Abstract
The purpose of this study is to investigate the efficacy of bilateral upper-limb training (BULT) in helping people with upper-limb impairments due to stroke or brain illness regain their previous level of function. Patients recuperating from a stroke or cerebral disease were given the option of undergoing BULT or conventional training to enhance their upper-limb function. Participants were randomly allocated to one of the several different fitness programs. Results from the action research arm test, Box and block test, Wolf motor function test, Fugal–Meyer evaluation, and any other tests administered were taken into account. Some researchers have found that exercising with BULT for just 30 min per day for 6 weeks yields significant results. There were a total of 1,411 individuals from 10 randomized controlled trials included in this meta-analysis. Meta-analysis findings revealed that biofeedback treatment outperformed conventional rehabilitation therapy in reducing lower leg muscular strain, complete spasm scale score, electromyography score, and inactive ankle joint range of motion. An analysis of the literature found that BULT improved limb use in people who had suffered a stroke and hemiplegia but it did not provide any additional benefit over unilateral training.
1 Introduction
Stroke’s great prevalence and potential for long-lasting impairment make it a major public health concern worldwide [1]. About 55–75% of patients suffer from different degrees of upper-limb dysfunction at the early onset stage [2,3]. After 6 months of stroke, more than one-third of patients will have persistent upper-limb dysfunction [4,5], which significantly reduces the self-care ability of patients and brings physical and psychological distress to patients and their families [2]. In the United States, the medical expenses of stroke, including hospitalization, rehabilitation, and subsequent care, were estimated to be $140,048 per capita [6]. The burden of care is upcoming at an unprecedented rate, and the development of effective strategies must be considered a national priority [4]. The upper limbs are mainly characterized by flexible, coordinated, and skilled motor functions, all of which are involved in fine motor and complex activities in daily life. Stroke rehabilitation has a significant hurdle in the form of the patient’s slow and laborious road to recovery. Increasing the probability of functional recovery in the upper limbs is one of the most serious topics in clinical research [7]. Research has demonstrated that a patient’s handgrip strength on the “healthy side,” which some studies have indicated is not the unaffected side in stroke patients, is an independent predictor of functional recovery and prognosis during short-term post-stroke therapy [8,9]. After a stroke, the activities of patients’ healthy limbs are also significantly reduced, and the healthy limbs are always ignored.
In recent years, bilateral training (BT) has been widely used in rehabilitation stroke patients, which has a certain curative effect on improving the function of the hemiplegic upper limbs [10]. Bilateral upper-limb training (BULT) is a training method in which both upper limbs work together symmetrically or asymmetrically in different motor patterns. Symmetrical training mainly emphasizes the synchronous extension, flexion, grasping, rotation, and movement of healthy and affected upper limbs [11,12]. In asymmetric training, activities of daily living (ADLs) are usually coordinated by both bilateral upper-limb coordination, such as knotting, ring tossing, unscrewing bottle caps, folding towels, wiping tables, drinking water, tying shoelaces, zipping up and opening backpacks, and so on [13,14]. BULT can be used alone or in conjunction with other forms of training to improve motor function. These include Retro-Tongue-Base-Pharynx (RTBP), basic metabolic panel, bilateral arm training with rhythmic auditory cueing (BATRAC), virtual reality (VR), neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), medical transcription (MT), etc. [15]. In addition, it can be used in different stages of stroke but there are some disputes regarding its training effect and intervention period. Moreover, the training time and period are quite different in the studies, and no unified standard has been established.
The comprehensive review includes BULT research that was proposed by Chen et al. [10] which included functional training, RTBP, and BATRAC. There was high heterogeneity among these studies, without further analysis or discussion on the different onset stages, training periods, or training doses. Lee et al. [13] introduces recovery of upper limb function after stroke: a comparison of the efficacy of BT and constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT). High-intensity, daily exercise is performed on the injured upper limbs for at least 6 h, with reduced activity for the healthy limbs. BT may be a better alternative for improving ADLs than CIMT because of the fatigue and other problems that may occur with CIMT.
Researchers conducted a comprehensive literature evaluation to establish which of BT and UT is more effective for restoring muscular function in the upper extremities after stroke. Furthermore, we confirmed BULT’s effectiveness and revealed the best intervention and training periods and doses for optimal clinical practice and decision-making.
The Jintronix system employs Microsoft Kinect to help stroke survivors regain movement in their arms and hands by way of engaging and difficult exercises tailored to their specific skill level. As a result of using this exergame approach, therapists can track their patients’ quantitative improvement during therapy and make appropriate adjustments to their training regimen as needed. Including a point system in its exergames, this method has been shown to boost physical education outcomes. This is accomplished by giving the patient progressively more challenging tasks and giving them instantaneous input on how they are doing. The exergame system’s built-in tracking capabilities suggest that patients may soon be able to work out without the constant presence of a medical professional. Because of this, it may become possible to provide more telerehabilitation services to people in their homes and to expand access to rehabilitation services provided in clinics. To rephrase, there would be no need for extra staff to enable patients recovering from strokes to receive more comprehensive therapy programs. The feasibility, safety, and efficacy of this exergame approach as an adjunct to conventional therapy have yet to be determined; however, so further study is warranted.
The goal of this research is to determine how well BULT can assist stroke and other neurological disorder survivors recover their upper-body movement. Debate and analysis of the past were undertaken to discover the origins of the present. The outcomes of any tests administered, such as the action research arm test (ARAT), Box and block test (BBT), Wolf motor function test (WMFT), Fugl–Meyer evaluation, and others, were considered. About 24,000 pieces of literature were analyzed in this research. From the data, it is clear that there is a sizable gap in functional movement assessment (FMA) protections [16]. Mind-wrecking disruption hemiplegics who undergo BULT treatment report a higher level of satisfaction with their circumstances. Proponents of BULT exercise argue that even 30 min a day, 5 days a week for 6 weeks can have positive effects. The meta-analysis incorporated data from 10 randomized controlled trials (RCTs), with a total of 1,411 participants. The results of this meta-analysis show that biofeedback is more effective than traditional physical therapy at decreasing lower-limb muscle tension, total spasm scale score, electromyography score, and passive ankle joint range of motion.
2 Literature review
According to Rodgers et al. (2020) [17], stroke has an unusually heavy illness burden as it is one of the major worldwide causes of chronic disability and low quality of life. The inability to use one’s hands and arms effectively is a common complaint among stroke survivors. So, the major focus of stroke rehabilitation is to restore the ability to utilize the affected limbs, especially the arms and hands. Modern therapies for the hands and arms have come a long way, with some even using electromechanical components to aid with training. Due to its potential to deliver a challenging, regular, and repetitive therapy, electromechanically assisted arm training has been proposed as a feasible addition to evidence-based rehabilitation. Systematic evaluations suggest that arm exercise with electromechanical aid may boost motor function in the upper limbs, although this seems to have little therapeutic value. Although researchers could not prove it, they hypothesized that robotic-assisted arm training would negatively affect upper-body muscular tone.
In a previous study [18], it was argued that a prosthetic, such as an exoskeleton or robotic arm, may be used to move the joints of a paralyzed arm. Torque actuators, which provide rotating forces at a joint, might be included in the design of exoskeletons to facilitate mobility. The robotic arm may hold the patient’s arm in the horizontal plane as the patient moves their trunk, aiding in the development of shoulder and elbow coordination.
Wu et al. (2021) [19] described that an end effector is the last point of control on a robotic prosthetic, possibly near the end of the prosthetic limb. After utilizing these devices, patients may have improved mobility in their proximal arms as well. A little touch on the caregiver’s part is enough to accomplish this. In robotics and medicine, end effectors serve as mechanical appendages that perform the functions of human hands [20]. They are multipurpose since they allow for separate arm movement. A patient’s hands may rest on either of the two handles while they operate the end effector. The patients may practice pronating or supinating their forearms and wrists by simply switching the position of the handles. Modifying the sound is as easy as resetting the controls to their original positions. In “active” mode, the healthy arm of the patient is utilized to assist the robot in moving the injured arm, whereas in “passive” mode, the robot performs all the work alone.
According to a meta-analysis study conducted by Saposnik and colleagues, VR is effective in rehabilitating upper-extremity muscle function after stroke. VR was found to significantly improve the limb function (seven studies) and daily living tasks (three studies) compared to control groups. This result was accomplished by cherry-picking research directly linked to how well UEs work. Twelve studies were pooled together for a recent Cochrane Review and meta-analysis, and the results showed that VR improved ADL completion and upper leg function [20].
Based on their findings, the authors conclude that VR therapy has a greater effect on patient outcomes in all three ICF domains than traditional treatment methods. However, there is a dearth of data, including the best time and amount to administer the medication. In addition, research examining the perspectives of either individuals or healthcare providers on the debut of such instruments is scarce. Lange and her coworkers’ emphasis on finding enjoyable exercise routines was not enough to change this. Cylinder and Peoples interviewed and observed stroke therapy inpatients to assess the system’s efficacy. A large number of people who have used the Wii to assist in their recovery have reported increased stimulus, the availability of more difficult tasks, and general pleasure compared to their prior methods of therapy. Research has shown that VR and video games can aid in the recovery of stroke patients, and most of these studies agree that these findings are promising but preliminary. Studies of technology adoption have also demonstrated the significance of the user’s viewpoint in achieving desirable results [21].
3 Methods
3.1 Search strategy
Two separate reviewers searched the databases PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Embase, the Web of Science, CINAHL, Scopus, PEDro, SinoMed, CNKI, VIP, and Wanfang Data from their respective launch dates on October 31, 1996, to the present day for articles on bilateral upper-limb training of stroke patients (October 31, 2021). The database was first released to the public on October 31, 1996. Stroke, cerebrovascular accident, cerebrovascular sickness, CVA, cerebral strokes, brain vascular accident, hemiparesis, hemiplegia, bilateral exercise, bimanual exercise, and bilateral motor were some of the phrases we used to find relevant articles. The website’s Appendix 1 offers advice on how to study effectively.
4 Eligibility criteria
4.1 Types of studies
RCTs with BULT for hemiplegic stroke patients were included, and reports were found in both English and Chinese.
4.2 Types of participants
The following people were included in the study: (1) a confirmed diagnosis of a stroke using CT or MRI in the presence of symptoms; (2) older than 18 years; and (3) at different stages, including acute, subacute, and chronic phases. We also applied the following exclusion criteria: (1) not the first stroke; (2), lesions on both sides of the brain; (3) combined with other severe diseases; (4) unable to complete training due to cognitive or vision impairment; and (5) primary limb movement disorders.
4.3 Types of interventions
BULT (functional task training) was performed on stroke patients with hemiplegia to improve upper-limb function. The control group received routine training or unilateral upper-limb training (UULT). We also developed the following exclusion criteria for the intervention: (1) BT in both the experimental and control groups; (2) BT containing RTBP, NMES, MT, VR, and BATRAC; and (3) CIMT as the UT.
4.4 Types of outcomes
According to the disability classification of the World Health Organization [22], upper-limb assessment indicators can be divided into different levels, such as motor impairment (injuries related to the body structure), limited movement (ability related to the body function), and limited participation (ability related to ADLs). The study includes one or more of the following outcome indicators: After completing the FMA, we evaluated upper-limb functionality using the WMFT, BBT, and ARAT.
4.5 Patient and public involvement
No patient was involved.
4.6 Data collection and analysis
4.6.1 Study selection
Two separate researchers used the aforementioned search strategy to identify relevant main documents. Our reviewers ran a quick Note Express title/abstract comparison to weed out duplicates. The full texts of the included articles were then assessed for eligibility for the review. When disagreements or issues developed between the two researchers, they discussed the situation and looked for ways to work together. A third, unbiased writer served as an arbitrator if a dispute could not be settled between the two original authors.
4.6.2 Data extraction
Following a thorough review of the whole text, the research design was classified, and information was acquired from the published literature using the predetermined framework, including trial design, characteristics of the included studies, study population, treatments, end measures, and conclusions. The data extraction was done independently by two researchers. Conflicting opinions on how to extract data were addressed and settled. When necessary, a third author was brought in to aid.
4.7 Risk of bias assessment
Higgins et al. used the Cochrane risk of bias calculator to assess the level of methodological rigor of the RCTs [23]. The standard bias risk chart takes into account a variety of issues, including the generation of sequences, the suppression of distribution sequences, the use of blocking procedures, a lack of appropriate outcome data, and selective outcome reporting. The chart included, in the first column of each column, a short description of each event that was discussed in this research, followed by the author’s evaluation of how successfully that event helped accomplish the objective of eradicating discrimination.
4.8 Data synthesis and analysis
We utilized RevMan5.3 to perform the statistical analysis (Cochrane Collaboration, version 5.3.4). The range of potential events was analyzed and quantified using both the Chi-square and the I 2 tests. When the I 2 number was below 50%, a fixed-effect model meta-analysis was performed. All studies with an I 2 number higher than 50% were analyzed using effect models in the meta-analysis. To analyze the data, we used a weighted mean difference (WMD) method and evaluated the signs for consistency on a scale. When comparing continuous data on varying dimensions, the standard mean difference (SMD) is a useful statistical measure. Statistical importance was assumed if the p-value was less than 0.05.
4.9 The rehabilitation exergaming system
Exergaming, a type of counseling, was used with the Jintronix system as part of this study. The company collaborated with a wide range of healthcare workers, including clinicians, doctors, and patients, to ensure that this system is intuitive and widely available. Using the Kinect sensor and without the need for any marks, this setup is an interactive video game for physical activity. Unlike the Nintendo Wii, this system does not necessitate a separate handheld gadget to track a player’s motion. A Kinect sensor is integrated into the exergaming system for recovery purposes so that players’ upper- and lower-body motions can be tracked in real time. This is achieved whether the musician is sitting, standing, holding, or even wearing their instrument. After capturing the player’s motions, the data are presented in the setting of a healing video game. The method allows for unidirectional and bilateral UE exercises to be performed on any surface and at various levels. The therapist can adjust the game’s pace, goal size, accuracy, and uniformity to meet the needs of the patient.
4.10 Study procedure
All of the study subjects had suffered a stroke and were enrolled in outpatient therapy at one of two facilities. During the therapy, they were able to take advantage of vocational therapy and/or physical recovery programs. Based on the patient’s individual needs, the interdisciplinary team saw them twice or three times per week, with the bulk of the time spent on vocational and physical therapy. In addition to traditional physical treatment, those in the control group also played exergames designed to improve leg muscle. Stroke survivors in the control group used the exergame system for 4 weeks, twice or three times a week, for 30 min each practice (not including setup and other contacts with the system). We ensured that they had opportunities for relaxation in between their gameplay and counseling appointments. Each location also had a clinician familiar with the therapy exergaming method present during the exergaming session. This medical professional was responsible for all of the clinic’s clients [24].
4.11 BULT is helpful in the case of stroke patients
Training with both arms and “bilateral arm training” has been shown to increase the activity in both the impacted and uninjured parts of the brain. This, in turn, may promote the recovery of stroke-harmed brain cells.
4.12 BULT therapy for stroke victim’s work in practice
First, the trainer focused on the basics, like getting out of bed, having a shower, and eating a healthy breakfast. When patients took part in routine tasks, they regained movement and their ability to operate in everyday living. Recovering from a stroke is made easier with the help of flexible technology, as shown by the research.
5 Results
5.1 Search process
According to the article retrieval strategy, we obtained 2,027 articles. After reference tracking, repeated screening, and independent screening by two researchers, 23 RCTs were finally included in the meta-analysis. Figure 1 shows the flow chart for article screening.
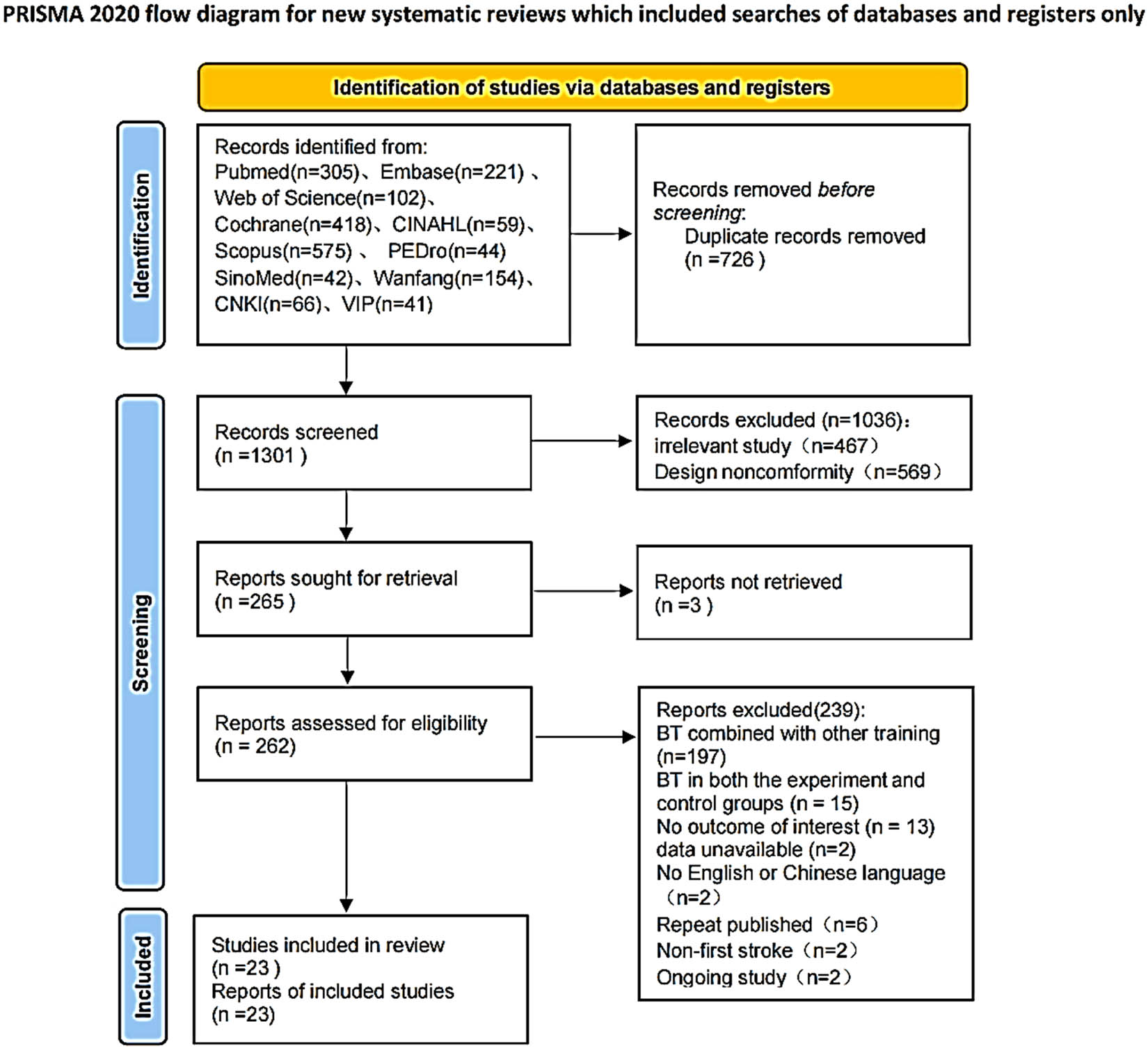
PRISMA search flow diagram.
5.2 Study characteristics
Table 1 presents an overview of the primary features shared by the studies that were taken into consideration. In this section, we provide a detailed introduction to each study’s first author, year, research fields, sample size, intervention, and outcome mea sure, as well as general information including participant age, gender, primary illness, lesion location, and start time.
Types, durations, frequencies, and results were all quantified in the studies that were included
| Study (Country/year) | Participate (M/F) | Age ± SD | Type (CI/ICH) | Duration (month ± SD) | Intervention type | Duration of therapy | Study outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desrosiers et al. (Canada/2005) [25] | BT: 9/11 | BT: 72.2 ± 10.8 | BT: 19/1 | BT: 34.2 ± 34.4 | BT: Examples of such activities include rolling out dough, opening and closing locks, measuring dry ingredients using a teaspoon, and folding towels | 45 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ①② |
| UT: 10/11 | UT: 74.3 ± 10.1 | UT: 21/0 | UT: 35.4 ± 33.7 (days) | UT: Conventional therapy for the affected upper extremity | |||
| Dhakate and Bhattad (India/2020) [12] | BT: 20 | 54 ± 10 | Not reported | 1–6 (mo) | BT: Lifting a shoebox overhead and lowering it again, pulling a chair, and lifting two polystyrene cups simultaneously and then putting them back | 45 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 20 | |||||||
| UT: Conventional therapy for the affected upper extremity | |||||||
| Easow et al. (India/2019) [26] | BT: 10/5 | BT: 60.00 ± 9.35 | BT: 15/0 | Acute | BT: Clasping the hands, then moving to mouth, the elevation of the arms, turning toward sound side keeping shoulder well forward | 20 min/d, 6 d/wk, 4 wk | ③ |
| UT: 10/5 | UT: 60.86 ± 9.96 | UT:15/0 | UT: Standard care treatment for affected upper limbs | ||||
| Han et al. (Korea/2016) [27] | BT: 5/8 | BT:78.8 | Not reported | BT: 83.0 | BT: Ring hanging, desk cleaning, and drinking are all examples of bilateral actions | 30 min/d, 5 d/wk, 6 wk | ② |
| UT: 3/9 | UT:72.9(avg) | UT: 77.8 (avg) | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with impaired arm | ||||
| He et al. (China/2016) [28] | BT: 11/7 | BT: 52.82 ± 11.25 | BT: 11/7 | BT: 24.52 ± 10.2 | BT: Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation of elbow and wrist joints, and hand grasping training | 40 min/d, 5 d/wk, 12 wk | ① |
| UT: 10/8 | UT: 50.37 ± 11.0 | UT: 12/6 | UT: 22.47 ± 9.17 | UT: Just like the bilateral group, this one exclusively included the affected hand | |||
| Kaur et al. (India/2019) [29] | Not reported | BT: 52 UT: 50 (avg) | 13/3 | 2–16 (wk) | BT: Holding a lock and unlocking it, holding a bowl and picking stones from it, pulling a rope, tying a shoelace while keeping the elbows in the extended position, and opening a drawer | 30 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ①③ |
| UT: Motor relearning program with impaired arm | |||||||
| Kumar et al. (India/2011) [43] | BT: 9/6 | BT: 66.67 ± 12.27 | Not reported | Not reported | BT: Passive/active movements of all the joints of upper limbs, weight-bearing, supportive reaction, reaching activities than grasping, holding, and releasing activities; lastly performed ADL activities | 45 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 9/6 | UT: 67.55 ± 9.69 | UT: Same as the bilateral group with the affected UE | |||||
| Lee et al. (Korea/2017) [30] | BT: 9/6 | BT: 57.33 ± 9.88 | BT: 8/7 | 7–12 mo: BT (4); UT (5); 13–24 mo: BT (3); UT (5); ≥25 mo: BT (8); UT (5) | BT: Some common household tasks include washing dishes, composing letters, chopping vegetables, and folding clothes | 30 min/d, 5 d/wk, 8 wk | ①② |
| UT: 10/5 | UT: 54.60 ± 16.03 | UT: 9/6 | UT: General occupational therapy | ||||
| Lee et al. (Korea/2019) [31] | BT: 6/9 | BT: 61.53 ± 8.81 | Not reported | BT: 3.60 ± 1.30 | BT: Wiping table with a towel, mimicking drinking, and moving blocks to boxes | 30 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 7/8 | UT: 62.00 ± 8.13 | UT: 3.20 ± 1.37 | UT: General upper-limb rehabilitation | ||||
| Zhenjing et al. (China/2019) [11] | BT: 7/9 | BT: 45.38 ± 9.78 | BT: 12/8 | BT: 4.63 ± 1.59 | BT: Stacking blocks, placing wooden nails, turning over chess pieces, folding towels, unscrewing bottle caps, simulating drinking water, and throwing and catching the ball | 60 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 7/8 | UT: 49.67 ± 10.6 | UT:11/10 | UT: 3.40 ± 1.5 | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with the affected hand | |||
| Lin et al. (Taiwan, China /2010) [32] | BT: 10/6 | BT: 52.08 ± 9.60 | Not reported | BT: 13.94 ± 12.73 | BT: One needs both hands and a cup to do just about anything: watering plants, playing checkers, picking up dry beans, folding towels, handling huge screws or coins, etc | 120 min/d, 5 d/wk, 3 wk | ① |
| UT: 9/8 | UT: 55.50 ± 13.17 | UT:13.12 ± 8.13 | UT: General upper limb rehabilitation with neurodevelopmental techniques | ||||
| Lin et al. (Taiwan, China/2015) [33] | BT: 12/4 | BT: 52.63 ± 10.49 | BT: 9/7 | BT: 27.75 ± 19.04 | BT: By gradually raising or decreasing their grip strength with both hands, participants in a bilateral isometric handgrip force training program mimicked the intended force action | 30 min/d, 3 d/wk, 4 wk | ①④ |
| UT: 16/1 | UT: 57.47 ± 10.29 | UT: 6/11 | UT: 21.82 ± 21.66 | UT: Routine clinical rehabilitation is generally helpful for people with upper-limb hemiplegia | |||
| Manjula et al. (India/2020) [44] | BT: 15 | 40–70 | Not reported | >6 (mo) | BT: Wiping the table, reaching and placing objects, moving an object from table to shelf, bilateral elbow extension during horizontal reach, grasping an empty glass, taking it to mouth, and returning to starting position | Each activity was repeated 30 times, 4 wk | ③ |
| UT: 15 | UT: Analogous to the unilateral class but with a broken hand | ||||||
| Meng et al. (China/2017) [34] | BT: 34/30 | BT: 55.38 ± 6.97 | BT: 50/14 | BT: 8.87 ± 2.69 | BT: Haptic perception training, bimanual coordination training, and functional training of the hands | 60 min, 2 times/d, 5 d/wk, 2 wk | ①③ |
| UT: 31/33 | UT: 55.19 ± 7.82 | UT: 45/19 | UT: 9.08 ± 2.35 (h) | UT: Conventional rehabilitation training | |||
| Morris et al. (England/2008) [35] | BT: 34/22 | BT: 67.9 ± 13.1 | BT: 3/53 | BT: 22.6 ± 5.6 | BT: To move a doweling peg from the tabletop to attach to the underside of a shelf; to move a block from the table onto a shelf; to grasp an empty glass, take it to the mouth and return to starting position; to point to targets raised | 20 min/d, 5 d/wk, 6 wk | ③ |
| UT: 27/33 | UT: 67.8 ± 9.9 | UT: 6/44 | UT: 23.2 ± 5.7 (d) | UT: The wounded hand is used in a manner analogous to the bilateral group | |||
| Renner et al. (Germany/2020) [36] | BT: 16/19 | BT: 63.70 ± 13.38 | BT: 13/22 | BT: 35.17 ± 11.03 | BT: Cycling movements of the arm, including forearm and wrist extension/flexion in passive–passive, motor-assisted, and actively moving against the resistance mode | 20 min, 2 times/d, 5 d/wk, 6 wk | ① |
| UT: 16/18 | UT: 63.34 ± 12.49 | UT: 11/23 | UT: 37.22 ± 13.56 | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with the affected hand | |||
| Song et al. (China/2020) [37] | BT: 35/24 | BT: 44.47 ± 8.41 | BT: 33/26 | BT: 99.54 ± 43.9 | BT: Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation of elbow and shoulder joints | 2 times/d, 6 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 37/24 | UT: 44.00 ± 7.90 | UT: 37/24 | UT: 92.26 ± 39.28 (d) | UT: Same as the bilateral group, only with the injured hand | |||
| Stoykov et al. (America/2020) [38] | BT: 7/1 | BT: 61 ± 7.60 | Not reported | BT: 62.9 ± 50.00 | BT: Continuous symmetrical wrist flexion and extension | 60 min/d, 5 d/wk, 6 wk | ① |
| UT: 68.13 ± 51.11 | UT: Played computerized Jeopardy games with the affected hand | ||||||
| UT: 6/2 | UT: 63 ± 5.21 | ||||||
| Tanavarapu et al. (India/2019) [39] | BT: 33 | BT: 54.3 | Not reported | Not reported | BT: Picking up a coin and manipulating it, catching a ball, wiping the table with a towel, elbow extension during horizontal reach, lifting a glass to drink, picking up a spoon to feed, and reaching forward/upward for a cup and replacing it | 30 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 32 | UT: 55.3 | UT: Same as the bilateral group, only with the injured hand | |||||
| Wang et al. (China/2015) [40] | BT: 16/10 | BT: 51.2 ± 10.1 | BT: 14/12 | BT: 2.8 ± 0.7 | BT: Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation of elbow and wrist joints, hand-grasping training | 30 min, 2 times/d, 5 d/wk, 6 wk | ① |
| UT: 17/9 | UT: 50.3 ± 11.5 | UT: 17/9 | UT: 3.0 ± 1.0 | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with the affected hand | |||
| Wang et al. (China/2016) [45] | BT: 18/9 | BT: 51.3 ± 5.6 | BT: 16/11 | BT: 3.0 ± 0.8 | BT: Flexion, extension, adduction, and rotation of elbow and shoulder joints | 60 min/d, 5 d/wk, 4 wk | ① |
| UT: 17/10 | UT: 50.9 ± 5.5 | UT: 14/13 | UT: 2.9 ± 0.6 | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with the affected hand | |||
| Wei et al. (China/2017) [41] | BT: 6/4 | BT: 62.0 ± 6.87 | BT: 10/0 | BT: 18.70 ± 4.03 | BT: All the joints of upper-limb flexion, extension, abduction, and rotation; hand grasping training | 30 min, 1time/d, 30 d | ① |
| UT: 5/5 | UT: 60.70 ± 5.37 | UT: 10/0 | UT: 20.00 ± 4.05 | UT: Same as the bilateral group but performed with the affected hand | |||
| Wu et al. (Taiwan, China/2011) [42] | BT: 18/4 | BT: 52.22 ± 10.72 | Not reported | BT: 15.92 ± 13.74 | BT: Lifting two cups, picking up two pegs, grasping and releasing two towels, and wiping the table with two hands | 120 min/d, 5d/wk, 3 wk | ④ |
| UT:16/6 | UT: 55.19 ± 2.50 | UT: 17.77 ± 12.45 | UT: Rehabilitation routines that target the affected limb’s range of motion, stability, and weight bearing |
① FMA. ② BBT. ③ ARAT. ④ WMFT. BT, bilateral training; UT, unilateral training; M, male; F, female; CI, cerebral infarct; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; h, hour; d, day; wk, week; mo, month; avg, average.
5.3 Critical appraisal of quality
The findings of the assessment of the primary methodological quality indicators are presented in Figure 2 for the original articles that were taken into consideration. Twenty articles [11,12,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] had low risk in the random allocation methods, whereas three articles [43,44,45] did not describe the particular random allocation methods. In total, 20 articles [11,12,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] had low risk in the random allocation methods. In addition, it was discovered that 9 of the articles had limited potential for allocation suppression; 3 of the articles used blindfolded methods for the patients; 11 of the articles used blinded methods to evaluate the findings; and 5 of the articles documented the loss of samples. There was no selective reporting of the findings in any of the 23 articles, and 9 of the articles displayed other ambiguous sources of prejudice. These publications, on the whole, had a standard level that was somewhere in the middle.

Risk-of-bias summary: authors’ judgments regarding the risk of bias of each item in each included study.
5.4 Outcome analysis
5.4.1 Motor impairment meta-analysis
The FMA has been utilized in 18 different research investigations to quantify hand and arm motor dysfunction. The high degree of variety was reflected in an I 2 score of 82%. The random-effects model showed that the BT group had a greater FMA than the UT group (MD = 5.80, 95% CI = [4.13–7.47], p = 0.00001). For this experiment, the p-value was so low that it could not even be measured in decimal places. In the FMA meta-analysis, no significant publication bias was found according to the Egger test (p = 0.929).
The length of time after the stroke was a statistically significant differentiator between the BT and UT groups (MD = 7.89, 95% CI = [5.86–9.92], p = 0.00001; MD = 5.01, 95% CI = [3.58–6.44], p = 0.00001, I 2 = 60%; MD = 9.11, 95% CI = [6.03–11.01], p = 0.00001, I 2 = 60%) (6.36–11.87) (Figure 3).

Subgroup analysis in the BT group and UT group at different stages.
When compared with the UT group, the BT group had significant improvements in the subgroups based on training periods (2–3 weeks: MD = 7.91, 95% CI = [5.97–9.86], p < 0.00001, I 2 = 0%; 4 weeks: MD = 5.05, 95% CI = [2.51–7.59], p < 0.0001, I 2 = 87%; 6 weeks: MD = 6.73, 95% CI = [5.10–8.37], p < 0.00001, I 2 = 0%; 8–12 weeks: MD = 7.06, 95% CI = [4.65–9.46], p < 0.00001, I 2 = 22%, Figure 4).

Subgroup analysis in the BT group and UT group at different training periods.
There was a significant amount of variation (I 2 = 86%) between the findings of the five different studies on the benefits of getting at least half an hour of exercise daily. When a random-effects model was applied to the overall effect values, we were able to determine that the BT group had a significantly higher FMA than the UT group (Figure 5; MD = 4.34, 95% CI = (0.45–8.22), p = 0.03). Eliminating individual research has not benefited all that much in terms of bringing down the variation.

Forest plot of the FMA in the BT group and UT group with training 30 min per day.
Three publications reported exercise for 45 min each day had a high degree of inconsistency (I 2 = 95%). When the article by Kumar [43] was taken out of the mix, the level of heterogeneity dropped to 0%. This research described ADL-related coordination training in addition to inactive and active symmetrical training of both the left and right upper extremities. This could be the source of the heterogeneity in the results (Figure 6).

Forest plot of the FMA in the BT group and UT group with training 45 min per day.
The amount of variation in daily exercise activities lasting 60 min or longer was modest (I 2 = 41%) across the two studies. A fixed-effect model was utilized to conclude that there was a statistically significant effect size (MD = 4.13, 95% CI = [0.35–7.90], p = 0.03) (Figure 7).

Forest plot of the FMA in the BT group and UT group with training 60 min per day.
5.4.2 Functional performance meta-analysis
A comprehensive review and meta-analysis were able to substantiate that BULT is successful in recovering upper-limb function in patients who had suffered hemiplegic strokes. The FMA-UE of BT and UT was evaluated across 18 studies in this comprehensive review and meta-analysis for patients with movement disabilities in their upper extremities as a consequence of stroke. Our data and the data from other investigations demonstrate that the FMA-UE has made significant progress since it was first developed (Figure 8).

Forest plots of WMFT, ARAT, and BBT analysis in the BT group and UT group.
People who had suffered a stroke and were now feeling better agreed to take part in the research. As a result of the difficulty of the research, five of the initial subjects dropped out before it was completed. Four individuals in the intervention group and one person in the control group dropped out before the initial assessment, despite having given their full consent. The absence of time, energy, or inspiration was the typical cause. One participant in the intervention group was unable to participate in post-intervention and follow-up assessments due to mobility limitations brought on by capsulitis. The experts were taken aback by this finding. Although information about this patient’s participation in the study’s mortality phase was included in the end report, it was omitted from the efficacy report. Eighteen stroke victims had their concluding days monitored. Stroke victims and research participants with identifiable features were chosen.
Disputes surfaced after exploring different options. At least 8 lessons were spaced out over 4 weeks, with the average length of each session being 44 min. The typical amount of time spent playing an exergame is around 22 min. About half of the time was spent performing the actual work, and the other half of the time was spent on things like orientation, training, data collection, analysis, fine-tuning, and downtime. Only about half of the allotted time was used for the exercise. Participants’ success ranged from 32 to 64%. Participants in the control group reported no negative side effects. After a complete day of labor, the average VAS pain score was 2.2 out of 9.9, while the average Borg score was 3.6. No injuries were recorded during training, and only one person mentioned feeling confused. Both participants rated their level of pain and fatigue at 1.8 out of 9.
6 Discussion
Patients with hemiplegia after a stroke benefited from BULT, as shown by a meta-analysis and systematic review. Patients with motor impairment in their upper limbs as a result of stroke were the focus of 18 studies that analyzed the FMA-UE of BT and UT. Our findings corroborated those of the earlier research, showing substantial improvement in the FMA-UE [10]. Some studies demonstrated that bilateral movement can enhance the activation and connection of the main motor area M1, the primary sensory area S1, and the supplementary motor area of the bilateral cerebral hemispheres, which can dominate the movement of the homologous muscle groups [46,47]. Neuroplasticity may also involve the corticospinal system after a stroke. Most of the corticospinal axons pass through the contralateral side at the medullary cone level and dominate the contralateral limbs. However, about 10–20% of nerve fibers descend directly rather than cross to form the anterior corticospinal tract and dominate the ipsilateral limbs [9,48].
Rehabilitation after a stroke usually happens in four phases: the acute phase, the subacute phase, the late subacute phase, and the chronic phase [48]. Patients with acute, subacute, and chronic strokes all showed greater FMA-UE improvement in the BT group compared to the UT group, as determined by subgroup analysis. It was shown that the acute and subacute phases were more influential than the chronic period. Since the articles are still in the “subacute” or “subacute late” stages, there is a contradiction between them (7 days to 3 months and 3 to 6 months). One possible explanation for the paucity of research into the acute phase is the high risk of complications and overall poor health that characterize it [49]. In the early recovery from stroke, the activation of motor areas in both hemispheres increased, which was more obvious in the contralateral hemisphere, and then gradually decreased in the subsequent treatment [47,50]. A study reported that the spontaneous biological recovery of the brain is the most significant in the first 3 months after stroke onset and gradually weakens and stabilizes after 6 months [19]. Borschmann et al. [47] conducted a longitudinal study that evaluated the upper-limb function at 14 days, 6 weeks, and 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24 months after stroke and found that the most significant improvement occurred at 2–6 weeks after stroke. In addition, some patients showed improvement at 12–18 months, and several patients still presented with improvement at 24 months, which is consistent with Lang’s study [48]. Thus, BULT could be performed early if the patient is stable and can cooperate. Ambreen et al. [49] compared the effect of BULT on the upper-limb function in a patient who had left and right hemisphere damage, and the intergroup analysis showed no statistically significant difference. In addition, Renner et al. [36] reported that the FMA-UE and grip strength of the affected hands of patients with subcortical lesions after BT were much better than those after UT, but the situation of patients with cortex involvement was different. The lesion site and degree of stroke might also influence factors that should be considered in BULT. Other articles did not mention the specific lesion sites or grouping. Therefore, this study failed in the analysis and discussion of the relevant subgroup.
In addition, our subgroup analysis showed that the BT had a statistically significant effect on the FMA-UE of stroke patients with hemiplegia in different training periods compared with UT. Five articles used a 6-week training period without heterogeneity in these articles. Compared with the studies that used a training time of 2–3, 4, and 8–12 weeks, 6 weeks effect sizes increased, while the heterogeneity was lower. Therefore, the best effect was observed at 6 weeks. The results of Savant [50] also showed that compared with routine training after 4 weeks, isometric movement improved the functions of the shoulder abductor and external rotator, elbow flexor, and forearm pronator on the affected side, and these improvements were more obvious at 6 weeks, with statistically significant differences. Another review concluded that the median of limb rehabilitation training after a stroke was 6 weeks [51]. For training 120 min per day, 5 days per week, the training cycle lasted less than 3 weeks in two studies [32]. It is reported that with the extension of daily training time, patients were prone to fatigue and found it challenging to insist on long-term training [13]. However, the studies of long-term training were not enough in our research, and 6 weeks may not be the only influential factor. We need more extensive sample size trials to confirm its long-term effects.
Patients with mildly diverse strokes were given a BULT for 4 weeks in 11 studies. Furthermore, we investigated how everyday exercise time affected the BULT. The results of this research demonstrated that the FMA-UE could be enhanced through daily training sessions of 30, 45, or 60 min. The impact values were comparable across groups, suggesting that adding more exercise time per day would not yield any additional gains. Instead of documenting training hours, one research detailed the training procedures and schedule [37]. Nerve rearrangement and exercise outcomes were influenced by training intensity (rehabilitation dosage), but the optimum therapy dose and intensity limits are still unclear [52,53]. Stroke patients in the low-dose and high-dose groups who received upper-arm training with a robot in conjunction with vocational therapy showed modest but clinically significant improvements in FMA-UE ratings, according to Pila et al. [54]. High-dose and low-dose groups had similar rates of manual function improvement in the upper limbs [55]. A systematic review compared the effects of high-dose and low-dose single-rehabilitation training on limb injury and activity limitation of patients after stroke, which reported there were no statistically significant differences in the effects of weekly training for <5, 5–10, and >10 h per week on post-stroke upper-limb function, lower-limb function, or ADLs. This discovery suggested the existence of a therapy “optimal dose,” beyond which the advantages of further treatment diminished. As with the frequency and length of workouts, a patient’s endurance and exhaustion indicator will guide what kind of exercise regimen is best for them. Patients’ collaboration, interest, and desire must be taken into account during each recovery training [56,57]. Our research suggests that people who have recovered from a stroke should do BULT exercises for at least 30 min daily. This result should be taken with care, however, because sensitivity analysis cannot determine the actual reason for the difference.
When comparing the functional increase of the BT group and the UT group, there was no statistically significant difference. The FMA was used to assess the harm to bodily function and structure, making it the main indicator for evaluating the hemiplegic upper limbs. However, the FMA is not able to adequately evaluate the high-level muscular function of the distal upper extremities [58]. The WMFT, ARAT, and BBT were designed to evaluate the patient’s performance on a variety of activities, including those requiring fine motor control of the arms, hands, and fingers, as well as the overall quality of their performance, including the presence or absence of abnormalities in their stance and rate of movement. Increases in FMA-UE are associated with increases in the overall functional ability of the upper extremity, though this relationship is not straight. The FMA-UE has modest to high correlations with several other measures, including the WMFT, the ARAT, and the BBT [59,60,61]. Studies have shown that BT contributes very little to the functional precision of the hemiplegic hand and that the opposite brain hemisphere’s corticospinal cord is mainly responsible for directing minute motions of the distal upper limb [62]. These findings lend support to the idea that the brain hemisphere not engaged in action is the primary control of the associated movement, which is one potential explanation for our research findings. More studies are required to fully untangle the variables that are added to the links.
There appears to be a link between the length of time spent in therapy and the extent of healing in the extended period following a stroke. This was the finding of meta-analyses that compared the efficacy of different treatments based on the amount of time and energy each required. However, because patients and doctors place a higher emphasis on regaining mobility after a stroke than they do on regaining function in the upper extremities, UE training is frequently reduced to less than 10 min per therapy session. Therefore, any UE exercise that is active in addition to the current routine would be beneficial and in line with the most recent guidelines for the practice of strokes. Our study’s control group was engaged in exergaming activities at a frequency of at least twice weekly throughout the whole study. After only 21 min of training from their clinicians, they were able to exercise their upper limbs for a total of 45 min during each exergaming practice.
The study shows that using exergames is not only effective but also completely safe. Users of the exergame gadget reported feeling a mild degree of fatigue after prolonged use. No accidents were reported as a consequence of the falling that occurred during this seated exercise regimen. With the assistance of exergame devices, the amount of upper-limb (UE) therapy activities a stroke patient completes can be raised. The complexity of an operation can be increased by using exergames or any of the other many options accessible. For instance, one of the nearby recovery centers has outfitted a specific area with exergames, allowing patients to engage in productive play for prolonged amounts of time. The inclusion of fitness and play spaces in recovery settings has the potential to be a cost- and time-effective use of available resources.
6.1 Direction for future research and practice
The discussion showed that the BULT of stroke patients with hemiplegia was worth learning and promoting. The basis for patients to return to family and society was to improve the independence of ADLs in their daily life. For many ADLs, both hands were required to enable cooperation and coordination of actions to perform complementary tasks [63]. Short-term BULT can improve the local function of the affected upper limb to some extent, but it might not reach the threshold of muscle movement required to perform functional tasks [17,64]. The rehabilitation resources were relatively concentrated in the rehabilitation departments of comprehensive hospitals or specialized rehabilitation hospitals, but the length of a hospital stay is limited. After discharge, stroke patients failed to receive effective continuous rehabilitation training in their communities [18].
The purpose of this article is to propose some fresh avenues of research. Patients recovering motor function in their upper limbs following a stroke-related injury or amputation were the focus of the BULT program [16,20]. Workouts for the upper body were made easier under the UULT setting. For hemiplegic individuals, it is possible that in the future, BT and UT may become more tightly associated [21]. The high usability and robust practicality of BULT were not constrained by external variables like site or equipment, unlike previous systems. While BULT served a purpose in the short term, it was ultimately inefficient. Therefore, BULT may be conducted as soon as possible with assistance, taking into consideration the degree of hemiplegia in the affected upper limb, provided the patient is stable and willing. Only doing the process will not get the desired results [24,65]. Based on in-hospital rehabilitation training, patients should continue to perform BULT after returning to the community to improve their upper-limb function and ADLs. Future studies should explore the feasibility and effectiveness of continuous nursing care and compare the long-term effects. In addition, the dose of BULT was not directly proportional to the upper-limb function in post-stroke hemiplegia [66]. The intensity and time of exercise training must also be determined based on the patient’s tolerance and fatigue index. Moreover, the cooperation, interest, and willingness of patients in each rehabilitation training must be considered. Implementing the optimal effective dose in BULT was recommended to save rehabilitation resources and implement continuous nursing, promoting the maximum rehabilitation training benefits. Multi-center randomized controlled studies are encouraged to investigate the benefits of combining BULT and UULT for patients with stroke hemiplegia (RCTs) [67].
6.2 Strengths and limitations of this study
By determining the optimum scheduling and length of the intervention and the least effective daily training dosage, this study departs from the previous systematic studies that concentrated on the effectiveness of BT. This article can be used as a guide when thinking about how to reduce costs associated with rehabilitation, how to execute round-the-clock care, and how to advertise the greatest possible advantage of rehabilitation training. Patients originate from eight various nations and areas, all with varying medical standards, so study findings may not generalize to other cultural and regional groups. Significant variation in various outcome indicators may have been caused, at least in part, by the potential for bias presented by the small sample size and study population. Only a limited number of articles report on long-term follow-up data, and there is no systematic classification of stroke damage locations. In the meantime, the long-term impacts and implications of various tumor locations remain unknown.
7 Conclusion
The researcher says that the study’s goal is to determine how well BULT helps people who have experienced a stroke or other nerve disease recover movement in their upper limbs. Discourse and investigation of the past with the intent of clarifying the antecedents of the present. Data from all administered assessments, such as theARAT, BBT, WMFT, Fugl-Meyer Evaluation, and others, were considered. The researchers in this investigation read and analyzed about 24,000 works of writing. The data clearly show that the FMA’s safeguards fall short in important respects. Extreme Disruption Patients with hemiplegia who undergo therapy with BULT report feeling happier with their lives. Proponents of BULT exercise argue that even brief bouts of physical activity, such as 30 min, 5 days a week, for 6 weeks, can have positive effects. The meta-analysis included information from ten RCTs involving a total of 1,411 individuals. This meta-analysis found that when it came to decreasing lower limb muscle strain, overall spasm scale score, electromyography score, and passive ankle joint range of motion, biofeedback was significantly more effective than traditional physical therapy. A review of the research found that BULT helped individuals with stroke and hemiplegia use their affected limbs more effectively, but that it didn’t offer any advantages over solo training. It is most important to act quickly after a stroke, within the first 6 months. More research is required to demonstrate that BULT is helpful because acute trials were neglected. Thirty minutes of BULT exercise, twice a day, for 6 weeks was determined to be the minimally effective dosage. A relatively small number of people participated, and the evidence was only marginally better than usual. Patients suffering from stroke may benefit more from a therapy approach that combines BULT and UULT, but this debate should wait until more robust RCTs have been performed.
8 Future scope
Individuals participating in the exergaming recovery trial had to be fully functional 1 year after a stroke, without showing signs of the usual secondary disabilities. Possible causes for the patient’s difficulties include hemianopia, hemineglect, or structural abnormalities in the brain. As a result, we cannot generalize the study’s results to include all stroke victims worldwide. If researchers are intending on conducting bigger investigations in the future, they would do well to include people with a wide range of clinical traits. After it became clear that patients could not be kept safe throughout the process, a single-blind strategy was adopted. One of the drawbacks of this study is that it does not evaluate the patients’ views and degrees of happiness with the exergaming system. Future studies must account for the potential bias brought by this form of data when reporting their findings.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by Zhejiang Medicine Health Science and Technology Project (Grant number: 2019332856).
-
Author contributions: L.J. and Z.Y. worked together on the search strategy, literature review, data processing, and quality assurance. L.J. performed all the work, from gathering information to drafting and revising the final draft. T.W. and Z.Z. completed the analysis and improvements to the text. H.P.’s dual role as an advisor and guarantor makes it ultimately responsible to both for any problems that may emerge. The ultimate harvest success was a group effort.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wafa HA, Wolfe C, Emmett E, Roth GA, Johnson CO, Wang Y. The burden of Stroke in Europe: Thirty-year projections of incidence, prevalence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years. Stroke. 2020;51:2418–27.10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029606Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Omar NH, Mohd Nordin NA, Chai SC, Abdul Aziz AF. Functionality among stroke survivors with upper limb impairment attending community-based rehabilitation. Med J Malays. 2020;75:146–51.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Arwert H, Schut S, Boiten J, Vliet Vlieland T, Meesters J. Patient-reported outcomes of hand function three years after stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2018;1:13–9.10.1080/10749357.2017.1385232Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Tosto-Mancuso J, Tabacof L, Herrera JE, Breyman E, Dewil S, Cortes M, et al. Gamified neurorehabilitation strategies for post-stroke motor recovery: Challenges and advantages. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2022;22:183–95.10.1007/s11910-022-01181-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Nijland RH, van Wegen EE, Harmeling-van DWB, Kwakkel G. Presence of finger extension and shoulder abduction within 72 hours after stroke predicts functional recovery: early prediction of functional outcome after stroke: the EPOS cohort study. Stroke. 2010;41:745–50.10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.572065Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Rochmah TN, Rahmawati IT, Dahlui M, Budiarto W, Bilqis N. Economic burden of stroke disease: A systematic review. Int J Env Res Public Health. 2021;18:7552.10.3390/ijerph18147552Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Coscia M, Wessel MJ, Chaudary U, Millán JR, Micera S, Guggisberg A, et al. Neurotechnology-aided interventions for upper limb motor rehabilitation in severe chronic stroke. Brain. 2019;142:2182–97.10.1093/brain/awz181Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Yi Y, Shim JS, Oh BM, Seo HG. Grip Strength on the Unaffected Side as an Independent Predictor of Functional Improvement After Stroke. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2017;9:616–20.10.1097/PHM.0000000000000694Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Cho TH, Jeong YJ, Lee HJ, Moon HI. The manual function of the unaffected upper extremity can affect functional outcomes after a stroke. Int J Rehabil Res. 2019;1:26–30.10.1097/MRR.0000000000000315Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Chen P, Kwong PWH, Lai CKY, Ng SSM. Comparison of bilateral and unilateral upper limb training in people with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019;14:e216357.10.1371/journal.pone.0216357Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Zhenjing L, Xianzhong M, Yu Q, Min R, Yan Z, Linling J. Bilateral hand function training can significantly improve the hand function of stroke survivors. Chin J Phys Med Rehabil. 2019;8:584–7.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Dhakate D, Bhattad R. Study the effectiveness of bilateral arm training on upper extremity motor function and activity level in patients with sub-acute stroke. Int J Curr Res Rev. 2020;12:31–7.10.31782/IJCRR.2020.122012Search in Google Scholar
[13] Lee Y, Kim MY, Park JH, Park HY. Comparison of the effects of bilateral and unilateral training after stroke: A meta-analysis. NeuroRehabil. 2017;40:301–13.10.3233/NRE-161418Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Kim SH, Park JH. The effect of occupation-based bilateral upper extremity training in a medical setting for stroke patients: A single-blinded, pilot randomized controlled trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;28:104335.10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104335Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Linna J, Zhaojun Z, Hongying P. A review of bilateral arm training in stroke patients. Chin J Nurs Educ. 2021;18:1110–4.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Zhan J, Ai Y, Zhan L, Pan R, Wang Y, Dong C, et al. Effect of abdominal acupuncture combined with routine rehabilitation training on shoulder-hand syndrome after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Integr Med Res. 2022;11:100805. 10.1016/j.imr.2021.100805.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Rodgers H, Bosomworth H, Krebs HI, van Wijck F, Howel D, Wilson N, et al. Robot assisted training for the upper limb after stroke (RATULS): A multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2019;394:51–62. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31055-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Shen L. Upper limb-rehabilitation service system for Chinese mild-stroke patients at home. Espoo, Finland: Aalto University; 2020.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Schneider EJ, Lannin NA, Ada L, Schmidt J. Increasing the amount of usual rehabilitation improves activity after stroke: a systematic review. J Physiother. 2018;62:182–7.10.1016/j.jphys.2016.08.006Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, Bushnell CD, Cucchiara B, Cushman M, et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 2011;42(4):1158–92. 10.1161/str.0b013e31820a8364.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Dash S, Chakraborty C, Giri SK, Pani SK. Intelligent computing on time-series data analysis and prediction of COVID-19 pandemics. Pattern Recognit Lett. 2021;151:69–75. 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.07.027.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Stephens D. World Health Organization’s international classification of functioning, disability and health-ICF. Egs General Assembly Conference; 2001.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.10.1136/bmj.d5928Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Nguyen TT, Nguyen QVH, Nguyen DT, Yang S, Eklund PW, Huynh-The T, et al. Artificial Intelligence in the Battle against Coronavirus (COVID-19): A survey and future research directions [WWW Document]. arXivorg. 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.07343v4(accessed 3.29.23).10.36227/techrxiv.12743933Search in Google Scholar
[25] Desrosiers J, Bourbonnais D, Corriveau H, Gosselin S, Bravo G. Effectiveness of unilateral and symmetrical bilateral task training for arm during the subacute phase after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation. 2005;19:581–93.10.1191/0269215505cr896oaSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Easow A, Chippala P. Effects of bilateral upper limb task training on upper limb function in acute stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Indian J Physiother Occup Ther. 2019;13:218–22.10.5958/0973-5674.2019.00164.3Search in Google Scholar
[27] Han KJ, Kim JY. The effects of bilateral movement training on upper limb function in chronic stroke patients. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;28:2299–302.10.1589/jpts.28.2299Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Bin H, Chao Z. Effects of bilateral movement training on upper limb function in acute stroke patients. Chin J Rehabil. 2017;31:342–4.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Kaur G, Kulkarni PS, Hazari A. Comparison of motor relearning program with bilateral arm training on upper-extremity control in subacute stroke survivors. Crit Rev Phys Rehabil Med. 2019;31:353–61.10.1615/CritRevPhysRehabilMed.2020031239Search in Google Scholar
[30] Lee MJ, Lee JH, Koo HM, Lee SM. Effectiveness of bilateral arm training for improving extremity function and activities of daily living performance in hemiplegic patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26:1020–5.10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.12.008Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Lee S, Song B, Kim H. The effect of bilateral upper limb training on the recovery of upper limb function in patients with acute stroke. Med Leg Update. 2019;19:515–20.10.5958/0974-1283.2019.00095.1Search in Google Scholar
[32] Lin C-H, Chou LW, Luo HJ, Tsai PY, Lieu FK, Chiang SL, et al. Effects of computer-aided interlimb force coupling training on paretic hand and arm motor control following chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2015;10:e131048.10.1371/journal.pone.0131048Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Lin KC, Chen YA, Chen CL, Wu C, Chen YF. The effects of bilateral arm training on motor control and functional performance in chronic stroke: a randomized controlled study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2010;24:42–51.10.1177/1545968309345268Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Meng G, Meng X, Tan Y, Yu J, Jin A, Zhao Y, et al. Short-term efficacy of hand-arm bimanual intensive training on upper arm function in acute stroke patients: A randomized controlled trial. Front Neurol. 2017;8:726.10.3389/fneur.2017.00726Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Morris JH, van Wijck F, Joice S, Ogston SA, Cole I, MacWalter RS. A comparison of bilateral and unilateral upper-limb task training in early poststroke rehabilitation: A randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89:1237–45.10.1016/j.apmr.2007.11.039Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[36] Renner CIE, Brendel C, Hummelsheim H. Bilateral arm training vs unilateral arm training for severely affected patients with stroke: Exploratory single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2020;101:1120–30.10.1016/j.apmr.2020.02.007Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Pengfei S. Effect of bilateral training on the recovery of upper limb motor function in patients with stroke [academic dissertation]. J Public Health Prev Med Southeast Univ. 2020.Search in Google Scholar
[38] Stoykov ME, King E, David FJ, Vatinno A, Fogg L, Corcos DM. Bilateral motor priming for post-stroke upper extremity hemiparesis: A randomized pilot study. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2020;38:11–22.10.3233/RNN-190943Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Tanavarapu B, Prakash PK, Thulasi PRS, Apparao P, Chintada GS, Margrett CM. A comparative study on bilateral and unilateral task-oriented exercises for improving upper extremity motor function in post-stroke subjects with learned nonuse phenomenon. Indian J Public Health Res Dev. 2019;10:56–60.10.5958/0976-5506.2019.03423.5Search in Google Scholar
[40] Qiang W, Fu-biao H, Ru-xiu Y, Tong Z, Hongyu L, Luping S. Effect of Bilateral Movement Training on Upper Extremity Dysfunction after Stroke. Chin J Rehabil Theory Pract. 2018;21:821–5.Search in Google Scholar
[41] Yikang W. Observation on effect of bilateral upper limb training on the recovery of upper limb motor function after cerebral infarction based on Bold-fMRI. Chengdu, Sichuan, China: Chengdu Sport University; 2017.Search in Google Scholar
[42] Wu CY, Lin KC, Wolf SL, et al. Randomized trial of distributed constraint-induced therapy versus bilateral arm training for the rehabilitation of upper-limb motor control and function after stroke. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. 2011;25:130–9.10.1177/1545968310380686Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Kumar C, Kumar M. The efficacy of bilateral training on functional recovery of upper extremity after stroke. Indian J Physiother Occup Ther. 2011;5:35–9.Search in Google Scholar
[44] Manjula S, Selvam PS. A study to compare the effects of unilateral arm training versus bilateral arm training in post-stroke patients with motor impairment of hand. Indian J Physiother Occup Ther. 2020;14:63–72.Search in Google Scholar
[45] Xiaofeng W, Huanxia X, Yuanyuan W. Clinical effect of bilateral upper limb training in stroke patients. Chin J Mod Drug Appl. 2019;10:271–2.Search in Google Scholar
[46] Wu J, Cheng H, Zhang J, Yang S, Cai S. Robot-assisted therapy for upper extremity motor impairment after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys Ther. 2021;101:1–13.10.1093/ptj/pzab010Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Borschmann KN, Hayward KS. Recovery of upper limb function is greatest early after stroke but does continue to improve during the chronic phase: a two-year, observational study. Physiotherapy. 2019;107:216–23.10.1016/j.physio.2019.10.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Lang CE, Waddell KJ, Barth J, Holleran CL, Strube MJ, Bland MD. Upper limb performance in daily life approaches plateau around three to six weeks post-stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021;35:903–14.10.1177/15459683211041302Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Ambreen H, Tariq H, Amjad I. Effects of bilateral arm training on upper extremity function in right and left hemispheric stroke. J Pak Med Assoc. 2021;71:302–5.Search in Google Scholar
[50] Sawant VS, Kanase SB. Effect of conventional therapy and positioning with isometric shoulder exercises on functional shoulder subluxation in post-stroke survivors. Indian J Public Health. 2019;10:536–40.10.5958/0976-5506.2019.01940.5Search in Google Scholar
[51] Han P, Zhang W, Kang L, Ma Y, Fu L, Jia L, et al. Clinical evidence of exercise benefits for stroke. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:131–51.10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[52] Ko H, Kim H, Kim Y, Sohn MK, Jee S. Dose-response effect of daily rehabilitation time on functional gain in stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44:101–8.10.5535/arm.2020.44.2.101Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Schiefelbein ML, Salazar AP, Marchese RR, Rech KD, Schifino GP, Figueiredo CS, et al. Upper-limb movement smoothness after stroke and its relationship with measures of body function/structure and activity- A cross-sectional study. J Neurol Sci. 2019;401:75–8.10.1016/j.jns.2019.04.017Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[54] Pila O, Koeppel T, Grosmaire AG, Duret C. Impact of dose of combined conventional and robotic therapy on upper limb motor impairments and costs in subacute stroke patients: A retrospective study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:770259.10.3389/fneur.2022.770259Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Zhang Q, Schwade M, Smith Y, Wood R, Young L. Exercise-based interventions for post-stroke social participation: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;111:103738.10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103738Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Gurbuz N, Afsar SI, Ayaş S, Cosar SNS. Effect of mirror therapy on upper extremity motor function in stroke patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;28:2501–6.10.1589/jpts.28.2501Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Xiaoguang L, Haoyu W, Chunhui Q, Haiyan G, Yuhua Z, Ping G, et al. Construction of community remote rehabilitation networks for stroke patients based on Internet of things technology. Chin J Hosp Adm. 2021;37:565–9.Search in Google Scholar
[58] Arya KN, Pandian S, Joshi AK, Chaudhary N, Agarwal GG. Active sensory therapies enhancing upper limb recovery among poststroke subjects: A systematic review. Ann Neurosci. 2022;29:104–15. 10.1177/0972753122108673.Search in Google Scholar
[59] Aşkın A, Atar E, Koçyiğit H, Tosun A. Effects of Kinect-based virtual reality game training on upper extremity motor recovery in chronic stroke. Somatosens Mot Res. 2018;35:25–32. 10.1080/08990220.2018.1444599.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Ballester BR, Maier M, Duff A, Cameirão M, Bermúdez S, Duarte E, et al. A critical time window for recovery extends beyond one-year post-stroke. J Neurophysiol. 2019;122:350–7. 10.1152/jn.00762.2018.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Edwards DJ, Cortes M, Rykman-Peltz A, Chang J, Elder J, Thickbroom G, et al. Clinical improvement with intensive robot-assisted arm training in chronic stroke is unchanged by supplementary tDCS. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2019;37:167–80. 10.3233/RNN-180869.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Hayward KS, Kramer SF, Dalton EJ, Hughes GR, Brodtmann A, Churilov L, et al. Timing and dose of upper limb motor intervention after stroke: A systematic review. Stroke [WWW Document]. 2021;52:3706–17. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034348(accessed 3.11.23).10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034348Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Li X, Lin Y-L, Cunningham DA, Wolf SL, Sakaie K, Conforto AB, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the contralesional dorsal premotor cortex for upper extremity motor improvement in severe stroke: Study protocol for a pilot randomized clinical trial. CED. 2022;51:557–64. 10.1159/000521514.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[64] Ravichandran H, Sharma HR, Haile TG, Gelaw AY, Gebremeskel BF, Janakiraman B. Effects of trunk exercise with physioball to improve trunk balance among subjects with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Exerc Rehabil. 2020;16:313–24. 10.12965/jer.2040292.146.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Chakraborty C, Gupta B, Ghosh SK. Mobile metadata assisted community database of chronic wound images. Wound Medicine. Vol. 6. Germany: Elsevier BV; 2014. p. 34–42. 10.1016/j.wndm.2014.09.002.Search in Google Scholar
[66] Ratta P, Kaur A, Sharma S, Shabaz M, Dhiman G. Application of blockchain and internet of things in healthcare and medical sector: applications, challenges, and future perspectives. J Food Qual. 2021;2021:1–20.10.1155/2021/7608296Search in Google Scholar
[67] Ye J. The role of health technology and informatics in a global public health emergency: Practices and implications from the COVID-19 pandemic. JMIR Med Inform. 2020;8:e19866. 10.2196/19866.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

