Abstract
The purpose of this study was to explore the potential mechanism of SATB2 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway promoting fracture healing in vivo. An SD model of humeral fracture in rats was established and treated. Following a 6-week treatment period, the morphology of the fracture was assessed. Serum interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), osteocalcin, C-telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-I), and bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) were determined. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL), osteoprotegerin (OPG), and other relevant molecules such as PI3K and p-AKT were measured. The results showed that SATB2 overexpression repaired humeral fracture and bone continuity. SATB2 overexpression resulted in a significant reduction in RANKL, IL-6, TNF-α, and CTX-I expression, while simultaneously increasing OPG, ALP, osteocalcin, and BMP-2. This indicates that SATB2 inhibits osteoclast activity and promotes osteoblast function. Additionally, SATB2 overexpression increased PI3K and p-AKT protein expression in humerus. Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of the PI3K/AKT inhibitor on PI3K and p-AKT protein expression was counterbalanced by upregulating SATB2. In conclusion, SATB2 promotes fracture healing in humeral fracture rats by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts, which is related to the activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
1 Introduction
Fracture is the most common traumatic injury that occurs in the human body [1]. Despite the inherent ability of bone to self-repair, a significant proportion of patients, ranging from 10 to 20%, experience bone non-union or delayed healing [2]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to accelerate the development of treatment strategies aimed at enhancing the process of bone regeneration during fracture healing.
A highly conserved gene, special AT-rich sequence-binding protein 2 (SATB2) encodes a transcription factor involved in bone, craniofacial, and nervous system development [3,4]. The transcription factor SATB2 plays a key role in the correct facial pattern and normal bone development, and its absence in mice has been observed to diminish bone mineralization, ultimately leading to shortened and fragile bones in all limbs. This defect is attributed to increased expression of specific members of the Hox gene cluster and decreased expression of osteoblast-specific genes [5]. It has been found that SATB2 acts as a molecular regulator in the transcriptional network and coordinates the expression of some osteogenic transcription factors and matrix proteins, thus playing an important role in osteoblastogenesis [6,7]. Studies have shown that SATB2 regulates the genesis by regulating the expression and function of osteoblast-specific genes, such as interacting with Runt-related transcription factor 2 and activating transcription factor 4 and enhancing their transcriptional activities, affecting the process of bone formation, osteoblast differentiation, and matrix formation [4,8,9]. A known role of SATB2 is to regulate osterix, a transcription factor that regulates mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts. Additionally, it is thought to be involved in bone remodeling [10]. In summary, SATB2 can be a powerful osteoinductive molecule that recruits other transcription factors to form a platform or act as a molecular regulator of the transcriptional network. It can synergize and amplify, thereby multiplying the activity of multiple osteogenic transcription factors to regulate bone development and osteoblast differentiation. Although SATB2 can induce bone regeneration, whether it can play a key role in humeral fractures and help healing still needs to be explored in depth.
Protein kinase B (AKT) was initially identified as a proto-oncogene, serving as a signaling pathway of considerable significance in the context of post-traumatic repair and healing, as well as functioning as a regulatory pathway mediating cellular growth [11]. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) is activated by a variety of growth factors through receptor binding. The resulting products then interact with AKT, leading to AKT phosphorylation and subsequent modulation of the downstream target proteins Bad and Caspase. Ultimately, this regulatory mechanism controls cellular proliferation and differentiation [12]. PI3K/AKT axis is a regulator of bone metabolism that promotes bone formation and differentiation of immature osteoblasts into mature ones [13–15]. Dexamethasone (Dex) exerts a dual inhibitory effect on the phosphorylation of AKT and levels of semaphorin 3A (Sema3A) in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). Furthermore, Dex hinders osteoblast differentiation by suppressing Sema3A via the PI3K/AKT pathway [16]. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is involved in the regulation of osteogenic precursor cell differentiation and activity [17]. The overall increase in PI3K signaling improves femoral regeneration by stimulating the proliferation of periosteal cells in the early stage of fracture healing. These studies have shown that the PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in bone metabolism and remodeling. Other studies have shown that inhibiting endothelial cell dysfunction by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway can reduce the age-related deterioration of angiogenesis at the fracture site, leading to increased angiogenesis and ultimately accelerating fracture healing [18,19]. The interaction between SATB2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and its regulatory mechanism on humeral fracture healing still need to be further explored.
The process of fracture healing is a multifaceted biological phenomenon, wherein bone regeneration is significantly influenced by osteoblasts and osteoclasts. This research aims to investigate the potential mechanism underlying fracture healing in vivo, with a particular focus on the SATB2 and PI3K/AKT pathways. To achieve this, an animal model of humeral fracture was established.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Humeral fracture animal model
A total of 60 male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing 180 ± 20 g and aged 6 weeks, were procured from The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang. The rats were housed in a facility with a regulated 12 h light–dark cycle and were given ad libitum access to food and water. The study was conducted with the approval of The Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang (No. 202106HB84) and adhered to the ethical principles outlined in the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
For anesthesia, a 10% chloral hydrate solution (Sigma, USA) was administered via intraperitoneal injection. The humeral shaft, as well as the internal and lateral condyles of the humerus, was fully exposed. Subsequently, a 1 mm Kirschner needle was retrogradely drilled upward into the humeral bone marrow cavity. After penetrating the skin, any excess portion of the needle was removed by cutting it off. The upper one-third of the humerus was intentionally truncated using bone forceps, resulting in transverse fractures. Following wound cleansing, a dose of 40 U gentamicin (Sigma, USA) was administered into the wound, while 200,000 U of penicillin (Sigma) was injected intraperitoneally.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals, and has been approved by the Third Hospital of Shijiazhuang Animal Experimental Ethics Committee (No. 202106HB84).
2.2 Treatment of fracture models
The rats were randomly divided into four groups: model group, SATB2 overexpression group, PI3K/AKT inhibition group, and SATB2 + PI3K/AKT inhibition group. Model group: humeral fracture + AAV5-GEP; SATB2 overexpression group: humeral fracture + AAV5-SATB2; PI3K/AKT inhibition group: humeral fracture + AAV5-GEP + PI3K/AKT-in-1; and SATB2 + PI3K/AKT inhibition group: humeral fracture + AAV5-SATB2 + PI3K/AKT-in-1.
To overexpress SATB2, an adenovirus encoding the SATB2 gene (AAV5-SATB2; HanBio, Shanghai, China) was injected into the tail vein of rats. AAV5-green fluorescent protein (HanBio) was used as a positive control (AAV5-GEP).
The rats were fasted for 24 h. The PI3K/AKT inhibition group and the SATB2 + PI3K/AKT inhibition group were administered with a PI3K/AKT inhibitor (PI3K/AKT-in-1, #HY-144806, MedChemExpress, USA) at 2 g/kg. The control group received an equivalent volume of normal saline.
2.3 Biomechanical test
At 3 and 6 weeks post-surgery, three rats were randomly chosen to undergo removal of the internal fixation (Kirschner needle) from the right humerus and bilateral fixation of the fractured humerus. The biomechanical characteristics were assessed using a three-point bending test, utilizing a mechanical testing apparatus with a 20 mm span and a loading rate of 1 mm/min. The maximum load and stiffness were recorded, with the callus serving as the point of loading.
2.4 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
At 6 weeks after surgery, six rats were chosen from each group and their abdominal venous blood was extracted and subjected to centrifugation to collect the supernatant. Interleukin 6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, osteocalcin, C-telopeptide-type-I-collagen (CTX-I), and bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) in the rat serum or plasma were determined using ELISA kits (R&D Systems, USA). Using a microplate reader, absorbance values were measured at 450 nm. NO level (Griess method and NO assay kit; Jiancheng Biological, Nanjing, China) and eNOS activity (Rat Endothelial NOS (eNOS) ELISA Kit; Jinln Biological) in rat plasma were determined.
2.5 Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
The tissue sections were treated with citrate buffer at 60°C. Subsequently, the slices underwent an 8 min incubation with protease K to facilitate antigen retrieval. Following this, the slices were incubated overnight at 4°C with PI3K (#4228; Cell Signaling Technology, USA), P-AKT (#4060; Cell Signaling Technology), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP; #ab83259, Abcam, USA). After incubation with the secondary antibody immunoglobulin G (#ab124055; Abcam) at room temperature for 1 h, the target signal was activated using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine substrate (Vector Labs, CA, USA). Finally, the slides were re-stained with hematoxylin for 2 min and subsequently observed. A semi-quantitative technique was employed for immunopositive assessments [20]. For each microscopic field, cells were counted as either immunopositive or negative and then expressed as percentages. Positive cell percentage was evaluated on a 5-point scale: 0 for no positive cells, 1 for 20%, 2 for 21–50%, 3 for 51–70%, and 4 for 71%. Immunostaining intensity was evaluated using a 4-level scoring system: 0 for no staining, 1 for low intensity, 2 for moderate intensity, and 3 for high intensity. The IHC score was calculated by multiplying the scores for cell positivity and signal intensity, ranging from a minimum of 0 to a maximum of 12.
2.6 Imaging analysis
Following the successful establishment of the fracture model and drug injection, lateral femoral radiographs were taken at 1, 3, and 6 weeks using specific parameters (52 kV, 4.5 mAs, 0.5 s). These radiographs were utilized to observe the growth of bone callus, the position of the internal fixation, the healing of the fracture line, and the alignment of the fracture line by X-ray film analysis. Each X-ray was independently reviewed by a radiologist, a lab researcher, and a plastic surgeon. Subsequently, the rats were euthanized, and the callus was extracted from the cadaver and placed in liquid nitrogen.
2.7 Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining
The skin incision was made and the muscles were promptly dissected. Subsequently, the humerus was immobilized in 10% formaldehyde solution (Beyotime, Shanghai, China), decalcified in 9% formic acid solution (Beyotime), and embedded in paraffin. Following standardized processing, the specimens were sectioned longitudinally at 5 μm thickness, embedded in paraffin, and subjected to staining with hematoxylin solution, followed by eosin solution. Imaging was conducted using a microscope (DS-Ri 2, Nikon, Japan).
2.8 Masson (MS) dyeing
The prepared paraffin sections were stained with Regaud’s Hematoxylin staining solution, then stained with Lichun red acid fuchsin dye (Sinopharm, Shanghai), and finally treated with aniline blue. New or mature bones were observed under a microscope.
2.9 Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
RNA was extracted from the fracture site using TRIzol® reagents (Invitrogen, CA, USA). The RNA quality was then measured by Nanodrop 2000. cDNA samples were obtained using TaKaRa RNA PCR kit (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) and Oligo dT primer (Invitrogen). Gene expression levels were detected using SYBR mixture (TaKaRa, Dalian, China) on a LightCycler 480 device (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Primer design is shown in Table 1. Gene expression was normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and the data were analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method.
Primers
| Name | Primer sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| SATB2 | TAAGCAGTCCCTGCGCGTTT |
| GAATCATCAGACCTCCCACGG | |
| GAPDH | CATCATCCCTGCCTCTACTGG |
| GTGGGTGTCGCTGTGTGAAGTC |
2.10 Western blotting analysis
Protein was extracted from the fracture site, which included the entire callus and adjacent bone less than 2 mm. Following the full protein extraction kit’s guidelines, the lysis buffer was introduced, blended in a tissue homogenizer for 1 min, and then spun at 12,000 rpm and 4°C for 15 min. After gathering the supernatant, the protein levels were measured using the bicinchoninic acid protein quantification kit (Pierce, MA, USA). The proteins were separated by 15% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (Beyotime) membranes, blocked at room temperature with 5% skim milk powder for 1 h, and washed three times with TBST (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). PI3K (#4228; Cell Signaling Technology), p-AKT (#4060; Cell Signaling Technology), AKT (#9272; Cell Signaling Technology), p65 (#10745-1-AP; Proteintech), p-p65 (#3033; Cell Signaling Technology), ALP (#ab83259; Abcam), receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL; #ab45039, Abcam), osteoprotegerin (OPG; #ab73400, Abcam), and GAPDH (#ab246513; Abcam) were incubated overnight at 4°C. After three washing of TBST, the secondary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) bound to the corresponding horseradish peroxidase was incubated at 37°C for 1 h and developed using an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Sigma).
2.11 Statistical analysis
The experimental design is shown in Figure 1. Statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, USA) and SPSS Statistics 20 (IBM, USA). The data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. All experiments were replicated biologically at least three times. Student’s t-test was employed to assess differences between the two groups, while one-way analysis of variance was used for multiple recombination comparisons. A significance level of *p < 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
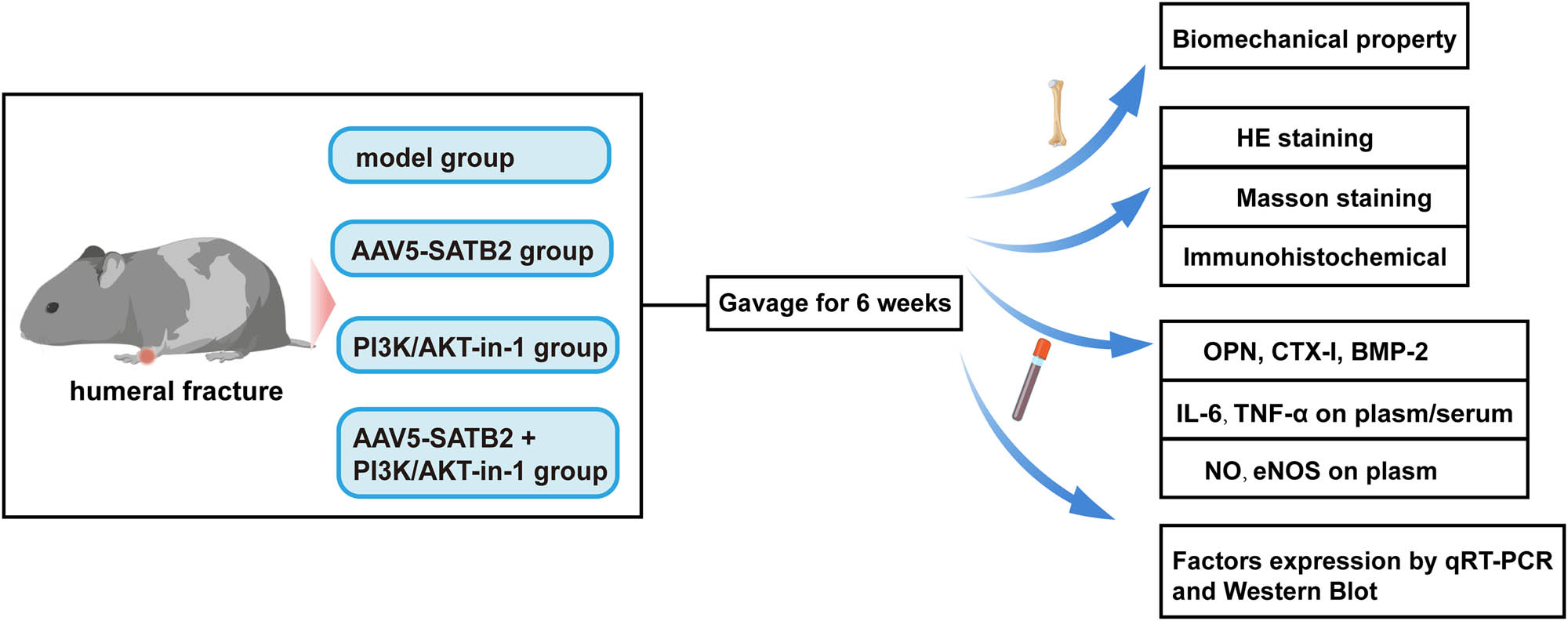
Experimental design. Stable humeral fractures were established in SD rats. Biomechanical properties were assessed by three-point bending test at postoperative weeks 3 and 6. Tissue sections were prepared and subjected to HE staining and Masson staining to assess osteogenic differentiation. IHC assay was performed to assess the expression of ALP and PI3K/Akt pathway-related proteins. The expression of SATB2 and its related factors was quantified by RT-qPCR, ELISA, and western blot.
3 Results
3.1 SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing
RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated a significant upregulation of SATB2 expression in the humerus of the SATB2 overexpression group compared to the model group (Figure 2a). Histological analysis using MS staining at week 6 revealed a greater extent of bone formation, improved bone quality, and increased blue staining indicative of favorable bone repair in the SATB2 overexpression group as compared to the model group. SATB2 overexpression promoted the healing of humeral fractures in rats based on these findings (Figure 2b). Further observation by HE staining showed that the fracture end of the SATB2 overexpression group was significantly repaired and the bone continuity was restored. In the model group, the bone repair of the fracture end was not obvious, and the continuity of the fracture end was poor (Figure 2c). As shown in Table 2, the maximum load, stiffness, and total energy absorption of fracture callus in the SATB2 overexpression group were significantly higher than those in the model group.
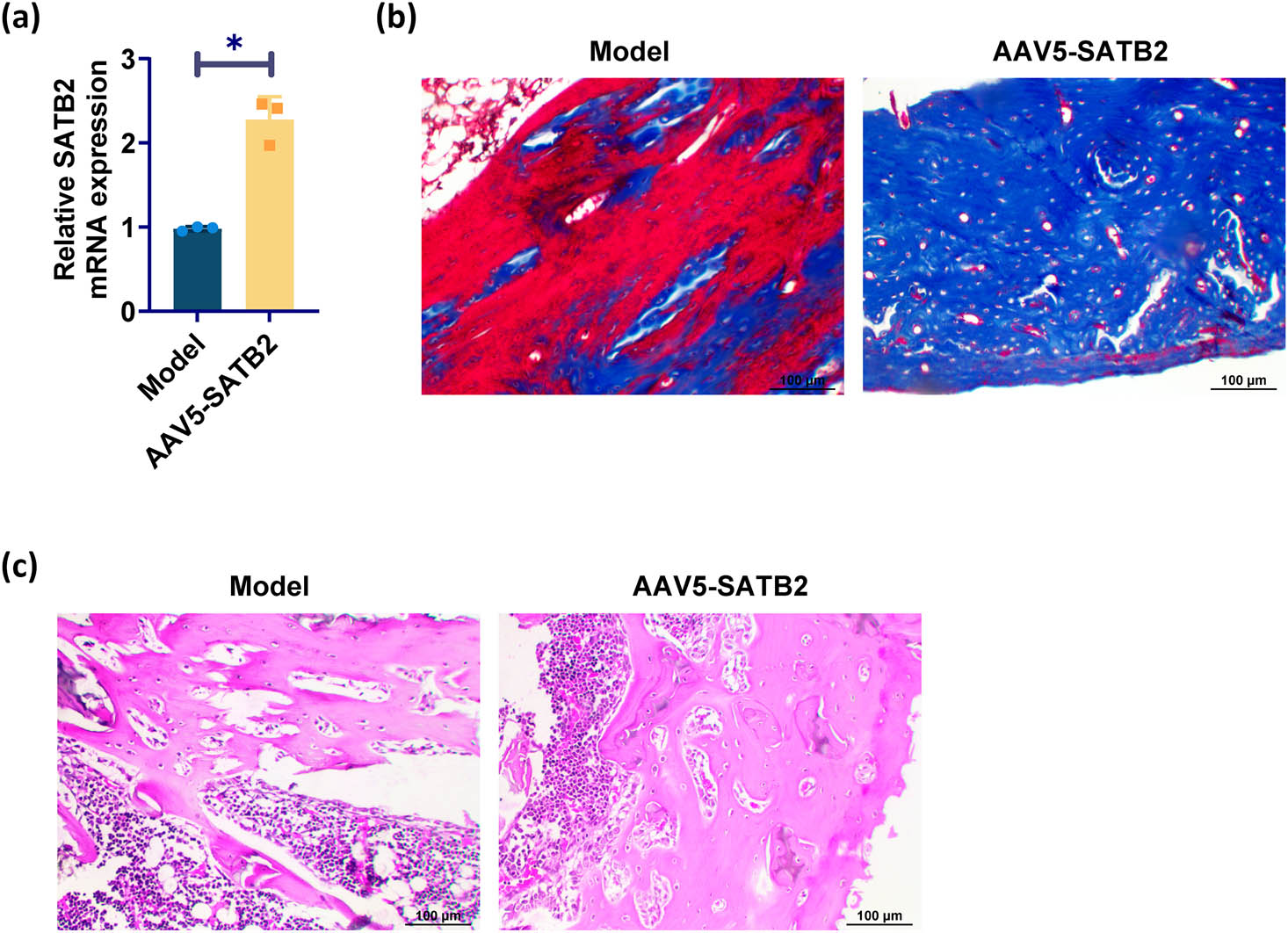
SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing: (a) RT-qPCR was used to detect SATB2 expression, (b) MS staining shows the degree of fracture healing, and (c) HE staining shows histological findings of bone healing. *p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Comparison of biomechanics of fracture callus between the two groups
| Time | Groups | Maximum load (N) | Stiffness (N/mm) | Total energy absorption (mJ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three weeks after fracture | Model group | 22.1 ± 4.5 | 101.6 ± 13.5 | 13.7 ± 3.7 |
| SATB2 overexpression group | 52.3 ± 9.8* | 226.8 ± 26.4* | 34.1 ± 5.7* | |
| Six weeks after fracture | Model group | 75.9 ± 10.2 | 158.4 ± 20.1 | 23.6 ± 4.2 |
| SATB2 overexpression group | 142.1 ± 19.8* | 267.3 ± 30.9* | 46.2 ± 8.10* |
*p < 0.05 indicates statistical significance of the difference.
3.2 Overexpression of SATB2 enhances osteogenic differentiation
To further elucidate the effect of SATB2 overexpression on osteogenic differentiation, western blotting was used to identify the presence of osteogenic markers such as ALP, RANKL, and OPG. The signaling pathways involving ALP, OPG, and RANKL are known to exert significant regulatory control over the process of osteoclast differentiation and maturation. The upregulation of RANKL can induce the transformation of osteoblasts into osteoclasts, thereby enhancing osteoclast activity and promoting bone resorption, ultimately culminating in fracture nonunion. IHC staining showed that the number of ALP-positive cells in the SATB2 overexpression group was significantly increased, which was confirmed by western blotting (Figure 3a and b). Compared with the model group, the SATB2 overexpression group exhibited significantly decreased RANKL expression and increased OPG, indicating that SATB2 overexpression inhibited osteoclast activity and promoted osteoblast function (Figure 3c and d).
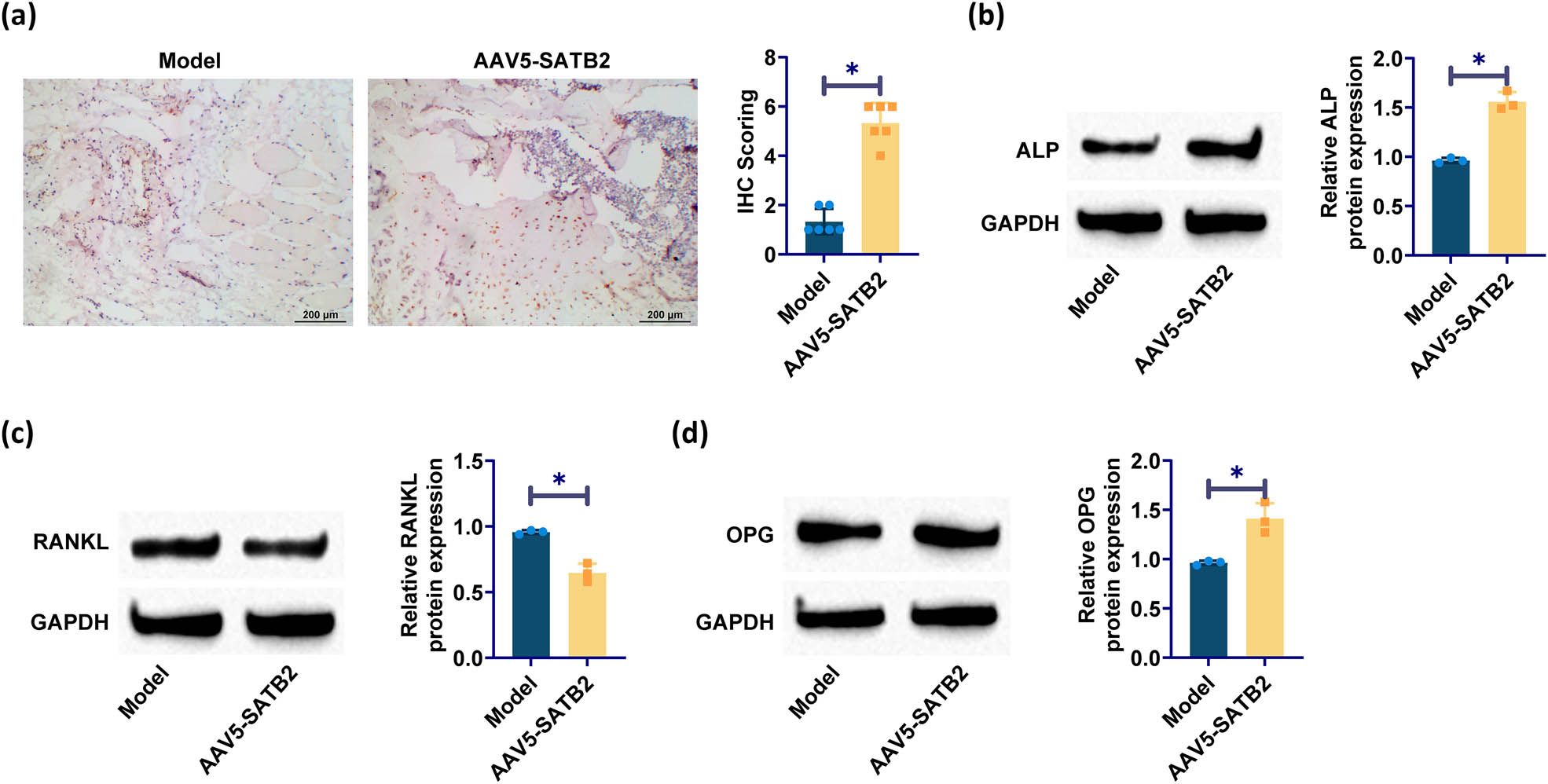
Overexpression of SATB2 enhances osteogenic differentiation: (a) IHC staining detected ALP; (b)–(d) western blotting detection of ALP, RANKL, and OPG. *p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.3 SATB2 affects serum osteocalcin, CTX-I, BMP-2, and inflammation
Osteocalcin and BMP-2 in the serum of model group was lower, and CTX-I was higher. Compared with the model group, osteocalcin and BMP-2 in the SATB2 overexpression group were increased, and CTX-I was decreased (Figure 4a–c). The expression of inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α was higher in the plasma and serum of rats in the model group, which was significantly reduced by SATB2 overexpression (Figure 4d and e). NO levels and eNOS activity were also detected in the plasma of rats. The plasma levels of NO and eNOS were significantly up-regulated under the effect of SATB2 overexpression (Figure 4f and g).
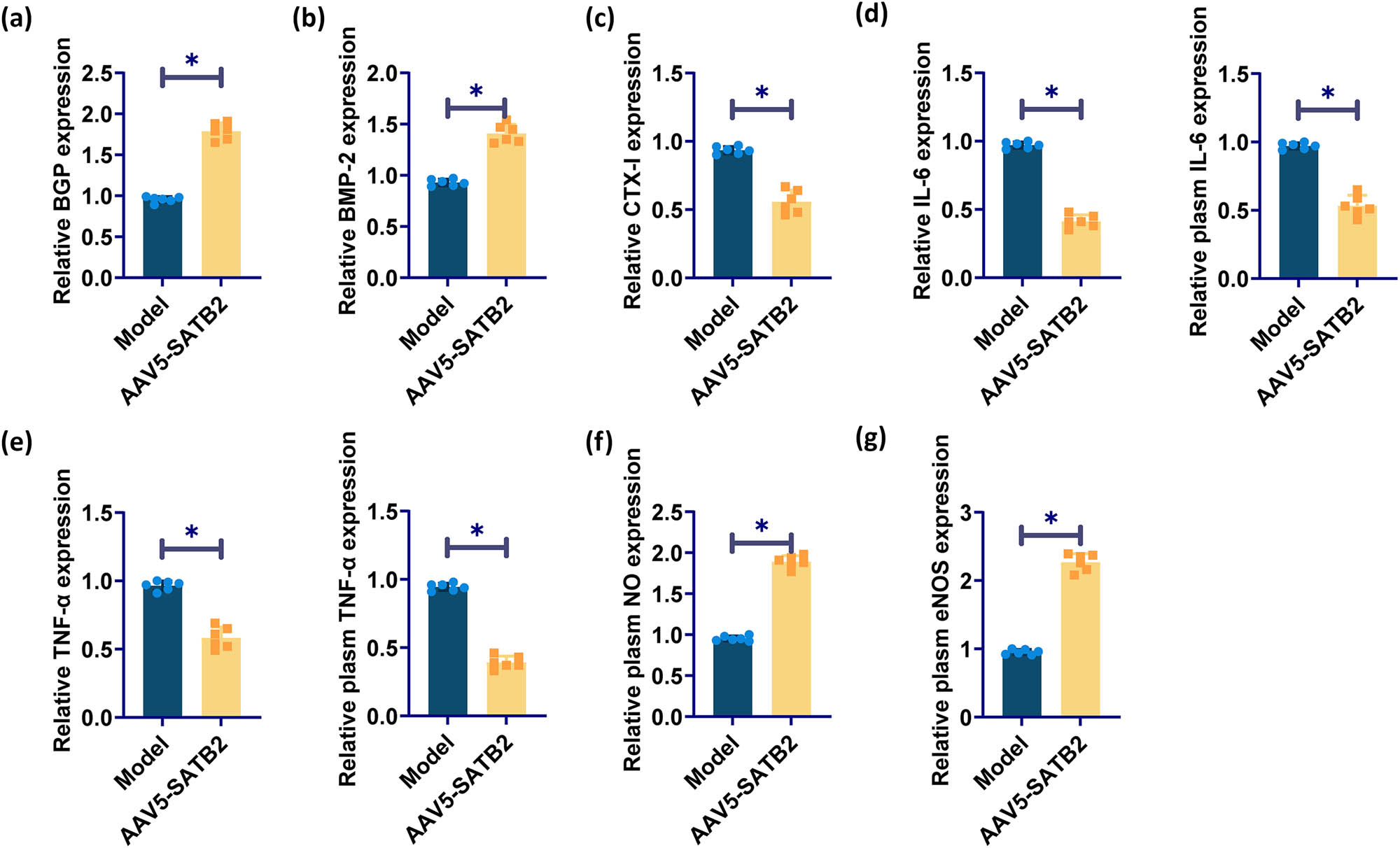
Effects of SATB2 on serum osteocalcin, CTX-I, BMP-2, and inflammation. (a)–(c) ELISA detected serum osteocalcin, BMP-2, and CTX-I in rats. (d) ELISA for the determination of IL-6 in rat plasma and serum. (e) ELISA for the detection of TNF-α in rat plasma and serum. (f) and (g) ELISA for plasma NO level and eNOS activity in rats. *p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.4 Expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway-related proteins in humerus tissues of rats
To detect whether the PI3K/AKT pathway is expressed and activated during the whole healing process of fractured rats, western blotting was conducted to detect key proteins. Compared with the model group, PI3K and p-AKT in the humerus in the SATB2 overexpression group was significantly increased, as well as p-p65/p65 (Figure 5a, b, and e). SATB2 indeed activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. It is worth noting that PI3K/AKT and p-p65/p65 expression was inhibited by PI3K/AKT inhibitor. However, upon overexpression of SATB2, the reduction in PI3K and p-AKT proteins induced by PI3K/AKT inhibitor was reversed (Figure 5c, d, and f). SATB2 affected the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to a greater extent. IHC staining results showed that compared with the model group and the PI3K/AKT inhibition group, the positive rate of PI3K and p-AKT in the fracture area of rats after SATB2 overexpression also confirmed that SATB2 can activate the PI3K/AKT pathway (Figure 5g). HE staining also showed poor healing and repair in the PI3K/AKT inhibition group, but the healing and repair difference caused by PI3K/AKT inhibitor was reversed after overexpression of SATB2 (Figure 5h).
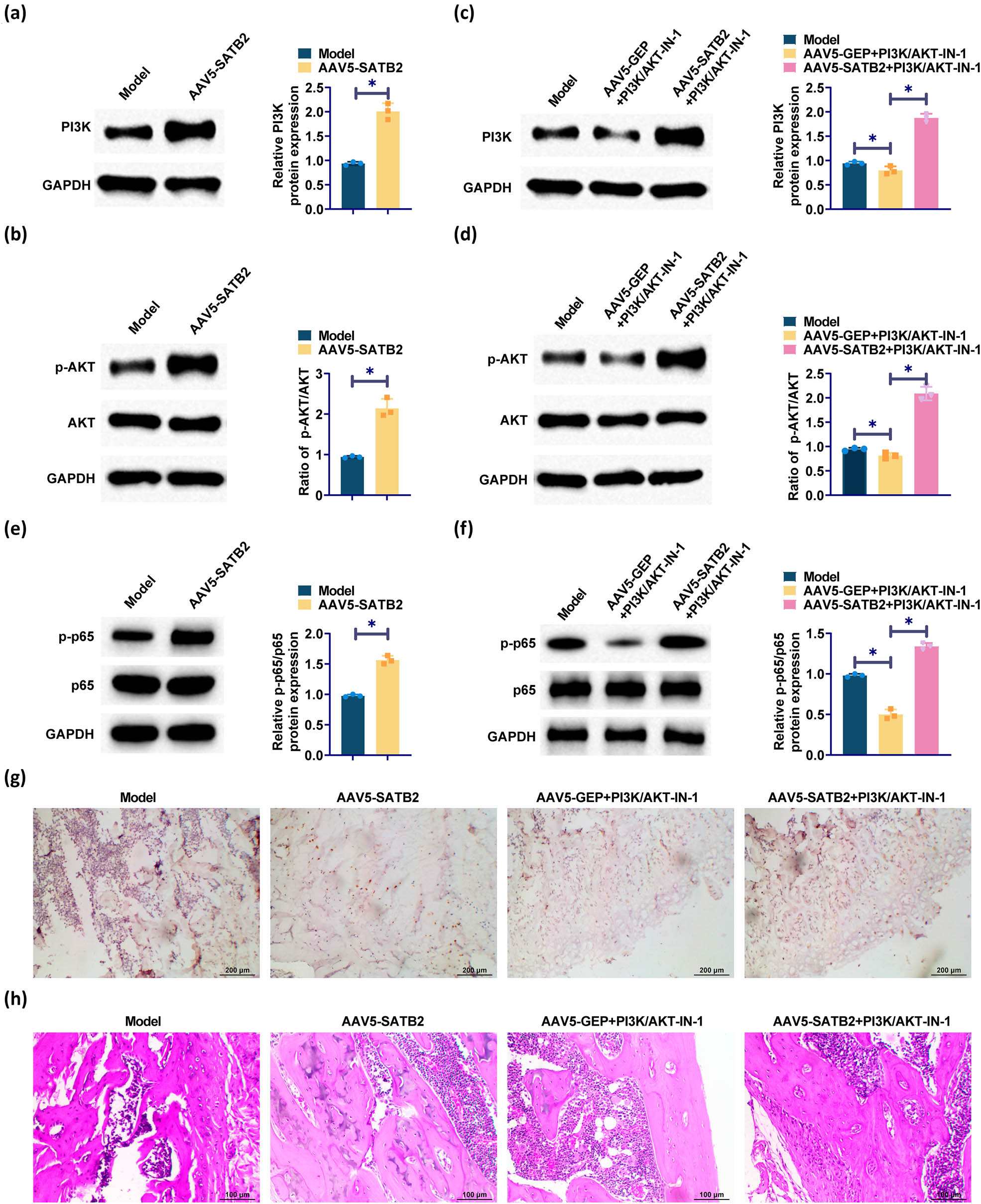
Expression of PI3K/AKT pathway-related proteins in humerus tissues of rats. (a) and (c) Western blotting detected PI3K expression. (b) and (d) Western blotting detected p-AKT expression. (e) and (f) Western bolt for p-65 and p-p65 expression. (g) Immunohistochemical staining to detect the expression of PI3K and AKT in the fracture region of rats in each group. (h) HE staining showed histological findings of bone healing. *p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4 Discussion
In recent times, there has been a significant focus on the comprehensive investigation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the process of fracture healing. In particular, the protein SATB2 has emerged as a key factor in the complex regulation of osteogenic differentiation and osteoblast formation [3,21]. This study investigated the potential therapeutic effect of SATB2 on fracture healing in a rat model of humeral fracture. In the SATB2 overexpression group, bone repair was evident and bone continuity was restored. In the model group, bone repair was not evident and fracture continuity was poor.
RANK is a specific receptor of RANKL, and both recognize and bind on the surface of osteoclasts, which can promote differentiation and maturation of osteoclasts and inhibit their apoptosis, thus leading to bone resorption and reducing bone density [22]. OPG is primarily secreted by osteoblasts and BMSCs, exerting a pivotal function in the suppression of bone resorption and the enhancement of bone density [23–25]. In this experiment, it was found that OPG protein was lower in the bone tissue of the model group, while RANKL was higher. During fracture repair, osteoblasts and vascular bone endothelium can synthesize ALP, and the secreted ALP can penetrate into the blood, increasing the blood levels of ALP [26]. In this study, ALP levels in the SATB2 overexpression group were significantly higher than those in the model group.
Osteocalcin, a polypeptide, is produced and released by bone cells in response to 1,25-(OH)2D3 stimulation. Its primary function is to impede the development of atypical hydroxyapatite crystals and uphold the customary rate of bone mineralization. The measurement of serum osteocalcin serves as an indicator of recent osteocalcin synthesis and bone formation [27]. BMP-2 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of cells. As a factor in promoting bone formation, BMP-2 plays a decisive role in the differentiation of osteoblasts [28]. Changes in CTX-I during fracture healing are more sensitive than changes in bone mineral density and can therefore be used to assess bone metabolism and bone resorption [29]. The inflammatory response is a significant contributor to the delayed healing process of fractures. The upregulation of IL-6, TNF-α, and other inflammatory mediators can lead to the degradation of the extracellular matrix of chondrocytes, thereby impeding chondrocyte differentiation and resulting in a decelerated fracture healing process [30,31]. This study showed that BMP-2 and osteocalcin in the serum of rats in the SATB2 overexpression group were increased, while CTX-I, IL-6, and TNF-α were decreased. These results suggest that SATB2 can promote osteoblast proliferation and differentiation and inhibit osteoclast activity to promote fracture healing.
In the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, AKT serves as an essential protein, functioning as a primary kinase downstream of PI3K and contributing to cell survival, growth, and proliferation. The activation of AKT is mediated by p-AKT, which then activates mTOR, a component downstream of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thus impacting life activities such as apoptosis. The role of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in bone formation and regeneration is considered important. Within the PI3K/AKT pathway, the regulatory role of PI3K signaling is significant in driving BMSCs to develop into osteoblasts and aid in bone formation [32]. MiR-21 promotes fracture healing in rats by activating PI3K–AKT signaling pathway [33]. The inhibition of β-catenin transcription weakens the PI3K–AKT-induced proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization of osteoblasts, highlighting the Wnt/PI3K/AKT/β-catenin signaling pathway in osteoblasts and implying a strong relationship between the PI3K–AKT pathway and fracture healing [34]. This is also consistent with our experimental results. Compared with the SATB2 overexpression group with fracture healing, PI3K and AKT were significantly decreased in the model group with poor fracture healing. PI3K/AKT pathway can promote fracture healing and may be a potential mechanism to promote fracture healing [35]. Western blotting detected lower PI3K and AKT in the PI3K/AKT inhibition, but PI3K/AKT expressions increased after SATB2 overexpression. We speculate that the mechanism of SATB2 promoting fracture healing may be to promote osteoblast function by inducing AKT phosphorylation and up-regulation of PI3K–AKT signaling pathway, thereby accelerating fracture healing. However, we still need to understand how these signaling pathways are related to each other to better understand the potential mechanism of SATB2’s effect on fracture healing.
Using a fracture rat model, we found that SATB2 significantly enhanced the regeneration of damaged bone tissue. For example, overexpression of SATB2 accelerated bone formation by positively regulating the expression of multiple osteoblast-specific genes and enhanced the increase of new bone formation in bone defects. The integration of SATB2 in bone tissue engineering offers novel and essential insights into gene detection, treatment, and molecular regulation of bone tissue regeneration, representing a promising alternative strategy to expedite bone regeneration. With further development, the use of SATB2 as a gene therapy for bone defects may shorten the healing time of human bone defects and become a valuable strategy to reduce recovery time and external fixation requirements.
Previous studies have shown that SATB2 is a high-order transcription factor that regulates genes required for osteogenic differentiation. A significant feature of this study is that in addition to its role in differentiation, it has also been found that SATB2 interacts with the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway to achieve dual regulation of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation and maturation, and to regulate the expression of factors associated with the inflammatory response. The involvement of SATB2 in the differentiation and inflammatory response processes and the promotion of the biological properties of the fracture callus make SATB2 an interesting target for the treatment and healing of bone regeneration disorders. Although this finding is the advantage of this study, there are still some limitations. This study used only rat models and did not validate the role of SATB2 in combined old age or osteoporotic fracture models. Micro-CT scans were not performed, and the assessment of bone healing quality was incomplete. Second, we were unable to determine whether there is a direct interaction between SATB2 and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Whether the upstream regulatory mechanism of eNOS/NO is dependent on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is also unknown. It is worth focusing on the fact that the current study found that SATB2 upregulation may be involved in tumorigenesis. Therefore it is necessary to evaluate it in future studies in the long term. We will attack these limitations one by one in the future. Extending the pathological state is also a direction we will further explore in the future. Meanwhile, knockdown of AKT or p65 using CRISPR is used to elucidate the precise regulation of key nodes by SATB2.
5 Conclusion
The present study systematically revealed the key role of transcription factor SATB2 and its molecular mechanism in promoting humerus fracture healing, which provides an important theoretical breakthrough and clinical translational prospect in the field of bone repair. SATB2 promotes the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, and inhibits osteoclastogenic activity by regulating the balance of OPG/RANKL. Meanwhile, SATB2 improves local blood supply by up-regulating eNOS/NO and reduces the level of inflammatory factors such as IL-6/TNF-α. Compared to traditional single-pathway pro-healing strategies, SATB2 exhibits multi-target synergistic benefits that make it of significant translational medicine value. Although the role of SATB2 in pathological states such as osteoporosis and diabetes mellitus has not yet been validated, the present study provides a theoretical basis for SATB2 in the clinical treatment of fractures. Future studies will further validate the therapeutic effect of SATB2, clarify the applicable types of SATB2 in clinical practice, and further deepen the understanding of the mechanism of SATB2’s action on bone repair.
-
Funding information: This work was funded by Shijiazhuang Science and Technology Research and Development Guidance Program Project in 2018 (No. 181201133).
-
Author contributions: Liantao Liu designed the research study; Shuai Rong and Xiaobin Zhou performed the research; Hao Li and Kepei Zhen provided help and advice on the experiments; Chong Zheng and Kewei Li analyzed the data; Liantao Liu wrote the manuscript; Liantao Liu and Kewei Li reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Boone PM, Chan YM, Hunter JV, Pottkotter LE, Davino NA, Yang Y, et al. Increased bone turnover, osteoporosis, progressive tibial bowing, fractures, and scoliosis in a patient with a final-exon SATB2 frameshift mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 2016;170(11):3028–32.10.1002/ajmg.a.37847Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Chalhoub N, Baker SJ. PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:127–50.10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092311Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Chen L, Yang L, Yao M, Cui XJ, Xue CC, Wang YJ, et al. Biomechanical characteristics of osteoporotic fracture healing in ovariectomized rats: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153120.10.1371/journal.pone.0153120Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Chow SK, Chim YN, Wang J, Zhang N, Wong RM, Tang N, et al. Vibration treatment modulates macrophage polarisation and enhances early inflammatory response in oestrogen-deficient osteoporotic-fracture healing. Eur Cell Mater. 2019;38:228–45.10.22203/eCM.v038a16Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Dobreva G, Chahrour M, Dautzenberg M, Chirivella L, Kanzler B, Fariñas I, et al. SATB2 is a multifunctional determinant of craniofacial patterning and osteoblast differentiation. Cell. 2006;125(5):971–86.10.1016/j.cell.2006.05.012Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Dong J, Xu X, Zhang Q, Yuan Z, Tan B. The PI3K/AKT pathway promotes fracture healing through its crosstalk with Wnt/β-catenin. Exp Cell Res. 2020;394(1):112137.10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112137Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Dong K, Zhou WJ, Liu ZH, Hao PJ. The extract of concentrated growth factor enhances osteogenic activity of osteoblast through PI3K/AKT pathway and promotes bone regeneration in vivo. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7(1):70.10.1186/s40729-021-00357-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Dong P, Liu WJ, Wang ZH. MiR-154 promotes myocardial fibrosis through β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(7):2052–60.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Einhorn TA, Gerstenfeld LC. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45–54.10.1038/nrrheum.2014.164Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Fioramonti M, Santini D, Iuliani M, Ribelli G, Manca P, Papapietro N, et al. Cabozantinib targets bone microenvironment modulating human osteoclast and osteoblast functions. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):20113–21.10.18632/oncotarget.15390Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Ge P, Cui Y, Liu F, Luan J, Zhou X, Han J. L-carnitine affects osteoblast differentiation in NIH3T3 fibroblasts by the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Biosci Trends. 2015;9(1):42–8.10.5582/bst.2015.01000Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Gong Y, Qian Y, Yang F, Wang H, Yu Y. Lentiviral-mediated expression of SATB2 promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Oral Sci. 2014;122(3):190–7.10.1111/eos.12122Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Guo Y, Dong SS, Chen XF, Jing YA, Yang M, Yan H, et al. Integrating epigenomic elements and GWASs identifies BDNF gene affecting bone mineral density and osteoporotic fracture risk. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30558.10.1038/srep30558Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Hofman M, Rabenschlag F, Andruszkow H, Andruszkow J, Möckel D, Lammers T, et al. Effect of neurokinin-1-receptor blockage on fracture healing in rats. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):9744.10.1038/s41598-019-46278-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Huang H, Dou L, Song J, Luo J. CBFA2T2 is required for BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;496(4):1095–101.10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.144Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Huang TB, Li YZ, Yu K, Yu Z, Wang Y, Jiang ZW, et al. Effect of the Wnt signal-RANKL/OPG axis on the enhanced osteogenic integration of a lithium incorporated surface. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(3):1101–16.10.1039/C8BM01411FSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Huang X, Chen Q, Luo W, Pakvasa M, Zhang Y, Zheng L, et al. SATB2: a versatile transcriptional regulator of craniofacial and skeleton development, neurogenesis and tumorigenesis, and its applications in regenerative medicine. Genes Dis. 2022;9(1):95–107.10.1016/j.gendis.2020.10.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Huang YZ, Zhao L, Wang CL, Tian SJ, Liu S, Ge JF. RBM5-AS1 participates in fracture healing and inhibits apoptosis of bone cells through the up-regulation of β-catenin. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(16):5091–7.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Leoyklang P, Suphapeetiporn K, Siriwan P, Desudchit T, Chaowanapanja P, Gahl WA, et al. Heterozygous nonsense mutation SATB2 associated with cleft palate, osteoporosis, and cognitive defects. Hum Mutat. 2007;28(7):732–8.10.1002/humu.20515Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Liu Y, Liu J, Xia T, Mi BB, Xiong Y, Hu LC, et al. MiR-21 promotes fracture healing by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7):2727–33.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Liu Y, Liu Q, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Zhou Y, Yan H, et al. The regulatory role of PI3K in ageing-related diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;88:101963.10.1016/j.arr.2023.101963Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Liu Y, Wang H, Zhou XZ, Li N, Guo YC, Chen TP. Pentraxin 3 promotes the osteoblastic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(6):BSR20201165.10.1042/BSR20201165Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] McGuire JF, Wu MS, Piacentini J, McCracken JT, Storch EA. A meta-analysis of D-cycloserine in exposure-based treatment: moderators of treatment efficacy, response, and diagnostic remission. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(2):196–206.10.4088/JCP.15r10334Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Ojeda L, Gao J, Hooten KG, Wang E, Thonhoff JR, Dunn TJ, et al. Critical role of PI3K/Akt/GSK3β in motoneuron specification from human neural stem cells in response to FGF2 and EGF. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23414.10.1371/journal.pone.0023414Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Öztürk Y, Öztürk M, Dörtbudak MB, Mariotti F, Magi GE, Di Cerbo A. Astaxanthin mitigates 5-fluorouracil-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress in male rats. Nutrients. 2025;17(7):1230.10.3390/nu17071230Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Peltier J, O’Neill A, Schaffer DV. PI3K/Akt and CREB regulate adult neural hippocampal progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Dev Neurobiol. 2007;67(10):1348–61.10.1002/dneu.20506Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Scanlon V, Walia B, Yu J, Hansen M, Drissi H, Maye P, et al. Loss of Cbl-PI3K interaction modulates the periosteal response to fracture by enhancing osteogenic commitment and differentiation. Bone. 2017;95:124–35.10.1016/j.bone.2016.11.020Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Stuss M, Sewerynek E, Król I, Stępień-Kłos W, Jędrzejczyk S. Assessment of OPG, RANKL, bone turnover markers serum levels and BMD after treatment with strontium ranelate and ibandronate in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Endokrynol Pol. 2016;67(2):174–84.10.5603/EP.a2016.0014Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Vezzani G, Quartesan S, Cancellara P, Camporesi E, Mangar D, Bernasek T, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy modulates serum OPG/RANKL in femoral head necrosis patients. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017;32(1):707–11.10.1080/14756366.2017.1302440Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Xin J, Ding W, Hao S, Jiang L, Zhou Q, Wu T, et al. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived hepatocytes express tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 4 and follistatin. Liver Int. 2015;35(10):2301–10.10.1111/liv.12797Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Xing Q, Feng J, Zhang X. Glucocorticoids suppressed osteoblast differentiation by decreasing Sema3A expression via the PIK3/Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2021;403(1):112595.10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112595Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Yuan FL, Xu RS, Jiang DL, He XL, Su Q, Jin C, et al. Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Bone. 2015;75:128–37.10.1016/j.bone.2015.02.017Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Zarate YA, Steinraths M, Matthews A, Smith WE, Sun A, Wilson LC, et al. Bone health and SATB2-associated syndrome. Clin Genet. 2018;93(3):588–94.10.1111/cge.13121Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Zhang J, Tu Q, Grosschedl R, Kim MS, Griffin T, Drissi H, et al. Roles of SATB2 in osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(13–14):1767–76.10.1089/ten.tea.2010.0503Search in Google Scholar
[35] Zhao X, Qu Z, Tickner J, Xu J, Dai K, Zhang X. The role of SATB2 in skeletogenesis and human disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25(1):35–44.10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.12.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- 10.1515/biol-2025-1170
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Sepsis complicated by haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis triggered by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and human herpesvirus 8 in an immunocompromised elderly patient: A case report
- Sarcopenia in liver transplantation: A comprehensive bibliometric study of current research trends and future directions
- Advances in cancer immunotherapy and future directions in personalized medicine
- Can coronavirus disease 2019 affect male fertility or cause spontaneous abortion? A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Heat stroke associated with novel leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor gene variant in a Chinese infant
- PSME2 exacerbates ulcerative colitis by disrupting intestinal barrier function and promoting autophagy-dependent inflammation
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- 10.1515/biol-2025-1170
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”

