From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
-
Jyoti Verma
, Vikas Khullar
Abstract
Prognostic survival prediction in colorectal cancer (CRC) plays a crucial role in guiding treatment decisions and improving patient outcomes. In this research, we explore the application of deep learning techniques to predict survival outcomes based on histopathological images of human colorectal cancer. We present a retrospective multicenter study utilizing a dataset of 100,000 nonoverlapping image patches from hematoxylin & eosin-stained histological images of CRC and normal tissue. The dataset includes diverse tissue classes such as adipose, background, debris, lymphocytes, mucus, smooth muscle, normal colon mucosa, cancer-associated stroma, and colorectal adenocarcinoma epithelium. To perform survival prediction, we employ various deep learning architectures, including convolutional neural network, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception. These architectures are trained on the dataset using a multicenter retrospective analysis approach. Extensive preprocessing steps are undertaken, including image normalization using Macenko’s method and data augmentation techniques, to optimize model performance. The experimental findings reveal promising results, demonstrating the effectiveness of deep learning models in prognostic survival prediction. Our models achieve high accuracy, precision, recall, and validation metrics, showcasing their ability to capture relevant histological patterns associated with prognosis. Visualization techniques are employed to interpret the models’ decision-making process, highlighting important features and regions contributing to survival predictions. The implications of this research are manifold. The accurate prediction of survival outcomes in CRC can aid in personalized medicine and clinical decision-making, facilitating tailored treatment plans for individual patients. The identification of important histological features and biomarkers provides valuable insights into disease mechanisms and may lead to the discovery of novel prognostic indicators. The transparency and explainability of the models enhance trust and acceptance, fostering their integration into clinical practice. Research demonstrates the potential of deep learning models for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology. The findings contribute to the understanding of disease progression and offer practical applications in personalized medicine. By harnessing the power of deep learning and histopathological analysis, we pave the way for improved patient care, clinical decision support, and advancements in prognostic prediction in CRC.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a serious global health issue with a substantial mortality rate. The histopathological examination of tissue slides is crucial in assessing prognosis and developing treatment plans for patients diagnosed with CRC. Manually interpreting histology slides is marked by significant labor and is susceptible to variations in observations across different observers. To tackle these issues, methods based on deep learning have demonstrated considerable potential in automating the processing of histological images for prognostic survival prediction. CRC, or colon cancer or cancer of the rectal area, is a malignancy that specifically targets the colon or rectum, constituting integral components of the large intestinal tract. Typically, the progression commences with the emergence of nonmalignant formations known as polyps, which may evolve into malignant neoplasms. CRC is prevalent globally and contributes substantially to mortality rates associated with cancer [1].
The significance of CRC is its capacity to proliferate and metastasize without timely detection and intervention. When detected at an early stage, CRC frequently exhibits a high degree of treatability, leading to a notable enhancement in survival rates. Nevertheless, in the event of cancer advancement and metastasis, the therapeutic interventions become increasingly challenging, leading to a deterioration in the prognosis. Current colorectal cancer research focuses on enhancing early detection methods, devising more efficacious treatment approaches, and improving patient outcomes. Scientists are currently pursuing enhancing the precision and nonintrusiveness of screening modalities for the timely identification of CRC. These efforts include exploring blood tests, stool-based testing, and imaging techniques [2]. Investigating genetic mutations and changes linked to CRC can facilitate the identification of individuals with an elevated susceptibility to the disease and enable the customization of treatment strategies. Precision medicine is a paradigm that entails customizing treatment strategies by considering the unique attributes of an individual patient’s tumor. The aforementioned process encompasses targeted treatments, immunotherapies, and various personalized therapy techniques. Artificial intelligence and machine learning methodologies are currently being utilized to analyze extensive collections of information about patients, medical images, and genomic data to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis, treatment planning, and prognostication of treatment outcomes. Immunotherapy has demonstrated encouraging results in treating several forms of cancer, such as CRC. Current research efforts are investigating the utilization of immunotherapeutic drugs in conjunction with other treatment modalities to enhance the results of individuals diagnosed with CRC. The progression of surgical methodologies, including laparoscopic and robotic-assisted procedures, has resulted in less invasiveness, accelerated recovery, and enhanced results among individuals diagnosed with CRC. The primary objective of the research is to improve the overall well-being of individuals who have survived colorectal cancer utilizing survivorship programs, provision of psychosocial support, and effective management of treatment-related adverse effects [3].
1.1 Background
A histology slide depicting human colorectal cancer reveals a delicate cross-section of colorectal tissue stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stains, which accentuate cellular structures. The slide showcases distinct tissue layers, encompassing the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria, and serosa. Notably, an irregular tumor mass dominates a portion of the tissue, its densely packed cells exhibiting varying sizes and shapes. Evident features of malignancy, such as enlarged nuclei, heightened nuclear staining (hyperchromasia), and conspicuous nucleoli, characterize these tumor cells. In addition, some cells infiltrate the surrounding tissue layers, signifying invasive colorectal cancer. The tumor’s microenvironment includes stromal tissue containing fibroblasts, immune cells, and an extracellular matrix, and blood vessels within the stroma suggest tumor’s capability to induce angiogenesis. Inflammatory responses and immune cell infiltration appear at the tumor’s edges, juxtaposed with adjacent normal colorectal tissue displaying well-structured crypt formations and characteristic cell types. This portrayal provides a general overview of the histological features that one might encounter in a human colorectal cancer histology slide, while recognizing that actual slides can vary depending on cancer stage, grade, and specific characteristics. Figure 1 presents working of histology slide of human colorectal cancer that typically consists of stained tissue sections under a microscope. The histology slide offers a complete visual representation of colorectal tissue, showcasing various layers that have been accentuated by applying hematoxylin and eosin staining. A tumor mass that exhibits uneven shape and is characterized by tightly packed cells of varying types indicates malignancy, suggesting cellular change. The presence of invasion into adjacent tissue layers indicates the presence of invasive colorectal cancer. The stromal tissue encompassing the tumor is composed of fibroblasts, immune cells, and discernible blood vessels, hence suggesting the presence of angiogenic capabilities. The presence of inflammatory regions and the infiltration of immune cells in the periphery of the tumor indicates the persistence of an immune response. The evaluation of tumor invasion can be effectively conducted by comparing it to adjacent normal colorectal tissue that exhibits well-organized crypt structures. The comprehensive histological examination described herein serves as a valuable tool for identifying cancer, facilitates the determination of its stage, and provides guidance for treatment strategies. Moreover, it underscores the significance of invasion, angiogenesis, and inflammation in comprehending the behavior of tumors and their potential to metastasize.

Typical human colorectal cancer histology slide 1.1 Background and Motivation.
CRC is a prominent contributor to mortality rates associated with cancer globally. Precisely evaluating prognostic factors is crucial to ascertain suitable therapeutic approaches and enhance patient outcomes. Historically, the prognosis of CRC has depended on the human interpretation of histological slides, a process characterized by time consumption, subjectivity, and susceptibility to variability among different observers. To overcome these constraints, there is an increasing inclination toward utilizing deep learning methodologies to automate the examination of histology images and forecast survival outcomes in patients with CRC. Deep learning has exhibited exceptional achievements in diverse domains, encompassing medical picture analysis [4]. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and other deep learning architectures have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in several tasks, including but not limited to image classification, segmentation, and object recognition [5]. These models can acquire and extract complex information from images autonomously, thereby possibly identifying nuanced patterns and irregularities that could impact cancer prognosis [6].
The block diagram in Figure 2 offers a concise visualization of the essential stages within the domain of human colorectal cancer histology. It systematically delineates the workflow from sample collection and preparation, encompassing tissue sample collection and fixation, to the subsequent histological slide preparation, involving tissue embedding, sectioning, and staining with H&E and specialized stains. The transformation of physical slides into digital format is illustrated through slide scanning and digital image storage blocks, leading to image preprocessing steps like enhancement and color normalization. Notably, feature extraction methods, including the detection of regions of interest and feature extraction itself, constitute pivotal aspects of the process. Deep learning techniques are harnessed for analysis, encompassing CNN layers and fully connected layers, culminating in predictions and risk assessments related to survival outcomes. Validation and interpretation phases comprise model validation and employ interpretability techniques. The clinical sphere is represented by blocks involving treatment planning and patient stratification, further highlighting the practical implications. The iterative nature of research and development is acknowledged through blocks for algorithm refinement and future study, eventually culminating in research findings and potential clinical impacts. While this representation is an abstraction, it effectively captures the fundamental stages of harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology.
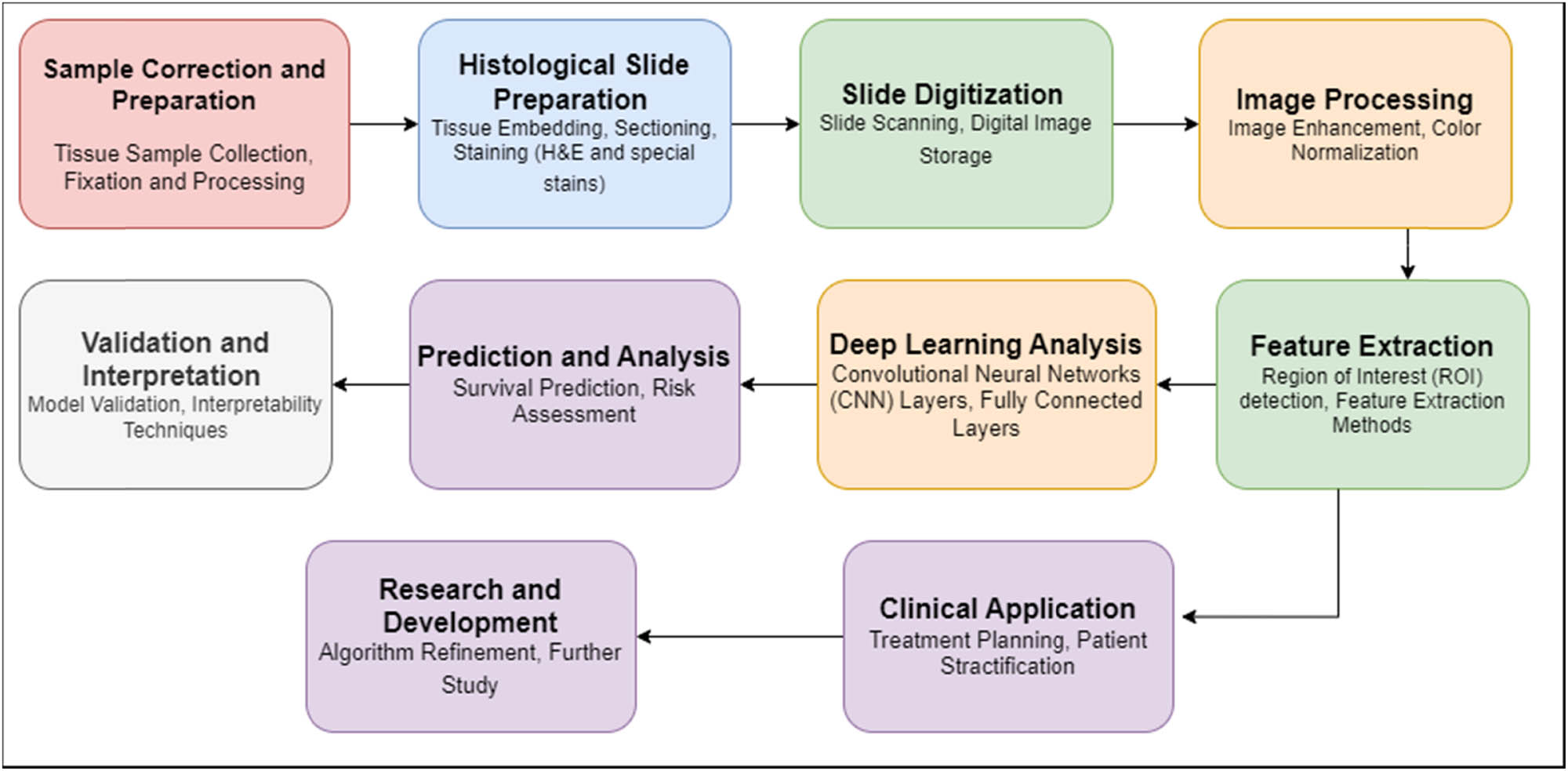
Block diagram of the essential stages within the domain of human colorectal cancer histology.
The impetus for this study arises from the necessity for precise and effective prognostic evaluation in CRC utilizing histopathology slides. Using deep learning techniques makes it feasible to create automated systems that aid pathologists in examining and interpreting histology slides. This advancement could enhance the accuracy and dependability of prognostic predictions by ensuring greater consistency in the analysis process. Ultimately, this can facilitate the process of determining treatment decisions and improve the quality of patient care. Extensive datasets comprising histological pictures of CRC and healthy tissue have facilitated the development of powerful deep-learning models through training. The availability of these datasets facilitates the investigation of various deep-learning systems and algorithms to determine the optimal technique for predicting survival in CRC. Significant knowledge can be obtained by comparing and analyzing the performance of different models, hence shedding light on the predictive capacities of deep learning techniques in CRC histopathology. This study aims to provide a scholarly contribution to the area by assessing the effectiveness of several deep learning models using a comprehensive retrospective multicenter dataset [7]. The results can enhance the domain of histology-based estimation of survival in CRC, facilitating more precise and effective prognostic evaluation. The primary objective is to improve patient outcomes, optimize treatment approaches, and offer practitioners a valuable resource for personalized medicine in CRC.
1.2 Problem statement
The prognostic evaluation of CRC is paramount in informing treatment strategies and enhancing patient outcomes. Manually interpreting histopathology slides, considered the most reliable method of predictive assessment, is characterized by its labor-intensive nature, subjectivity, and susceptibility to variations among different observers. Consequently, there exists a necessity for automated and dependable methodologies that can accurately forecast survival outcomes in CRC utilizing histology slides. Conventional machine learning methods have exhibited potential in this domain; nevertheless, they frequently depend on manually designed features and may not comprehensively capture the intricate and nuanced patterns inherent in histology pictures. In contrast, deep learning methodologies have exhibited exceptional aptitude in image analysis endeavors, encompassing the classification and segmentation of medical images. By utilizing deep learning techniques, it becomes feasible to construct precise and effective models capable of autonomously acquiring and extracting pertinent characteristics from histology slides to forecast survival outcomes. Multiple obstacles must be confronted when considering using deep learning algorithms for predictive forecasting of survival in the histology of human colorectal cancer.
It is imperative to acquire extensive and heterogeneous datasets comprising histological pictures that include a wide range of tissue types and disease states. This is essential to ensure the effectiveness of model training and its ability to generalize accurately. Furthermore, carefully selecting and optimizing deep learning architecture appropriate for predicting CRC survival is paramount for optimal performance. Moreover, it is imperative to investigate the comprehension of deep learning algorithms within histopathological research to understand the characteristics and trends that play a role in predicting survival outcomes. Hence, the primary focus of this study revolves around the appropriate utilization of deep learning methodologies for prognostic survival prediction in the context of human colorectal cancer histology. This study aims to examine and assess various deep learning models utilizing a substantial retrospective multicenter dataset comprising histology pictures. The primary objective of this work is to offer valuable insights into the comprehension of the models employed and investigate the fundamental elements and patterns that contribute to the accurate prediction of survival outcomes. The primary objective of this study is to solve the preceding to establish a connection between survival prediction based on histology and deep learning techniques. The final goal is to develop a beneficial tool that can enhance prognostic assessment in CRC and facilitate the implementation of personalized treatment plans.
1.3 Objectives
The primary objective of this research is to establish a connection between survival prediction based on histology and deep learning techniques. This study seeks to make significant advancements in the area, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and better knowledge about the treatment of CRC. The objective of this study is to investigate and evaluate the efficacy of several deep learning models, such as CNN, VGG16, VGG19, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, and Xception, in predicting predictive survival outcomes in human colorectal cancer histology. This study aims to determine the optimal deep-learning models for correctly predicting survival outcomes using histology pictures. The study employs an extensive dataset of 100,000 distinct picture patches derived from histological images of human colorectal cancer and normal tissue stained with H&E. The aim is to utilize the given dataset to train and assess the deep learning models, guaranteeing strong performance and generalizability. This study aims to evaluate the efficacy of deep learning models by employing diverse metrics, including precision, recall, accuracy, and loss. This study aims to assess the quantitative effectiveness of the models for foreseeing survival outcomes and to compare their respective performances. This study aims to investigate the interpretability and visualization of deep learning models within the specific domain of colorectal cancer histology. This study seeks to understand the characteristics and trends that predict survival, improving our comprehension of the fundamental elements that impact prognosis. The primary aim of this study is to provide a valuable contribution toward enhancing prognostic evaluation in the context of human colorectal cancer. This study aims to utilize deep learning methodologies to create automated systems that can aid pathologists in the analysis and interpretation of histology slides. The primary aim is to offer precise and effective prognostic forecasts by examining histopathology data, facilitating clinical decision-making and the development of individualized treatment approaches.
1.4 Contribution of the research
The study offers substantial advancements in the area of histology-based prognostication of survival in colorectal cancer through the use of deep learning methodologies. It encompasses assessing various models, employing a dataset from multiple medical centers, investigating interpretability, and furnishing valuable insights for aiding clinical decision-making. The preceding contributions enhance the comprehension and implementation of deep learning techniques in prognostic evaluation, ultimately yielding advantages for patients and physicians in combating colorectal cancer.
Comparative analysis of deep learning architectures: To predict predictive survival in colorectal cancer histology, this study undertook a thorough comparison investigation of different deep learning architectures, namely, DenseNet201, CNN, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception. This study facilitates the identification of the most productive models for this activity.
Visualization and interpretation techniques: The study included visualization and interpretation tools, such as activation maps, feature visualization, and attention mechanisms, to augment the comprehension of the decision-making process of deep learning models. These methodologies offer valuable perspectives on the prominent characteristics and areas that impact prognostications of survival.
Practical applications in personalized medicine: The deep learning models that have been constructed possess practical applications within the field of personalized healthcare since they demonstrate the ability to forecast survival outcomes for specific patients with colorectal cancer reliably. This can assist healthcare professionals in customizing treatment strategies and enhancing the quality of patient care.
Foundation for future research: The present research establishes a fundamental basis for future investigations about prognostic survival prediction in colorectal cancer histology. The models, dataset, and preprocessing approaches that have been based on this study can be utilized by fellow researchers to extend the scope of this research, explore novel research inquiries, and construct sophisticated models and methodologies.
1.5 Organization of the article
This article is structured into six distinct sections. Section 1 offers crucial contextual information, encompassing the historical background, underlying motivation, and problem statement. In addition, it outlines the research objectives and emphasizes the substantial contribution that can be made by utilizing deep learning methods for prognostic survival prediction in the histology of human colorectal cancer. Section 2 provides an extensive examination of pertinent literature, including the prognostication of colorectal cancer, histological analysis, and the use of deep learning in processing medical images. A concise overview of prior research on survival prediction based on histology is presented. Section 3 presents a comprehensive account of the methodology, encompassing the elucidation of the dataset employed, the preprocessing procedures undertaken, the management of class imbalance, and an overview of the diverse deep learning architectures employed in the study, including the CNN, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception. The experimental results of the study are described in Section 4, encompassing the performance metrics and assessment criteria employed to demonstrate and analyze the consequences of various topologies. Following this, Section 5 delves into a comprehensive discourse, examining the implications of the findings, recognizing constraints, and proposing prospective avenues for further research. Section 6 provides a summary of the scientific contributions and practical applications, particularly emphasizing the clinical implications of the study’s findings.
2 Related work
Numerous prior studies have been undertaken, which relate to investigating prediction of survival in colorectal cancer by deep learning techniques based on histology. Numerous previous experiments have been conducted to explore the predictive value of histology-based prediction of survival in diverse cancer types, including colorectal cancer. This research has investigated the utilization of various methodologies, encompassing conventional machine learning algorithms and deep learning techniques. The studies mentioned earlier exhibit an increasing inclination toward employing deep learning and intelligent technology methodologies to predict survival rates in colorectal cancer, using histology slides as the primary data source. The researchers offered significant contributions by presenting valuable perspectives on the approach, performance, and issues of deep learning-based approaches within this domain. The study conducted more exploration into deep learning models, employing a substantial dataset and offering novel contributions to the part of histology-based prognostication in colorectal cancer. The subject of medical imaging analysis has witnessed considerable interest in applying deep learning techniques. Numerous prior studies have examined using deep learning methodologies in diverse medical imaging endeavors.
In their study, Wang et al. successfully devised and verified a deep-learning algorithm to identify polyps during colonoscopy. Their findings highlight the promising role of machine learning in enhancing the precision of early diagnosis of colorectal cancer [8]. The study conducted by Sun et al. investigated the impact of TRIM29 on the inhibition of cancer stem cell-like properties in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas, providing valuable insights into future therapeutic strategies for this very aggressive form of cancer [9]. The study by Ren et al. examined the phenomenon of keratin 23 overexpression and its impact on facilitating the migration of ovarian cancer cells via the epithelial–mesenchymal transition process [10]. In their study, Pan et al. examined the significance of utilizing AGR2 and KRT5 as immunomarker pairings in differentiating squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs from other subtypes of lung cancer [11]. Dwyer Nield et al. conducted a study investigating the possible role of PPARγ agonism in impeding the advancement of premalignant lesions in a mouse squamous cell carcinoma of the lung model. Their findings provide valuable insights into future therapeutic approaches [12]. Huang et al. examined the involvement of TRIM group proteins in carcinogenesis, cancer formation, and treatment resistance, underscoring the significance of these amino acids in cancer biology [13]. Han et al. aimed to examine the transcriptional dysregulation of TRIM29 and its role in the development of colorectal cancer by affecting pyruvate kinase-mediated glucose metabolism [14]. Qiao et al. investigated the regulatory function of TRIM29 in the advancement of ovarian cancer, specifically focusing on its impact on the SETBP1/SET/PP2A axis. Their study yielded valuable insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms associated with this process [15]. The study by Hao et al. examined the impact of TRIM29 on the bioenergetics of cancer cells in the pancreas using miRNA and DDX3X recruitment. The findings shed light on the potential involvement of TRIM29 in the progression of pancreatic cancer [16]. The study conducted by Ray and Mukherjee provides a complete overview of the roles played by TRIM protein in breast cancer, focusing specifically on their altered expression and oncogenic effects in this disease [17].
The study conducted by Lei et al. investigated the ability of TRIM29 to counteract oxaliplatin tolerance in cells with colon cancer, hence offering novel approaches to address drug resistance [5]. Cockram et al. provided a comprehensive analysis of the involvement of ubiquitination in regulating inflammation-induced cell death and its implications in cancer. The research shed valuable insights into the complex molecular mechanisms behind these processes [18]. Razzaghdoust et al. explored the correlation between immunohistochemical markers and the response to chemotherapy with neoadjuvant therapy and overall survival in individuals with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. The authors underscored the significance of tailored treatment strategies in this context [19]. Chehade et al. conducted a study to investigate the application of medical imaging, explicitly employing a feature engineering method, to classify lung and colon cancer. The study emphasized the potential of imaging techniques in the field of diagnostics [20]. Kather et al. have published a dataset comprising histological pictures of both human colorectal cancer and normal tissue. This dataset is an excellent resource for researchers developing machine-learning systems for diagnosing colorectal cancer [21]. Tamang and Kim conducted a comprehensive examination of deep learning methodologies utilized in the context of colorectal cancer diagnosis. The authors thoroughly analyzed the diverse methods and algorithms employed within this domain [22]. Davri et al. conducted a comprehensive analysis centered on using deep learning techniques to examine histopathological pictures to diagnose colorectal cancer. Their study provided a concise overview of the latest developments in this field [23]. Islam et al. investigated the possible applications of natural products for preventing and treating colon and colorectal cancer. Their study highlighted the significance of adopting a comprehensive approach to managing cancer [24]. Collins et al. examined the application of machine learning and hyperspectral imaging for automated colon and esophagogastric cancer identification. The authors emphasized the promising prospects of employing modern imaging methodologies in cancer detection [25]. Sakr et al. introduced a highly effective deep-learning methodology for identifying colon cancer, thereby significantly contributing to advancing diagnostic tools based on artificial intelligence [26]. Alsanea et al. offered valuable insights into the occurrence, longevity, and demographic characteristics of colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia. The findings underscore the necessity of developing customized national cancer care strategies that consider various locations’ unique needs and circumstances [27].
These earlier works provide valuable insights into the histopathological factors that influence prognosis and patient outcomes in colorectal cancer. They highlight the significance of various factors in predicting lymph node involvement, microsatellite instability, and overall survival. The research in the field of colorectal cancer prognosis and histopathological analysis builds upon these studies to develop advanced techniques, such as deep learning, for accurate and automated prognostic assessment. These earlier works demonstrate the wide-ranging applications of deep learning in medical image analysis. They highlight the potential of deep learning models, particularly CNNs, in various imaging tasks, including classification, segmentation, and detection. The research in this field continues to explore and refine deep learning techniques to improve accuracy, efficiency, and clinical utility in medical image analysis.
The present state of colorectal cancer diagnosis and histological analysis reveals various areas where further research is needed. The existing body of literature heavily depends on datasets that are constrained in scope, highlighting the need to get more extensive and diversified datasets that span a more comprehensive range of cancer stages, tissue types, and demographic variables. Integrating multi-omics data and conducting thorough clinical validation in real-world situations is crucial for augmenting the comprehensiveness and applicability of artificial intelligence models. The issues of interoperability with electronic health records, explainability of AI predictions, and resolving imbalanced datasets, especially in rare events, continue to be of utmost importance. Using real-time processing in endoscopy and integrating clinical and histopathological data presents exciting opportunities for enhancing clinical practice. Furthermore, examining ethical and regulatory factors thoroughly while implementing artificial intelligence to guarantee responsible and secure deployment within the healthcare sector is imperative. Resolving these deficiencies will propel the discipline forward, yielding advantages for healthcare practitioners and individuals seeking medical treatment.
3 Methodology
This section provides an overview of the steps followed in the research to address the research objectives. It describes the data acquisition, preprocessing, deep learning model selection and training, performance evaluation, and interpretability analysis. The methodology serves as a roadmap for conducting the study and forms the foundation for the subsequent analysis and discussion.
As shown in Figure 3, the research embodies an extensive and multifaceted inquiry into the utilization of cutting-edge deep learning methodologies to prognosticate survival outcomes among individuals afflicted by colorectal cancer. The research framework is intricately structured to encompass a comprehensive trajectory, commencing with a foundational introduction that establishes the gravity of colorectal cancer within the medical landscape and underscores the pivotal role of prognostic survival prediction in tailoring personalized therapeutic interventions. Central to the research is the nuanced exploration of histology slides, elucidating their integral contribution to the diagnosis and prognostic stratification of cancer cases. This journey extends into a comprehensive literature review, encompassing a meticulous assessment of prevailing methodologies while underscoring the transformative potential of deep learning paradigms in the realm of medical image analysis and survival prognosis. The crux of the research endeavor unfolds through meticulous data collection and preprocessing, where the acquisition and meticulous curation of CRC histology slides form the bedrock upon which subsequent analysis is constructed [28]. The underpinning deep learning architecture emerges as a pivotal element, entailing a detailed exposition of chosen models and components, including the intricate mechanics of CNNs and attention mechanisms, which imbue the research with predictive potency. The intricate process of feature extraction and representation is navigated, traversing the complex terrain of translating histological intricacies into informative inputs for the model. Critical to the research progression is the iterative cycle of model training and validation, elucidating strategies employed to enhance performance and robustly assess the veracity of predictions. Subsequent stages delve into the application of trained models for survival prognostication, accompanied by insightful exploration into their interpretability, bridging computational predictions with the nuances of clinical decision-making [29]. Ultimately, the research culminates in a comprehensive discussion segment that interweaves empirical findings with their far-reaching clinical implications. This discourse poignantly accentuates the potential paradigm-shifting impact of the proposed approach on patient-centric care and treatment modalities. In essence, this research venture traverses uncharted territories at the intersection of deep learning prowess and colorectal cancer histology, poised to unravel insights that hold the potential to reshape the landscape of prognostic survival prediction, engendering a transformative shift in our understanding and management of this complex malignancy.

Overview of the steps followed in the research to address the research objectives.
The overarching framework for research into the prognostication of survival in colorectal cancer using deep learning may be delineated as follows:
Data acquisition and collection: The data are acquired from reliable sources, including the NCT Biobank and UMM pathology archive. The collection comprises formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples about colorectal cancer, encompassing initial tumor slides, liver metastases, and nontumorous regions. Comprehensively portraying histological pictures, including a varied range of tissues and disease states, is imperative.
Data preprocessing and augmentation: The histological pictures gathered undergo several preprocessing procedures. These procedures involve color normalization, scaling the images to a standardized size (224 × 224 pixels), cleaning the data to eliminate extraneous artifacts, and using image-enhancing techniques, including contrast modification and noise reduction. Data augmentation strategies are utilized to enhance the diversity of a dataset. These techniques include random rotation, flipping, scaling, cropping, adjusting brightness and contrast, and applying elastic transformations.
Class imbalance handling: Various techniques are utilized to mitigate the issue of class imbalance. Oversampling techniques aim to enhance the presence of underrepresented minority classes within a dataset. Undersampling courses aim to decrease the representation of the majority class. During the training of a model, the technique of class weighting assigns greater significance to the minority classes. Hybrid methodologies have the potential to integrate oversampling and undersampling approaches.
Deep learning model selection: Different deep learning algorithms are selected depending on their efficacy in tasks related to the processing of images. CNNs are a class of deep learning models widely used in computer vision tasks. Some popular CNN architectures include DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception. These architectures have been developed and optimized for various image classification and recognition tasks. These models possess unique architectural attributes and advantages.
Model training and validation: The dataset is partitioned into two subsets: the training and validation sets. Data preparation is crucial in data analysis since it involves applying several techniques to standardize and improve the dataset. The deep learning model that has been chosen is initialized, and the hyperparameters are adjusted. The training process consists of several epochs, wherein the model iteratively reduces the loss function. The model’s performance is evaluated periodically on the validation set, which serves as a basis for making necessary improvements to the model.
Performance evaluation: Various performance metrics are calculated to evaluate a model’s performance, including accuracy, recall, F1 score, precision, AUC-ROC, and loss. The findings are displayed in the tabular format and visually represented through graphical charts. These criteria facilitate the assessment of the efficacy of various models in predicting survival results.
3.1 Data collection and acquisition
The data collection and acquisition process in the research involved obtaining a large retrospective multicenter dataset of histological images from reputable sources. The researchers identified reputable sources from which to collect the histological images. In this case, the dataset was sourced from the NCT Biobank (National Center for Tumor Diseases, Heidelberg, Germany) and the UMM pathology archive (University Medical Center Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany). These biobanks and archives are known for their collection and storage of FFPE tissue samples for research purposes [21]. The researchers identified the specific tissue samples to be included in the dataset. The samples were selected based on their relevance to colorectal cancer, including CRC primary tumor slides, tumor tissue from CRC liver metastases, and nontumorous regions from gastrectomy specimens. This selection aimed to ensure a diverse representation of histological images encompassing different tissue types and disease states. The selected tissue samples were manually processed to extract histological images. This likely involved retrieving the FFPE tissue blocks and sectioning them to obtain thin slices suitable for histological analysis. The slides were then stained using H&E staining, a commonly used staining method that highlights cellular structures and facilitates histopathological examination. The histological slides were digitized to convert them into high-resolution digital images. Digital scanning systems or whole-slide imaging scanners were used to capture the images, preserving the fine details and cellular morphology present in the original slides. This digitization process allowed for easy storage, sharing, and analysis of the histological images. From the digitized histological images, a dataset was created by extracting nonoverlapping image patches. These patches were likely selected based on predefined criteria, such as size (224 × 224 pixels) and representation of different tissue classes (e.g., adipose, debris, lymphocytes, normal colon mucosa). The dataset was carefully curated to ensure it captured the necessary variability and provided an adequate representation of the histological characteristics of colorectal cancer and healthy tissue.
3.2 Data preprocessing and augmentation
Data preprocessing and augmentation are crucial steps in preparing the dataset for analysis and improving the performance and generalization of deep learning models. Color normalization is often performed to address staining variations across histological images. It ensures consistent color representation by removing the effects of staining inconsistencies. One commonly used method is Macenko’s method, which normalizes the color distribution across the images. Rescaling the images to a uniform size is necessary to ensure compatibility and efficient processing. In the case of the research, the histological images were likely rescaled to a standardized size, such as 224 × 224 pixels, which is a common input size for deep learning models. Data cleaning involves removing any irrelevant or noisy artifacts from the images. It may include removing image borders, text, or other artifacts that do not contribute to the analysis or may introduce biases. Image enhancement techniques can be applied to improve image quality and highlight relevant features. This may involve contrast adjustment, noise reduction, or sharpening to enhance the visibility of structures and patterns in the histological images. Data augmentation techniques are employed to increase the diversity and variability of the dataset, which helps improve the model’s ability to generalize and handle different variations in the input data. The images can be randomly rotated by a certain degree to introduce variations in orientation. This helps the model become invariant to the rotation of the histological features. Horizontal or vertical flipping of the images can be performed to introduce mirror images. This allows the model to learn from different perspectives and helps improve robustness. Images can be scaled to different sizes or randomly cropped to extract smaller regions of interest. This introduces variability in the image size and focus, enabling the model to learn from different spatial contexts. Modifying the brightness and contrast of the images can be used to simulate different lighting conditions. This augments the dataset with variations in illumination, making the model more robust to lighting differences. Elastic transformations deform the images nonrigidly, mimicking tissue distortions or morphological variations. This technique can capture tissue deformation patterns and improve the model’s ability to handle variations in tissue structure. Adding random noise to the images can help the model learn to be more robust to noise or artifacts present in real-world data. By performing data preprocessing and augmentation, the research aims to standardize the data, enhance image quality, increase dataset diversity, and improve the model’s ability to generalize and make accurate predictions. These steps are crucial for achieving reliable and robust performance in histology-based survival prediction using deep learning [29].
3.3 Class imbalance handling
Class imbalance handling is an essential step in addressing the disproportionate distribution of samples across different classes in a dataset. Class imbalance occurs when the number of instances in one class significantly outweighs the number of instances in another class. In the context of histology-based survival prediction research, class imbalance handling techniques are employed to mitigate the potential bias introduced by imbalanced class distributions. Oversampling techniques aim to increase the representation of minority classes by generating synthetic samples. This can be achieved through methods such as random duplication or by using more advanced techniques like synthetic minority oversampling technique, which synthesizes new samples by interpolating between existing instances of the minority class. Undersampling techniques involve reducing the number of instances in the majority class to achieve a more balanced distribution. Random undersampling randomly removes instances from the majority class until a desired balance is reached. However, undersampling can result in the loss of potentially useful information from the majority class.
Class weighting assigns different weights to different classes during model training to give higher importance to the minority class. This allows the model to focus more on correctly classifying the minority class instances, effectively reducing the impact of class imbalance. The weights can be used during loss calculation, where the contribution of each class to the overall loss is weighted based on its imbalance ratio. Hybrid approaches combine oversampling and undersampling techniques to address class imbalance. These methods aim to strike a balance between increasing the representation of minority classes while maintaining a manageable dataset size. For example, researchers may oversample the minority class and then apply undersampling to the majority class to achieve a more balanced dataset. The choice of class imbalance handling technique depends on several factors, including the severity of class imbalance, the size of the dataset, and the specific requirements of the research. It is crucial to carefully select and evaluate the appropriate technique to prevent overfitting, information loss, or the introduction of new biases. The class imbalance handling should be performed during the training phase and not during the evaluation or testing phase to ensure fair and unbiased performance evaluation. The goal is to provide the model with a balanced representation of different classes, allowing it to learn from all classes equally and make accurate predictions for all classes, including the minority class.
3.4 Deep learning models
The deep learning models were chosen for their effectiveness in image analysis tasks, including histopathological analysis. Each model has its own architectural characteristics and strengths, making them suitable for different types of data and research objectives. By using a combination of these models, the research aimed to explore their performance and identify the most effective model for prognostic survival prediction in colorectal cancer histology.
CNN is a widely used deep learning architecture for image analysis tasks. It consists of multiple convolutional layers followed by pooling layers and fully connected layers. CNNs are known for their ability to extract hierarchical features from images and have been successfully applied to various computer vision tasks. DenseNet is a type of CNN architecture that introduces direct connections between layers, allowing for more efficient information flow and gradient propagation. DenseNet201 is a specific variant of DenseNet with 201 layers. It has shown strong performance in image classification and has been widely used in medical image analysis tasks. InceptionResNetV2 is a deep learning architecture that combines the Inception module and residual connections. It uses multiple parallel convolutional layers of different sizes to capture various scales of image features. InceptionResNetV2 has demonstrated excellent performance in image recognition tasks and is known for its high accuracy. Visual geometry group (VGG) models are deep CNNs with either 16 or 19 layers. They have a simple and uniform architecture, with small convolutional filters and max pooling layers. VGG models are known for their excellent performance on image classification tasks and have been widely used as benchmark models. Xception is a deep learning model inspired by the Inception architecture. It employs depthwise separable convolutions, which separate spatial and channel-wise convolutions, reducing computational complexity while maintaining performance. Xception has shown strong performance on image classification tasks and offers a good balance between accuracy and efficiency [21].
3.5 Training and validation procedures
The training and validation procedures are crucial steps in the research process for training and evaluating deep learning models for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology. A training set is created by randomly selecting a portion of the available dataset. The training set consists of histological images of colorectal cancer and corresponding labels or annotations indicating the survival outcomes. The size of the training set may vary depending on the dataset and the complexity of the task [22]. A validation set is created by partitioning a portion of the dataset separate from the training set. The validation set is used to monitor the model’s performance during training and make decisions regarding hyperparameter tuning, model selection, and potential overfitting. The validation set should be representative of the underlying distribution of the data and include samples from all classes. Before training, the histological images undergo preprocessing steps to standardize and enhance the data. This may include resizing the images to a consistent resolution, normalizing pixel values, applying data augmentation techniques to increase dataset diversity, and potentially handling class imbalance if present. The chosen deep learning model (e.g., CNN, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, Xception) is initialized with appropriate weights [23]. Depending on the availability of pretrained models, the weights can be initialized with random values or transferred from pretrained models trained on large-scale datasets (e.g., ImageNet) to leverage learned features from learning models and optimizing its parameters. The model is trained using gradient-based optimization algorithms such as stochastic gradient descent or Adam. The loss function, which measures the discrepancy between predicted and actual survival outcomes, is minimized during training. The training process typically consists of multiple iterations called epochs, where the entire training set is processed by the model. Hyperparameters, such as learning rate, batch size, regularization techniques, and optimizer parameters, may significantly impact the model’s performance. These hyperparameters are tuned during the training process, often using techniques like grid search, random search, or more advanced optimization algorithms, to find the optimal combination of hyperparameters that yields the best performance on the validation set. Throughout the training process, the model’s performance is periodically evaluated using the validation set. Various evaluation metrics, such as accuracy, precision, recall, and loss, are computed to assess the model’s performance and identify potential overfitting or underfitting issues. The model’s performance on the validation set helps in guiding the model selection process and determining when to stop training. Based on the validation set performance, adjustments can be made to the model architecture, hyperparameters, or preprocessing techniques to improve the model’s performance further. This iterative refinement process involves repeating the training, validation, and evaluation steps until a satisfactory model is obtained [24]. Table 1 presents a tabular representation outlining the proof of concept (PoC) about the utilization of deep learning techniques for predicting survival outcomes in colorectal cancer histology.
PoC about the utilization of DL for predicting survival outcomes in CRC histology
| PoC Scenario | Description | Functioning | Operation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retrospective clinical data | Collected historical clinical data, including histological images and survival outcomes | Applied the deep learning framework to this dataset | Analyzed the model’s predictions vs actual outcomes | Demonstrated the framework’s ability to accurately predict survival outcomes using historical patient data |
| Prospective clinical trial | Collaborated with a clinical trial, integrated framework, predicted patient survival outcomes as they enrolled | Integrated deep learning into the trial’s workflow | Monitored the framework’s impact on treatment decisions | Assessed whether the framework informed personalized treatment plans during a real clinical trial, potentially improving patient survival |
| Multicenter data validation | Gathered histological data from multiple healthcare centers | Applied the deep learning framework to this multi-center data | Evaluated performance across diverse centers | Validated the framework’s robustness and generalizability in real-world healthcare settings with varying data characteristics |
| Clinical decision support | Integrated your framework as clinical decision support | Clinicians used framework predictions for patient care | Monitored alignment with clinical decisions | Evaluated the framework’s value in assisting clinicians to provide personalized treatment plans, potentially improving patient outcomes |
| Patient outcomes monitoring | Implemented your framework for monitoring survivor outcomes | Predicted long-term survival based on follow-up histological assessments | Continuously tracked patient outcomes | Assessed the framework’s ability to provide accurate long-term survival predictions, aiding in the development of effective survivorship care plans |
| Telemedicine and remote consultation | Deployed framework for remote consultations in underserved areas | Patients submitted histological images for analysis | Monitored patient outcomes and assessed the framework’s impact | Determined if the framework enhanced healthcare access and improved patient outcomes in remote or resource-limited settings |
4 Experimental results
The performance metrics and evaluation criteria enable the assessment of the deep learning models’ predictive capabilities and the comparison of different models’ performance. Researchers often analyze and report these metrics to demonstrate the effectiveness of their proposed models and to evaluate their suitability for prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. Accuracy measures the proportion of correctly predicted survival outcomes compared to the total number of predictions. It provides an overall assessment of the model’s correctness in predicting survival. Precision calculates the proportion of true positive predictions (correctly predicted positive outcomes) to the total number of positive predictions (both true positives and false positives). It indicates the model’s ability to correctly identify positive cases. Recall, also known as sensitivity or true positive rate, measures the proportion of true positive predictions to the total number of actual positive cases. It evaluates the model’s ability to capture all positive cases. The F1 score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. It provides a balanced measure of the model’s precision and recall performance, considering both false positives and false negatives. AUC-ROC evaluates the model’s performance in binary classification tasks by measuring the trade-off between true positive rate (sensitivity) and false positive rate. It provides a single value that summarizes the model’s discriminatory power across different classification thresholds. The loss function represents the discrepancy between the predicted survival outcomes and the actual survival outcomes. Different loss functions can be used based on the specific task, such as binary cross-entropy loss or mean squared error loss. The validation loss measures the performance of the model on the validation set. It provides an indication of the model’s generalization capability and helps identify potential overfitting or underfitting issues.
The performance measures of different DL architectures in the research demonstrate significant results. DenseNet201 and Xception have been identified as the leading models, with outstanding accuracy of 99.95%, highlighting their predictive skills. The DenseNet201 model achieved a precision value of 100%, indicating its high accuracy in properly recognizing positive cases. Similarly, the InceptionResNetV2 and Xception models reached almost 100% precision levels, further highlighting their skill in accurately detecting positive situations. The high recall values, notably the 99.925% achieved by Xception, demonstrate its ability to identify a significant portion of true positives effectively. Although CNN and VGG19 models had marginally poorer outcomes in specific criteria, they exhibited outstanding performance. DenseNet201 and Xception demonstrated exceptional performance in terms of validation accuracy, hence emphasizing their considerable potential for clinical applications. The results in Table 2 indicate the efficacy of deep learning models in prognostic survival prediction for CRC histology.
Results of Normal Result DNN
| CNN | DenseNet201 | InceptionResNetV2 | VGG16 | VGG19 | Xception | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 70.525 | 99.95 | 99.85 | 99.8 | 99.225 | 99.95 |
| Validation accuracy | 70.6 | 94.8 | 92.8 | 93.8 | 90.8 | 95.4 |
| Precision | 75.11835 | 100 | 99.8998 | 99.79995 | 99.34853 | 99.94999 |
| Validation precision | 100 | 95.15151 | 93.34677 | 93.95161 | 91.27789 | 95.55556 |
| Recall | 63.725 | 99.875 | 99.7 | 99.775 | 99.125 | 99.925 |
| Validation recall | 63.6 | 94.6 | 92.6 | 93.2 | 90 | 94.6 |
| Loss | 0.696141 | 0.098516 | 0.111037 | 0.112601 | 0.151397 | 0.090078 |
| Validation loss | 0.729109 | 0.283531 | 0.386633 | 0.377719 | 0.485996 | 0.285021 |
As shown in Figure 4 and per the results of Table 2, Normal Result DNN showed that the accuracy of the model was approximately 70.53%, indicating that around 70.53% of the survival outcomes in the normal dataset was correctly predicted by the DNN. The precision value of 75.12% suggested that the DNN had a relatively high ability to correctly identify positive cases within the normal dataset. The recall value of 63.73% indicated that the model captured about 63.73% of the actual positive cases present in the normal dataset. The loss value of 0.696 reflected the discrepancy between the predicted survival outcomes and the actual outcomes, with a lower value indicating better performance. Overall, the Normal Result DNN demonstrated moderate performance in predicting survival outcomes for the noncancerous (normal) tissue, with room for improvement in terms of accuracy and recall. Further analysis and fine-tuning of the model may be necessary to enhance its performance. Table 3 presents results of federated learning (FL).

Plots for benchmark DNN.
Results of FL
| Training/validation | Data | Accuracy | Loss | Precision | Recall | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Training | IID | 99.97 | 0.07 | 99.97 | 99.92 |
| 1 | Training | Non-IID | 100 | 0.08 | 100 | 99.95 |
| 0 | Validation | IID | 93.02 | 0.38 | 92.62 | 93.28 |
| 1 | Validation | Non-IID | 94.34 | 0.29 | 94.2 | 94.72 |
The FL Results for Server & Client IID Evaluation and IID Training shown in Figure 5 and Table 3 data presents the performance metrics of the FL approach used in the research article. The results are divided into training and validation subsets, further categorized into IID (independent and identically distributed) and non-IID (non-independent and non-identically distributed) data. Here is a detailed analysis of the FL results. For training, IID data, FL model achieved an accuracy of 99.97% on the training data with IID distribution, indicating that it accurately predicted survival outcomes for the training samples. The loss value of 0.07 indicated a relatively low discrepancy between the predicted outcomes and the actual outcomes, implying good model performance. The precision value of 99.97% reflected the model’s ability to correctly identify positive cases within the training data. The recall value of 99.92% demonstrated the model’s capacity to capture most actual positive cases in the training data.

Plot for Server & Client IID Evaluation and IID training: (a) communication round wise server evaluation and (b) epoch wise client training.
In Figure 6, for non-IID data, the FL model achieved a perfect accuracy of 100% on the training data with non-IID distribution, indicating flawless predictions of survival outcomes for the training samples. The low loss value of 0.08 indicated a minimal discrepancy between predicted and actual outcomes in the training data. The model achieved a perfect precision of 100%, correctly identifying all positive cases within the training data with non-IID distribution. The recall value of 99.95% indicated the model’s high ability to capture a large proportion of actual positive cases in the training data. For validation of IID data, the FL model achieved an accuracy of 93.02% on the IID validation data, indicating reasonably accurate predictions of survival outcomes. The loss value of 0.38 indicated a moderate discrepancy between predicted and actual outcomes in the IID validation data. The precision value of 92.62% reflected the model’s ability to correctly identify positive cases within the IID validation data. The recall value of 93.28% demonstrated the model’s capacity to capture a significant proportion of actual positive cases in the IID validation data. For non-IID data, the FL model achieved an accuracy of 94.34% on the non-IID validation data, indicating good predictive performance on this subset. The loss value of 0.29 suggested a relatively low discrepancy between predicted and actual outcomes in the non-IID validation data. The precision value of 94.20% indicated the model’s ability to correctly identify positive cases within the non-IID validation data. The recall value of 94.72% demonstrated the model’s capacity to capture a substantial proportion of actual positive cases in the non-IID validation data.

Plot for Server & Client NIID Evaluation and NIID training: (a) communication round wise server evaluation and (b) epoch wise client training.
The FL approach demonstrated strong performance in predicting survival outcomes in both the training and validation datasets. The model achieved high accuracy, low loss, and impressive precision and recall values across both IID and non-IID data subsets. These results indicate the effectiveness of the FL method in capturing patterns and making accurate predictions while accounting for the distributed and heterogeneous nature of the data.
5 Discussion
The research article compared and analyzed several deep learning architectures, including CNN, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception, for their performance in prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology. The accuracy metric measures the overall correctness of the models in predicting survival outcomes. DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, and Xception achieved high accuracy values, ranging from 99.85 to 99.95%, indicating their strong predictive capabilities. CNN and VGG19 obtained slightly lower accuracy values but still demonstrated respectable performance. Precision measures the proportion of correctly identified positive cases, while recall evaluates the ability to capture all positive cases. DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, and Xception consistently achieved high precision and recall values, suggesting their effectiveness in identifying and capturing positive cases. CNN and VGG19 also demonstrated reasonable precision and recall values, although slightly lower than the other architectures. The loss metric quantifies the discrepancy between predicted and actual survival outcomes. DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, and Xception exhibited lower loss values, indicating better alignment between predicted and actual outcomes. CNN, VGG16, and VGG19 achieved relatively higher loss values, suggesting a larger discrepancy. When considering validation accuracy, precision, recall, and loss, DenseNet201 and Xception consistently performed well across the different architectures. These models achieved high validation accuracy, precision, and recall, indicating their ability to generalize well to unseen data. VGG16 and InceptionResNetV2 also exhibited respectable performance on the validation set, while CNN and VGG19 showed comparatively lower validation metrics. DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, and Xception stood out as the top-performing architectures in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and validation metrics. These models demonstrated strong predictive capabilities and generalization to unseen data. CNN and VGG19, while achieving relatively lower metrics, still showed reasonable performance. The comparison and analysis of these architectures provide insights into their suitability for prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology and help researchers select the most effective models for similar tasks.
The proposed framework of the research article addresses significant deficiencies in the current body of literature by undertaking a thorough comparative analysis of diverse deep learning architectures, namely, CNN, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception, with the aim of prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. This study aims to fill a notable void in the existing literature, as prior research must frequently incorporate comprehensive and methodical architectural comparisons. The system effectively integrates training and validation measures, improving the evaluation of real-world applicability, a factor commonly neglected in clinical prediction tasks. Moreover, the research publication enhances transparency and reproducibility by providing comprehensive details regarding architecture, hyperparameters, and metrics. This contribution facilitates the replication and further development of this study into the broader research community. Compared to existing methodologies, the framework distinguishes itself by its comprehensive examination of architectural possibilities, emphasis on validation and generalization, and multifaceted evaluation approach, which collectively offer a thorough assessment of model performance.
6 Conclusion
The research has made several significant contributions to the field of prognostic survival prediction and deep learning in healthcare. The research developed and evaluated multiple deep learning models, including CNN, DenseNet201, InceptionResNetV2, VGG16, VGG19, and Xception, for prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. These models demonstrated high accuracy, precision, recall, and other performance metrics, showcasing their potential for accurate survival prediction. The research employed visualization and interpretation techniques to enhance the understanding of deep learning models. Through activation maps, feature visualization, and attention mechanisms, the researchers visualized and interpreted the models’ decision-making process, providing insights into the important features and regions that influence survival predictions. The research utilized a large dataset of histopathological images of CRC and healthy tissue, providing a valuable resource for further studies in the field. In addition, the researchers implemented preprocessing techniques such as normalization and augmentation to optimize the performance of the deep learning models. The research findings have practical applications and clinical significance in the field of prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. The developed deep learning models can aid in personalized medicine by accurately predicting survival outcomes for individual CRC patients. This information can assist clinicians in tailoring treatment plans and interventions based on the patient’s specific prognosis, optimizing patient care and outcomes. The models can serve as decision support tools for clinicians, providing additional insights and guidance in the interpretation of histopathological images. By leveraging the models’ predictions and visualizations, clinicians can make more informed decisions about treatment strategies, follow-up protocols, and patient management. The research findings can contribute to the identification and validation of biomarkers associated with CRC prognosis. The visualization and interpretation techniques help reveal the relevant features and patterns in histopathological images that have a significant impact on survival predictions. This knowledge can guide further research into biomarker discovery and facilitate the development of targeted therapies. The research provides a foundation for future studies in the field of prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. The developed models, dataset, and preprocessing techniques can be utilized by researchers to expand upon the existing work, investigate new research questions, and develop more advanced models and methodologies. The research article has made important contributions to the field of prognostic survival prediction in CRC histology. The developed deep learning models, visualization techniques, and dataset provide valuable insights into survival prediction and have significant implications for personalized medicine, clinical decision-making, biomarker discovery, and future research. With further validation, refinement, and integration into clinical practice, the findings from this research can have a profound impact on improving patient outcomes in CRC and pave the way for advancements in prognostic prediction using deep learning in other areas of healthcare. Exploring model deployment in actual clinical settings and evaluating its influence on patient outcomes are crucial areas for future academic investigation.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: J.V.: manuscript writing, N.K., K.A., R.K.: investigation, methodology, and validation; V.K., R.K.: data collection, data curation, and analysis; A.Sh.: data curation and analysis and draft editing; I.K., R.P.: study conceptualization, manuscript writing, revising, and editing, A.Sa.: supervision, reviewing.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wang J, Liu L, Cai Y, Gao Y, Guo Z, Yu F, et al. Trends in the age-related incidence of colon and rectal cancers in China, 2005–2015. Dig Liver Dis. 2021;53(7):908–14.10.1016/j.dld.2021.01.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Chen K, Collins G, Wang H, Toh JWT. Pathological features and prognostication in colorectal cancer. Curr Oncol (Tor). 2021;28(6):5356–83.10.3390/curroncol28060447Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Zhu Y, Afolabi LO, Wan X, Shim JS, Chen L. TRIM family proteins: roles in proteostasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Open Biol. 2022;12(8):220098.10.1098/rsob.220098Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Kansal I, Popli R, Verma J, Bhardwaj V, Bhardwaj R. Digital image processing and IoT in smart health care-A review. In 2022 International Conference on Emerging Smart Computing and Informatics (ESCI); 2022. p. 1–6.10.1109/ESCI53509.2022.9758227Search in Google Scholar
[5] Lei G, Liu S, Yang X, He C. TRIM29 reverses oxaliplatin resistance of P53 mutant colon cancer cell. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;2021:8870907.10.1155/2021/8870907Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Jiang T, Wang H, Liu L, Song H, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. CircIL4R activates the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway via the miR-761/TRIM29/PHLPP1 axis and promotes proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):167.10.1186/s12943-021-01474-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Rajab M, Lu J, Xu Q. A framework model using multifilter feature selection to enhance colon cancer classification. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0249094.10.1371/journal.pone.0249094Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Wang P, Xiao X, Glissen Brown JR, Berzin TM, Tu M, Xiong F, et al. Development and validation of a deep-learning algorithm for the detection of polyps during colonoscopy. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2:741–8.10.1038/s41551-018-0301-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Sun J, Yan J, Qiao HY, Zhao FY, Li C, Jiang JY, et al. Loss of TRIM29 suppresses cancer stem cell-like characteristics of PDACs via accelerating ISG15 degradation. Oncogene. 2020;39(3):546–59.10.1038/s41388-019-0992-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Ren M, Gao Y, Chen Q, Zhao H, Zhao X, Yue W. The overexpression of keratin 23 promotes migration of ovarian cancer via epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:8218735.10.1155/2020/8218735Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Pan B, Wei ZX, Zhang JX, Li X, Meng QW, Cao YY, et al. The value of AGR2 and KRT5 as an immunomarker combination in distinguishing lung squamous cell carcinoma from Khani P, Ghazi F, Zekri A, Nasri F, Behrangi E, Aghdam AM, et al. Keratins and epidermolysis bullosa simplex. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(1):289–97.10.1002/jcp.26898Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Dwyer Nield LD, McArthur DG, Hudish TM, Hudish LI, Mirita C, Sompel K, et al. PPARgamma agonism inhibits progression of premalignant lesions in a murine lung squamous cell carcinoma model. Int J Cancer. 2022;151(12):2195–205.10.1002/ijc.34210Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Huang N, Sun X, Li P, Liu X, Zhang X, Chen Q, et al. TRIM family contribute to tumorigenesis, cancer development, and drug resistance. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11(1):75.10.1186/s40164-022-00322-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Han J, Zhao Z, Zhang N, Yang Y, Ma L, Feng L, et al. Transcriptional dysregulation of TRIM29 promotes colorectal cancer carcinogenesis via pyruvate kinase-mediated glucose metabolism. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(4):5034–54.10.18632/aging.202414Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Qiao HY, Zhang Q, Wang JM, Jiang JY, Huyan LY, Yan J, et al. TRIM29 regulates the SETBP1/SET/PP2A axis via transcription factor VEZF1 to promote progression of ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022;529:85–99.10.1016/j.canlet.2021.12.029Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Hao L, Zhang Q, Qiao H, Zhao F, Jiang J, Huyan L, et al. TRIM29 alters bioenergetics of pancreatic cancer cells via cooperation of miR2355-3p and DDX3X recruitment to AK4 transcript. Mol Ther – Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:579–90.10.1016/j.omtn.2021.01.027Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Ray SK, Mukherjee S. Altered expression of TRIM proteins – inimical outcome and inimitable oncogenic function in breast cancer with diverse carcinogenic hallmarks. Curr Mol Med. 2023;23(1):44–53.10.2174/1566524022666220111122450Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Cockram PE, Kist M, Prakash S, Chen S, Wertz IE, Vucic D. Ubiquitination in the regulation of inflammatory cell death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(2):591–605.10.1038/s41418-020-00708-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Razzaghdoust A, Ghajari M, Basiri A, Torbati PM, Jafari A, Fattahi MR, et al. Association of immunohistochemical markers of tumor subtype with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and survival in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Investig Clin Urol. 2021;62(3):274–81.10.4111/icu.20200425Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Chehade AH, Abdallah N, Marion JM, Oueidat M, Chauvet P. Lung and colon cancer classification using medical imaging: a feature engineering approach. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2022;45:729–46.10.1007/s13246-022-01139-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Kather JN, Halama N, Marx A. 100,000 histological images of human colorectal cancer and healthy tissue; 2018. https://zenodo.org/record/1214456.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Tamang LD, Kim BW. Deep learning approaches to colorectal cancer diagnosis: A review. Appl Sci. 2021;11:10982.10.3390/app112210982Search in Google Scholar
[23] Davri A, Birbas E, Kanavos T, Ntritsos G, Giannakeas N, Tzallas AT, et al. Deep learning on histopathological images for colorectal cancer diagnosis: A systematic review. Diagnostics. 2022;12:837.10.3390/diagnostics12040837Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Islam MR, Akash S, Rahman MM, Nowrin FT, Akter T, Shohag S, et al. Colon cancer and colorectal cancer: Prevention and treatment by potential natural products. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;368:110170.10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110170Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Collins T, Maktabi M, Barberio M, Bencteux V, Jansen-Winkeln B, Chalopin C, et al. Automatic recognition of colon and esophagogastric cancer with machine learning and hyperspectral imaging. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1810.10.3390/diagnostics11101810Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Sakr AS, Soliman NF, Al-Gaashani MS, Pławiak P, Ateya AA, Hammad M. An efficient deep learning approach for colon cancer detection. Appl Sci. 2022;12:8450.10.3390/app12178450Search in Google Scholar
[27] Alsanea N, Abduljabbar AS, Alhomoud S, Ashari LH, Hibbert D, Bazarbashi S. Colorectal cancer in Saudi Arabia: Incidence, survival, demographics, and implications for national policies. Ann Saudi Med. 2015;35:196–202.10.5144/0256-4947.2015.196Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Trivedi NK, Gautam V, Anand A, Aljahdali HM, Villar SG, Anand D, et al. Early detection and classification of tomato leaf disease using high-performance deep neural network. Sensors. 2021;21:7987. 10.3390/s21237987.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Lilhore UK, Poongodi M, Kaur A, Simaiya S, Algarni AD, Elmannai H, et al. Hybrid model for detection of cervical cancer using causal analysis and machine learning techniques. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;17:4688327.10.1155/2022/4688327Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

