Abstract
Essential tremor (ET) is a common neurological disorder with a difficult clinical diagnosis, primarily due to the lack of relevant biomarkers. The current study aims to identify possible biomarkers for ET by screening miRNAs using machine learning algorithms. In this investigation, public datasets and our own datasets were used to examine the ET disorder. The ET datasets originated from public sources. To generate our own dataset, high-throughput sequencing analyses were performed on ET and control samples from the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province. Functional enrichment analysis was employed to identify the potential function of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Using datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, Lasso regression analysis and support vector machine recursive feature elimination were used to screen potential diagnostic genes for ET. To identify the genes responsible for the final diagnosis, area under the curves (AUCs) of the receiver operating characteristic was examined. Finally, an ssGSEA representing an ET immune landscape was created. The sample exhibited expression profiles that corresponded with six genes in the public database. Three diagnostic genes were discovered with AUCs >0.7 that can distinguish ET from normal data: APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148. Single-gene GSEA indicated that these diagnostic genes were closely associated with the cholinergic, GABAergic, and dopaminergic synapse networks. The immune microenvironment of ET was also affected by these diagnostic genes. According to the findings, these three DEGs (APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148) may successfully differentiate between samples from ET patients and normal controls, serving as a helpful diagnostic tool. This effort provided a theoretical foundation for elucidating the pathogenesis of ET and raised hopes of overcoming the diagnostic difficulty of ET clinically.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Essential tremor (ET) is a widely prevalent movement disorder that is characterized by bilateral tremors in the upper limbs during both postural and kinetic activities. It has been suggested that ET is among the most frequently occurring neurodegenerative conditions [1–3]. Clinical symptoms and epidemiology in ET appear to be related. For instance, a study discovered that the incidence of ET has two peaks: early-onset (before the age of 25) and late-onset (after the age of 65) [4]. Positive family history and sensitivity to alcohol are more frequent characteristics of young-onset ET. A higher incidence of dementia has been related to late-onset ET [5]. A meta-analysis conducted globally revealed that the prevalence of ET was 0.4–0.9% across all age groups, while it was 4.6–6.3% in populations aged 65 years and above [6,7]. In addition to tremor, other symptoms of ET include gait and balance impairment, moderate cognitive deficiency, psychiatric symptoms, and hearing loss [8–11]. Recently, the term ET-Plus has been used to characterize these soft signs [12,13].
The pathogenesis of ET is complex and inconclusive due to the involvement of multiple genetic and environmental etiologies. The precise etiology and pathogenesis of ET remains uncertain. Numerous studies in academic literature have indicated the significant influence of genetic factors [14]. The etiology of ET is supported by the prevalence of positive family history of tremor in patients with ET, indicating the involvement of genetic factors. It is estimated that genetic factors contribute to ET in a range of 20–90% of patients. Additionally, genetic anticipation, which refers to the earlier onset of tremor in the next generation, has been observed in ET patients. Furthermore, twin studies have shown higher concordance rates of ET for monozygotic twins compared to dizygotic twins [15,16]. The diagnosis of ET poses a challenge due to its diverse clinical manifestations, resulting in a high rate of misdiagnosis [17,18].
At present, the clinical diagnosis of ET heavily relies on the subjective clinical evaluation of medical professionals, and a minimum disease duration of 3 years is typically necessary for diagnosis [19]. Globally, there is a severe shortage of experienced neurologists. Therefore, researchers are focusing on incorporating objective measurement indices into the auxiliary diagnosis of ET [20]. Neuroimaging and neurophysiology technologies provide new ideas for confirming the specific pathogenesis of ET. High-precision invasiveness diagnosis, such as 123I-FP-CIT SPECT, has been determined to be the most effective diagnostic instrument in this respect; however, only developed nations can afford it due to its high cost and high consumption [21]. The International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society (IPMDS) standardized the diagnostic criteria for ET, stating that a 3-year history of isolated action tremor in the absence of any other neurologic condition is required [19]. In order to accurately diagnose a patient, doctors meticulously collect clinical information, including historical features (age at onset, family history), tremor characteristics (body distribution, activation condition), related indicators, and laboratory testing (electrophysiology, imaging, and scales). Due to their age and poor mobility, many ET patients may be unable to see a doctor right away, which would delay receiving an accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment. To help with diagnosis and to distinguish between diagnoses at the early stage of ET, various sensitive and specific detection indexes are still anticipated. As a result, noninvasive auxiliary solutions that are low cost and high efficiency are a new hotspot for ET early diagnosis.
The ET has been linked to cerebellar function, according to the research. The cerebellar degeneration hypothesis is now regarded as a significant player on the ET stage, encompassing movement disorders, cognitive disorders, and affective disorders [22,23]. According to certain scholars, a minimum of 27 miRNAs participate in the regulation of gene expression after transcription and are implicated in the processes of apoptosis and necrosis in cerebellar neurons [24]. Microarrays and bioinformatics analytical tools have been extensively utilized for the identification of differentially expressed miRNAs in ET over the years [25]. A number of miRNAs have been documented to exhibit anomalous expression in individuals with ET, and could potentially have clinical implications [26,27]. In addition, miRNAs have been suggested as potential non-invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response of various neurodegenerative conditions, including Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) [28].
The field of bioinformatics has undergone significant advancements, enabling the screening of a greater number of genes in a more efficient and precise manner compared to traditional experimental research, which is often costly and time-consuming. Bioinformatics analysis has the potential to offer exploratory predictions at a reduced cost, thereby informing subsequent biological experiments and clinical applications [29]. The Hub gene, due to its significant connectivity within the gene expression network, is believed to have a crucial impact on the advancement of the disease [30]. In earlier investigations, hub genes were frequently discovered using the STRING (Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes) or cytoHubba program [30]. However, the quality of the screening process and the reproducibility of the experiment are compromised when researchers are allowed to use their personal preferences to determine whether the top 5 or 10 of total differential expression genes (DEGs) should be chosen as hub genes [31]. Various machine learning (ML) approaches have recently been introduced to bioinformatics analysis in an effort to reduce this type of inaccuracy, and it has been demonstrated that doing so improves the accuracy and stability of the screening procedure [32]. As a normalized linear regression method, the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression can disregard unimportant features and construct a sparse and easily interpretable model to prevent overfitting. With the support vector machine recursive feature elimination (SVM-RFE) method, the support vector machine is incorporated into the recursive feature elimination approach and its inherent feature selection function is used to continuously screen important features. In several sectors, the combination of LASSO and SVM-RFE algorithms has demonstrated adequate sensitivity and accuracy. High classification performance is achieved by this model, which is recognized to remove irrelevant information effectively [33,34]. Additionally, the most effective techniques currently employed in studies on miRNA biomarkers include bioinformatics and biological tools [35].
In order to assess the potential of the miRNAs to serve as ET biomarkers, this study screened miRNAs based on ML methods utilizing sequencing data from both public databases and the own dataset. Three diagnostic genes, APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148, all with area under the curves (AUCs) >0.7, were found to have significant diagnostic values for distinguishing ET from normal samples. The synaptic signaling transmission and immunological microenvironment of neurons were thought to be closely related to these diagnostic genes. The present study employed an innovative bioinformatics approach to identify putative biomarkers for ET, which could potentially enhance the accuracy of clinical diagnosis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 The public data source
The Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database, which can be accessed at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/ as of November 1, 2022, is a publicly available international repository that contains functional genome datasets generated through high-throughput microarray and next-generation sequencing techniques. The National Center for Biotechnology Information is responsible for the creation and maintenance of this database [36]. This database contains virtually all gene expression assay data that is useful for scientific investigation [37]. Twenty normal samples and 32 ET samples were included in the GSE134878 dataset, which was downloaded for this investigation from the GEO database. For the primary analysis of this study, this dataset was used.
2.2 Patient preparation
The Department of Neurology at the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, China, recruited three patients with ET. All patients underwent clinical and neuropsychological examinations, brain magnetic resonance imaging, and thyroid function evaluations in accordance with IPMDS [19] criteria. Exclusion criteria included concurrent or recent exposure to tremorgenic drugs, hyper- and hypothyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, physiological and psychogenic tremor, premorbid clinically significant psychiatric disorders, alcohol and narcotic addictions, inflammatory diseases, cancer, chronic diseases, and a history of major surgery. All of the patients had a 3-year history of bilateral upper limb tremors. In addition, three age- and gender-matched healthy subjects were recruited as controls [38]. Fahn Tolosa Marin scale was utilized to evaluate the severity of tremor [39]. The Chinese version of the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (score 0–30) was used to evaluate cognitive function. The Beck Depression Inventory (score 0–63) was used to assess affective symptoms.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by Medical Ethics Committee of the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province (YYLH005, February 2019).
2.3 RNA-seq analysis
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from ET patients and healthy controls by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation and Lymphoprep (Stemcell, USA). Following their separation, PBMCs were lysed using a TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA) and kept at −80°C for further processing. Then, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, total RNA was isolated using a mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Ambion, Foster City, CA). The quantity of RNA was assessed using a NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA), while RNA quality was evaluated using an Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). Purified libraries were created using Illumina TruSeq Stranded Total RNA Sample Preparation Kits (Illumina, San Diego, CA) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, and their quantities were determined using an Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer and a Qubit 2.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA). Libraries were utilized to create a cluster using the cBot software. Subsequently, the cluster underwent sequencing utilizing the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform, which is located in San Diego, CA. The sequencing procedures were conducted by Origin-Biotech Inc. (Ao-Ji Bio-Tech, Shanghai, China).
2.4 Analysis of DEGs
The differential expression files, which had undergone DESeq2 processing, were acquired directly from the GEO database (Table S1). DEGs were identified based on the statistical criteria of a significance level of P < 0.05 and a false discovery rate threshold of <0.25. [41]. The t-test assay was utilized to obtain the expression pattern of the DEGs in the own dataset, as indicated in Table S2.
2.5 Functional enrichment analysis
The DEGs underwent functional enrichment analysis using the clusterProfiler package, specifically through the utilization of Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Cellular component (CC), biological process (BP), and molecular function (MF) were the three basic categories used in the GO analysis. The KEGG signaling pathway was considered a pre-established gene set, and subsequently, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was conducted on individual diagnostic markers to identify the specific pathway associated with each diagnostic marker. The adjusted (adj.) P < 0.05 values were regarded as significant for all statistical analyses.
2.6 LASSO and SVM-RFE algorithms
DEGs with consistent expression trends in their own and GSE134878 datasets were regarded to be potential ET-related DEGs. The LASSO and SVM-RFE algorithms were utilized to filter candidate diagnostic genes for ET from among the candidate DEGs associated with ET. The glmnet (version 3.0) and e1071 (version 1.7−3) R package (version 3.6.0) were utilized to conduct LASSO and SVM-RFE, respectively. The genes that were identified by both algorithms were considered as potential diagnostic genes. By comparing the AUC of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, the efficacy of candidate diagnostic genes in differentiating ET samples from normal samples was evaluated. A gene with AUCs greater than 0.7 in both the GSE134878 and own datasets was considered the diagnostic gene.
2.7 Single sample GSEA (ssGSEA)
ssGSEA is a GSEA deconvolution algorithm that translates gene expression profiles into quantitative fractions of immune cells in a single sample. The GSVA function in the R package was utilized to evaluate the distribution of 24 immune cell subtypes in each sample of the GSE134878 dataset [42]. Since no sample included evidence of the expression of the IL3RA-only gene in pDC cells, these cells were specifically excluded of all subsequent analyses.
2.8 Statistical analysis
Pearson correlation analysis was employed to calculate correlations, and a correlation was deemed significant if it satisfied the criteria of |correlation (cor)| ≥0.3 and P < 0.05. The regulatory networks in which diagnostic genes may be engaged were revealed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA). The statistical analyses were primarily conducted using the R package (version 3.6.0). Statistical analyses were conducted with a significance level of P < 0.05, indicating statistical significance.
3 Results
3.1 Filtering of ET-related DEGs and unveiling of their potential functions
A total of 231 DEGs related to ET were identified in the GSE134878 dataset, as shown in Table S3. Figure 1a shows that of these, 171 were up-regulated and 60 were down-regulated. Furthermore, the expression pattern of the DEGs in the GSE134878 dataset was demonstrated through a heat map, as depicted in Figure 1b.
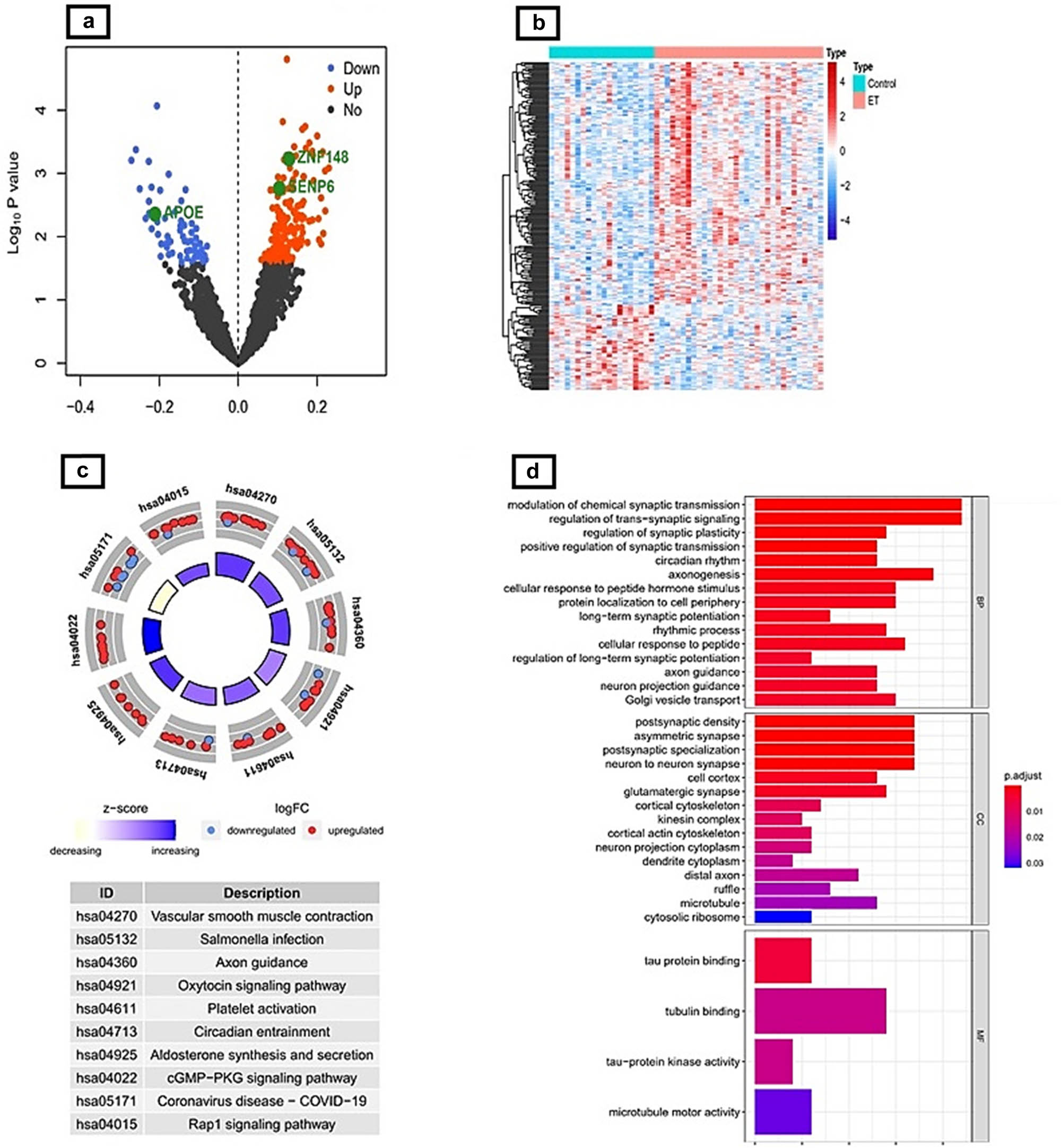
(a) Volcano plot showing DEGs for the ET and control groups (black dots denote no significant difference, red dots denote differential expression that was up-regulated, blue dots denote differential expression that was down-regulated). (b) Heat map of DEGs between the ET and control groups. (c) Results of GO enrichment analysis for DEGs. (d) Results of the investigation of KEGG enrichment for DEGs.
The potential roles of DEGs in the pathogenic progression of ET were then investigated using GO analysis (Figure 1c; Table S4). The DEGs identified in the BP category were observed to have a close association with synaptic transmission and neuronal conduction. Specifically, the DEGs were found to be involved in various processes such as modulation of chemical synaptic transmission, regulation of trans-synaptic signaling, regulation of synaptic plasticity, positive regulation of synaptic transmission, neuron projection guidance, positive regulation of neuron projection development, neurotransmitter secretion, and positive regulation of neuron differentiation. The identified genes were observed to have significant involvement in cellular structures such as the postsynaptic density, asymmetric synapse, postsynaptic specialization, and neuron-to-neuron synapse. In addition, it was observed that four terms exhibited significant enrichment in the MF category. These terms include tau protein binding, tubulin binding, tau-protein kinase activity, and microtubule motor activity. In addition, the KEGG analysis revealed that the DEGs were primarily associated with various biological processes such as vascular smooth muscle contraction, Salmonella infection, axon guidance, and oxytocin signaling pathway (as shown in Figure 1d and Table S5).
3.2 Identification of candidate ET-related DEGs
The expression pattern of the aforementioned DEGs was verified between a collection of three normal and three ET samples using t-tests. A total of 231 DEGs were identified, out of which eight DEGs exhibited differential expression in the dataset under investigation. Subsequently, six out of the eight DEGs exhibited consistent expression patterns in the GSE134878 dataset. The study found that the genes EFR3A, FAM169A, SENP6, and ZNF148 exhibited overexpression in ET, while APOE and NISCH showed repression in ET, as depicted in Figure 2. These genes were identified as potential ET-related DEGs and were selected for further analysis (Figure S1).


Expression boxplot of eight different genes in GSE134878 (a) and the own dataset (b), respectively.
3.3 Screening for ET diagnostic markers and assessment of their diagnostic validity
Two distinct methodologies were utilized to identify the most effective diagnostic markers for ET by analyzing potential DEGs associated with ET. The LASSO algorithm was utilized to identify a set of characteristic genes, which consisted of five DEGs, as depicted in Figure 3a and b. On the other hand, the SVM-RFE algorithm was employed to select a set of four DEGs, as illustrated in Figure 3c and d. Through the process of overlapping the biomarkers selected by the two algorithms, a total of four DEGs were identified, as illustrated in Figure 3e. These DEGs were subsequently identified as potential feature genes for the classification of ET. In this study, a cohort of 52 test samples sourced from the GSE134878 dataset, alongside six validation samples from an own dataset, were classified into ET and normal groups based on the utilization of four potential feature genes. The results of the ROC curve analysis indicate that APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148 achieved a high level of classification accuracy in both the GSE134878 dataset (with all AUCs greater than 0.7, as shown in Figure 3f) and the researcher’s own dataset (with all AUCs equal to 1, as shown in Figure 3g). Therefore, these genes have been validated as diagnostic markers for ET. Figure 1a depicts the annotation of ET diagnostic markers’ expression patterns in the GSE134878 dataset.
![Figure 3
(a and b) The LASSO algorithm identified a characteristic gene set containing five DEGs. (c and d) The SVM-RFE algorithm identified a characteristic gene set containing four DEGs. (e) Four DEGs were discovered by overlapping the characteristic genes selected by the LASSO algorithm and the SVM-RFE algorithm. (f) ROC curve analysis of characteristic genes in GSE134878 dataset. (g) Examination of the ROC curves for the characteristic genes in the own dataset. (The results of the ROC curve analysis indicate that APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148 exhibited high classification accuracy in both the GSE134878 dataset [with all AUCs greater than 0.7] and the researcher’s own dataset [with all AUCs equal to 1]).](/document/doi/10.1515/biol-2022-0622/asset/graphic/j_biol-2022-0622_fig_003.jpg)
(a and b) The LASSO algorithm identified a characteristic gene set containing five DEGs. (c and d) The SVM-RFE algorithm identified a characteristic gene set containing four DEGs. (e) Four DEGs were discovered by overlapping the characteristic genes selected by the LASSO algorithm and the SVM-RFE algorithm. (f) ROC curve analysis of characteristic genes in GSE134878 dataset. (g) Examination of the ROC curves for the characteristic genes in the own dataset. (The results of the ROC curve analysis indicate that APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148 exhibited high classification accuracy in both the GSE134878 dataset [with all AUCs greater than 0.7] and the researcher’s own dataset [with all AUCs equal to 1]).
3.4 Single-gene GSEA for ET diagnostic markers
The KEGG signaling pathway was utilized as a pre-gene set, and GSEA was used to reveal the signaling pathways implicated in each of the three diagnostic markers. The study found that APOE was associated with 151 enriched pathways. The three most enriched pathways were identified as “Ribosome,” “Herpes simplex virus 1 infection,” and “Coronavirus disease – COVID-19,” as shown in Figure 4a and Table S6. The study identified 32 pathways associated with SENP6, with the “Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis,” “Complement and coagulation cascades,” and “AD” pathways being the most significant, as depicted in Figure 4b and Table S7. The study identified 145 pathways associated with ZNF148 through GSEA. Among these pathways, “Endocytosis,” “Thyroid hormone signaling pathway,” and “Sphingolipid signaling pathway” were found to have the strongest correlation with ZNF148, as depicted in Figure 4c and Table S8. Remarkably, the investigation revealed a significant correlation between the genes and specific synaptic pathways, namely “GABAergic synapse” [43] (APOE, ZNF148), “Cholinergic synapse” [44] (ZNF148), “Dopaminergic synapse” [45] (ZNF148), and “Serotonergic synapse” [46] (ZNF148). Moreover, these diagnostic markers were implicated in diverse neurodegenerative disease pathways, including Huntington’s disease (HD), PD, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, AD, and spinocerebellar ataxia. The findings indicate that the aforementioned genes could potentially play a role in the development of ET and other associated neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, Figure S1 illustrates a potential regulatory network implicated in the diagnostic markers identified by IPA.

(a) Single-gene GSEA for APOE, (b) single-gene GSEA for SENP6, and (c) single-gene GSEA for ZNF148.
3.5 Immune landscape analysis of ET patients
The study conducted a functional enrichment analysis of DEGs and diagnostic markers associated with ET. The results indicated a strong association between these genes and the immune response, including pathways such as the cAMP signaling pathway, cell adhesion molecules, antigen processing and presentation, Th17 cell differentiation, ECM–receptor interaction, T cell receptor signaling pathway, and AMPK signaling pathway. Inspired by this, the ssGSEA algorithm was used to estimate the proportion of immune infiltrating cells between normal and ET patients in the GSE134878 dataset. The findings indicate that the fractions of Tgd and Th1 cells were the only statistically significant differences observed between the two groups. Specifically, Tgd cells were found to be less infiltrated in ET patients, while Th1 cells were more widely distributed in ET patients (Figure 5a and Figure S1). Subsequently, the correlation between diagnostic markers and immune infiltrating cells was calculated using Pearson correlation analysis (Figure 5b and Table S9). The findings indicate a significant positive association between APOE and Tgd (cor = 0.56, P = 1.32 × 10−5), macrophages (cor = 0.42, P = 0.00185), TFH (cor = 0.37, P = 0.006253), and eosinophils (cor = 0.36, P = 0.009681). The findings suggest that SENP6 exhibits a negative correlation with cytotoxic cells (cor = −0.36, P = 0.008547) and TFH (cor = −0.33, P = 0.015557), whereas a positive correlation was observed with T helper cells (cor = 0.38, P = 0.005584). Only CD8 T cells exhibited a positive correlation with ZNF148 (cor = 0.39, P = 0.004593) (Figure S3).

(a) Expression of immune infiltrating cells between the ET and control groups (only the fractions of Tgd and Th1 cells were significant between normal and ET patients, with Tgd being less infiltrated in ET patients, while Th1 cells were more widely distributed in ET patients). (b) Relationship between diagnostic markers and immune infiltrating cells by Pearson correlation analysis. (c) Expression levels of 29 immune checkpoint molecules in the ET and control groups. (d) Relationship between diagnostic markers and immune checkpoint molecules by Pearson correlation analysis.
The study conducted revealed a significant association between ZNF148 and the expression of PD-L1 and the PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer. As a result, an investigation was carried out to determine the expression levels of 29 immune checkpoint molecules in both normal and ET patients, as illustrated in Figures S2 and S3. The results revealed that CD47 and TNFSF4 exhibited high expression levels in patients with ET, while LGALS9, PDCD1, and TNFRSF14 were highly expressed in the normal group, as depicted in Figure 5c. The results of Pearson correlation analysis indicated that CD47 exhibited a strong positive correlation with SENP6 (cor = 0.35, P = 0.010676). Additionally, LGALS9 demonstrated significant positive and negative correlations with APOE (cor = 0.36, P = 0.008381) and SENP6 (cor = −0.37, P = 0.006177), respectively. However, no significant correlation was observed among TNFSF4, TNFRSF14, and the diagnostic markers, as shown in Figure 5d and Table S10 (Figure S2).
4 Discussion
This study represents a novel investigation into the diagnostic markers of ET utilizing ML algorithms, with the aim of elucidating the underlying pathogenesis. During the preliminary investigation, it was observed that three diagnostic genes played a significant role in the diagnosis process and were implicated in complex pathophysiological mechanisms. The aforementioned discoveries have facilitated a redefinition of our comprehension of the mechanism and have provided clarification regarding the complexity of clinical manifestations.
The manifestation of tremors, as observed in clinical settings, can be attributed to the interaction between the cerebellar thalamus, cortex, and muscle, resulting in involuntary muscle contractions [47,48]. Several neuroimaging studies have demonstrated the existence of functional, metabolic, and structural defects in the cerebellum of individuals with ET [49–51]. The postmortem literature has been expanding and has identified microscopic abnormalities in the brain of individuals with ET. These abnormalities are primarily focused on the Purkinje cells and synaptic transmission [52–54]. According to certain researchers, compared to controls, ET patients had significantly lower dendritic complexity and spine density [55]. The Purkinje cells, acting as efferent neurons within the cerebellar cortex, receive primary excitatory inputs from the climbing fibers of olivary cells via synapses. Subsequently, they transmit information through synapses to establish a one-to-one relationship [56,57]. The cerebellum of individuals with ET has been found to exhibit anomalies in Glu synapses and GABA synapses, particularly in terms of synapse density, as indicated by postmortem studies [58–60]. The aberrant formation of Purkinje cells and their synapses, leading to cellular remodeling and degeneration, has been found to give rise to novel or atypical cortical circuits in individuals with ET, thereby contributing to the manifestation of associated clinical symptoms [61,62].
The potential functions of DEGs in the pathogenic course of ET were investigated via GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. Despite the lack of clear correlation between DEGs and the nervous system in the KEGG analysis, it is postulated that the DEGs primarily impact synaptic transmission and neuronal conduction, as indicated by the results of the GO analysis (Figure 1c and d). The findings of the analysis indicated a close correlation between the DEGs and the functions of tau protein and microtubule-associated protein. These DEGs were found to be responsible for inducing abnormalities in the cytoskeleton. These genes were also discovered to play crucial roles in CCs such postsynaptic density, asymmetric synapses, and postsynaptic specialization. This finding explained the axonal and dendritic structural alterations in compromised Purkinje cells, as well as the underlying degenerative process involving the Purkinje cells and/or their microenvironment [63].
Three diagnostic genes were identified as the optimal markers for ET diagnosis from candidate DEGs associated with ET. The three diagnostic genes were found to have significant involvement in the process of cellular structure remodeling and metabolic function anomalies specifically in Purkinje cells. The GSEA analysis revealed that three diagnostic genes were significantly linked to diverse neurodegenerative disease pathways across distinct synapses, as depicted in Figure 4.
The APOE gene, which controls multifactorial/complex processes resulting in the early death of neurons, had been thoroughly investigated in ET. The APOE gene is known to regulate the metabolism of amyloid precursor protein and the accumulation of amyloid-beta (Aβ). It has also been found to promote the hyperphosphorylation of tau-protein, reduce choline acetyltransferase activity, increase oxidative processes, modify inflammation-related neuroimmunotropic activity, and alter synapse structure, among other effects [64,65]. An elevation in insoluble Aβ42 levels was previously observed in the cerebral parietal cortex of all individuals with ET, as well as in the cerebellar white matter of the majority of ET cases [66]. This accumulation of cerebellar Aβ42 indicated continuous neurodegeneration in a subset of ET patients and clarified the cognitive impairment of ET-plus patients [65]. The findings of this investigation indicate a decrease in the expression of APOE in individuals with ET, as demonstrated in Figure 2. The results were in agreement with prior research indicating that the reduction of plasma APOE levels could serve as a peripheral biomarker. This decrease may indicate an increase in ET brains, which has also been noted in individuals with AD [67].
The close association between SENP6 and hereditary stability has been suggested as a role that is evolutionarily conserved in regulating chromatin dynamics and genome stability networks. This is achieved through the maintenance of a balance in the chromatin residency of protein complexes [68]. The results of the GSEA conducted on SENP6 indicated that the pathways of “Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis” and “AD” were notably prominent, as illustrated in Figure 4b. Extensive research has been carried out suggesting that SENP6 was responsible for modifying synaptic transmission and neuronal excitability in neurons via small ubiquitin-related modifier, which is compatible with the finding of this work [69]. ZNF148 has been linked to various cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and programmed cell death, and has been identified as a potential tumor suppressor [70,71]. In research for HD, as well as a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, the researchers described that ZNF148 directly interacted with three known-HD genes (BCL2, CASP6, and IRS2) [72]. Additionally, ZNF148 had been identified as a previously unknown yet significant transcription factor in the corpus callosum’s development [73,74]. The evidence suggests that ZNF148 may have a significant impact on abnormal neuronal proliferation or migration, as well as abnormal axonal growth or guidance [74]. The aforementioned results indicate that SENP6 and ZNF148 could potentially contribute to the development of ET and other associated neurodegenerative disorders.
It had been established that an imbalance in GABAergic inhibition can result in excitotoxicity and the upregulation of glutamatergic and cholinergic neurons, ultimately leading to the manifestation of delirium and involuntary tremors in patients with ET [75,76]. These three genes were found to be significantly linked to synapses and were observed to participate in the gene network of neurotransmitters. Learning disabilities and memory deficits were observed as a consequence of abnormal APOE gene expression in GABAergic interneurons [77,78]. The post-translational modifications occurring at both presynaptic buttons and post-synaptic terminals were found to regulate the activity of SENP6 [69]. SENP6 controlled a number of synaptic functions, including the degradation of target proteins, which is crucial for the creation and recall of memories [79]. Furthermore, it was demonstrated that ZNF148 exhibited the ability to stimulate the promoter of SLC6A1, a transporter responsible for the termination of GABA activity through the elimination of GABA from the synaptic cleft [80]. Conversely, certain antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) have potential for employment in the clinical treatment of ET, including Mysoline (Primidone), Klonopin (Clonazepam), Ativan (Lorazepam), and Valium (Diazepam). The pharmacological targets of these AEDs were mainly focused on glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses [43]. The involvement of APOE and ZNF148 in GABAergic synapses has been observed, indicating that these synapses may serve as potential targets for the treatment of ET using AEDs.
It was observed that the DEGs associated with (ETs were linked to the immune response, as depicted in Figure 5a–d. Despite ET being classified as a neurodegenerative disorder, increasing evidence has suggested that the activation of lymphocytes and microglia may contribute to neuroinflammation in ET [81–83]. The findings indicate that there were significant differences in the fractions of Tgd and Th1 cells between normal individuals and those with ET. Specifically, Tgd cells were found to be less infiltrated in ET patients, while Th1 cells were more widely distributed in ET patients, as depicted in Figure 5a. Th1 cells stimulated macrophages by means of interleukin 2 (IL-2), which caused the release of interleukin 8 (IL-8) [84]. A recent study has reported that patients with ET exhibit considerably elevated serum levels of IL-8 in comparison to control patients. Additionally, the study found a positive correlation between the severity of tremor and the serum IL-8 level, which further supports our conclusion [81]. Tgd cells have been observed to participate in a multifaceted immune response within the gut–brain axis, which has been shown to exert a substantial impact on the pathogenesis of central nervous system neurodegenerative disorders, including PD and AD, through immune cell-mediated mechanisms [85,86]. The intestinal microflora in the context of autoimmune disease may also have an impact on the pathological and clinical outcome of ET [87].
The findings of our study indicate a significant positive association between APOE and Tgd, macrophages, TFH, and eosinophils. The study revealed that SENP6 exhibited an inverse association with cytotoxic cells and TFH, whereas it displayed a direct association with T helper cells. The results presented in Figure 5b indicate a positive correlation between ZNF148 and CD8 T cells. The relevant research was examined, revealing that APOE has an impact on physiology and pathophysiology at various levels. These levels include the inhibition of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes, regulation of macrophage function, modulation of inflammation and oxidation, and reduction of IL-2 production [88,89]. The inhibition of neuroinflammation was achieved through the dampening of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activation by SENP6 [90]. ZNF148 was found to exert an influence on immunoreactivity in T cells through its regulatory role in the expression of immune molecules [91]. The findings of this study suggest an indirect association between neuroimmune activity and the onset of ET.
The study conducted an in-depth analysis of the expression levels of immune checkpoint molecules in patients with ET and explored the correlation between immune checkpoint molecules and diagnostic markers, representing truly an innovative approach in the field. In particular, it was discovered that CD47 had a high level of expression in ET patients, and that this expression was both positive and substantially linked with SENP6. The aforementioned results have exposed the fundamental inflammatory mechanisms involved in ET and have also identified SENP6 as a potentially efficacious gene therapy tool that could be further explored in the context of treating ET patients.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, the findings revealed that these three DEGs (APOE, SENP6, and ZNF148) may effectively differentiate between samples from ET patients and normal controls, hence providing a useful diagnostic tool. The study employed bioinformatic methodology to anticipate the potential functional roles of DEGs and investigate their plausible involvement in the pathogenesis of ET. The finding had the potential to contribute to an improved understanding of the pathogenic processes that ultimately result in ET. However, the validation trial for detecting plasma miRNA expression levels in a large sample size of ET patients and controls has not been conducted due to financial limitations. Subsequently, additional verification experiments will be conducted in the forthcoming work. In addition, consistency of the findings of ML approaches needs to be evaluated on a larger dataset in the future to further establish the universality of ML. The precise biological roles and molecular processes by which these three DEGs contribute to the pathogenesis of ET will also be the subject of future studies.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Kunming University of Science and Technology, Yunnan, China.
-
Funding information: This study was supported by Yunnan Health Training Project of High Level Talents (L-2017013) and Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology –Kunming Medical University Joint Special Program of Applied Basic Research (202001AY070001-305).
-
Author contributions: Y.G. and L.D. designed the experiment. Y.G. and J.L. conducted the analysis. X.W. and Q.M. prepared the manuscript with the contribution of all co-authors. All authors have read and approved the final version of manuscript. The authors applied the SDC approach for the sequence of authors.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Supplementary data to this article is available in data repository under DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.7971542.
References
[1] Ma C, Zhang P, Pan L, Li X, Yin C, Li A, et al. Two-stage framework for automatic diagnosis of multi-task in essential tremor via multi-sensory fusion parameters. J King Saud Univ. 2022;34(10):8284–96.10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.08.009Search in Google Scholar
[2] Louis ED, Faust PL. Essential tremor: the most common form of cerebellar degeneration? Cerebellum Ataxias. 2020;7(1):1–10.10.1186/s40673-020-00121-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Huang H, Yang X, Zhao Q, Ning P, Shen Q, Wang H, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with essential tremor or essential tremor plus. Acta Neurol Scand. 2020;141(4):335–41.10.1111/ane.13209Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Lou J-S, Jankovic J. Essential tremor: clinical correlates in 350 patients. Neurology. 1991;41(2 Part 1):234.10.1212/WNL.41.2_Part_1.234Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Louis ED. Essential tremor and the cerebellum. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;155:245–58.10.1016/B978-0-444-64189-2.00016-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Louis ED, Ferreira JJ. How common is the most common adult movement disorder? Update on the worldwide prevalence of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2010;25(5):534–41.10.1002/mds.22838Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Louis ED, Ottman R, Allen Hauser W. How common is the most common adult movement disorder? Estimates of the prevalence of essential tremor throughout the world. J Mov Disord. 1998;13(1):5–10.10.1002/mds.870130105Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Fois AF, Briceño HM, Fung VS. Nonmotor symptoms in essential tremor and other tremor disorders. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;134:1373–96.10.1016/bs.irn.2017.05.010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Hopfner F, Deuschl G. Is essential tremor a single entity? Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(1):71–82.10.1111/ene.13454Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Louis ED. Essential tremor:“Plus” or “Minus”. Perhaps now is the time to adopt the term “the essential tremors”. Park Relat Disord. 2018;56:111–2.10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.06.026Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Fabbrini G, Berardelli I, Falla M, Moretti G, Pasquini M, Altieri M, et al. Psychiatric disorders in patients with essential tremor. Park Relat Disord. 2012;18(8):971–3.10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.05.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Bellows ST, Jankovic J. Phenotypic features of isolated essential tremor, essential tremor plus, and essential tremor-Parkinson’s disease in a movement disorders clinic. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov. 2021;11:12–22.10.5334/tohm.581Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Bologna M, Berardelli I, Paparella G, Ferrazzano G, Angelini L, Giustini P, et al. Tremor distribution and the variable clinical presentation of essential tremor. Cerebellum. 2019;18:866–72.10.1007/s12311-019-01070-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Jiménez-Jiménez FJ, Alonso-Navarro H, García-Martín E, Álvarez I, Pastor P, Agúndez JA. Genomic markers for essential tremor. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14(6):516.10.3390/ph14060516Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Soto MCS, Fasano A. Essential tremor: new advances. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2020;3:100031.10.1016/j.prdoa.2019.100031Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Jiménez‐Jiménez F, Alonso‐Navarro H, García‐Martín E, Lorenzo‐Betancor O, Pastor P, Agúndez J. Update on genetics of essential tremor. Acta Neurol Scand. 2013;128(6):359–71.10.1111/ane.12148Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Jain S, Lo SE, Louis ED. Common misdiagnosis of a common neurological disorder: how are we misdiagnosing essential tremor? Arch Neurol. 2006;63(8):1100–4.10.1001/archneur.63.8.1100Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Schrag A, Münchau A, Bhatia K, Quinn N, Marsden C. Essential tremor: an overdiagnosed condition? J Neurol. 2000;247:955–9.10.1007/s004150070053Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Bhatia KP, Bain P, Bajaj N, Elble RJ, Hallett M, Louis ED, et al. Consensus Statement on the classification of tremors. From the task force on tremor of the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Mov Disord. 2018;33(1):75–87.10.1002/mds.27121Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Pan M-K, Kuo S-H. Essential tremor: clinical perspectives and pathophysiology. J Neurol Sci. 2022;435:120198.10.1016/j.jns.2022.120198Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Wang Y, Yang J, Cai M, Liu X, Lu K, Lou Y, et al. Application of optimized convolutional neural networks for early aided diagnosis of essential tremor: automatic handwriting recognition and feature analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2023;113:103962.10.1016/j.medengphy.2023.103962Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Louis ED. The evolving definition of essential tremor: what are we dealing with? Park Relat Disord. 2018;46:S87–91.10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.07.004Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Lawrenson C, Bares M, Kamondi A, Kovács A, Lumb B, Apps R, et al. The mystery of the cerebellum: clues from experimental and clinical observations. Cerebellum Ataxias. 2018;5(1):1–11.10.1186/s40673-018-0087-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Pieczora L, Stracke L, Vorgerd M, Hahn S, Theiss C, Theis V. Unveiling of miRNA expression patterns in Purkinje cells during development. Cerebellum. 2017;16:376–87.10.1007/s12311-016-0814-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Houle G, Ambalavanan A, Schmouth J-F, Leblond CS, Spiegelman D, Laurent SB, et al. No rare deleterious variants from STK32B, PPARGC1A, and CTNNA3 are associated with essential tremor. Neurol Genet. 2017;3(5):e195–7.10.1212/NXG.0000000000000195Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Delay C, Tremblay C, Brochu E, Paris‐Robidas S, Emond V, Rajput AH, et al. Increased LINGO1 in the cerebellum of essential tremor patients. Mov Disord. 2014;29(13):1637–47.10.1002/mds.25819Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Kosmowska B, Ossowska K, Głowacka U, Wardas J. Tremorolytic effect of 5′‐chloro‐5′‐deoxy‐( ±)‐ENBA, a potent and selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist, evaluated in the harmaline‐induced model in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017;23(5):438–46.10.1111/cns.12692Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Batistela MS, Josviak ND, Sulzbach CD, de Souza RLR. An overview of circulating cell-free microRNAs as putative biomarkers in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Int J Neurosci. 2017;127(6):547–58.10.1080/00207454.2016.1209754Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Blauwendraat C, Nalls MA, Singleton AB. The genetic architecture of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(2):170–8.10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30287-XSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Chen H, Yang J, Wu W. Seven key hub genes identified by gene co-expression network in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2021;21:1–12.10.1186/s12885-021-08604-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Fang KY, Liang GN, Zhuang ZQ, Fang YX, Dong YQ, Liang CJ, et al. Screening the hub genes and analyzing the mechanisms in discharged COVID‐19 patients retesting positive through bioinformatics analysis. J Clin Lab. 2022;36(7):e24495.10.1002/jcla.24495Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Moradi S, Tapak L, Afshar S. Identification of novel noninvasive diagnostics biomarkers in the Parkinson’s diseases and improving the disease classification using support vector machine. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022:8.10.1155/2022/5009892Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Goñi M, Eickhoff SB, Far MS, Patil KR, Dukart J. Smartphone-based digital biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease in a remotely-administered setting. IEEE Access. 2022;10:28361–84.10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3156659Search in Google Scholar
[34] Wang Y, Huang X, Xian B, Jiang H, Zhou T, Chen S, et al. Machine learning and bioinformatics-based insights into the potential targets of saponins in Paris polyphylla smith against non-small cell lung cancer. Front Genet. 2022;3123:19.10.3389/fgene.2022.1005896Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X, Li T. miRecords: an integrated resource for microRNA–target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;37(suppl_1):D105–10.10.1093/nar/gkn851Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets – update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;41(D1):D991–5.10.1093/nar/gks1193Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Bao Y, Wang L, Yu F, Yang J, Huang D. Parkinson’s disease gene biomarkers screened by the LASSO and SVM algorithms. Brain Sci. 2023;13(2):175.10.3390/brainsci13020175Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Huang D, Liu J, Cao Y, Wan L, Jiang H, Sun Y, et al. RNA sequencing for gene expression profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with ankylosing spondylitis RNA. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:13.10.1155/2020/5304578Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Jankovic J. Parkinson’s disease and movement disorders: moving forward. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(1):9–11.10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70302-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Association WM. World medical association declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Bull World Health Organ. 2001;79(4):373.Search in Google Scholar
[41] Martuscello RT, Kerridge CA, Chatterjee D, Hartstone WG, Kuo S-H, Sims PA, et al. Gene expression analysis of the cerebellar cortex in essential tremor. Neurosci Lett. 2020;721:134540.10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134540Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Waldner M, Obenauf AC, et al. Spatiotemporal dynamics of intratumoral immune cells reveal the immune landscape in human cancer. Immunity. 2013;39(4):782–95.10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Landmark CJ. Antiepileptic drugs in non-epilepsy disorders: relations between mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy. CNS Drugs. 2008;22:27–47.10.2165/00023210-200822010-00003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[44] Hampel H, Mesulam M-M, Cuello AC, Farlow MR, Giacobini E, Grossberg GT, et al. The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2018;141(7):1917–33.10.1093/brain/awy132Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Antonini A, Moresco R, Gobbo C, De Notaris R, Panzacchi A, Barone P, et al. The status of dopamine nerve terminals in Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor: a PET study with the tracer [11-C] FE-CIT. Neurol Sci. 2001;22:47–8.10.1007/s100720170040Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[46] Bang D, Kishida KT, Lohrenz T, White JP, Laxton AW, Tatter SB, et al. Sub-second dopamine and serotonin signaling in human striatum during perceptual decision-making. Neuron. 2020;108(5):999–1010.e6.10.1016/j.neuron.2020.09.015Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Elble RJ, Higgins C, Elble S. Electrophysiologic transition from physiologic tremor to essential tremor. Mov Disorders: J Mov Disord. 2005;20(8):1038–42.10.1002/mds.20487Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Kavanagh JJ, Keogh JW. Correlates between force and postural tremor in older individuals with essential tremor. Cerebellum. 2016;15:688–95.10.1007/s12311-015-0732-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Louis ED, Huang CC, Dyke JP, Long Z, Dydak U. Neuroimaging studies of essential tremor: how well do these studies support/refute the neurodegenerative hypothesis? Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov. 2014;4:235–44.10.5334/tohm.224Search in Google Scholar
[50] Sharifi S, Nederveen AJ, Booij J, van Rootselaar A-F. Neuroimaging essentials in essential tremor: a systematic review. Neuroimage Clin. 2014;5:217–31.10.1016/j.nicl.2014.05.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Mavroudis I, Petridis F, Kazis D. Neuroimaging and neuropathological findings in essential tremor. Acta Neurol Scand. 2019;139(6):491–6.10.1111/ane.13101Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[52] Louis ED, Vonsattel JPG. The emerging neuropathology of essential tremor. Mov Disord. 2008;23(2):174–82.10.1002/mds.21731Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Louis ED, Yi H, Erickson-Davis C, Vonsattel J-PG, Faust PL. Structural study of Purkinje cell axonal torpedoes in essential tremor. Neurosci Lett. 2009;450(3):287–91.10.1016/j.neulet.2008.11.043Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Louis ED, Faust PL, Vonsattel JPG, Honig LS, Rajput A, Rajput A, et al. Torpedoes in Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, essential tremor, and control brains. J Mov Disord. 2009;24(11):1600–5.10.1002/mds.22567Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Louis ED, Lee M, Babij R, Ma K, Cortes E, Vonsattel J-PG, et al. Reduced Purkinje cell dendritic arborization and loss of dendritic spines in essential tremor. Brain. 2014;137(12):3142–8.10.1093/brain/awu314Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Louis ED, Faust PL, Vonsattel J-PG, Honig LS, Rajput A, Robinson CA, et al. Neuropathological changes in essential tremor: 33 cases compared with 21 controls. Brain. 2007;130(12):3297–307.10.1093/brain/awm266Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[57] Babij R, Lee M, Cortes E, Vonsattel J-PG, Faust PL, Louis ED. Purkinje cell axonal anatomy: quantifying morphometric changes in essential tremor versus control brains. Brain. 2013;136(10):3051–61.10.1093/brain/awt238Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[58] Lee D, Gan S-R, Faust PL, Louis ED, Kuo S-H. Climbing fiber-Purkinje cell synaptic pathology across essential tremor subtypes. Park Relat Disord. 2018;51:24–9.10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.02.032Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Zhang X, Santaniello S. Role of cerebellar GABAergic dysfunctions in the origins of essential tremor. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019;116(27):13592–601.10.1073/pnas.1817689116Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[60] Marin-Lahoz J, Gironell A. Linking essential tremor to the cerebellum: neurochemical evidence. Cerebellum. 2016;15:243–52.10.1007/s12311-015-0735-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] Zhou M, Melin MD, Xu W, Südhof TC. Dysfunction of parvalbumin neurons in the cerebellar nuclei produces an action tremor. J Clin Investig. 2020;130(10):5142–56.10.1172/JCI135802Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[62] Schaefer SM, Vives Rodriguez A, Louis ED. Brain circuits and neurochemical systems in essential tremor: insights into current and future pharmacotherapeutic approaches. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018;18(2):101–10.10.1080/14737175.2018.1413353Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Yu M, Ma K, Faust PL, Honig LS, Cortés E, Vonsattel JP, et al. Increased number of Purkinje cell dendritic swellings in essential tremor. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19(4):625–30.10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03598.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[64] Filippini N, Ebmeier KP, MacIntosh BJ, Trachtenberg AJ, Frisoni GB, Wilcock G, et al. Differential effects of the APOE genotype on brain function across the lifespan. Neuroimage. 2011;54(1):602–10.10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.08.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[65] Saunders A, Schmader K, Breitner J, Benson M, Brown W, Goldfarb L, et al. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet (London, England). 1993;342(8873):710–1.10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-USearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Béliveau E, Tremblay C, Aubry-Lafontaine É, Paris-Robidas S, Delay C, Robinson C, et al. Accumulation of amyloid-β in the cerebellar cortex of essential tremor patients. Neurobiol Dis. 2015;82:397–408.10.1016/j.nbd.2015.07.016Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[67] Wang Z, Qin W, Wei C, Tang Y, Zhao L, Jin H, et al. The microRNA‐1908 up‐regulation in the peripheral blood cells impairs amyloid clearance by targeting ApoE. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2018;33(7):980–6.10.1002/gps.4881Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[68] Keiten-Schmitz J, Schunck K, Müller S. SUMO chains rule on chromatin occupancy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;7:343.10.3389/fcell.2019.00343Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[69] Colnaghi L, Conz A, Russo L, Musi CA, Fioriti L, Borsello T, et al. Neuronal localization of SENP proteins with super resolution microscopy. Brain Sci. 2020;10(11):778.10.3390/brainsci10110778Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[70] Yan S-M, Wu H-N, He F, Hu X-P, Zhang Z-Y, Huang M-Y, et al. High expression of zinc-binding protein-89 predicts decreased survival in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97(6):1966–73.10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.01.058Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[71] Wang N, Li M-Y, Liu Y, Yu J, Ren J, Zheng Z, et al. ZBP-89 negatively regulates self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via suppression of Notch1 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020;472:70–80.10.1016/j.canlet.2019.12.026Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[72] Chandrasekaran S, Bonchev D. Network analysis of human post-mortem microarrays reveals novel genes, microRNAs, and mechanistic scenarios of potential importance in fighting Huntington’s disease. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2016;14:117–30.10.1016/j.csbj.2016.02.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Stevens SJ, van Essen AJ, van Ravenswaaij CM, Elias AF, Haven JA, Lelieveld SH, et al. Truncating de novo mutations in the Krüppel-type zinc-finger gene ZNF148 in patients with corpus callosum defects, developmental delay, short stature, and dysmorphisms. Genome Med. 2016;8:1–10.10.1186/s13073-016-0386-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[74] Edwards TJ, Sherr EH, Barkovich AJ, Richards LJ. Clinical, genetic and imaging findings identify new causes for corpus callosum development syndromes. Brain. 2014;137(6):1579–613.10.1093/brain/awt358Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[75] Liu D, Cao H, Kural KC, Fang Q, Zhang F. Integrative analysis of shared genetic pathogenesis by autism spectrum disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(12):9.10.1042/BSR20191942Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[76] Aisa B, Gil-Bea FJ, Solas M, Garcia-Alloza M, Chen CP, Lai MK, et al. Altered NCAM expression associated with the cholinergic system in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010;20(2):659–68.10.3233/JAD-2010-1398Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[77] Knoferle J, Yoon SY, Walker D, Leung L, Gillespie AK, Tong LM, et al. Apolipoprotein E4 produced in GABAergic interneurons causes learning and memory deficits in mice. J Neurosci Res. 2014;34(42):14069–78.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2281-14.2014Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[78] Huang Y, Mucke L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell. 2012;148(6):1204–22.10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.040Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[79] Fioravante D, Byrne JH. Protein degradation and memory formation. Brain Res Bull. 2011;85(1–2):14–20.10.1016/j.brainresbull.2010.11.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[80] Hirunsatit R, George ED, Lipska BK, Elwafi HM, Sander L, Yrigollen CM, et al. Twenty-one-base-pair insertion polymorphism creates an enhancer element and potentiates SLC6A1 GABA transporter promoter activity. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2009;19(1):53–65.10.1097/FPC.0b013e328318b21aSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Muruzheva ZM, Ivleva IS, Traktirov DS, Zubov AS, Karpenko MN. The relationship between serum interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-8, interleukin-10, tumor necrosis factor-α levels and clinical features in essential tremor. Int J Neurosci. 2022;132(11):1143–9.10.1080/00207454.2020.1865952Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[82] Shi T, Xie J, Xiong Y, Deng W, Guo J, Wang F, et al. Human HS1BP3 induces cell apoptosis and activates AP-1. BMB Rep. 2011;44(6):381–6.10.5483/BMBRep.2011.44.6.381Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[83] Gannushkina I, Zhirnova I, Toropova N, Toporkina T, Markova E. Quantitative evaluation of the T-and B-systems of immunity in various hereditary diseases of the nervous system. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr im SS Korsakova. 1981;81(7):1009–13.Search in Google Scholar
[84] Teijeira A, Garasa S, Ochoa MDC, Cirella A, Olivera I, Glez‐Vaz J, et al. Differential Interleukin‐8 thresholds for chemotaxis and netosis in human neutrophils. Eur J Immunol. 2021;51(9):2274–80.10.1002/eji.202049029Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[85] Giau VV, Wu SY, Jamerlan A, An SSA, Kim S, Hulme J. Gut microbiota and their neuroinflammatory implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Nutrients. 2018;10(11):1765.10.3390/nu10111765Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[86] Kaur G, Behl T, Bungau S, Kumar A, Uddin MS, Mehta V, et al. Dysregulation of the gut–brain axis, dysbiosis and influence of numerous factors on gut microbiota associated Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(2):233–47.10.2174/18756190MTA3fMTUq5Search in Google Scholar
[87] Agirman G, Hsiao EY. SnapShot: the microbiota–gut–brain axis. Cell. 2021;184(9):2524.e1.10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.022Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[88] Tudorache IF, Trusca VG, Gafencu AV. Apolipoprotein E – a multifunctional protein with implications in various pathologies as a result of its structural features. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2017;15:359–65.10.1016/j.csbj.2017.05.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[89] Kockx M, Traini M, Kritharides L. Cell-specific production, secretion, and function of apolipoprotein E. J Mol Med. 2018;96:361–71.10.1007/s00109-018-1632-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[90] Li Q, Liu D, Pan F, Ho CS, Ho R. Ethanol exposure induces microglia activation and neuroinflammation through TLR4 activation and SENP6 modulation in the adolescent rat hippocampus. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:12.10.1155/2019/1648736Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[91] Isogai S, Yamamoto N, Hiramatsu N, Goto Y, Hayashi M, Kondo M, et al. Preparation of induced pluripotent stem cells using human peripheral blood monocytes. Cell Reprogramming. 2018;20(6):347–55.10.1089/cell.2018.0024Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

