Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic, an unprecedented global health crisis, has thrust humanity into a relentless battle with a variety of treatments and vaccines against the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Recent developments in nanotechnology have garnered significant interest in the application of metallic nanoparticles (NPs); specifically, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have demonstrated antimicrobial and antiviral properties. This study investigates the molecular interactions between the receptor binding domains of five SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants (Alpha, Beta, Delta, Omicron, and Gamma) and the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor, followed by the docking of AuNPs and AgNPs and the natural compound Beta-escin onto these complexes. As well as the inspection of both NPs against the virus main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Comprehensive computational simulations utilizing Autodock 4.2 and HDOCK server were employed to evaluate the binding affinities of these NPs toward key viral targets, SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, RdRp, and the spike glycoprotein. The results revealed that both AgNPs and AuNPs exhibited successful binding to the active pockets of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, with slightly varying binding energies. In contrast, for RdRp, AgNPs demonstrated superior binding affinity compared to AuNPs, with differences in the residues involved in the binding pocket. AuNPs exhibited stronger binding affinities in the spike protein pocket. We also determined robust binding affinities between ACE2 and the spike variants, with the Omicron variant exhibiting the highest affinity. Subsequent docking of AuNPs and AgNPs revealed strong interactions with all ACE2–spike complexes, with AuNPs showing slightly higher affinities. The findings contribute to a deeper understanding of the interactions between NPs and viral proteins, shedding light on their mechanisms of action and their potential to offer innovative solutions for combating infectious diseases, particularly those caused by SARS-CoV-2.
1 Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has precipitated a global health crisis, necessitating the rapid development of effective therapeutic and diagnostic strategies [1]. Central to the virus’s pathogenicity is the spike protein, which facilitates viral entry by binding to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor on host cells. Variants of concern such as Alpha, Beta, Delta, Omicron, and Gamma have emerged, characterized by mutations in the spike protein that enhance transmissibility and potentially alter vaccine efficacy [2]. Understanding the molecular interactions between these spike protein variants and the ACE2 receptor is critical for developing targeted interventions. Molecular docking, a computational method that predicts the preferred orientation of one molecule to a second, provides valuable insights into these interactions [3]. Also, among the various targets within the realm of coronaviruses, particular focus has been placed on the main protease (Mpro), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RDRP), and the spike protein [4].
These metallic nanoparticles (NPs), notably silver and gold, have emerged as highly promising agents due to their demonstrated effectiveness against a spectrum of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and other eukaryotic entities. This heightened interest among researchers is a response to the escalating problem of microbial resistance and the development of resilient strains [5,6]. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) exhibit remarkable antimicrobial properties attributed to their distinctive physiochemical attributes and superior biological functionalities [7]. They also possess antiviral properties, with reports indicating that AgNPs synthesized in Hepes buffer can impede the replication of HIV-1, displaying anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) activity, in addition to inhibiting hepatitis B virus and herpes simplex virus [8,9]. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have garnered significant attention in various domains, including industry and nanomedicine, owing to their exceptional electrical, optical, mechanical, and biological attributes [10,11]. The antiviral properties of AuNPs have been supported by research studies, with their minute particle size, low toxicity, non-immunogenicity, and capacity to bind biological ligands rendering them promising candidates for antibacterial and antiviral purposes. Previous investigations have demonstrated the ability of AuNPs to hinder multiple stages in the life cycles of various viruses, including Herpes simplex virus type 1, Zika virus, HIV, dengue virus, and foot-and-mouth disease virus [12,13]. Beta-escin (B-escin) is a natural saponin compound extracted from the seeds of the horse chestnut tree (Aesculus hippocastanum). Known for its anti-inflammatory, antiviral, vasoprotective, and anti-edematous properties, it has been used in traditional medicine and continues to be explored for its therapeutic potential [14,15,16]. Investigating its synergistic potential when combined with NPs in binding to the ACE2–spike complex could reveal novel strategies to combat SARS-CoV-2 [17].
The primary objective of this study is to investigate and elucidate the binding affinities and interaction dynamics among the molecules including the ACE2 receptor and the five SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants, with the Au and Ag NPs onto these protein–protein complexes, followed by B-escin. And also to explore the potential of AgNPs and AuNPs interactions with key viral targets, namely the Mpro and RdRp, providing insights into their potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications in managing COVID-19 and its variants.
2 Materials and methods
The molecular docking procedure involved utilizing the HDOCK server to conduct docking simulations for the receptor binding domain (RBD) of five different SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants: Alpha, Beta, Delta, Omicron, and Gamma (Protein Data Bank [PDB] ID 7R13, 7WEV, 7VHH, 7QO7, and 8DLO, respectively). In this investigation, the amino acid sequence of ACE2 wild type (PDB ID 1R42) served as the ligand, while the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein RBD variants acted as receptors. Subsequently, AuNPs and AgNPs were docked onto the resulting protein–protein complexes. The structural information for AgNPs (CID_23954) and AuNPs (CID_23985) was retrieved from PubChem, and their geometries underwent optimization through Autodock 4.2 [18,19]. Crystal structures’ water molecules were removed, polar hydrogen atoms were added, and only the relevant chains were retained. Marsili–Gasteiger partial charges were assigned using a two-phase algorithm. The receptor crystal structures underwent energy minimization via the AutoDockTools (ADT, v1.5.6) prepare_receptor4.py command, employing Kollman-united charges for calculating partial atomic charges [20]. For NP docking, it was allowed to be docked in all the protein pockets to find a suitable site for binding.
B-escin structure was allowed to dock against all the 10 obtained Au/Ag NP–spike–ACE2 complexes. The docking parameters were set to an energy evaluation of 2500.00, 100 runs, and a population size of 150, based on the Lamarckian genetic algorithm [21]. Ten binding modes were produced for the ligand with a maximum of 3 kcal/mol energy difference between each mode, and the best conformations, showing the lowest binding free energy, were retrieved. PyMOL(TM) 2.5.2 was used for generating 3D interaction figures [22].
Both AgNPs and AuNPs were tested again against two crystal structures of key proteins of SARS-CoV-2 that were chosen and procured from the Protein Data Bank Mpro (PDB ID 7CAM), RdRp (PDB ID 6YYT), which were all obtained from Zhang Lab’s I-Tasser receptor-binding domain, to find out a potent target for of the NPs [23,24].
In preparing the protein for the molecular docking, only the needed chains were kept, and the receptor structures were prepared using the AutoDock tool. Water molecules in the three crystal structures were deleted, while polar hydrogen atoms were added. Marsili–Gasteiger partial charges were appointed employing a two-phase algorithm. Furthermore, the receptor crystal structures were subjected to energy minimization using the AutoDockTools 1.5.6 applying the command, prepare_receptor4.py where Kollman-united charge was used for calculating the partial atomic charge. In determining the preferred binding sites of the protein, the grid box center xyz-coordinates were set to 13.688, 13.076, 5.396 for Mpro, 89.178, 106.82, and 99.62 for RdRp. The outputs from AutoDock were further analyzed through the UCSF Chimera and PyMOL software package [25].
3 Results and discussion
The molecular docking studies conducted using the HDOCK server reveal significant insights into the binding interactions between ACE2 and various spike protein variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The results in Table 1 underscore a strong affinity of ACE2 toward all examined spike receptor variants, with docking scores ranging from −269.59 to −359.33 kcal/mol. Notably, the Omicron variant exhibited the highest binding affinity, succeeded by the Delta variant, while the Gamma variant displayed the least binding affinity. These findings align with the epidemiological data suggesting higher transmissibility associated with the Omicron variant, potentially due to its robust interaction with ACE2 [26,27,28].
HDOCK results of docking ACE2 as a ligand on the five spike receptor variants
| Complex | ACE2–spike Alpha variant | ACE2–spike Beta variant | ACE2–spike Delta variant | ACE2–spike Omicron variant | ACE2–spike Gamma variant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Docking score (kcal/mol) | −298.59 | −281.90 | −333.36 | −359.33 | −269.59 |
| Confidence score | 0.9513 | 0.9333 | 0.9751 | 0.9850 | 0.9162 |
| Ligand rmsd (Å) | 1.19 | 84.66 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 47.17 |
Corroborating the docking scores, the confidence score, reflecting the probability of binding between two molecules, showed a consistent correlation. The ACE2–spike Omicron variant recorded the highest confidence score (0.9850), followed closely by the ACE2–spike Beta variant (0.9751). Conversely, the ACE2–spike Gamma variant reported the lowest confidence score at 0.9162. Given that a confidence score exceeding 0.7 indicates a high probability of binding, these scores affirm that all five tested interactions possess a strong binding capability. These data provide a molecular basis for the varying degrees of infectivity observed with different variants, highlighting the enhanced binding efficiency of the Omicron variant as a potential factor in its rapid spread.
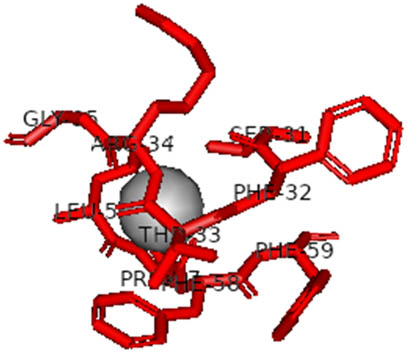
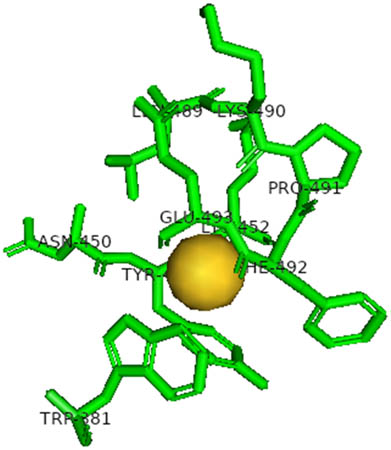
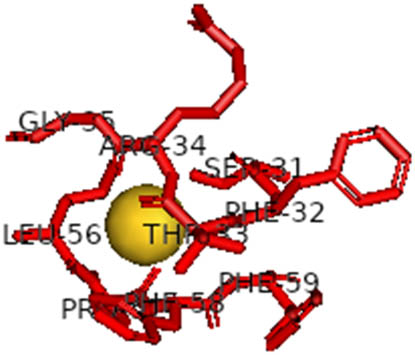
The docking analysis of AuNPs and AgNPs onto the resulting protein–protein complexes, as detailed in Table 2, underscores their notable affinity toward all five ACE2–spike receptor variants. Notably, the binding affinities range between 0.18 and 0.27 kcal/mol, indicative of strong interactions. Across the complexes, AuNPs generally exhibit a slightly higher affinity compared to AgNPs. Particularly noteworthy is the elevated affinity observed towards the ACE2–spike Beta variant, while the ACE2–spike Omicron variant shows relatively lower affinity. Detailed interactions are provided in Table 3, highlighting the 2D interactions of both AgNPs and AuNPs across all ACE2–spike receptor variant complexes. Remarkably, both NPs demonstrate consistent binding within the same pocket across all variants, emphasizing their consistent mode of interaction.
Binding energy results of docking AuNPs and AgNPs on ACE2–5 spike receptor variant complexes
| Ligand | Score | ACE2–spike Alpha variant | ACE2–spike Beta variant | ACE2–spike Delta variant | ACE2–spike Omicron variant | ACE2–spike Gamma variant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | −0.21 | −0.23 | −0.22 | −0.18 | −0.20 |
| AuNPs | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | −0.25 | −0.27 | −0.26 | −0.20 | −0.23 |
2D interaction results from docking AuNPs and AgNPs on ACE2–5 spike receptor variant complexes
| Ligand | ACE2–spike Alpha variant | ACE2–spike Beta variant | ACE2–spike Delta variant | ACE2–spike Omicron variant | ACE2–spike Gamma variant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| AuNPs |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Our docking results indicate strong interactions between AuNPs/AgNPs and the active sites of Mpro and RdRp. Mpro, being essential for processing viral polyproteins, plays a pivotal role in viral replication. Inhibiting Mpro’s active site may prevent the proteolytic cleavage necessary for generating functional non-structural proteins, ultimately halting viral replication. Similarly, RdRp is critical for synthesizing viral RNA, and its inhibition would disrupt the transcription and replication of the viral genome.
The strong binding affinities observed in this study suggest that AuNPs/AgNPs may act as steric inhibitors, blocking substrate access or inducing conformational changes that impair enzymatic activity. Additionally, the unique properties of metallic NPs, such as their ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) and disrupt viral protein structures, may further enhance their antiviral efficacy. However, further experimental validation is necessary to confirm these proposed mechanisms.
The resulting docked complexes of NPs were further examined through docking with B-escin to evaluate potential synergistic activity. B-escin’s amphipathic nature also allows it to integrate into lipid membranes, which could potentially destabilize the viral envelope, further impairing infectivity. Additionally, B-escin’s ability to modulate host immune responses by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress may provide a dual benefit in combating the virus and mitigating COVID-19-associated complications. However, further experimental and pharmacological studies are required to validate these findings and establish their efficacy and safety in vivo. As presented in Table 4, B-escin exhibited notable binding affinities across the 10 NP–ACE2–spike variant complexes, ranging from −8.11 to −10.46. Notably, the highest affinity was observed toward the NP–ACE2–spike Alpha variant, while the lowest was toward the NP–ACE2–spike Delta variant. In each complex, B-escin occupied distinct binding pockets, as delineated in Table 5.
Docking binding energy results of B-escin docked on AuNP and AgNP complexes with ACE2–5 spike receptor variant complexes
| Ligand | NP –complex | ACE2–spike Alpha variant | ACE2–spike Beta variant | ACE2–spike Delta variant | ACE2–spike Omicron variant | ACE2–spike Gamma variant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B-escin | AgNPs | −10.46 | −9.22 | −8.50 | −8.98 | −9.29 |
| AuNPs | −10.21 | −9.35 | −8.11 | −9.25 | −8.94 |
2D interaction results from docking B-escin on NPs–ACE2–spike receptor variant complexes
| B-escin–NP complex | ACE2–spike Alpha variant | ACE2–spike Beta variant | ACE2–spike Delta variant |
|---|---|---|---|
| AgNPs |
 |
 |
 |
| AuNPs |
 |
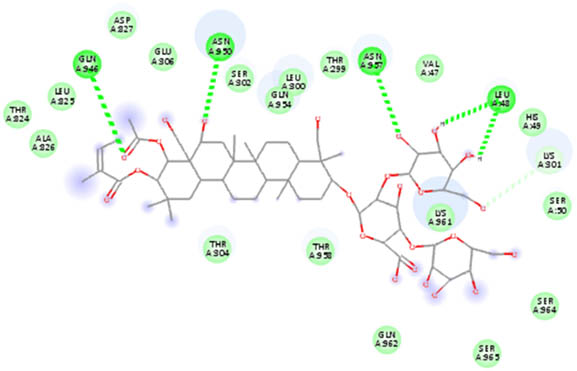 |
 |
| B-escin–NP complex | ACE2–spike Omicron variant | ACE2–spike Gamma variant |
|---|---|---|
| AgNPs |
 |
 |
| AuNPs |
 |
 |
In the NP–ACE2–spike Alpha variant complexes of both Ag and AuNPs, B-escin preferentially bound to a pocket at the intersection of ACE2 and spike proteins, forming eight and six hydrogen bonds, respectively, with the AgNP and AuNP complexes (Table 5). Despite the numerous interactions and high binding scores (−10.46 and −10.21 kcal/mol for AgNP and AuNP complexes, respectively), some unfavorable interactions were noted in both complexes.
For the NP–ACE2–spike Beta variant complexes of Ag and AuNPs, B-escin bound to a pocket at the center of the spike beta variant, demonstrating significant binding affinities (−9.22 and −9.35, respectively) (Table 4). In these complexes, B-escin formed three and five hydrogen bonds, respectively, with no unfavorable clashes observed, unlike the alpha variants.
Distinct from the alpha and beta complexes, B-escin adopted two different binding pockets when docked onto Ag and AuNP–ACE2–spike Delta variant complexes. It occupied a terminal pocket in the AgNP–ACE2–spike Delta variant complex and a pocket at the intersection of both proteins in the AuNP–ACE2–spike Delta variant complex. Although the binding affinities toward Ag and AuNP–ACE2–spike Delta variant complexes were the lowest (−8.5 and −8.11, respectively) (Table 4), numerous hydrogen bond interactions were formed with their binding pockets (6 and 4, respectively) (Table 5).
In both NP–ACE2–spike Omicron and Gamma variant complexes, B-escin exhibited similar binding affinities (Table 4) with a large number of favorable binding interactions (Table 5). It predominantly occupied pockets at the center of the spike variant protein, akin to the reported interactions with NP–ACE2–spike Beta variant complexes.
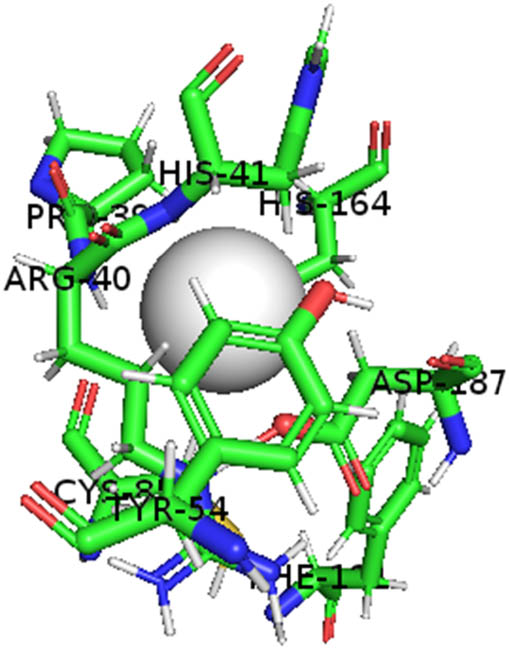
This study also investigated the potency of AgNPs and AuNPs against the Mpro and the RdRp. The choice of these proteins lies in the insightful features and key roles they play in the virus. In particular, primary proteases (Mpros), also known as 3-chymotrypsin-like proteases (3CLpros), are a group of cysteine hydrolases found in β-coronaviruses that are highly conserved. Growing evidence suggests that these 3CLpro enzymes are vital for viral replication and are crucial targets for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases caused by coronaviruses, such as COVID-19. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is involved in both RNA replication and transcription, facilitating the production of an RNA strand that is complementary to a specific RNA template through catalysis. This protein is highly considered because it is employed by SARS-CoV-2 to replicate its genetic material and transcribe its genetic information. The result of this analysis disclosed that both AgNPs and AuNPs were able to fit into the active pockets of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with binding energies of −0.16 and −0.13 kcal/mol, respectively. Their 3D interactions (Table 6) showed that they occupied the same pocket as reported in the literature, and the residues involved in this binding affinity are listed in Table 6. His41, an important residue involved in interactions with potential inhibitors, as reported in the literature, is involved in both pockets [29]. Specifically, upon targeting the AgNPs and AuNPs on the primary protease, binding affinities of −0.16 and −0.13 kcal/mol, respectively, were reported. The residues associated with the interaction with AgNPs are Pro39, Arg40, His41, Tyr45, Cys85, His164, Phe181, and Asp187. The Pro39, Arg40, His41, Cys85, and Asp187 residues were shown to interact with AuNPs. When the AgNP and AuNp were targeted at RdRp, binding affinities of −0.13 and −0.07 kcal/mol, respectively, were recorded. These interactions were observed with Gly485, Gly486, His572, Gln573, Lys574, and Leu575 for AgNPs and with Ser564, Thr565, Asn568, Asp684, and Ala685 for AuNPs. Further exploration of the effects of the compounds against protein spikes, −0.13 and −0.17 kcal/mol, was reported for AgNPs and AuNPs, respectively. This interaction is observed with the Asn121, Asn122, Ala123, Thr124, Phe 175, and Leu 176 residues of AgNPs and with the Asn121, Asn122, Ala123, Thr124, Asn125, Val126, Phe175, Leu176, and Met177 residues of AuNPs. In comparison, AgNPs show better binding affinity than AuNPs when targeted at the RdRp. The residues involved in the pocket are completely different from those of the NPs, as presented in Table 6. On the other hand, AuNPs showed better binding affinities for spike pockets than AgNPs, as more pocket residues were involved in this interaction. The identified residues involved in this interaction are the same as those reported for other reported inhibitors, such as elbasvir (DB11574), daclatasvir (DB09102), and glecaprevir (DB13879) [30].
PDB ID targets and bonded residues’ 3D interactions with their receptors and their binding energies
| PDB | NP | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | Residues | 3D interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB ID 7CAM (Mpro) | AgNP | −0.16 | Pro39, Arg40 His41, Tyr45, Cys85, His164, Phe181, Asp187 |
 |
| AuNP | −0.13 | Pro39, Arg40, His41, Cys85, Asp187 |
 |
|
| PDB ID 6YYT (RdRp) | AgNP | −0.13 | Gly485, Gly486, His572, Gln573, Lys574, Leu575 |
 |
| AuNP | −0.07 | Ser564, Thr565, Asn568, Asp684, Ala685 |
 |
|
| PDB ID 6VXX (spike) | AgNP | −0.14 | Asn121, Asn122, Ala123, Thr124, Phe175, Leu176 |
 |
| AuNP | −0.17 | Asn121, Asn122, Ala123, Thr124, Asn125, Val126, Phe175, Leu176, Met177 |
 |
While this study provides valuable insights into the binding interactions between SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants, ACE2, NPs, and B-escin, it is important to acknowledge several limitations. First, the results are derived solely from in silico molecular docking simulations, which may not fully replicate dynamic biological systems. Experimental validation, including in vitro and in vivo assays, is essential to confirm these findings. Second, this study does not evaluate the cytotoxicity or biocompatibility of AuNPs and AgNPs, which are critical considerations for therapeutic applications.
NPs, while promising, are known to exhibit dose-dependent toxicity. For example, AgNPs can induce oxidative stress by generating ROS, potentially leading to cellular damage. Furthermore, NP accumulation in vital organs, such as the liver and kidneys, has been observed in preclinical studies, raising concerns about their long-term safety. Mitigation strategies, such as NP functionalization with biocompatible materials and rigorous toxicity testing, are imperative before considering clinical applications. These limitations underline the necessity for a cautious approach and further experimental studies to assess the safety and efficacy of these therapeutic agents.
While B-escin has demonstrated promising pharmacological activity, it is not without limitations. Potential side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, diarrhea, and, in rare cases, allergic reactions. Additionally, caution is advised in patients with renal impairment due to potential nephrotoxic effects at higher doses. Regarding the spike protein, it is important to emphasize that its use in this study is limited to in silico simulations using structural data from the PDB. In therapeutic applications, proteins or their derivatives undergo extensive modifications to ensure safety and efficacy. Further preclinical studies are required to assess the safety, bioavailability, and therapeutic window of B-escin and NP-based delivery systems before advancing to clinical trials. These steps are crucial to ensure the safety of potential pharmacological interventions.
4 Conclusion
In summary, the docking analysis highlights the robust affinity of AuNPs and AgNPs toward various ACE2–spike receptor variants. Furthermore, the distinct binding pockets and interactions observed underscore the nuanced nature of NP–protein interactions. These findings not only deepen our understanding of NP–receptor interactions but also underscore their potential as therapeutic agents or diagnostic tools against viral infections. The docking study elucidates the synergistic potential of B-escin with both AuNPs and AgNPs across various ACE2–spike receptor variant complexes. The varying binding affinities and preferred binding pockets of B-escin underscore its dynamic interaction with NP–protein complexes. Despite differences in binding preferences, B-escin demonstrates consistently favorable interactions, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic adjunct in combating viral infections mediated by ACE2–spike receptor variants. Both AgNPs and AuNPs have also shown binding affinities to the Mpro and RDRP, suggesting their potential in antiviral drug development. These insights pave the way for further exploration of B-escin–NP combinations as potential antiviral strategies.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. Daniel Clement Agurokpon from Computational and Bio-Simulation Research Group, University of Calabar, Calabar, Nigeria, for editing and reviewing the manuscript.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: All authors accepted the responsibility for the content of the manuscript and consented to its submission, reviewed all the results, and approved the final version of the manuscript. I.Z.: conceptualization, data collection, literature search, data collection, data analysis, manuscript writing, manuscript editing. L.B.: manuscript review, validation, and supervision of the project.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Chow EJ, Uyeki TM, Chu HY. The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on community respiratory virus activity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2023;21(3):195–210.10.1038/s41579-022-00807-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Jacobs JL, Haidar G, Mellors JW. COVID-19: challenges of viral variants. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74:31–53.10.1146/annurev-med-042921-020956Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Vernet-Crua A, Cruz DM, Mostafavi E, Truong LB, Barabadi H, Cholula-Díaz JL, et al. Green-synthesized metallic nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. In Nanomedicine: Technologies and Applications. 2nd ed. Cambridge, UK: Woodhead Publishing; 2023. p. 297–338.10.1016/B978-0-12-818627-5.00014-2Search in Google Scholar
[4] Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell. 2020;181(2):281–92.10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Chen L, Liang J. An overview of functional nanoparticles as novel emerging antiviral therapeutic agents. Mater Sci Eng: C. 2020;112:110924.10.1016/j.msec.2020.110924Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Rai M, Yadav A, Gade A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol Adv. 2008;27(1):76–83.10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Gurunathan S, Qasim M, Choi Y, Do JT, Park C, Hong K, et al. Antiviral potential of nanoparticles – can nanoparticles fight against coronaviruses? Nanomaterials. 2020;10(9):1645.10.3390/nano10091645Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Yu SJ, Yin YG, Liu JF. Silver nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Sci Process Impacts. 2013;15(1):78–92.10.1039/C2EM30595JSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Ratan ZA, Mashrur FR, Chhoan AP, Shahriar SM, Haidere MF, Runa NJ, et al. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(12):2034.10.3390/pharmaceutics13122034Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Ravindran A, Chandran P, Khan SS. Biofunctionalized silver nanoparticles: advances and prospects. Colloids Surf B. 2013;105:342–52.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.07.036Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Babaei A, Mousavi SM, Ghasemi M, Pirbonyeh N, Soleimani M, Moattari A. Gold nanoparticles show potential in vitro antiviral and anticancer activity. Life Sci. 2021;284:119652.10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119652Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Sardar R, Funston AM, Mulvaney P, Murray RW. Gold nanoparticles: past, present, and future. Langmuir. 2009;25(24):13840–51.10.1021/la9019475Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Liu S, Hu M, Liu X, Liu X, Chen T, Zhu Y, et al. Nanoparticles and antiviral vaccines. Vaccines. 2023;12(1):30.10.3390/vaccines12010030Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Khushnuma R, Gupta D, Dubey A, Singh Y. A review on β-escin. Clin Rep. 2021;15:16.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Saravanan K, Elavarasi S, Revathi G, Karuppannan P, Ashokkumar M, Muthusamy C, et al. Targeting SARS-CoV2 spike glycoprotein: molecular insights into phytocompounds binding interactions – in-silico molecular docking. J Biomater Sci. 2024;1–18.10.1080/09205063.2024.2399395Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Lai Z, Shen H, Lee Y. Inhibitory effect of β-escin on Zika virus infection through the interruption of viral binding, replication, and stability. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):1–10.10.1038/s41598-023-36871-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Lutfi FM, Yu ES. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobial prophylaxis. Жypнaл Cибиpcкoгo фeдepaльнoгo yнивepcитeтa. Биoлoгия. 2019;12(3):266–76.10.17516/1997-1389-0301Search in Google Scholar
[18] Wasukan N, Kuno M, Maniratanachote R. Molecular docking as a promising predictive model for silver nanoparticle-mediated inhibition of cytochrome P450 enzymes. J Chem Inf Model. 2019;59(12):5126–34.10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00572Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Kaushik AC, Wang YJ, Wang X, Kumar A, Singh SP, Pan CT, et al. Evaluation of anti-EGFR-iRGD recombinant protein with GOLD nanoparticles: synergistic effect on antitumor efficiency using optimized deep neural networks. RSC Adv. 2019;9(34):19261–70.10.1039/C9RA01975HSearch in Google Scholar
[20] Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Huey R, Olson AJ. Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins: parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1996;4:293–304.10.1007/BF00124499Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Ross BJ. A Lamarckian evolution strategy for genetic algorithms. In Practical handbook of genetic algorithms. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 2019. p. 1–16.10.1201/9780429128356-1Search in Google Scholar
[22] Lakshmanan K. A new Schrodinger Pymol plugin to view docking score of Autodock and Autodock vina virtual screening results. SSRN; 2022.10.2139/ssrn.4170089Search in Google Scholar
[23] Hussain M, Jabeen N, Amanullah A, Baig AA, Aziz B, Shabbir S, et al. Molecular docking between human TMPRSS2 and SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: conformation and intermolecular interactions. AIMS Microbiol. 2020;6(3):350.10.3934/microbiol.2020021Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Zatla I, Boublenza L. A computational study on gold and silver nanoparticles against SARS-CoV-2 proteins. Proceedings. 2024;103(1):23.10.3390/proceedings2024103023Search in Google Scholar
[25] Chibber S, Ahmad I. Molecular docking, a tool to determine interaction of CuO and TiO 2 nanoparticles with human serum albumin. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2016;6:63–7.10.1016/j.bbrep.2016.03.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Shah M, Woo HG. Omicron: a heavily mutated SARS-CoV-2 variant exhibits stronger binding to ACE2 and potently escapes approved COVID-19 therapeutic antibodies. Front Immunol. 2022;12:830527.10.3389/fimmu.2021.830527Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Abeywardhana S, Premathilaka M, Bandaranayake U, Perera D, Peiris LD. In silico study of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein RBD and human ACE‐2 affinity dynamics across variants and Omicron subvariants. J Med Virol. 2023;95(1):e28406.10.1002/jmv.28406Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Kim S, Liu Y, Ziarnik M, Seo S, Cao Y, Zhang XF, et al. Binding of human ACE2 and RBD of omicron enhanced by unique interaction patterns among SARS‐CoV‐2 variants of concern. J Comput Chem. 2023;44(4):594–601.10.1002/jcc.27025Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Hassan A, Arafa RK. On the search for COVID-19 therapeutics: identification of potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors by virtual screening, pharmacophore modeling and molecular dynamics. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(17):7815–28.10.1080/07391102.2021.1902399Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Thakur A, Bansode D, Ghare P, Sakpal S. Molecular docking and dynamic simulation of approved drugs targeting against spike protein (6VXX) of 2019-nCoV (novel coronavirus). J Ind Chem Soc. 2022;99(8):100571.10.1016/j.jics.2022.100571Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

