY, Kim BS. Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2013;88(11):1971–7.10.1002/jctb.4052Search in Google Scholar
[24] Berta L, Coman NA, Rusu A, Tanase C. A review on plant-mediated synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles, characterisation and their biological applications. Materials. 2021;14(24):7677.10.3390/ma14247677Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Pandey KB, Rizvi SI. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid Med Cel Longev. 2009;2(5):270–8.10.4161/oxim.2.5.9498Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Behzad F, Naghib SM, Tabatabaei SN, Zare Y, Rhee KY. An overview of the plant-mediated green synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. J Ind Eng Chem. 2021;94:92–104.10.1016/j.jiec.2020.12.005Search in Google Scholar
[27] Mahomoodally MF, Zengin G, Aumeeruddy MZ, Sezgin M, Aktumsek A. Phytochemical profile and antioxidant properties of two Brassicaceae species: Cardaria draba subsp. draba and Descurainia sophia. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. 2018;16:453–8.10.1016/j.bcab.2018.09.020Search in Google Scholar
[28] Sadeghi M, Borujeni FE, Ghodsi S, Moshtaghian J. Investigating the effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl on blood glucose, biochemistry parameters, fatty profile, and serology factor in diabetic male rats. Int J Health Life Sci. 2021;7(3):e115280.10.5812/ijhls.115280Search in Google Scholar
[29] Li D, Xie L, Zhang P, Liu R, Shi M, Mei Y, et al. Characterization of resistance and fitness cost of Descurainia sophia L. populations from Henan and Xinjiang, China. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):14655.10.1038/s41598-021-94317-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Shen J, Yang Q, Hao L, Zhang L, Li X, Zheng M. The metabolism of a novel cytochrome P450 (CYP77B34) in tribenuron-methyl-resistant Descurainia sophia L. to herbicides with different mode of actions. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5812.10.3390/ijms23105812Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Feng WS, Li CG, Zheng XK, Li LL, Chen WJ, Zhang YL, et al. Three new sulphur glycosides from the seeds of Descurainia sophia. Natl Prod Res. 2016;30(15):1675–81.10.1080/14786419.2015.1135141Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Moshaie-Nezhad P, Bahari Z, Jangravi Z, Zarei SM, Iman M. The effect of Descurainia sophia seed extract on nephrotoxicity markers induced by acetaminophen in mice. J Adv Med Biomed Res. 2021;29(134):139–44.10.30699/jambs.29.134.139Search in Google Scholar
[33] Yi JM, Kim YA, Lee YJ, Bang OS, Kim NS. Effect of an ethanol extract of Descurainia sophia seeds on Phase I and II drug metabolizing enzymes and P-glycoprotein activity in vitro. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:1–8.10.1186/s12906-015-0965-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Sherahi MH, Fathi M, Zhandari F, Hashemi SMB, Rashidi A. Structural characterization and physicochemical properties of Descurainia sophia seed gum. Food Hydrocolloid. 2017;66:82–9.10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.12.010Search in Google Scholar
[35] Lee YJ, Kim NS, Kim H, Yi JM, Oh SM, Bang OS, et al. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory constituents from the seeds of Descurainia sophia. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36:536–41.10.1007/s12272-013-0066-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[36] Kim BY, Lee J, Park SJ, Bang OS, Kim NS. Gene expression profile of the A549 human non‐small cell lung carcinoma cell line following treatment with the seeds of Descurainia sophia, a potential anticancer drug. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2013;2013(1):584604.10.1155/2013/584604Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Hsieh PC, Kuo CY, Lee YH, Wu YK, Yang MC, Tzeng IS, et al. Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of actions of Descurainia sophia. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(14):2163.10.7150/ijms.47357Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Sadeghi M, Khomartash MS, Gorgani-Firuzjaee S, Vahidi M, Khiavi FM, Taslimi P. α-glucosidase inhibitory, antioxidant activity, and GC/MS analysis of Descurainia sophia methanolic extract: in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. Arab J Chem. 2022;15(9):104055.10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104055Search in Google Scholar
[39] An X, Gao Y, Liu X, Yin Q, Meng L, Wei L. Gold nanoparticles green-mediated by Descurainia sophia extract for the treatment of ovalbumin-induced asthma in rats. Inorg Chem Commun. 2024;161:112011.10.1016/j.inoche.2023.112011Search in Google Scholar
[40] Ge J, Wen J, Jiang M, Huang K, Qi S, Huang W, et al. Targeting the HLC-1, LC-2/ad, and PC-14 lung cancer cell lines by the silver nanoparticles green-formulated by Descurainia sophia leaf extract. Mol Cell Prob. 2025;79:102001.10.1016/j.mcp.2024.102001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Khatami M, Mehnipor R, Poor MHS, Jouzani GS. Facile biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Descurainia sophia and evaluation of their antibacterial and antifungal properties. J Clust Sci. 2016;27:1601–12.10.1007/s10876-016-1028-5Search in Google Scholar
[42] Lamayi WD, Shehu Z, Mai AJ, Magaji B, Adam MM, Bunu MA. Green synthesis, characterization and larvicidal activity of Cu/Ni bimetallic nanoparticles using fruit extract of Palmyra palm. Int J Chem Mat Res. 2020;8(1):20–5.10.18488/journal.64.2020.81.20.25Search in Google Scholar
[43] Yu S, Zhao L, Kang W, Amraii SA. Characterization and cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and anti-lung carcinoma effects of Matricaria chamomilla extract green-synthesized Ag nanoparticles: describing a modern chemotherapeutic supplement. Inorg Chem Commun. 2024;168:112904.10.1016/j.inoche.2024.112904Search in Google Scholar
[44] Kiefer J, Grabow J, Kurland HD, Müller FA. Characterization of nanoparticles by solvent infrared spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2015;87(24):12313–7.10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03625Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[45] Kumar M, Ranjan R, Sinha MP, Raipat BS. Different techniques utilized for characterization of metallic nanoparticles synthesized using biological agents: a review. Balneo PRM Res J. 2023;14(1):534.10.12680/balneo.2023.534Search in Google Scholar
[46] Faisal S, Al-Radadi NS, Jan H, Abdullah, Shah SA, Shah S, et al. Curcuma longa mediated synthesis of copper oxide, nickel oxide and Cu–Ni bimetallic hybrid nanoparticles: characterization and evaluation for antimicrobial, anti-parasitic and cytotoxic potentials. Coatings. 2021;11(7):849.10.3390/coatings11070849Search in Google Scholar
[47] Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajjadi M, Komber H, Khonakdar HA, Sajadi SM. In situ green synthesis of Cu–Ni bimetallic nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide as an effective and recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of N‐benzyl‐N‐aryl‐5‐amino‐1H‐tetrazoles. Appl Organomet Chem. 2019;33(7):e4938.10.1002/aoc.4938Search in Google Scholar
[48] Mourdikoudis S, Pallares RM, Thanh NT. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale. 2018;10(27):12871–934.10.1039/C8NR02278JSearch in Google Scholar
[49] Isaeva IY, Ostaeva GY, Eliseeva EA, Golovin AL, Vasiliev AL. Effect of synthesis temperature on the formation of nickel–copper composite nanoparticles. Lett Mat. 2023;13(2):49–152.10.22226/2410-3535-2023-2-149-152Search in Google Scholar
[50] Scimeca M, Bischetti S, Lamsira HK, Bonfiglio R, Bonanno E. Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis: a powerful tool in biomedical research and diagnosis. Eur J Histochem. 2018;62(1):2841.10.4081/ejh.2018.2841Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Gu J, Aidy A, Goorani S. Anti-human lung adenocarcinoma, cytotoxicity, and antioxidant potentials of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized by Calendula officinalis. J Exp Nanosci. 2022;17(1):285–96.10.1080/17458080.2022.2066082Search in Google Scholar
[52] Mahdavi B, Paydarfard S, Rezaei‐Seresht E, Baghayeri M, Nodehi M. Green synthesis of NiONPs using Trigonella subenervis extract and its applications as a highly efficient electrochemical sensor, catalyst, and antibacterial agent. Appl Organomet Chem. 2021;35(8):e6264.10.1002/aoc.6264Search in Google Scholar
[53] Callister WD Jr, Rethwisch DG. Materials science and engineering: an introduction. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2020. p. 98–102.Search in Google Scholar
[54] Sastry S. Green synthesis and characterization of silver nano particles. J Water Environ Nanotechnol. 2020;5(1):81–91.Search in Google Scholar
[55] Khan MJ, Shameli K, Sazili AQ, Selamat J, Kumari S. Rapid green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles arbitrated by curcumin in an alkaline medium. Molecule. 2019;24(4):719.10.3390/molecules24040719Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Li J, Mahdavi B, Baghayeri M, Rivandi B, Lotfi M, Zangeneh MM, et al. A new formulation of Ni/Zn bi-metallic nanocomposite and evaluation of its applications for pollution removal, photocatalytic, electrochemical sensing, and anti-breast cancer. Environ Res. 2023;233:116462.10.1016/j.envres.2023.116462Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[57] Shu M, Mahdavi B, Balčiūnaitienė A, Goorani S, Mahdavi AA. Novel green synthesis of tin nanoparticles by medicinal plant: chemical characterization and determination of cytotoxicity, cutaneous wound healing and antioxidant properties. Micro Nano Lett. 2023;18(2):e12157.10.1049/mna2.12157Search in Google Scholar
[58] Yao Y, Sun W, Ge J, Wang H. Prevention of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury in mice by Tragopogon dubius green-mediated silver/palladium nanoparticles and its potential mechanisms. Inorg Chem Commun. 2023;157:111153.10.1016/j.inoche.2023.111153Search in Google Scholar
[59] Liyuan T, Lijun Z, Wei H, Meixuan J, Man Z, Zhihui Y, et al. Green synthesised CuNPs using Alhagi maurorum extract and its ability to amelioration of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infected pneumonia mice model. J Exp Nanosci. 2022;17(1):585–98.10.1080/17458080.2022.2104451Search in Google Scholar
[60] Li S, He J, Xu QH. Aggregation of metal-nanoparticle-induced fluorescence enhancement and its application in sensing. ACS Omega. 2019;5(1):41–8.10.1021/acsomega.9b03560Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Qian LW. Primary studies on anti-tumor activities and HMGR gene of Descurainia sophia (Linn.). MSc thesis. China: Anhui Normal University; 2006.Search in Google Scholar
[62] Sun K, Li X, Liu JM, Wang JH, Li W, Sha Y. A novel sulphur glycoside from the seeds of Descurainia sophia (L.). J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005;7:853–6.10.1080/1028602042000204072Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Sun K, Li X, Li W, Wang J, Liu J, Sha Y. Two new lactones and one new aryl-8-oxa-bicyclo [3,2,1] oct-3-en-2-one from Descurainia sophia. Chem Pharm Bull. 2004;52:1483–6.10.1248/cpb.52.1483Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[64] Dehshahri S, Afsharypuor S, Asghari G, Mohagheghzadeh A. Determination of volatile glucosinolate degradation products in seed coat, stem and in vitro cultures of Moringa peregrina (Forssk.) Fiori. Res Pharm Sci. 2012;7:51–6.Search in Google Scholar
[65] Gamet L, Li P, Lumeau S, Cassar G, Dupont MA, Chevolleau S, et al. Sulforaphane, a naturally occurring isothiocyanate, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1426–33.Search in Google Scholar
[66] Wei Z, Hao J, Yuan S, Li Y, Juan W, Sha X, et al. Paclitaxel-loaded pluronic P123/F127 mixed polymeric micelles: formulation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Int J Pharm. 2009;376:176–85.10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.04.030Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[67] Firdhouse MJ, Lalitha P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the extract of Alternanthera sessilis – antiproliferative effect against prostate cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2013;4:137–43.10.1007/s12645-013-0045-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Gajendran B, Chinnasamy A, Durai P, Raman J, Ramar M. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver NPs from Datura inoxia and its apoptotic effect on human breast cancer cell line MCF7. Mater Lett. 2014;122:98–102.10.1016/j.matlet.2014.02.003Search in Google Scholar
[69] Nagajyothi PC, Sreekanth TVM, Lee JI, Lee KD. Mycosynthesis: antibacterial, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Inonotus obliquus (Chaga mushroom) extract. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol. 2014;130:299–304.10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2013.11.022Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[70] AshaRani PV, Low KMG, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2009;3:279–90.10.1021/nn800596wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[71] Xu L, Li X, Takemura T, Hanagata N, Wu G, Chou LL. Genotoxicity and molecular response of silver nanoparticle (NP)-based hydrogel. J Nanobiotechnol. 2012;10:1–11.10.1186/1477-3155-10-16Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[72] Akter M, Sikder MT, Rahman MM, Ullah AKMA, Hossain KFB, Banik S, et al. A systematic review on silver nanoparticles-induced cytotoxicity: physicochemical properties and perspectives. J Adv Res. 2017;9:1–16.10.1016/j.jare.2017.10.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Abdolmaleki S, Aliabadi A, Khaksar S. Unveiling the promising anticancer effect of copper-based compounds: a comprehensive review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024;150(4):213.10.1007/s00432-024-05641-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[74] Huang T, Ma K, Wang Y. Characterization and evaluation of the cytotoxic, antioxidant, and anti-human lung cancer properties of copper nanoparticles green-synthesized by fennel extract following the PI3K/AKT/Mtor signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2025;20(1):e0309207.10.1371/journal.pone.0309207Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[75] Sun J, Tang SM, Sun J, Gao W. Exploring the anticancer potential of green synthesized Zn/Cu nanocomposites from olive leaves against lung cancer. Hereditas. 2025;162(1):65.10.1186/s41065-025-00426-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[76] Pandey N, Dhiman S, Srivastava T, Majumder S. Transition metal oxide nanoparticles are effective in inhibiting lung cancer cell survival in the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Chem Bio Interact. 2016;254:221–30.10.1016/j.cbi.2016.06.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

