Abstract
This study proposes the theoretical design of an optical setup of a heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope (HIFOG). The polarized IFOG utilizes a coherent light source and an electro-optic modulator to generate a dual-frequency laser light source. The Sagnac interferometric signal can be measured from the amplitude term of the temporal interference fringe as well as beat frequency signal. The beat frequency signal can be processed using filtering techniques or the lock-in technique to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio. This approach effectively reduces external environmental noise interference in the interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope, as well as the polarization state changes caused by fiber birefringence.
Abbreviations
- AC
-
alternative current
- CCW
-
counterclockwise
- CW
-
clockwise
- DC
-
direct current
- DIFOG
-
depolarized interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- EOM
-
electro-optic modulator
- FOG
-
fiber-optic gyroscope
- HIFOG
-
heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- IFOG
-
interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- LPR
-
linear polarization rotator
- MEMS
-
micro-electromechanical systems
- NPBS
-
non-polarizing beam splitter
- PIFOG
-
polarizing interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- PMD
-
polarization mode dispersion
- SMF
-
single-mode fiber
- SNR
-
signal-to-noise ratio
1 Introduction
A gyroscope is a sensing device used to measure the rotational rate of an object and is an essential component in aerospace applications. Currently, rotational rate measurements can be performed using traditional mechanical gyroscopes, micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS) gyroscopes [1], 2], ring laser gyroscopes [3], [4], [5], and interferometric fiber-optic gyroscopes (IFOGs) [6], where the sensitivity of an IFOG can be enhanced by increasing the number of fiber coil turns [7].
Conventional IFOGs face a significant challenge posed by fiber birefringence, arising particularly from the bending-induced stress of the coiled fiber. This effect results in zero-bias error and degrades the signal through polarization-related mechanisms [8], 9]. To mitigate these effects, depolarized IFOGs (DIFOGs) are commonly implemented, wherein a depolarizer converts polarized light into unpolarized light, thereby reducing polarization noise at the cost of reduced interference visibility [7], 9], 10].
In recent years, the polarizing interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope (PIFOG) has evolved significantly, with growing interest in architectures employing single-mode fiber (SMF) and laser light sources due to their potential for high-performance navigation and attitude control. By leveraging high-coherence laser sources, this alternative approach suppresses backscattering-induced phase noise while improving scale factor stability, thereby addressing a critical requirement for high-precision aerospace and defense applications [11], 12]. Compared to conventional broadband sources, lasers offer narrow linewidth and exceptional wavelength stability, enabling scale factor accuracies better than 1 part per million [11]. Furthermore, the low attenuation (0.2 dB/km) [13] and inherently low backscattering of SMF make it particularly suitable for laser-driven systems, contributing to significantly improved signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs). In contrast, air-core photonic bandgap fibers, despite their reduced Kerr effect, exhibit high attenuation (∼13 dB/km) [14] and are prone to higher-order mode coupling, which can degrade overall performance.
Emerging IFOG architectures have begun to leverage fully polarized laser sources together with polarizing components to actively suppress birefringence-induced phase errors, thereby improving signal quality and system sensitivity without the need for depolarizers. Building on this trend, this study introduces a heterodyne interferometry approach based on a dual-frequency laser source combined with tailored polarization control elements. This method effectively mitigates the birefringent effects inherent in standard SMF, which are a major source of phase error in conventional designs.
A key distinction of our approach from traditional heterodyne FOGs [15], [16], [17] is the deliberate use of low-cost SMF as the sensing coil. Whereas conventional heterodyne FOGs often rely on polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) to passively avoid birefringence effects, our system actively compensates for these effects through optical and signal processing means. This shift offers a significant potential reduction in the cost and complexity of the sensing coil, which is a critical component in practical deployments. Furthermore, the Sagnac phase shift is precisely extracted from a time-domain beat signal, a process enhanced by lock-in amplification technique for superior SNR. This combination of active birefringence compensation in standard fiber and advanced electronic detection provides a robust and cost-effective pathway toward high-stability, high-precision fiber-optic gyroscopes for tactical and inertial-grade applications.
2 Basic theory
2.1 Polarization effect of the fiber coil
Consider a fiber coil subjected to fiber bending, temperature effect and mechanical stress induced birefringence, which alters the polarization state of the incident light wave. This effect is referred to as the polarization effect of the fiber coil, and its polarization transfer function can be represented using the Jones matrix as [8]:
and
where the subscript 12 and 21 respectively stand for the clockwise (CW, from end 2 to end 1) and counterclockwise (CCW, from end 2 to end 1) propagation directions,
2.2 Dual-frequency laser light source
The central innovation of this study is its light source, namely a dual-frequency laser [18]. The unique characteristics of this light source allow the interferometric signal of the Sagnac loop interferometer to be carried within time-domain interference fringes, which helps improve the SNR.
The dual-frequency laser generates two orthogonal linearly polarized components with a slight frequency difference. A Zeeman He–Ne laser inherently exhibits these characteristics [19].
An alternative method, as shown in Figure 1, utilizes a single-wavelength laser and an electro-optic modulator (EOM) driven by a high-voltage sawtooth signal [18]. The polarization state is then described by the Jones vector:
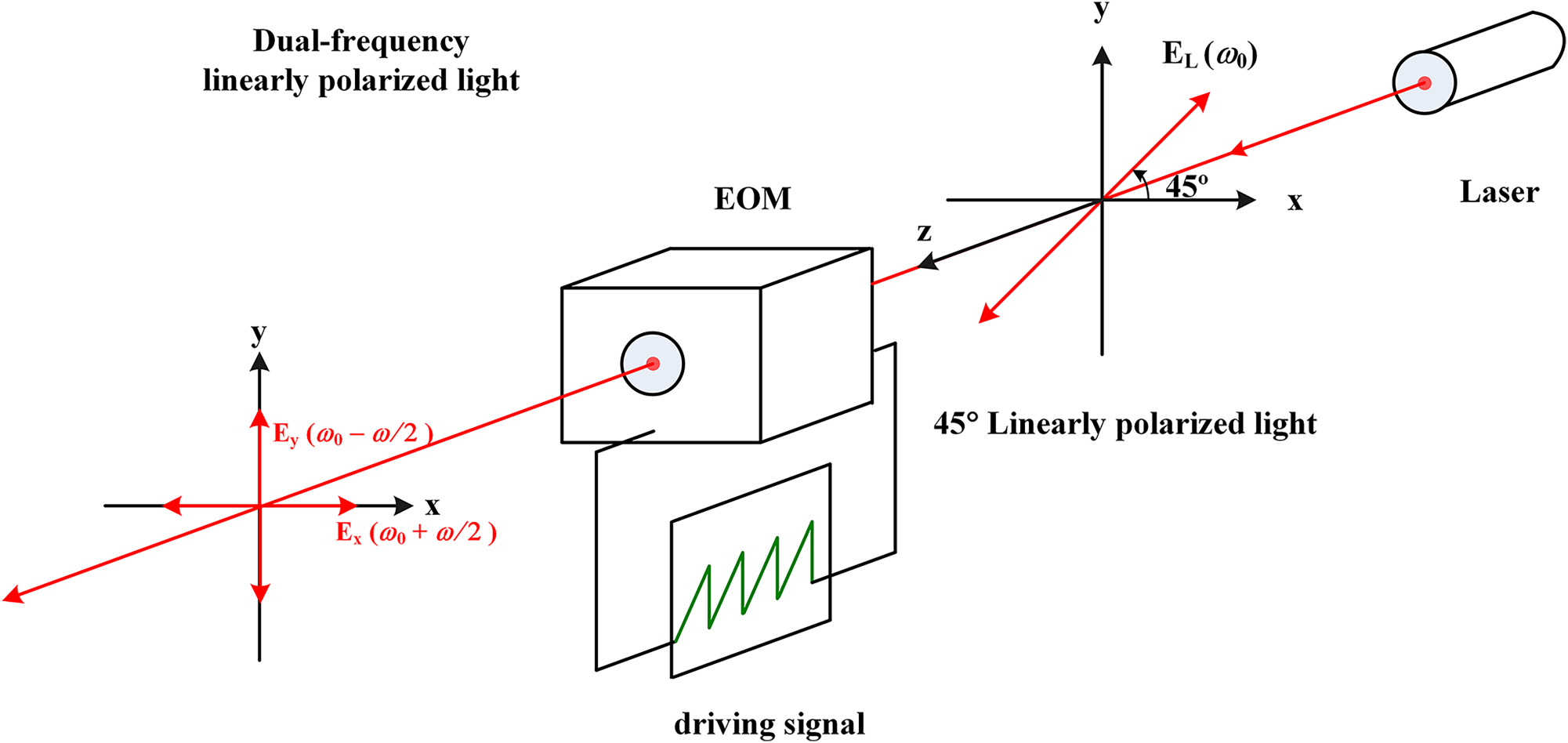
Optical setup of a dual-frequency laser composed by a single frequency laser and an electro-optic modulator. EOM: electro-optic modulator.
Here, A represents the amplitude of the dual-frequency laser source, ω 0 is the central frequency of the single-wavelength laser source, and ω is the driving signal frequency of the EOM, typically ranging from kHz to MHz. From Eq. (3), it can be observed that the frequency of the x-component of the laser beam’s electric field is ω 0 + (ω/2), while the frequency of the y-component is ω 0 − (ω/2). The frequency difference between these two orthogonal electric field components equals the driving frequency of the EOM.
When this dual-frequency laser passes through a quarter-wave plate, it becomes a linearly polarized modulated light source, also known as a linear polarization rotator (LPR) [20], 21],
Equation (4) represents the normalized Jones vector of the linearly polarized modulated light source with an intensity value of 1.
3 Optical setup
Figure 2 shows the optical setup of a heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope (HIFOG). The incident light used here is the previously mentioned LPR light source. The incident beam is split by the first non-polarizing beam splitter (NPBS1). The transmitted and reflected beams are designated as the signal beam and reference beam, respectively. The signal beam is first transmitted through a polarizer with a horizontal transmission axis and is subsequently split by NPBS2 into two components: the transmitted signal beam and the reflected signal beam. These designations will be used to describe the optical paths and electric fields in the following analysis.
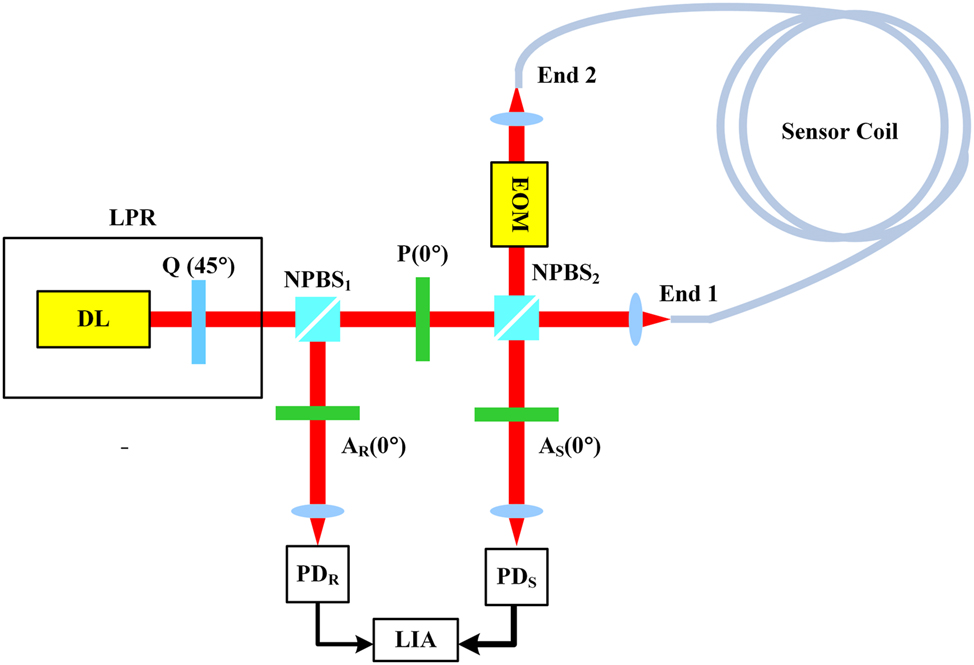
Optical setup of a heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope (HIFOG). DL: dual-frequency laser, Q: quarter wave plate, LPR: linear polarization rotator, NPBS1 and NPBS2: non-polarizing beam splitters, P: polarizer, AR and AS: analyzer, PDR and PDS: photodetectors, LIA: lock-in amplifier.
The transmitted signal beam travels CCW through an EOM, the Sagnac loop formed by the fiber coil, then passes again through the transmission side of the NPBS2, and finally goes through an analyzer with its transmission axis set horizontally.
The reflected signal beam, on the other hand, travels CW through the Sagnac loop, an EOM then passes again through the reflection side of the NPBS2, and finally goes through an analyzer with its transmission axis set horizontally.
The electric fields of the transmitted and reflected signal beams are derived using Jones calculus as:
and
As described by Eqs. (5) and (6), the fundamental phase shifts φ cw and φ ccw are due to the unidirectional propagation of light within the rotating Sagnac loop. The additional phase components of ±φ m /2 are imparted by the EOM’s bias phase in conjunction with the temporal delay of the fiber coil [22]. These additional phase components are the crucial parameters employed to enhance the sensitivity, as will be explained later.
represent the Jones matrices of a polarizer and an analyzer with their transmission axes set at 0°, respectively.
represent the Jones matrices of the transmission and reflection surfaces of the NPBS, respectively. The two superimposed electric fields of the CW, and CCW propagating light waves, E cw and E ccw , after passing through the analyzers, form the output electric field of the optical system. The output electric field, E sig , can be expressed as a Jones vector:
The optical intensity signal received by the photodetector PDS after the output light passes through it can be expressed as:
The Sagnac phase, φ sag, is the phase difference between the CW and CCW beams,
where N and R are the coil number and radius of the fiber coil, respectively, Ω is the angular velocity, λ is the wavelength, and c is the wave velocity in vacuum. From Eq. (10), it can be observed that the light intensity signal exhibits reciprocity. The coherence length of standard frequency-stabilized lasers can extend to approximately 100 m, significantly exceeding the optical path difference produced in a Sagnac interferometer. As indicated in Eq. (10), the high coherence of the laser source enables the generation of a beat signal with ideal interference visibility. Figure 3 schematically illustrates the optical intensity signal measured at the photodetector as a function of the Sagnac phase shift. This signal can be extracted from either the DC component or the AC (beat-frequency) component in Eq. (10), both of which exhibit the same interference pattern as depicted. However, due to the higher susceptibility of the DC signal to noise, this study emphasizes AC signal detection. To further improve the SNR, a lock-in amplification technique is employed [23], which utilizes correlation processing between the detected signal and a reference signal. For a detailed description of the lock-in amplification method, please refer to reference [24].
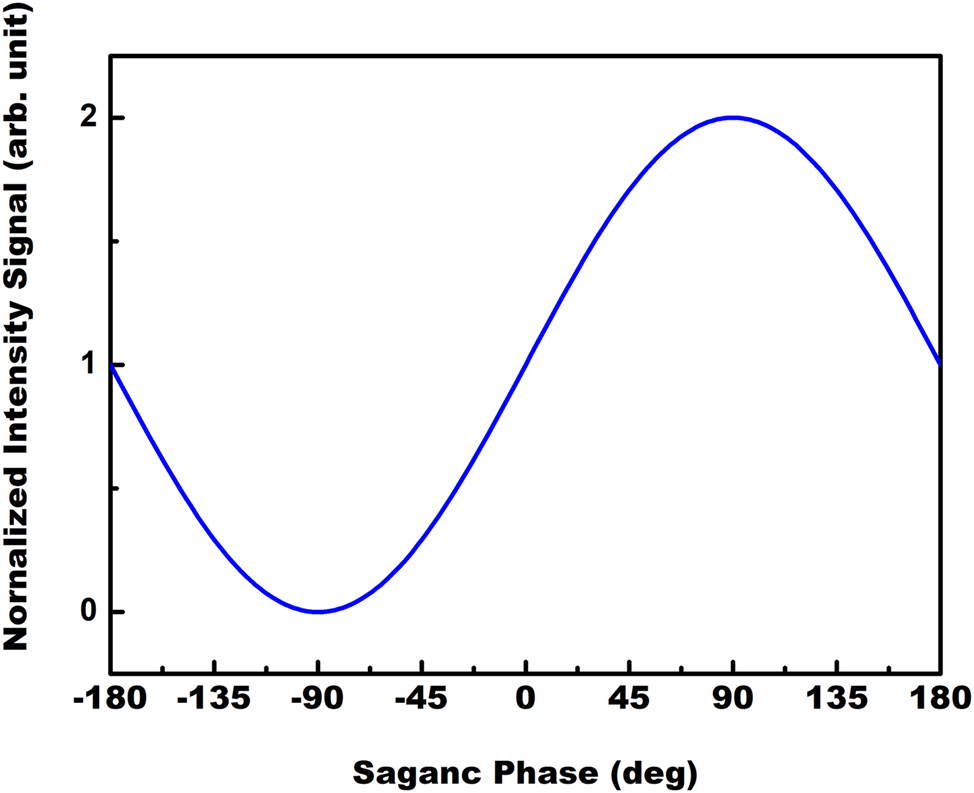
Normalized intensity versus Sagnac phase, showing the enhanced sensitivity achieved by operating the interferometer with a phase bias near zero phase shift.
As described earlier, the reference signal in Figure 2 is generated by splitting a portion of the incident laser beam at NPBS1 and is detected by the photodetector PDR. The corresponding electric field can be expressed as:
Thus, the intensity of this reference signal can be expressed as:
By performing correlation between this reference optical signal, I ref with the Sagnac interferometer output signal, I sig, the lock-in amplifier effectively extracts the beat-frequency component while suppressing out-of-band noise and rejecting the DC component. Signal conditioning is performed by the lock-in amplifier, featuring an internal differential preamplifier with a gain of 30. This stage reduces common-mode noise, including fluctuations in laser intensity, noise source from photodetector, and electromagnetic interference, thereby enhancing measurement stability. Theoretical simulations of noise suppression in interferometric fiber-optic gyroscopes indicate that, under a 10 kHz modulation signal and with a 1 kHz low-pass filter in the lock-in amplifier, this configuration can achieve an SNR improvement by a factor of 10 [24].
The primary goal of the gyroscope is to detect extremely low rotational speeds, i.e., when the Sagnac phase shift φ sag approaches zero. To enhance the detection sensitivity of interferometric fiber optic gyroscopes at low rotation rates, this goal can be achieved by the EOM, placing in the Sagnac interferometer by employing a square wave as the driving signal for this modulator effectively induces a bias phase of φ m = ±π/2. Consequently, the detected signal can be expressed as [22]:
Figure 3 depicts the response of the normalized optical intensity to the Sagnac phase under an applied phase bias. This bias configures the interferometer at the quadrature point, maximizing the sensitivity of the intensity output to small phase changes near zero and thus allowing for the precise measurement of low rotation rates.
4 Discussion on system scalability
The scalability of the proposed HIFOG setup, which refers to its adaptability for different measurement ranges and performance grades, is a crucial consideration for practical deployment. As governed by the Sagnac effect, the scale factor,
is a deterministic function of the fiber coil’s physical parameters, length, L, diameter, D, and the wavelength of the light source, λ. This inherent scalability is well-supported by the key design choices in our system. Firstly, the use of a high-power, dual -frequency laser source provides a high SNR, which is essential to compensate for the increased propagation loss when longer fiber lengths are employed to achieve higher sensitivity. Secondly, the low attenuation of standard SMF makes it a cost-effective and practical medium for implementing extended coil lengths.
The simple and flexible interferometric architecture allows the system to be tailored for specific applications by adjusting L and D. For example, to achieve tactical-grade performance with moderate bias stability (e.g., 0.1–10 °/h) [25], a compact coil with shorter fiber length (e.g., 100–500 m) can be used, prioritizing small size and fast response time. Conversely, for inertial-grade applications requiring higher sensitivity and lower bias stability (e.g., <0.01 °/h) [25], the system can be scaled up using a longer fiber (e.g., 1–2 km) wound into a larger diameter coil. In such cases, the excellent coherence and power stability of the laser source become even more critical for maintaining measurement fidelity.
It is important to note that while the scale factor scales linearly with LD, other performance metrics, particularly bias stability, are also influenced by environmental factors like the Shupe effect [26], which becomes more pronounced in larger coils. Therefore, achieving optimal performance at a scaled configuration would necessitate advanced coil-winding techniques (e.g., quadrupolar winding) [27] and precise thermal management, which are beyond the scope of this proof-of-concept study but constitute a vital direction for future investigation. The primary contribution of this work is to establish a robust and scalable core architecture. The results presented here confirm the viability of this architecture as a foundation, which can be subsequently optimized for specific performance targets through parameter scaling as discussed.
5 Conclusion and future work
In this study, we propose a method using a specially designed dual-frequency laser source that simultaneously generates two orthogonal, linearly polarized beams with a slight frequency difference. This laser source can be implemented directly using a Zeeman He–Ne laser or by combining a standard laser source with an EOM. Moreover, the frequency stability is an important issue that affect the detection performance of the proposed optical setup, a commercial frequency-stabilized Zeeman He–Ne laser can be a better choice to be a dual-frequency laser light source.
By placing a pair of parallel polarizers at both ends of the Sagnac loop, the polarization effects caused by fiber birefringence can be completely eliminated, ensuring the reciprocity of the detected light intensity signal. As a result, it is unnecessary to use polarization-maintaining fibers or polarization controllers to mitigate the birefringence effects, while still achieving maximum interference visibility.
The introduction of the dual-frequency laser source enables the generation of a time-domain interference signal through the beating phenomenon, ensuring the reciprocity of the interference signal.
In this study, we present a theoretical framework with the intention of guiding future experimental implementation. In subsequent work, we plan to transition the free-space optical setup illustrated in Figure 2 into an all-fiber configuration to construct a practical interferometric system. The actual performance of the fiber-optic gyroscope will then be systematically evaluated, with emphasis on critical metrics such as bias stability, long-term reliability study, involving continuous operation over weeks or months, temperature robustness, and laser light source stability.
The primary objective of this paper is to address the mitigation of non-ideal characteristics specific to SMF, particularly focusing on static birefringence effects. Therefore, all other optical components have been assumed ideal in the current analysis. In future experimental phases, we will expand the investigation to include the non-ideal behavior of other components, as well as dynamic birefringence effects arising from polarization mode dispersion (PMD), based on empirical measurements.
-
Funding information: This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Council of Taiwan under grant number NSTC 114-2221-E-182-008.
-
Author contribution: All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
1. Eminoglu, B, Kline, MH, Izyumin, I, Yeh, YC, Boser, BE. Background calibrated MEMS gyroscope. Sensors 2014:922–5.10.1109/ICSENS.2014.6985152Search in Google Scholar
2. Cao, H, Cai, Q, Zhang, Y, Shen, C, Shi, Y, Liu, J. Design, fabrication, and experiment of a decoupled multi-frame vibration MEMS gyroscope. IEEE Sens J 2021;21:19815–24. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2021.3095762.Search in Google Scholar
3. Ciminelli, C, Dagostino, D, Carnicella, G, DellOlio, F, Conteduca, D, Ambrosius, HPMM, et al.. A high-Q InP resonant angular velocity sensor for a monolithically integrated optical gyroscope. IEEE Photon J 2016;8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/jphot.2015.2507549.Search in Google Scholar
4. Ciminelli, C, Campanella, CE, Armenise, MN. Optimized design of integrated optical angular velocity sensors based on a passive ring resonator. J Lightwave Technol 2009;27:2658–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/jlt.2009.2014784.Search in Google Scholar
5. Faucheux, M, Fayoux, D, Roland, J. The ring laser gyro. J Opt 1988;19:101–15. https://doi.org/10.1088/0150-536x/19/3/001.Search in Google Scholar
6. Arditty, HJ, Lefevre, HC. Sagnac effect in fiber gyroscopes. Opt Lett 1981;6:401–3. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.6.000401.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
7. Szafraniec, B, Sanders, GA. Theory of polarization evolution in interferometric fiber-optic depolarized gyros. J Lightwave Technol 1999;17:579–90. https://doi.org/10.1109/50.754787.Search in Google Scholar
8. Pavlath, GA, Shaw, HJ. Birefringence and polarization effects in fiber gyroscopes. Appl Opt 1982;21:1752–7. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.21.001752.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
9. Burns, WK, Kersey, AD. Fiber-optic gyroscopes with depolarized light. J Lightwave Technol 1992;10:992–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/50.144925.Search in Google Scholar
10. Pérez, RJ, Álvarez, I, Enguita, JM. Theoretical design of a depolarized interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope (IFOG) on SMF-28 single-mode standard optical fiber based on closed-loop sinusoidal phase modulation with serrodyne feedback phase modulation using simulation tools for tactical and industrial grade applications. Sensors 2016;16:604. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050604.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
11. Lloyd, SW, Digonnet, MJF, Fan, S. Tactical-grade interferometric fiber optic gyroscope driven with a narrow-linewidth laser. Adv Photonics 2011:SMC3. https://doi.org/10.1364/sensors.2011.smc3.Search in Google Scholar
12. Lloyd, SW, Digonnet, MJF, Shanhui, F. Modeling coherent backscattering errors in fiber optic gyroscopes for sources of arbitrary line width. J Lightwave Technol 2013;31:2070–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/jlt.2013.2261283.Search in Google Scholar
13. Miya, T, Terunuma, Y, Hosaka, T, Miyashita, T. Ultimate low-loss single-mode fibre at 1.55 μm. Electron Lett 1979;15:106–8. https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19790077.10.1049/el:19790077Search in Google Scholar
14. Poletti, F, Petrovich, M, van Brakel, A, Richardson, D. Hollow core photonic bandgap fibre for truly single mode operation. In: 2008 IEEE/LEOS winter topical meeting series. IEEE; 2008:182–3 pp.10.1109/LEOSWT.2008.4444461Search in Google Scholar
15. Zheng, J. Birefringent fibre frequency-modulated continuous-wave Sagnac gyroscope. Electron Lett 2004;40:1520–2. https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20046922.10.1049/el:20046922Search in Google Scholar
16. Zheng, J. All-birefringent-fiber frequency-modulated continuous-wave Sagnac gyroscope. Opt Eng 2005;44:080501–2. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2000987.Search in Google Scholar
17. Zheng, J. Differential all-birefringent-fiber frequency-modulated continuous-wave Sagnac gyroscope. Opt Eng 2006;45:050501–2. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.2195465.Search in Google Scholar
18. Su, D-C, Chiu, M-H, Chen, C-D. Simple two-frequency laser. Precis Eng-J Int Soc Precis Eng Nanotechnol 1996;18:161–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-6359(96)80485-5.Search in Google Scholar
19. Taksaki, H. Stabilized transverse Zeeman laser as a new light source for optical measurement. Appl Opt 1980;19:3.10.1364/AO.19.000435Search in Google Scholar PubMed
20. Shamir, J, Fainman, Y. Rotating linearly polarized light source. Appl Opt 1982;21:364–5. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.21.000364.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
21. Yu, CJ, Lin, CE, Yu, LP, Chou, C. Paired circularly polarized heterodyne ellipsometer. Appl Opt 2009;48:758–64. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.48.000758.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
22. Martin, J, Winkler, J. Fiber optic laser gyro signal detection and processing technique. In: Guided wave optical systems and devices I. SPIE; 1978:98–103 pp.10.1117/12.956249Search in Google Scholar
23. Kishore, K, Akbar, S. Evolution of lock-in amplifier as portable sensor interface platform: a review. IEEE Sens J 2020;20:10345–54. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2020.2993309.Search in Google Scholar
24. Zhang, X, Li, T, Song, X, Jiang, C. Research on fiber-optic gyroscope signal detection with lock-in amplifier. In: 5th international symposium on advanced optical manufacturing and testing technologies: optical test and measurement technology and equipment. SPIE; 2010:426–31 pp.10.1117/12.864203Search in Google Scholar
25. Nayak, J. Fiber-optic gyroscopes: from design to production [Invited]. Appl Opt 2011;50:E152–61. https://doi.org/10.1364/ao.50.00e152.Search in Google Scholar
26. Cao, Y, Zhu, L, Shi, F, Chen, Y, Cao, X, Wang, W, et al.. Dual-polarization interferometric fiber optic gyroscope with shupe effect compensation. Appl Phys Lett 2023;123:011104. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0154973.Search in Google Scholar
27. Wang, Z, Wang, G, Wang, Y, Wang, Z, Gao, W. Research on the birefringence distribution of the fiber coil with quadrupole symmetrical winding method. IEEE Sens J 2021;22:3219–27. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2021.3139626.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0117
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0119
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0120
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0108
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0127
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0144
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0135
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0137
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0142
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0150
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0145
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0132
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0124
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0178
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0174
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0185
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0179
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0190
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0192
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0188
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0200
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0199
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0201
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0189
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0160
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0211
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0210
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0233
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0197
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0234
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0230
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0241
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0231
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0245
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0250
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0253
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0251
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0214
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0117
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0119
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0120
- 10.1515/phys-2024-0108
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0127
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0144
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0135
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0137
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0142
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0150
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0145
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0132
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0124
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0178
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0174
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0185
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0179
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0190
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0192
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0188
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0200
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0199
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0201
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0189
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0160
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0211
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0210
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0233
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0197
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0234
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0230
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0241
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0231
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0245
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0250
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0253
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0251
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- 10.1515/phys-2025-0214

