Abstract
Monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data refers to evaluating the anesthesia depth status of patients during the surgical process by monitoring their physiological index data, and conducting analysis and judgment. The depth of anesthesia is crucial for the safety and success of the surgical process. By monitoring the state of anesthesia depth, abnormal conditions of patients can be detected in a timely manner and corresponding measures can be taken to prevent accidents from occurring. Traditional anesthesia monitoring methods currently include computer tomography, electrocardiogram, respiratory monitoring, etc. In this regard, traditional physiological indicator monitoring methods have certain limitations and cannot directly reflect the patient’s neural activity status. The monitoring and analysis methods based on neuroscience can obtain more information from the level of brain neural activity. Purpose: In this article, the monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data would be studied through neuroscience. Methods: Through a controlled experiment, the monitoring accuracy of traditional anesthesia status monitoring algorithm and neuroscience-based anesthesia status monitoring algorithm was studied, and the information entropy and oxygen saturation of electroencephalogram signals in patients with different anesthesia depth were explored. Results: The experiment proved that the average monitoring accuracy of the traditional anesthesia state monitoring algorithm in patients’ blood drug concentration and oxygen saturation reached 95.55 and 95.00%, respectively. In contrast, the anesthesia state monitoring algorithm based on neuroscience performs better, with the average monitoring accuracy of drug concentration and oxygen saturation reaching 98.00 and 97.09%, respectively. This experimental result fully proved that the monitoring performance of anesthesia state monitoring algorithms based on neuroscience is better. Conclusion: The experiment proved the powerful monitoring ability of the anesthesia state monitoring algorithm based on neuroscience used in this article, and explained the changing trend of brain nerve signals and oxygen saturation of patients with different anesthesia depth states, which provided a new research method for the monitoring and analysis technology of anesthesia depth state data.
1 Introduction
Anesthesia is a medical practice that involves administering medication to patients during surgical procedures to keep them unconscious or reduce their sensitivity to pain. Anesthesia plays a vital role in modern medicine, allowing surgical procedures to be performed safely and effectively. Otherwise, these surgeries can be very painful or dangerous. To ensure the safety and effectiveness of anesthesia, it is important to monitor the patient’s anesthesia depth throughout the entire surgical process. This process helps anesthesiologists accurately evaluate the level of sedation, analgesia, and amnesia required to maintain the appropriate level of anesthesia during the surgical process. By closely monitoring and adjusting the depth of anesthesia for patients, anesthesiologists can minimize the risk of side effects and complications related to anesthesia, and promote faster and more successful postoperative recovery. As an emerging technology, neuroscience has a wide range of applications and potential. Here are some of the main applications: brain science, neural engineering, psychology, psychiatry, etc. It can provide better healthcare, scientific research, and human welfare services for people.
Based on the relevant information consulted, the following scholars’ research on anesthesia technology is listed. Pandya et al. studied the origin, evolution, and dissemination of anesthesia monitoring standards. He documented the significant changes in medical practice caused by the activities of a small group of anesthesiologists at Harvard Affiliated Hospital, ending with the current strategy of minimizing anesthesia-related risks. In addition, he also consulted public domain documents and major source materials, which led to the establishment of Harvard University’s groundbreaking minimum monitoring anesthesia monitoring standards [1]. Shander pointed out that anesthesia practice has historically been rooted in the management needs for issues such as pain and consciousness, which belong to the field of the nervous system, and many anesthetics play a major role in the brain. In addition, he discussed the challenges of monitoring brain function during anesthesia. Although brain function is an important aspect of anesthesia, technological limitations make monitoring brain function more difficult. In contrast, the functions of the heart, circulatory system, blood, lungs, and kidneys are easier to understand and measure [2]. Romagnoli believed that individual responses to sedatives and hypnotic are highly variable, and determining personalized doses during anesthesia in the operating room and sedation in the intensive care unit may have beneficial effects. He discussed the importance of electroencephalography in exploring anesthesia and sedative responses. The processed electroencephalogram (EEG) provides easy-to-use indicators that can be used to optimize anesthesia management. Moderate or deep sedation in operating room anesthesia and intensive care units driven by EEG monitors may become a standard practice. Therefore, electroencephalography can be used to optimize anesthesia management, which may become a standard practice for future anesthesia and sedation management [3]. Saito used a repeated measure design to study the ECG responses under 1% halothane anesthesia, 1.5% isoflurane nitrous oxide anesthesia, and awake state by comparing the ECG responses and exploring the effects of different anesthetics on ECG indicators, providing good research information on anesthesia techniques [4]. The above research involves multiple research fields of anesthesia technology and provides guidance for the research of this topic. These literature did not conduct joint research on anesthesia technology and neuroscience, which limited the in-depth research of this topic.
After further literature review, the following research literature on anesthesia technology and neuroscience was found. Mangia pointed out that more and more otorhinolaryngological operations have adopted sedative local anesthesia, which may be related to reducing the incidence rate and cost of surgery. He discussed the feasibility of facial nerve monitoring in otologic surgery. Although facial nerve monitoring is usually used for surgery under general anesthesia, objective reports show that intraoperative facial nerve monitoring under local anesthesia and sedation is feasible and reliable. As the level of anesthesia increases, a gradually decreasing low amplitude baseline value is usually obtained, and isolated oscillations can be distinguished from those of surgical procedures or nerve electrical stimulation. Therefore, intraoperative facial nerve monitoring is feasible under less active anesthesia management, and the need for intraoperative nerve monitoring should not become an obstacle to otology surgery [5]. Nunes emphasized the importance of wise selection of anesthetics and evaluated the effects of anesthesia depth, hemodynamic status, and other factors that may interfere with signal capture during intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring. In addition, he pointed out that due to the advancement of neural monitoring technology in recent years, it is possible to gain a deeper understanding of neural function during anesthesia during surgery and evaluate intraoperative awareness and neural integrity in real-time. Neurophysiological monitoring can be used for surgeries that pose risks to targeted nerve tissue and adjacent structures, which can be highly sensitive and specific in linking surgical procedures with neurophysiological changes, and identify risk situations before surgery to prevent postoperative neurological deficits [6]. Through reading, it is evident that scholars have provided valuable insights into the research direction. However, their research mainly focuses on theoretical research and lacks empirical verification. In order to optimize this issue, the aim is to conduct more data research and analysis to strengthen their research.
In this article, anesthesia status data was monitored and analyzed using a neuroscience-based anesthesia status monitoring algorithm. The experiment showed that the average value of information entropy of EEG signal in conscious state, mild anesthesia state, and severe anesthesia state was 0.794, 0.573, and 0.3975, respectively. With the increase of the depth of anesthesia, the information entropy of EEG signals gradually decreased, the complexity decreased, and the intensity reflecting the brain neural activity decreased. In addition, the average oxygen saturation in conscious state, mild anesthesia state, and severe anesthesia state was 97.97, 93.50, and 90.71%, respectively, which indicated that with the deepening of anesthesia, the patients’ oxygen saturation would decrease. The innovation of this article lies in the use of neuroscience-based monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data. Compared to traditional anesthesia status monitoring methods, this method can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s brain neural activity and blood oxygen levels at different anesthesia depths, and achieve more accurate monitoring of anesthesia status.
2 Evaluation on monitoring anesthesia depth status data
2.1 Monitoring aspects of anesthesia status data
Anesthesia status data monitoring plays an important role in modern anesthesia medicine, as it can improve surgical safety and patient’s quality of life [7,8]. This monitoring refers to the monitoring and recording of the patient’s physiological parameters during the anesthesia process to ensure that the patient is in a safe anesthesia state during surgery. By monitoring the physiological parameters of patients, anesthesiologists can promptly detect and handle abnormal situations that occur during anesthesia, in order to ensure the safety of patients. Anesthesia status data monitoring usually requires monitoring the following aspects.
2.1.1 Consciousness level
Consciousness level refers to a person’s level of awakening and cognitive state, which can be evaluated through various methods, such as observing a patient’s facial expressions, language responses, motor responses, etc. [9,10]. During the anesthesia process, monitoring the level of consciousness is very important, as changes in the depth of anesthesia directly affect the safety and success rate of the surgical process. The following is a detailed explanation of the different levels of consciousness.
Awakening state refers to the patient’s complete awakening and clear state of consciousness, which allows them to make appropriate responses and reactions. Before and after anesthesia surgery, a clear state needs to be maintained.
Drowsiness refers to the patient being in a very mild state of anesthesia, but still able to breathe autonomously and have certain reactions. The drowsiness state is usually used during the sedation stage before surgery to make the patient feel comfortable and relaxed.
Sedative state refers to a conscious and relatively deep state of anesthesia in which the patient’s conscious state weakens, but can still be awakened. It is usually used during surgery to make patients feel comfortable and relaxed, while also reducing pain and discomfort during the surgery process.
Unconscious state refers to the state in which a patient is completely unconscious and unable to respond in any way, requiring the use of auxiliary equipment such as a ventilator for breathing and maintaining life functions. It needs to be used during surgery to ensure safe operation in the surgical department.
2.1.2 Breathing
Breathing is one of the important functions of the human body to maintain life, and monitoring respiratory changes is also very important in monitoring anesthesia depth status data. The following is a detailed explanation of the different aspects of breathing.
Breathing depth: The depth of exhalation and inhalation can usually be determined by the breathing amplitude. During anesthesia, changes in respiratory depth may affect the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs, leading to respiratory dysfunction.
Respiratory rate refers to the number of breaths per unit time. The respiratory rate of normal adults is 12–20 times per minute. During anesthesia, the change of respiratory rate usually reflects the influence of anesthetic drugs on respiratory control.
Respiratory rhythm refers to the regularity of breathing, including the pause time between exhalation, inhalation, and breathing. Abnormal respiratory rhythm may lead to problems such as alveolar collapse and hypoxia.
2.1.3 Circulation system
The circulatory system is a human system composed of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Its main function is to transport oxygen and nutrients to various parts of the body, while also transporting metabolic products and carbon dioxide from within the body to the lungs and kidneys for excretion. By monitoring the status of the circulatory system, the degree of anesthesia can be analyzed. The following is a detailed explanation of the different aspects of the loop.
Heart rate refers to the number of beats per minute of the heart, with a normal adult heart rate of 60–100 beats per minute. During anesthesia, changes in heart rate may reflect the impact of anesthetic drugs on the heart, and the occurrence of heart rate abnormalities may lead to problems such as poor blood flow and impaired cardiac function.
Blood pressure refers to the pressure of blood flow on the walls of blood vessels, including two values: systolic and diastolic blood pressure. During anesthesia, changes in blood pressure may be influenced by anesthetic drugs and surgical stimuli.
Oxygen saturation refers to the amount of oxygen in the blood, usually expressed as oxygen saturation. Under normal circumstances, the oxygen saturation should be above 95%, and below 90% may lead to hypoxia.
2.1.4 Muscle state
During the surgery process, muscle relaxants can help doctors perform the surgery better and avoid affecting the quality and safety of the surgery due to the patient’s muscle resistance. The following is a detailed explanation of muscle status.
Degree of muscle relaxation: During anesthesia, the use of muscle relaxants can cause muscle relaxation. Improper use may lead to muscle stiffness or inability to move during consciousness recovery.
Muscle resistance: After the action of anesthetic drugs, some patients may experience muscle resistance, which means that muscle contraction is difficult to be completely suppressed. At this point, the doctor needs to reassess the degree of muscle relaxation and adjust the medication use and dosage.
2.1.5 Pupillary response
The pupils are black circles in the eyes, through which light can enter. Pupil response refers to the automatic adjustment of the pupils to changes in light. Under normal circumstances, when light shines on the eyes, the pupils would quickly contract to limit excessive light from entering the eye and causing damage. Under deep anesthesia, due to the suppression of nervous system function, the contraction response of the pupils would weaken or disappear. Therefore, monitoring the pupillary response can help to understand the patient’s level and depth of anesthesia, adjust the dosage of anesthesia in a timely manner, and handle sudden situations to ensure anesthesia safety. The following is a detailed explanation of the pupil response.
Pupil size: Under normal circumstances, a person’s pupil size ranges from 2 to 6 mm. The size of the pupils is influenced by various factors, such as light intensity and surrounding environment.
Response to light: This refers to the reaction of the pupils to light. Normally, when light strikes an eye, the pupil of that eye contracts to protect the retina from damage. The pupils of the other eye would slightly dilate to adapt to dark environments.
Pupil reflex: Pupil reflex refers to the automatic contraction and dilation of the pupils caused by light shining on the eyes. By observing changes in pupil size, doctors can determine whether a patient is under anesthesia and whether the nervous system is functioning properly.
The above aspects can be monitored using professional instruments to help doctors determine whether the depth of anesthesia has reached an appropriate level. Monitoring anesthesia depth status data can effectively improve the safety and success rate of anesthesia surgery. The monitoring aspect of anesthesia status data is shown in Figure 1.
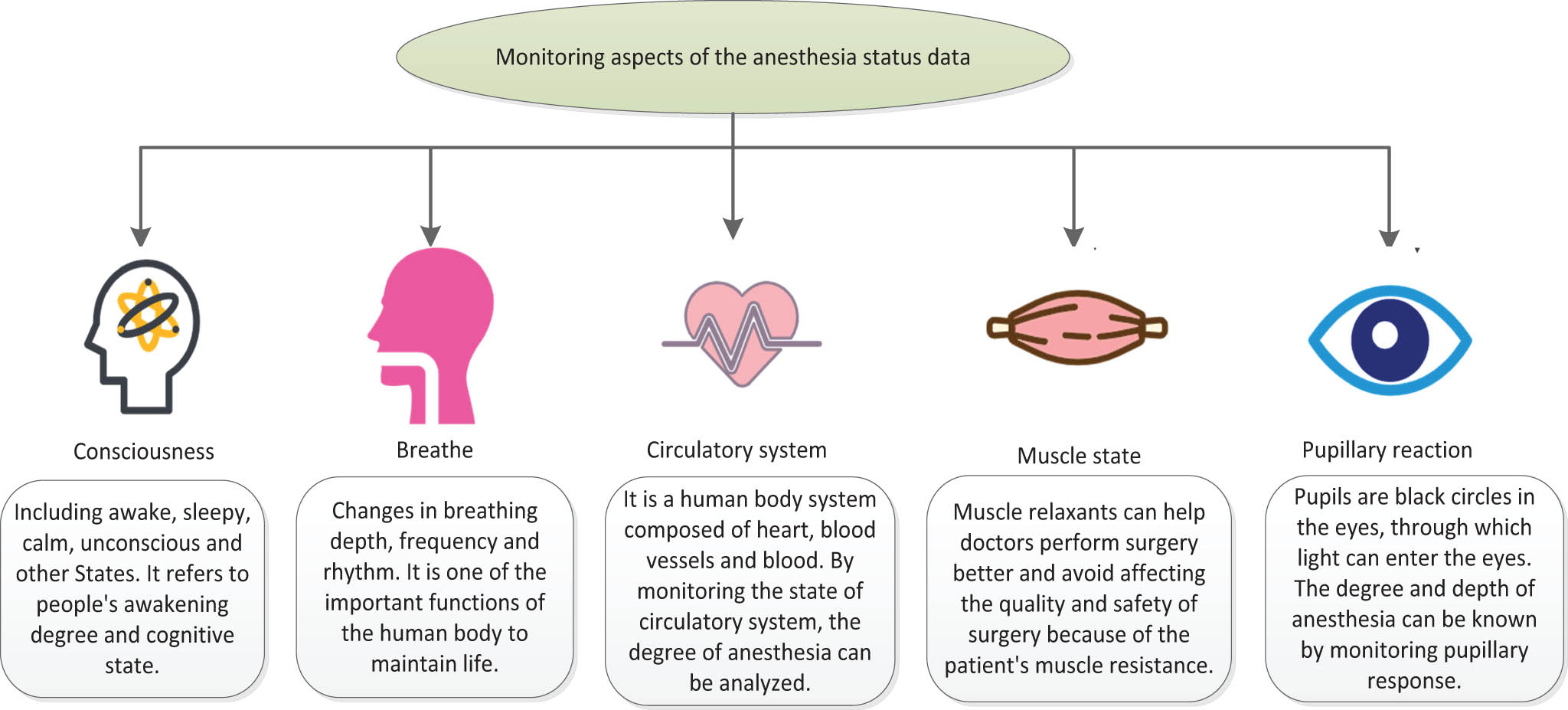
Monitoring aspect of anesthesia status data.
2.2 Monitoring process of anesthesia status data
In anesthesia operations, monitoring anesthesia status data is very important. It can help anesthesiologists detect changes in the patient’s vital signs and anesthesia depth in a timely manner, and take necessary measures to ensure the patient’s safety [11,12]. Therefore, the monitoring process of anesthesia status data needs to strictly follow the prescribed processes and standards to ensure the accuracy and reliability of monitoring. Anesthesiologists should be proficient in the techniques and methods of monitoring anesthesia status, timely record monitoring data, analyze and judge monitoring data, take corresponding anesthesia control measures, and ensure that patients are in a safe state during the anesthesia process. The monitoring process of anesthesia status data mainly includes the following steps.
2.2.1 Pre-anesthesia assessment
Pre-anesthesia assessment refers to a detailed assessment of a patient’s physical condition by medical personnel before undergoing anesthesia, in order to determine whether anesthesia is suitable and which anesthesia method to choose. At the same time, it can also identify some risk factors related to anesthesia [13,14]. Pre-anesthesia assessments are usually completed by anesthesiologists or other professional healthcare personnel.
During the pre-anesthesia assessment, medical staff need to collect the patient’s medical history and family history information, including the patient’s past medical history, family medical history, surgical experience, allergies, smoking, alcohol consumption, drug use, and so on, and whether the patient has special needs, such as arranging the ventilator in advance. Medical staff also need to understand the patient’s current physical condition, including vital signs, height, weight, respiratory status, heart condition, liver and kidney function, blood test results, etc.
Based on the results of the pre-anesthesia assessment, medical staff would assess the patient’s anesthesia risk and develop corresponding plans [15]. If a patient is found to have a high risk of anesthesia, necessary measures need to be taken to handle it, such as selecting safer anesthesia methods, adjusting the amount of anesthesia, and regularly monitoring vital signs.
2.2.2 Anesthesia induction
Anesthesia induction refers to the process of injecting a certain dose of anesthetic into a patient before undergoing medical procedures such as surgery, causing them to lose consciousness, become insensitive to external stimuli, relax their muscles, and feel painless. This process requires a detailed evaluation by professional medical personnel based on the patient’s physical condition and the type of surgery.
During the anesthesia induction process, medical staff would inject drugs into the patient to put them into a state of anesthesia. The choice of medication would depend on the patient’s physical condition, surgical type, and the physician’s personal experience. Usually, anesthetic drugs can be divided into two types: intravenous anesthesia and inhalation anesthesia.
In addition, medical personnel need to closely monitor the patient’s awareness level, breathing, heart rate, and other indicators to ensure that the patient is in a safe state to complete the surgery. If the dosage of anesthetic drugs is insufficient, patients may wake up during the surgery and feel pain and discomfort. If the dosage is too large, it may lead to respiratory depression and other complications, and even endanger the patient’s life.
2.2.3 Anesthesia maintenance
Anesthesia maintenance refers to the continuous monitoring of the patient’s vital signs and depth of anesthesia after the patient enters the anesthesia state. Medical personnel need to adjust the dosage and method of anesthesia medication to maintain the patient in an appropriate anesthesia state. At the same time, medical personnel should also pay attention to monitoring the patient’s respiratory and circulatory functions to avoid intraoperative accidents and complications. In addition, medical personnel also need to pay attention to the comfort of patients, adjust the operating room environment and posture, and other factors to minimize patient’s discomfort and pain, and improve surgical effectiveness and safety. In summary, anesthesia maintenance is a crucial task that directly affects the patient’s life safety and surgical quality.
2.2.4 Anesthesia relief
After the surgery is completed, medical staff need to take a series of measures to help patients recover smoothly from anesthesia, ensuring that they can smoothly return to a conscious state and have stable physical indicators, and facilitating the smooth return to the ward for further treatment. These measures include observing the patient’s vital signs, monitoring the depth of anesthesia, and alleviating pain, which helps medical personnel identify and handle potential risks in a timely manner, and improves the safety and success rate of the anesthesia relief process.
2.2.5 Post-anesthesia observation
Post-anesthesia observation refers to the need for medical personnel to conduct detailed observation and evaluation of patients after receiving anesthesia treatment. This process is very important as it can help identify and promptly address potential complications or sequelae. During anesthesia, the vital signs of patients may be affected, including changes in breathing, circulation, nervous system, and other aspects. If medical personnel do not observe and evaluate in a timely manner, corresponding measures cannot be taken in a timely manner, which may worsen the patient’s health condition and even endanger their life. Therefore, post-anesthesia observation is an indispensable part of the anesthesia treatment process. Meanwhile, during the post-anesthesia observation process, medical personnel also need to evaluate the metabolism and excretion of anesthetic drugs to determine when the patient can be safely discharged.
3 Evaluation on monitoring anesthesia status
3.1 Application of neuroscience in anesthesia technology
Neuroscience is the discipline that studies the structure, function, and development of the nervous system. It involves multiple levels, from molecular and cellular level research, physiological and behavioral experiments, to imaging research of the nervous system, and the development of computer models. Research in this field has helped researchers better understand the mechanisms of the brain and other nervous systems, thereby driving the development of many fields related to nerves, such as cognitive neuroscience, neuropharmaceutics, neurological diseases, and so on. Neuroscience plays an important role in exploring the fundamental research of the nervous system, and also has a significant impact on application fields such as neuromedicine and neuroengineering. The application of neuroscience in anesthesia technology mainly involves two aspects: one is to understand the neural mechanisms of anesthesia, and the other is to evaluate and regulate the depth of anesthesia through neural monitoring.
First, neuroscience has helped researchers better understand the neural mechanisms of anesthesia. Anesthetic drugs can affect signal transmission between neurons, thereby reducing consciousness levels and sensitivity to external stimuli. Research in neuroscience has revealed the molecular basis and neural circuit mechanisms of these effects, providing guidance for the search for more effective and safer anesthetic drugs.
Second, neural monitoring technology can effectively evaluate and regulate the depth of anesthesia. Neuromonitoring can monitor the depth of anesthesia through neuroelectrophysiological techniques (such as electroencephalography, spinal cord evoked potential, etc.) or physiological monitoring (such as respiration, blood pressure, heart rate, etc.), and adjust medication based on the monitoring results to achieve more accurate and safe anesthesia effects. In addition, neural monitoring can help anesthesiologists better understand the patient’s neurological condition and avoid potential risks of neurological damage.
The application of neuroscience in anesthesia technology provides a deeper and more comprehensive understanding and control of anesthesia effects for medical surgeries, which helps to improve the safety and effectiveness of anesthesia.
3.2 Anesthesia status monitoring algorithm based on neuroscience
In pharmacodynamic models, the S-type maximum effect chamber model can be used to evaluate the monitoring of anesthesia status data. The formula is
where s is the steepness constant. When studying the effects of anesthetic drugs, an S-type maximum effect chamber model with nonlinear inhibition is used, and is represented as follows:
where
Then, it is necessary to quantitatively describe the drug characteristics. Under the condition of constant blood drug concentration, the time required when the drug concentration in the effect chamber reaches half of the blood drug concentration is called the half-life, and the formula is
Here
The relationship between blood concentration and effect chamber concentration can be described as
where
In the above formula,
This algorithm can accurately evaluate the depth and state of anesthesia of patients by monitoring and analyzing these signals, helping doctors better control the amount of anesthesia used, thereby reducing the occurrence of adverse reactions. In addition, the algorithm can also provide a scientific basis for clinicians to guide clinical anesthesia operations, so as to better protect the safety of patient safety.
4 Experimental monitoring of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
In this section, in order to evaluate the effectiveness and reliability of anesthesia state monitoring algorithms based on neuroscience in practical applications, performance testing is needed to deeply understand the specific performance of the algorithm in anesthesia depth state monitoring, thereby providing strong support for its further optimization and improvement.
The first is to test the accuracy of monitoring drug concentration and oxygen saturation in patients’ blood based on neuroscience anesthesia state monitoring algorithm and traditional anesthesia state monitoring algorithm. The detailed data is shown in Figure 2.

Monitoring accuracy of two algorithms.
From the data in Figure 2, it can be seen that compared to traditional anesthesia status monitoring algorithms, neuroscience-based anesthesia status monitoring algorithms had higher monitoring accuracy. After calculation, the average monitoring accuracy of the traditional anesthesia state monitoring algorithm for drug concentration and oxygen saturation was 95.55 and 95.00%, respectively. The average monitoring accuracy of anesthesia state monitoring algorithm based on neuroscience for drug concentration and oxygen saturation was 98.00 and 97.09%, respectively. This experiment proved that the monitoring performance of anesthesia status monitoring algorithms based on neuroscience was more excellent.
During the anesthesia process, as the degree of anesthesia deepens, the EEG signals change from active disorder to regular and stable. Therefore, applying the information entropy theory to the analysis of anesthesia EEG signals can accurately reflect the depth of anesthesia. In short, the more complex the EEG signal, the greater the information entropy. The more stable the EEG signal is, the smaller the information entropy value is. Therefore, in the following experiment, the information entropy of EEG signals of patients with different anesthesia states would be tested and counted to explore the change trend of anesthesia depth state and brain nerve signals. The detailed data is shown in Figure 3.
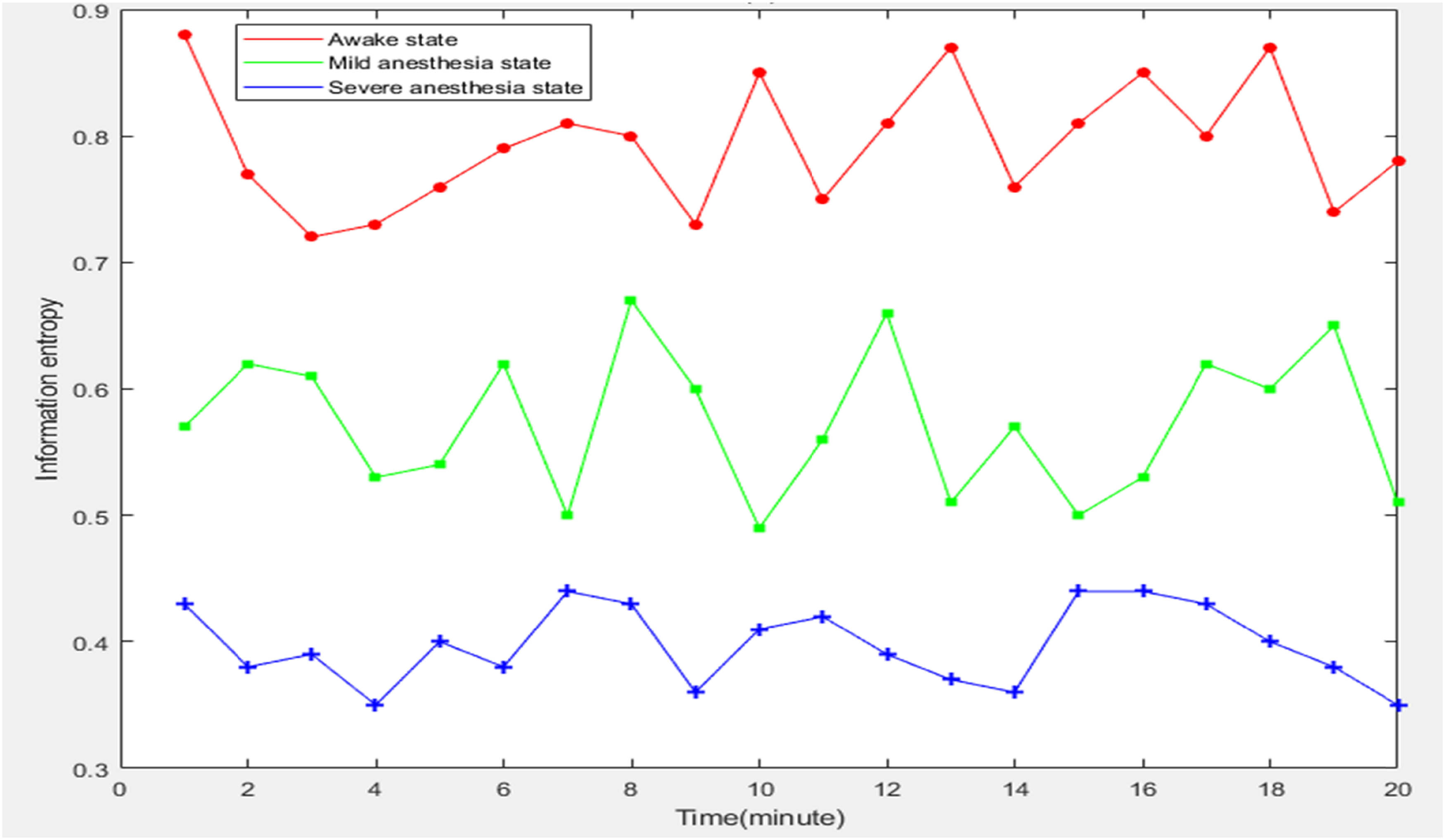
Information entropy of EEG signals in patients with different anesthesia states.
From the data in Figure 3, it was obvious that there was a large difference in the information entropy of EEG signals among patients in awake state, mild anesthesia state, and severe anesthesia state. After calculation, the average information entropy of EEG signals of patients in awake state, mild anesthesia state, and severe anesthesia state was 0.794, 0.573, and 0.3975, respectively. This showed that with the increase of the depth of anesthesia, the information entropy value of EEG signals decreased, the complexity of EEG signals decreased, and the brain neural activity decreased.
Similarly, oxygen saturation is also an important analytical indicator of anesthesia depth data monitoring. Therefore, in the following experiments, oxygen saturation of patients in different anesthesia states would be tested and counted to explore the change trend of anesthesia depth state and oxygen saturation. The detailed data is shown in Figure 4.

Oxygen saturation of patients in different anesthesia states.
From the data in Figure 4, it can be seen that the oxygen saturation of patients under different anesthesia conditions had a relatively large change. After calculation, the average oxygen saturation of patients in awake state, mild anesthesia state, and severe anesthesia state was 97.97, 93.50, and 90.71%, respectively. This indicated that with the deepening of anesthesia depth, the patient’s oxygen saturation would decrease.
This is because in the state of deep anesthesia, the metabolic rate of the body slows down, vital capacity decreases, respiration becomes shallow and slow, leading to insufficient oxygen supply, which leads to the reduction of oxygen saturation. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and maintain the patient’s blood oxygen levels during anesthesia to avoid serious complications.
5 Conclusions
The monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience refers to the precise monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status by studying the impact of anesthesia depth status on brain neural activity. Compared with traditional anesthesia monitoring methods, neuroscience based monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data has higher accuracy and reliability, providing doctors with more accurate monitoring and analysis results of anesthesia depth status to ensure the safety and success of the surgical process. Through the neuroscience-based anesthesia status monitoring algorithm, the anesthesia depth status is more accurately monitored, and the EEG information entropy and oxygen saturation of patients with different anesthesia status can be obtained, ensuring the safety of anesthesia surgery. Experiments have proved that during anesthesia, EEG signals would change with the amount of anesthetic. The deeper the depth, the lower the complexity and information entropy of EEG signals. The physiological information contained in EEG signals under different anesthesia states also varies. EEG signals are very sensitive to anesthetics, and as anesthesia deepens, the EEG signals become more and more stable. In addition, in the state of deep anesthesia, the metabolic rate of the body slows down, vital capacity decreases, and oxygen saturation decreases. Therefore, it is crucial to monitor and maintain the patient’s blood oxygen levels during anesthesia to avoid serious complications. In summary, the monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience is a beneficial method for anesthesia depth monitoring, which would be more widely applied and promoted in the future. However, there are still some shortcomings that need to be further addressed in the monitoring and analysis of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience. For example, current monitoring methods mainly rely on physiological indicators such as EEG signals, but these indicators are influenced by multiple factors, making it difficult to accurately monitor each patient. In addition, current monitoring equipment is often cumbersome and difficult to use in real-time in scenarios such as operating rooms, resulting in limited monitoring effectiveness. Therefore, future research needs to address these issues, and improve the accuracy and real-time nature of monitoring, in order to better ensure the safety and health of patients.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Pandya AN, Majid SZ, Desai MS. The origins, evolution, and spread of anesthesia monitoring standards: from Boston to across the world. Anesth Analg. 2021;132(3):890–8.10.1213/ANE.0000000000005021Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Shander A, Lobel GP, Mathews DM. Brain monitoring and the depth of anesthesia: another goldilocks dilemma. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(2):705–9.10.1213/ANE.0000000000002383Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Romagnoli S, Franchi F, Ricci Z. Processed EEG monitoring for anesthesia and intensive care practice. Minerva Anestesiol. 2019;85(11):1219–30.10.23736/S0375-9393.19.13478-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Saito H, Kambayashi R, Hagiwara-Nagasawa M, Nunoi Y, Goto A, Izumi-Nakaseko H, et al. In vivo comparison of dl-sotalol-induced electrocardiographic responses among halothane anesthesia, isoflurane anesthesia with nitrous oxide, and conscious state. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;145(1):16–22.10.1016/j.jphs.2020.10.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Mangia LR, Santos VM, Mansur TM, Wiemes GR, Hamerschmidt R. Facial nerve intraoperative monitoring in otologic surgeries under sedation and local anesthesia – a case series and literature review. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020;24(01):e11–7.10.1055/s-0039-1697991Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Nunes RR, Bersot CD, Garritano JG. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in neuroanesthesia. Curr Opin Anesthesiol. 2018;31(5):532–8.10.1097/ACO.0000000000000645Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Harbell MW, Methangkool E. Patient safety education in anesthesia: current state and future directions. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2021;34(6):720–5.10.1097/ACO.0000000000001060Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Huang VW, Jones CB, Gomez ED. State of the art of virtual reality simulation in anesthesia. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2020;58(4):31–5.10.1097/AIA.0000000000000298Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Sairyo K, Chikawa T, Nagamach A. State-of-the-art transforaminal percutaneous endoscopic lumbar surgery under local anesthesia: discectomy, foraminoplasty, and ventral facetectomy. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(2):229–36.10.1016/j.jos.2017.10.015Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Blackwood EB, Shortal BP, Proekt A. Weakly correlated local cortical state switches under anesthesia lead to strongly correlated global states. J Neurosci. 2022;42(48):8980–96.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0123-22.2022Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Lee H, Wang S, Hudetz AG. State-dependent cortical unit activity reflects dynamic brain state transitions in anesthesia. J Neurosci. 2020;40(49):9440–54.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0601-20.2020Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Lee HH, Faundez L, Yarbrough C, Lewis CW, LoSasso AT. “Patterns in pediatric dental surgery under general anesthesia across 7 state Medicaid programs. JDR Clin Transl Res. 2020;5(4):358–65.10.1177/2380084420906114Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Pooya K, Lau F, Simpao AF, Williams RJ, Clyde M. The state of adoption of anesthesia information management systems in Canadian academic anesthesia departments: a survey. Can J Anesthesia. 2021;68(5):693–705.10.1007/s12630-021-01924-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Martsolf GR, Baird M, Catherine CC, Koirala N. Relationship between state policy and anesthesia provider supply in rural communities. Med Care. 2019;57(5):341–7.10.1097/MLR.0000000000001106Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Mihretu F. The current state of anesthesia safety in a third world country: a cross-sectional survey among anesthesia providers in Ethiopia. Patient Saf Surg. 2021;15(1):1–8.10.1186/s13037-021-00290-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

