Abstract
The integration of deep neural networks and cloud computing has become increasingly prevalent within the domain of medical image processing, facilitated by the recent strides in neural network theory and the advent of the internet of things (IoTs). This juncture has led to the emergence of numerous image segmentation networks and innovative solutions that facilitate medical practitioners in diagnosing lung cancer. Within the contours of this study, we present an end-to-end neural network model, christened as the “semi-residual Multi-resolution Convolutional Neural Network” (semi-residual MCNN), devised to engender precise lung nodule segmentation maps within the milieu of cloud computing. Central to the architecture are three pivotal features, each coalescing to effectuate a notable enhancement in predictive accuracy: the incorporation of semi-residual building blocks, the deployment of group normalization techniques, and the orchestration of multi-resolution output heads. This innovative model is systematically subjected to rigorous training and testing regimes, using the LIDC-IDRI dataset – a widely embraced and accessible repository – comprising a diverse ensemble of 1,018 distinct lung CT images tailored to the realm of lung nodule segmentation.
1 Introduction
Lung disease constitutes a predominant and lamentable cause of mortality in both male and female populations [1]. Noteworthy among these ailments are lung cancer and respiratory infections like COVID-19, which collectively confront significant challenges in the realm of diagnostics. The prognosis of individuals grappling with pulmonary afflictions exhibits a discernible variance contingent upon the disease’s stage at the juncture of diagnosis. For instance, the prognosis for early-stage lung cancer treatment yields remarkably high survival rates. However, as the malaise advances, ushering in metastasis, the survival rates witness a precipitous decline, concomitant with the diminishing efficacy of therapeutic interventions. Regrettably, the symptoms of lung diseases frequently remain latent until an advanced disease stage has been reached. Furthermore, the symptomatic manifestations of lung cancer are frequently misconstrued, with patients often attributing them to long-term smoking consequences, thereby exacerbating diagnostic delays. It is against this backdrop that early screening for lung nodules emerges as a preeminent prophylactic strategy in the combat against lung cancer [2].
Lung nodules, minute external structures within the lung characterized by diameters spanning 3–30 mm, present a formidable challenge in detection due to their diminutive size. Their identification is compounded by their morphological resemblance to non-nodular structures, thus engendering ambiguity [3]. Traditional computer vision algorithms have historically grappled with the distinction between lung nodules and other pulmonary structures, necessitating an extensive reliance on the clinical acumen of radiologists for the early-stage diagnosis of lung cancer. The advent of deep learning, marked by recent advancements, has catalyzed the ascendancy of neural networks in the arenas of lung nodule detection, classification, and segmentation. It is imperative to underscore the pivotal nature of investigating image segmentation methodologies tailored explicitly for lung nodules. Given the inherent intricacies and intricacies of medical imaging, particularly underscored by the prevalent imbalances between nodule and non-nodule samples, the associated learning tasks and their application contexts impose rigorous demands upon the precision and interpretability of deep learning techniques.
Conventional techniques for image classification and detection predominantly yield generalized insights, encompassing aspects such as tumor location and typology. However, they regrettably fall short in furnishing the requisite granularity and precision sought in medical diagnoses. In stark contrast, segmentation methodologies have the potential to furnish pixel-level predictive maps, thereby endowing medical practitioners with the capacity to minutely scrutinize attributes such as precise location, shape, dimensions, and the numerical prevalence of potential lung nodules. Such pixel-level insights form a robust foundational bedrock for the identification and assessment of risk and malignancy associated with each distinct pulmonary tumor.
A pioneering milestone in harnessing neural networks for image segmentation was achieved through the advent of Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN) [4]. Within this paradigm, the neural network is imbued with the transformative capacity to process the original image. The process begins with the computation of a feature map, which is subtly scaled in size through a sequence of convolutional operations and sequential downsampling layers. This preliminary computation engenders a critical substrate. Subsequently, the network embarks on the discrete prediction of classification outcomes for each individual pixel nestled within the feature map. This orchestration culminates in the synthesis of a high-level heatmap, emblematic of the synthesized spatial organization of the target entities.
Expanding upon the bedrock established by FCN, the U-Net architecture introduces a novel interpretative layer, effecting a pivotal augmentation [5]. Herein, an expansive decoder pathway is ingeniously woven into the framework. The purpose of this decoder trajectory is to accurately remap the downsampled feature map, resulting in the generation of an improved heatmap. This heatmap, hewn from the encoded dimensions, duly proffers a segmentation map – a visual artifact that faithfully preserves the resolution of the source image. Functionally, the encoder trajectory of U-Net embraces the mantle of feature extraction, nurturing the discernment of salient attributes. Conversely, the decoder pathway is tasked with the precise localization of feature points, culminating in a masterful restoration of the original spatial resolution. Notably, this duality of functional trajectories imparts a symmetrical disposition, coalescing into a silhouette that evocatively mirrors a “U” shape.
U-Net’s efficacy in diverse image segmentation scenarios has yielded a progeny of variants. Notable among these are Residual U-Net, U-Net++, Bi-Directional ConvLSTM U-Net (BCDU-Net), and Attention U-Net [6,7,8,9]. Residual U-Net innovatively incorporates residual connections to mitigate network degradation. U-Net++, a departure from the norm, redesigns skip pathways to enhance model robustness through cross-convolutional information fusion. BCDU-Net introduces LSTM modules to foster efficient feature propagation, enhancing the coupling of encoder and decoder outputs. Attention U-Net employs an attention mechanism to refine focus on salient regions, suppressing inconsequential backgrounds. These U-Net variants optimize distinct components, consistently yielding improved segmentation outcomes across varied image segmentation tasks.
Efforts to cross-pollinate from disparate deep learning domains into image segmentation have yielded noteworthy results. Mask R-CNN, a consequential two-stage object segmentation network, extends Faster R-CNN via a novel branch dedicated to target mask prediction [10,11]. This technique finds utility in scenarios where computational resources are sufficient for tackling minuscule targets. UNETR leverages the Vision Transformer concept within the U-Net framework, harnessing multiple transformers in the encoder to augment global context and spatial dependency learning [12]. However, despite their triumphs, a salient limitation resides in their reliance on single final outputs for model training. Deeper layer feature outputs remain underutilized, potentially impacting convergence efficiency and ultimate training outcomes.
In the year 2020, a comprehensive neural architecture denominated as the multi-resolution convolutional neural network (MCNN) surfaced, uniquely tailored to address diverse image-to-image inverse predicaments [13]. The fundamental tenet underpinning MCNN resides in its ingenious incorporation of multiple branches within concealed strata of the neural network structure, thereby engendering predictions at varying resolutions. This pioneering design philosophy has found extensive validation across a gamut of computational challenges, spanning domains such as image super-resolution, denoising, and phase retrieval. Empirical evaluation has evidenced the substantial augmentation in model training stability, coupled with the triumphant outperformance vis-à-vis an array of state-of-the-art methodologies across each respective domain.
While MCNN inherently bears semblance to the U-Net paradigm, a discernible departure is underscored by MCNN’s augmentation via the integration of multiple branches into the decoder architecture [13]. These branches intertwine with supplementary convolutional layers, thereby furnishing auxiliary outputs encapsulating distinct resolutions. The crux of the loss function transpires in the comprehensive juxtaposition of outputs and annotation maps spanning the spectrum of resolutions, a departure from the conventional approach of isolating the final output solely at the original resolution.
It warrants acknowledgment that although MCNN’s original intent did not encompass image segmentation undertakings, the striking parallels it shares with U-Net tantalizingly beckon its potential application in the realm of lung nodule segmentation. The inherent architectural blueprint of MCNN conveys an inherent propensity to acquire insights from diverse resolutions, manifesting as an asset particularly germane to tasks such as lung nodule segmentation. In the context of datasets characterized by a pronounced imbalance between positive and negative samples, the adoption of MCNN’s architectural paradigm emerges as a strategic overture, catalyzing swift and incisive approximations of nodule localization at a macroscopic level. Subsequent network strata delve deeper into the finer intricacies of nodule boundaries at a pixel-level, culminating in a cascading refinement.
Notably, the incorporation of multi-resolution branches within the U-Net architecture mandates only a marginal augmentation of computational resources [13]. This conveys the salient advantage of imperceptibly infusing the utilization of multi-resolution output heads without obfuscating the original usage scenarios of the U-Net paradigm.
Presently, the broader landscape of scholarship has largely remained reticent concerning the potential integration of MCNN into the ambit of lung nodule segmentation [13]. In response, this research endeavor aspires to bridge this void, contemplating the viability of this application. Drawing inspiration from a medley of U-Net variants, this inquiry sets forth the ambitious objective of conceiving a model solution that bears the hallmark of reusability. The ultimate ambition is succinctly encapsulated within the twin imperatives of heightening the precision and efficiency of automated lung nodule segmentation across authentic, real-world datasets.
2 Methodology and model structure
This section expounds upon the comprehensive procedure employed for the construction of the lung nodule segmentation model through the innovative semi-residual MCNN method. The endeavor unfolds through distinct phases, meticulously delineated within the ensuing subsections.
2.1 Dataset and pre-processing
Adherence to the pertinent regulations underscores every facet of the experimental endeavors undertaken in this project. The foundational cornerstone of this investigation resides within the Lung Image Database Consortium and Image Database Resource Initiative (LIDC-IDRI) Dataset, an open repository generously endowed with the prerogative of browsing, downloading, and deployment for commercial, scientific, and pedagogical pursuits, all under the umbrella of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License. Gratitude is extended to the National Cancer Institute and the National Institutes of Health Foundation, whose collaborative contributions have engendered this freely accessible database [14].
The LIDC-IDRI dataset contains 1,018 CT images from 1,010 patients, annotated by 4 experienced chest radiologists. The data in this dataset were obtained from seven different academic institutions, using different scanners and their parameters, thus ensuring a wide distribution of data. In this project, we examined nodules that were annotated by all four radiologists and were at least 3 mm in diameter, following previous studies [15,16]. To construct each CT scan’s ground truth segmentation map, a 50% consensus criteria was applied for each annotated nodule.
The LIDC-IDRI dataset was chosen to train and evaluate the model for this experiment because it has a large amount of data and high-quality annotations. Among 1,018 CT images in this dataset, 200 images between LIDC-IDRI-0730 and LIDC-IDRI-0951 were randomly selected as the test set and 540 images from the remaining dataset were randomly selected as the training and validation sets. These images are randomly shuffled, and 390 of them are assigned to the training set, while the remaining 150 images are assigned to the validation set. The data splitting approach aims to distinguish the data distribution of the test set data from that of the training and validation sets, thus better reflecting the model’s ability to predict random data samples in the real world.
All raw CT images have the size of 512 × 512 × Z, where Z varies as the slice thickness of each CT image changes. However, the designed input size of this model is 256 × 256 × 32, and it is essential to resize and crop the original image to fit the model. The data pre-processing procedures are as follows:
Reduce the image to half its original size in X-Y directions. The resized image has a size of 256 × 256 × Z.
Iterate over every slice of the image and compare it with its corresponding annotation map. If the slice contains a nodule sample, keep the slice in the image. Otherwise, discard this slice. The shape of the image becomes 256 × 256 × Z′.
If Z′ is smaller than 32, take additional subsequent non-nodule slices to make complete volume data.
Randomly sample one or several 256 × 256 × 32 image blocks from the processed image. Add these sampled images to the training or validation set.
An overview of the aforementioned methods is depicted in Figure 1. In comparison to conventional techniques that solely extract data from the vicinity of nodules, the method of this experiment aims to preserve extensive global information. This encourages the model to undertake not only the fundamental segmentation task but also to identify nodule targets that might be merely tens of pixels in size, originating from the original image that encompasses millions of pixels. This situation presents a challenge to the model’s capacity for detecting small targets.
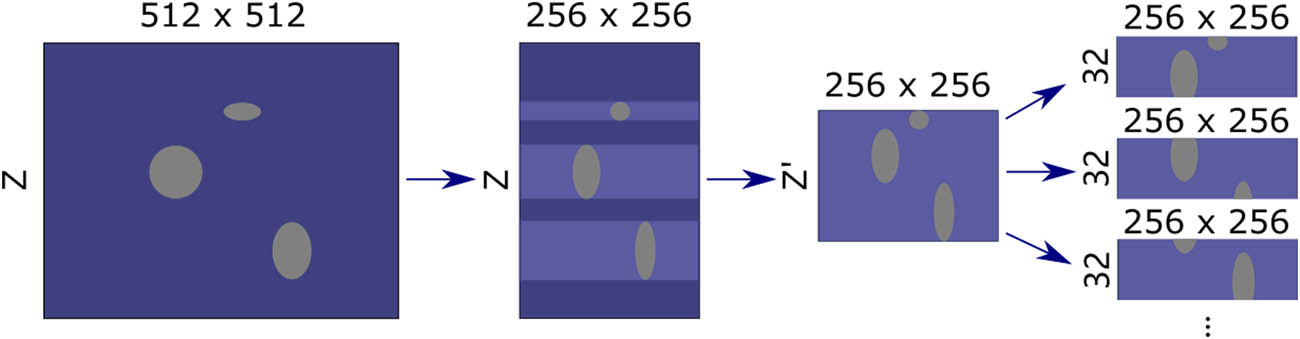
Overview of image crop and resize methods. The horizontal direction corresponds to the x and y axes and the vertical direction corresponds to the z axis. Purple color indicates non-nodule regions and gray color indicates nodule regions.
Furthermore, by exclusively retaining the data layers containing at least one nodule pixel, the density of positive samples is enhanced without compromising the global information. This, in turn, mitigates the issue of substantial imbalance between positive and negative samples and reduces the complexity associated with model training.
In a raw CT image, the pixel values are quantified using the Hounsfield Unit (HU), a measurement of radiation absorption and attenuation within tissues [17]. Following established research conventions, those pixels with HU values ranging from –1000 to 600 were solely retained. This filtration process eliminates elements like water, air, and body tissues that lack relevance to the current project. Subsequently, the filtered region is normalized to a range of 0–1 through the utilization of the following function:
where
To enable the network’s training with multi-resolution outputs, low-resolution annotations are generated through an iterative resizing procedure applied to the original annotated segmentation map, utilizing a reduction factor of 0.5. Figure 2 provides an illustrative depiction of the resulting pre-processed data across various resolution scales.

An example of multi-resolution image and annotations to train on MCNN. Only one slice of 3-dimensional image and annotation is shown per resolution scale.
Data augmentation techniques, such as geometric and pixel transformations applied to raw data, have been proven effective in augmenting data volume and preventing overfitting. Nonetheless, in the context of our dataset, these methods do not yield substantial benefits. The inherent complexity of the original data and the potential for these techniques to introduce noise to training samples typically result in suboptimal training outcomes. Therefore, only random image flips were used on either x-axis or y-axis.
2.2 Training device
Training neural networks on three-dimensional images demands substantial computing power, and the utilization of a capable GPU significantly enhances the efficiency of network computations. For this project, the execution took place on an online server equipped with 6 Intel® Xeon® Gold 6142 CPU and an NVIDIA® RTX 3090 graphics card featuring 25.4 GB of graphic memory.
2.3 Model structure
Every blue box in the visualization represents a multi-channel feature map, with the number of channels indicated at the top of each box. The dimensions in the x-y-z axes are presented on the lower left edge of the initial box within each resolution. Gray boxes signify duplicated feature maps, while arrows delineate distinct operations.
In this project, a custom architecture named the semi-residual MCNN, visually represented in Figure 3, was devised. The architecture encompasses both a contracting and an expansive path. The contracting path functions as an encoder, extracting features from the original image. On the other hand, the expansive path serves as a decoder, mapping these derived features back to the original image and generating output segmentation maps across various resolution scales. The core components of the model are semi-residual building blocks.

Overview of semi-residual MCNN architecture.
Each semi-residual building block comprises three consecutive 3 × 3 convolutions, each accompanied by a Group normalization (GN) layer and a ReLU activation. Notably, a skip connection path is introduced between alternate convolutional layers within each block. The initial building block in the contracting path is somewhat simplified for enhanced computational efficiency. Moreover, within the contracting path, a 2 × 2 max-pooling operation is inserted between neighboring semi-residual building blocks at each step. Conversely, the expansive path incorporates a 2 × 2 up-convolutional layer in every step, halving the channel count, and involves concatenation with the corresponding feature map from the contracting path.
Crucially, the expansive path links to four output heads through the feature map. Each of these output heads encompasses one or more 3 × 3 Convolution + GN + ReLU intermediate layers, culminating in an output convolutional layer. Ultimately, these output heads generate segmentation maps at distinct resolution scales.
2.4 Loss and metrics
Drawing inspiration from other cutting-edge image segmentation networks, the classic binary cross-entropy loss (BCEloss) have been adopted to train networks [18]. In essence, binary cross-entropy evaluates each predicted probability against the corresponding actual class outcome, which can assume values of either 0 or 1. It subsequently calculates a score that penalizes probabilities according to their deviation from the predicted value. The mathematical expression for BCEloss is as follows:
where y i indicates the real value of each pixel and p(y i ) indicates its predicted value.
In terms of evaluation metrics, the dice coefficient is used as the main metric to evaluate the quality of model prediction outcomes. The dice coefficient, also known as the Sørensen–Dice index, is a statistical tool that evaluates the similarity between two sets of data [19]. The General formula of the dice coefficient is as follows:
The dice coefficient strikes a balance between false negative and false positive samples, contributing to an overall measure of similarity. This attribute makes it particularly adept at evaluating lung nodule segmentation results, as it disregards true negative samples. In this experiment, the dice coefficient is employed to assess the prediction outcomes of both the validation and test sets, providing insights into prediction quality for both scenarios.
Furthermore, precision and recall are incorporated as supplementary metrics, offering assessments of a model’s direct costs and opportunity costs, respectively. The formulas for these metrics are as follows:
2.5 Optimization techniques
The learning rate stands out as a pivotal hyper-parameter in the training process, exerting a profound impact on the training outcome. Its selection warrants meticulous consideration. An effective approach to learning rate management involves initiating with a higher value to swiftly navigate the vicinity of a minimum region. Subsequently, a gradual decay towards a smaller value aid in pinpointing the local minimum point. This strategy contributes to optimizing the model’s convergence and overall performance.
Concerning this strategy, the step decay method was chosen as the learning rate scheduler in this project, with an initial learning rate equal to 2 × 10−4 and decay by a factor of 0.6 every 25 epochs [20]. According to experimental result, the network converges as the training process continues, where the learning rate gradually drops to 7.25 × 10−7.
In terms of the optimizer, Adam was chosen in this project with the default exponential decay rate factors of β 1 = 0.9 and β 2 = 0.999. Compared with another commonly used optimizer, SGD with momentum, Adam generally enables the model to converge faster and leads to better prediction results [16,21].
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Results
Data distribution in the test set is described in Table 1. Out of 200 images in the test set, 103 contain at least one nodule pixel, while the remaining 97 images contain no nodule pixels at all. All test set images with at least one positive pixel are split into three categories based on the density of nodule pixels. To be more specific, images with a ratio between nodule and non-nodule pixels smaller than 5 × 10−6 fall in the category SPARSE, images with a ratio between 5 × 10−6 and 2 × 10−5 falls into the category MODERATE, and those with a ratio greater than 2 × 10−5 falls in the category DENSE. The amount of data that fall in each category is shown in Table 1.
Data distribution in the test set
| Total images | SPARSE | MODERATE | DENSE | Fully negative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 34 | 31 | 38 | 97 |
In this study, seven models were set up to compare performance with our method and other state-of-the-art approaches. These models are basic MCNN, residual MCNN, semi-residual U-Net, semi-residual MCNN (the solution of this experiment), semi-residual MCNN with squeeze-and-excitation modules, semi-residual MCNN without GN, and 3D Recurrent DenseUNet (proposed in 2020, achieved state-of-the-art performance on another similar lung nodule segmentation dataset named NSCLC) [22].
Dice coefficients, precision, and recall are evaluated on the test set with at least one nodule pixel, while the percentage of correct prediction and average false positive pixels per image are evaluated on the test set with non-nodule pixels only.
Tables 2 and 3 summarize the lung nodule segmentation performance of each method, and Figure 4 shows a visualized example of a good prediction result using semi-residual MCNN.
Results on the test set with at least one positive pixel
| Model type | Dice_sparse | Dice_moderate | Dice_dense | Dice_average | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic MCNN | 0.2302 | 0.4824 | 0.5942 | 0.4380 | 0.8091 | 0.4277 |
| Residual MCNN | 0.2250 | 0.4736 | 0.5248 | 0.4080 | 0.7550 | 0.3781 |
| Semi-residual U-Net | 0.1692 | 0.4258 | 0.5001 | 0.3660 | 0.7610 | 0.3618 |
| Semi-ResMCNN (SE) | 0.1578 | 0.3672 | 0.5274 | 0.3397 | 0.8845 | 0.3055 |
| Semi-ResMCNN (NO GN) | 0.0378 | 0.0984 | 0.2750 | 0.1436 | N/A | N/A |
| Semi-residual MCNN | 0.2484 | 0.4767 | 0.6011 | 0.4479 | 0.7962 | 0.4391 |
| Recurrent DenseNet | 0.2800 | 0.4627 | 0.5437 | 0.4204 | N/A | N/A |
Results on the test set with no positive pixels
| Model type | Correct rate | Average FP per image |
|---|---|---|
| Basic MCNN | 0.6907 | 51.59 |
| Residual MCNN | 0.6701 | 31.30 |
| Semi-residual U-Net | 0.6598 | 39.41 |
| Semi-residual MCNN (SE) | 0.7528 | 13.60 |
| Semi-residual MCNN (NO GN) | 0.4226 | 246.7 |
| Semi-residual MCNN | 0.6701 | 36.68 |
| Recurrent DenseNet | 0.3505 | N/A |

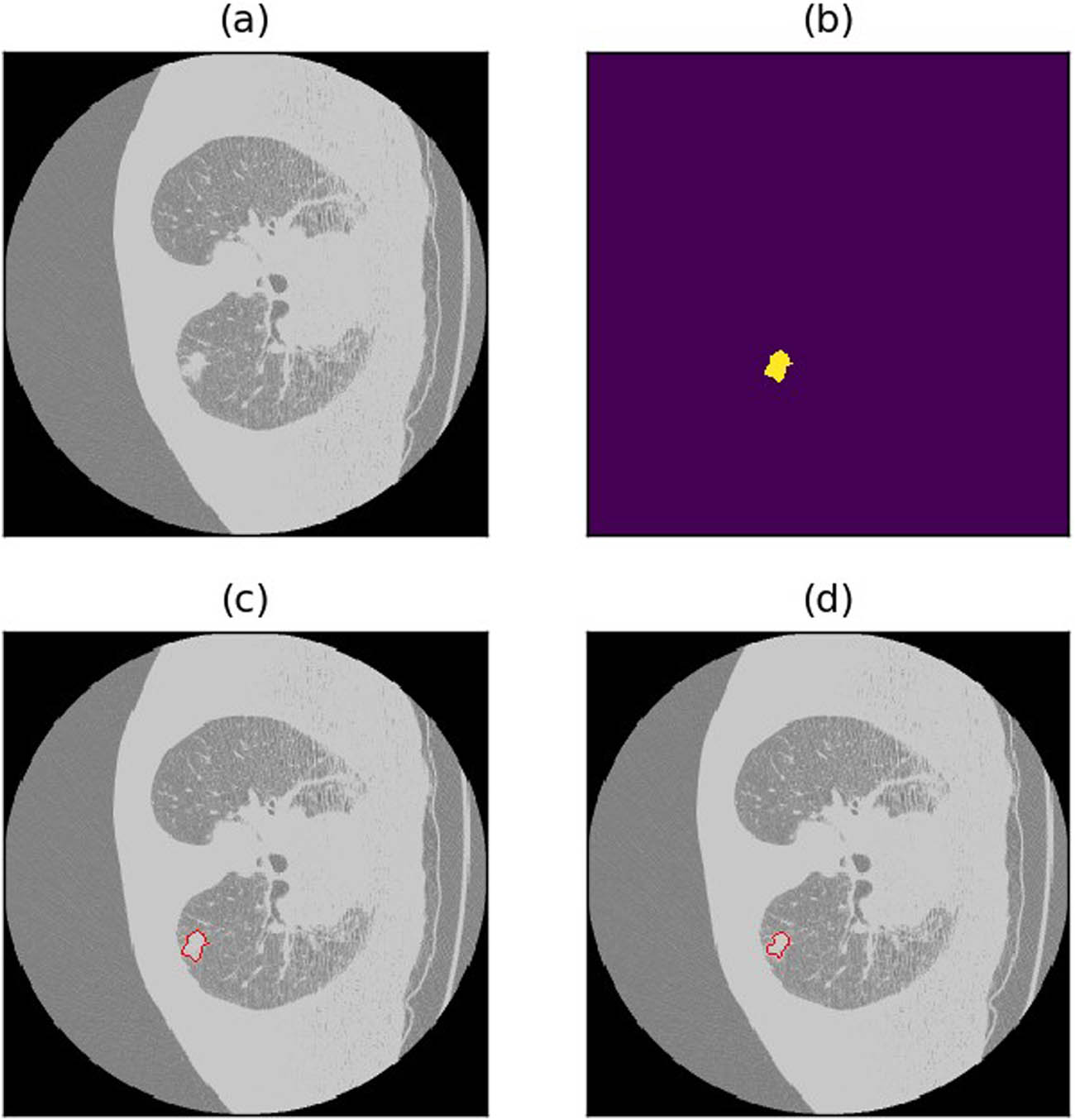
Result visualization of patient LIDC_IDRI_0785. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations. (c) Annotated image. (d) Raw image annotated with predicted result.
According to the results above, semi-residual MCNN achieved average dice coefficients of 0.4479, which is the highest among methods. A few significant observations are as follows:
The incorporation of GN and multi-resolution output head modules yields a substantial enhancement in the comprehensive performance of network.
Out of the basic MCNN, semi-residual MCNN, and residual MCNN architectures, it is evident that the semi-residual MCNN achieves the most superior performance. This outcome underscores the advantageous impact of employing semi-residual building blocks in achieving enhanced performance.
In nearly all network configurations, a notable trend emerged wherein precision attained exceptionally high values, while recall remained relatively low. This observation indicates that instances of missed detection are significantly more probable than instances of misdetection across all cases.
In scenarios involving images devoid of positive pixels, the semi-residual MCNN exhibits superior performance compared to Semi-ResMCNN (NO GN) and Recurrent DenseNet. However, its performance remains comparable to that of other employed methods.
Broadly, the superiority of semi-residual MCNN over other methods can be attributed to three pivotal components: the semi-residual building block, GN, and multi-resolution output heads. A comprehensive breakdown of each of these components is provided in the subsequent sections for detailed analysis.
3.2 Component analysis
3.2.1 Semi-residual U-Net building block
Earlier studies have highlighted that the incorporation of residual connections can alleviate the problem of network degradation [23]. Nevertheless, based on experimental findings, it remains beneficial to retain certain basic convolutional units within the network. This ensures that feature maps are comprehensively utilized before advancing to subsequent layers. In light of this consideration, we introduce semi-residual building blocks to network. These building blocks are structured by integrating residual connections that bypass two convolutional units, while maintaining one unskippable unit within each building block. This strategic arrangement effectively balances the utilization of feature maps while harnessing the advantages of residual connections.
Figures 5 and 6 provide a comparative analysis of the internal structures of various types of building blocks. The key distinction between a semi-residual U-Net block and a residual U-Net block lies in the residual connection setup. In the case of a semi-residual U-Net block, the residual connection skips over 2 out of the 3 convolutional units within the block. Conversely, a residual U-Net block employs a residual connection that bypasses all convolutional units. Employing semi-residual U-Net blocks offers a significant advantage. Under extreme conditions where parameters of convolutional layers along the skip connection path become zero, a standard convolutional operation remains operative for data processing at every resolution scale. This strategic design ensures that essential feature extraction operations are consistently performed while leveraging residual connections to avert network degradation. As a result, a more balanced training approach is achieved compared to residual U-Net blocks. It is worth noting that a U-Net block, distinct from the aforementioned designs, lacks residual connections and incorporates a shallower structure. This mitigates network degradation concerns while maintaining effective performance.

Comparison between the structure of semi-residual U-Net block, residual U-Net block, and U-Net block in the encoder section.

Comparison between the structure of semi-residual U-Net block, residual U-Net block, and U-Net block in the decoder section.
Table 4 presents the outcomes of experiments on the training, validation, and test sets using models constructed with U-Net blocks, residual U-Net blocks, and semi-residual U-Net blocks, respectively. Notably, several key observations emerge from these results. First, the model employing U-Net building blocks exhibits the least favorable performance on the training set, marked by the lowest training loss and training dice coefficient among the three networks. This suggests that the U-Net block model is encountering underfitting issues, failing to adequately capture the complexity of the training data. On the other hand, the model integrating semi-residual building blocks demonstrates marginally improved outcomes, not only on the training set but also across the validation and test sets compared to the U-Net block model. This indicates that the semi-residual U-Net block model has a better ability to generalize beyond the training data, avoiding significant underfitting concerns. Interestingly, the residual U-Net block model showcases the most effective fit to the training set, evident from superior training outcomes. However, this strength translates to poorer results in terms of validation loss and test dice coefficient. This discrepancy indicates that the residual U-Net block model is grappling with overfitting, as it exhibits excessive adaptation to the training data at the expense of generalization. In summation, these findings underscore the advantages of the semi-residual U-Net block model, which achieves a balance between fitting the training data and generalizing to new, unseen data.
Optimal results comparison between models built with U-Net blocks, residual U-Net blocks, and semi-residual U-Net blocks over 300 epochs
| Block type | train_loss | train_dice | val_loss | val_dice | test_dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U-Net | 1.55 × 10−5 | 0.6539 | 5.97 × 10−5 | 0.4515 | 0.4380 |
| Residual U-Net | 1.17 × 10−5 | 0.6722 | 8.50 × 10−5 | 0.4622 | 0.4080 |
| Semi Residual U-Net | 1.50 × 10−5 | 0.669 | 4.19 × 10−5 | 0.4553 | 0.4479 |
3.2.2 GN
Batch normalization (BN) is a common and useful method in training networks to improve training stability and efficiency [24]. However, one disadvantage of using BN is that when the batch size is small, the standard deviation is likely to be very tiny within the mini-batch, resulting in numerical instability in normalization. This issue becomes evident in 3D image segmentation tasks, as a substantial amount of memory is required to store high-dimensional training data. In practice, the maximum batch size that NVIDIA RTX 3090 GPU could accommodate is only 2, which is very likely to result in numerical instability during training.
Layer normalization (LN) is an alternative normalization method that bypasses the issue of batch size [25]. Instead of BN normalizing each mini-batch, LN normalizes each data across all channels for every single image in a mini-batch. In this case, all spatial information for each image is preserved. Most of the extracted key features are retained in the normalization process and lead to better training outcomes than BN.
However, normalizing the whole input layer could be computationally expensive for three-dimensional inputs. Thus, GN was proposed as a generalized method of LN by selecting a few groups for each normalization to be computed along with the layer [26]. It is worth mentioning that when there is only one group, GN becomes LN. When the number of groups equals the number of channels, GN becomes instance normalization (IN), where information between channels is not considered [27]. In general, GN leads to better training results and improved computational efficiency compared to LN and IN. A good explanation is that GN allows different distributions to be learned for each group of channels, which is a regularization method to improve the model’s generalization capability.
Illustrated in both Figures 5 and 6 within the preceding subsection, GN is implemented following each convolutional operation. The group size for each GN layer has been chosen as a hyperparameter to fine-tune during training endeavors. Notably, both group sizes of 4 and 8 have resulted in optimal prediction outcomes for the model. A comparison of experimental results is detailed in Table 5.
Optimal result comparison between models built with GN and without GN
| Model type | Train loss | Train dice | Val loss | Val dice | Test dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without GN | 1.64 × 10−5 | 0.6331 | 3.11 × 10−4 | 0.3785 | 0.1436 |
| With GN | 1.50 × 10−5 | 0.669 | 4.19 × 10−5 | 0.4553 | 0.4479 |
It is evident that GN plays a pivotal role in two crucial aspects: enhancing the model’s convergence on the training set and effectively regularizing the model to achieve a superior fit on both the validation and test sets. In terms of dice coefficients on the validation set, Figure 7 presents a comparison of the curves over 300 epochs between a model without GN and one with GN during the training phase. It is evident that the model without GN encounters challenges in optimization after 100 epochs, whereas the model with GN exhibits steady convergence and ultimately outperforms the GN-absent counterpart significantly.
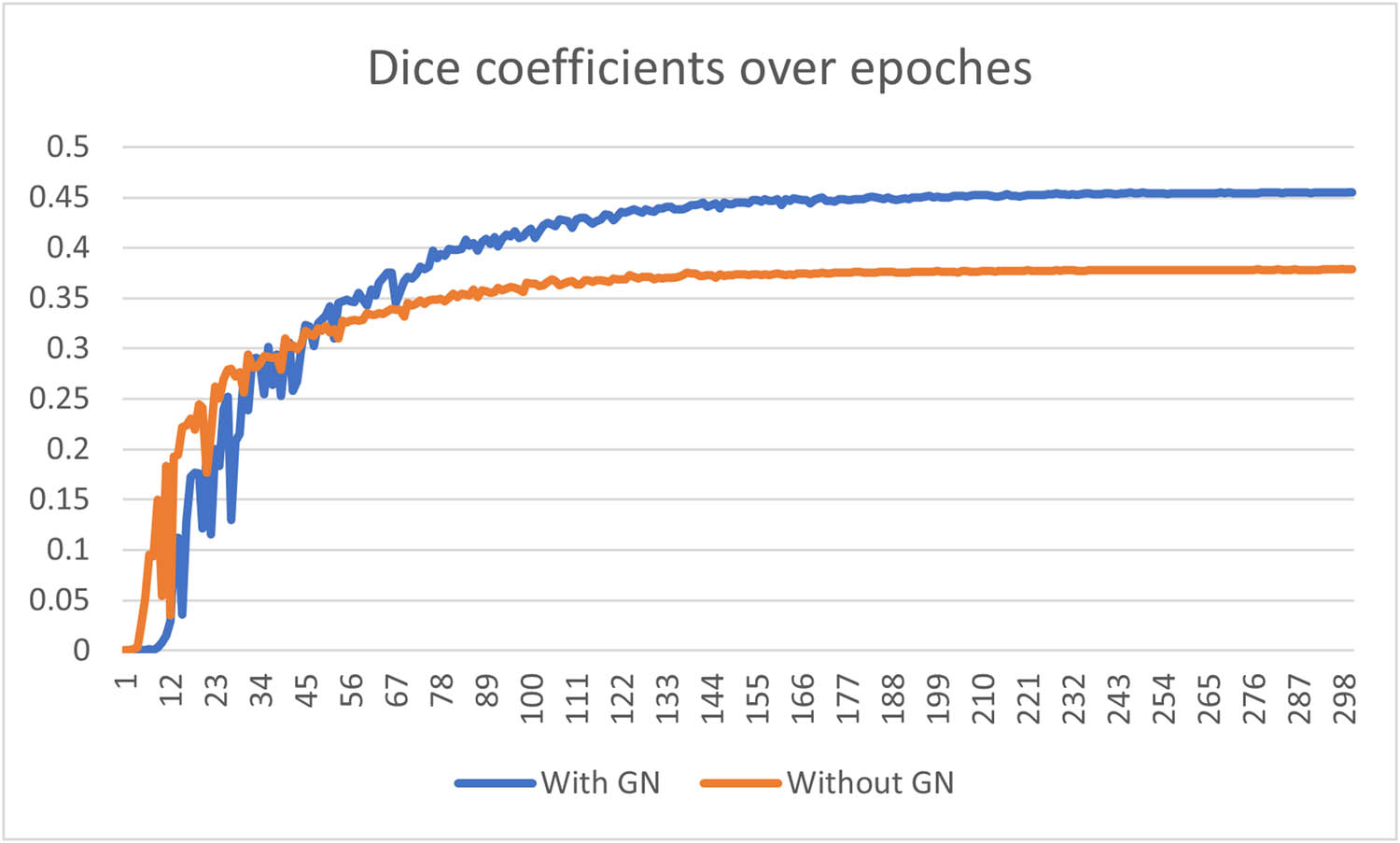
Comparison of dice coefficient on the validation set over epochs between the semi-residual MCNN with GN and the semi-residual MCNN without GN.
Furthermore, when the training was conducted using BN, a distinctive pattern was noted, i.e., while the training loss and dice coefficient converge, the validation loss escalates substantially, and the validation dice coefficient nears zero. This observation serves as confirmation that BN is unsuitable as a normalization method in scenarios where the batch size is minimal.
3.2.3 Multi-resolution output heads
As shown in the structure overview of semi-residual MCNN in Figure 3, four multi-resolution output heads are added to the generated feature maps from the decoder at each resolution scale. For each multiresolution head, several convolutional layers are introduced before the final output convolutional layer for smoothing and refinement purposes. The resolution of these output segmentation maps is 4 × 32 × 32, 8 × 64 × 64, 16 × 128 × 128, and 32 × 256 × 256, respectively. Only the head with outputs having the same resolution as the input images is considered a main output path, while the remaining three low-resolution heads are considered auxiliary output paths.
The following formula computes the training loss:
where L mean is the BCEloss of the main output, L aux_n is the BCEloss of the nth auxiliary output, and α is a coefficient starting from 0.4, decaying by a factor of 0.8 every 25 epochs.
The rationale behind introducing a penalty to the auxiliary loss stems from the fundamental principle that the main output remains the primary task, whereas auxiliary outputs are auxiliary in nature, aiding the model in grasping low-level features. These auxiliary outputs do not take precedence. As the model progressively converges, this factor should gradually decrease, empowering the model to center its attention on refining based on the ultimate output. Notably, during the validation and testing phases, auxiliary outputs are disregarded. Consequently, the loss function for the network in these stages effectively reduces to the BCELoss solely for the main output.
As illustrated in Figure 8 and corroborated by Table 6, the utilization of multi-resolution output heads has yielded a substantial enhancement in model performance across nearly all metrics. Focusing on the dice coefficient curve, both the model featuring multi-resolution outputs and the model devoid of such outputs exhibit comparable validation outcomes during the initial 100 epochs. However, subsequent to this point, the model lacking multi-resolution output heads encounters challenges in achieving convergence. In contrast, the model incorporating multi-resolution output heads demonstrates a gradual yet consistent convergence, ultimately attaining a superior final outcome.

Comparison of dice coefficient of the validation set over epochs between the model with multi-resolution output heads and the model without multi-resolution output heads.
Optimal result comparison between models built with multi-resolution output heads and without multi-resolution output heads over 300 epochs
| Model type | train_loss | train_dice | val_loss | val_dice | test_dice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without multi-head | 1.91 × 10−5 | 0.6377 | 4.13 × 10−5 | 0.4398 | 0.3660 |
| With multi-head | 1.50 × 10−5 | 0.669 | 4.19 × 10−5 | 0.4553 | 0.4479 |
Turning attention to the model’s performance on the test set, the incorporation of multi-resolution output heads has yielded a noteworthy improvement. The dice coefficient on the test set has escalated from 0.3660 to 0.4479, marking a substantial increase of 22.4%. This reinforcement highlights the tangible advantage of integrating multi-resolution output heads in elevating the model’s efficacy.
The rationale behind the efficacy of auxiliary outputs lies in their ability to activate hidden layers and facilitate improved gradient propagation within the networks. When a deep neural network is trained without auxiliary outputs, the optimization and evaluation of parameters within the network’s low-level features rely solely on other higher-level network layers. This process can potentially trigger network degradation and gradient vanishing issues due to the intricate and lengthy sequence of computations involved.
Furthermore, this approach can lead to a situation where the outputs of low-level hidden layers become inconsequential to the primary task. In such cases, since all parameters in the hidden layers exclusively contribute to the final outcomes, the low-level convolutional layers may struggle to extract pertinent features that directly align with the ultimate objective without direct supervision.
The integration of auxiliary outputs serves to alleviate these two concerns. By introducing auxiliary outputs, low-level features attain meaningful significance, and the pathways between hidden layers and output layers are truncated [28]. This configuration not only imparts significance to low-level features but also shortens the paths between different layers, mitigating the issues of network degradation, gradient vanishing, and the diminishing relevance of low-level hidden layers in the network’s learning process.
In the context of MCNN within this specific scenario, the overarching objective of employing a decoder lies in effectively pinpointing and localizing the feature information that has been extracted by the encoder. The integration of auxiliary output paths further serves to guide the model’s attention towards learning parameters that yield enhanced outcomes at each distinct resolution scale.
As the network delves deeper into its architecture, the model’s emphasis gradually shifts towards fine-tuning prediction boundaries and intricate features. This approach holds the potential to deter unnecessary pixel-level sprawl and, in turn, amplifies the efficiency of parameter utilization. The interplay between encoder and decoder, along with the introduction of auxiliary outputs, facilitates a more refined and strategic learning process, ultimately contributing to heightened model performance and more effective utilization of parameters.
3.3 Bad case analysis
A dice loss of 0.4479 still falls short of meeting the accuracy threshold required for real-world applications. In this section, an analysis of potential scenarios where the model’s predictions fall short through visual observations was conducted. This examination offers insights that guide subsequent optimization efforts for the semi-residual MCNN. Several prevalent types of suboptimal cases include:
Missed detection due to lung nodules being in close proximity to the lung margins or other lung tissue. This challenge can arise for both large and smaller nodules (refer to Figures 11–13 for visual examples).
Misdetection and missed detection instances emerge due to the model’s incapacity to differentiate between normal lung tissue and lung nodules (see Figure 14 for an illustrative example).
Missed detection of diminutive nodules is prevalent. The likelihood of such missed detection rises notably when candidate nodules are exceedingly small (refer to Figure 15 for a visual example).
Example of shrunk borders. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.

Example of shrunk borders. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
Example of missed detection due to lung nodules too close to the lung margins or other lung tissues. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
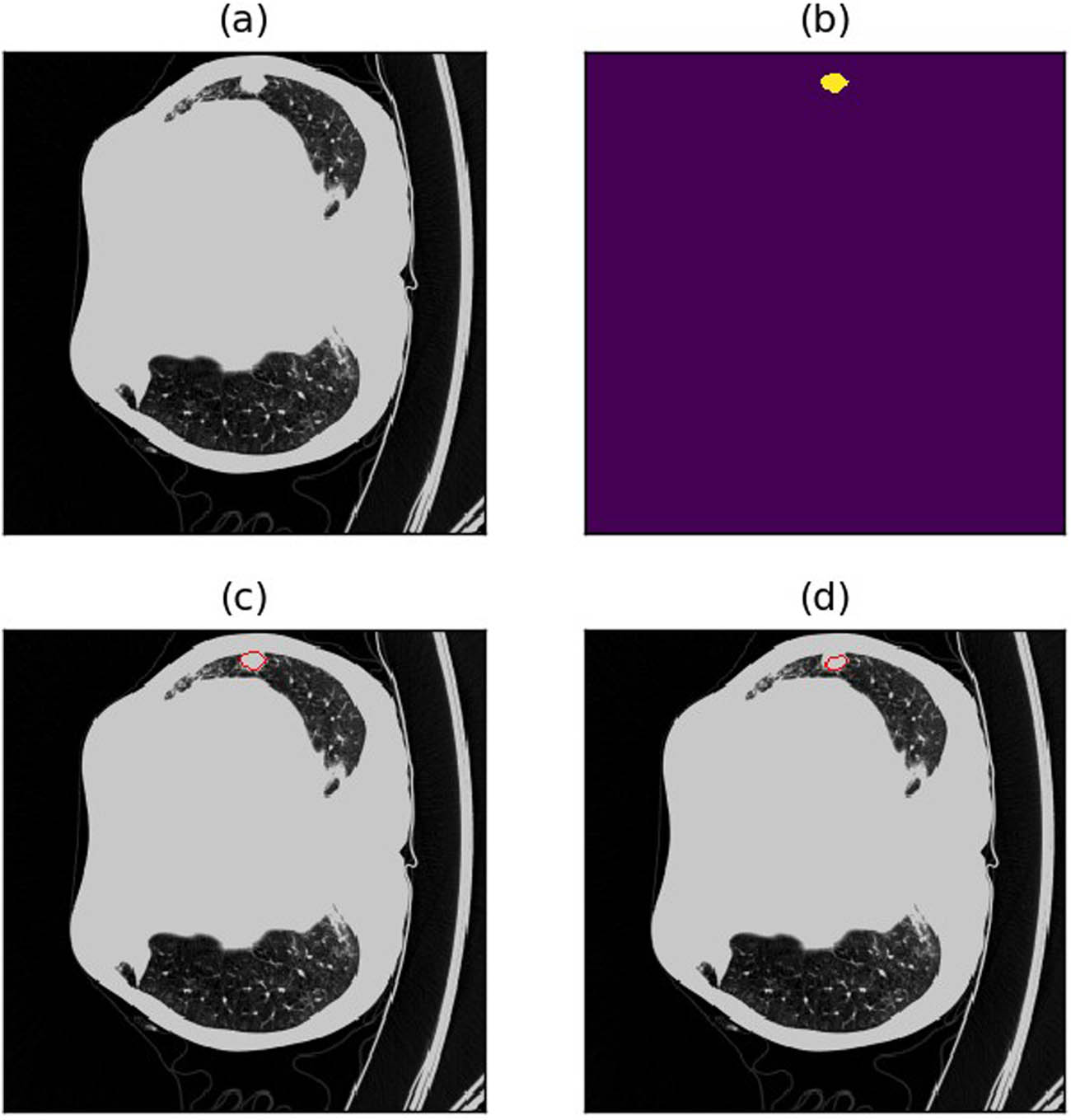
Example of poor detection outcomes due to lung nodules too close to the lung margins or other lung tissues. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
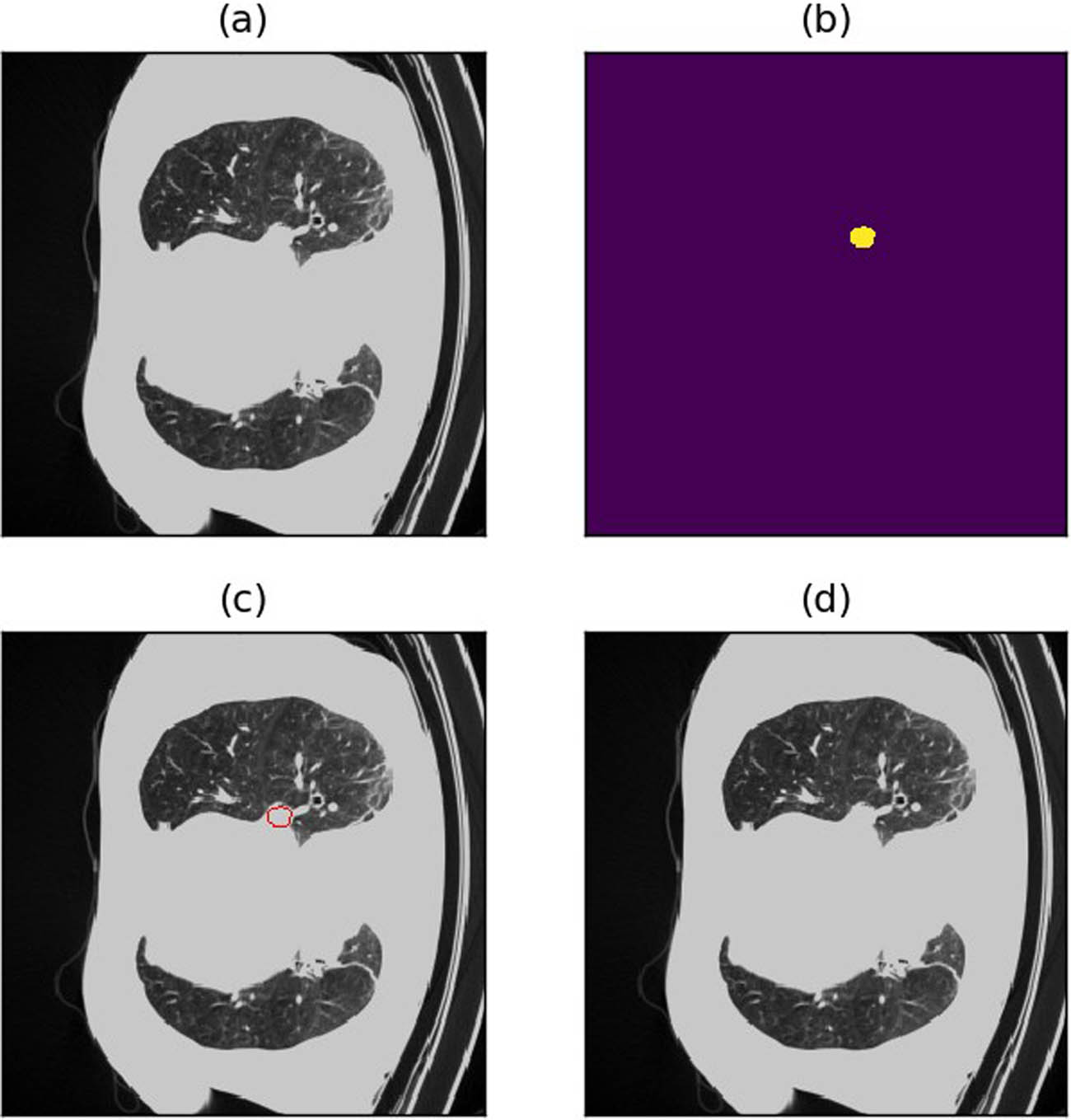
Example of missed detection due to lung nodules too close to the lung margins or other lung tissue. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
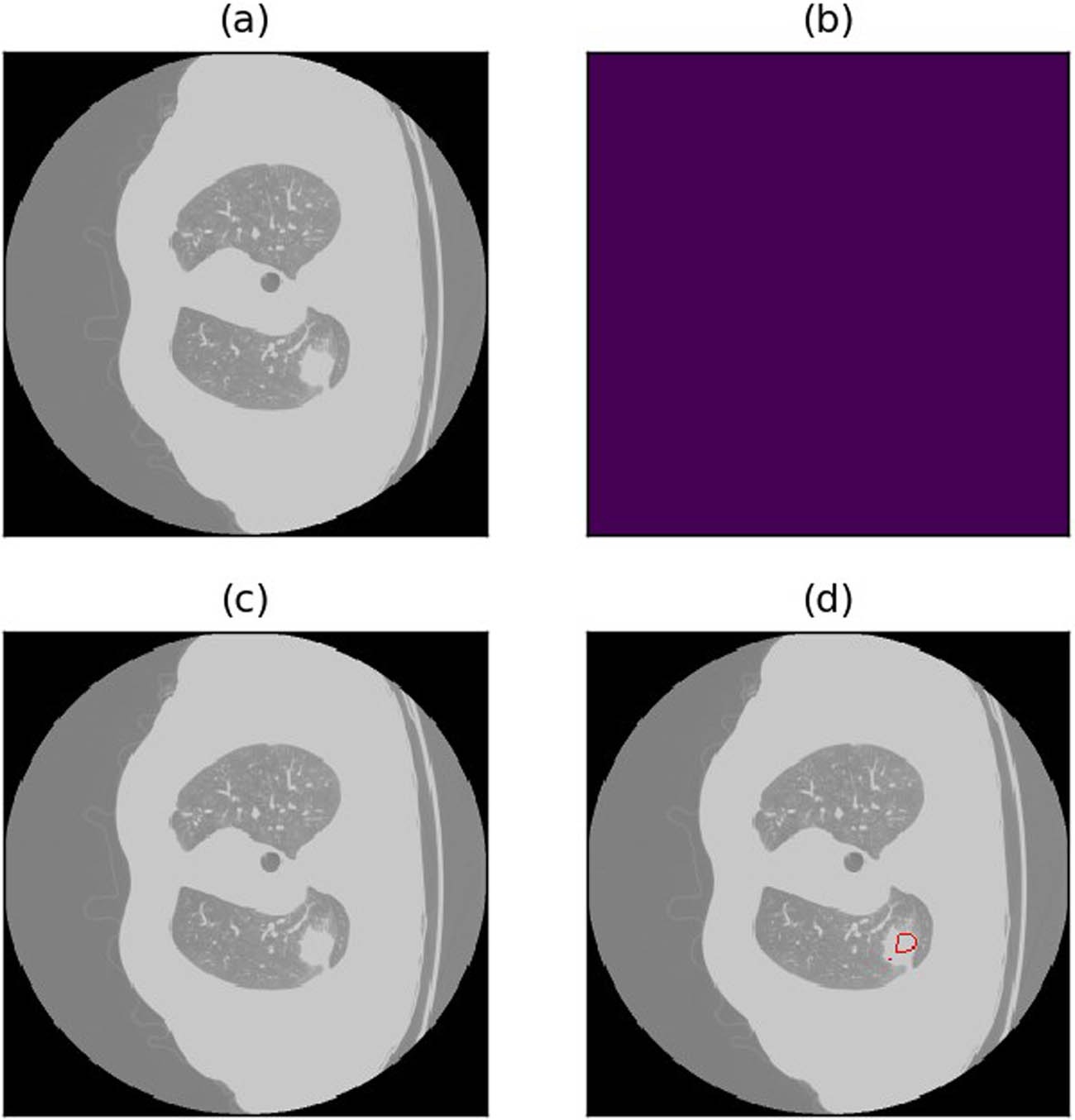
Example of misdetection due to the model’s inability to distinguish normal lung tissue from lung nodules. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.

Example of missed detection of tiny nodules. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations. (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
In conclusion, the model designed in this experiment generally performs well if the following conditions are satisfied:
Candidate nodules have a moderate or large size.
Candidate nodules are not too close to lung margins or other internal lung tissue.
Image slice thickness is neither too small nor too large.
The image noise level is low, and image boundaries could be clearly observed.
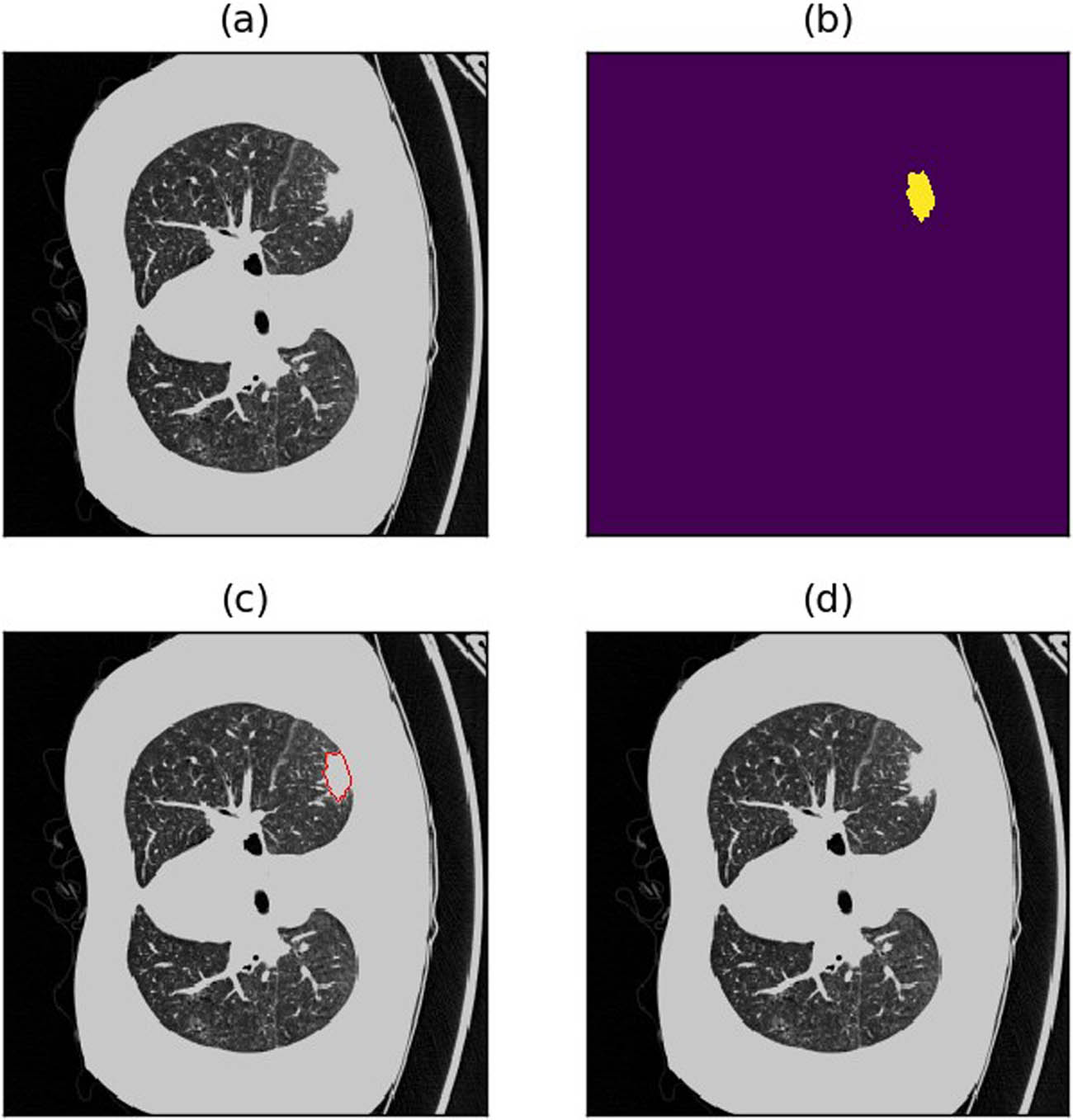
Figure 16 shows an example of good segmentation results, with a dice coefficient greater than 0.9.

Example of a piece with good segmentation result. (a) Raw image. (b) Annotations (c) Annotated image. (d) Predicted image.
4 Future work and conclusion
The primary objective of this study was to present an efficient approach for lung nodule segmentation utilizing lung CT images. To this end, a technique known as semi-residual MCNN for nodule segmentation was introduced. This method autonomously generates 3D nodule segmentation maps from lung CT images, minimizing the need for human intervention. The core innovations of the model encompass semi-residual building blocks, GN, and multi-resolution output heads. Each of these concepts has been demonstrated to hold pivotal significance in enhancing the overall accuracy of predictions.
Through this model, remarkable achievements have been realized, with dice coefficients reaching 0.4479 on the test subset of the LIDC-IDRI dataset. This notable performance surpasses that of a previously acclaimed state-of-the-art network, specifically the 3D Recurrent DenseNet, which exhibited dice coefficients of 0.4204 on the same dataset. The outcomes underscore the efficacy and advancements achieved by the proposed semi-residual MCNN technique in the realm of lung nodule segmentation.
The method proposed in this study, the semi-residual MCNN, serves as a notable advancement in enhancing the accuracy of neural networks for lung nodule segmentation tasks, building upon established methods. This progression not only paves the way for the integration of artificial intelligence into the clinical diagnosis of lung cancer but also offers valuable insights for real-life applications. Furthermore, the training methodologies and techniques outlined in this study exhibit a high level of adaptability and hold promising potential for application in analogous scenarios involving image segmentation tasks.
As underscored in preceding chapters, it is worth noting that the method proposed in this experiment does not delve into the specific delineation of individual nodules. Despite its notable improvements, the achieved accuracy still falls short of the requisites for real-world applications. Consequently, directing further efforts towards the exploration of two key domains is recommended:
Data post-processing holds potential for significant enhancement. Introducing an additional module to refine the model’s prediction outcomes could furnish medical professionals with more actionable insights. This augmentation could encompass several valuable aspects, such as extracting pertinent information about each nodule’s size and shape, quantifying the total nodular count within an image, and even potentially evaluating the potential malignancy of individual nodules.
By incorporating these refinements into the post-processing pipeline, the generated results could offer a comprehensive and nuanced view, equipping medical experts with invaluable details for informed decision-making. This augmentation not only complements the segmentation aspect of the model but also amplifies its utility in clinical practice.
An alternative strategy involves the development of a two-stage detection system. Instead of directly generating a complete segmentation map, this approach entails a twofold process. In the initial stage, the model identifies and extracts the volumes of interest (VOI). Subsequently, in the second stage, precise segmentation maps are predicted for each extracted VOI [29].
This two-stage paradigm serves to mitigate certain challenges. Notably, it alleviates the model’s struggle in detecting smaller targets by focusing on localized VOIs. Moreover, it circumvents the predicament of imbalance between positive and negative samples in lung CT raw images. Consequently, this method holds the potential to elevate the efficiency and accuracy of detection. By strategically segmenting the task into two stages, this approach offers a refined and potentially more effective framework for lung nodule detection.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: C.W.: manuscript writing, investigation, methodology, validation, data collection, data curation and analysis, and draft editing; W.D.: study conceptualization, supervision, reviewing, manuscript writing, revising, and editing.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statements: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Reference
[1] Samal KKR, Babu KS, Das SK. Multi-output spatio-temporal air pollution forecasting using neural network approach. Appl Soft Comput. 2022;126:109316.10.1016/j.asoc.2022.109316Search in Google Scholar
[2] Lei Y, Lei Y, Shi X, Wang J. EML4‑ALK fusion gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2022;24(2):1–6.10.3892/ol.2022.13397Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Xiao Z, Liu B, Geng L, Zhang F, Liu Y. Segmentation of lung nodules using improved 3D-UNet neural network. Symmetry. 2020;12:1787.10.3390/sym12111787Search in Google Scholar
[4] Nagendram S, Singh A, Harish Babu G, Joshi R, Pande SD, Ahammad SH, et al. Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. Open Life Sci. 2023;18(1):20220665.10.1515/biol-2022-0665Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Rodríguez JI, Kobus V, Téllez I, Pérez G. Prophylaxis with rivaroxaban after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy could reduce the frequency of portomesenteric venous thrombosis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2020;102(9):712–6.10.1308/rcsann.2020.0209Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Song L, Sun H, Liu J, Yu Z, Cui C. Automatic segmentation and quantification of global cracks in concrete structures based on deep learning. Measurement. 2022;199:111550.10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111550Search in Google Scholar
[7] Wen T, Tong B, Liu Y, Pan T, Du Y, Chen Y, et al. Review of research on the instance segmentation of cell images. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;227:107211.10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.107211Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Imak A, Çelebi A, Polat O, Türkoğlu M, Şengür A. ResMIBCU-Net: an encoder–decoder network with residual blocks, modified inverted residual block, and bi-directional ConvLSTM for impacted tooth segmentation in panoramic X-ray images. Oral Radiol. 2023;39:614–28.10.1007/s11282-023-00677-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Chen W, He Z, Zhang J. Online monitoring of crack dynamic development using attention-based deep networks. Automation Constr. 2023;154:105022.10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105022Search in Google Scholar
[10] Zhang X, Shen Y, Li P, Cai R, Lu C, Li Q, et al. Clinical heterogeneity and intrafamilial variability of Joubert syndrome in two siblings with CPLANE1 variants. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2021;9(6):e1682.10.1002/mgg3.1682Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Fei H, Wu Y, Wang Y, Zhang J. Exome sequencing and RNA analysis identify two novel CPLANE1 variants causing Joubert syndrome. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2022;10(3):e1877.10.1002/mgg3.1877Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Radha Rama Devi A, Naushad SM, Lingappa L. Clinical and molecular diagnosis of Joubert syndrome and related disorders. Pediatr Neurol. 2020;106:43–9.10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2020.01.012Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Wang F, Eljarrat A, Müller J, Henninen TR, Erni R, Koch CT. Multi-resolution convolutional neural networks for inverse problems. Sci Rep. 2020;10:5730.10.1038/s41598-020-62484-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Alhassan Y, Zaizay Z, Dean L, McCollum R, Watson V, Kollie K, et al. Perceived impacts of COVID-19 responses on routine health service delivery in Liberia and UK: cross-country lessons for resilient health systems for equitable service delivery during pandemics. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):304.10.1186/s12913-023-09162-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Han AY, John MAS. Predictors of nodal metastasis in cutaneous head and neck cancers. Curr Oncol Rep. 2022;24(9):1145–52.10.1007/s11912-022-01249-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Chaouki A, Berrada O, Najib Z, Oukessou Y, Abada RA, Rouadi S, et al. Primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland: a case report and review of the literature. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020;60:660–3.10.1016/j.amsu.2020.11.085Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Healy J, Searle E, Panta RK, Chernoglazov A, Roake J, Butler P, et al. Ex-vivo atherosclerotic plaque characterization using spectral photon-counting CT: Comparing material quantification to histology. Atherosclerosis. 2023;378:117160.10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2023.06.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Chu H, Wang W, Deng L. Tiny‐Crack‐Net: A multiscale feature fusion network with attention mechanisms for segmentation of tiny cracks. Comput-Aided Civil Infrastruct Eng. 2022;37(14):1914–31.10.1111/mice.12881Search in Google Scholar
[19] Carass A, Roy S, Gherman A, Reinhold JC, Jesson A, Arbel T, et al. Evaluating white matter lesion segmentations with refined Sørensen-Dice analysis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):8242.10.1038/s41598-020-64803-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Sathyabama K, Saruladha K. An effective learning rate scheduler for stochastic gradient descent-based deep learning model in healthcare diagnosis system. Int J Electr Healthcare. 2022;12:1–21.10.1504/IJEH.2022.119587Search in Google Scholar
[21] Millet A, Martin AR, Ronco C, Rocchi S, Benhida R. Metastatic melanoma: insights into the evolution of the treatments and future challenges. Med Res Rev. 2017;37(1):98–148.10.1002/med.21404Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Li D, Li Y, Sun H, Yu L. Deep image compression based on multi-scale deformable convolution. J Vis Commun Image Represent. 2022;87:103573.10.1016/j.jvcir.2022.103573Search in Google Scholar
[23] Den Hondt M, Starr MW, Millett MC, Smyth J, Scolyer RA, Shannon KF, et al. Surgical management of the neck in patients with metastatic melanoma in parotid lymph nodes. J Surg Oncol. 2019;120(8):1462–9.10.1002/jso.25732Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Zhao B, Zhang X, Li H, Yang Z. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearings based on normalized CNN considering data imbalance and variable working conditions. Knowl-Based Syst. 2020;199:105971.10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105971Search in Google Scholar
[25] Xu W, Lian B, Cui C, Guo J. The combination therapy with the cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 and programmed death 1 antibody-induced asthma in a patient with advanced melanoma. J Cancer Res Ther. 2021;17(3):808–10.10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_419_21Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Scott JF, Thompson CL, Vyas R, Honda K, Zender C, Rezaee R, et al. Parotid melanoma of unknown primary. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016;142(7):1529–37.10.1007/s00432-016-2156-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Chen Z, Mauricio A, Li W, Gryllias K. A deep learning method for bearing fault diagnosis based on cyclic spectral coherence and convolutional neural networks. Mech Syst Signal Process. 2020;140:106683.10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106683Search in Google Scholar
[28] Saini R, Patle KS, Kumar A, Surya SG, Palaparthy VS. Attention-based multi-input multi-output neural network for plant disease prediction using multisensor system. IEEE Sensors J. 2022;22:24242–52.10.1109/JSEN.2022.3219601Search in Google Scholar
[29] Usman M, Lee BD, Byon S-S, Kim S-H, Lee B-I, Shin, Y-G. Volumetric lung nodule segmentation using adaptive ROI with multi-view residual learning. Sci Rep. 2020;10:12839.10.1038/s41598-020-69817-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

