Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
Abstract
Melatonin is a potent antioxidant that can prevent plant damage caused by adverse stresses. It remains unclear whether exogenous melatonin can mitigate the effects of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). The aim of this study was to decipher the protective mechanisms of exogenous melatonin (100 μmol/L) on sorghum seedlings under NaCl-induced salt stress (120 mmol/L). Plant morphological, photosynthetic, and physiological characteristics were analyzed at different timepoints after sowing. Results showed that salt stress inhibited seed germination, seedling growth, and plant biomass accumulation by reducing photosynthetic pigment contents, photosynthetic efficiency, root vigor, and mineral uptake. In contrast, seed priming with melatonin enhanced photosynthetic pigment biosynthesis, photosynthetic efficiency, root vigor, and K+ content under salt stress. Melatonin application additionally enhanced the activities of antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase, catalase, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione reductase) and increased the levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants (reduced glutathione, ascorbic acid) in the leaves. These changes were accompanied by increase in the leaf contents of soluble sugars, soluble proteins, and proline, as well as decrease in hydrogen peroxide accumulation, malondialdehyde content, and electrolyte leakage. Our findings indicate that exogenous melatonin can alleviate salt stress-induced damage in sorghum seedlings through multifaceted mechanisms, such as improving photosynthetic performance and root vigor, facilitating ion homeostasis and osmoregulation, and promoting antioxidant defense and reactive oxygen species scavenging.
Graphical abstract

1 Introduction
Soil salinity is one of the major abiotic stresses limiting agricultural production worldwide [1], and ∼7% of the world’s land is affected by salt stress [2]. High soil salinity can cause osmotic stress and trigger ion toxicity in plants [3]. It also hinders plant growth and development processes, such as germination, photosynthesis, respiration, ion transport, and nutrient uptake [4], leading to lower yields. Plants have evolved endogenous protective mechanisms to deal with adverse stresses, including activation of antioxidant defense systems and increased accumulation of osmoprotectants. The antioxidant defense system scavenges excessive cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), and as such, mitigates membrane lipid peroxidation [5]. The accumulation of osmoprotectants, such as proline, soluble sugars, and soluble proteins, neutralizes or mitigates cellular damage from harmful substances by facilitating water uptake [6]. However, these endogenous protective mechanisms are insufficient to overcome the adverse effects of salt stress, which necessitates the application of exogenous protectants.
Melatonin is a potent antioxidant that can mitigate the effects of abiotic stresses on various crops [7–11]. As an indoleamine, melatonin has an outstanding ability to scavenge cellular ROS. Despite its trace amounts in crop plants, melatonin plays a crucial role in physiological regulation and stress response [12]. Like indole acetic acid, melatonin is involved in promoting plant flowering and seed germination, delaying crop senescence [13], and enhancing lateral root development and main root thickening [7]. Exogenous melatonin can improve plant tolerance to abiotic stresses by enhancing endogenous melatonin biosynthesis, antioxidant activity, and osmoprotectant accumulation [5,14]. Elevated melatonin levels also contribute to photosynthesis [9] and ion homeostasis [14] while reducing electrolyte leakage [8]. Melatonin reportedly modulates the expression of genes associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis, transporter protein biosynthesis [15], glucose metabolism, and flavonoid biosynthesis [16].
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) in the family Gramineae is a potential crop for production on saline soils because of its wide adaptability and high tolerance to drought, flood, and salinity stresses [17]. Since seed germination and seedling establishment are the most sensitive stages to soil salt concentration, crop plants can be irreversibly damaged if exposed to adverse conditions at these two stages [18]. When soil salinity is higher than 0.3%, the seed germination and emergence of sweet sorghum are affected, and the grain yield is reduced [19]. Therefore, enhancing seed germination and seedling emergence under salt stress is a prerequisite for the promotion of sorghum cultivation and the exploitation of saline soil. An et al. [20] showed that the application of Bacillus subtilis strain SN3 could effectively alleviate salt stress-induced damage and improve salt resistance in sorghum seedlings. Whether exogenous melatonin can mitigate the effects of salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of sorghum remains unknown, despite evidence for its protective role against flooding [21].
In this study, we investigated the protective effects of exogenous melatonin on sorghum seedlings under salt stress from a morphological, photosynthetic, and physiological perspective. The aim of the study was to ascertain the role of melatonin in mitigating salt stress in sorghum and unravel the underlying multifaceted mechanisms. The results could be useful for efficient utilization of saline soils and sustainable sorghum production in saline environments.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Seeds of sorghum variety “Jinza 2002” were provided by the Sorghum Research Institute of Shanxi Agricultural University (Jinzhong, China). Melatonin (chromatographically pure) was purchased from Sigma (USA). Sodium chloride (NaCl, analytically pure) was purchased from Shandong Xiya Chemical Industry Co., Ltd (Linyi, Shandong Province, China).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Experimental design and setup
Salt stress level (120 mmol/L NaCl) and melatonin solution concentration (100 μmol/L) were selected based on the results of a pre-experiment. Seed germination and seedling growth experiments were conducted in petri dishes and pots, respectively. Each experiment had four treatments and three replications: control (CK; 0 mmol/L NaCl + 0 μmol/L melatonin), MT (0 mmol/L NaCl + 100 μmol/L melatonin), NaCl (120 mmol/L NaCl + 0 μmol/L melatonin), and MT + NaCl (120 mmol/L NaCl + 100 μmol/L melatonin). Each group contained three replicates of 12 plants.
The Petri dish experiment was conducted in a light incubator (16 h/8 h day/night, 25 ± 1°C) on April 15, 2022. Uniform-sized seeds were surface disinfected with 5% NaClO solution for 5 min and then rinsed with distilled water. After that, the seeds were immersed in 0 or 100 μmol/L melatonin solution for 12 h at 25°C in darkness. Then, the seeds were rinsed with distilled water and blotted with filter paper. A total of 21 seeds were placed in each dish (9 cm diameter), followed by the addition of 10 mL of 120 mmol/L NaCl solution or distilled water. The NaCl solution was changed every 24 h to maintain a consistent salt concentration. Seed germination was measured on the third and seventh days.
The pot experiment was conducted in a greenhouse (25/15 ± 2°C day/night) on April 19, 2022. Each pot (12 cm high, 13 cm diameter) was filled with 1 kg of substrate (soil: sand = 2:1, w/w) and ten seeds treated with or without melatonin were sown uniformly at a depth of 4 cm. On the day of sowing, water was applied at 100% field capacity and no stress treatments were applied to all pots. Four and eight days later, 60 mL of 120 mmol/L NaCl solution or distilled water was added to each pot. Twelve days later, 60 mL distilled water was added to each pot. On the 10th, 12th, and 14th days after sowing, seedlings were sampled to measure chlorophyll content, root vigor, antioxidant enzyme activities, and the contents non-enzymatic antioxidants, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), malondialdehyde (MDA), and osmoprotectants. Seedling survival, plant height, leaf area (top second leaves), fresh and dry weights, relative water content (RWC), ion contents, and electrolyte leakage (EL) were measured on the 14th day. Leaf photosynthesis was measured on the 25th day.
2.2.2 Germination and growth analysis
Seed germination energy (equation (1)) and rate (equation (2)) were calculated based on the number of germinated seeds.
Seedling survival rate (equation (3)) was calculated from the number of surviving seedlings. Seedling height and leaf size were measured using a ruler, with leaf area calculated based on leaf size (equation (4)). The fresh weight (FW) of seedlings was determined using an electric balance. Then, seedlings were deactivated at 105°C and oven-dried at 65°C until constant weight.
2.2.3 Seedling physiological measurement
The EL measurement of leaves was done using a conductivity meter [22]. To determine leaf water content, the FW of leaf samples was first measured. Then, the fresh samples were placed in deionized water protected from light overnight. After the saturated fresh weight (TW) was determined, the samples were dried in an oven to constant weight (DW) [23]. RWC was calculated using the following equation:
The dry samples of crushed leaves (0.1 g each) were extracted with 25.0 mL of 1 mol/L HCl solution. The K+ and Na+ contents in sample extracts were determined using a flame spectrophotometer [24].
The photosynthetic parameters of the top second leaves were measured using a LI-6400 portable photosynthesizer (LI-COR Inc., USA). The measurements of net photosynthetic rate (Pn), stomatal conductance (Gs), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci), and transpiration rate (Tr) were completed between 10:00 am and 12:00 am on a sunny day. Leaf chlorophyll (a, b) contents were determined by spectrophotometry [25]. Root vigor was analyzed using trimethyl tetrazolium reduction method [25].
Fresh leaf samples (0.5 g) were homogenized in 5 mL of 100 mmol/L phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) using a pre-chilled mortar and pestle. The homogenate was centrifuged at 15,000×g for 10 min at 4°C and the supernatant was collected as crude enzyme extract. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were measured using the method described by Li and Zhang [25]. Ascorbate peroxidase (APX) activity was assayed following the method of Nakano and Asada [26]. The method of Foyer and Halliwell [27] was used for quantification of glutathione reductase (GR) activity. SOD, CAT, APX, and GR activities were recorded at wavelengths of 560, 240, 290, and 340 nm, respectively.
Leaf ascorbate (AsA) content was analyzed as described by Jahan et al. [28]. Briefly, a 0.1 g sample of fresh leaves was extracted with 6% perchloric acid and then centrifuged at 4°C at 12,000×g for 15 min. The supernatant was added with 200 mM sodium acetate buffer (pH 5.6), and absorbance at the wavelength of 265 nm was recorded before and after incubation with 0.5 units of AsA oxidase for 10 min. The change in absorbance was used to calculate the AsA content. The protocol of Ellman [29] was followed to determine the reduced glutathione (GSH) content. A 0.5 g sample of fresh leaves was homogenized in phosphate buffer (pH 8.0) and then centrifuged at 3,000×g for 15 min. The supernatant was incubated with 5,5-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid for 10 min. The resulting change in absorbance at 412 nm was recorded and used to calculate the GSH content.
Soluble sugar, soluble protein, and proline contents in leaf samples were determined based on the method described by Li and Zhang [25]. To determine H2O2 content, fresh leaves (0.25 g each) were homogenized on ice with 5 mL of trichloroacetic acid (0.1%) and then centrifuged, and the absorbance of supernatant at 390 nm was recorded [25]. Leaf MDA content was determined using the thiobarbituric acid method [25].
2.3 Statistical analysis
The experiments were performed in triplicates (n = 3) with the exception of growth parameters (where n = 10). SPSS Statistics 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used to conduct one-way analysis of variance. Significant differences between group means were determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05). Pearson correlation coefficients were used to evaluate the relationship between seedling morphological and physiological parameters. Principal component analysis was conducted to explore the effects of melatonin on seedling characteristics. Figures were plotted using OriginPro 2021 (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA).
3 Results
3.1 Seed germination and seedling growth
The germination energy and rate of sorghum seeds under salt stress were lower than those under non-stress conditions. Both the germination indicators of melatonin-treated seeds considerably increased compared with those of non-treated seeds under salt stress. Specifically, compared with the CK treatment, the seed germination energy and rate of MT treatment increased slightly by 2.47 and 1.75%, respectively; in contrast, those of NaCl treatment decreased significantly by 31.05 and 28.11%, respectively (p < 0.05). Despite their remarkable increase in the MT + NaCl treatment relative to the NaCl treatment (30.37 and 26.24%; p < 0.05), the seed germination energy and rate were still lower than those of MT and CK treatments (p < 0.05). The results of seed germination on the seventh day after sowing mirrored the patterns observed on the third day (Figure 1a).
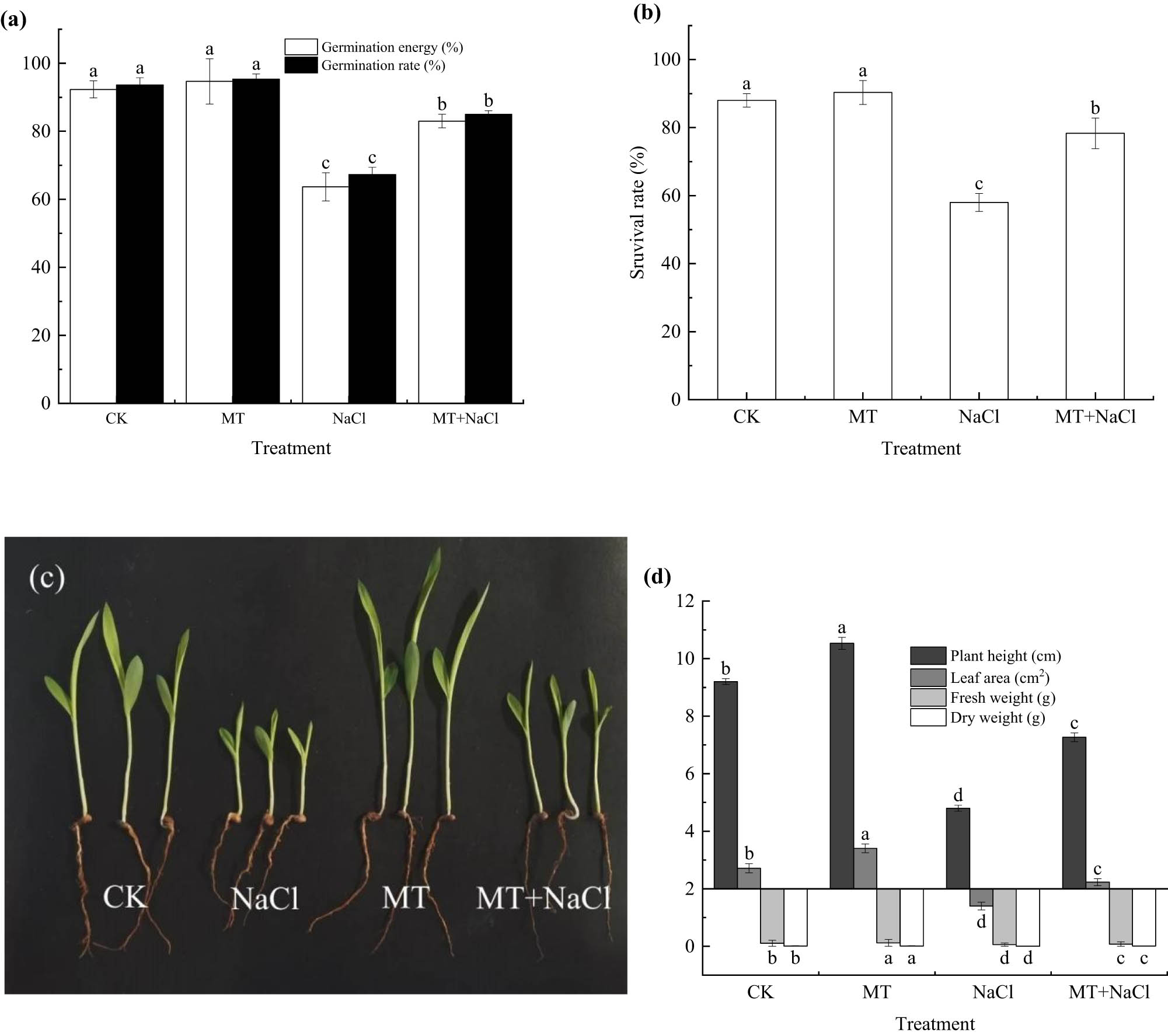
Seed germination (a), seedling survival rate (b), and growth performance (c and d) of sorghum treated with and without melatonin under salt stress. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
Compared with the CK treatment, the seedling survival rate of MT treatment showed a minimal increase of 2.58% under non-stress conditions (Figure 1b), whereas a substantial decrease of 34.09% was observed for the NaCl treatment under salt stress on the 14th day after sowing (p < 0.05). The seedling survival rate of MT + NaCl treatment was 35.06% higher than that of NaCl treatment (p < 0.05), albeit significantly lower than that of CK and MT treatments (p < 0.05).
Under non-stress conditions, the seedling plant height, leaf area, fresh weight, and dry weight of MT treatment all increased by 14.49, 25.48, 14.34, and 8.54%, respectively, compared with those of CK treatment (p < 0.05). Under salt stress, the four seedling growth indicators of NaCl treatment decreased by 47.83, 48.50, 48.35, and 41.99%, respectively (p < 0.05), compared with those of CK treatment. There were remarkable increases in the indicator values of MT + NaCl treatment (21.01, 17.88, 27.43, and 25.20%; p < 0.05), compared with those of NaCl treatment (Figure 1c and d).
3.2 Seedling water content, electrolyte leakage, and ion homeostasis
On the 14th day after sowing, the RWC of seedlings increased by 6.96% in the MT treatment compared with the CK treatment, and this change was accompanied by a 24.68% decrease in EL (p < 0.05). The opposite patterns were observed for the NaCl treatment, with an 11.45% decrease in RWC (p < 0.05) and an 11.76% increase in EL (p < 0.05). In the MT + NaCl treatment, the RWC was 7.42% higher (p < 0.05) and the EL was 5.89% lower than in the NaCl treatment (Figure 2).

(a) RWC and (b) electrolyte leakage of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
On the 15th day after sowing, MT alone caused a 11.36% increase in the K+ content (p < 0.05) and a 6.96% decrease in the K+/Na+ ratio (p < 0.05) compared with the CK treatment, despite no significant change in the Na+ content of seedling leaves. Leaf Na+ content significantly increased in response to salt stress, whereas the K+ content and K+/Na+ ratio both decreased in the NaCl treatment compared with the CK treatment. Under salt stress, leaf Na+ accumulation was significantly reduced by 28.77% in the MT + NaCl treatment (p < 0.05), whereas K+ uptake and the K+/Na+ ratio were increased by 25.67% (p < 0.05) and 76.37%, respectively, as compared with the NaCl treatment (Table 1).
Accumulation of Na+ and K+ in leaves of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
| Treatment | Na+ (mg g−1 DW) | K+ (mg g−1 DW) | K+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2.51 ± 0.32c | 14.40 ± 0.20b | 5.80 ± 0.72b |
| MT | 2.32 ± 0.26c | 16.04 ± 0.54a | 6.96 ± 0.54a |
| NaCl | 7.83 ± 0.34a | 8.40 ± 0.25d | 1.07 ± 0.07c |
| MT + NaCl | 5.58 ± 0.37b | 10.51 ± 0.41c | 1.88 ± 0.08c |
3.3 Leaf photosynthetic performance and root vigor
The photosynthetic parameters of seedling leaves showed consistent patterns in response to salt stress, with lower Pn, Gs, Ci, and Tr values in the NaCl treatment compared with the CK treatment on the 25th day after sowing (p < 0.05; Figure 3). NaCl-induced reduction in leaf photosynthetic performance was alleviated in the MT + NaCl treatment. Under salt stress, the Pn, Gs, Ci, and Tr values of MT + NaCl treatment significantly increased by 33.85, 28.94, 15.79, and 22.97% (p < 0.05), respectively, compared with the NaCl treatment (p < 0.05); however, all parameter values were still lower than in the CK and MT treatments (p < 0.05).
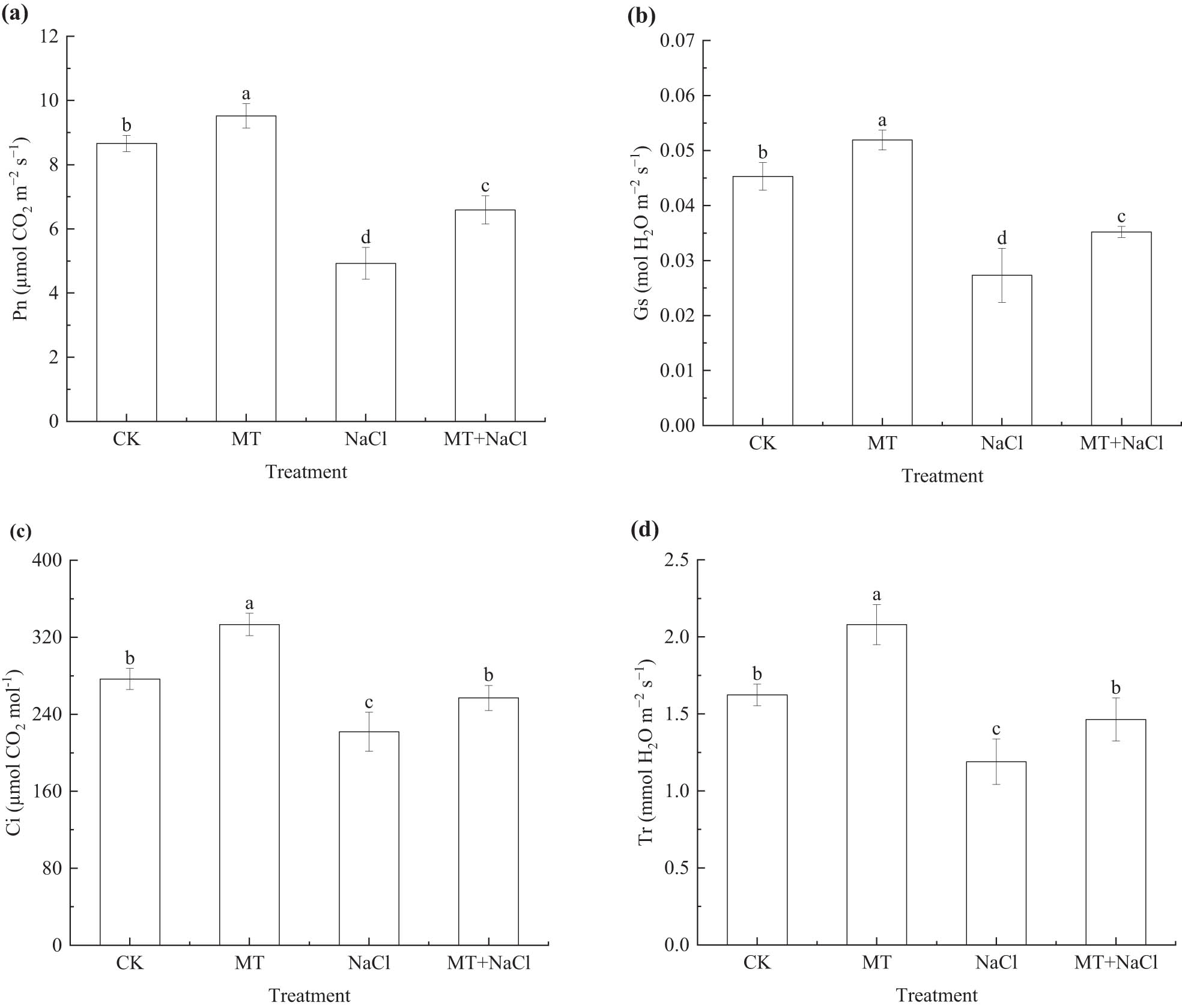
Net photosynthetic rate (Pn; a), stomatal conductance (Gs; b), intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci; c), and transpiration rate (Tr; d) of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
Among different treatments, the photosynthetic pigment contents of seedling leaves were highest in the MT treatment on the 10th, 12th, and 14th days after sowing (Figure 4a–c). Salt stress caused a significant decrease in leaf chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll contents in the NaCl treatment compared with the CK treatment. Although their significant increase in the MT + NaCl treatment compared with the NaCl treatment (a: 15.83–24.10%, b: 15.10–34.82, total: 7.31–23.29%; p < 0.05), the pigment contents remained lower than in the CK and MT treatments (p < 0.05).

Photosynthetic pigments (a)–(c) and root vigor (d) of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
The root vigor of sorghum seedlings increased from the 10th to the 14th day after sowing (Figure 4d). Under non-stress conditions, the root vigor increased by 0.22–9.14% in the MT treatment compared with the CK treatment (p < 0.05 on the 14th day). Due to salt stress, the root vigor significantly decreased by 19.76–41.33% in the NaCl treatment compared with the CK treatment (p < 0.05). In contrast, seed priming increased root vigor in the MT + NaCl treatment by 14.16–27.72% compared with the NaCl treatment (p < 0.05 on the 12th and 14th days).
3.4 Leaf antioxidant defense
Under non-stressed conditions, seed priming significantly enhanced the SOD and CAT activities of seedling leaves in the MT treatment compared with the CK treatment, by 6.91–11.55 and 14.13–26.56%, respectively (p < 0.05). Leaf APX and GR activities also increased in the MT treatment, albeit not significantly. Under salt stress, all four antioxidant enzymes exhibited markedly higher activities in the leaves of NaCl-treated seedlings compared with the CK treatment (p < 0.05). Notably, the SOD, CAT, APX, and GR activities further increased by 13.29–22.01, 13.99–25.63, 14.76–22.01, and 13.32–37.79% (p < 0.05), respectively, in the MT + NaCl treatment compared with the NaCl treatment (Figure 5a–d).

Enzymatic (SOD: a, CAT: b, APX: c, GR: d) and non-enzymatic (AsA: e, GSH: f) antioxidants in leaves of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
The AsA and GSH contents of seedling leaves consistently increased from the 12th to the 14th days after sowing. Compared with the CK treatment, there was no significant difference in leaf AsA and GSH contents in the MT treatment. Nevertheless, both antioxidant contents varied significantly in the NaCl treatment, with the greatest increase of 39.14 and 41.05% on the 12th day, respectively. A further increase in leaf AsA and GSH contents was observed for the MT + NaCl treatment compared with the NaCl treatment, by 13.16–17.57% and 10.29–25.12%, respectively (p < 0.05; Figure 5e and f).
3.5 Leaf osmoregulation, ROS accumulation, and membrane lipid peroxidation
The soluble sugar and soluble protein contents of seedling leaves initially increased and then decreased, reaching a maximum on the 12th day (Figure 6a and b). The leaf proline content consistently increased from the 10th to the 14th day (Figure 6c). Salt stress significantly increased the leaf contents of all three osmoprotectants in the NaCl treatment compared with the CK treatment (p < 0.05), and seed priming further promoted their leaf accumulation in the MT + NaCl treatment. This promotion effect tended to increase first and then decrease with the extension of treatment time, and was not significant on soluble protein or proline on the 14th day.

Soluble sugar (a), soluble protein (b), proline (c), H2O2 (d), and MDA (e) contents in leaves of sorghum seedlings under different treatments. Error bars represent standard deviation of the mean (n = 3). Different letters above error bars indicate significant differences among the treatments at the 0.05 level.
Compared with the CK treatment, there was an increase in the H2O2 and MDA contents of seedling leaves in the NaCl treatment, indicating enhanced ROS production and membrane lipid peroxidation under salt stress. Seed priming led to a substantial decrease in leaf H2O2 and MDA contents in the MT + NaCl treatment compared with the NaCl treatment (Figure 6d and e).
3.6 Correlations between seedling morphological and physiological characteristics
Correlation analysis was conducted on 31 representative indicators to clarify the correlations between the morphological and physiological characteristics of sorghum seedlings under salt stress. Seed germination, seedling survival, and plant growth indicators were all positively correlated with RWC, K+ content, K+/Na+ ratio, photosynthetic parameters (Pn, Gs, Ci, Tr), chlorophyll contents (a, b, total), and root vigor. The germination and growth indicators also had positive correlations with antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, APX, CAT, GR), non-enzyme antioxidant contents (AsA, GSH), and osmoprotectant contents (soluble sugar, soluble protein, proline). They were negatively correlated with H2O2 content, MDA content, EL, and Na+ content (p < 0.05 or 0.01; Figure 7).

Correlation matrix between leaf morphological and physiological indicators of sorghum seedlings under salt stress. Blue color indicates positive correlations and red color indicates negative correlations. GE: germination energy; GR: germination rate; SR: survival rate, PL: plant height, LA: leaf area, FW: seedling fresh weight, DW: seedling dry weight, RWC: relative water content, EL: electrolyte leakage, Na+: Na+ content, K+: K+ content, K+/Na+: K+/Na+ ratio, Pn: photosynthetic rate, Gs: stomatal conductance, Ci: intercellular CO2 concentration, Tr: transpiration rate, SOD: superoxide dismutase activity, CAT: catalase activity, APX: ascorbate peroxidase activity, GR: glutathione reductase activity, AsA: ascorbate content, GSH: reduced glutathione content SS: soluble sugar content, SP: soluble protein content, Pro: proline content, H2O2: hydrogen peroxide content, MDA: malonaldehyde content, RV: root vigor, Chla: chlorophyll a; Chlb: chlorophyll b; ChlT: total chlorophyll.
Under salt stress, Pn was significantly negatively correlated with EL and positively correlated with RWC, indicating that increased leakage rate of electrolytes was a key factor in the growth of salt-stressed seedlings (Figure 7). Both soluble sugar and protein contents were significantly positively correlated with RWC, AsA, and GSH contents, which means that accumulation of these two osmoprotectants contributed to the regulation of water and non-enzymatic antioxidant contents in seedling leaves.
Both CAT and GR activities were significantly negatively correlated with H2O2 content (Figure 7), suggesting their role in the reduction of cellular ROS accumulation. K+ content and K+/Na+ ratio were significantly positively correlated with RWC, whereas a significant negative correlation was observed between Na+ content and RWC; this indicates that Na+ accumulation and K+ depletion were key factors affecting leaf water content. Total chlorophyll content and root vigor showed a significant positive correlation with K+ content and a significant negative correlation with Na+ content, which reflects that Na+ accumulation and K+ depletion could lead to a decrease in leaf pigment content and root vigor.
3.7 Effects of exogenous melatonin on seedling characteristics
Principal component analysis was conducted to determine the effects of melatonin priming on the morphological, photosynthetic, and physiological characteristics of sorghum seedlings under salt stress. The 31 indicators were grouped into two principal components with contributions of 80.96 and 12.68%, respectively, cumulatively explaining 93.64% of the total variation (Figure 8). Based on the factor loading matrix (Table 2), chlorophyll a content had the highest loading in PC1 and was positively correlated with PC1 scores. Soluble protein content had the highest loading in PC2 and was positively correlated with PC2 scores. Accordingly, the effects of exogenous melatonin on seedling physiological characteristics were mainly attributable to the differences in leaf chlorophyll a and soluble protein contents.

Plots of principal component analysis of sorghum seedling characteristics under different treatments. Abbreviations are defined in Figure 7 caption.
Factor loading matrix of principal component analysis. Abbreviations are defined in Figure 7 caption.
| Indicator | PC1 (80.96%) | PC2 (12.68%) |
|---|---|---|
| GE | 0.17766 | 0.13680 |
| GR | 0.18290 | 0.12057 |
| SR | 0.18115 | 0.12912 |
| PL | 0.19491 | 0.09306 |
| LA | 0.19029 | 0.13602 |
| FW | 0.19669 | 0.04834 |
| DW | 0.19588 | 0.03052 |
| RWC | 0.18922 | 0.08328 |
| EL | −0.17538 | −0.16093 |
| Na+ | −0.19421 | −0.01056 |
| K+ | 0.19870 | 0.02260 |
| K+/Na+ | 0.19657 | −0.05554 |
| Pn | 0.19552 | 0.04428 |
| Gs | 0.19166 | 0.06271 |
| Ci | 0.17864 | 0.13044 |
| Tr | 0.17684 | 0.13978 |
| SOD | −0.13907 | 0.33206 |
| APX | −0.13951 | 0.34076 |
| CAT | −0.14701 | 0.30784 |
| GR | −0.17412 | 0.23865 |
| AsA | −0.16112 | 0.26870 |
| GSH | −0.16507 | 0.26748 |
| SS | −0.14548 | 0.33321 |
| SP | 0.13080 | 0.35618 |
| Pro | −0.17181 | 0.20695 |
| H2O2 | −0.19555 | −0.02887 |
| MDA | −0.19286 | −0.03155 |
| RV | 0.19104 | 0.1046 |
| Chla | 0.19685 | −0.01542 |
| Chlb | 0.17600 | 0.1383 |
| ChlT | 0.19230 | 0.07717 |
4 Discussion
Seed germination and seedling growth are the most sensitive stages of plants to adverse stress [30]. We found that salt stress simulated with 120 mmol/L NaCl considerably inhibited seed germination and seedling survival of sorghum in Petri dishes and pots, respectively (Figure 1a and b). This is compatible with the previous findings in buckwheat [31]. A high concentration of salt can trigger osmotic stress in plant cells, thus causing physiological drought. In the high-salt environment, seeds are unable to take up sufficient water from the external environment for the biosynthesis of enzymes and proteins related to germination. As a consequence, it is difficult to complete cell division and differentiation, as well as embryo growth, which inhibits seed germination [32].
Under NaCl-induced salt stress, seed priming with 100 μmol/L melatonin facilitated seed germination and seedling survival of sorghum. Zhang et al. [33] also found that the application of 300 μmol/L melatonin prominently increased the germination rate of wheat under salt stress. The reason may be that melatonin promotes the formation of globulins and microtubule filaments in seeds, or up-regulates the activities of isocitrate lyase and malate synthase in the glyoxylate cycle, which in turn promotes cell division and elongation to provide energy for seed germination [34,35].
Importantly, the effect of exogenous melatonin is closely related to its concentration applied as well as the crop species treated. For example, foliar spraying of low concentration melatonin (11.61 mg/L) had a remarkable effect on inducing resistance to rust in adzuki bean; this effect diminished with the increase of melatonin concentration [36]. The addition of 0.05 and 1 μmol/L melatonin in Murashige and Skoog medium considerably increased the rooting of rootstock PHL-C, but supplementation with 5 μmol/L of melatonin notably reduced both the number of roots and rooting [37]. When applied at the concentration of 50–200 μmol/L, melatonin promoted seedling growth of tartary buckwheat under AlCl3 stress [38]. Therefore, the melatonin concentration for sorghum still needs to be optimized based on stress level and crop variety.
Plant responses to stress are manifested as changes in seedling growth characteristics, which can be used to evaluate plant stress resistance [18]. We found that salt stress inhibited the growth of sorghum seedlings in terms of plant height, leaf area, and fresh and dry weights. Melatonin priming enhanced seedling growth performance under both salt stress and non-stress conditions (Figure 1c and d). Previously, Cui et al. [34] also found that seed priming with melatonin at 1–1,000 μmol/L increased the fresh and dry weights of wheat seedlings under drought stress. In principle, plants accumulate metabolic products through leaf photosynthesis and root nutrient uptake. Salt stress inhibits plant growth primarily by affecting leaf photosynthetic efficiency and root cell activity [39,40]. Additionally, plant growth and biomass formation are challenged by reduced RWC coupled with enhanced ionic and oxidative stresses [4,6].
Chlorophyll, as the most important pigment for photosynthesis in plants, is essential for light energy absorption and conversion. As such, the chlorophyll content not only characterizes plant physiological state, but also provides strong support for photosynthesis [41]. Our results showed that salt stress caused a decrease in chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll contents in leaves of sorghum seedlings (Figure 4a–c), similar to the pattern observed in wheat [42]. Salt stress is likely to reduce chlorophyll pigment biosynthesis by impairing enzyme functions, which in turn triggers structural and functional changes in the protein–pigment–lipid complex [43]. Additionally, a decrease in Fe2+ and Mg2+ uptake by salt-stress plants is responsible for the reduction of chlorophyll biosynthesis [44].
Seed priming with melatonin increased the chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and total chlorophyll contents in seedling leaves. This priming effect was much more pronounced under salt stress than under non-stress conditions. It is most likely that melatonin mitigates salt stress-induced oxidative damage in plants by regulating antioxidant enzyme activities and osmoprotectant contents; this in turn leads to an increase in leaf photosynthetic pigments and a decrease in cell membrane permeability [45]. For example, exogenous application of 200 μmol/L melatonin alleviated the adverse effects of salinity on the chlorophyll content and organic matter biosynthesis in wheat [46]. In the case of bitter melon, melatonin application resulted in increased photosynthetic pigment content and enhanced photosynthesis under salt stress [47].
With respect to photosynthetic performance, NaCl-induced salt stress negatively affected Pn, Gs, Ci, and Tr in sorghum leaves, whereas exogenous melatonin application increased these photosynthetic parameters in the presence/absence of salt stress (Figure 3). The decrease in Pn under salt stress is most likely a result of stomatal limitation, and melatonin could increase the photosynthetic rate by alleviating stomatal limitation, as observed in alfalfa [48]. Accumulating evidence suggests that exogenous melatonin improves plant photosynthesis and salt tolerance by mitigating the inhibitory effects of salt stress on chlorophyll biosynthesis, gas exchange, and photosystem II photochemistry [48,49]. Foliar spraying of melatonin reportedly reduced leaf damage, enhanced photosystem activity, and improved photosynthetic efficiency in tobacco plants under high-Mn stress [8] As for cotton, foliar spraying with 200 μmol/L of melatonin promoted seedling growth and biomass accumulation as a consequence of improved stomatal limitation, alleviated chlorophyll degradation, and enhanced photosynthetic capacity under salt stress [50]. In summary, seed priming with melatonin can enhance the growth and development of crop seedlings by enhancing their photosynthetic performance.
Roots are an important organ for the assimilation and transformation of physiologically active substances during crop growth and development. They are also the first organ to perceive and respond physiologically to adverse stress [51,52]. Therefore, root growth and metabolism directly affect plant shoot development, dry matter accumulation, and final yield formation [51]. Root vigor is a key indicator of root metabolic capacity. Under adverse stress, a more vigorous root system supports more active plant metabolism, as it has a greater capacity for water and nutrient uptake and transport [53]. Our results showed that the root vigor of sorghum seedlings was reduced under salt stress. This reduction was partially attenuated following application of exogenous melatonin (Figure 4d), consistent with previous results obtained from rice [54]. Taken together, seed priming with melatonin can increase seedling root vigor and photosynthetic efficiency under salt stress, it is expected to enhance the translocation of water and minerals from the roots to the shoots and accelerate normal plant metabolism [28], thereby enhancing photosynthetic production and biomass accumulation, but the effects of exogenous melatonin on sorghum yield and quality are still unclear, which warrants further investigations.
When salinity leads to an increase in soil osmotic potential, the plant is unable to absorb sufficient water from the soil, thus triggering osmotic stress [55]. Under salt stress, excessive Na+ and Cl– ions enter the plant and accumulate at high levels, causing ion toxicity. Given their similar ionic radius and hydration energy, K+ and Na+ show a remarkable antagonistic effect. As a result, the presence of excessive Na+ often causes K+ leakage, which affects plant physiological and metabolic processes [56]. Like wheat [23], sorghum seedlings showed a decrease in RWC in response to salt stress (Figure 2a). Salt stress decreased the K+/Na+ ratio of sorghum seedlings due to decreased shoot K+ content and increased Na+ content (Table 1). The K+/Na+ ratio characterizes the balance of plant ion content and the level of salt stress, so it is often used to evaluate plant salt tolerance [24]. Both salt-induced osmotic stress and ion toxicity can lead to excessive ROS production in plant cells and disruption of membrane stability or integrity, causing leakage of electrolytes and increased lipid peroxidation of cell membranes [50,56]. As we observed in this study, an increase in leaf H2O2 content (Figure 6d) was accompanied by an increase in EL (Figure 2b) and MDA content (Figure 6e) in sorghum seedlings under salt stress.
Melatonin maintains the osmotic balance of cells by inhibiting Na+ uptake and increasing K+ levels, as well as alleviating electrolyte leakage and cell membrane lipid peroxidation; these mechanisms mitigate the negative effects of salt stress and improve the overall water status of the plant [43,54]. Our results showed that melatonin seed priming with melatonin increased the K+/Na+ ratio and RWC while decreasing EL, H2O2, and MDA accumulation in sorghum seedlings irrespective of salt stress (Figures 2 and 6d and e and Table 1). Similar results have been reported in white beans [5] and chickpea [45]. Melatonin has the ability to modulate Na+/K+ ion homeostasis in crop plants through upregulating the transcript levels of K+ channel genes (SKOR), Na/H reverse transporter (SOS1), and plasma membrane H-ATPases in root cells [47]. K+ reportedly modulates the expression of water channel protein genes and maintains water balance. K+ additionally plays an essential role in osmoregulation, stomatal regulation, and ROS detoxification [8]. It was also found that the limitation of Na+ influx by melatonin facilitated the accumulation of K+, Ca2+, and P in bitter melon [47]. The collective results indicate that seed priming with melatonin can promote cell water absorption by regulating ion homeostasis, so as to maintain normal crop growth. Additionally, melatonin application maintains cell membrane stability by reducing cellular ROS accumulation, which is achieved through upregulating the function of the antioxidant system and glyoxalase [45].
Salt stress leads to excessive ROS accumulation in plants, which induces oxidative damage and consequently activates antioxidant defense [5]. In the enzymatic antioxidant system, SOD, CAT, APX, and GR are key enzymes involved in plant responses to stresses. These enzyme activities were all enhanced in leaves of salt-stressed sorghum seedlings in the present study. Seed priming with melatonin further increased leaf SOD, CAT, APX, and GR activities under salt stress (Figure 5a and d). Altaf et al. [57] also reported that 100 μmol/L melatonin application improved antioxidant enzyme activities in tomato seedlings under salt stress (150 mmol/L NaCl), which mirrored the patterns observed in soybean and chickpea [43,45]. Additionally, Luo et al. [58] showed that exogenous melatonin application resulted in higher CAT, SOD, POD, and APX activities in rice seedlings under drought stress by elevating the expression levels of ALM1, OsPOX, OsCATC, and OsAPX2 genes.
In the non-enzymatic antioxidant system, AsA and GSH are major antioxidants that promote the stability of cell membrane proteins, because they reduce the rate of O2 – production and catalyze the generation of H2O and O2 from H2O2 [43]. While salt stress induced an increase in the AsA and GSH contents of sorghum leaves, melatonin seed priming with melatonin triggered a further increase in these antioxidant contents (Figure 5e and f), which is consistent with the finding by Li et al. [18]. Exogenous melatonin also substantially increased AsA and GSH contents in pepper under combined stress of low temperature and low light [18], as well as in wheat under Cd stress [59]. Furthermore, Luo et al. [60] showed that melatonin treatment enhanced the cold resistance of pumpkin, as plant antioxidant capacity was increased by promoting the AsA–GSH cycle. Collectively, these results indicate that seed priming with melatonin can enhance salt tolerance in sorghum seedlings by activating the antioxidant defense systems, most likely due to the regulation of resistance-related gene expression at the transcriptional level [28].
Myriad studies have shown that organic compounds, such as proline, soluble proteins, and soluble sugars, play major roles in plant osmoregulation and are necessary components for plants to cope with stresses [14,61]. Under the experimental conditions, salt stress resulted in an increase in the soluble sugar, soluble protein, and proline contents of sorghum leaves (Figure 6a–c), in support of previous findings in maize [61]. However, Zhang et al. [33] showed that salt stress induced by 100 mmol/L NaCl decreased the soluble sugar and protein contents while increasing the proline content in wheat. These inconsistent results demonstrate the distinct patterns of osmoprotectants in response to salt stress, depending on crop species. Seed priming with melatonin also increased the soluble sugar, soluble protein, and proline contents in sorghum leaves under salt stress and non-stress conditions (Figure 6a–c). Li et al. [18] observed that melatonin enhanced low-temperature and low-light stress tolerance in pepper by upregulating its soluble sugar and soluble protein accumulation to maintain cellular homeostasis. Additionally, 100 μmol/L melatonin increased the soluble sugar, soluble protein, and proline contents in rice under 80 mmol/L NaCl stress [54].
In summary, exogenous melatonin enhances organic matter accumulation and consequently attenuates NaCl-induced osmotic damage in crop plants, possibly through modulation of gene expression levels. For example, foliar spraying of melatonin was found to increase the leaf proline, fructose, and sucrose contents of rice seedlings under drought stress by upregulating the expression levels of OsP5CS, OsSUS7, and OsSPS1 genes [58]. Melatonin was additionally shown to promote endogenous proline accumulation by upregulating P5CS and OAT gene expression and enzyme activity, as well as reduce proline catabolism by downregulating PDH gene expression and enzyme activity [62]. In addition to modulating osmoregulation, soluble sugars and proteins are essential sources of energy for plant growth and development, providing key nutrients for cell survival [1]. Proline is considered to play a role in scavenging ROS [23]. Therefore, seed priming with melatonin may enhance salt tolerance in sorghum seedlings by upregulating osmoprotectant accumulation.
5 Conclusions
Salt stress (120 mmol/L NaCl) negatively affected sorghum seed germination and seedling growth of sorghum in petri dishes and pots. Seed priming with melatonin (100 µmol/L) effectively alleviated the effects of salt stress on sorghum, leading to increased seed germination and seedling survival rates (by 26.24 and 35.06%, respectively). Melatonin application improved leaf photosynthetic performance, root vigor, ion homeostasis, antioxidant defense, and osmotic metabolism, in addition to mitigating salt-induced oxidative damage (Figure 9). Chlorophyll a and soluble protein contents were identified as key factors that could explain the protective mechanisms of melatonin on sorghum seedlings. This result of this study can be helpful to improve the stress tolerance and sustainable production of sorghum in saline soils with exogenous melatonin application. Further study of molecular pathways is needed to identify the mechanisms underlying melatonin-mediated enhancement of salt tolerance in sorghum.

A schematic model figure is showing how melatonin confers salt stress in the sorghum plant.
-
Funding information: The research program sponsored by The Shanxi Provincial Science and Technology Assistance Cooperation Project (grant number 202204041101048), The Shanxi Province Brewing Sorghum Seed Industry Innovation and Superior Varieties Joint Research (grant number YZGG-04), National Laboratory of Minor Crops Germplasm Innovation and Molecular Breeding (in preparation) (grant number 202204010910001-28), Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of Shanxi Province (grant number 2023CYJSTX03-08), and Biological Breeding Project of Shanxi Agricultural University (grant number YZGC062).
-
Author contributions: M.N. and N.N. launched the study. M.N. and S.L. performed the data analysis. M.N., S.L., and L.Z. wrote the main manuscript text. N.N., Y.Z., C.J., and H.Z. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Gul Z, Tang ZH, Arif M, Ye Z. An insight into abiotic stress and influx tolerance mechanisms in plants to cope in saline environments. Biology. 2022;11(4):597.10.3390/biology11040597Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Fardin G, Majid B, Afsaneh A. Exogenous application of selenium and nano-selenium alleviates salt stress and improves secondary metabolites in lemon verbena under salinity stress. Sci Rep-UK. 2023;13(1):5352.10.1038/s41598-023-32436-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Zhao SS, Zhang QK, Liu MY, Zhou HP, Ma CL, Wang PP. Regulation of plant responses to salt stress. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(9):4609.10.3390/ijms22094609Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Angon PB, Tahjib-Ul-Arif Md, Samin SI, Habiba U, Hossain MA, Brestic M. How do plants respond to combined drought and salinity stress? A systematic review. Plants. 2022;11(21):2884.10.3390/plants11212884Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Muhammad A, Neelofar H, Zainul A, Faisal Z, Anam M, Muhammadet N, et al. Exogenous melatonin application stimulates growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant potential of white beans under salinity stress. S Afr J Bot. 2023;160:219–28.10.1016/j.sajb.2023.07.014Search in Google Scholar
[6] Abd El-Mageed TA, Gyushi MAH, Hemida KA, El-Saadony MT, Abd El-Mageed SA, Abdalla H, et al. Coapplication of effective microorganisms and nanomagnesium boosts the agronomic, physio-biochemical, osmolytes, and antioxidants defenses against salt stress in ipomoea batatas. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:883274.10.3389/fpls.2022.883274Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Duan WJ, Meng YJ, Jiang D, Liu LT, Zhang K, Zhang YJ, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on morphology and antioxidant system of cotton seedlings under salt stress. Chin J Eco-Agric. 2022;30(1):92–104.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Gao HS, Huang LZ, Gong ZJ, Wang XT, Qiao XQ, Xiao F, et al. Exogenous melatonin application improves resistance to high manganese stress through regulating reactive oxygen species scavenging and ion homeostasis in tobacco. Plant Growth Regul. 2022;98(2):219–33.10.1007/s10725-022-00857-2Search in Google Scholar
[9] Hasan MK, Xing QF, Zhou CY, Wang KX, Xu T, Yang P, et al. Melatonin mediates elevated carbon dioxide-induced photosynthesis and thermotolerance in tomato. J Pineal Res. 2023;74(3):12858.10.1111/jpi.12858Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Ihsan M, Li Y, Shakeel A, Saqib F, Ahmad K, Nisar M, et al. Melatonin priming enhances maize seedling drought tolerance by regulating the antioxidant defense system. Plant Physiol. 2023;191(4):2301–15.10.1093/plphys/kiad027Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Zhang SN, Bao QL, Huang YZ, Han NA. Exogenous plant hormones alleviate As stress by regulating antioxidant defense system in Oryza sativa L. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023;30(3):6454–65.10.1007/s11356-022-22627-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Pan Y, Xu XS, Li L, Sun QL, Wang QG, Huang HH, et al. Melatonin-mediated development and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Plant Sci. 2023;14:1100827.10.3389/fpls.2023.1100827Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Zhang M, Gao CX, Xu L, Niu H, Liu Q, Huang YX, et al. Melatonin and indole-3-acetic acid synergistically regulate plant growth and stress resistance. Cells. 2022;11(20):3250.10.3390/cells11203250Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Chen L, Liu LT, Lu B, Ma TT, Jiang D, Li J, et al. Exogenous melatonin promotes seed germination and osmotic regulation under salt stress in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). PLoS One. 2020;15(1):0228241.10.1371/journal.pone.0228241Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Jan R, Asif S, Asaf S, Lubna, Du XX, Park JR, et al. Melatonin alleviates arsenic (As) toxicity in rice plants via modulating antioxidant defense system and secondary metabolites and reducing oxidative stress. Environ Pollut. 2022;318:120868.10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120868Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Wang J, Gao XQ, Wang X, Song WX, Wang Q, Wang XC, et al. Exogenous melatonin ameliorates drought stress in Agropyron mongolicum by regulating flavonoid biosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:1051165.10.3389/fpls.2022.1051165Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Wang Q, Liu SX, Chai XJ, Li H, Zhang F, Lu P, et al. Content diversity of phenolic compounds of waxy sorghum grains in different provinces, cities, and autonomous regions of China. Acta Agron Sin. 2022;48(10):2505–16.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Li J, Xie JM, Yu JH, Lyv J, Zhang JF, Ding DX, et al. Melatonin enhanced low-temperature combined with low-light tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) seedlings by regulating root growth, antioxidant defense system, and osmotic adjustment. Front Plant Sci. 2022;13:998293.10.3389/fpls.2022.998293Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Qiu X, Zhang XF, Lin ZC, Zhang YG. Study of salt tolerance in different varieties of sweet sorghum under different salt soil. Chin Agric Sci Bull. 2012;28:66–70.Search in Google Scholar
[20] An MZ, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xu JJ, Wang Y. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on seed germination, seedling growth and physiological characteristics of sorghum under salt stress. Shandong Agric Sci. 2022;54(12):81–90.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Zhang RD, Yue ZX, Chen XF, Wang YT, Zhou YF, Xu WJ, et al. Foliar applications of urea and melatonin to alleviate waterlogging stress on photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism in sorghum seedlings. Plant Growth Regul. 2021;97(2):429–38.10.1007/s10725-021-00705-9Search in Google Scholar
[22] Chen AK, Han RH, Li DY, Ling LL, Luo HX, Tang SJ. A comparison of two methods for electrical conductivity about plant leaves. J Guangdong Univ Educ. 2010;30(05):88–91.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Singh P, Kumar V, Sharma J, Saini S, Sharma P, Kumar S, et al. Silicon supplementation alleviates the salinity stress in wheat plants by enhancing the plant water status, photosynthetic pigments, proline content and antioxidant enzyme activities. Plants. 2022;11(19):2525.10.3390/plants11192525Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Li JW, Liu JH, Wang JY, Guo LC, Wang CL, Ren CZ. Effect of salt and alkali stress on oat ion balance and organic acid content. Acta Bot Boreali-Occident Sin. 2022;42(10):1700–10.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Li XF, Zhang ZL. Experimental guidance of plant physiology. 5th edn. Beijing: Higher Education Press; 2016.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Nakano Y, Asada K. Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol. 1981;22(05):867–80.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Foyer CH, Halliwell B. The presence of glutathione and glutathione reductase in chloroplasts: a proposed role in ascorbic acid metabolism. Planta. 1976;133(1):21–5.10.1007/BF00386001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Jahan MS, Guo SR, Baloch AR, Sun J, Shu S, Wang Y, et al. Melatonin alleviates nickel phytotoxicity by improving photosynthesis, secondary metabolism and oxidative stress tolerance in tomato seedlings. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2020;197(C):110593.10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110593Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Ellman GL. Reprint of: tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022;726(15):109245.10.1016/j.abb.2022.109245Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Li RZ, Jin Q, Li ZH, Wang Y, Peng Z, Duan LS. Salicylic acid improved salinity tolerance of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch during seed germination and seedling growth stages. Acta Agron Sin. 2020;46(11):1810–6.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Lei XH, Wan CX, Tao JC, Leng JJ, Wu YX, Wang JL, et al. Effects of soaking seeds with MT and EBR on germination and seedling growth in buckwheat under salt stress. Acta Agron Sin. 2020;48(05):1210–21.10.3724/SP.J.1006.2022.11040Search in Google Scholar
[32] Attia H, Alamer K, Algethami B, Zorrig W, Hessini K, Gupta K, et al. Gibberellic acid interacts with salt stress on germination, growth and polyamine gene expression in fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.) seedlings. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022;28(3):607–22.10.1007/s12298-022-01140-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Zhang ZH, Liu LT, Li HY, Zhang SC, Fu XY, Zhai XZ, et al. Exogenous melatonin promotes the salt tolerance by removing active oxygen and maintaining ion balance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Plant Sci. 2022;12:787062.10.3389/fpls.2021.787062Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Cui GB, Sun FL, Gao XM, Xie KL, Zhang C, Liu SD, et al. Proteomic analysis of melatonin-mediated osmotic tolerance by improving energy metabolism and autophagy in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planta. 2018;248(1):69–87.10.1007/s00425-018-2881-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Zhang JL, Li HR, Guo SY, Wang SM, Shi ZH, Han QQ, et al. Research advances in higher plant adaptation to salt stress. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2015;24(12):220–36.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Guo BC, Ke XW, Gao SY, Yu XH, Sun QM, Zuo YH. A preliminary study on the mechanisms of melatonin-induced rust resistance of adzuki bean. Plant Prot. 2020;46(1):145–50 + 156.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Sarropoulou V, Dimassi-Theriou K, Therios I, Koukourikou-Petridou M. Melatonin enhances root regeneration, photosynthetic pigments, biomass, total carbohydrates and proline content in the cherry rootstock PHL-C (Prunus avium × Prunus cerasus). Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012;61:162–8.10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.10.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[38] Wu WJ, Jiang Y, Ruan JJ, Zhou ML, Yao X, Ma C, et al. Effects of exogenous MT on growth and physiological characteristics of tartary buckwheat seedlings under AlCl3 stress. Mol Plant Breed. 2023;21:1–17. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1068.S.20230531.1607.022.html.Search in Google Scholar
[39] Zhang XY, He PY, Guo RY, Huang KF, Huang XY. Effects of salt stress on root morphology, carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and yield of Tartary buckwheat. Sci Rep-UK. 2023;13(1):12483.10.1038/s41598-023-39634-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Zhu D, Luo F, Zou R, Liu JX, Yan YM. Integrated physiological and chloroplast proteome analysis of wheat seedling leaves under salt and osmotic stresses. J Proteom. 2021;234:104097.10.1016/j.jprot.2020.104097Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Trukhachev VI, Seregina II, Belopukhov SL, Dmitrevskaya II, Fomina TI, Zharkikh OA, et al. The effect of stressful ecological conditions on chlorophyll content in the leaves of spring wheat plants. IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci. 2022;981(3):032093.10.1088/1755-1315/981/3/032093Search in Google Scholar
[42] Alam P, Balawi TA, Faizan M. Salicylic acid’s impact on growth, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzyme activity of Triticum aestivum when exposed to salt. Molecules. 2022;28(1):100.10.3390/molecules28010100Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Alharbi BM, Elhakem AH, Alnusairi GSH, Soliman MH, Hakeem KR, Hasan MM, et al. Exogenous application of melatonin alleviates salt stress-induced decline in growth and photosynthesis in Glycine max (L.) seedlings by improving mineral uptake, antioxidant and glyoxalase system. Plant Soil Environ. 2021;67(4):208–20.10.17221/659/2020-PSESearch in Google Scholar
[44] Marschner P, Rengel Z. Nutrient availability in soils. 5th edn. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants. Cambridge: Academic Press; 2012.10.1016/B978-0-12-384905-2.00012-1Search in Google Scholar
[45] Dadasoglu E, Turan M, Ekinci M, Argin S, Yildirim E. Alleviation mechanism of melatonin in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under the salt stress conditions. Horticulturae. 2022;8(11):1066.10.3390/horticulturae8111066Search in Google Scholar
[46] Ahmad I, Munsif F, Mihoub A, Jamal A, Saeed MF, Babar S, et al. Beneficial effect of melatonin on growth and chlorophyll content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown under salt stress conditions. Gesunde Pflanz. 2022;74(4):997–1009.10.1007/s10343-022-00684-5Search in Google Scholar
[47] Sheikhalipour M, Mohammadi SA, Esmaielpour B, Zareei E, Kulak M, Ali S, et al. Exogenous melatonin increases salt tolerance in bitter melon by regulating ionic balance, antioxidant system and secondary metabolism-related genes. BMC Plant Biol. 2022;22(1):380.10.1186/s12870-022-03728-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Su LN, Ma DM, Li JW, Zhang L, Hou WJ. Implications of exogenous melatonin on the physiological and photosynthetic characteristics of the seedlings of two alfalfa varieties. Acta Pratac Sin. 2023;31(03):726–32.Search in Google Scholar
[49] Liu JQ, Li L, Yang HH, Sun M, Feng HQ. Effects of melatonin on seed germination and seedling physiological characteristics of wheat under salt stress. J Triticeae Crop. 2022;42(7):857–63.Search in Google Scholar
[50] Jiang D, Lu B, Liu LT, Duan WJ, Meng YJ, Li J, et al. Exogenous melatonin improves the salt tolerance of cotton by removing active oxygen and protecting photosynthetic organs. BMC Plant Biol. 2021;21(1):331.10.1186/s12870-021-03082-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Yan QQ, Zhang JS, Xu HJ, Li XX, Wang YT. Effects of saline-alkali stress on biomass allocation and root morphology of sea island cotton seedlings. Acta Ecol Sin. 2019;39(20):7632–40.10.5846/stxb201809091929Search in Google Scholar
[52] Sun XL, Han W, Wang HF, Zhang SF, Sun HX, Liu Q, et al. Effects of salt tolerance exercise on morphological and root growth of wheat seedlings under salt stress. Shandong Agric Sci. 2021;53(12):33–7.Search in Google Scholar
[53] Niu JR, Jian MF, Rao JX, Zhang JY, Yang WJ, Ding HJ. Effects of exposure to polyethylene microplastics in a simulated soil environment on the ecophysiology of Viola philippica. Chin J Appl Environ Biol. 2022;28(5):1190–8.Search in Google Scholar
[54] Xiang J, Huang Q, Ju CY, Huang LX, Zhao ZW. Effect of exogenous melatonin on seed germination and seedling growth of rice under salt stress. Plant Physiol J. 2021;57(02):393–401.Search in Google Scholar
[55] Shahnaz MM, Iqbal M, Akhter N. Tissue-specific modulation of metabolism and nutrients acquisition through seed priming with sodium selenate confers salt tolerance in wheat. Arch Agron Soil Sci. 2020;67(10):1434–47.10.1080/03650340.2020.1797999Search in Google Scholar
[56] Yan FY, Wei HM, Li WW, Liu ZH, Tang S, Chen L, et al. Melatonin improves K+ and Na+ homeostasis in rice under salt stress by mediated nitric oxide. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2020;206:111358.10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111358Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[57] Altaf MA, Shahid R, Ren MX, Altaf MM, Khan LU, Shahid S, et al. Melatonin alleviates salt damage in tomato seedling: a root architecture system, photosynthetic capacity, ion homeostasis, and antioxidant enzymes analysis. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam. 2021;285:110145.10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110145Search in Google Scholar
[58] Luo CK, Min WF, Akhtar M, Lu XP, Bai XR, Zhang YX, et al. Melatonin enhances drought tolerance in rice seedlings by modulating antioxidant systems, osmoregulation, and corresponding gene expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12075.10.3390/ijms232012075Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Li GZ, Wang YY, Liu J, Liu HT, Liu HP, Kang GZ. Exogenous melatonin mitigates cadmium toxicity through ascorbic acid and glutathione pathway in wheat. Ecotox Environ Safe. 2022;237:113533.10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113533Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Luo Y, Wang R, Lei XQ, Ren YM, Yuan CL. Melatonin treatment delays senescence and alleviates chilling injury in spaghetti squash during low-temperature storage. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam. 2023;310:113533.10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111778Search in Google Scholar
[61] Wang MQ, Gong SC, Fu LX, Hu GH, Li GL, Hu SX, et al. The involvement of antioxidant enzyme system, nitrogen metabolism and osmoregulatory substances in alleviating salt stress in inbred maize lines and hormone regulation mechanisms. Plants. 2022;11(12):1547.10.3390/plants11121547Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[62] Aghdam MS, Luo ZS, Jannatizadeh A, Sheikh-Assadi M, Sharafi Y, Farmani B, et al. Employing exogenous melatonin applying confers chilling tolerance in tomato fruits by upregulating ZAT2/6/12 giving rise to promoting endogenous polyamines, proline, and nitric oxide accumulation by triggering arginine pathway activity. Food Chem. 2019;275:549–56.10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.157Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Systemic investigation of inetetamab in combination with small molecules to treat HER2-overexpressing breast and gastric cancers
- Immunosuppressive treatment for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: An updated network meta-analysis
- Identifying two pathogenic variants in a patient with pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy
- Effects of phytoestrogens combined with cold stress on sperm parameters and testicular proteomics in rats
- A case of pulmonary embolism with bad warfarin anticoagulant effects caused by E. coli infection
- Neutrophilia with subclinical Cushing’s disease: A case report and literature review
- Isoimperatorin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis by downregulating ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathways
- Immunoregulation of synovial macrophages for the treatment of osteoarthritis
- Novel CPLANE1 c.8948dupT (p.P2984Tfs*7) variant in a child patient with Joubert syndrome
- Antiphospholipid antibodies and the risk of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms
- Immunological responses of septic rats to combination therapy with thymosin α1 and vitamin C
- High glucose and high lipid induced mitochondrial dysfunction in JEG-3 cells through oxidative stress
- Pharmacological inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease 8 effectively suppresses glioblastoma cell growth
- Levocarnitine regulates the growth of angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cells via TIMP-1
- Age-related changes in peripheral T-cell subpopulations in elderly individuals: An observational study
- Single-cell transcription analysis reveals the tumor origin and heterogeneity of human bilateral renal clear cell carcinoma
- Identification of iron metabolism-related genes as diagnostic signatures in sepsis by blood transcriptomic analysis
- Long noncoding RNA ACART knockdown decreases 3T3-L1 preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation
- Surgery, adjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy for primary malignant melanoma of the parotid gland (PGMM): A case report
- Dosimetry comparison with helical tomotherapy, volumetric modulated arc therapy, and intensity-modulated radiotherapy for grade II gliomas: A single‑institution case series
- Soy isoflavone reduces LPS-induced acute lung injury via increasing aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 5 in rats
- Refractory hypokalemia with sexual dysplasia and infertility caused by 17α-hydroxylase deficiency and triple X syndrome: A case report
- Meta-analysis of cancer risk among end stage renal disease undergoing maintenance dialysis
- 6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase inhibition arrests growth and induces apoptosis in gastric cancer via AMPK activation and oxidative stress
- Experimental study on the optimization of ANM33 release in foam cells
- Primary retroperitoneal angiosarcoma: A case report
- Metabolomic analysis-identified 2-hydroxybutyric acid might be a key metabolite of severe preeclampsia
- Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy
- Effect of spaceflight on the phenotype and proteome of Escherichia coli
- Comparison of immunotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy for patients with brain metastases: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation
- Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy
- The role of IL-31 and IL-34 in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Triple-negative mouse breast cancer initiating cells show high expression of beta1 integrin and increased malignant features
- mNGS facilitates the accurate diagnosis and antibiotic treatment of suspicious critical CNS infection in real practice: A retrospective study
- The apatinib and pemetrexed combination has antitumor and antiangiogenic effects against NSCLC
- Radiotherapy for primary thyroid adenoid cystic carcinoma
- Design and functional preliminary investigation of recombinant antigen EgG1Y162–EgG1Y162 against Echinococcus granulosus
- Effects of losartan in patients with NAFLD: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trial
- Bibliometric analysis of METTL3: Current perspectives, highlights, and trending topics
- Performance comparison of three scaling algorithms in NMR-based metabolomics analysis
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its related molecules participate in PROK1 silence-induced anti-tumor effects on pancreatic cancer
- The altered expression of cytoskeletal and synaptic remodeling proteins during epilepsy
- Effects of pegylated recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on lymphocytes and white blood cells of patients with malignant tumor
- Prostatitis as initial manifestation of Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by metagenome next-generation sequencing: A case report
- NUDT21 relieves sevoflurane-induced neurological damage in rats by down-regulating LIMK2
- Association of interleukin-10 rs1800896, rs1800872, and interleukin-6 rs1800795 polymorphisms with squamous cell carcinoma risk: A meta-analysis
- Exosomal HBV-DNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of chronic hepatitis B
- Shear stress leads to the dysfunction of endothelial cells through the Cav-1-mediated KLF2/eNOS/ERK signaling pathway under physiological conditions
- Interaction between the PI3K/AKT pathway and mitochondrial autophagy in macrophages and the leukocyte count in rats with LPS-induced pulmonary infection
- Meta-analysis of the rs231775 locus polymorphism in the CTLA-4 gene and the susceptibility to Graves’ disease in children
- Cloning, subcellular localization and expression of phosphate transporter gene HvPT6 of hulless barley
- Coptisine mitigates diabetic nephropathy via repressing the NRLP3 inflammasome
- Significant elevated CXCL14 and decreased IL-39 levels in patients with tuberculosis
- Whole-exome sequencing applications in prenatal diagnosis of fetal bowel dilatation
- Gemella morbillorum infective endocarditis: A case report and literature review
- An unusual ectopic thymoma clonal evolution analysis: A case report
- Severe cumulative skin toxicity during toripalimab combined with vemurafenib following toripalimab alone
- Detection of V. vulnificus septic shock with ARDS using mNGS
- Novel rare genetic variants of familial and sporadic pulmonary atresia identified by whole-exome sequencing
- The influence and mechanistic action of sperm DNA fragmentation index on the outcomes of assisted reproduction technology
- Novel compound heterozygous mutations in TELO2 in an infant with You-Hoover-Fong syndrome: A case report and literature review
- ctDNA as a prognostic biomarker in resectable CLM: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Diagnosis of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing: A case report
- Phylogenetic analysis of promoter regions of human Dolichol kinase (DOLK) and orthologous genes using bioinformatics tools
- Collagen changes in rabbit conjunctiva after conjunctival crosslinking
- Effects of NM23 transfection of human gastric carcinoma cells in mice
- Oral nifedipine and phytosterol, intravenous nicardipine, and oral nifedipine only: Three-arm, retrospective, cohort study for management of severe preeclampsia
- Case report of hepatic retiform hemangioendothelioma: A rare tumor treated with ultrasound-guided microwave ablation
- Curcumin induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by decreasing the expression of STAT3/VEGF/HIF-1α signaling
- Rare presentation of double-clonal Waldenström macroglobulinemia with pulmonary embolism: A case report
- Giant duplication of the transverse colon in an adult: A case report and literature review
- Ectopic thyroid tissue in the breast: A case report
- SDR16C5 promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
- Vaginal metastasis from breast cancer: A case report
- Screening of the best time window for MSC transplantation to treat acute myocardial infarction with SDF-1α antibody-loaded targeted ultrasonic microbubbles: An in vivo study in miniswine
- Inhibition of TAZ impairs the migration ability of melanoma cells
- Molecular complexity analysis of the diagnosis of Gitelman syndrome in China
- Effects of maternal calcium and protein intake on the development and bone metabolism of offspring mice
- Identification of winter wheat pests and diseases based on improved convolutional neural network
- Ultra-multiplex PCR technique to guide treatment of Aspergillus-infected aortic valve prostheses
- Virtual high-throughput screening: Potential inhibitors targeting aminopeptidase N (CD13) and PIKfyve for SARS-CoV-2
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with COVID-19
- Utility of methylene blue mixed with autologous blood in preoperative localization of pulmonary nodules and masses
- Integrated analysis of the microbiome and transcriptome in stomach adenocarcinoma
- Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy
- DUSP2 inhibits the progression of lupus nephritis in mice by regulating the STAT3 pathway
- Lung abscess by Fusobacterium nucleatum and Streptococcus spp. co-infection by mNGS: A case series
- Genetic alterations of KRAS and TP53 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma associated with poor prognosis
- Granulomatous polyangiitis involving the fourth ventricle: Report of a rare case and a literature review
- Studying infant mortality: A demographic analysis based on data mining models
- Metaplastic breast carcinoma with osseous differentiation: A report of a rare case and literature review
- Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells
- Inhibition of pyroptosis and apoptosis by capsaicin protects against LPS-induced acute kidney injury through TRPV1/UCP2 axis in vitro
- TAK-242, a toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, against brain injury by alleviates autophagy and inflammation in rats
- Primary mediastinum Ewing’s sarcoma with pleural effusion: A case report and literature review
- Association of ADRB2 gene polymorphisms and intestinal microbiota in Chinese Han adolescents
- Tanshinone IIA alleviates chondrocyte apoptosis and extracellular matrix degeneration by inhibiting ferroptosis
- Study on the cytokines related to SARS-Cov-2 in testicular cells and the interaction network between cells based on scRNA-seq data
- Effect of periostin on bone metabolic and autophagy factors during tooth eruption in mice
- HP1 induces ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells through NRF2 pathway in diabetic nephropathy
- Intravaginal estrogen management in postmenopausal patients with vaginal squamous intraepithelial lesions along with CO2 laser ablation: A retrospective study
- Hepatocellular carcinoma cell differentiation trajectory predicts immunotherapy, potential therapeutic drugs, and prognosis of patients
- Effects of physical exercise on biomarkers of oxidative stress in healthy subjects: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Identification of lysosome-related genes in connection with prognosis and immune cell infiltration for drug candidates in head and neck cancer
- Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
- Research progress on gas signal molecular therapy for Parkinson’s disease
- Adiponectin inhibits TGF-β1-induced skin fibroblast proliferation and phenotype transformation via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- The G protein-coupled receptor-related gene signatures for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- α-Fetoprotein contributes to the malignant biological properties of AFP-producing gastric cancer
- CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in placenta tissues of patients with placenta previa
- Association between thyroid stimulating hormone levels and papillary thyroid cancer risk: A meta-analysis
- Significance of sTREM-1 and sST2 combined diagnosis for sepsis detection and prognosis prediction
- Diagnostic value of serum neuroactive substances in the acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with depression
- Research progress of AMP-activated protein kinase and cardiac aging
- TRIM29 knockdown prevented the colon cancer progression through decreasing the ubiquitination levels of KRT5
- Cross-talk between gut microbiota and liver steatosis: Complications and therapeutic target
- Metastasis from small cell lung cancer to ovary: A case report
- The early diagnosis and pathogenic mechanisms of sepsis-related acute kidney injury
- The effect of NK cell therapy on sepsis secondary to lung cancer: A case report
- Erianin alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by inhibiting Th17 cell differentiation
- Loss of ACOX1 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and its correlation with clinical features
- Signalling pathways in the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells
- Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure
- Clinicopathological features and differential diagnosis of gastric pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma
- Traumatic brain injury and rTMS-ERPs: Case report and literature review
- Extracellular fibrin promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through integrin β1/PTEN/AKT signaling
- Knockdown of DLK4 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer tumor growth by downregulating CKS2
- The co-expression pattern of VEGFR-2 with indicators related to proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation of anagen hair follicles
- Inflammation-related signaling pathways in tendinopathy
- CD4+ T cell count in HIV/TB co-infection and co-occurrence with HL: Case report and literature review
- Clinical analysis of severe Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: Case series study
- Bioinformatics analysis to identify potential biomarkers for the pulmonary artery hypertension associated with the basement membrane
- Influence of MTHFR polymorphism, alone or in combination with smoking and alcohol consumption, on cancer susceptibility
- Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don counteracts the ampicillin resistance in multiple antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by downregulation of PBP2a synthesis
- Combination of a bronchogenic cyst in the thoracic spinal canal with chronic myelocytic leukemia
- Bacterial lipoprotein plays an important role in the macrophage autophagy and apoptosis induced by Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus
- TCL1A+ B cells predict prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer through integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk transcriptomic data
- Ezrin promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression via the Hippo signaling pathway
- Ferroptosis: A potential target of macrophages in plaque vulnerability
- Predicting pediatric Crohn's disease based on six mRNA-constructed risk signature using comprehensive bioinformatic approaches
- Applications of genetic code expansion and photosensitive UAAs in studying membrane proteins
- HK2 contributes to the proliferation, migration, and invasion of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by enhancing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway
- IL-17 in osteoarthritis: A narrative review
- Circadian cycle and neuroinflammation
- Probiotic management and inflammatory factors as a novel treatment in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hemorrhagic meningioma with pulmonary metastasis: Case report and literature review
- SPOP regulates the expression profiles and alternative splicing events in human hepatocytes
- Knockdown of SETD5 inhibited glycolysis and tumor growth in gastric cancer cells by down-regulating Akt signaling pathway
- PTX3 promotes IVIG resistance-induced endothelial injury in Kawasaki disease by regulating the NF-κB pathway
- Pancreatic ectopic thyroid tissue: A case report and analysis of literature
- The prognostic impact of body mass index on female breast cancer patients in underdeveloped regions of northern China differs by menopause status and tumor molecular subtype
- Report on a case of liver-originating malignant melanoma of unknown primary
- Case report: Herbal treatment of neutropenic enterocolitis after chemotherapy for breast cancer
- The fibroblast growth factor–Klotho axis at molecular level
- Characterization of amiodarone action on currents in hERG-T618 gain-of-function mutations
- A case report of diagnosis and dynamic monitoring of Listeria monocytogenes meningitis with NGS
- Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on new bone formation and viability of a Marburg bone graft
- Small breast epithelial mucin as a useful prognostic marker for breast cancer patients
- Continuous non-adherent culture promotes transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into retinal lineage
- Nrf3 alleviates oxidative stress and promotes the survival of colon cancer cells by activating AKT/BCL-2 signal pathway
- Favorable response to surufatinib in a patient with necrolytic migratory erythema: A case report
- Case report of atypical undernutrition of hypoproteinemia type
- Down-regulation of COL1A1 inhibits tumor-associated fibroblast activation and mediates matrix remodeling in the tumor microenvironment of breast cancer
- Sarcoma protein kinase inhibition alleviates liver fibrosis by promoting hepatic stellate cells ferroptosis
- Research progress of serum eosinophil in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Clinicopathological characteristics of co-existing or mixed colorectal cancer and neuroendocrine tumor: Report of five cases
- Role of menopausal hormone therapy in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis
- Precisional detection of lymph node metastasis using tFCM in colorectal cancer
- Advances in diagnosis and treatment of perimenopausal syndrome
- A study of forensic genetics: ITO index distribution and kinship judgment between two individuals
- Acute lupus pneumonitis resembling miliary tuberculosis: A case-based review
- Plasma levels of CD36 and glutathione as biomarkers for ruptured intracranial aneurysm
- Fractalkine modulates pulmonary angiogenesis and tube formation by modulating CX3CR1 and growth factors in PVECs
- Novel risk prediction models for deep vein thrombosis after thoracotomy and thoracoscopic lung cancer resections, involving coagulation and immune function
- Exploring the diagnostic markers of essential tremor: A study based on machine learning algorithms
- Evaluation of effects of small-incision approach treatment on proximal tibia fracture by deep learning algorithm-based magnetic resonance imaging
- An online diagnosis method for cancer lesions based on intelligent imaging analysis
- Medical imaging in rheumatoid arthritis: A review on deep learning approach
- Predictive analytics in smart healthcare for child mortality prediction using a machine learning approach
- Utility of neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio and platelet–lymphocyte ratio in predicting acute-on-chronic liver failure survival
- A biomedical decision support system for meta-analysis of bilateral upper-limb training in stroke patients with hemiplegia
- TNF-α and IL-8 levels are positively correlated with hypobaric hypoxic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats
- Stochastic gradient descent optimisation for convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation
- Comparison of the prognostic value of four different critical illness scores in patients with sepsis-induced coagulopathy
- Application and teaching of computer molecular simulation embedded technology and artificial intelligence in drug research and development
- Hepatobiliary surgery based on intelligent image segmentation technology
- Value of brain injury-related indicators based on neural network in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- Analysis of early diagnosis methods for asymmetric dementia in brain MR images based on genetic medical technology
- Early diagnosis for the onset of peri-implantitis based on artificial neural network
- Clinical significance of the detection of serum IgG4 and IgG4/IgG ratio in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy
- Forecast of pain degree of lumbar disc herniation based on back propagation neural network
- SPA-UNet: A liver tumor segmentation network based on fused multi-scale features
- Systematic evaluation of clinical efficacy of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer observed by medical image
- Rehabilitation effect of intelligent rehabilitation training system on hemiplegic limb spasms after stroke
- A novel approach for minimising anti-aliasing effects in EEG data acquisition
- ErbB4 promotes M2 activation of macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Clinical role of CYP1B1 gene polymorphism in prediction of postoperative chemotherapy efficacy in NSCLC based on individualized health model
- Lung nodule segmentation via semi-residual multi-resolution neural networks
- Evaluation of brain nerve function in ICU patients with Delirium by deep learning algorithm-based resting state MRI
- A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis
- Markov model combined with MR diffusion tensor imaging for predicting the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
- Effectiveness of the treatment of depression associated with cancer and neuroimaging changes in depression-related brain regions in patients treated with the mediator-deuterium acupuncture method
- Molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer and screening of molecular markers based on bioinformatics analysis
- Monitoring and evaluation of anesthesia depth status data based on neuroscience
- Exploring the conformational dynamics and thermodynamics of EGFR S768I and G719X + S768I mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: An in silico approaches
- Optimised feature selection-driven convolutional neural network using gray level co-occurrence matrix for detection of cervical cancer
- Incidence of different pressure patterns of spinal cerebellar ataxia and analysis of imaging and genetic diagnosis
- Pathogenic bacteria and treatment resistance in older cardiovascular disease patients with lung infection and risk prediction model
- Adoption value of support vector machine algorithm-based computed tomography imaging in the diagnosis of secondary pulmonary fungal infections in patients with malignant hematological disorders
- From slides to insights: Harnessing deep learning for prognostic survival prediction in human colorectal cancer histology
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Monitoring of hourly carbon dioxide concentration under different land use types in arid ecosystem
- Comparing the differences of prokaryotic microbial community between pit walls and bottom from Chinese liquor revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing
- Effects of cadmium stress on fruits germination and growth of two herbage species
- Bamboo charcoal affects soil properties and bacterial community in tea plantations
- Optimization of biogas potential using kinetic models, response surface methodology, and instrumental evidence for biodegradation of tannery fleshings during anaerobic digestion
- Understory vegetation diversity patterns of Platycladus orientalis and Pinus elliottii communities in Central and Southern China
- Studies on macrofungi diversity and discovery of new species of Abortiporus from Baotianman World Biosphere Reserve
- Food Science
- Effect of berrycactus fruit (Myrtillocactus geometrizans) on glutamate, glutamine, and GABA levels in the frontal cortex of rats fed with a high-fat diet
- Guesstimate of thymoquinone diversity in Nigella sativa L. genotypes and elite varieties collected from Indian states using HPTLC technique
- Analysis of bacterial community structure of Fuzhuan tea with different processing techniques
- Untargeted metabolomics reveals sour jujube kernel benefiting the nutritional value and flavor of Morchella esculenta
- Mycobiota in Slovak wine grapes: A case study from the small Carpathians wine region
- Elemental analysis of Fadogia ancylantha leaves used as a nutraceutical in Mashonaland West Province, Zimbabwe
- Microbiological transglutaminase: Biotechnological application in the food industry
- Influence of solvent-free extraction of fish oil from catfish (Clarias magur) heads using a Taguchi orthogonal array design: A qualitative and quantitative approach
- Chromatographic analysis of the chemical composition and anticancer activities of Curcuma longa extract cultivated in Palestine
- The potential for the use of leghemoglobin and plant ferritin as sources of iron
- Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Biocompatibility and osteointegration capability of β-TCP manufactured by stereolithography 3D printing: In vitro study
- Clinical characteristics and the prognosis of diabetic foot in Tibet: A single center, retrospective study
- Agriculture
- Biofertilizer and NPSB fertilizer application effects on nodulation and productivity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Sodo Zuria, Southern Ethiopia
- On correlation between canopy vegetation and growth indexes of maize varieties with different nitrogen efficiencies
- Exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas tolaasii inhibit the growth of Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia
- A transcriptomic evaluation of the mechanism of programmed cell death of the replaceable bud in Chinese chestnut
- Melatonin enhances salt tolerance in sorghum by modulating photosynthetic performance, osmoregulation, antioxidant defense, and ion homeostasis
- Effects of plant density on alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) seed yield in western Heilongjiang areas
- Identification of rice leaf diseases and deficiency disorders using a novel DeepBatch technique
- Artificial intelligence and internet of things oriented sustainable precision farming: Towards modern agriculture
- Animal Sciences
- Effect of ketogenic diet on exercise tolerance and transcriptome of gastrocnemius in mice
- Combined analysis of mRNA–miRNA from testis tissue in Tibetan sheep with different FecB genotypes
- Isolation, identification, and drug resistance of a partially isolated bacterium from the gill of Siniperca chuatsi
- Tracking behavioral changes of confined sows from the first mating to the third parity
- The sequencing of the key genes and end products in the TLR4 signaling pathway from the kidney of Rana dybowskii exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila
- Development of a new candidate vaccine against piglet diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli
- Plant Sciences
- Crown and diameter structure of pure Pinus massoniana Lamb. forest in Hunan province, China
- Genetic evaluation and germplasm identification analysis on ITS2, trnL-F, and psbA-trnH of alfalfa varieties germplasm resources
- Tissue culture and rapid propagation technology for Gentiana rhodantha
- Effects of cadmium on the synthesis of active ingredients in Salvia miltiorrhiza
- Cloning and expression analysis of VrNAC13 gene in mung bean
- Chlorate-induced molecular floral transition revealed by transcriptomes
- Effects of warming and drought on growth and development of soybean in Hailun region
- Effects of different light conditions on transient expression and biomass in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves
- Comparative analysis of the rhizosphere microbiome and medicinally active ingredients of Atractylodes lancea from different geographical origins
- Distinguish Dianthus species or varieties based on chloroplast genomes
- Comparative transcriptomes reveal molecular mechanisms of apple blossoms of different tolerance genotypes to chilling injury
- Study on fresh processing key technology and quality influence of Cut Ophiopogonis Radix based on multi-index evaluation
- An advanced approach for fig leaf disease detection and classification: Leveraging image processing and enhanced support vector machine methodology
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Protein Z modulates the metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells”
- Erratum to “BRCA1 subcellular localization regulated by PI3K signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and hormone-sensitive T47D cells”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “Protocatechuic acid attenuates cerebral aneurysm formation and progression by inhibiting TNF-alpha/Nrf-2/NF-kB-mediated inflammatory mechanisms in experimental rats”

