Abstract
Moringa is a perennial tree with high nutritional value, and it is drought tolerant and barren but has poor cold resistance during the seedling stage. This study selected Piriformospora indica (PI) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AM) as inoculants, Moringa seedlings were inoculated, and their growth and physiological responses were evaluated under different low-temperature stress times. The research results show that PI and AM can symbiotically associate with Moringa successfully and promote their nutritional growth. At low temperature, Moringa inoculated with PI and AM exhibited better physiological resistance. However, the effect of mixed inoculation of PI and AM is not as significant as that of single inoculation of any strain. Inoculating plant growth-promoting rhizobia (PGPR) reduced the richness of fungal communities and the number of unique operational taxonomic units (OTUs), with PI being the most prominent. Vaccination with PGPR also increased bacterial diversity, richness, and the number of unique OTUs, with AM inoculation showing the most prominent performance. This suggests that Moringa seedling growth and responsiveness to low-temperature stress are significantly influenced by PGPR, and there may be interactions between different bacterial strains. The results suggest that PGPR can improve the yield and quality of Moringa by promoting growth and regulating stress resistance.
1 Introduction
Moringa oleifera Lam. is a perennial tree of the Moringa genus in the Moringaceae family, native to India [1]. Due to its rapid growth, strong adaptability, and high nutritional value, it is widely planted in tropical and subtropical regions [2]. Due to its unique nutritional value and wide range of uses, Moringa is praised by Western scientists as the “magical tree” [3]. Therefore, it has been found that Moringa leaves can be developed into new feed resources and applied to the livestock and poultry breeding industry [4,5,6]. However, Moringa has poor cold resistance, and severe cold may cause the aboveground parts of Moringa to die, which significantly limits its promotion and application.
Inoculating plant growth-promoting rhizobia (PGPR) usually refers to bacteria or fungi that can colonize the rhizosphere of plants and promote the growth of plants. PGPR encompasses not only rhizobia but also various other types of beneficial bacteria and fungi that colonize the rhizosphere and enhance plant growth, including Piriformospora indica (PI) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (AM). PGPR has the most significant influence in the agricultural field, and the application of the PGPR mechanism can reduce the amount of nitrogen fertilizer, reduce production costs, and improve crop yield and quality. Secondly, in horticulture and forestry, the PGPR mechanism can promote root development and improve the survival rate of transplanting, which can be used for the cultivation of flowers and seedlings.
PI is an endophytic fungus belonging to the Sebacinales order of the Basidiomycota phylum [7]. Research has shown that the PI can interact symbiotically with various crops such as rice and wheat, promoting the increase of plant biomass and resistance stability in environments such as drought stress, salt stress, and heavy metal stress [8,9]. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are a kind of fungi that have a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, and Funnelifor mismosseae in AMF. Originally known as Glomus mosseae, which belongs to the genus Glomus in Glomeraceae, it is an AMF in soil. Funneliformes mossae (FM), formerly known as Fusarium graminearum, is a common fungus in soil with strong environmental adaptability. It is easy to infect plant roots and has a good symbiotic relationship with most plants [10,11]. Research has shown that arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can enhance the nutrient absorption capacity of plants and increase antioxidant enzyme activity, thereby protecting membrane integrity and stabilizing protein resistance to stress [12].
PI and AM, as beneficial bacteria and fungi [13], have been increasingly studied, but there is relatively little research on the effects of inoculation of Moringa and beneficial fungi and bacteria on the growth of Moringa. At present, there is no article that simultaneously inoculates PI and AM on M. oleifera. Some studies have found that the colonization of AM has not changed the total growth of M. oleifera, which is in sharp contrast with previous studies that showed positive effects [14]. But the article also found that: AM inoculation improved the growth and biomass of two Moringa species [15]. PI confers banana with enhanced cold resistance by cumulative antioxidant capacity, ss accumulation, And the expression of cold-responsive genes in leaves [16]. In addition, it is found that inoculating fungi can improve the survival rate of wheat in low-temperature environment [17]. This enriches the research content of the interaction mechanism between plants and beneficial fungi and bacteria, provides a new case for deeply understanding how to establish and operate the symbiotic system, provides new ways and ideas for improving the study of plant stress resistance, and promotes the expansion and application of this field in other plant varieties.
M. oleifera seedlings showed poor cold resistance at low temperature, which reduced its survival rate. Under low temperature stress, the cell membrane integrity of M. oleifera was destroyed, the antioxidant defense system was unbalanced, and the photosynthetic activity was inhibited. These findings clearly highlight the problem gap in M. oleifera cultivation and emphasize the urgent need for effective strategies to enhance its cold resistance. PI and AM fungi can form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, which can enhance the production of antioxidants in plants and help improve the ability of plants to resist cold stress. So this study conducted PI and AM inoculation with Moringa. By analyzing the effects of inoculation on Moringa seedlings, a theoretical basis was provided for fully utilizing microbial resources to promote plant growth and improve plant stress resistance. By applying this inoculation method, we aim to significantly improve Moringa’s cold resistance during seedling cultivation and afforestation, thereby overcoming the limitations posed by its inherent cold sensitivity.
16S amplicon sequencing refers to the amplification of 16S of microorganisms in the environment using suitable universal primers 16SrDNA/18SrDNA/ITS high-variable regions or functional genes, using high-throughput sequencing technology to detect the sequence variation and abundance information of PCR products, analyze the diversity and distribution of microbial communities in this environment, so as to reveal the types, relative abundance, and evolutionary relationships of microorganisms in environmental samples.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material and treatments
2.1.1 Test materials and processing
Soak Moringa seeds in a solution containing carbendazim with a concentration of 0.1% for 4 h to kill fungus, and then place them in a suitable temperature incubator for germination [18]. After 3–4 days, remove and sow the seeds, select healthy Moringa seedlings that grow consistently, and transplant them into potted plants. In addition to the control, the seedlings were inoculated with three microbial treatments, PI, AM, and AP, a combination of both (AM + PI) [19].
PI comes from the Forest Genetics and Breeding Laboratory of the College of Forestry and Landscape Architecture, South China Agricultural University. The inoculant is a 5 mm bacterial cake cultured on PDA solid medium for 7 days. AM was purchased from the Guangdong Institute of Microbiology, and the experimental inoculum consisted of a mixture of spores(70 spores/g soil), infected root segments, propagation substrate, and mycelium.
2.2 Experimental design
In this experiment, the peat soil pot planting method was adopted, and the soil was put into a sterilizer at 120° for high-temperature sterilization for 30 min, with 1 plant per pot. There are four treatments, namely control, inoculation with Pi, inoculation with AM, and simultaneous inoculation with PI and AM. Each treatment involves five seedlings, repeated three times [20]. The PI treatment group was inoculated with six pieces of 5 mm PI per pot, the AM treatment group was inoculated with 10 g of AM agent per pot, the AP treatment group was inoculated with three pieces of 5 mm PI and 5 g of AM, and the CK treatment group was not inoculated with fungal and bacteria. Low temperature stress was carried out on the 85th day after inoculation with PI and AM. Low-temperature stressed seedlings were placed in the sterilized artificial climate incubator and subjected to gradient cooling exercises at 20, 15, and 10°C for 4 days each. Afterward, they were cooled down at a rate of 2°C/h to 4°C and kept constant [21].
2.3 Characteristic determination method
Ninety days after inoculation with PI and AM, 50 fresh root segments of approximately 1 cm were selected for each treatment, and the mycorrhizal infection rate was determined using the triple blue staining method. Using vernier calipers, tape measures, etc., to measure plant height, ground diameter, and leaf number (excluding cotyledons), and using Li-6400XT photosynthetic fluorescence analyzer to measure the photosynthesis of the third to fifth functional leaves of Moringa from top to bottom; after separating the roots, stems, and leaves of the plant, use a root scanner to scan the roots and leaves (excluding cotyledons), and analyze them using WINRHIZO root analysis software to obtain their root surface area and leaf surface area; Subsequently, it was placed in a 100°C oven for high-temperature withering for 30 min and then placed in a 50°C oven for constant temperature drying to a constant weight. Then, an electronic balance was used to weigh the roots, stems, and leaves (excluding cotyledons) to obtain biomass. In the low-temperature stress treatment, six pots of Moringa with consistent growth were selected for each treatment, and 1 g of mature leaves were taken for physiological index measurement. Physiological indicator materials used for measuring the content of various enzymes and chlorophyll are stored at −80°C ultra-low temperature for future use [22]. The kits for testing plants PRO, MDA, H2O2, superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT) all came from China Suzhou Keming Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.4 Soil microbial community detection
After 90 days of inoculation, soil samples were collected at a depth of 5 cm around the ground diameter of potted Moringa plants using a three-point sampling method. Three pots were collected for each treatment (nonmixed sampling). Place the collected soil samples in sterile self-sealing bags and store them in a −80°C ultra-low temperature freezer for microbial diversity testing. The collected soil samples will be sent to Guangzhou Gidio Co., Ltd., for determination using lllumina Miseq™ sequencing technology. The 16S rRNA gene of bacteria and the ITS gene of fungi will be amplified and sequenced.
2.5 Data statistics and analysis
Data acquired in the experiments were sorted using Microsoft Office Excel (Microsoft Crop., Redmond, WA, USA), and then, statistical analyses were performed with SPSS software (Version 26.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). P values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 PI and AM form symbiotic associations with roots in Moringa
3.1.1 Root colonization by PI and AM in Moringa
After 90 days of symbiosis between PI and Moringa root system, bead-like hyphae were observed under a 40× biological microscope, with elliptical thick-walled spores clustered together, as indicated by the arrows in Figure 1. After 90 days of inoculation with AM, Y-shaped clustered hyphae can be observed, as indicated by the arrows in Figure 1. The combination of AP and beneficial fungi and bacteria with Moringa includes two separate inoculation methods, mainly based on hyphal structure, followed by pear-shaped spores. This indicates that PI and AM can form a good mycorrhizal symbiotic relationship with Moringa.
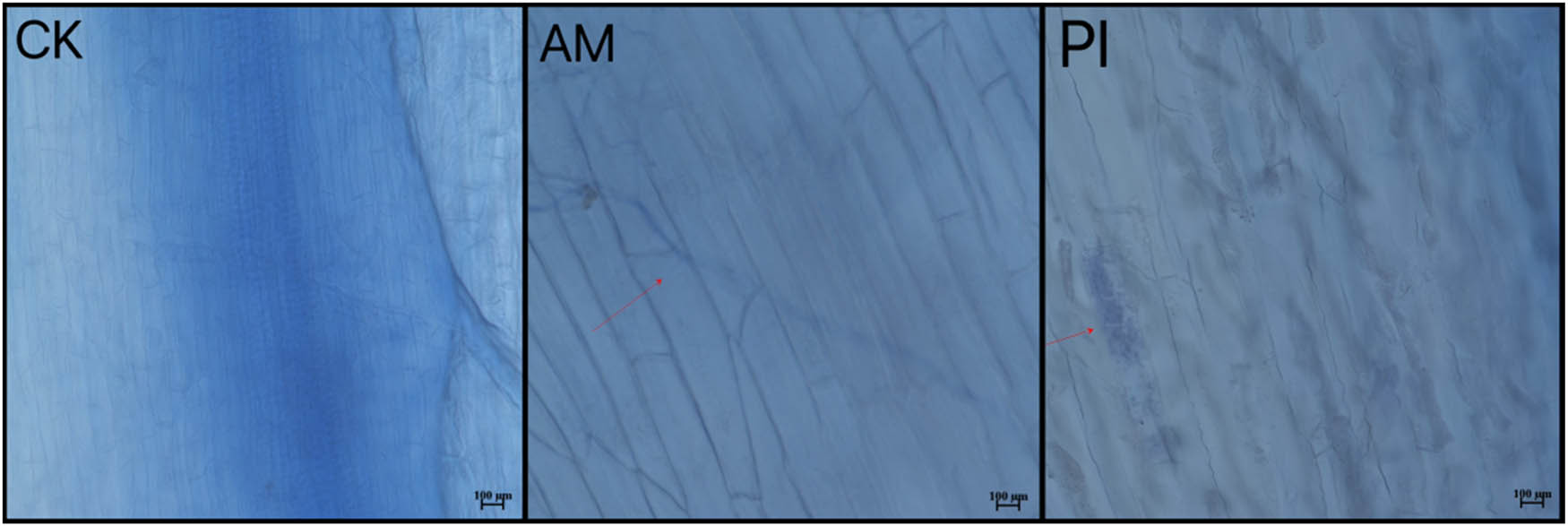
Observation under a microscope of the CK group without inoculation of Moringa, inoculation with AM and PI bacteria.
3.2 The effect of inoculating AM and PI on the growth morphology of Moringa
3.2.1 Effect on growth index
Plant height, ground diameter, and number of leaves are important indicators reflecting the level of plant growth(see Figure 2). Take 15 plants from each treatment in this experiment, analyze the average value, and explore the effects of different beneficial fungi and bacteria on the growth of Moringa (Table 1). In summary, PI treatment accelerated plant height growth, while AM treatment accelerated ground diameter growth and increased the number of leaves.
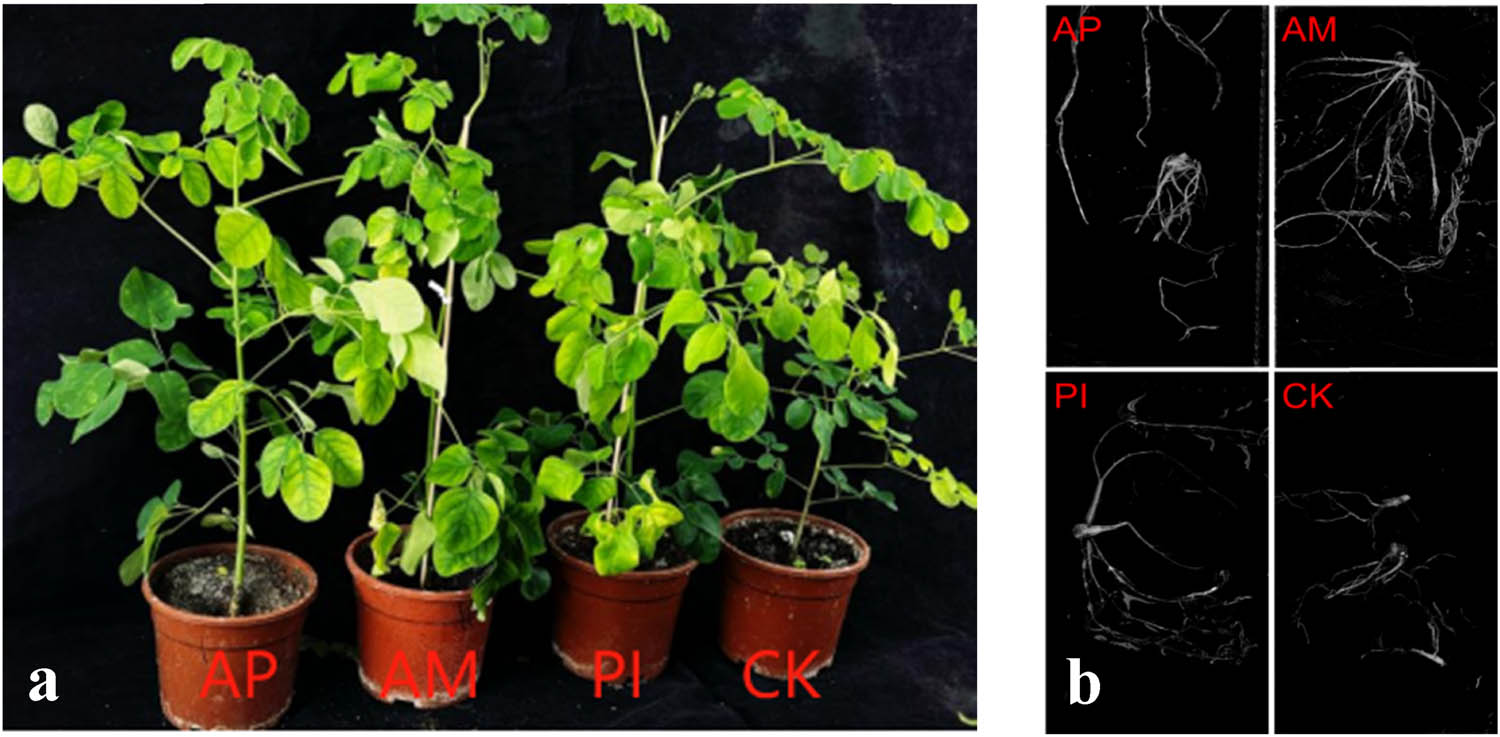
60 days after inoculation with PI and AM (a). Root surface area of various treatments of M. oleifera (b).
Effects of inoculation with endophytic fungi on the infection rate and growth indicators of Moringa Mycorrhiza
| Index | Treatments* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | PI | AM | AP | |
| Colonization level (%) | 0 | 35.03 ± 0.73a | 40.08 ± 8.45a | 14.54 ± 4.05b |
| Plant height (cm) | 24.78 ± 1.94c | 31.47 ± 2.44a | 31.10 ± 2.85a | 28.20 ± 3.31b |
| Ground diameter (mm) | 3.03 ± 0.43c | 3.32 ± 0.23ab | 4.15 ± 0.42a | 2.68 ± 0.22c |
| Number of leaves/plant (piece) | 8.4 ± 0.61bc | 9.7 ± 0.66ab | 10.8 ± 0.92a | 6.5 ± 0.65c |
| Surface area (cm2) | 103.50 ± 3.17c | 144.50 ± 3.75b | 180.50 ± 2.02a | 109.63 ± 5.87c |
| Root surface area (cm2) | 167.73 ± 16.56c | 281.48 ± 4.54b | 346.76 ± 3.68a | 202.55 ± 22.83c |
| Mean root diameter (cm) | 0.0828 ± 0.0036c | 0.1204 ± 0.0003b | 0.1400 ± 0.0023a | 0.0996 ± 0.0054d |
| Total root length (cm) | 96.43 ± 3.146c | 133.81 ± 513.01b | 186.25 ± 2.72a | 105.38 ± 4.07c |
| Total biomass (g) | 1.43 ± 0.06c | 1.67 ± 0.04ab | 2.14 ± 0.05a | 1.5 ± 0.07c |
| Root–shoot ratio (%) | 0.09 ± 0.01b | 0.10 ± 0.01ab | 0.17 ± 0.012a | 0.12 ± 0.012ab |
*Means followed by the same letter in the same column are not significantly different from each other at P ≤ 0.05 level, according to Duncan’s multiple range test. The same goes for the other tables. abcd stands for significance and is usually used to indicate whether the differences between different groups are significant.
In terms of height, the impact on plant height was most significant in the PI treatment group, with an increase of 26.99% compared to CK, followed by AM, AP, and CK;
In terms of ground diameter, the order of influence on ground diameter is AM > PI > CK > AP.
In terms of the number of plant leaves, the AM treatment group significantly increased the leaf number of Moringa by 28.57% compared to the CK group in terms of its impact on leaf number.
In terms of the surface area of roots and leaves, the AM treatment raised the surface area of the leaves by 74.39% and the root surface area by 106% when compared to CK.
In terms of the average root diameter, except for the AM group, the PI and AP group had no significant effect on the average root diameter. The AM group’s average root diameter was 75% greater than the non-inoculated group’s;
In terms of the total root length, endophytic bacterial inoculation significantly increases the overall length of the roots. Compared to the infected treatment, the non-inoculated treatment’s total root length was noticeably shorter. The AM, PI, and AP treatments increased by 92.88, 39.28, and 9.28%, respectively, compared to the control treatment.
In terms of the root–shoot ratio, the root–shoot ratio of Moringa is obtained by drying them in a drying oven to a constant weight. The root–shoot ratio of each treatment ranged from 0.09 to 0.17, and the root–shoot ratio of the inoculant treatment and the not-inoculated treatment differed significantly. Among them, the root–shoot ratio of the AM-inoculated treatment group was higher than that of the non-inoculated treatment group.
This indicates that inoculation with endophytic bacteria increased the biomass of Moringa to varying degrees and allocated more biomass to the aboveground parts of Moringa.
3.2.2 Effect on photosynthetic index
After 60 days of inoculation with endophytic bacteria, the determination results of photosynthetic parameters in comparison with non-inoculated Moringa plants are shown in Table 2. There is a significant difference compared with the control treatment, and the net photosynthetic rates of PI, AM, and AP treatments increased by 5, 65, and 45%, respectively; there was no significant difference in transpiration rate between the control group and the CK group, but the transpiration rate increased significantly after inoculation with PI bacteria; after inoculation with PI or AM, the intercellular CO2 of Moringa trees showed an increase of 2.2 and 5.0%, respectively, while the treatment of simultaneous inoculation with both decreased by 7.9%; the stomatal conductance of Moringa trees inoculated with PI or AM showed a significant decrease, with reductions of 41.2 and 31.4% compared to the CK group, respectively. However, the treatment in the AP group did not show a significant decrease, with a reduction of 9.8%. Endophytic bacteria have an impact on the photosynthetic parameters of Moringa leaves.
Effects of endophytic bacteria inoculation on light response parameters of Moringa
| Index | Treatments* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | PI | AM | AP | |
| Net photosynthetic rate (μmol m−2 s−1) | 0.20 ± 0.03b | 0.21 ± 0.02b | 0.33 ± 0.01a | 0.29 ± 0.02c |
| Transpiration rate (mmol m−2 s−1) | 0.11 ± 0.02a | 0.26 ± 0.18a | 0.080 ± 0.01a | 0.10 ± 0.01a |
| Intercellular CO2 concentration (μL L−1) | 426.533 ± 16.00a | 435.96 ± 17.49a | 447.66 ± 19.91a | 392.87 ± 15.82a |
| Stomatal conductance (mol H2O m−2 s−1) | 0.0051 ± 0.0009a | 0.0030 ± 0.0003a | 0.0035 ± 0.0004a | 0.0046 ± 0.0004a |
*Means followed by the same letter in the same column are not significantly different from each other at P ≤ 0.05 level, according to Duncan’s multiple range test. The same goes for the other tables. abcd stands for significance and is usually used to indicate whether the differences between different groups are significant.
3.3 Effects of AM and PI inoculation on physiological resistance of Moringa under cold stress
All four treatments showed cold stress symptoms and the leaves began to wilt and dewater after being treated at 4°C for 12 h. The degree of cold damage increased with the extension of treatment time. However, the symptoms after vaccination were significantly better than those of the control group. Figure 3 shows the changes in the content of physiological indexes of Moringa inoculated with different strains at low temperatures (4°C) for 0 h (T0), 12 h (T12), and 24 h (T24), respectively.
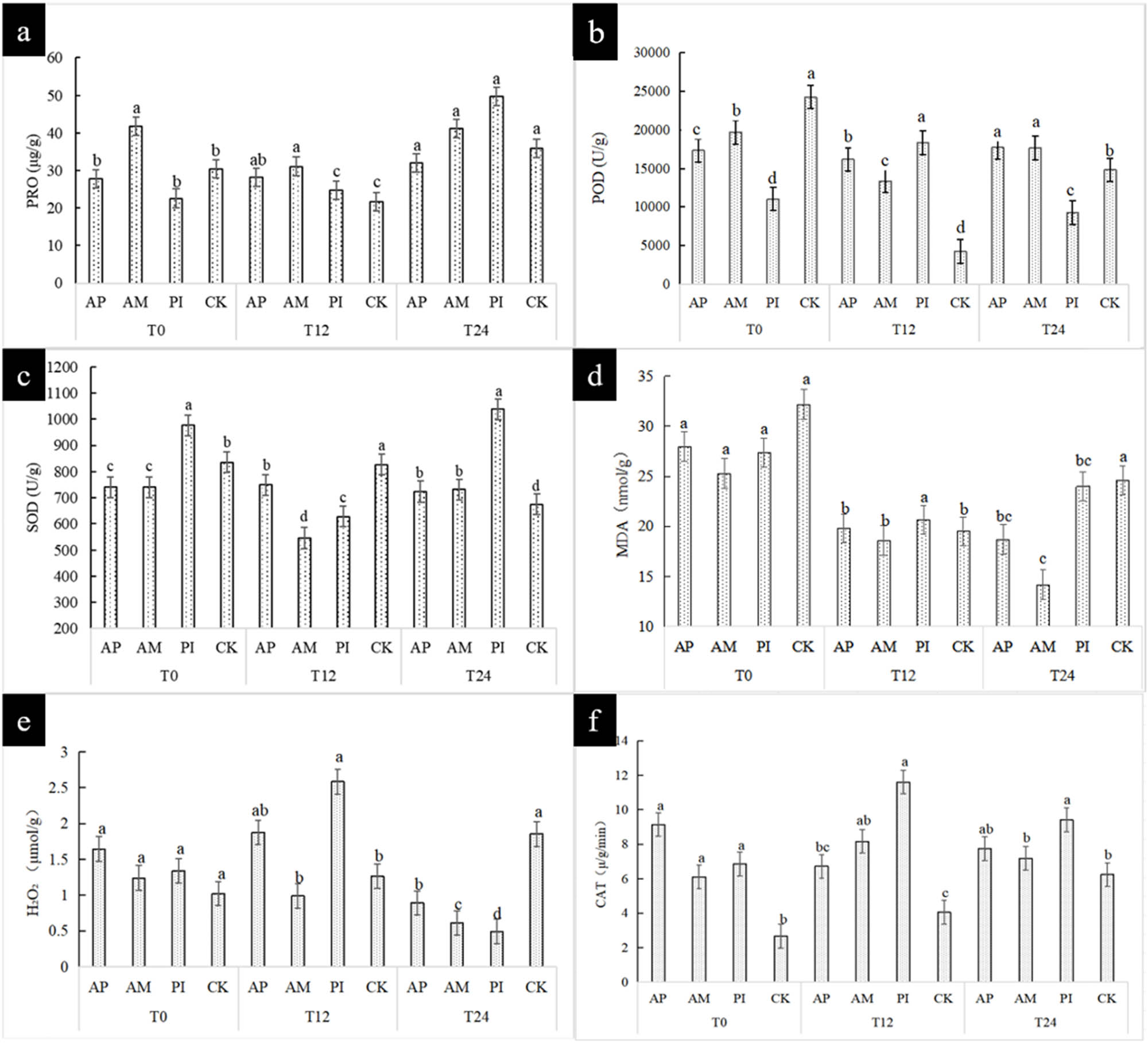
Plant physiological index (a)–(f) reflects the determination of physiological and biochemical parameters of Moringa oleifera injury.
With the extension of treatment time, the degree of freezing damage increased. However, the vaccinated symptoms were significantly better than those in the control group. With the increase in freezing time, the proline content of all treatment groups showed an increasing trend, and the PI treatment group was the most significant, which increased by 39% compared with CK. At room temperature, there was no significant difference in the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in seedlings. Under low-temperature stress, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide first increased and then decreased. With the extension of low-temperature treatment time, the difference between treatments became more and more significant. After 24 h of low-temperature stress, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in plants inoculated with Pi was the lowest, which was significantly different from the other three treatments, the PI content was 74% less than CK, indicating that PI had a great influence on the hydrogen peroxide content. At room temperature, the MDA content in the control group was significantly 20% higher than that in the inoculation group. After 12 h of treatment, all treatment groups tended to be stable. After 24 h of treatment, the MDA content in plants inoculated with AM was the lowest, which was 42% less than CK, indicating that AM could greatly reduce the MDA content. Inoculation alleviated the damage of the leaf cell membrane of Moringa at low temperatures. This may be due to the activation of the antioxidant defense system in plants after inoculation with AM fungi. Antioxidants can remove excessive ROS in time, thus reducing MDA content and alleviating the damage of low temperatures to the cell membrane of M. oleifera leaves. After 24 h of low-temperature stress, the contents of CAT and SOD tended to be stable, and the contents of CAT and SOD in the treatment group were significantly higher than those in the control group by 30 and 23%. After 24 h of low temperature, the content of POD in the inoculation group increased by 19–22% except the PI group. The activity of SOD, POD, and CAT was increased by inoculation, which enhanced the plant’s ability to withstand adversity. For the increase of POD content in the inoculation group except the PI group, it may be because different inoculation treatments have different activation modes and degrees of plant antioxidant system. However, the PI group may not cause an obvious increase in POD content because of its interaction with plants, or its regulation and control focus on plant antioxidant system is more on other aspects, such as giving priority to enhancing the activities of CAT and SOD.
3.4 Effects of AM and PI inoculation on soil microbial community of Moringa
As can be seen from Figure 4a, the dominant fungal phyla of the four treatments were consistent in the composition of major species, but there were some differences in relative abundance. The three treatment groups infected with bacteria enriched fungal species to varying degrees, among which PI was the most significant. The top ten bacteria at the gate level were detected. As shown in Figure 4b, compared with CK, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria decreased in the inoculation group, while that of pontomyces, patella, and Bacteroidetes increased. Except for Proteobacteria, the relative abundance of other inoculation groups increased compared with the control group.
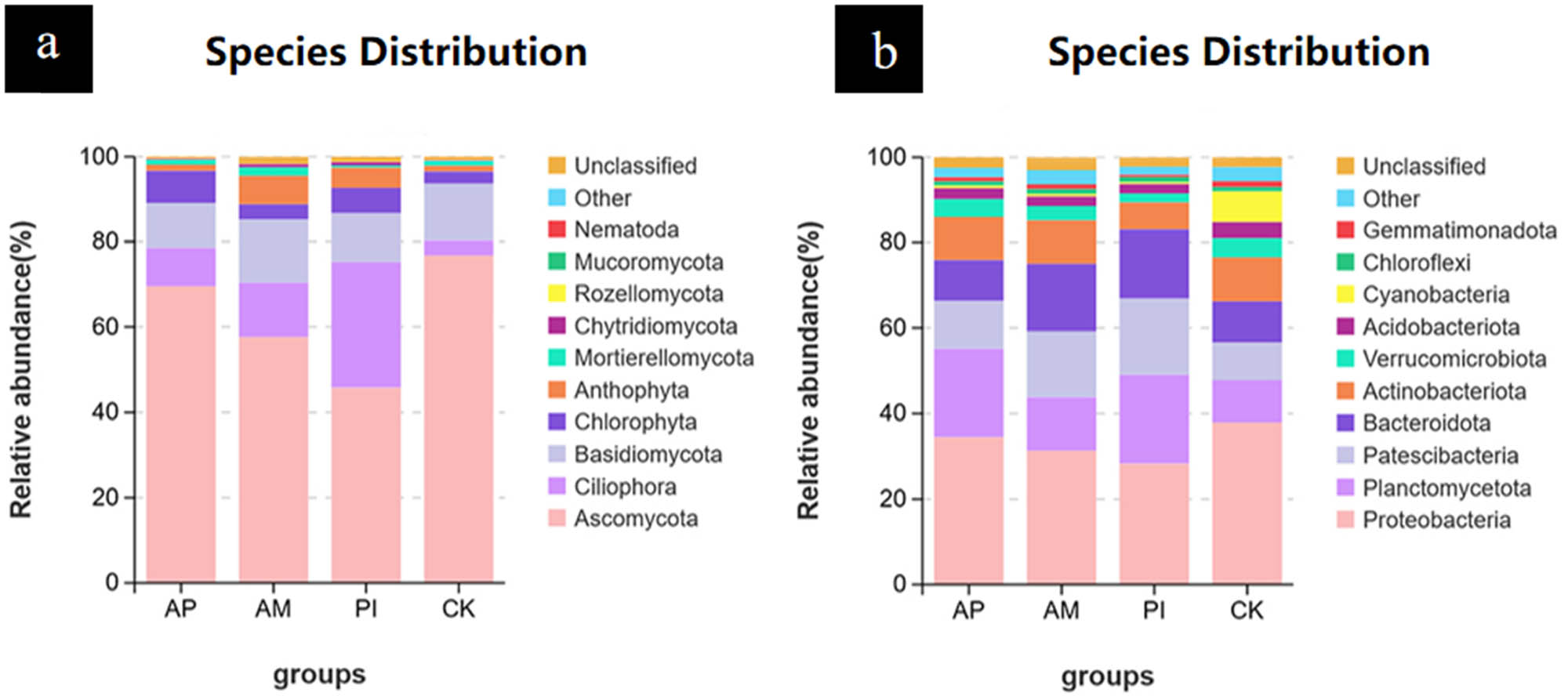
Composition of soil fungal (a) and bacterial (b) communities in different treatments of Moringa at gate level.
Indicating that bacteria-inoculation decreased the richness and evenness of fungal communities in soil, the average values of Sobs, ACE, and Chao1 indices in the control treatment were all greater than those in the bacteria-inoculation treatment. The Shannon and Simpson indices of AP, AM, and PI treatments were higher than those of the control group, indicating that inoculation of processed groups could improve the diversity of soil fungal community. The bacterial richness and diversity in the AM and AP groups were higher than those in the control group, as evidenced by the higher average values of the Sobs, ACE, Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson index of the bacterial communities in those groups. The Shannon index of the AM treatment group was the highest, indicating that AM inoculation was the most prominent in improving soil bacterial diversity.
Species Venn diagrams can be used to visualize the similarity and overlap of OTU numbers and composition of species. In a Venn diagram, each color represents a different process, and the number of OTUs shared by the groupings is shown by the numbers in the overlapping segments. According to Figure 5a, the number of OTUs of soil fungi under different treatments showed that the total number of OTUs of soil fungi was 621, and the total number of OTUs of the four treatments was 238. Among them, the unique OTUs of CK, AP, AM, and PI accounted for 8.37, 8.21, 10.14, and 9.33% of the total OTUS. It can be seen that AM is the highest, and CK and AP are the least significant, respectively. The OTU number of soil bacteria under different treatments was analyzed, as shown in Figure 5b. The total OTU number of soil bacteria was 4,411, and the total number of bacterial OTUs in the four treatments was 767, among which the OTUs specific to CK, AP, AM, and PI accounted for 18.25, 19.89, 22.99, and 16.2%, respectively. It can be seen that AM is the highest, and CK and PI are the least significant. Inoculation of PI and AM could not significantly increase the OUT number of soil fungal community and might even inhibit it but could increase the OTUs number of soil bacterial community. Overall, inoculation raised the diversity and richness of the bacterial population in the soil to varied degrees while decreasing the diversity and richness of the fungus community.
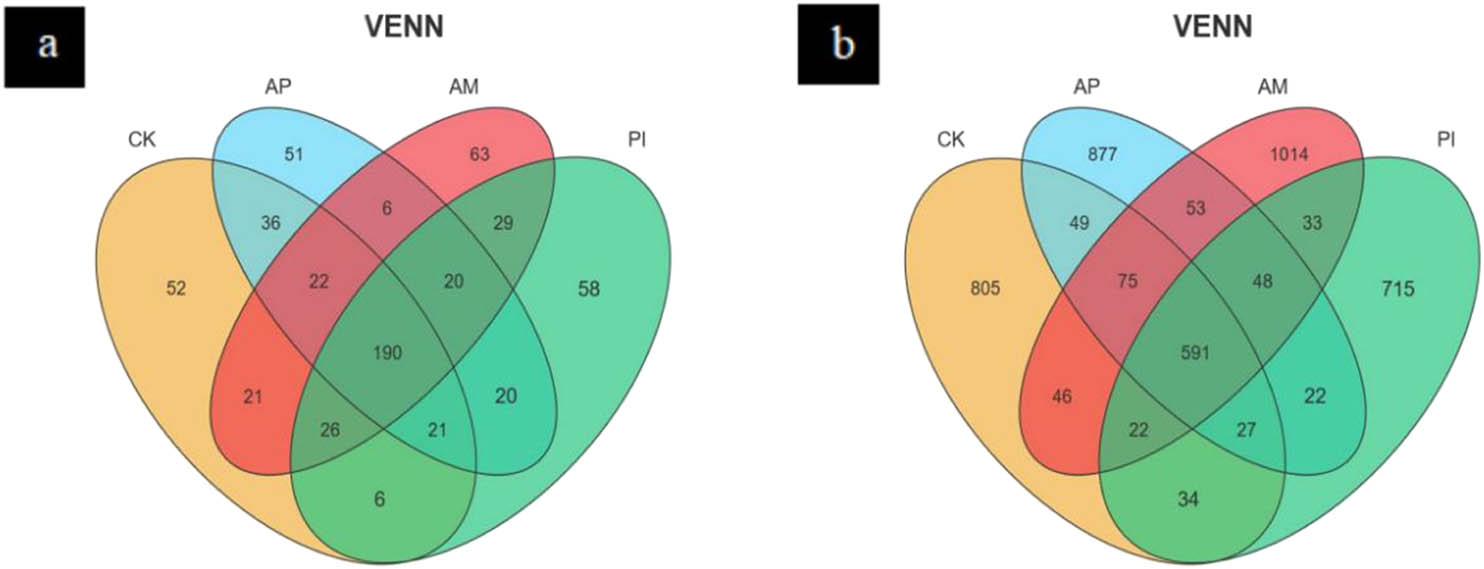
OTUs are common and endemic to different treated soil fungi (a) and bacteria (b).
4 Discussion
In general, the higher the concentration of proline, the higher the concentration of soluble glucose, and proline can maintain the balance activity of intracellular enzymes, protect cells, accelerate plant energy recovery, and thus improve plant cold tolerance [23,24]. The results of this study showed that with the extension of low-temperature stress time, the proline content of Moringa in the inoculation group of piriformis indica and the double bacteria inoculation group showed a gradual increase trend, while it decreased first and then increased in the control group. This indicated that Moringa could achieve resistance stability by increasing proline content under low-temperature stress for a long time. It is worth mentioning that the inoculated pyriformis group was 120.41% higher than the initial value after 24 h of low-temperature stress, and the content of proline was significantly increased.
When PI or AM are inoculated alone, the absorption of phosphorus can be increased, which is essential for the synthesis of ATP and NADPH, which are the key molecules in the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, but the carbon sequestration rate in the Calvin cycle may not keep up immediately. Therefore, the consumption of CO2 in cells decreases, leading to an increase in the level of CO2 between cells; When PI and AM are inoculated at the same time, the combined effect of them may improve the metabolic efficiency of plants. Optimize the supply of various nutrients, enhance the activity of key photosynthetic enzymes (such as Rubisco), and improve the overall efficiency of the photosynthetic electron transfer chain. This will lead to faster consumption of CO2 in the process of carbon fixation in the Calvin cycle, resulting in the decrease in intercellular CO2 concentration [25].
Antioxidant enzymes are SOD, POD, CAT, polyphenol oxidase, phenylalanine aminolyase, thioredoxin POD, glutathione POD, and other general names [26]. Antioxidant enzymes can convert excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals (i.e., free radicals) in the body into less toxic or harmless substances, balancing the active oxygen content in the body, and its value can indicate that the plant has been stressed by the external environment [27,28,29]. The results of this study showed that with the extension of low-temperature stress time, the contents of POD, SOD, and CAT of the antibacterial treatment group were higher than those of the CK control group. These results indicated that inoculated PI and AM could resist the inhibitory effect of low-temperature stress on growth by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes to a certain extent; however, the control system of antioxidant enzymes in plants was harmed and their activity decreased as the duration of low temperatures increased.
Under cold stress, the permeability of cell membrane will increase, polyunsaturated fatty acids will fall off, and then, membrane lipid peroxy will be formed on the cell membrane, and the content of malondialdehyde will increase [30]. This study showed that with the extension of low-temperature stress time, the contents of MDA and H2O2 in potted Moringa showed a decreasing trend, and the contents of the inoculation group were lower than that of the control group under various stress duration periods, which may be due to the increased SOD, POD, and CAT activities of the inoculated PI and AM. As a result, the scavenging ability of ROS in plant cells is improved, which balances the production and scavenging of free radicals in cells, and reduces the peroxidation of membrane lipids, alleviating the cell membrane damage caused by low-temperature [31]. Low-temperature stress increased the peroxidation degree of Moringala moringala’s cell membrane, but the treated seedlings could effectively reduce the contents of MDA and H2O2 in leaves, thereby alleviating the damage of stress on the permeability of the lipid membrane of plant cells and improving the stress resistance of plants [32].
The inoculation of PI and AM decreased the richness of the fungal community and the number of unique OTUs but increased the diversity. The inoculation of PI and AM increased the abundance of ciliata, basidiomycetes, chlorophyta, and xanthophyta, and decreased the abundance of ascomycetes, with PI being the most prominent. Inoculation with PI and AM increased the diversity and abundance of bacteria and the number of unique OTUs, and the preponderant Bacteroides, patella, and Bacteroidetes had the highest abundance. It promoted the metabolism of soil bacteria, such as terpenoids and polyketones, biosynthesis of other secondary metabolites, and cell activity, among which inoculation with AM was the most prominent.
5 Conclusion
In terms of physiological characteristics, The treatment of PI under cold stress is better than the normal content and other treatment groups, indicating that inoculation of PI in a cold environment is a potential ideal technology to improve the growth and development of Moringa. PI treatment is slightly better than AM treatment, which may be because PI can improve the stress resistance of plants and resist stress by stimulating the activity of antioxidant enzymes and the accumulation of osmotic adjustment substances.
In terms of growth and development, inoculation of AM alone has a more positive effect on Moringa growth, which may be due to AM’s extensive extraroot mycelium network, which can make the host plants get more soil nutrients and water.
Compared with the current research, the study on the effect of combined inoculation of bacteria and fungi on Moringa growth also involves cold-resistant physiology and soil microbial community. The relationship between beneficial fungi and bacteria and Moringa was explored from multiple dimensions. In the study of cold resistance physiology, the changes in cell membrane permeability and antioxidant enzyme activity at low temperatures are involved, and the study of soil microbial community can reveal the influence of beneficial fungi and bacteria on the microbial structure and function of Moringa rhizosphere soil. This multi-dimensional study is helpful to understand the role of beneficial fungi and bacteria in the entire ecosystem of M. oleifera.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1300901). We are very grateful to our predecessors for their research foundation, which makes it convenient for us to study more deeply.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1300901).
-
Author contributions: Guo Zhou: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis investigation, methodology, software, visualization, writing – original draft, and writing – review and editing. Sini Wu: conceptualization, software, supervision, formal analysis, and investigation. Meichun Qiu: investigation, conceptualization, software, and data curation. Yingtong Long: investigation, conceptualization, software, and data curation. Qian He (corresponding author): conceptualization, methodology, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing, and funding acquisition. Junjie Zhang (corresponding author): conceptualization, methodology, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing, and funding acquisition.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Qin SX, Shen WJ, Liu MJ, Liu MJ, Su XL, Huang SH. Research, exploitation, application and prospects of moringa oleifera. J Changjiang Veg. 2016;2016(18):32–8.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Jiao J, Chen WZ, Mu Y, Bater, Kang YX, Gao Y, et al. Current status and reflections on the development of moringa industry at home and abroad. World Agric. 2015;(5):126–8.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Xiao ZC, Zhang GL. Chinese wild plant resources, nanjing institute for comprehensive utilization of wild plants. Chin Wild Plant Resour. 2016;35(1):64–6.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Shi PW, Guan QF, Wang XM, Wu KB, Zhang HW. The research status of the application effect of moringa leaves in livestock, poultry and aquatic products. Heilongjiang Anim Sci Vet Med. 2018;(1):83–6.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Long JM, Lei FH, Yang YJ, Duan B, Li HQ, Zhang ZB, et al. Nutritional value of moringa oleifera lam. and its application in poultry production. China Poult. 2024;46(4):101–6.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Luo HY, Jin J, Deng HS, Pu TL, Fan JC, Han XQ. Research progress on the nutritional value of moringa oleifera and its application in livestock and poultry breeding. Pratac Sci. 2023;40(11):2937–47.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Gao J, Tian PC, Dang YJ, Li XR, Wang C, Liu C, et al. Establishment of Piriformospora indica-peanut symbiosis system and its promoting effect on peanut growth. Chin J Oil Crop Sci. 2024;46(2):385–93.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Chen JZ. Research progress on Piriformospora indica in enhancing crop resistance. Jiangsu Agric Sci. 2023;51(24):11–20.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Fan Y, Luo PR, Wang W, Xie Q, Chen QX. Establishment of symbiotic system between piriformospora indica and rhododendron and improvement of drought resistance effect. Sci Silvae Sin. 2024;60(1):93–102.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wang WM, Kuang XS, Hu JY, Liu WS. Effects of manganese stress on seed germination, seeding growth and physiological and biochemical characteristic of Rhus chinensis. Acta Ecol Sin. 2022;42(9):3706–15.10.5846/stxb202104261101Search in Google Scholar
[11] Wang W, Mu HN, Yang HM, Sun TZ. The effect of inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the growth status and photosynthetic characteristics of summer snow lotus. J Nanjing Univ. 2024;18(4):1–10.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Chu W, Guo XL, Zhang C, Zhou LT, Wu ZY, Lin WX. Research progress and future directions of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-plant-rhizosphere microbial interaction. Chin J Eco-Agric. 2022;30(11):1709–21.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Liu Y, Ying NZ, Zhi HT, Qiang SW, Kamil K. Effects of beneficial endophytic fungal inoculants on plant growth and nutrient absorption of trifoliate orange seedlings. Sci Hortic. 2021;277:109815. 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109815.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Cosme M, Franken P, Mewis I, Baldermann S, Wurst S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect glucosinolate and mineral element composition in leaves of moringa oleifera. Mycorrhiza. 2014;24(7):565–70.10.1007/s00572-014-0574-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Knopf E, Blaschke H, Munch JC. Improving moringa growth by using autochthonous and allochthonous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in lakevictoria basin. West Afr J Appl Ecol. 2013;21(1):47–58.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Li D, Bodjrenou DM, Zhang S, Wang B, Pan H, Yeh K, et al. The endophytic fungus piriformospora indica reprograms banana to cold resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4973.10.3390/ijms22094973Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Hajiboland R, Joudmand A, Aliasgharzad N, Tolrá R, Poschenrieder C. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alleviate low-temperature stress and increase freezing resistance as a substitute for acclimation treatment in barley. Crop Pasture Sci. 2019;70(3):218.10.1071/CP18385Search in Google Scholar
[18] Zhang TX, Lin YH, Lin ZK, Chen ZD, Yang JJ, Cao MH. Effects of different temperature treatments on seed germination, seedling growth and physiological characteristics of m. oleifera lam. Chin J Trop Crop. 2017;38(3):438–43.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Wu GQ, Yu ZL, Wei M. The mechanism of PGPR regulation in plant response to stress and adversity. Acta Prataculturae Sin 1–16 [2400-03-31]. 2024;33(6):203–18.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Yang L, Zou Y, Tian Z, Wu Q, Kuča K. Effects of beneficial endophytic fungal inoculants on plant growth and nutrient absorption of trifoliate orange seedlings. Sci Hortic. 2021;277:109815.10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109815Search in Google Scholar
[21] Li WC, Peng YJ, Liu YB. Research progress in light signal and circadian rhythm regulating the perception of plants to cold stress. Biotechnol Bull. 2024;40(8):1–12.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Wang B, Lin FK, Li D, Liu JP, Huang YJ, Cheng CZ. Effects of Piriformospora indica and CaCl, treatments on cold resistance of banana. J Fujian Agric Univ Nat Sci Ed. 2021;50(6):753–8. 10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).Search in Google Scholar
[23] Lai M, Chen J, Zhang J, Liu HY, Wang B, Song FP, et al. Research progress in plant response mechanism to low temperature stress and improvement of cold resistance. Mol Plant Breed. 2023;1–11.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Aloo BN, Dessureault-Rompré J, Tripathi V, Nyongesa BO, Were BA. Signaling and crosstalk of rhizobacterial and plant hormones that mediate abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1171104.10.3389/fmicb.2023.1171104Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Taghvimi P, Mohsenzadeh Golfazani M, Taghvaei MM, Samizadeh Lahiji H. Investigating the effect of drought stress and methanol spraying on the influential genes in the calvin cycle and photorespiration of rapeseed (brassica napus). Funct Plant Biol. 2024;51(3).10.1071/FP23280Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Rajput VD, Harish, Singh RK, Verma KK, Sharma L, Quiroz-Figueroa FR, et al. Recent developments in enzymatic antioxidant defence mechanism in plants with special reference to abiotic stress. Biol. 2021;10(4):267.10.3390/biology10040267Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Li DX. Effect of arsenic-reducing bacteria on arsenic enrichment efficiency of Pteris vittata and its mechanism. Northwest A & F Univ. 2021.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Zhou Y, Xie K, Cai H, Huang CB. The effects of exogenous melatonin and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and physiological characteristics of rose seedlings under salt stress. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin. 2024;44(3):370–80.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Zong JW, Huang XD, Jin YA, Yang YH. The effect of Aspergillus niger on the growth, leaf anatomical structure, and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge fruit under NaCl stress. J Plant Resour Environ. 2023;32(2):73–81.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Meng D, Li S, Feng X. CsBPC2is essential for cucumber survival under cold stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2023;23(1).10.1186/s12870-023-04577-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Tian ZM, Gong XC, Kang YH, Wang P, Ding Q, Zai CN, et al. Research progress on the physiological response of plants to drought stress. J Anhui Agric Sci. 2011;39(26):16475–7.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Chen Q, Sun JH, Ma WJ, Wang JH, Zhao XY, Hu RY. Regulation mechanism of low-temperature stress on plants: Research progress. Chin Agric Sci Bull. 2022;38(17):51–61.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state with severe hypernatremia coexisting with central diabetes insipidus: A case report and literature review
- Efficacy and mechanism of escin in improving the tissue microenvironment of blood vessel walls via anti-inflammatory and anticoagulant effects: Implications for clinical practice
- Merkel cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological analysis of three patients and literature review
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Eleonora’s falcon trophic interactions with insects within its breeding range: A systematic review
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Molecular mechanism of follicular development in laying hens based on the regulation of water metabolism
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”

