Abstract
Aquatic plants, such as water hyacinths, Eichhornia crassipes, are indicators of environmental changes. This study explores the response of water hyacinths to wastewater exposure by analyzing their bioelectrical signals. The analysis includes time, frequency, and joint time-frequency domains, evaluating the plant’s response to water quality variation. In the time domain, the Lempel-Ziv complexity analysis was used to demonstrate how the plant’s response evolves over time, while spectral entropy was used for frequency domain analysis. By using adaptive Gabor representation, the joint time-frequency behavior of the signal was evaluated. All these advanced digital signal processing techniques were used to evaluate the plant’s ability to detect and adapt to the presence of pollutants. The results show that water hyacinths can serve as part of a reliable instrumentation system for real-time aquatic ecosystem monitoring, as the plant’s bioelectrical signals changed both in the time domain and frequency domain.
Graphical abstract
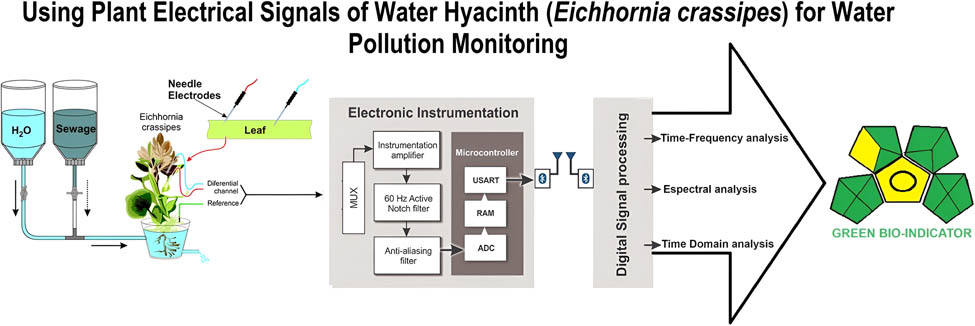
1 Introduction
The use of plant bioelectrical signals as a measurement system is a challenge in the field of bio-detectors, which has gained considerable attention in scientific literature. Traditional analytical methods, such as chromatography and spectroscopy, have practical limitations for real-time monitoring [1,2,3]. A long-term alternative would be to use plant bioelectricity to monitor the environment by interfacing with electronic systems and tracking their bioelectrical responses [4,5]. Currently, the monitoring of pollution sources in a water supply network based on smart electronic instrumentation methods has become the state-of-the-art approach to fulfill the need for information on water quality. This requirement arises from the necessity of ensuring a specific quality of water for various purposes. Indeed, there is a growing academic consensus that “water quality” should encompass the monitoring and investigation of the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water [6]. Over time, new challenges in water monitoring have emerged, such as acquiring data on the relationship between the environment and water quality and integrating the systemic constituents of water, such as aquatic plants, within the context of water monitoring [7]. The water hyacinth (“Eichhornia crassipes”) plays a prominent role among aquatic plants in relation to water pollution control. Among aquatic macrophytes, water hyacinth is considered a suitable species for phytoremediation and bio-remediation [8]. Under controlled growth conditions, it surpasses conventional methods by efficiently extracting and absorbing industrial and agricultural effluents contaminated with organic, inorganic, and toxic residues [9,10].
Most studies have focused on the use of water hyacinth for wastewater treatment [11]. Therefore, a systematic technique was developed to evaluate the potential of water hyacinth in improving water quality monitoring by harnessing bioelectricity [12]. The phenomenon of electrical biopotentials in plants has raised new scientific questions about plant physiology [13]. These electrical signals are generated through transient depolarization/hyperpolarization events, resulting from changes in the membrane potential induced by various stimuli. These events modulate ion channels and the voltage of the plasma membrane, causing an imbalance of ions [14].
Four types of electrical signals have been reported in plants: action potentials (AP), variation potentials (VP), local electrical potentials (LEP), and system potentials (SP) [15]. Among these signals, APs have been the most extensively studied. Essentially, bioelectrical activity involves the transient disruption of the ion balance (such as Ca2+, K+, and Cl−) across the plasma membrane, often triggered by external stimuli [16]. On the other hand, SP is a systemic hyperpolarization event that propagates from leaf to leaf, depending on the intensity and nature of the original stimulus [17], while LEP represents a sub-threshold response induced by changes in environmental factors (such as water, air temperature, and humidity, light, and fertility). LEP is generated locally and does not spread to other parts of the plant [18,19].
Plant electrical signals play significant physiological roles in nutrient absorption, respiration, photosynthesis [20], and phloem transport [21]. It has been demonstrated that not only plant activities but also the plant environment can be monitored using bioelectrical signals [22]. In aquatic plants like water hyacinths, it is well established that their roots play a crucial role in the interaction between plants and pollutants [23,24]. Therefore, it is reasonable to assume that changes in root physiology will propagate through the plant’s vascular system and subsequently affect the patterns of bioelectrical signals. Consequently, integrating bioelectrical signals from plants with digital signal processing (DSP) techniques can enhance the monitoring of water pollutants using water hyacinth, coupled with an integrated electronic signal acquisition and processing system.
Advancements in DSP have equipped researchers with robust tools to analyze the intricate bioelectrical signals in plants. Spectral entropy, introduced by Inouye et al. [25], has been effectively utilized to quantify the complexity of time-series data, including bioelectric signals, by measuring the disorder or unpredictability within the signal. Similarly, Lempel-Ziv complexity, initially developed as a data compression algorithm, serves as a metric for assessing the irregularity and unpredictability of time-series data. Its application in analyzing physiological signals, such as electroencephalograms, has demonstrated its efficacy in capturing the complexity inherent in biological systems [25,26]. The adaptive Gabor transform is a powerful means to analyze the time-frequency characteristics of non-stationary signals [27]. By providing a joint time-frequency representation, it facilitates the detection of transient features and dynamic changes within the signal. In the realm of biological signal analysis, the adaptive Gabor transform has shown promise in elucidating the temporal and spectral components of plant bioelectrical activity. Integrating these advanced DSP techniques into an electronic signal acquisition and processing system enables real-time and continuous monitoring of water pollutants through the bioelectrical responses of water hyacinths. This approach leverages the inherent sensitivity of plants to environmental changes, enhancing our understanding of plant–environment interactions and offering a novel method for environmental monitoring [28]. In the context of monitoring water pollutants using aquatic plants like water hyacinths, these DSP techniques can play a pivotal role. Spectral entropy can capture changes in the complexity of bioelectrical signals as the plants respond to varying pollutant concentrations and environmental conditions. Lempel-Ziv complexity can provide insights into the unpredictability of the bioelectric signals, potentially indicating stress or perturbations in the plant’s physiological state. Adaptive Gabor transform, with its ability to analyze time-frequency patterns, can unveil dynamic changes in bioelectrical signal patterns that might correlate with pollutant exposure events. Coupling the inherent sensitivity of water hyacinths to pollutants with advanced DSP techniques not only enhances our understanding of plant–environment interactions but also offers a novel approach to environmental monitoring. This integrated approach aligns with the principles of green analytical chemistry (GAC), which encourages the reduction of toxic chemicals, the use of energy-efficient equipment, and the generation of minimal waste [29].
The objective of this article is to demonstrate, under laboratory conditions, that the bioelectrical response of water hyacinth differs when exposed to sewage water compared to clean water. This study investigates the bioelectrical activity of water hyacinths under controlled conditions, utilizing advanced DSP techniques to assess their response to sewage water exposure. The research explores the viability of employing aquatic plants, specifically water hyacinth, as bio-detectors for water monitoring through precise DSP methodologies.
2 Botanic material: Description and cultivation
Water hyacinth samples were collected from water catchment ponds on the University of São Paulo campus in Pirassununga. These samples were transferred to thermally insulated tank boxes (made of Styrofoam), measuring 1 m × 0.40 m × 0.25 m and with a capacity of 100 L. The samples were placed outdoors under natural light for a 30-day acclimatization period. A protective covering was provided using polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubes covered with transparent plastic and shade netting (Figure 1).
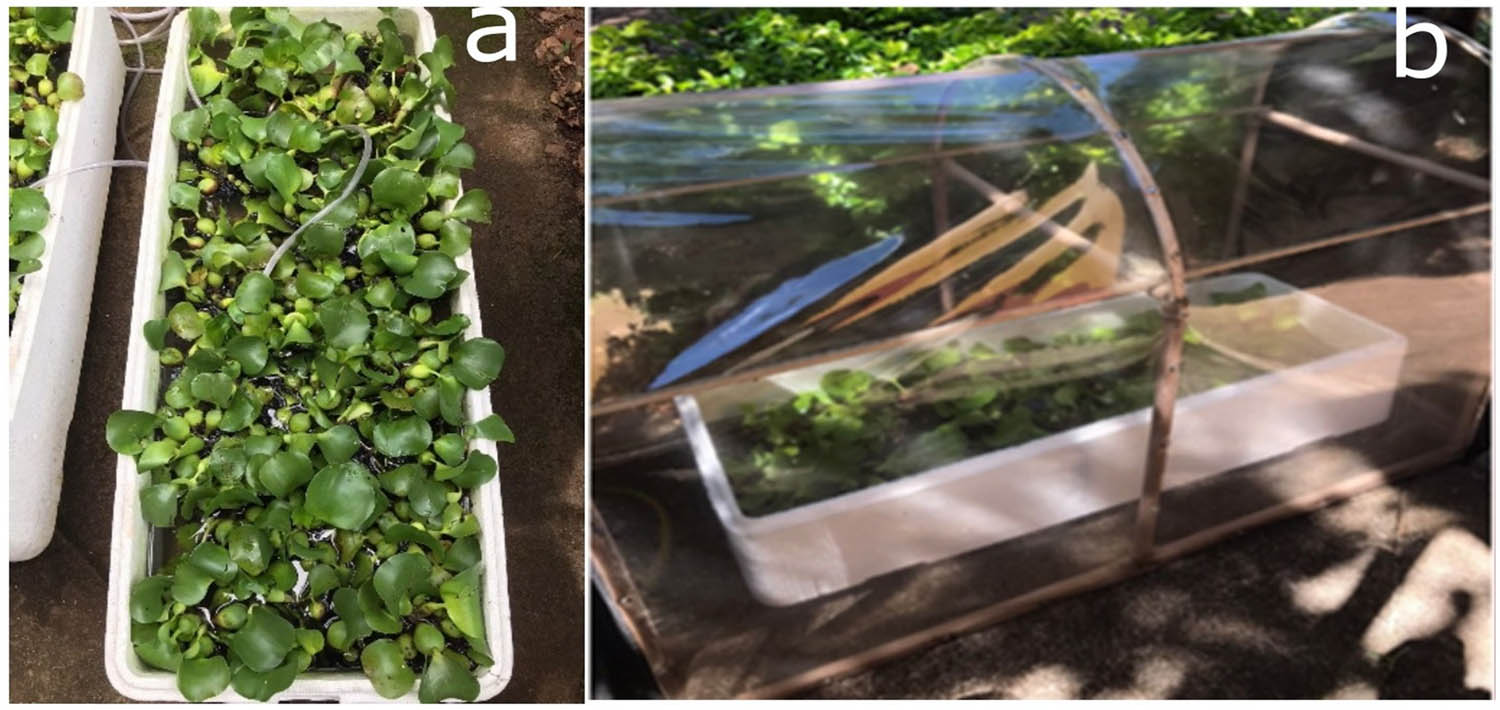

Water hyacinth tank box with protection and aeration.
Physicochemical monitoring of the tank boxes was conducted, including pH control within the range of 5.5–6.5, turbidity measurement using a Hanna HI98703 device, as well as monitoring light and temperature.
The analyte used was raw urban sewage, collected from the Water and Sewage Treatment Station of the municipality of Pirassununga. The collected material was placed in plastic containers and maintained at a controlled temperature of 22°C for a maximum of 6 h during each experiment.
3 Experimental setup
From the cultivated water hyacinth plants, 30 most vigorous and robust adult specimens were randomly selected from a larger population of healthy plants and used for the proposed experiments. This approach minimizes selection bias and enhances the generalizability of the findings. Each of these plants was individually placed in an experimental unit composed of a container with a capacity of 1 L of nutrient solution, along with a silicone hose and a flow control device (Figure 2).
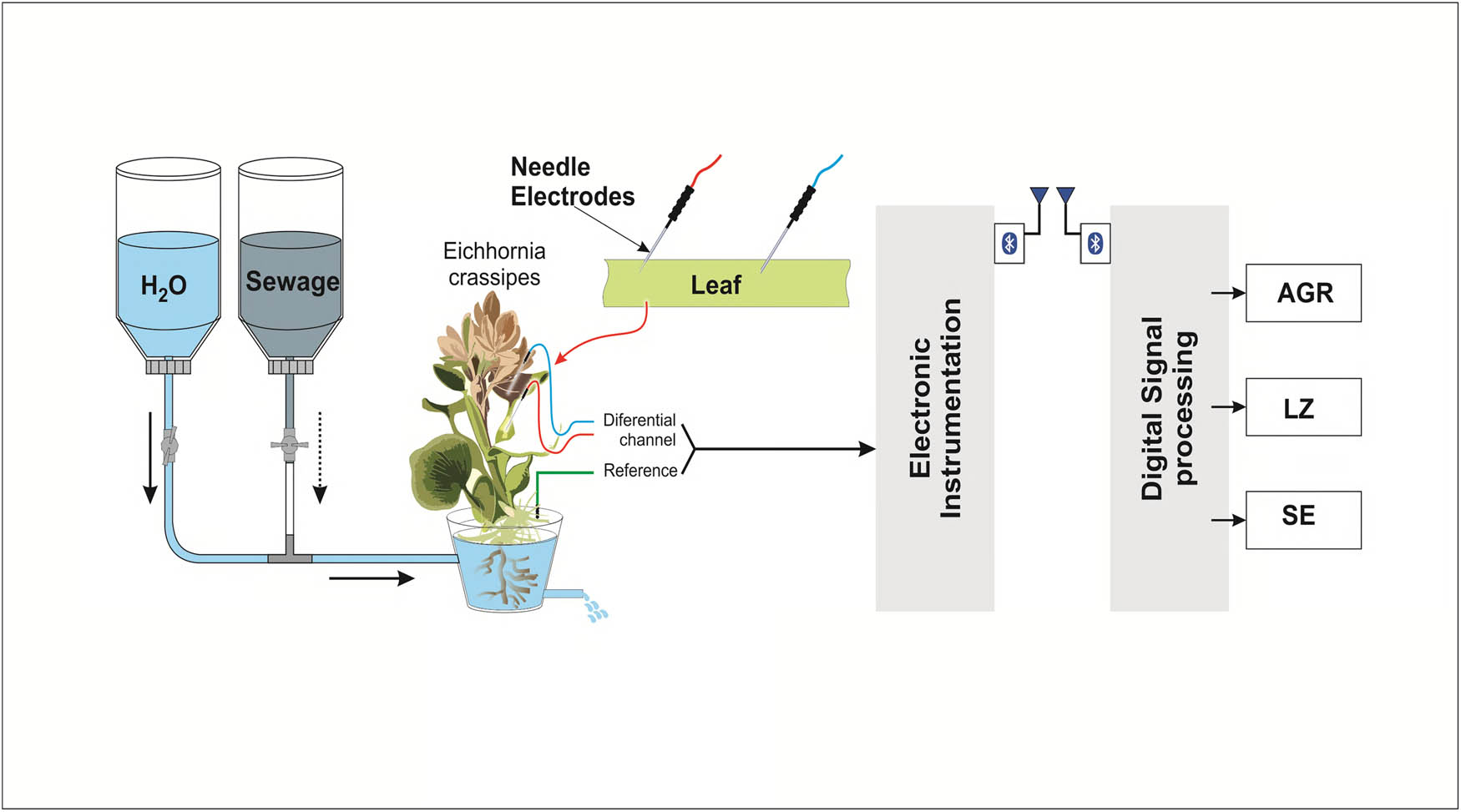
Experimental setup.
The bioelectrical signals were monitored using two Ag/AgCl needle electrodes positioned on one of the plant’s leaves, maintaining a distance of 5 cm between them. A ground electrode was connected to the container system. To ensure stable experimental conditions and minimize external interference, each plant remained inside a Faraday cage, an electromagnetically isolated environment, at an average temperature of 23°C and a light intensity of 100 lux for 1 h. After this adaptation period, the bioelectric potentials began to be recorded. The experimental setup also included a 5-L reservoir directly attached above the experimental unit. This reservoir worked in conjunction with a gravity drainage system, providing a flow rate of 1 L of solution at intervals of 3 min. The transfer of this solution was carried out through a silicone hose connecting the reservoir to the experimental unit. Additionally, another container of identical capacity was incorporated just below the experimental unit, specifically designed to collect and direct the flow of released solutions. The bioelectrical signals (bioelectric potentials) were recorded using Ag/AgCl needle electrodes and an electronic device designed for data acquisition. Two minutes after the start of the plant’s biopotential recording in the culture medium, a flow of 2 L of sewage from container 1 begins, and completely replaces the culture medium in the experimental unit. At the same time, the culture medium is gradually transferred to vessel 2. Thus, in 18 min, it was possible to record the plant’s biopotentials under different conditions: in its culture medium, when the analyte entered the experimental unit, and in the complete replacement of the medium by the analyte.
3.1 Acquisition of bioelectric signals
The bioelectrical signal acquisition system employed in this study was adapted from the design proposed by Cabral [30]. The original system utilized an instrumentation amplifier with four inputs to operational amplifiers, designed to pre-amplify the signal, apply both high-pass (cutoff frequency of 0.5 Hz) and low-pass (cutoff frequency of 1.5 kHz) filters, and subsequently post-amplify the signal to ensure a clean and robust output. The digitization was performed using a bipolar 10-bit analog-to-digital converter, with a microprocessor controlling the signal sampling frequency and data transmission via an RS232 interface. In our implementation, we employed the ATmega328P [31] microcontroller to manage the signal sampling at a frequency of 100 Hz and facilitate wireless data transmission using the Bluetooth protocol. The choice of a 100 Hz sampling rate was deliberate to effectively capture the physiological dynamics of plant bioelectrical signals, which predominantly occur below 50 Hz. This rate ensures adequate temporal resolution to detect rapid signal variations while mitigating potential aliasing effects. Lower sampling frequencies might overlook these swift transients and be more susceptible to low-frequency noise interferences, such as thermal fluctuations and environmental variations, which could obscure the bioelectrical signals of interest.
3.2 Signal processing and data analysis
The recorded bioelectrical signals were processed using Python-based algorithms. Three primary signal metrics were analyzed.
3.2.1 Adaptive Gabor representation (AGR)
This technique captured time-frequency coefficients, enabling the characterization of dynamic spectral changes in the signals. Coefficients were computed over non-overlapping 2-min windows to observe temporal variations in response to analyte exposure. For each non-overlapping 2-min window, time-frequency coefficients were calculated using the AGT, resulting in a representation of the signal in the time-frequency domain. Mathematically, the AGT involves the calculation of time-frequency coefficients G(t, f) by convolving the signal x(t) with a set of adaptive Gabor filters. These coefficients are obtained as follows (1):
where G(t, f) represents the calculated time-frequency coefficient, x(t) is the original signal, and g(t, f) denotes the adaptive Gabor filter. The coefficients G(t, f) collectively form the AGR for the given signal segment.
Spectral entropy: Shannon entropy of the power spectral density (PSD) quantifies the complexity of the signals. PSD was estimated using Welch’s method, and entropy was calculated for each 2 min segment to assess frequency-domain variations. Mathematically, this can be expressed as follows (2):
where H(x, f s) represents the spectral entropy, P(f) denotes the normalized PSD, and f s corresponds to the sampling frequency. To calculate P(f), Welch’s method was employed, which estimates PSD by partitioning the signal into segments, computing periodograms for each segment, and then averaging the resulting periodograms. A 95% confidence interval was considered in the estimation process.
3.2.2 Lempel-Ziv complexity
This metric evaluated the irregularity and unpredictability of the signals by analyzing binary representations of the data. Complexity values were computed for each 2-min window, providing insights into signal anomalies or stress responses. For each non-overlapping 2-mine window, the binary representation of the signal was analyzed using the LempelZiv algorithm, resulting in the complexity value (3):
where LZC(x) represents the LempelZiv complexity of the signal segment x, C(x) denotes the compressed length, and N(x) corresponds to the original length of the data after conversion to a binary sequence. The analysis facilitated by LZC provided insights into the patterns and anomalies present in the bioelectrical signals.
3.3 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted in two stages. Initially, the results were presented as the mean and standard error of the mean. Subsequently, the bootstrap statistical technique was employed to provide a deeper analysis of the data. The bootstrap method was selected because it enables the estimation of a statistic’s distribution (e.g., the mean) by resampling with replacement from the original dataset. This approach allows inferences to be made about the general behavior of plants as bioindicators.
The bootstrap process involves generating a large number (typically thousands) of resampled datasets, each of the same size as the original dataset. For each resampled dataset, the statistic of interest is calculated, and the resulting distribution of resampled statistics is used to derive the standard error and confidence intervals. This methodology is particularly beneficial in ecological studies with limited sample sizes, as it provides a robust framework for estimating the variability and reliability of observed effects.
The bootstrap algorithm can be summarized as follows:
From a sample of size n, generate a new sample by randomly drawing observations with replacement from the original dataset.
Calculate the statistic of interest (e.g., mean, variance) for the resampled dataset.
Repeat steps 1 and 2 a large number of times (e.g., 1,000 or 10,000 iterations).
Use the distribution of the resampled statistics to calculate the standard error, bias, and confidence intervals.
The experimental design accounted for minimizing natural environmental variations by conducting experiments under controlled conditions. The use of spectral entropy, LZC, and AGR ensures that the observed signal variations are specific to wastewater exposure, as these methods are sensitive to changes in signal irregularity and complexity induced by external stressors.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Bioelectrical signal response
The bioelectrical signals recorded from water hyacinths under different conditions (nutrient solution, sewage introduction, and complete sewage replacement) exhibited distinct variations. In the time domain, abrupt changes in the signal amplitude were observed when sewage was introduced, indicating an immediate physiological response to the altered environment. This aligns with previous studies suggesting that external stressors trigger measurable bioelectrical changes in plants [14,16]. Figure 3 illustrates the time-domain variation in bioelectrical signals during the three phases of the experiment. The signals displayed a significant increase in amplitude within the first 4 min of sewage introduction, stabilizing once the medium was fully replaced.
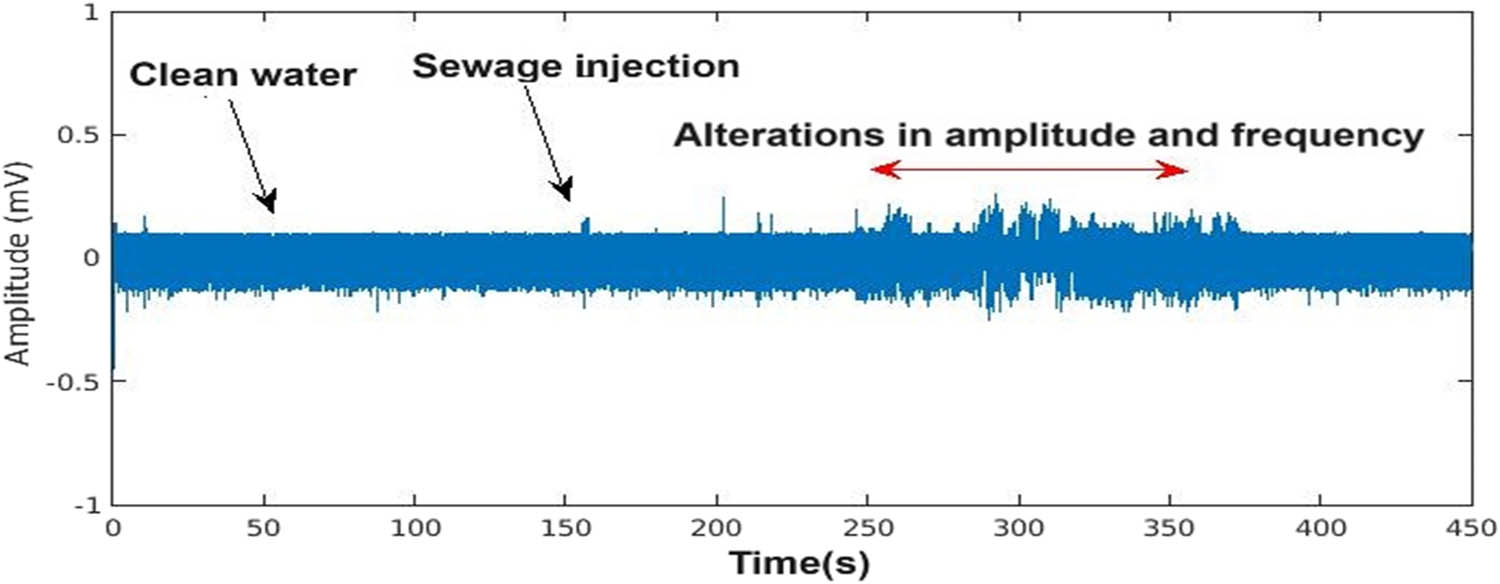
Time-domain variations in the bioelectrical signal.
This distinct change occurred precisely when the wastewater began flowing through the water hyacinth vessel. However, this temporal representation does not allow for quantifying the signal’s frequency behavior or other subtle variations in the time domain, such as signal complexity.
4.2 Time-domain analysis
Lempel–Ziv analysis revealed a marked increase in signal complexity during the sewage replacement phase (Figure 4). This increase corresponds to the plant’s adaptive response to the pollutants, as the LempelZiv algorithm captures changes in the regularity of the signal in the time domain. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that stress-induced physiological changes in plants are reflected in the complexity of their bioelectrical activity [25]. Each coefficient represents the average of 30 measurements, with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean to highlight statistical differences. Normalized coefficients within the 2-min window prior to wastewater exposure (labeled as “a”) are statistically distinct, as evidenced by the error bars, from those calculated after 100% of wastewater had flowed through the roots (labeled as “b”). A notable trend emerged, showing that coefficients began to increase significantly after just 4 min, corresponding to 28% of wastewater exposure.
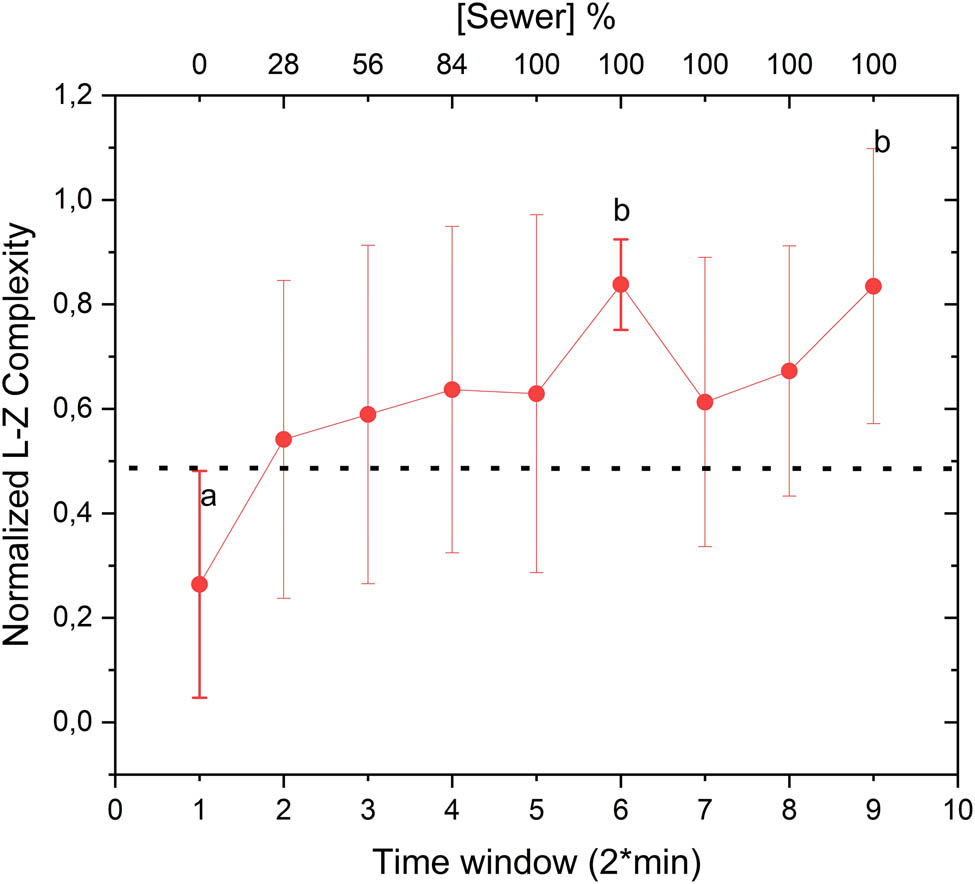
Temporal variation of LempelZiv complexity coefficients, with “a” and “b” indicating statistically distinct points based on error bars.
To confirm the statistical validity of this observed trend, a bootstrap analysis was performed, as illustrated in Figure 5. The bootstrap method was utilized to evaluate the statistical behavior of the mean trend by generating resampled datasets and recalculating the coefficients. Starting from the 2-min window (corresponding to 28% wastewater exposure), the analysis revealed significant differences in the coefficients, reinforcing the trend within the calculated error margins. These error margins represent the standard deviation of the mean coefficients derived from all plants included in the experiment. Collectively, these results emphasize how the complexity metric effectively captured the temporal behavior of the bioelectrical signals observed in Figure 3, where the time-domain signal demonstrated distinct responses to wastewater exposure.
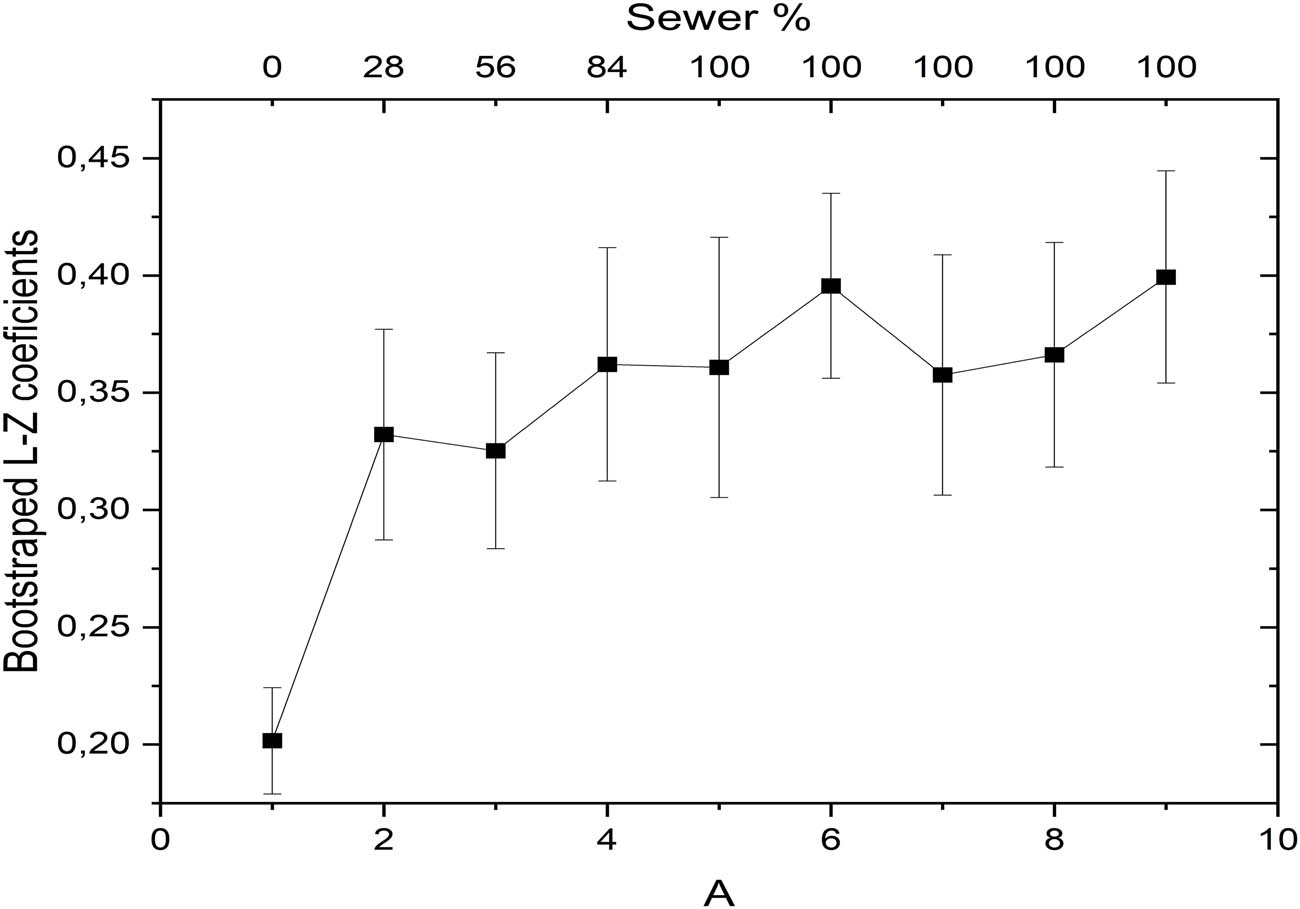
Bootstrap analysis confirming statistical significance of LempelZiv complexity trends during wastewater exposure.
4.3 Frequency-domain analysis
Spectral entropy analysis revealed variations in signal complexity during the sewage replacement phase in the frequency domain (Figure 6), a finding that is consistent with previous reports in the literature. Recent studies, such as Gómez Acosta and Chacón Pacheco [26], have emphasized the sensitivity of spectral entropy to physiological signal irregularities and its potential for detecting subtle changes in bioelectrical patterns, supporting its applicability to environmental signal analysis. Notably, the spectral entropy coefficients exhibited changes at the same pollutant concentrations observed in the LempelZiv complexity coefficients, as shown in Figure 5. These similarities indicate that the spectral entropy metric captured the same temporal behavior reflected in the complexity analysis, further strengthening the robustness of the observed trend.
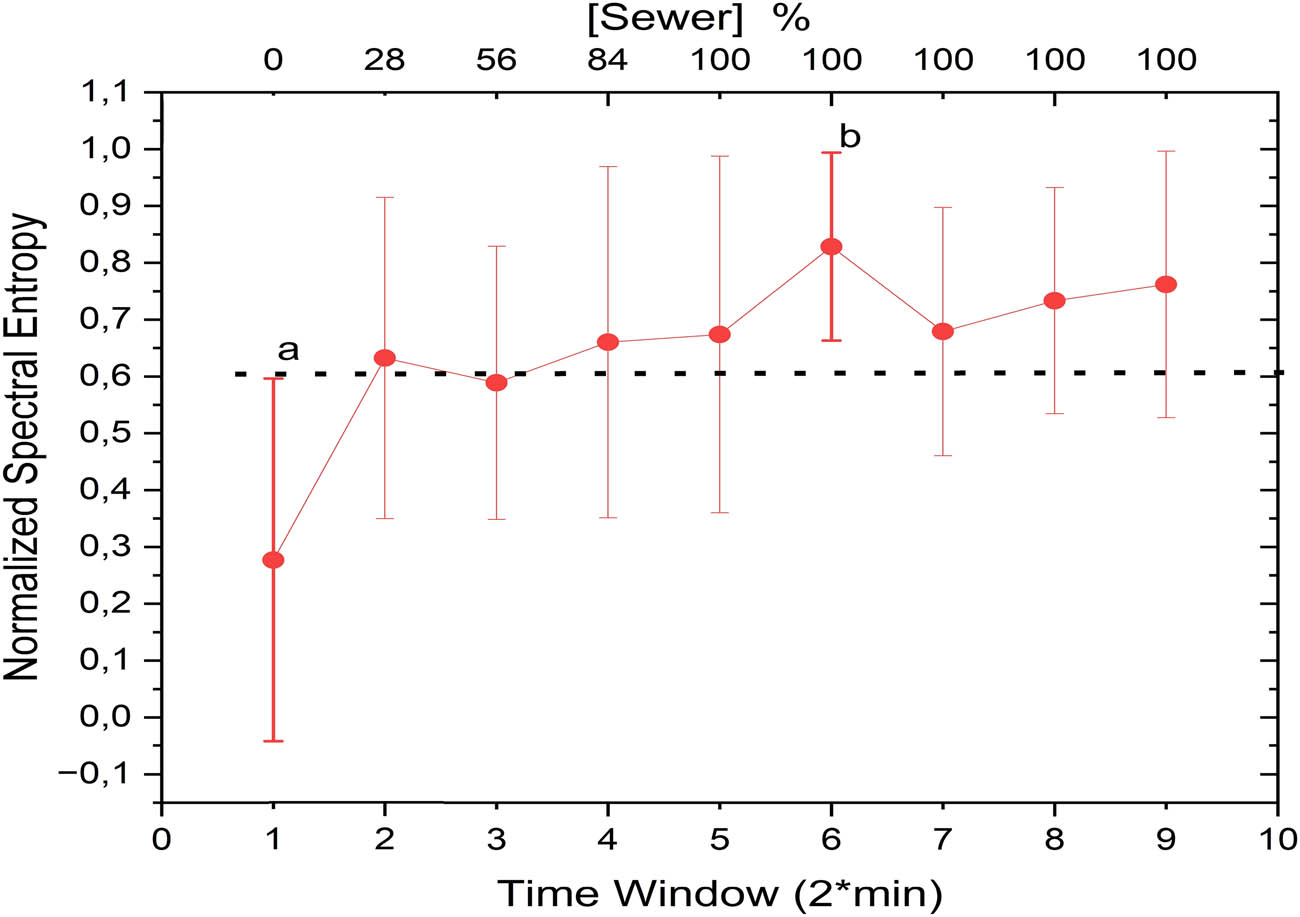
Temporal variations in spectral entropy where “a” and “b” denote statistically distinct values correlating with pre- and post-exposure conditions.
The increase in spectral entropy during sewage exposure corresponds to the plant’s adaptive response to pollutants, capturing irregularities in signal patterns within the frequency domain. These results mirror the findings in the time domain (Figure 3), where significant changes in the signal amplitude were observed. To validate these trends, bootstrap analysis was also performed on the spectral entropy coefficients, confirming the statistical reliability of the observed variations. This additional validation underscores the utility of spectral entropy in characterizing the plant’s physiological responses to environmental stressors.
The results of the bootstrap analysis applied to spectral entropy are shown in Figure 7.
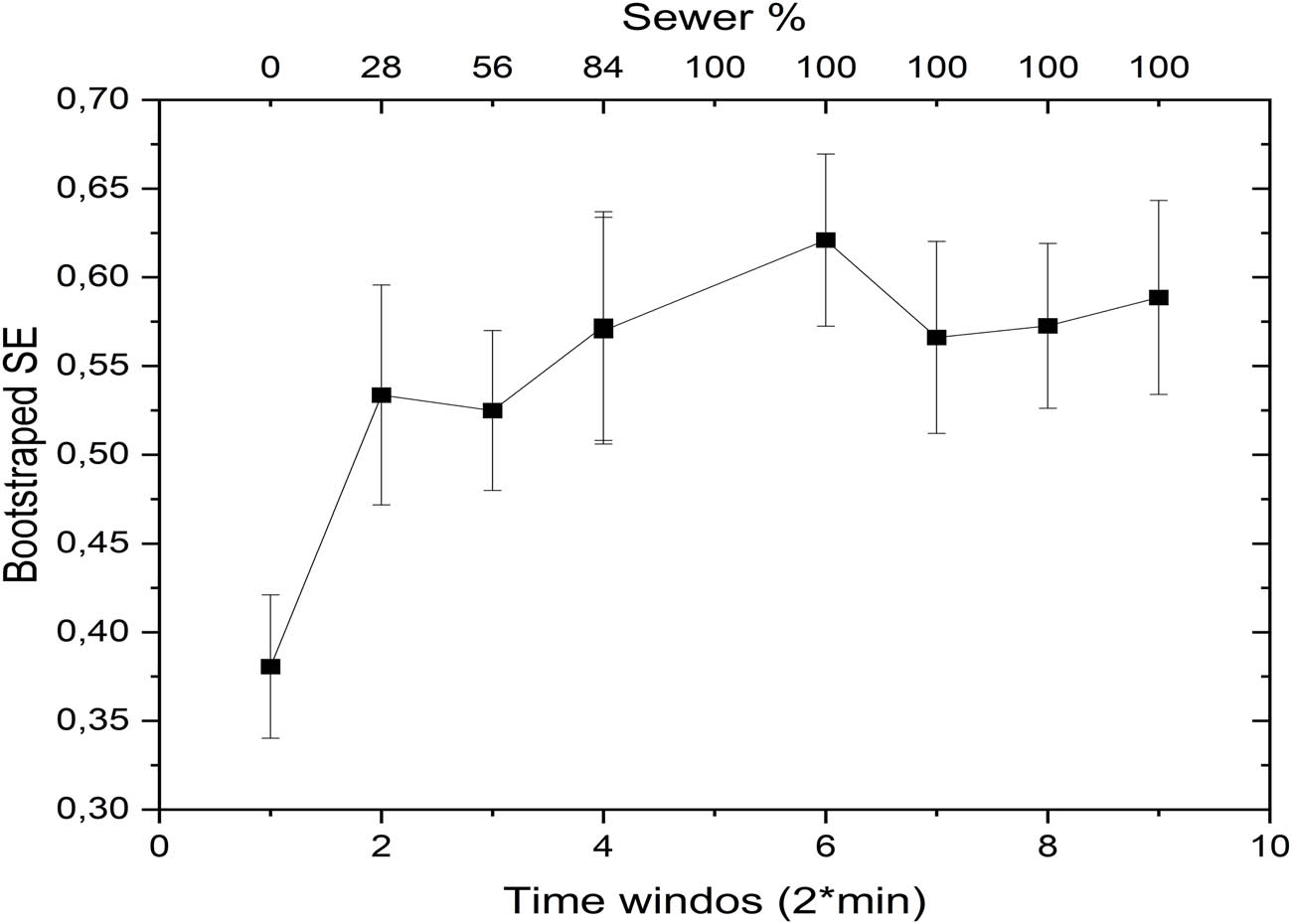
Bootstrap analysis of spectral entropy.
4.4 Time-frequency analysis
The investigation into the AGR coefficients, which combine both time and frequency domains, yielded intriguing observations. Figure 8 displays how the AGR coefficients vary when the water hyacinth is exposed to 28% of wastewater. Notably, these coefficients rapidly revert to their baseline values within 5–10 min following wastewater exposure. This behavior suggests that, in the joint time-frequency domain, the plant initially senses the presence of wastewater but later adapts, eventually reverting to its pre-exposure state. These findings align with the time-domain observations shown in Figure 3, where the amplitude of the signal also returned to baseline levels after adaptation.
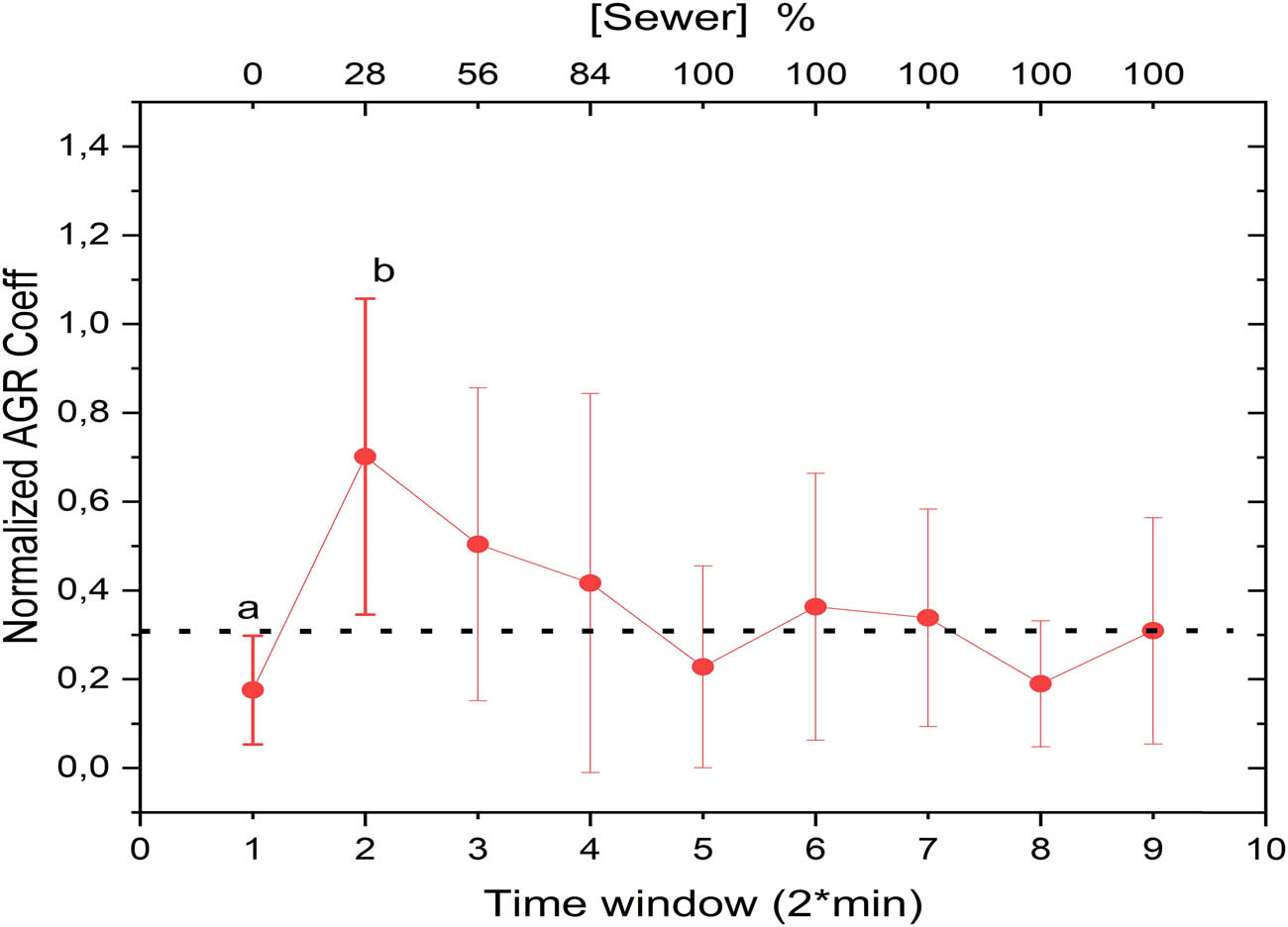
Temporal variations in normalized AGR coefficients with “a” and “b” indicating statistically distinct points representing pre- and post-exposure conditions.
To confirm the statistical validity of the AGR trends, bootstrap analysis was conducted on the AGR coefficients (Figure 9). This validation confirmed the robustness of the observed patterns, providing additional confidence in the results.
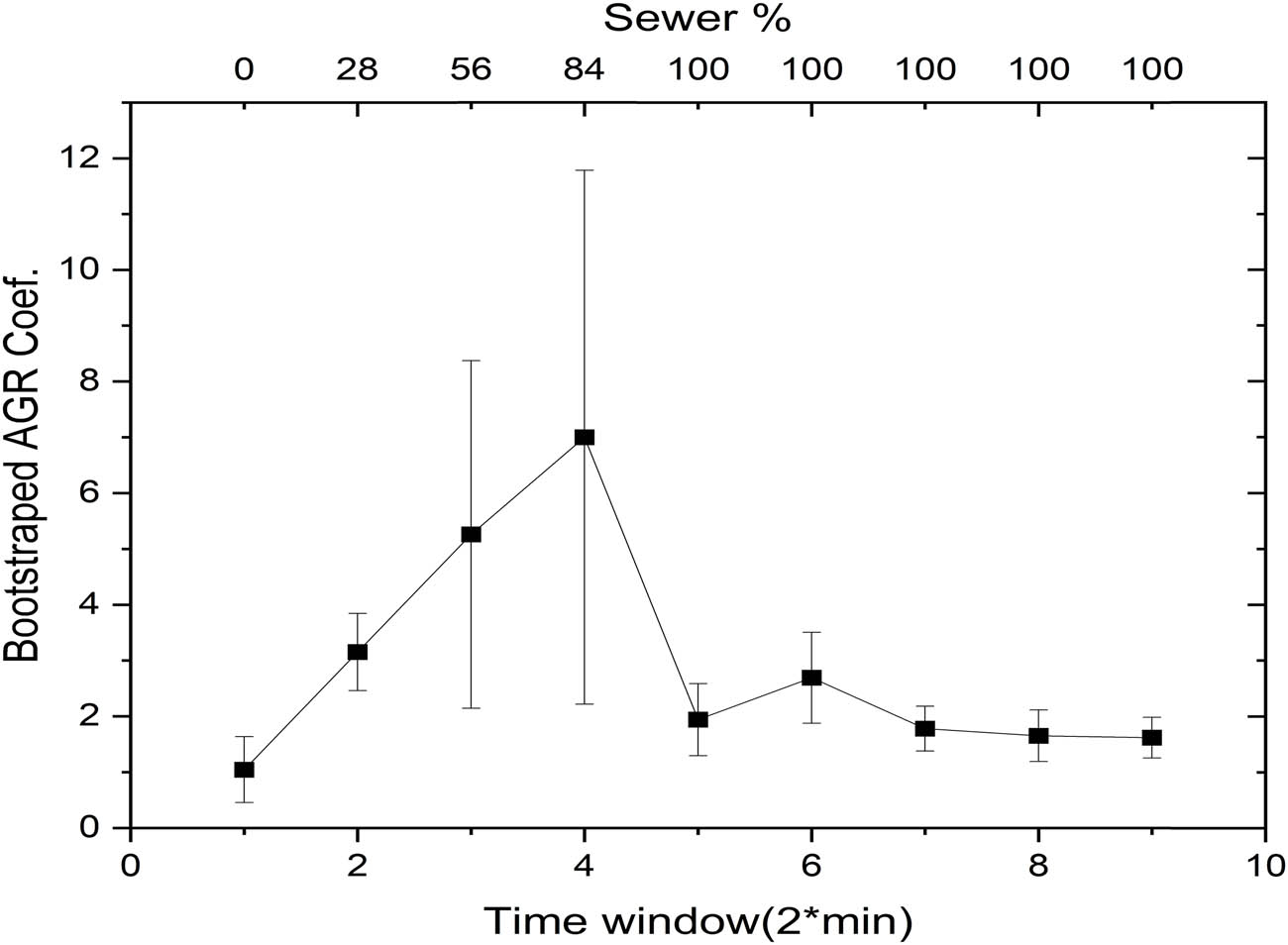
Bootstrap analysis of normalized AGR coefficients.
Interestingly, the time-frequency domain analysis may better capture the plant’s stimulus-response behavior compared to the time- or frequency-domain methods. This could be attributed to the AGR algorithm’s ability to capture localized changes in the signal, as opposed to the other two techniques, which are more suited to detecting broader-scale changes. The number of points analyzed could reasonably explain the observed variations among the methods used. Both spectral entropy and LempelZiv complexity measurements are more sensitive to the number of points analyzed, achieving greater precision when the dataset is sufficiently large. In contrast, the AGR method appears to capture localized changes effectively, making it less dependent on the number of points and potentially explaining the difference observed.
The effectiveness of AGR in capturing dynamic changes in the bioelectrical signals of water hyacinth aligns with previous studies that have applied Gabor transforms to non-stationary biological signals, particularly in the low-frequency range, highlighting its capability to provide detailed time-frequency representations [32].
These observations highlight the potential of AGR for practical applications, where a more precise understanding of localized plant responses to environmental stimuli is critical. Our findings also corroborate previous research that has utilized bioelectrical signals to monitor the physiological responses of plants to environmental stimuli. For example, Volkov and Markin [12] demonstrated that electrical signals in plants can serve as reliable indicators of responses to various environmental stresses, reinforcing the potential of bioelectricity as a monitoring tool. By integrating time-frequency analysis, the study advances the potential for water hyacinths as bio-sensors in real-world monitoring scenarios. Also, while the experimental design prioritizes eco-friendly practices, the use of wastewater in a controlled laboratory setup raises questions about potential environmental impacts. Proper disposal of wastewater post-experiment was ensured to mitigate contamination risks, aligning with the principles of GAC. Future research should explore the reproducibility of these findings under diverse environmental conditions, such as varying temperatures, pollutant concentrations, and light intensities. This would validate the robustness of the observed trends and expand the applicability of this approach to real-world scenarios. Compared to conventional water quality monitoring techniques, such as chemical assays and spectrometric analyses, the integration of bioelectrical signals and advanced DSP offers a cost-effective, real-time alternative. However, traditional methods may provide higher specificity for certain pollutants, underscoring the need for a hybrid approach in comprehensive monitoring systems.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we employed a multifaceted approach to investigate the response of water hyacinths to wastewater exposure through bioelectrical signal analysis. By combining bioelectrical signal measurements with advanced DSP techniques, the research highlights a novel approach to real-time environmental monitoring. The results presented here provide strong evidence that water hyacinths respond sensitively to wastewater exposure, with measurable variations in bioelectrical signal amplitude, complexity, and frequency characteristics.
In the time domain, abrupt changes in the signal amplitude upon wastewater exposure underscore the plant’s ability to detect environmental stressors rapidly. In the frequency domain, spectral entropy captured variations consistent with those observed in LempelZiv complexity, demonstrating that both metrics effectively characterize the plant’s adaptive response to pollutants. However, the time-frequency domain analysis, utilizing AGR, emerged as a particularly promising method, capturing localized and transient changes in bioelectrical signals. This adaptability to both short-term responses and recovery behaviors suggests AGR may be especially suitable for practical applications requiring precise and dynamic monitoring. The findings also reveal methodological insights: while spectral entropy and Lempel-Ziv complexity depend heavily on the number of points analyzed, AGR’s localized focus offers a complementary perspective, making it less sensitive to dataset size. This distinction could be pivotal in tailoring monitoring systems for specific environmental contexts. Despite the promising results, this study has limitations. The experiments were conducted under controlled laboratory conditions, which may not fully replicate the complexity of natural aquatic ecosystems. Future research should validate these findings in field settings, examining the reproducibility and scalability of this approach over extended monitoring periods and across diverse environmental conditions. Although this study demonstrates the potential of water hyacinths for real-time monitoring, the long-term stability and adaptability of this approach remain unexplored. Addressing this limitation would provide insights into the feasibility of continuous monitoring over extended periods.
In conclusion, integrating water hyacinths as bioindicators in pollutant detection systems holds significant potential for practical applications, particularly in remote areas where conventional monitoring infrastructure is limited. However, to enhance the system’s robustness under environmental conditions that differ from controlled laboratory settings, in situ studies are essential. Field research will provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of water hyacinth-based detection systems, ensuring their effectiveness in diverse and challenging environments. Such studies are crucial for developing sustainable and efficient water quality monitoring solutions tailored to the specific needs of remote communities. This approach aligns with the principles of GAC, emphasizing minimal environmental impact. With further refinement, this system has the potential to improve water monitoring practices, combining the sensitivity of biological systems with the analytical power of digital technology.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, Brazil, for financial support (FAPESP, Grant 2017/22219-5). Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil (CNPq) is recognized for fellowships.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), Grant 2017/22219-5, and by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Brazil.
-
Author contributions: Gustavo Maia Souza and Ana Carolina de Souza Silva were responsible for the design of the experiments and performed the data analysis. Valeria Maria Melleiro Gimenez and Ernane Jose Xavier Costa contributed to the preparation of materials and conducted the data collection. Ernane Jose Xavier Costa conceived the study and supervised the overall project. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the results. The manuscript was written by Ernane Jose Xavier Costa and revised critically by all authors. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Gieva E, Nikolov G, Nikolova B. Biosensors for environmental monitoring challenges in higher education and research. In: Tashev T, Deliyski B, Lepadatescu B, editors. Challenges in higher education & research. Sofia: Heron Press; 2014. p. 123–7.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Markert BA, Breure AM, Zechmeister HG. Bioindicators and biomonitors: principles, concepts, and applications. Trace metals and other contaminants in the environment. Vol. 6, Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2003.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Dolfi M, Dini C, Morosi S, Comparini D, Masi E, Pandolfi C, et al. Electrical signaling related to water stress acclimation. Sens Bio-Sens Res. 2021;32:100420. 10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100420.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Tian L, Shang C, Li M, Wang Y. Research on classification of water stress state of plant electrical signals based on PSO-SVM. IEEE Access. 2023;11:125021–32. 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3330651.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Asif N, Malik M, Chaudhry FN. A review on environmental pollution bioindicators. Pollution. 2018;4(1):57–70. 10.22059/poll.2017.237440.296.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Rabello JR, Gonzáles JM, Batista JR, Silva ACS, Costa EJX. A simple, effective, and low-cost system for water monitoring in remote areas using optical and conductivity data signature. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021;232(3):1–13. 10.1007/s11270-021-04982-y.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Volkov AG, Ranatunga DRA. Plants as environmental biosensors. Plant Signaling Behav. 2006;1(3):105–15. 10.4161/psb.1.3.3000.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Tripathi BD, Shukla SC. Biological treatment of wastewater by selected aquatic plants. Environ Pollut. 1991;69(1):69–78. 10.1016/0269-7491(91)90164-R.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Adewumi I, Ogbiye AS. Using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) to treat wastewater of a residential institution. Toxicol Environ Chem. 2009;91(5):891–903. 10.1080/02772240802614648.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Khan AU, Khan AN, Waris A, Ilyas M, Zamel D. Phytoremediation of pollutants from wastewater: A concise review. Open Life Sci. 2022;17(1):488–96. 10.1515/biol-2022-0056.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Jones JL, Jenkins RO, Haris PI. Extending the geographic reach of the water hyacinth plant in removal of heavy metals from a temperate Northern Hemisphere river. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11071. 10.1038/s41598-018-29387-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Volkov AG, Markin VS. Active and passive electrical signaling in plants. Plant electrophysiology. Berlin: Springer; 2015. p. 143–76. 10.1007/978-3-319-08807-5_6.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Barbosa-Caro JC, Wudick MM. Revisiting plant electric signaling: Challenging an old phenomenon with novel discoveries. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024;79:102528. 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102528.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Volkov AG, ed. Plant electrophysiology. Berlin: Springer; 2012. 10.1007/978-3-642-29119-7.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Su W, Sun Q, Xia M, Wen Z, Yao Z. The resource utilization of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes [Mart.] Solms) and its challenges. Resources. 2018;7(3):46. 10.3390/resources7030046.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Huber AE, Bauerle TL. Long-distance plant signaling pathways in response to multiple stressors: the gap in knowledge. J Exp Bot. 2016;67(7):2063–79. 10.1093/jxb/erw099.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Sukhova E, Akinchits E, Sukhov V. Mathematical models of electrical activity in plants. J Membr Biol. 2017;250(5):407–23. 10.1007/s00232-017-9969-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Zimmermann MR, Maischak H, Mithöfer A, Boland W, Felle HH. System potentials, a novel electrical long-distance apoplastic signal in plants, induced by wounding. Plant Physiol. 2009;149(3):1593–600. 10.1104/pp.108.133884.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Yan X, Wang Z, Huang L, Wang C, Hou R, Xu Z, et al. Research progress on electrical signals in higher plants. Prog Nat Sci. 2009;19(5):531–41. 10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.08.009.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Tovar-Sánchez E, Suarez-Rodríguez R, Ramírez-Trujillo A, Valencia-Cuevas L, Hernández-Plata I, Mussali-Galante P. The use of biosensors for biomonitoring environmental metal pollution. In: Rinken T, Kivirand K, editors. Biosensors for environmental monitoring. London: IntechOpen; 2019. 10.5772/intechopen.84309.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Lautner S, Grams TEE, Matyssek R, Fromm J. Characteristics of electrical signals in poplar and responses in photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 2005;138(4):2200–9. 10.1104/pp.105.064196.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Fromm J, Lautner S. Electrical signals and their physiological significance in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2007;30(3):249–57. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01614.x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Hirobayashi S, Tamura Y, Yamabuchi T, Oyabu T. Monitoring of human activity using plant bioelectric potential. IEEE J Trans Sens Micromachines. 2007;127(4):258–9. 10.1541/ieejsmas.127.258.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Dersseh MG, Melesse AM, Tilahun SA, Abate M, Dagnew DC. Water hyacinth: Review of its impacts on hydrology and ecosystem services—Lessons for management of Lake Tana. Extreme hydrology and climate variability: monitoring, modelling, adaptation and mitigation. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2019. p. 237–51. 10.1016/B978-0-12-815998-9.00019-1.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Inouye T, Shinosaki K, Sakamoto H, Toi S, Ukai S, Iyama A, et al. Quantification of EEG irregularity by use of the entropy of the power spectrum. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1991;79(3):204–10. 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90138-T.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Gómez Acosta LG, Chacón Pacheco M. Entropy and statistical complexity in bioelectrical signals: A literature review. Signals. 2025;6(1):7. 10.3390/signals6010007.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Costa EJX, Tech ARB, Sousa Silva AC. Linking non-extensive entropy with Lempel-Ziv complexity to obtain the entropic Q-index from EEG signals. Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies. Porto: SCITEPRESS; 2017. p. 101–5. 10.5220/0006077901010105.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Costa EJX, Cabral EF. EEG-based discrimination between imagination of left and right hand movements using adaptive Gaussian representation. Med Eng Phys. 2000;22(5):345–8. 10.1016/S1350-4533(00)00051-5.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Souza GM, Pincus SM, Monteiro JAF. The complexity-stability hypothesis in plant gas exchange under water deficit. Braz J Plant Physiol. 2005;17(4):363–73. 10.1590/S1677-04202005000400004.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Sajid M, Płotka-Wasylka J. Green analytical chemistry metrics: A review. Talanta. 2022;238:123046. 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123046.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Cabral BP, Costa EJX. The oscillatory bioelectrical signal from plants explained by a simulated electrical model and tested using Lempel-Ziv complexity. Comput Electron Agric. 2011;76(1):80–5.10.1016/j.compag.2010.12.001Search in Google Scholar
[32] Zherebtsov AV, Tropskaya NS. Application of the Gabor transform for analysis of electromyographic signals of the intestine in the low-frequency region. Biophysics. 2018;63(2):248–53. 10.1134/S0006350918020276.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Longitudinal monitoring of autoantibody dynamics in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing surgery
- The potential role of rutin, a flavonoid, in the management of cancer through modulation of cell signaling pathways
- Construction of pectinase gene engineering microbe and its application in tobacco sheets
- Construction of a microbial abundance prognostic scoring model based on intratumoral microbial data for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Temperature-dependent development, predation, and life table of Sphaerophoria macrogaster (Thomson) (Diptera: Syrphidae) feeding on Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae)
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Using plant electrical signals of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for water pollution monitoring
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”

