Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
-
Aparna Shil
Abstract
It is essential to revisit the global biodiversity, search for ethnopharmacologically relevant plants, and unveil their untapped potential to overcome the complications associated while treating infections triggered by multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don of the Apocynaceae family is a medicinal plant used for remedial purposes against infectious diseases from ancient times. In this study, we intended to evaluate the mechanism by which the ethanolic extract of C. roseus root (EECRR) causes the reversal of ampicillin resistance in S. aureus. To achieve this goal, we have stained EECRR-treated S. aureus with acridine orange, analysed DNA damage by comet assay, and studied the alteration of plasmid band pattern and expression of penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) protein. Experiments revealed better S. aureus killing efficiency of EECRR at its minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) doses due to DNA damage and reducing plasmid band intensities along with a decline in the expression of PBP2a in EECRR-treated cells at half-MIC dose. EECRR proved to be an efficient growth inhibitor of S. aureus that reduces the expression of PBP2a. Therefore, EECRR can also render ampicillin-resistant S. aureus susceptible to the antibiotic.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Staphylococcus aureus, a well-known commensal microbe found in human skin and mucous membranes, is known to cause bacterial infections upon gaining an opportunity to invade these physical barriers. According to a case study report by Cai et al., a patient with atypical hip pain had developed systemic sepsis due to an infection caused by S. aureus and ultimately died of multiple organ failure [1]. It can also colonize in urinary stents and cause urinary tract infection (UTI) in renal transplant patients [2]. Penicillin was initially used to treat these infections, which was replaced by methicillin due to the appearance of penicillin-resistant mutants, as was primarily reported in 1946 [3]. Eventually, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) appeared in 1961, and the treatment of MRSA infection became more difficult gradually due to its multidrug-resistant properties. One of the reasons behind the emergence of antibiotic-resistant mutants of S. aureus is the improper use of antibiotics [4]. Acquisition of the mecA gene in MRSA enables them to exhibit resistance against β-lactam antibiotics. Penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a), the product of the mecA gene, confers a lower affinity for all β-lactam antibiotics and restricts their therapeutic use [5]. Vancomycin and teicoplanin have reduced effectiveness on many MRSA strains since they have acquired resistance against those drugs [6]. New drugs, such as linezolid, daptomycin, dalfopristin, fidaxomicin, and tigecycline, are used to treat the infection as an alternative to those antibiotics. However, the dynamic changes in the susceptibilities of S. aureus to these antibiotics have also been reported [7]. The number of currently approved drugs is insufficient to meet the needs of the therapeutic world, and therefore, the necessity of new antibiotics is on the rise.
Researchers now focus on finding alternative therapeutic agents from natural compounds and restrict the use of synthetic products due to their adverse effects on the host system [8]. Indian biodiversity has flourished with medicinally important plants, several of which have been used as traditional healing remedies since ancient times [9]. One such kind of ethnopharmacologically relevant plant is Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don (CR) that belongs to the Apocynaceae family, which has been used as a folk medicine for treating fatal diseases [10]. Previously published reports suggest that C. roseus has antioxidant, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-helminthic, antimicrobial, hypotensive, and wound-healing properties [10,11]. Moreover, scientific evidence also supports that root and leaf extracts of C. roseus have antibacterial effects against many pathogenic strains [12,13]. Recently, in our previous studies, we detected the presence of various bioactive phytoconstituents in C. roseus, such as fatty acids and essential oils that have an antibacterial efficacy [13], and uncovered the mechanism of their antibacterial action against S. aureus in a rat model [14]. Even though there are only a handful of studies, including our previous work, on C. roseus fighting against resistant strains of S. aureus and Candida albicans [15], the mechanism by which C. roseus effectively render S. aureus vulnerable to ampicillin has not been elucidated to date.
Despite the recent trend of using natural resources to manage infections, microorganisms have also developed strategies to overcome bactericidal or bacteriostatic effects of natural product-based drugs [16]. Given the gravity of the situation, our objective was to address bacterial antibiotic resistance and explore strategies to reuse and enhance the effectiveness of currently ineffective antibiotics against multidrug-resistant bacteria. The resistant bacteria were subjected to an herbal extract treatment, which targets to reduce their antibiotic resistance property.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents and chemicals
Mueller–Hinton agar, Mueller–Hinton broth (MHB), and ampicillin discs were purchased from HiMedia (Mumbai, India). Tris–HCl, Tris base, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), agarose, sucrose, 1 kb DNA ladder, bovine serum albumin (BSA), tris buffered saline (TBS)–Tween-20, and Triton-X 100 were purchased from SRL (India). Sodium chloride, disodium hydrogen phosphate, di-hydrogen sodium phosphate, methanol, ethanol, acetic acid, sodium hydroxide, sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS), and sodium acetate were purchased from E Merck (India), and water was deionized using Millipore Milli-Q system (Bedford, MA). Acridine orange (AO), PBP2a monoclonal antibody, lysostaphin, and proteinase K were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). An anti-GAPDH monoclonal antibody was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT) and 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (BCIP) were purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). Ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid (EGTA) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) was purchased from Merck-Millipore (Bengaluru, India).
2.2 Preparation of plant extract
C. roseus plants were obtained from the garden maintained by Presidency University, Kolkata, India. The C. roseus plant samples were subsequently identified and authenticated by the Botanical Survey of India (No: CNH/57/2013/Tech II/1088, 4th October 2013). For the preparation of ethanol extract of C. roseus root (EECRR), a previously published method with a slight modification was followed [14]. The modified step is that the dried root powder was soaked in 100 mL of ethanol for 72 h instead of 48 h for better extraction of components.
2.3 Bacterial strains
In this study, multiple antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains, namely, PU-CA-14 and MC-CL-10, belonging to the category of community-associated and clinical S. aureus strains, respectively, were used. The data regarding their collection and confirmation have been described in our previous studies [13,14]. S. aureus ATCC 25923 was used as a standard reference strain.
2.4 Antibiotic resistance pattern (ARP) of EECRR-treated bacterial cells
The Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method [17] was used to determine the ARP of bacterial cells. The cells were grown overnight in the presence of half of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) dose of EECRR (192.4, 48.4, and 196.4 µg/mL for PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10, respectively, as determined in our previous studies [13,14]). The turbidity of this overnight culture was adjusted by diluting with MHB to make it equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standard so that the culture contains approximately 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL of bacterial cells. Then, 100 µL of such culture was spread over a sterile nutrient agar plate and allowed to stand for 30 min, and commercially available ampicillin discs (10 µg/disc, HiMedia, India) were placed aseptically at the centre of the plate and were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. For the maintenance of proper testing conditions and interpretation of the result, clinical and laboratory standards institute guideline was followed [18].
2.5 Determination of MIC of ampicillin by micro-broth dilution assay
MIC values of ampicillin against EECRR-treated multiple antibiotic-resistant S. aureus (MAR-SA) strains were determined by the micro-broth dilution assay method [13]. Briefly, 0.05 mL of cell suspension from overnight bacterial culture, having 106 CFU/mL colony count, was added to the wells of a microtiter plate containing serially diluted test solutions of ampicillin, starting from a stock concentration of 1 mg/mL. The microtiter plate was incubated at 37°C overnight. Then, the optical density was recorded spectrophotometrically at 600 nm using a multi-mode reader (Biotek Synergy H1, Vermont, USA) to determine MIC values.
2.6 Detection of live and dead bacterial cells by staining with AO
Bacteria were grown in the presence of EECRR, i.e., bacteria were allowed to grow in nutrient broth containing MIC doses of EECRR extract (384.8, 96.8, and 392.8 µg/mL of EECRR for PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10 respectively), as determined in our previous studies [13,14] for one set and 1/2 MIC doses of EECRR (192.4, 48.4, and 196.4 µg/mL of EECRR for PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10, respectively) for another set of experiments. Cells were washed and resuspended in 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and spread over clean grease-free slides to form a thin smear after its density was adjusted to be equivalent to 0.5 McFarland standard (1.5 × 108 CFU/mL). The smears were then fixed in methanol/acetic acid (3:1) solution at 4°C for 14 h and then stained with AO solution (0.19% of AO in 0.1 M phosphate citrate buffer, pH 2.5) for 10 min in the dark. The stained slides were washed with distilled water for 5 min, air-dried, and observed under a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss Axioscope A1, Thornwood, NY, USA) at 1,000× magnification using immersion oil [19]. The excitation filter used was 470 nm, and the barrier filter used was 540–580 nm. The bacterial cells that fluoresce green (maximum emission wavelength: 525 nm) were considered viable, and those that fluoresce red (emission wavelength: ≥630 nm) were considered non-viable due to the abundant damaged DNA. The number of viable cells, the number of dead cells, and the intensity of green and red fluorescence emitted by AO were assessed by ImageJ (NIH, USA; Version 1.52a) software.
2.7 Isolation and electrophoresis of plasmid DNA from EECRR-treated bacteria
Two sets of 1.5 mL bacterial cultures of PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10 strains were grown overnight to extract plasmid DNA. One set was grown in the presence of a 1⁄2 MIC dose of EECRR (192.4, 48.4, and 196.4 µg/mL, respectively), as determined by our previous studies [13,14]. The other set was grown without EECRR, which served as the control for this experiment. Subsequently, the cell pellets were collected, exposed to 2 μL of lysostaphin solution (1.0 μg/mL), and incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Then, 200 μL of an alkaline detergent solution (0.2 N NaOH and 1% SDS) was added, and 150 μL of 3 M sodium acetate (pH 4.8) was introduced. The resulting mixture was then maintained on ice for 10 min.
After centrifugation (Eppendorf, 5424 R, Hamburg. Germany) at 15,000 rpm for 5 min, the supernatant was collected and 1 mL of 95% ice-cold ethanol was added to it and kept at −20°C for 10 min. The supernatant was discarded after centrifugation, and the sediment was resuspended in 50 μL of Tris/EDTA (10 mM Tris–HCl and 1 mM EDTA) pH 8.0. Then, electrophoresis was carried out in 0.5% agarose gel at 30 mA (90 V), and the DNA band was visualized under the ChemiDoc imaging system (BioRad) [20].
2.8 Replica plating
To obtain isolated colonies, overnight bacterial culture (1.5 × 108 CFU/mL) of PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10 was spread on nutrient agar (NA) plates. For preparing the master plate, the isolated colonies were again streaked on fresh NA plates by the streak plate method, which were then replica-plated on NA containing antibiotics (ampicillin, 130 µg/mL), to which the strain is resistant. Then, the cells were treated with a 1/2 MIC dose of EECRR, and replica plating was performed again. Colonies that grew on master plates but failed to grow on plates containing antibiotics were considered plasmid-cured derivatives [21].
2.9 Extraction of protein and Western blot analysis
For extracting protein from control and EECRR-treated cells (with 1/2 MIC dose), bacterial cells were harvested from 500 mL of culture, suspended in 4 mL of lysis buffer (0.25 M sucrose, 20 mM Tris–HCl, 2 mM EDTA, and 2 mM EGTA, pH 7.5), and sonicated three times for 30 s at 100 µA in an ultrasonicator (Hielscher UP100H, Teltow, Germany) at an interval of 30 s in between. The supernatant was collected after centrifugation at 8,000×g for 10 min, and the protein concentration was measured by the Lowry method [22]. Separation of protein was performed on 10% sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with a marker (Precision Plus Dual Color Protein standard, California, USA). Then, the bands were transferred electrically to PVDF (Millipore) membranes and blocked with 5% BSA in TBS–Tween 20 at room temperature for 30 min. Blots were incubated with MRSA anti-PBP2a (1:1,000) monoclonal antibody (Sigma, Aldrich) and anti-GAPDH (1:1,000) monoclonal antibody (Invitrogen, GA1R) at 4°C overnight consecutively. After washing, the blots were again incubated with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G secondary antibody (1:2,000) for 1 h at room temperature. Immunoreactive proteins present in the membrane were detected by staining it with a substrate solution of NBT–BCIP. Band intensities were measured using ImageJ (NIH, USA; Version 1.52a) software, and densitometric analysis was carried out using MS Excel and Statsdirect. The significance level so obtained is based on Mann–Whitney U multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
2.10 Evaluation of DNA integrity by comet assay
This single-cell gel electrophoresis experiment was carried out following the protocol of Solanky and Haydel [23] with some modifications. Briefly, for preparing the microgel, 100 µL of 5% agarose in PBS was spread over the slide. Aliquot of 10 µL of bacterial culture (grown in the presence of MIC doses that were 384.8, 96.8, and 392.8 µg/mL of EECRR for PU-CA-14, ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10, respectively, determined in our previous studies [13,14]) containing 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL cells was mixed with 50 µL of 0.5% agarose (low melting) in PBS, spread uniformly over the agarose, and kept it at 4°C for solidification. Then, the microgel was immersed in lysis solution (NaCl, l2.5 M; EDTA, 100 mM; Triton X-100, 1% (v/v); Tris 10 mM, pH 10), supplemented with lysostaphin (1 µg/mL in PBS) for 1 h followed by dipping it into the enzyme digestion solution (NaCl, 2.5 M; Tris, 10 mM; pH 7.4; EDTA, 10 mM) containing 1 mg/mL of proteinase K for 1 h at 37°C. It was placed in an electrophoresis unit flooded with an electrophoretic buffer (NaOH, 300 mM; EDTA, 1 mM; pH 13) and allowed to stand for 20 min to permit the unwinding of damaged DNA under the buffer. Then, it was exposed to neutralizing buffer (0.4 M Tris, pH 7.5) for 30 min after the continuation of electrophoresis in the electrophoretic buffer for 25 min at 25 V. To visualize DNA, the microgel was stained with ethidium bromide (100 µg/mL) for 10 min and focused under a fluorescence microscope (Zeiss Axioscope A1, Thornwood, NY, USA) with fluorescein isothiocyanate filter combination (excitation: 490 nm, dichroic: 500 nm and emission: 510 nm). The degree of DNA damage was calculated in percentage using the CASP software (http://www.casp.of.pl) [24]. The significance level is based on Mann–Whitney U multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
2.11 Statistical analysis
The significance levels, based on Mann–Whitney U multiple comparison tests, were used for all analyses using Statsdirect 3.0 software. Data were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE), and p values less than 0.05 and 0.01 were considered significant.
3 Results
3.1 Effect of ampicillin on EECRR-treated bacterial cells
Around the ampicillin disc, a clear bacterial growth-free region was detected with measurements of 17 and 28 mm for EECRR-treated S. aureus strains MC-CL-10 and PU-CA-14, respectively (Figure 1), whereas control cells were resistant to this antibiotic [9,10]. MIC values of ampicillin were noted as 15.5 and 34 µg/mL for EECRR-treated PU-CA-14 and MC-CL-10 cells, respectively (Table 1). There were 8-and 4-fold reductions in MIC values of ampicillin for respective bacterial cells as MICs of control cells were 124.2 and 136.75 µg/mL [13,14].

Disc diffusion test with ampicillin (10 µg/disc). (a) PU-CA-14 (control) before treatment with EECRR; (b) PU-CA-14 after treatment with EECRR; (c) MC-CL-10 (control) before treatment with EECRR; and (d) MC-CL-10 after treatment with EECRR.
MIC values and zones of inhibition of ampicillin against bacterial strains, both before and after treatment with EECRR, respectively
| Bacterial strains | MIC (µg/mL) | Zone of inhibition (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before treatment with EECRR | After treatment with EECRR | Before treatment with EECRR | After treatment with EECRR | |
| PU-CA-14 | 124.2 ± 0.56 [12] | 15.5 ± 0.42 | 0.0 | 28.0 ± 0.04 |
| MC-CL-10 | 136.75 ± 0.52 [12] | 34 ± 0.37 | 0.0 | 17.0 ± 0.02 |
3.2 Impact of AO staining on EECRR-treated bacterial cells
While observing bacterial cells stained with AO under a fluorescence microscope, we found that control cells fluoresce green, whereas treated cells appeared red, as AO gives green fluorescence when it intercalates with double-stranded DNA and red fluorescence after electrostatic interaction with single-stranded DNA or RNA. All control merged images (Figure 2a) represent viable cells that are depicted as green bacterial cells. Additionally, the red green blue (RGB) plot profile analysis of the control images (Figure 2b) demonstrates a substantial degree of overlapping of the green fluorescence peaks over the red fluorescence peaks, providing further evidence that the bacterial cells observed in the control images are viable. Likewise, the intensity of red fluorescence peaks overlaps the green fluorescence peaks, indicating dead bacterial cells on exposure to MIC dosage of EECRR.
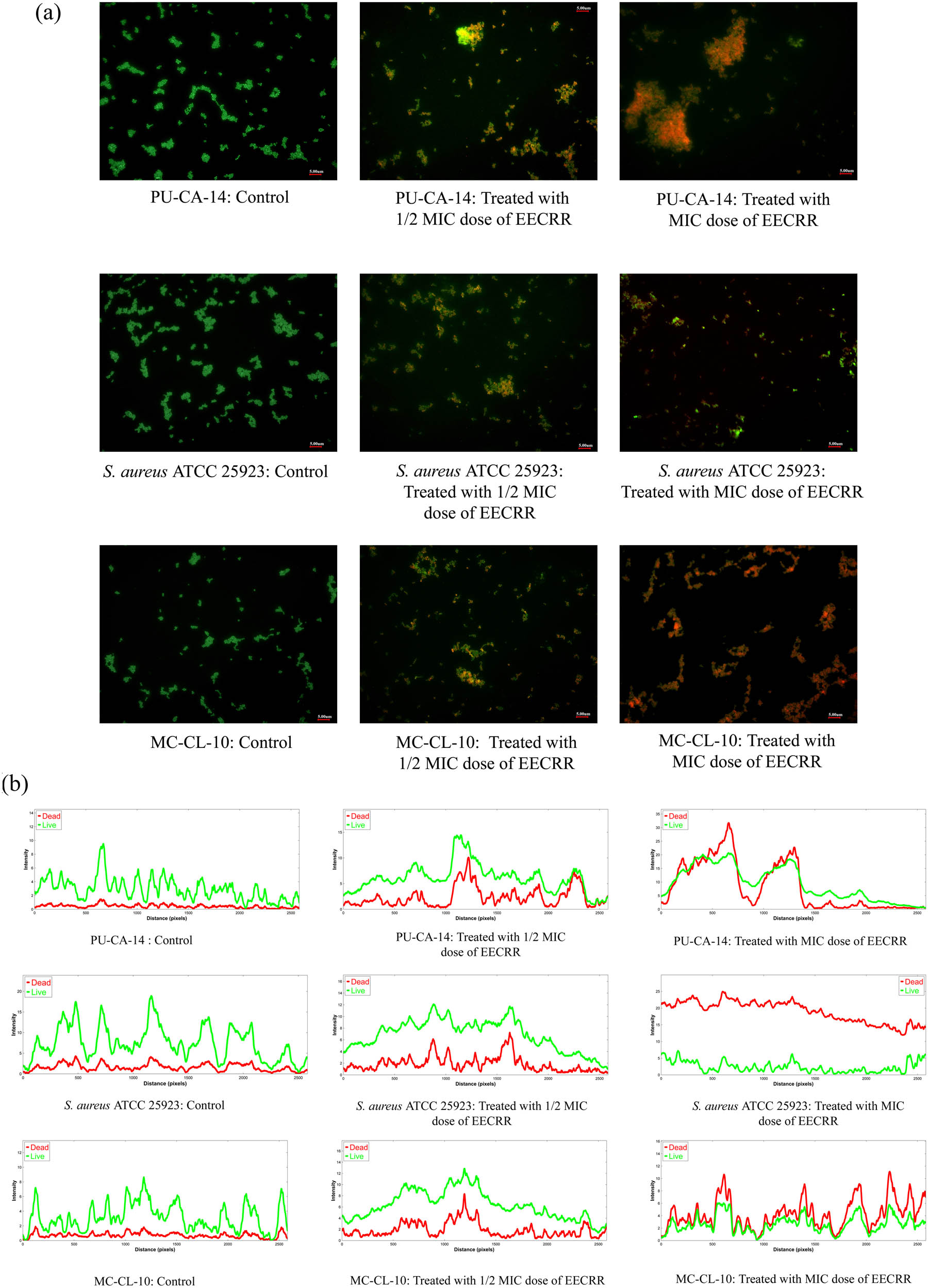
Impact of ampicillin and AO staining on EECRR-treated bacterial cells. (a) Control and EECRR-treated PU-CA-14 and S. aureus ATCC 25923 cells were stained with AO (scale bar = 5.0 µm), and (b) graphs show the RGB plot profiles for treated bacteria with different doses of EECRR based on fluorescence intensity profiles on merged images.
3.3 Impact of EECRR on plasmid band pattern of bacterial cells
After extracting plasmid DNA from EECRR-treated cells, we observed the presence of band (>10,000 bp) in all control cells, whereas in treated cells (PU-CA-14 and MC-CL-10), bands were blurred and no visible band was noted in S. aureus ATCC 25923 after EECRR treatment (Figure 3a).

(a) Impact of EECRR on plasmid band integrity. Prominent plasmid bands are visible in control samples of PU-CA-14 (L1), ATCC 25923 (L3), and MC-CL-10 (L5) when compared to the EECRR-treated samples of PU-CA-14 (L2), ATCC 25923 (L4), and MC-CL-10 (L6). (b) Inhibition of the growth of MAR-SA on treatment with EECRR in the presence of ampicillin. Growth of control bacterial cells on NA plate without ampicillin (a) and with ampicillin (c), growth of EECRR-treated bacterial cells on NA plate without ampicillin (b) and with ampicillin (d). (c) Expressions of PBP2a in control and EECRR-treated cells of PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10 analysed by immunoblotting. PBP2a expressions decreased in EECRR-treated samples of PU-CA-14 (lane 2), S. aureus ATCC 25923 (lane 4), and MC-CL-10 (lane 6) compared to control samples (lanes 1, 3, and 5, respectively). GAPDH was used as the loading control in this study. (d) Densitometric analysis of immunoblots to quantitate PBP2a expression in control and EECRR-treated cells of PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10. The PBP2a protein levels were quantified by analysing the band intensity of each PBP2a and GAPDH band using ImageJ software. PBP2a levels were normalized to GAPDH protein levels and used as a control of total protein loading. The significance level is based on Mann–Whitney U multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01). Data are presented as mean ± SE, n = 3.
3.4 Growth of EECRR-treated bacterial cells in the presence of antibiotics
The growth of bacterial cells on NA plates was checked in the presence and absence of antibiotics by the replica-plating method. The results of this experiment revealed that the cells were unable to grow on NA plates with antibiotic (ampicillin) after treatment with EECRR (Figure 3b).
3.5 Influence of EECRR on the expression of PBP2a protein
Western blot technique was applied to analyse the expression of PBP2a protein in control and EECRR-treated S. aureus cells (PU-CA-14, S. aureus ATCC 25923, and MC-CL-10) by anti-PBP2a antibody. Treated bacterial cells were exposed to a 1/2 MIC dose of EECRR. The expressions of PBP2a (molecular mass: 72 kDa) were remarkably low (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01) in all treated cells when compared to the control cells that exhibited prominent bands of PBP2a (Figure 3c and d). The difference between the expressions of PBP2a is maximum in control and treated cells of MC-CL-10 (p < 0.01).
3.6 Impact of EECRR on DNA integrity
Detection of damaged DNA double strands by comet assay was studied, and it was found that under constant electrophoretic conditions, the distance migrated by severely damaged DNA is longer compared to that by intact DNA. Data obtained from the comet assay by treatment with EECRR at concentrations of 384.8, 96.8, and 392.8 µg/mL are shown in Figure 4. The length of the DNA tail was significantly longer in all three types of S. aureus cells treated with EECRR in the form of a “comet” compared to the control sets.

Effect of EECRR on genomic DNA of S. aureus by (a) comet assay (scale bar = 1.0 μm) and (b) its characteristic analysis. The length of the head and tail of DNA was altered in control (C) and treated (T) bacterial cells. The degree of damage was represented as the percentage of the lengths of the head and tail of comets formed with the help of the CASP software. The significance level is based on Mann–Whitney U multiple comparison test (*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01).
4 Discussion
The skin and mucous membranes of 30% of the human population serve as the natural habitat for microbiota like S. aureus [25]. S. aureus has been detected as a causative agent for ailments, ranging from mere skin infection to severe life-threatening diseases, such as endocarditis, pneumonia, food poisoning, septicaemia, septic shock, post-transplantation liver infection, UTI, and end-stage kidney failure in haemodialysis patients [2,12]. The emergence of MRSA strains has made the management of these diseases more complicated.
The severity of infections can be determined by the physical state of patients since elderly patients are more prone to S. aureus self-infection owing to various other types of age-related illnesses [26]. The health status of elderly individuals may not allow them to cope with the adverse effects caused by the application of new drugs with different chemical configurations. The present study is a follow-up to our previous investigation based on the antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective role of C. roseus. The composition of the plant extract has already been discussed in our previous studies. To highlight a few findings from those studies, EECRR contains two fatty acid esters, 9,12-octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)-2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl) ethyl ester and 9,12-octadecadienoyl chloride, an essential oil, namely, 1-nonadecene and pentacyclic triterpenoid called ursolic acid, as assessed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry [13] and high-performance liquid chromatography [14]. Existing literature provides evidence that these bioactive compounds are found in EECRR and are effective against the growth of bacteria. Essential oils and fatty acids mainly have membrane-damaging effects on bacterial cells. In our previous study, we have shown that EECRR causes the inhibition of efflux pump activity, which helps the antibacterial agents to exert their maximum effects without being flushed out from the cells and also generates intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), which kills bacteria by damaging DNA [14]. Moreover, ursolic acid, being one of the active phyto-components present in EECRR, can have such DNA-damaging properties as stated in the study of Messner et al. [27].
In this study, AO staining of S. aureus shows that a high dose of EECRR (MIC dose) can kill more bacterial cells as indicated by high intensities of red fluorescence, possibly due to DNA damage that results in the accumulation of ssDNA. A comet assay is a sensitive approach developed recently to quantify DNA damage at the single-cell level and identifies genotoxic substances [28]. Prominent DNA damage, observed by the comet assay, validates the cause of cell death on treatment with MIC doses of EECRR. It is already evident that the generation of ROS is one of the reasons for damaging DNA [29] and EECRR has the potency to produce a huge amount of ROS within the bacterial cells [14]. However, the amount of ROS generated by EECRR in mammalian cells is not that significant to cause damage to eukaryotic cells, as observed in the experimental rat model of our earlier investigation [14]. The extract may also influence the other structures of the bacterial cells, as we have previously reported, and it damages the cell envelope as assessed by scanning electron microscopy [13], inactivates efflux pumps present on bacterial cell membranes, and generates ROS within bacterial cells [14]. Our current finding is that the bacterial DNA-damaging capability of EECRR is another key attribute and is essential to combat MAR-SA infection.
Exposure of S. aureus cells to low doses of EECRR results in low intensities of red fluorescence in comparison with that of MIC dose, indicating a lesser number of dead cells. The remaining live cells were subjected to plasmid isolation to investigate whether there was any alteration in plasmid DNA. Our observation was in favour of the results that we obtained after AO staining. This finding persuades us to further explore the mechanism of the loss of antibiotic resistance genes, as in most cases, they reside on the bacterial plasmid. Reported literature suggests that plant extracts have the potential to suppress the antibiotic resistance gene by eliminating or curing plasmids [30,31] and reducing the antibiotic resistance capacity of MRSA [32]. It is also documented that the plasmid-curing effects of the herbal extract can be visualized in gel images, which is analogous to our study [33].
The satisfactory outcome of the replica-plating experiment demonstrates that the underlying mechanism is perhaps due to plasmid curing, as the cells after treatment with EECRR were unable to grow on ampicillin-containing plates. Relevant observation is mentioned by other researchers in this regard [21].
To achieve conclusive results, we targeted the PBP2a expression level as a precise indicator of beta-lactam antibiotic resistance. Resistance to the β-lactam antibiotics, including ampicillin, penicillin, and oxacillin, is principally mediated by the production of PBP2a, encoded by the mecA gene [34]. Čuvalová et al. also detected the presence of the mecA gene in multiresistant staphylococcal species producing PBP2a [35]. According to our experiment, the expression of PBP2a was downregulated in EECRR-treated bacterial cells. Reduced expression of the same protein was also observed in an experiment where MRSA was treated with phlorofucofuroeckol-A [36]. The unavailability or reduced synthesis of PBP2a, due to the effects induced by EECRR on S. aureus, is likely to be the key determinant for the decline in antibiotic resistance observed in MAR-SA strains.
Moreover, eight- and four-fold reduction in MIC values of ampicillin was observed in S. aureus strains of PU-CA-14 and MC-CL-10, respectively, after treatment with EECRR, and increased diameter of zone of bacterial growth inhibition in disc diffusion assay supports the finding that ampicillin-resistant bacterial cells became quite sensitive to β-lactam antibiotics. This outcome is supported by the works of other investigators also [37]. This implies that the extract has inactivated the normal activity of bacterial cells and made them incapable to harm the host. Therefore, EECRR has the potential to increase the susceptibility of MAR-SA to ampicillin. Figure 5 presents a schematic diagram elucidating the EECRR's potential role in augmenting the sensitivity of ampicillin-resistant S. aureus.

Summary of the current study. EECRR has the potential to enhance the sensitivity of ampicillin-resistant S. aureus strains to ampicillin by decreasing the levels of PBP2a protein, which promotes antibiotic resistance. The decrease in PBP2a expression results in a negative impact on the bacteria’s ability to resist antibiotics, as it disrupts the integrity of their plasmid DNA.
5 Conclusion
This study shows that a high dose of EECRR (at MIC value) was capable of killing S. aureus cells by causing DNA damage. Additionally, at a low dose (1/2 MIC value), EECRR can reduce the expression of the PBP2a protein and affect the plasmid DNA of S. aureus. The plasmid in bacterial cells carries genes responsible for antibiotic resistance, which led to a change in the ARP in S. aureus strains. Consequently, S. aureus strains, previously resistant to ampicillin, have become partially sensitive to it due to the effects of EECRR. Additional experiments are required to enhance the susceptibility of bacteria, transitioning them from partially susceptible to completely susceptible to the combined effect of the plant extract and antibiotic. Nevertheless, this achievement is beneficial as it will allow previously ineffective antibiotics to regain the effectiveness, thereby simplifying the treatment of infectious diseases caused by multidrug-resistant bacterial strains. Moreover, this treatment approach, after EECRR passes the safety assessment to conduct clinical trials, would be cost-effective as affordable antibiotics like ampicillin can be reused again for therapeutic purposes.
Acknowledgement
The authors are thankful to Presidency University, Kolkata, for providing the central instrument facilities.
-
Funding information: The authors acknowledge the financial assistance received from the FRPDF Grant of Presidency University Kolkata, to the corresponding author, the DST-FIST Programme of the Department of Life Sciences, Presidency University, Kolkata (Grant No. SR/FST/LSI-560/2013(c), dated 23-06-2015), and DBT-BUILDER (Department of Biotechnology Boost to University Interdisciplinary Life Science Departments for Education and Research) Grant of Department of Life Sciences, Presidency University, Kolkata (Grant No. BT/INF/22/SP45088/2022; dated 17-02-2022).
-
Author contributions: All the authors have accepted liability for the entire content of this submitted manuscript and confirmed its submission. Aparna Shil, Sushmit Mukherjee, Prerona Biswas, and Sudipta Majhi were equally responsible for the concept, experimental design, and performing experiments. Aparna Shil has performed the formal analysis and has written the original draft. Aparna Shil, Prerona Biswas, and Sudipta Majhi are responsible for software handling, data presentation, and revising it for confirmation of submission. Sudipta Majhi provided some valuable resources for the experiments. Sushmit Mukherjee helped to overcome the difficulties faced during the experiment comet assay. Sima Sikdar was involved in collecting samples, maintaining them, and helping in the investigation. Biswadev Bishayi and Mausumi Sikdar (née Bhakta) were responsible for the concept and experimental design, reviewing the original draft and data analysis. Mausumi Sikdar (née Bhakta) has provided instrumental, infrastructural, and financial support and final approval for the submission of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on a reasonable request.
References
[1] Cai D, Ma X, Zhou Y, Zhu Y, Yu H, Cheng W. Multiple organ failure and death caused by Staphylococcus aureus hip infection: A case report. Open Life Sci. 2022;17(1):1129–34. 10.1515/biol-2022-0481.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Sarier M, Seyman D, Tekin S, Duman I, Uygun B, Demir M, et al. Comparison of ureteral stent colonization between deceased and live donor renal transplant recipients. Transpl Proc. 2017;49:2082–5.10.1016/j.transproceed.2017.09.028Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Harkins CP, Pichon B, Doumith M, Parkhill J, Westh H, Tomasz A, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus emerged long before the introduction of methicillin into clinical practice. Genome Biol. 2017;18(1):1–11. 10.1186/s13059-017-1252-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Llor C, Bjerrum L. Antimicrobial resistance: risk associated with antibiotic overuse and initiatives to reduce the problem. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2014;5(6):229–41.10.1177/2042098614554919Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Fergestad ME, Stamsås GA, Morales Angeles D, Salehian Z, Wasteson Y, Kjos M. Penicillin-binding protein PBP2a provides variable levels of protection toward different β-lactams in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiologyopen. 2020;9:e1057. 10.1002/mbo3.1057.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Szymanek-Majchrzak K, Mlynarczyk A, Mlynarczyk G. Characteristics of glycopeptide-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from inpatients of three teaching hospitals in Warsaw, Poland. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018;7(1):4–9. 10.1186/s13756-018-0397-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Jian Y, Lv H, Liu J, Huang Q, Liu Y, Liu Q, et al. Dynamic changes of Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to vancomycin, teicoplanin, and linezolid in a central teaching hospital in Shanghai, China, 2008–2018. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:1–10. 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00908.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Mohsen S, Dickinson JA, Somayaji R. Update on the adverse effects of antimicrobial therapies in community practice. Can Fam Physician. 2020;66:651–9.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Rupani R, Chavez A. Medicinal plants with traditional use: Ethnobotany in the Indian subcontinent. Clin Dermatol. 2018;36:306–9.10.1016/j.clindermatol.2018.03.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Nisar A, Mamat AS, Hatim MI, Aslam MS, Ahmad MS. An updated review on Catharanthus roseus: phytochemical and pharmacological analysis. Indian Res J Pharm Sci. 2016;3(2):631–53.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Aruna MS, Prabha MS, Priya NS, Nadendla R. Catharanthus roseus: Ornamental plant is now medicinal boutique. J Drug Deliv Ther. 2015;5(3):1–4.10.22270/jddt.v5i3.1095Search in Google Scholar
[12] Hanawa T, Shimoda-Komatsu Y, Araki K, Ohyama M, Ohnishi H, Kamiya S, et al. Skin and soft tissue infections caused by different genotypes of PVL-positive community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2020;73:72–5.10.7883/yoken.JJID.2019.162Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Shil A, Mukherjee S, Bishayi B, Sikdar (Nee) Bhakta M. A comparison of antibacterial effects of Catharanthus roseus and Camellia sinensis (Black Tea) and their synergistic effect along with antibiotic against multiple antibiotic resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J Herbs Spices Med Plants. 2021;27(2):135–48. 10.1080/10496475.2020.1815921.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Shil A, Banerjee A, Maji BK, Biswadev B, Sikdar M. Multiple antibiotic resistant Staphylococcus aureus induced hepatocellular anomaly: A possible amelioration by Catharanthus roseus (L.) G.Don. South Afr J Bot. 2022;148(2022):446–59. 10.1016/j.sajb.2022.05.014.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Neglo D, Adzaho F, Agbo IA, Arthur R, Sedohia D, Tettey CO, et al. Antibiofilm activity of Azadirachta indica and Catharanthus roseus and their synergistic effects in combination with antimicrobial agents against fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans strains and MRSA. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med. 2022;2022:1–13. 10.1155/2022/9373524.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Vadhana P, Singh BR, Bharadwaj M. Emergence of herbal antimicrobial drug resistance in clinical bacterial isolates. Pharm Anal Acta. 2015;6(10):434. 10.4172/21532435.1000434.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Uddin SA, Bashir L, Naz S, Naz H, Baig SY. Linezolid study on isolates of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli through disc diffusion method. RADS J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2018;6(4):264–9.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility tests: Approved standard - 11th edn; 2012.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Kayumov AR, Nureeva AA, Trizna EY, Gazizova GR, Bogachev MI, Shtyrlin NV, et al. New derivatives of pyridoxine exhibit high antibacterial activity against biofilm-embedded Staphylococcus cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:1–10. 10.1155/2015/890968.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Hemamalini V, Kavitha V, Ramachandran S. In vitro antibiogram pattern of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from wound infection and molecular analysis of mecA gene and restriction sites in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2015;6:170–5. 10.4103/2231-4040.165019.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Patwardhan RB, Shinde PS, Chavan KR, Devale A. Reversal of plasmid encoded antibiotic resistance from nosocomial pathogens by using Plumbago auriculata root extracts. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2015;2:187–98.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr AL, Randall R. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6Search in Google Scholar
[23] Solanky D, Shelley EH. Adaptation of the neutral bacterial comet assay to assess antimicrobial-mediated DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Methods. 2012;23(2):257–61. 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.08.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Końca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Góźdź S, et al. A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res. 2003;534:15–20.10.1016/S1383-5718(02)00251-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Laux C, Peschel A, Krismer B. Staphylococcus aureus colonization of the human nose and interaction with other microbiome members. Gram-Positive Pathog. 2019;7:723–30. 10.1128/9781683670131.ch45.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Tang H, Long N, Lin L, Liu Y, Li J, Sun F, et al. Effect of MRSA on CYP450: Dynamic changes of cytokines, oxidative stress, and drug-metabolizing enzymes in mice infected with MRSA. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:229–38. 10.2147/IDR.S153871.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Messner B, Zeller I, Ploner C, Frotschnig S, Ringer T, Steinacher-Nigisch A, et al. Ursolic acid causes DNA-damage, P53-mediated mitochondria- and caspase-dependent human endothelial cell apoptosis, and accelerates atherosclerotic plaque formation in vivo. Atherosclerosis. 2011;219:402–8.10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.05.025Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Dong Y, Zhu H, Shen Y, Zhang W, Zhang L. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles of different particle size against Vibrio natriegens. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):22322. 10.1371/journal.pone.0222322.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Hong Y, Zeng J, Wang X, Drlica K, Zhao X. Post-stress bacterial cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116(20):10064–71. 10.1073/pnas.190173011.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Soman YP, Mohite JA, Thakre SM, Raokhande SR, Mujumdar SS. Plasmid curing activity by seed extracts of Cuminum cyminum, Coriandrum sativum and Myristica fragrans Houtt. and fruit peel extracts of orange, banana and pineapple against gram negative bacteria. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2015;4(Special Issue 2):302–16.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Srivastava P, Wagh RS, Puranik NV, Puntambekar HM, Jahagirdar SS, Dhakephalkar PK. In vitro plasmid curing activity of aqueous extract of Terminalia chebula fruit against plasmids of Bacillus subtilis and Shigella sonnei. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2015;7(4):298–301.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Oyedemi SO, Oyedemi BO, Prieto JM, Coopoosamy RM, Stapleton P, Gibbons S. In vitro assessment of antibiotic-resistance reversal of a methanol extract from Rosa canina L. South Afr J Bot. 2016;105(2016):337–42. 10.1016/j.sajb.2016.03.013.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Patwardhan RB, Dhakephalkar PK, Chopade BA, Dhavale DD, Bhonde RR. Purification and characterization of an active principle, lawsone, responsible for the plasmid curing activity of Plumbago zeylanica root extracts. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1–10. 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02618.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Foster TJ. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2017;41:430–49. 10.1093/femsre/fux00.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Čuvalová Z, Pipová M, Kantíková M, Brtková A, Fajber J. Virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of coagulase-negative Staphylococci isolated from drinking water. Open Life Sci. 2015;10:328–38. 10.1515/biol-2015-0034.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Eom SH, Lee DS, Jung YJ, Park JH, Choi JI, Yim MJ, et al. The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98:9795–804. 10.1007/s00253-014-6041-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] Bharathan S, Sundaramoorthy NS, Chandrasekaran H, Rangappa G, ArunKumar GP, Subramaniyan SB, et al. Sub lethal levels of platinum nanoparticle cures plasmid and in combination with carbapenem, curtails carbapenem resistant Escherichia coli. Sci Rep. 2019;9:1–13. 10.1038/s41598-019-41489-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

