Abstract
Potassium plays an important role in improving crop growth, yield, and quality; however, choosing the right potassium fertiliser remains challenging. To determine the optimal potassium fertiliser for kiwifruit, this study investigated the effects of different potassium sources on kiwifruit yield and postharvest quality as well as plant and soil nutrient contents in an orchard in Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Two types of potassium fertiliser were examined (K2SO4 and KCl; total K2O = 584 kg ha−1) at two different application stages (basal and topdressing) under the following four treatments: basal K2SO4 + KCl topdressing, basal K2SO4 + K2SO4 topdressing, basal KCl + K2SO4 topdressing, and basal KCl + KCl topdressing. The different potassium sources had no significant effect on kiwifruit yield; however, a slight increase in yield and economic gain was observed under combined treatment with K2SO4 and KCl compared to single fertiliser treatment. Meanwhile, the single fruit weight and vitamin C content of the fruit were 7.0 and 4.6% higher under treatment with basal K2SO4 + KCl topdressing compared with K2SO4 treatment alone, and 3.1 and 14.9% higher compared with KCl treatment alone. Moreover, application of KCl promoted potassium and chlorine absorption by both the leaves and fruit. However, no significant differences in the content of sulphate or chloride ions in the surface soil (0–40 cm) were observed between potassium sources. In contrast, in deeper soil, the content of chloride ions was highest after KCl treatment, while that of sulphate ions was highest after K2SO4 topdressing. Overall, these findings suggest that the most appropriate potassium source for kiwifruit production is basal application of K2SO4 followed by KCl as topdressing in the study region.
1 Introduction
Potassium is one of the macroelements required for plant growth, playing an important role in a number of physiological processes such as enzyme activation, protein synthesis, photosynthesis, osmoregulation, phloem transport, energy transfer, cation–anion balance, and stress resistance [1,2]. All plants require potassium, especially crops high in carbohydrates such as potatoes and various fruits [3–6]. Crops absorb some potassium from the soil; however, growth and development mainly rely on the application of potassium fertiliser.
Potassium fertilisers include potassium chloride (KCl), potassium sulphate (K2SO4), potassium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium salt, potassium magnesium salt, carnallite, potassium nitrate, and kiln powder. Of these, KCl and K2SO4 are most widely used in agricultural production [6–8]. However, due to the different anions involved, the effects of KCl and K2SO4 on crops are inconsistent [9–11]. A number of studies have examined the effects of different potassium fertilisers on crops [12–14], such as potatoes [15–17], cabbage, cucumber, and lettuce [18–20]; however, little is known about the effects on fruit trees.
Kiwifruit is very popular due to its high nutrient content and desired flavour [21]. China is a major producer of kiwifruit, with production and harvest areas both ranking first in the world [22]. Shaanxi Province is one of the main kiwifruit producing areas in China, which accounts for 32 and 55% of the total planting area and annual production, respectively [23]. Potassium (K) is a crucial plant nutrient, widely recognised as the “quality element” due to its significant role in enhancing the yield and quality of various crops. Potassium deficiency can lead to significant yield losses and quality defects [24]. Kiwifruit has a higher demand for potassium compared to other crops, as potassium is the most abundant mineral element in kiwifruits [25]. With an annual yield reaching tens of thousands of kilograms per hectare, kiwifruit cultivation removes a large amount of potassium from the soil. Therefore, to ensure optimal yield and quality, substantial potassium fertiliser supplementation is required annually in kiwifruit orchards. However, choosing the right potassium fertiliser for kiwifruit production remains a problem [26]. Improper use of chloride-containing fertilisers can have an adverse effect on some sensitive crops [27,28] and, as a result, they are rarely used on cash crops in China. Accordingly, K2SO4 is therefore the most popular potassium fertiliser; however, kiwifruit tends to prefer K2SO4, while having a high demand for chlorine [29]. Whether potassium chloride is more suitable than potassium sulphate to increase kiwifruit yield and improve fruit quality?
Overall, the effects of different potassium fertilisers on kiwifruit yield and quality are poorly understood. The objective of this study, therefore, was to examine the effects of two different sources of potassium (K2SO4 and KCl) applied as different potassium sources and different application method (as basal and topdressing fertilisers) in kiwifruit orchards. The results provide a basis for rational fertiliser management of kiwifruit production.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental site
Two experiments were conducted. An experiment was conducted to explore which potash fertiliser is suitable as the potassium source for kiwifruit, called as “Experiment One.” The experimental site was located in Hengqu Town, Meixian County, Shaanxi Province (N34°11′, E107°58′), a semi-humid drought-prone area with an annual average temperature of 12.9°C, annual average of 2015.2 h sunshine, annual average frost-free period of 216 days, and annual average rainfall is 600 mm. The kiwifruit orchard was established in 2006, covering a total area of 0.17 hectares. Tree spacing was 2 × 3 m and the kiwifruit variety planted was “Hayward” (Actinidia deliciosa). The rootstock is a seedling, and the scion is “Hayward.” The training system is T-shaped scaffold. The orchard soil was alluvial soil, calcareous soil, with a pH of 8.0, organic matter content of 12.3 g kg–1, mineral nitrogen content of 30.8 mg kg–1, available phosphorus content of 231.4 mg kg–1, and available potassium content of 127.9 mg kg–1.
Another experiment is to explore the application methods (as basal or topdressing fertilisers) of different potash fertilisers, called as “Experiment Two.” The experiment site was located in Yangling, Shaanxi Province, China (N34°17′, E108°6′), a semi-humid drought area, with an average temperature of 13.2°C, annual rainfall of approximately 600 mm (mainly concentrated in July to September), and annual evaporation of 1,400 mm. The selected kiwifruit orchard was built in 2005, with a total planted area of 0.2 hectares. Actinidia deliciosa “Hayward” scions were grafted onto2-year-old seedlings then planted at a spacing of 1.7 m × 3 m, and growing vines were trained along a T-shaped scaffold. The orchard is flat and comprised Lou soil, calcareous soil, with a pH of 8.2, organic matter content of 11.3 g kg–1, mineral nitrogen content of 36.2 mg kg–1, available phosphorus content of 222.4 mg kg–1, and available potassium content of 154.3 mg kg–1.
2.2 Experimental design
Experiment 1. Three treatments were examined: K2SO4, potassium sulphate as potash fertiliser; K2SO4 + KCl, whenever potash fertiliser is applied, it is half potassium sulphate and half potassium chloride; KCl, potassium chloride as potash fertiliser. The experiment was conducted from October 2014 through November 2017. The experimental design employed a randomised block of five chlorine treatments, with three replications per treatment, and seven trees in each plot. Each plot was 42 m2. Nitrogen fertilisers were in the form of urea (N 46%), phosphate fertiliser as triple superphosphate (P2O5 46%), and potassium fertiliser as potassium sulphate (K2O 51%) and potassium chloride (K2O 62%). All the treatments maintained consistent N (450 kg ha−1), P2O5 (225 kg ha−1), and K2O (450 kg ha−1) nutrients dose. Fifty percent of all the fertiliser was applied as base fertiliser in autumn, and 50% as topdressing at the young fruit stage.
Experiment 2. Four treatments were examined: S + Cl, basal K2SO4 + KCl topdressing; S + S, basal K2SO4 + K2SO4 topdressing; Cl + S, basal KCl + K2SO4 topdressing; and Cl + Cl, basal KCl + KCl topdressing. To do so, 14 healthy and consistent kiwi plants were selected as a single plot, following a randomised complete block design with three replicates. Under each treatment, the same amount of K2O (297 kg ha−1) was used for basal and topdressing, while nitrogen and phosphate were maintained at conventional rates (528 kg ha−1 N and 363 kg ha−1 P2O5, respectively). Half of all chemical fertilisers were applied as basal fertiliser and the remaining half as topdressing after previous season’s fruit harvest (October 2014) and young fruit stage (June 2015), respectively.
Irrigation, weeding, pruning, and other field management measures were consistent with local farming practices.
2.3 Sampling and analysis
At the fruit ripening stage (fruit soluble solids of 6.5%), fruit samples were collected from each of the four directions of growth of the trees in each plot. As a result, approximately 50 samples were collected from each plot. Sampling of leaves was similar to that of the fruit, with samples obtained from the middle of branches bearing fruit, in four directions. The total weight of fruit harvested from each plot was recorded as the production rate, which was then divided by the plot area to determine the yield.
When edible (following storage for 20 days in plastic bags at room temperature), five fruits from each treatment were chopped into a mixed sample to determine the quality indicators. The content of soluble solids was determined using a PAL-1 type sugar concentration detector (ATAGO, Japan). Soluble total sugars were determined by anthrone colorimetry. The titratable acid content was determined via NaOH titration. The vitamin C (Vc) content was determined by 2,6-dichloroindophenol colorimetry. Total nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium contents of the leaves and fruit were determined using a continuous flow analyser (AA3, Seal Analytical, Germany), an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (UV-1900, Shimazu Co., Ltd, China), and a flame photometer (FP 6410, Shanghai Yidian Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd, China), respectively, after digestion in H2O2–H2SO4. The chlorine content was determined using an automatic discontinuous chemical analyser (Cleverchem 200, DeChem-Tech.GmbH, Germany) after dry ashing. The sulphur content was determined by barium sulphate turbidimetry using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (UV-1900, Shimazu Co., Ltd, China) after digestion in HNO3–HClO4.
Soil samples were collected near the canopy drip line in fall (after harvest) using a stainless-steel auger. Samples were obtained at 20 cm intervals from a depth of 0–200 cm (Experiment 1) and 0–100 cm (Experiment 2). Three random samples were taken from each plot, mixed into a single composite sample then air-dried at room temperature. After removing the roots and debris, the dry soil samples were ground and passed through a 1 mm sieve then stored in polyethylene bottles. Determination of soil chloride ions (Cl−) was carried out based on a soil water ratio (w/v) of 1:5 using an automatic discontinuous chemical analyser (Cleverchem 200, DeChem-Tech. GmbH). Soil available sulphur was determined by barium sulphate turbidimetry using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (UV-1900, Shimazu Co., Ltd, China).
2.4 Data analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0 (IBM SPSS, Somers, USA). Experimental data are expressed as mean ± SD. All data were subjected to one-way analysis of variance followed by Duncan’s multiple range test. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05. The relationship between leaf and fruit nutrient contents was examined by Pearson correlation analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Yield and economic gain
Kiwifruit yield was 48.6, 43.1, 50.5, 45.1 t ha−1 under T1 to T4, respectively, with no significant differences among treatments (Table 1). The lowest fertiliser input value was observed under T4, with application of KCl alone. Overall, T3 resulted in the highest yield and net income, followed by T1. These findings suggest that application of both fertilisers is beneficial in terms of kiwifruit yield and economic gain.
Effects of each treatment on kiwifruit yield and economic gain
| Treatment | Yield (t ha−1) | Output value (104 RMB ha−1) | Input value (104 RMB ha−1) | Net income (104 RMB ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1(S + Cl) | 48.6 ± 5.5a | 19.46 | 1.15 | 18.31 |
| T2(S + S) | 43.1 ± 4.6a | 17.23 | 1.31 | 15.92 |
| T3(Cl + S) | 50.5 ± 5.6a | 20.21 | 1.15 | 19.06 |
| T4(Cl + Cl) | 45.1 ± 6.8a | 18.40 | 0.99 | 17.05 |
For the yield, different letters in the same column indicate significant difference between treatments (P < 0.05). Price of fertilisers: urea, 2.0 RMB kg−1; superphosphate, 1.0 RMB kg−1; K2SO4, 6.0 RMB kg−1; KCl, 4.0 RMB kg−1; and commercial organic fertiliser, 1.0 RMB kg−1. In the net income analysis, other costs rather than the cost of the fertiliser were not considered.
3.2 Postharvest quality
No significant differences in the contents of soluble solids, soluble sugars, and titratable acid or the sugar/acid ratio were observed between treatments (Table 2). However, T2 with K2SO4 alone resulted in a single fruit weight of 115.2 g, lower than that under T1 with combined K2SO4 and KCl application (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, T4 with KCl alone resulted in the lowest fruit Vc content of 57.9 mg 100 g−1, which was lower than that under combined T1 and T2 treatments (P < 0.05).
Effect of different treatments on kiwifruit postharvest quality
| Treatment | Single fruit weight (g) | Vc (mg 100 g−1) | Soluble sugar (%) | Titratable acid (%) | Soluble solids (%) | Sugar/acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1(S + Cl) | 123.3 ± 0.5a | 66.5 ± 3.3a | 7.4 ± 0.6a | 1.28 ± 0.01a | 12.1 ± 0.3a | 5.8 ± 0.4a |
| T2(S + S) | 115.2 ± 5.2b | 63.6 ± 0.2ab | 7.8 ± 1.0a | 1.28 ± 0.05a | 11.9 ± 0.3a | 6.1 ± 1.0a |
| T3(Cl + S) | 120.2 ± 3.8ab | 59.7 ± 2.2bc | 7.8 ± 0.5a | 1.34 ± 0.11a | 11.7 ± 0.2a | 5.9 ± 0.9a |
| T4(Cl + Cl) | 119.6 ± 4.6ab | 57.9 ± 1.9c | 8.0 ± 0.6a | 1.26 ± 0.08a | 12.4 ± 0.6a | 6.4 ± 0.2a |
Different letters in the same column indicate significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05).
3.3 Nutrient contents of the leaves and fruits
No significant differences in the total nitrogen and phosphorus contents of the leaves were observed between treatments (Figure 1). The leaf potassium content was highest under T1, with K2SO4 as a basal fertiliser and KCl as topdressing (P < 0.05). This was followed by T3, while lowest leaf potassium content was observed under T2. Meanwhile, the fruit potassium content was also higher under T4 with KCl alone compared to T2 with K2SO4 alone.
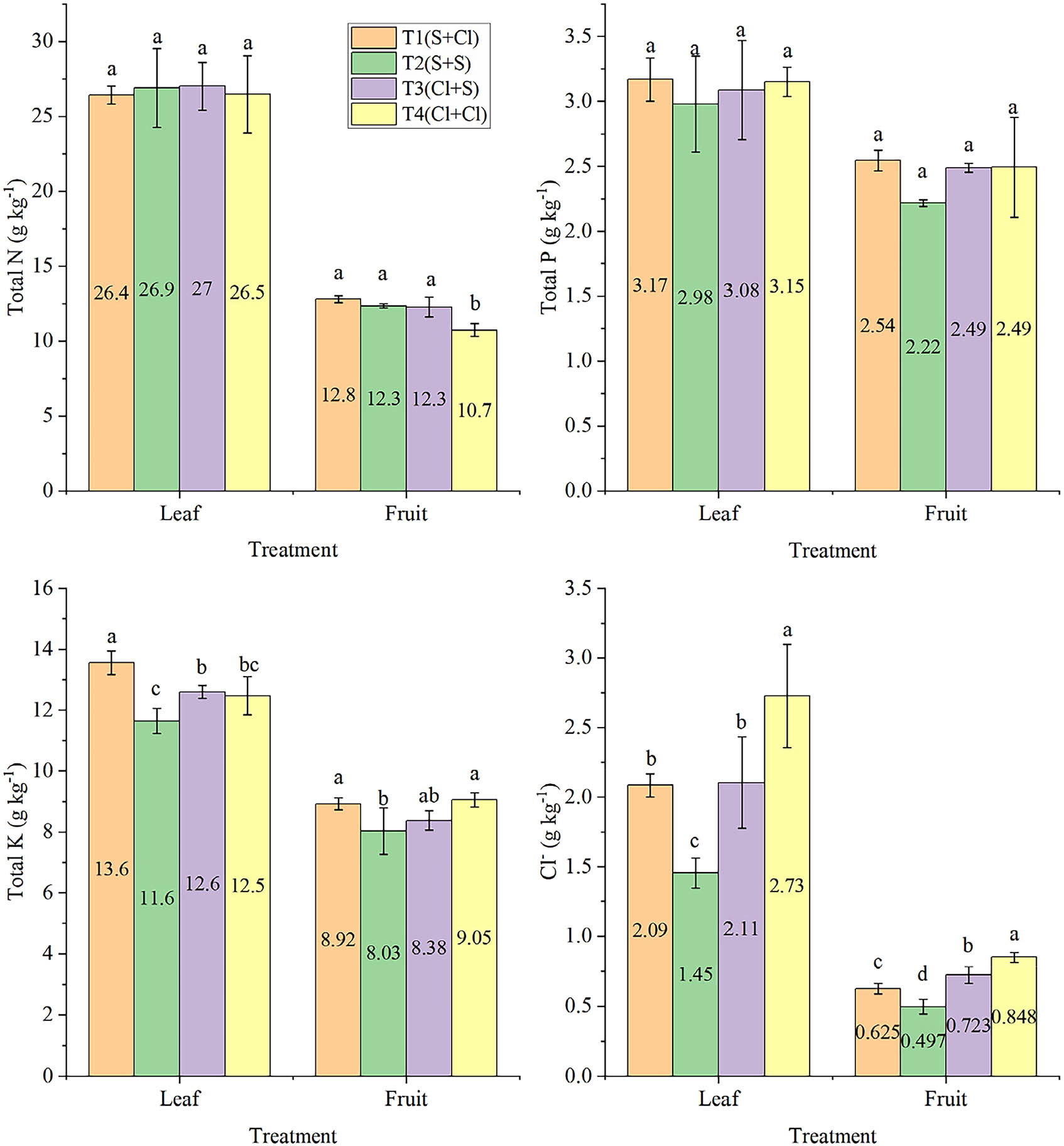
Effects of different treatments on nutrient contents of kiwifruit leaves and fruit at harvest. Different letters above the column represent a significant difference in nutrient content between treatments (P < 0.05).
The Cl− content of the leaves was positively correlated with the amount of chlorine applied (Figure 1). The leaf Cl− content was highest under T4 and lowest under T2 (P < 0.05). The Cl− content of the leaves was about three times that of the fruit, which was also related to the amount of chlorine applied and the application stage. For example, the fruit Cl− content was higher under T4 than T2, while T3 resulted in a higher fruit Cl− content than T1 (P < 0.05).
Pearson correlation analysis of the leaf and fruit nutrient contents (Table 3) revealed a significant negative correlation between the leaf nitrogen and potassium contents (P < 0.01). Only the leaf and fruit Cl− contents were significantly positively correlated with each other (P < 0.05).
Pearson correlation analysis of leaf and fruit nutrient contents
| Leaf N | 1 | |||||||
| Leaf P | −0.905** | 1 | ||||||
| Leaf K | −0.621 | 0.86 | 1 | |||||
| Leaf Cl | −0.562 | 0.82 | 0.429 | 1 | ||||
| Fruit N | 0.255 | −0.249 | 0.281 | −0.733 | 1 | |||
| Fruit P | −0.533 | 0.946 | 0.878 | 0.764 | −0.122 | 1 | ||
| Fruit K | −0.877 | 0.957 | 0.71 | 0.869 | −0.446 | 0.821 | 1 | |
| Fruit Cl | −0.334 | 0.691 | 0.287 | 0.967* | −0.767 | 0.697 | 0.719 | 1 |
| Leaf N | Leaf P | Leaf K | Leaf Cl | Fruit N | Fruit P | Fruit K | Fruit Cl |
*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (2-tailed).
3.4 Chloride and sulphate contents of the soil
Very little difference in the Cl− content of the soil was observed between treatment with K2SO4 alone (T2) and combined treatment with KCl and K2SO4 (T1 or T3), both of which were below 20 mg kg−1 (Figure 2). Meanwhile, the soil Cl− content at depths of 60–100 cm was highest after treatment with KCl alone (T4), with the highest content of 27 mg kg−1 at a depth of 80–100 cm. Under all treatments, the SO4 2− content was below 25 mg kg−1 at a soil depth of 0–40 cm, but this increased at depths of 60–100 cm under T1 and T2 compared to T3 and T4. These findings suggest that Cl− and SO4 2− in the surface soil (0–40 cm) are generally unaffected by potassium fertiliser source, unlike in deeper soil, particularly in the case of SO4 2−. However, by applying K2SO4 as topdressing, the SO4 2− content in deeper soil should increase.
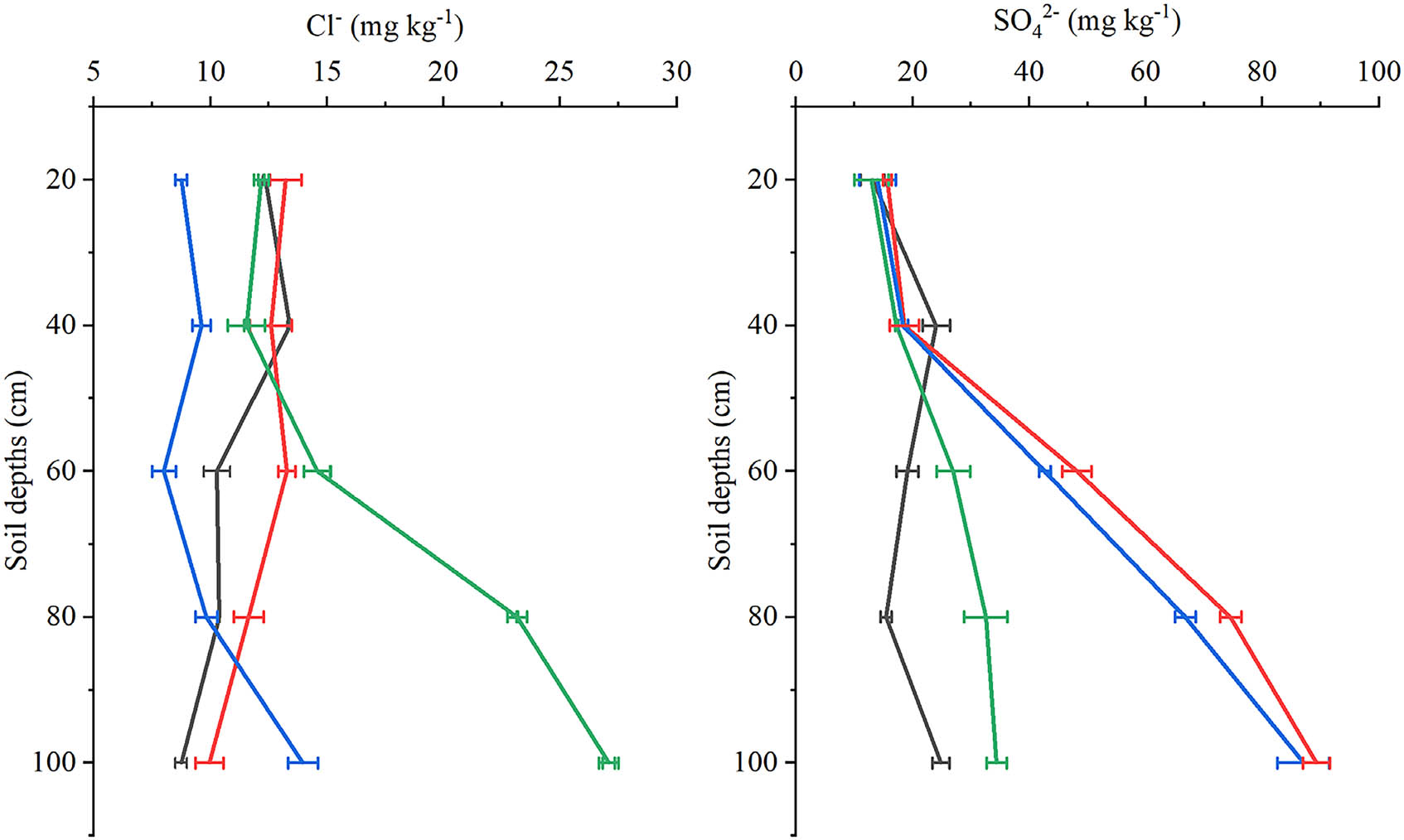
Effects of different treatments on the soil contents of chloride (Cl−) and sulphate (SO4 2−) ions at depths of 0–100 cm at kiwifruit harvest.
4 Discussion
The interactions between potassium ions and their companion ions determine the effects of potassium fertiliser on crop growth [30]. The effects of K2SO4 and KCl remain controversial and have been extensively studied because of their differing anions. While KCl is cheap, it is considered harmful to crop growth and quality compared to K2SO4. However, these effects vary depending on the crop species, in addition to the amount and stage of fertiliser application [31–33]. Here we examined the effects of two different potassium fertilisers on kiwifruit yield and postharvest quality as well as plant and soil nutrient contents. The results suggest that combined application of K2SO4 and KCl (T1 and T3) were beneficial in terms of yield, economic gain, postharvest quality, and nutrient contents compared to KCl (T4) and K2SO4 application alone (T2). This was especially true when K2SO4 was used as a basal fertiliser and KCl as topdressing for kiwifruit production.
No significant differences in kiwifruit yield were observed between treatments; however, the yield and economic gain were higher under combined K2SO4 and KCl application. One reason for this is that combined application provides the sulphur and chlorine elements required for kiwifruit growth, both of which function to increase yield. Different crops respond differently to K2SO4 and KCl under different experimental conditions. For example, application of K2SO4 and KCl was found to have no significant effect on potato yield, with only a slight increase under KCl treatment [34,35]. However, others suggest that potato yield decreases under KCl compared to K2SO4 treatment [11,33]. Meanwhile, Inthichack [20] found that celery yield increased under KCl treatment, while cabbage and lettuce yield were higher under K2SO4 treatment.
The effect of different potassium fertilisers on crop quality is also affected by the amount of potassium applied [31,35], the crop type [36,37], and the experimental conditions [11,16]. In the present study, the effects of different potassium fertilisers on kiwifruit postharvest quality were observed in the single fruit weight and fruit Vc content, both of which were highest under combined application of K2SO4 and KCl (T1) and lowest under K2SO4 (T2) and KCl application alone (T4). Meanwhile, other studies suggest that application of chloride-containing fertilisers decreases the Vc content of some crops [38–40]. Although kiwifruit plants require more chlorine than other crops, excess application of KCl can have adverse effects on fruit Vc, possibly due to the physiological metabolism of chlorine [41].
The effect of different potassium fertilisers on crop absorption of nitrogen and potassium varies greatly; however, they have less of an effect on phosphorus absorption [42]. Meanwhile, the absorption of chlorine by crops is positively correlated with the amount of chlorine applied [43,44]. Herein, kiwifruit treated with KCl alone (T4) resulted in the lowest fruit nitrogen content, but the highest fruit Cl and K contents, as well as the highest leaf K and Cl contents. Kiwifruit is well adapted to using Cl− rather than organic-acid anions to charge balance, and therefore, maintain K+ absorption [45]. In this study, the K and Cl contents of the kiwifruit leaves and fruit were higher after combined treatment with K2SO4 and KCl (T1 and T3) compared to K2SO4 treatment alone (T2), which may be one of the reason for the higher yield and improved quality under T1 and T3. Although the Cl content of the leaves and fruit was highest after treatment with KCl alone (T4), the highest leaf Cl 2.7 g kg−1 values did not reach the reported safe concentration for kiwifruit of 20–25 g kg−1 [46,47]. It is generally believed that chloride-containing fertilisers inhibit nitrate reductase activity, thereby reducing nitrogen absorption by crops [48]. Moreover, the anion accompanying K+ in the solution surrounding plant roots can also influence K+ absorption. Notably, SO4 2− absorption is slow compared to that of other inorganic anions such as CI−, which can limit K+ absorption [49].
The correlation analysis of nutrients between leaves and fruits can better reflect the relationship between plant nutrients in “source” and “sink.” In this study, their relationship was also analysed to explore whether chlorine in the leaves affects the major mineral nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) in both leaves and fruits. Different mineral nutrients in plants may exhibit antagonistic or synergistic effects [50]. Some studies suggest a positive correlation between chlorine and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in kiwifruit [25], indicating a synergistic relationship. However, the results of this study are not entirely consistent with those findings, which may be related to differences in kiwifruit varieties and the types of nitrogen fertilisers used.
SO4 2− and Cl− ions are easily leached into the soil [51], with contents related to soil depth and application rate. Long-term localisation experiments further suggest that SO4 2− is more likely to accumulate in the soil than Cl− [52]. Moreover, Shen et al. [51] found that long-term application of chloride-containing fertiliser resulted in a consistent soil SO4 2− content of 26.5 mg kg−1, while an increase was observed after application of sulphur-containing fertiliser. In the present study, SO4 2− and Cl− contents were low in the surface soil (0–40 cm), possibly due to the management of kiwifruit orchards, whereby irrigation is very high at approximately 3,000–6,000 m3 ha–1 per year. The soil Cl− content remained basically unchanged after treatment with KCl and K2SO4 alone (T1 and T3); however, in deep soil (80–100 cm) values were highest after treatment with KCl alone (T4, 27 mg kg−1; way below the safe concentration of 400 mg kg−1 [53]). These findings suggest that normal application of KCl in local kiwifruit orchards does not cause soil or leaf toxicity. Meanwhile, K2SO4 applied as topdressing (T3 and T2) resulted in an increase in the SO4 2− content of deep soil, with the highest content of 89 mg kg−1. Kiwifruit is sensitive to high levels of SO4 2− in the soil [46], which may be one of the reasons why the kiwifruit quality was better under T1 than T3.
Considering the fruit yield, postharvest quality, and nutrient contents of the plants and soil, our findings suggest that combined treatment with K2SO4 as basal fertiliser and KCl as topdressing (T1) is more beneficial for kiwifruit production than treatment with K2SO4 (T2) or KCl alone (T4). Combined application of K2SO4 and KCl increased the yield and economic gain while improving fruit quality and increasing the potassium content of both the leaves and fruit. Moreover, it caused no significant increase in salt ions (SO4 2− and Cl−) in the soil. Other studies using different potassium sources also suggest that combined application of K2SO4 and KCl is superior to K2SO4 or KCl alone [27]. However, KCl is advocated as a basal fertiliser, to be applied before plant growth in order to allow excessive chlorine to leach from the soil [12,13]. In the present study, using K2SO4 as a basal fertiliser and KCl as topdressing was the optimal treatment in terms of the various indicators examined. This may be related to the chlorophilic characteristics of kiwifruit. That is, applying KCl as topdressing provides the chlorine required during the growing season, thereby benefiting kiwifruit growth as well as yield and quality.
In conclusion, our findings suggest that combined application of K2SO4 and KCl in kiwifruit orchards is better than each fertiliser alone. Use of K2SO4 as a basal fertiliser and KCl as topdressing promotes nutrient absorption, increases yield, and improves postharvest quality of kiwifruit, without causing soil salt toxicity.
-
Funding information: This study was financially supported by Tarim University President’s Fund doctoral project “Research and development of new liquid organic fertilizer and its effect on improving the quality and efficiency of jujube” (TDZKBS202202), The XPCC Guiding Science and Technology Program Project in 2022 (2022ZD117), and Tarim University “Tianchi Talents” introduction program young doctor program.
-
Author contributions: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and consented to its submission to the journal, reviewed all the results and approved the final version of the manuscript. Yan’an Tong and Lili Yang designed the experiments and Long Ma carried them out. Chunming Chi and Shuangqing Lv contributed to data analysis and figure editing. Long Ma prepared the manuscript with contributions from all co-authors.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Li GQ, Ma L, Shi Y. Effect of different potassium fertilizer on growth, development and yield of Stevia rebaudiana. Sugar Crop China. 2011;(1):36–8.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Marschner P. Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants. 3rd edn. London: Academic Press; 2012.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Fawzy ZF, El-Nemr MA, Saleh A. Influence of levels and methods of potassium fertilizer application on growth and yield of eggplant. J Appl Sci Res. 2007;3(1):42–9.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Gunadi N. Response of potato to potassium fertilizer sources and application methods in andisols of west Java. Indones J Agric Sci. 2009;10(2):65–72.10.21082/ijas.v10n2.2009.p65-72Search in Google Scholar
[5] Baky AE, Ahmed AA, Nemr MAE, Zaki MF. Effect of potassium fertilizer and foliar zinc application on yield and quality of sweet potato. Res J Agric Biol Sci. 2010;6(4):386–94.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Meena VS, Maurya BR, Verma JP, Meena RS. Potassium solubilizing microorganisms for sustainable agriculture. This Springer imprint is published by Springer Nature; 2015.10.1007/978-81-322-2776-2Search in Google Scholar
[7] Jaiswal VP, Shukla SK, Sharma L, Singh I, Pathak AD, Nagargade M, et al. Potassium influencing physiological parameters, photosynthesis and sugarcane yield in subtropical India. Sugar Tech. 2020;23(2):343–59.10.1007/s12355-020-00905-zSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Yang XY, Geng JB, Li CL, Zhang M, Chen BC, Tian XF, et al. Combined application of polymer coated potassium chloride and urea improved fertilizer use efficiencies, yield and leaf photosynthesis of cotton on saline soil. Field Crop Res. 2016;197:63–73.10.1016/j.fcr.2016.08.009Search in Google Scholar
[9] Angadi SG, Vijayakumar N. Influence of different sources and rates of potassium fertilizers on the disease incidence in Anab-e-Shahi grapes. Karnataka J Agric Sci. 2000;13(3):783–6.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Sanghamitra M, Bhaskar VV, Rao AVDD, Subbaramamma P. Effect of different sources and levels of potassium on yield and carotenoids content of African marigold (Tagetes erecta Linn.) cv. Maxima Yellow. Plant Arch. 2015;15(2):633–6.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Manolov I, Neshev N, Chalova V. Tuber quality parameters of potato varieties depend on potassium fertilizer rate and source. Agric Agric Sci Procedia. 2016;10:63–6.10.1016/j.aaspro.2016.09.010Search in Google Scholar
[12] Wilcox GE. Effect of sulfate and chloride sources and rates of potassium on potato growth and tuber quality. Am Potato J. 1961;38(7):215–20.10.1007/BF02864794Search in Google Scholar
[13] Rowberry RG, Ketcheson JW. Sources of potassium in potato fertilizer and times of application. Can J Plant Sci. 1978;58:779–82.10.4141/cjps78-115Search in Google Scholar
[14] Kostova D, Mehandjiev D. Influence of fertilization and the kind of fertilizer upon the content of manganese and antioxidants in tomatoes. J Univ Chem Technol Metall. 2012;47(2):181–6.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Terman GL. Effect of source of potash in the fertilizer on yield and starch content of potatoes. Am Potato J. 1949;26(8):291–9.10.1007/BF02884596Search in Google Scholar
[16] Mondy NI, Munshi CB. Effect of type of potassium fertilizer on enzymic discoloration and phenolic, ascorbic acid, and lipid contents of potatoes. J Agric Food Chem. 1993;41(6):849–52.10.1021/jf00030a001Search in Google Scholar
[17] Khan MZ, Akhtar ME, Mahmood-Ul-Hassan M, Mahmood MM, Safdar MN. Potato tuber yield and quality as affected by rates and sources of potassium fertilizer. J Plant Nutr. 2012;35(5):664–77.10.1080/01904167.2012.653072Search in Google Scholar
[18] Correa CV, Cardoso AII, Claudio MDR. Yield of cabbage depending on rates and sources of potassium in top dressing. Semina Cienc Agrár. 2013;34(5):2129–37.10.5433/1679-0359.2013v34n5p2129Search in Google Scholar
[19] Barnea D, Yermiyahu U, Rav-David D, Elad Y. Effect of mineral nutrition and salt spray on cucumber downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis). Plants. 2022;11(8):2223–7747.10.3390/plants11081007Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Inthichack P, Nishimura Y, Fukumoto Y. Effect of potassium sources and rates on plant growth, mineral absorption, and the incidence of tip burn in cabbage, celery, and lettuce. Hortic Environ Biotechnol. 2012;53(2):135–42.10.1007/s13580-012-0126-zSearch in Google Scholar
[21] Cassano A, Jiao B, Drioli E. Production of concentrated kiwifruit juice by integrated membrane process. Food Res Int. 2004;37:139–48.10.1016/j.foodres.2003.08.009Search in Google Scholar
[22] Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Food and Agriculture Data. 2018. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Yang LL, Zhu ZJ, Zhang JS, Gao YM, Wang XM, Liu GY, et al. Response of kiwifruit yield and fruit quality to chloride-containing fertilizers. Agron J. 2020;112(2):1012–20.10.1002/agj2.20074Search in Google Scholar
[24] Budak E, Güneş A. The effects of potassium applied at different doses and times on the yield and nutrient content of pumpkin seed (Cucurbita pepo L.). Gesunde Pflanz. 2023;75:2879–87.10.1007/s10343-023-00865-wSearch in Google Scholar
[25] Li DW, Min Y, Cheng C, Liu XY, Xie XD, Gudeta C, et al. The diversity and disparity of mineral elements in global kiwifruits. Food Res Int. 2025;203:115844.10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115844Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Lu YL, Kang TT, Zhang XJ, Gao JB, Chen ZJ, Zhou JB. Evaluation of current fertilization status in kiwifruit orchards on the northern slope of Qinling Mountains: a case study of Yujiahe catchment, in Zhouzhi County. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci. 2016;22:380–7.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Wilmer L, Pawelzik E, Naumann M. Comparison of the effects of potassium sulphate and potassium chloride fertilisation on quality parameters, including volatile compounds, of potato tubers after harvest and storage. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:920212.10.3389/fpls.2022.920212Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Mengel K, Kirkby EA, Kosegarten H, Appel T. Principles of plant nutrition. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands; 2001.10.1007/978-94-010-1009-2Search in Google Scholar
[29] Smith GS, Clark CJ, Holland PT. Chlorine requirement of kiwifruit (Actinodia deliciosa). N Phytol. 1987;106:71–80.10.1111/j.1469-8137.1987.tb04792.xSearch in Google Scholar
[30] Pervez H, Makhdum MI, Ashraf M, Din Shabab-ud SU. Influence of potassium nutrition on leaf area index in cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) under an arid environment. Pak J Bot. 2006;38(4):1085–92.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Stanley R, Jewell S. The influence of source and rate of potassium fertilizer on the quality of potatoes for french fry production. Potato Res. 1989;32(4):439–46.10.1007/BF02358499Search in Google Scholar
[32] Makhdum MI, Pervez H, Ashraf M. Dry matter accumulation and partitioning in cotton (Gossypium hirsutumL.) as influenced by potassium fertilization. Biol Fert Soils. 2007;43(3):295–301.10.1007/s00374-006-0105-6Search in Google Scholar
[33] Naumann M, Koch M, Thiel H, Gransee A, Pawelzik E. The importance of nutrient management for potato production part II: plant nutrition and tuber quality. Potato Res. 2020;63:121–37.10.1007/s11540-019-09430-3Search in Google Scholar
[34] Khan MZ, Akhtar ME, Safdar MN, Mahmood MM, Ahmed S, Ahmed N. Effect of source and level of potash on yield and quality of potato tubers. Pak J Bot. 2010;42(5):3137–45.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Mohr RM, Tomasiewicz DJ. Effect of rate and timing of potassium chloride application on the yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L. Russet Burbank). Can J Plant Sci. 2012;92:783–94.10.4141/cjps2011-195Search in Google Scholar
[36] Qu ZM, Chen Q, Feng HJ, Hao M, Niu GL, Liu YL. Interactive effect of irrigation and blend ratio of controlled release potassium chloride and potassium chloride on greenhouse tomato production in the Yellow River Basin of China. Agric Water Manage. 2022;261:107346.10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107346Search in Google Scholar
[37] Chen C, Tong YA, Lu YL, Gao YM. Effects of different potassium fertilizers on production, quality and storability of Fuji apple. J Plant Nutr Fertil. 2016;22:216–24.Search in Google Scholar
[38] Guo XS, Wu LS, Zhu HB, Wang WJ, Ye SY, Wu J. Effects of different types and rates of potassium fertilizer on yield and quality of cauliflower. Plant Nutr Fertil Sci. 2007;13(3):464–70.Search in Google Scholar
[39] Gonçalves YD, Freitas MS, Carvalho AJ, Vieira ME, Peçanha DA, Cunha JM, et al. Potassium sources impact on cassava plant productivity, quality and mineral composition. J Plant Nutr. 2022;45(1):86–94.10.1080/01904167.2021.1949465Search in Google Scholar
[40] Moradinezhad F, Dorostkar M. Pre-harvest foliar application of calcium Chloride and potassium nitrate influences growth and quality of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) fruit cv. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. 2021;21(2):1642–52.10.1007/s42729-021-00468-2Search in Google Scholar
[41] Xu GH, Magen H, Tarchitzky J, Kafkafi U. Advances in chloride nutrition of plants. Adv Agron. 2000;68:97–110.10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60844-5Search in Google Scholar
[42] Li J, Zhou YG, Gu HH, Lu ZF, Cong RH, Li XK, et al. Synergistic effect of nitrogen and potassium on seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency in winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Eur J Agron. 2023;148:126875.10.1016/j.eja.2023.126875Search in Google Scholar
[43] Dzida K, Jarosz Z, Michalojc Z. The effect of diversified potassium fertilization on the yield and chemical composition of Beta vulgaris L. Acta Sci Pol-Hortoru. 2011;33(342):1095–106.Search in Google Scholar
[44] Naoyuki I, Gen I, Mikiko Y, Takata K, Murakami M. Effects of ammonium chloride fertilizer and its application stage on cadmium concentrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain. Plant Prod Sci. 2015;18:137–45.10.1626/pps.18.137Search in Google Scholar
[45] Buwalda JG, Smith GS. Influence of anions on the potassium status and productivity of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa) vines. Plant Soil. 1991;133:209–18.10.1007/BF00009193Search in Google Scholar
[46] Smith GS, Buwalda JG, Clark CJ. Nutrient dynamics of a kiwifruit ecosystem. Sci Hortic. 1988;37:87–109.10.1016/0304-4238(88)90153-7Search in Google Scholar
[47] Smith GS, Clark CJ, Buwalda JG, Gravett IM. Influence of light and form of nitrogen on chlorine requirement of kiwifruit. N Phytol. 1988;110:5–12.10.1111/j.1469-8137.1988.tb00231.xSearch in Google Scholar
[48] Venkatesan S, Senthurpandian VK, Murugesan S, Maibuam W, Ganapathy MN. Quality standards of CTC black teas as influenced by sources of potassium fertiliser. J Sci Food Agric. 2010;86(5):799–803.10.1002/jsfa.2418Search in Google Scholar
[49] Kochian LV, Lucas WJ. Potassium transport in roots. Adv Bot Res. 1989;15:136–51.10.1016/S0065-2296(08)60045-2Search in Google Scholar
[50] Jiang FH, Xiao X, Tang LN, Kuang S, Xu YL, Song WJ, et al. The response of tobacco mineral composition and absorption to application of potassium sulfate fertilizer. Ind Crop Prod. 2024;210:118115.10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118155Search in Google Scholar
[51] Shen P, Li DC, Gao JS, Xu MG, Wang BR, Hou XJ. Effects of long-term application of sulfur-containing and chloride-containing chemical fertilizers on rice yield and its components. Agric Sci China. 2011;10:747–53.10.1016/S1671-2927(11)60058-8Search in Google Scholar
[52] Zou CM, Gao JS, Wang BR, Shen HP. Effects of long-term application of chloride-containing or sulfur-containing fertilizers on the soil property. J Nanjing Agric Univ. 2004;27(1):117–9.Search in Google Scholar
[53] Zhang FY, Mao FC, Zhao XG. A study on the chlorine and sulphur tolerance of Actinidia deliciosa. J Northwest Univ. 2000;15:37–40.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Genetic variants in VWF exon 26 and their implications for type 1 Von Willebrand disease in a Saudi Arabian population
- Lipoxin A4 improves myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the Notch1-Nrf2 signaling pathway
- High levels of EPHB2 expression predict a poor prognosis and promote tumor progression in endometrial cancer
- Knockdown of SHP-2 delays renal tubular epithelial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
- Exploring the toxicity mechanisms and detoxification methods of Rhizoma Paridis
- Concomitant gastric carcinoma and primary hepatic angiosarcoma in a patient: A case report
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Down-regulation of miR-539 indicates poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer”

