Abstract
This article is intended to propose a novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high half power beam-width (HPBW) end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications. The proposed radiating structure composes of a 5-element off-set feed rectangular patch antenna array fed by a tapered microstrip line to accomplish high HPBW. Off-set feeding and parasitic patch resonators are incorporated to access the end-fire radiation characteristics. This antenna operating frequency ranges from 277.5 to 315 GHz with a peak gain and HPBW of the antenna as 4.98 dBi and around 100°, respectively, at 300 GHz, making it a good radiator at the specified band. A gold material of thickness 5 μm is used as the metal, while the SiO2 with a thickness of 60 μm is adopted for the substrate material. Design, parametric analysis, and lumped element circuit models are also explored in this work. End-fire pattern, high HPBW, and good performance make this antenna to be eligible to use in THz applications such as imaging, scanning, communication, and bio-medical.
1 Introduction
Nowadays, terahertz (THz) frequency radiation has grabbed significant attention for its high data rates in wireless communications. Therefore, many broadband communication systems are currently being developed in the THz frequency range [1,2,3,4,5,6]. But Lossy propagation and high-power shortage are the issues associated with the THz frequencies. Antennas radiating in end-fire direction find several applications in the present advanced wireless communications. The short pulses, ultra-high-frequency carriers, and the very high bandwidth of the THz spectrum are able to revolutionize the today’s wireless communication by achieving maximum data rates of 100 GB/s [4]. As a result, the wireless data traffic, which is increasing exponentially, can be solved significantly [5]. Since THz frequencies have extremely small wavelengths and coherent non-ionizing property, the techniques used at THz are useful to facilitate high-resolution imaging and positioning, mainly for security and scanning the human body [6].
In the mentioned THz systems, the end-fire radiation antennas are the vital components to launch the electromagnetic energy into free space. A few finest end-fire antennas such as traveling wave antennas, Yagi-Uda antennas, substrate-integrated waveguide (SIW) antennas, and horn antennas, exist at THz bands as well. Horn antennas, which have advantages of simple structure, high gain, and wide band characteristics, have been reported in the literature at THz bands [7,8,9,10,11]. A 3D horn antenna that operates at 325–500 GHz was proposed in Fan et al. [9]. The radiation aperture of the horn antenna in E-plane and H-plane was enlarged for enhancing gain by employing a quasi-planar reflector. A dual polarized horn antenna was reported in Liang et al. [11]. To increase the impedance matching in its operational frequency band (i.e., 220–330 GHz), effective medium lens was introduced. Reported horn antennas at THz frequencies require complex fabrication procedures such as deep reactive ion etching and computer numerical control matching. Moreover, integration with other planar terahertz components is difficult as waveguides are used for exciting them.
SIWs are also used for microwave applications similar to waveguides. This technology is applied to design antennas with end-fire radiation at microwave and millimeter wave frequencies [12,13,14,15,16]. An end-fire SIW antenna, which operates at 26.6–38.7 GHz, was proposed in Li and Chen [13]. It achieved wideband characteristics by loading two face rectangular-shaped patches, which act as a meta-surface. A SIW antenna with circular polarization characteristic at Ka band was reported in Wang et al. [15]. Two antipodal notches were etched to make a complementary source. Also, to increase the gain of the antenna in the end-fire direction, a dielectric rod-like structure was loaded. Even though the SIW antennas have some advantageous characteristics at microwave and millimeter wave frequencies, they are very difficult to fabricate at THz frequencies due to the presence of metallic vials. Hence, they are very limited at THz frequencies.
Another category of antennas known for generating end-fire radiation are Yagi-Uda antennas [17,18,19,20]. In the study by Deal et al. [17], a novel quasi-Yagi antenna is proposed using active planar array method. They comprise many directors, a reflector, and a driven element. This antenna achieves a measured 48% frequency bandwidth with 12 front-to-back-ratio (FBR), and less than-15 dB cross-polarization, and 3–5 dBi of absolute gain. In the study by Hu et al. [18], a vertically polarized top hat monopole Yagi-Uda antenna that operates at 0.55 GHz was presented. The folded top hat monopole acts as a driven element, whereas the four short-circuit monopoles act as directors. A Yagi-Uda antenna, which has an impedance bandwidth of 10 GHz, was presented in Pavanello et al. [19]. A transition balun, which originates from a co-planar waveguide to a co-planar strip-line at a frequency of 300 GHz, is used to excite the antenna. Moreover, the antenna was planar and was fabricated on a cyclic olefin co-polymer film, which has a thickness of 100 µ m. In the study by Wang et al. [20], a compact shared aperture antenna with high isolation characteristics is developed. The antenna is shown to give a peak radiation efficiency of 80%. This antenna uses the concept of combining monopole and dipole concept involving reconfigurable concept.
Another class of antennas that produces end-fire radiation is traveling wave antenna. It is generally based on a condition given by Hansen-Woodyard. The propagation constant of the antenna is typically needed to be more than the free space wavenumber slightly [21,22,23,24,25]. In the study by Hou et al. [22], a periodic leaky wave antenna with air as substrate is fed by a microstrip line. It has end-fire radiation characteristic and phase constant is manipulated by employing multiple monopoles. A traveling wave antenna was proposed in the study by Ge et al. [24] with end-fire radiation characteristic. It comprises crossover structures for phase reversal and satisfies the Hansen-Woodyard condition. As a result, it radiates electromagnetic energy into the free space constructively in the end-fire direction. The above-mentioned traveling wave antennas and Yagi-Uda antennas have some drawbacks such as limited bandwidth, complex 3-D geometries, and delicate structures with very thin substrates. Some other related works are also discussed in the available literature [26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Moreover, none of the reported antenna structures in the literature has high HPBW. Hence, this article proposes a novel compact, lightweight, cost-effective, simple planar, and high performance 5-element off-set feed high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications. This design adopts novelty by constructing a radiator with 5-element off-set feed rectangular patch antenna array fed by a tapered feedline to obtain high HPBW. This article is organized as follows: Section 2 reports the proposed antenna design, performance characteristics, equivalent model, and discussion. Section 3 presents the design steps, parametric variation, and results analysis. Section 4 concludes the work.
2 Proposed high HPBW antenna structure
In this design, gold of thickness 5 µm and silicon dioxide (SiO2) of thickness 60 µm are used as metal and dielectric substrate, respectively. Top and bottom layers of the proposed antenna are shown in Figure 1(a) and (b), respectively. Overall dimensions (L × W) of the antenna are 1.25 × 1.3 mm2.

Proposed antenna: (a) top view and (b) bottom view.
In the radiating structure, each patch element (L p × W p) is of size 0.075 mm × 0.15 mm, while the feed line length (L f) is 0.125 mm. Each parasitic resonator (L r × W r) is with 0.05 mm × 0.1 mm, and partial ground has a length (L 1) of 0.16 mm. Spacing between the parasitic elements along horizontal direction (h) is 0.135 mm, while that along vertical direction (v) is 0.2 mm. All the specified dimensions are mentioned in Table 1.
Dimensions of the proposed antenna
| Parameter | W | L | W r | L r | L f | L 1 | v | h | a | b | f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm) | 1.3 | 1.25 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.125 | 0.16 | 0.2 | 0.135 | 0.085 | 0.15 | 0.002 |
The scattering parameters of this developed antenna are presented in Figure 2. Figure 2 depicts that the antenna is operating in a frequency range between 277.5 and 315 GHz with a resonant frequency at 300 GHz.
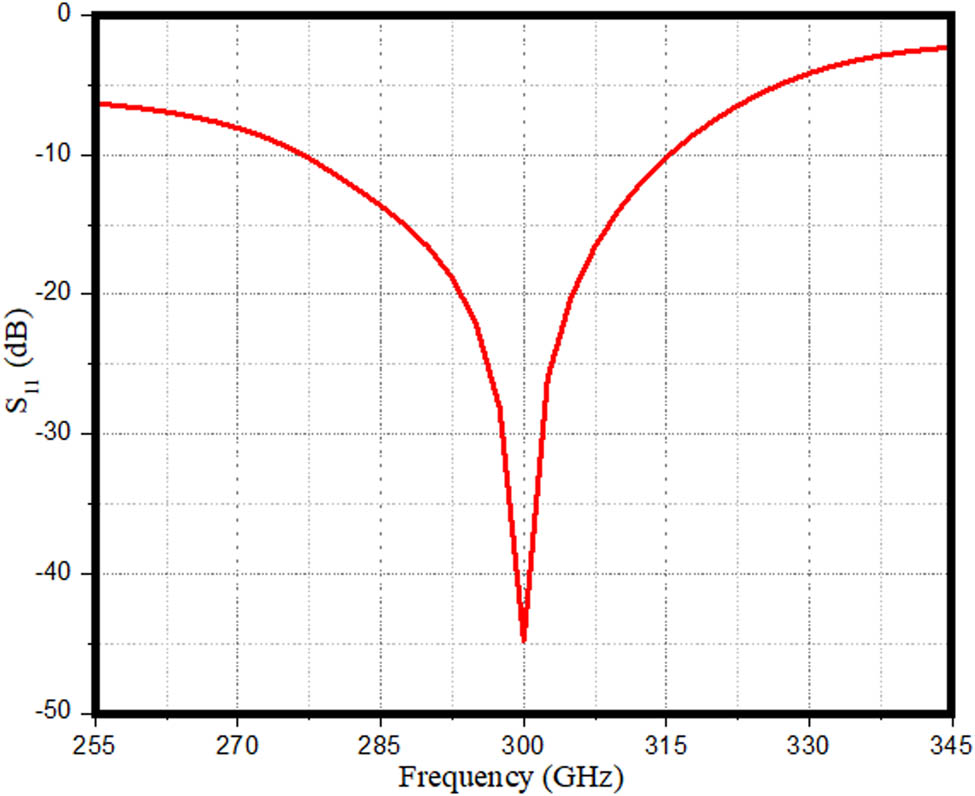
S11-parameter of proposed antenna.
3D-radiation pattern is shown in Figure 3(a), while the 2D-pattern is shown in Figure 3(b). The 3D-pattern in Figure 3(a) presents a peak gain of 4.98 dBi at 300 GHz with end-fire radiation pattern. The 2D-pattern in Figure 3(b) reveals high HPBW of around 100°. Surface current distribution on the proposed antenna at 300 GHz is also shown in Figure 4. Hence, it is evident that the strong surface currents are almost residing uniformly in the patch antenna array elements.
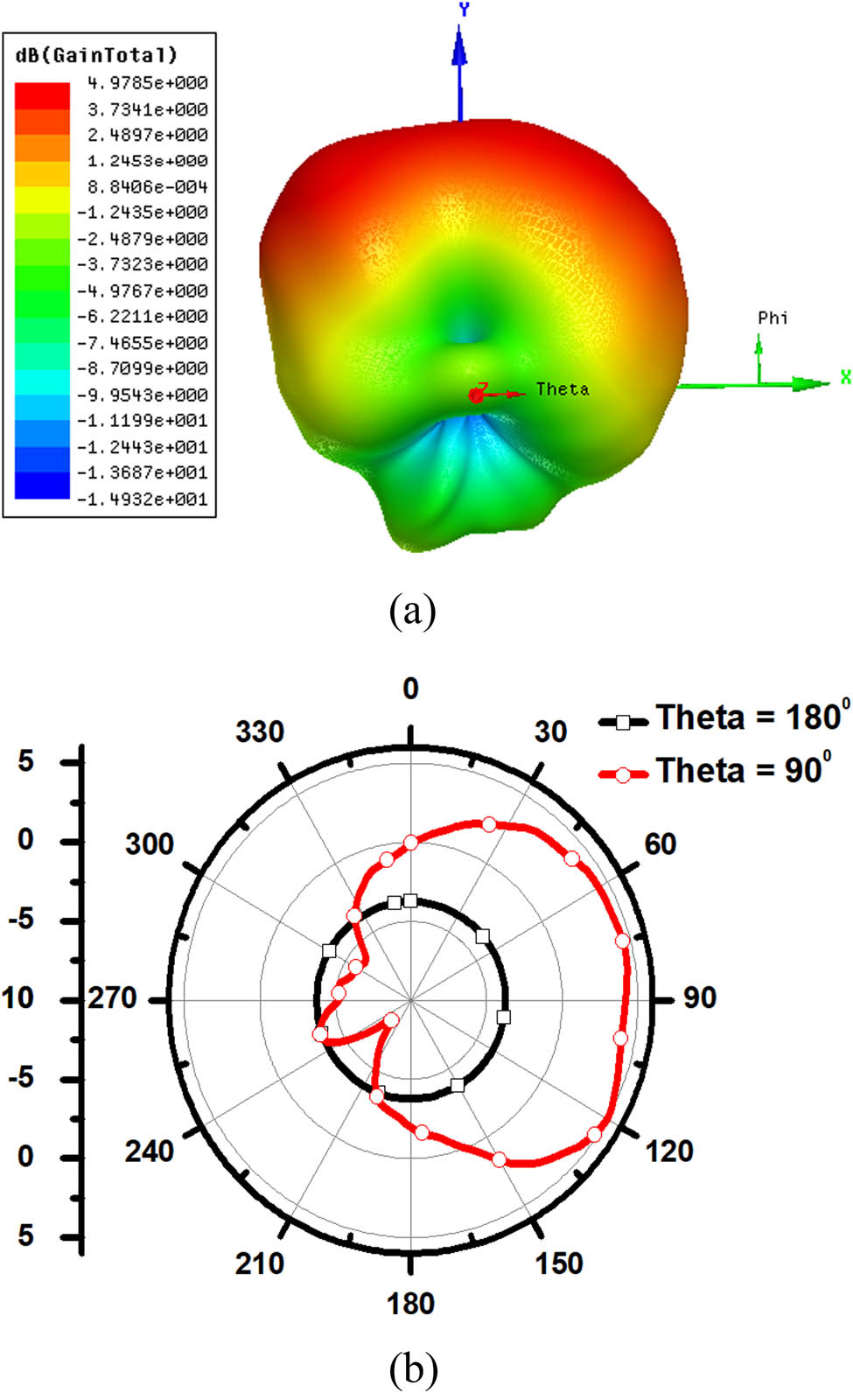
Radiation patterns at 300 GHz: (a) 3-D and (b) 2-D.
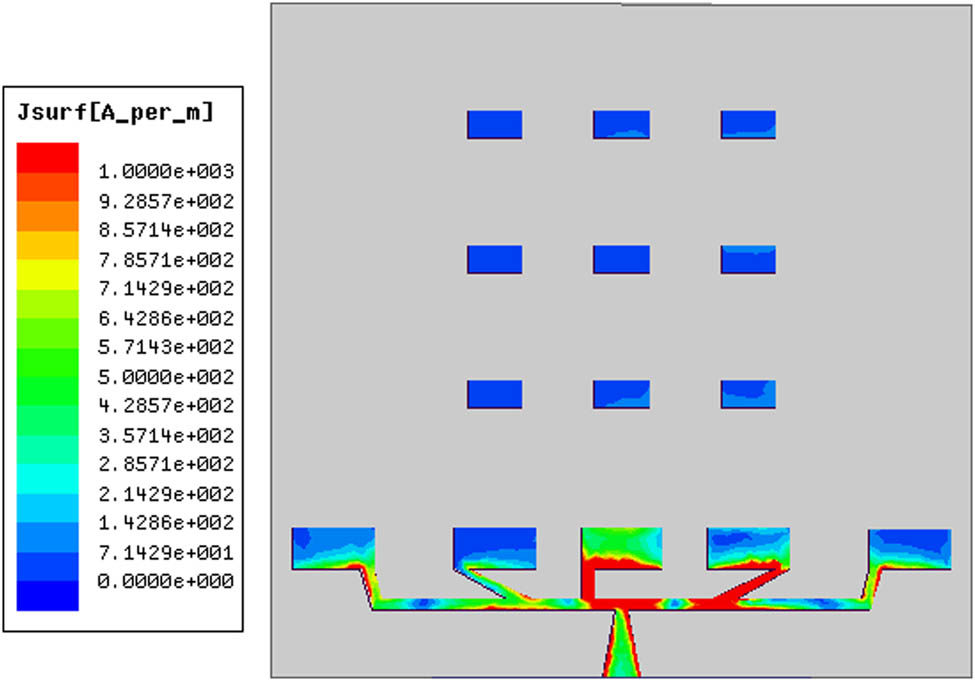
Surface current distribution at 300 GHz.
A lumped element equivalent model of the proposed antenna is shown in Figure 5. This circuit model is developed on the basis of conventional approach to approximate a microstrip antenna using R, L, and C model. In general, the feed line is assumed as a series combination of R and L. The antenna radiator is denoted using a series combination of R, L while a parallel combination of R, L, and C is considered between the top and bottom planes. Hence, in the proposed 5-element antenna array, each element is represented using a series R, L and a parallel R, L, and C, as shown in Figure 5(a). Moreover, each antenna element is terminated with a free-space impedance of 377 Ω. The equivalent model design, optimization, and performance study are executed using ADS tool. The quality of the presented image can be enhanced using the image pre-processing techniques such as discussed in the study by Versaci et al. [33], where fuzzy logic is used for better image quality. However, for brevity, the lumped model of the image is presented here. In this model, each parameter is tuned over a range of values so that overall model S-parameter performance matches with the antenna performance as shown in Figure 5(b). From the figure, it is observed that S11-parameter values of both simulated and equivalent circuit model take same resonance, however giving different impedance bandwidth values.

(a) Proposed antenna equivalent circuit model and (b) S-parameter performance.
3 Design steps and parametric study
This section presents the design steps to realize the proposed antenna. This process follows three design steps. In the Design 1, an off-set fed monopole antenna with parasitic patch elements is designed with a tapered microstrip feed line as depicted in Figure 6(a) and (b). Off-set feeding mechanism is used to obtain the directional pattern in end-fire direction, while the parasitic patch elements are used to enhance the gain of the antenna. In the radiating structure, the patch element (L p × W p) is of size 0.09 mm × 0.185 mm, while the feed line length (L f) is 0.125 mm. Each parasitic resonator (L r × W r) is with 0.05 mm × 0.123 mm, and partial ground has a length (L 1) of 0.145 mm. These dimensions are noted to obtain the resonant frequency at 300 GHz as shown in Figure 7. The Design 1 radiation 3D and 2D patterns are shown in Figure 8. Peak gain of the antenna with this configuration is 8.58 dBi, as illustrated in Figure 8(a). Figure 8(b) also reveals that the pattern has less HPBW noting a narrow directional pattern. But the main objective of this design is to enhance the HPBW.

Evolution design steps (a) and (b) Design 1 (c) and (d) Design 2 (e) and (f) Design 3 (proposed antenna).

Reflection coefficient performance of the design steps.
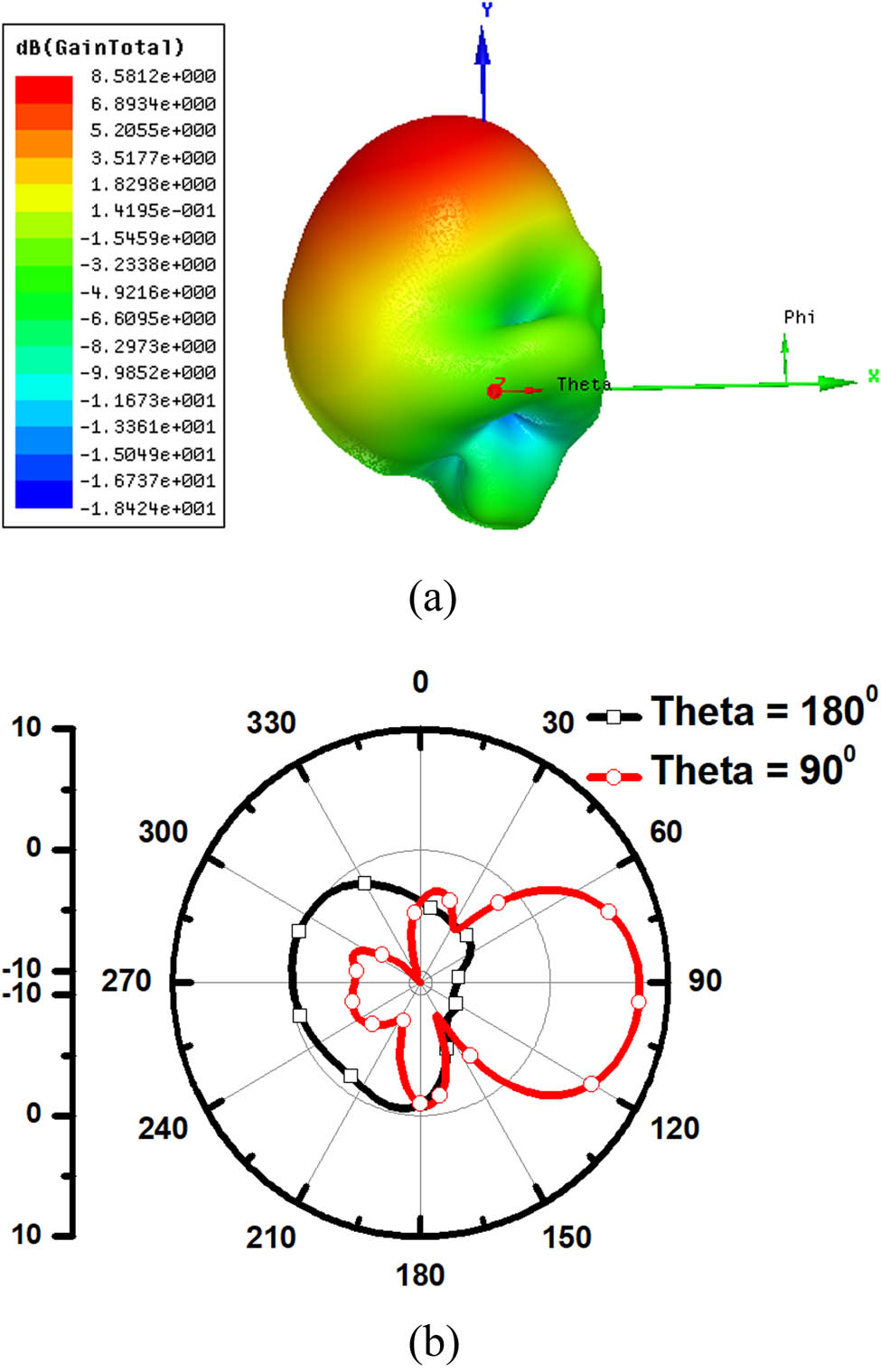
Radiation patterns at 300 GHz for Design 1: (a) 3-D and (b) 2-D.
Hence, Design 2 is enhanced by adding three rectangular radiators using a tapered microstrip line, as depicted in Figure 6(c) and (d). In the radiating structure, the patch element (L p × W p) is of size 0.075 mm × 0.148 mm, while each parasitic resonator (L r × W r) is with 0.05 mm × 0.097 mm. A total of nine parasitic patch elements are used to get end-fire radiation characteristics. The -10 dB reflection coefficient bandwidth achieved with this configuration ranges from 280 to 313 GHz, as shown in Figure 7. The Design 2 radiation 3D and 2D patterns are shown in Figure 9. Peak gain of the antenna designed with this configuration is 7.03 dBi, as illustrated in Figure 9(a). It can be observed that the HPBW is enhanced, as depicted in Figure 9(b), due to the deployment of three patch elements. To further increase the HPBW, five rectangular radiators are fed by a tapered microstrip line, as depicted in Figure 1(a).

Radiation patterns at 300 GHz for Design 2: (a) 3-D and (b) 2-D.
An important observation in this present work is the study of S11-parameters on ground length variation and material changes. The impact of ground length L 1 on the variation of S11-parameters is studied and portrayed in Figure 10. From the figure, it is obvious that for L 1 = 0.16 mm, better reflection coefficient values are obtained compared to the other values of L 1 such as 0.1, 0.125, 0.15, and 0.175 mm. Hence, in the design of this antenna, the value of L 1 considered is 0.16 mm, giving better return loss. Another important parameter to study in the present work is to know the impact of material selected on the reflection coefficient values of the designed antenna as the chosen material may affect the antenna’s radiation properties at THz frequencies. The variation of S11-parameters on the material used in the antenna is presented in Figure 11. From the figure, it is clearly seen that at the chosen THz frequencies, the material has almost no impact on the reflection coefficient values, and hence, in this study, gold is selected in the design of the antenna.

S11-parameter variation w.r.t ground length (L 1).
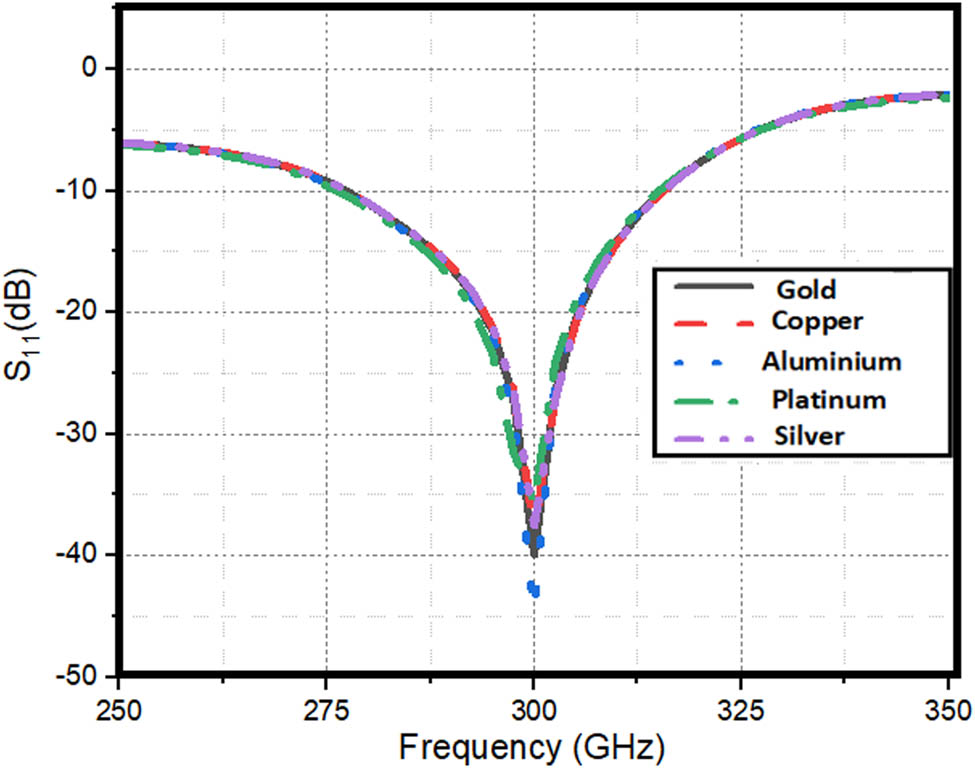
S11-parameter variation w.r.t to metal.
The proposed work is compared with some existing antennas in the literature as in Table 2. In the study by Ohno et al. [26], a novel phased array of dielectric cuboid is designed at 300 GHz having a size of 1 mm × 5.5 mm. In the study by Rey et al. [27], a phased array of horn antenna operating at 300 GHz is designed. The antenna has an overall size of 3 mm × 3.5 mm with HPBW of 20°. In the study by Yamada et al. [28], another cuboid antenna operating at 300 GHz is designed with a size of 1.36 mm × 1.36 mm and HPBW of 25°. In the study by Zheng et al. [29], a 130 nm × 130 nm sized SiGe patch antenna operating at 300 GHz is designed and developed. In the study by Ishihara et al. [30], lens-based dielectric antenna with 10 mm × 10 mm dimension is designed. The proposed antenna covers the band 277.5–315 GHz with dimensions 1.25 mm × 1.3 mm, and HPBW of 100° is designed and developed.
Comparison with existing works
| Ref. | Technique used | Resonant frequency (GHz) | Dimensions | HPBW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | Dielectric cuboid | 300 | 1 mm × 5.5 mm | 17.6° |
| [27] | Horn antenna | 300 | 3 mm × 3.5 mm | 20° |
| [28] | Dielectric cuboid | 300 | 1.36 mm × 1.36 mm | 25° |
| [29] | SiGe patch | 300 | 130 nm × 130 nm | — |
| [30] | Dielectric lens antenna | 270 | 10 mm × 10 mm | 7.4° |
| [31] | On chip horn | 300 | 1 mm × 1.5 mm | 20° |
| [32] | Vivaldi antenna | 292 | 1.8 mm × 0.76 mm | — |
| This work | Microstrip patch | 300 | 1.25 mm × 1.3 mm | 100° |
4 Conclusion
A novel planar HPBW 5-element end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications has been presented. It has a fractional bandwidth of 12.6% and a peak gain of 4.98 dBi. Design steps, parametric variation, and equivalent circuit model have also been presented. It is very advantageous at 300 GHz applications where high HPBW and end-fire radiation patterns are major concerns. Moreover, the antenna design is simple, planar and obtains good directional performance. Hence, the structure can find its THz applications, including THz imaging, scanning, communication, and security.
-
Funding information: This work was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, under Grant No (RG-46-135-42).
-
Author contributions: The conceptualization, simulation, and experimental part were carried out by A. K. N. Conceptualization, methodology, and supervising the research were done by R. W. A. The manuscript preparation and part of simulations were carried out by J. B. K. Result validation and formal analysis were carried out by K.H.A. and M.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript, design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Siegel PH. Terahertz technology in biology and medicine. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech. Oct 2004;52(10):2438–47.10.1109/TMTT.2004.835916Search in Google Scholar
[2] Balanis CA. Antenna theory: Analysis and design. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley; 2016.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Song H-J, Nagatsuma T. Present and future of terahertz communications. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol. Sep 2011;1(1):256–63, 481.10.1109/TTHZ.2011.2159552Search in Google Scholar
[4] Elayan H, Amin O, Shihada B, Shubair RM, Alouini M-S. Terahertz band: The last piece of RF spectrum puzzle for communication systems. IEEE Open J Commun Soc. 2020;1:1–32.10.1109/OJCOMS.2019.2953633Search in Google Scholar
[5] Rodriguez-Vazquez P, Grzyb J, Heinemann B, Pfeiffer UR. A QPSK 110-Gb/s polarization-diversity MIMO wireless link with a 220–255 GHz tunable LO in a SiGe HBT technology. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech. Sep 2020;68(9):3834–51.10.1109/TMTT.2020.2986196Search in Google Scholar
[6] Sarieddeen H, Saeed N, Al-Naffouri TY, Alouini M-S. Next generation terahertz communications: A rendezvous of sensing, imaging, and localization. IEEE Commun Mag. May 2020;58(5):69–75.10.1109/MCOM.001.1900698Search in Google Scholar
[7] Liu Y, Lu H, Wu Y, Cui M, Li B, Zhao P, et al. Millimeter wave and terahertz waveguide-fed circularly polarized antipodal curvedly tapered slot antennas. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. May 2016;64(5):1607–14.10.1109/TAP.2016.2536174Search in Google Scholar
[8] Sekiguchi S, Sugimoto M, Shu S, Sekimoto Y, Mitsui K, Nishino T, et al. Broadband corrugated horn array with direct machined fabrication. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol. Jan 2017;7(1):36–41.10.1109/TTHZ.2016.2634321Search in Google Scholar
[9] Fan K, Hao Z-C, Yuan Q, Hong W. Development of a high gain 325–500 GHz antenna using quasi-planar reflectors. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jul 2017;65(7):3384–91.10.1109/TAP.2017.2705022Search in Google Scholar
[10] Gonzalez A, Kaneko K, Asayama S. 1.25–1.57 THz dual polarization receiver optics based on corrugated horns. IEEE Trans Terahertz Sci Technol. May 2018;8(3):321–8.10.1109/TTHZ.2018.2813088Search in Google Scholar
[11] Liang J, Gao W, Lees H, Withayachumnankul W. All-silicon terahertz planar horn antenna. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett. 508 Nov 2021;20(11):2181–5.10.1109/LAWP.2021.3094310Search in Google Scholar
[12] Taringou F, Dousset D, Bornemann J, Wu K. Broadband CPW feed for millimeter-wave SIW-based antipodal linearly tapered slot antennas. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Apr 2013;61(4):1756–62.10.1109/TAP.2012.2232270Search in Google Scholar
[13] Li T, Chen ZN. Wideband substrate-integrated waveguide-fed endfire metasurface antenna array. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Dec 2018;66(12):7032–40.10.1109/TAP.2018.2871716Search in Google Scholar
[14] Wu Q, Hirokawa J, Yin J, Yu C, Wang H, Hong W. Millimeter wave multibeam endfire dual-circularly polarized antenna array for 5G wireless applications. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Sep 2018;66(9):4930–5.10.1109/TAP.2018.2851667Search in Google Scholar
[15] Wang J, Li Y, Ge L, Wang J, Chen M, Zhang Z, et al. Millimeter-wave wideband circularly polarized planar complementary source antenna with endfire radiation. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jul 2018;66(7):3317–26.10.1109/TAP.2018.2829824Search in Google Scholar
[16] Ruan X, Chan CH. An end fire circularly polarized complementary antenna array for 5G applications. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jan 2020;68(1):266–74.10.1109/TAP.2019.2934888Search in Google Scholar
[17] Deal WR, Kaneda N, Sor J, Qian Y, Itoh T. A new quasi-Yagi antenna for planar active antenna arrays. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech. Jun 2000;48(6):910–8.10.1109/22.846717Search in Google Scholar
[18] Hu Z, Shen Z, Wu W, Lu J. Low-profile top-hat monopole Yagi antenna for end-fire radiation. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Dec 2015;63(12):5484–91.10.1109/TAP.2015.2496119Search in Google Scholar
[19] Pavanello F, Ducournau G, Peytavit E, Lepilliet S, Lampin J-F. High-gain Yagi–Uda antenna on cyclic olefin copolymer substrate for 300-GHz applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett. 2014;13:939–42.10.1109/LAWP.2014.2322628Search in Google Scholar
[20] Wang Z, Ning Y, Dong Y. Compact shared aperture quasi-Yagi antenna with pattern diversity for 5G-NR applications. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jul 2021;69(7):4178–83.10.1109/TAP.2020.3044633Search in Google Scholar
[21] Hou Y, Li Y, Zhang Z, Feng Z. Narrow-width periodic leaky-wave antenna array for endfire radiation based on Hansen–Woodyard condition. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Nov 2018;66(11):6393–6.10.1109/TAP.2018.2864328Search in Google Scholar
[22] Hou Y, Li Y, Zhang Z, Feng Z. High-gain leaky-wave end-fire antenna based on Hansen–Woodyard condition. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett. Oct 2019;18(10):2155–9.10.1109/LAWP.2019.2939298Search in Google Scholar
[23] Ge S, Zhang Q, Rashid AK, Wang H, Murch RD. Design of high-gain and small-aperture endfire antenna using a phase-reversal technique. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jul 2020;68(7):5142–50.10.1109/TAP.2020.2975586Search in Google Scholar
[24] Ge S, Zhang Q, Rashid AK, Zhang Y, Wang H, Murch RD. General design technique for high-gain traveling-wave endfire antennas using periodic arbitrary-phase loading technique. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Jun 2021;69(6):3094–105.10.1109/TAP.2020.3037646Search in Google Scholar
[25] Zhang X, Sun L, Li Y, Zhang Z. A grooved half-mode waveguide leaky-wave antenna for vertically-polarized endfire radiation. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag. Dec 2021;69(12):8229–36.10.1109/TAP.2021.3090845Search in Google Scholar
[26] Ohno T, Sakai R, Hisatake S. Phased array of dielectric cuboid antenna at 300 GHz band. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Sydney. Australia. 2022. p. 363–4.10.1109/ISAP53582.2022.9998671Search in Google Scholar
[27] Rey S, Merkle T, Tessmann A, Kürner T. A phased array antenna with horn elements for 300 GHz communications. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Okinawa, Japan. 2016. p. 122–3.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Yamada K, Samura Y, Minin OV, Kanno A, Sekine N, Nakajima J, et al. Short-range wireless transmitter using mesoscopic dielectric cuboid antenna in 300-GHz band. 50th European Microwave Conference (EuMC), Utrecht, Netherlands. 2021. p. 195–8.10.23919/EuMC48046.2021.9338193Search in Google Scholar
[29] Zheng S, Tang S, Xia X, Zhou P, Chen J, Hong W. A 300 GHz SiGe patch antenna with 5.3 dBi gain using off-chip package. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Sydney, Australia. 2022. p. 209–10.10.1109/ISAP53582.2022.9998628Search in Google Scholar
[30] Ishihara R, Sakakibara K, Kikuma N, Sugimoto Y, Yamada Y, Abd Rahman NH. Measured performance of high gain dielectric lens antenna in 300 GHz band. International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Osaka, Japan. 2021. p. 17–8.10.23919/ISAP47053.2021.9391165Search in Google Scholar
[31] Chen W-H, Ma T-G, Tsai J-H, Cheng Y-H. 300 GHz on-chip horn antenna with WR-03 to SIW transition using integrated passive device. IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (USNC-URSI), Portland, OR, USA. 2023. p. 429–30.10.1109/USNC-URSI52151.2023.10237793Search in Google Scholar
[32] Chen Z-F, Tu Z-H, Lin C-H, Cheng Y-H. 300 GHz low-cost PCB vivaldi antenna array and transition structure to WR-3 waveguide. IEEE Access. 2024;12:92169–74.10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3421993Search in Google Scholar
[33] Versaci M, Angiulli G, La Foresta F, Laganà F, Palumbo A. Intuitionistic fuzzy divergence for evaluating the mechanical stress state of steel plates subject to bi-axial loads. Integr Comput-Aided Eng. 2024;31(4):363–79.10.3233/ICA-230730Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- Explicit exact solutions and bifurcation analysis for the mZK equation with truncated M-fractional derivatives utilizing two reliable methods
- Optical and laser damage resistance: Role of periodic cylindrical surfaces
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- Solving an isotropic grey matter tumour model via a heat transfer equation
- Study on the penetration protection of a fiber-reinforced composite structure with CNTs/GFP clip STF/3DKevlar
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- Interpreting optical effects with relativistic transformations adopting one-way synchronization to conserve simultaneity and space–time continuity
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- Dynamic behavior and modulation instability of the generalized coupled fractional nonlinear Helmholtz equation with cubic–quintic term
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- The mechanism of carbon monoxide fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser-induced plasma
- Numerical solution of a nonconstant coefficient advection diffusion equation in an irregular domain and analyses of numerical dispersion and dissipation
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- Impacts of sinusoidal heat flux and embraced heated rectangular cavity on natural convection within a square enclosure partially filled with porous medium and Casson-hybrid nanofluid
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- Solitonic wave solutions of a Hamiltonian nonlinear atom chain model through the Hirota bilinear transformation method
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- Influence of decaying heat source and temperature-dependent thermal conductivity on photo-hydro-elasto semiconductor media
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- Single-step fabrication of Mn(iv) oxide-Mn(ii) sulfide/poly-2-mercaptoaniline porous network nanocomposite for pseudo-supercapacitors and charge storage
- Novel constructed dynamical analytical solutions and conserved quantities of the new (2+1)-dimensional KdV model describing acoustic wave propagation
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- Robust control and preservation of quantum steering, nonlocality, and coherence in open atomic systems
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- Finite element analysis of turbulent thermal enhancement in grooved channels with flat- and plus-shaped fins
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- On solutions of the Dirac equation for 1D hydrogenic atoms or ions
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- Stability analysis, circuit simulation, and color image encryption of a novel four-dimensional hyperchaotic model with hidden and self-excited attractors
- A high-accuracy exponential time integration scheme for the Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson fluid flow with temperature-dependent conductivity
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- Hydraulic fracturing radioactive source tracing technology based on hydraulic fracturing tracing mechanics model
- Numerical solution and stability analysis of non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid flow subject to exponential heat source/sink over a Riga sheet
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- Irreversibility analysis of a bioconvective two-phase nanofluid in a Maxwell (non-Newtonian) flow induced by a rotating disk with thermal radiation
- Hydrodynamic and sensitivity analysis of a polymeric calendering process for non-Newtonian fluids with temperature-dependent viscosity
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- Insights into chemical reactions occurring in generalized nanomaterials due to spinning surface with melting constraints
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- Soliton-like solutions for a nonlinear doubly dispersive equation in an elastic Murnaghan's rod via Hirota's bilinear method
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- Analyzing the role of length and radius of MWCNTs in a nanofluid flow influenced by variable thermal conductivity and viscosity considering Marangoni convection
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- Exact bound state solutions of the radial Schrödinger equation for the Coulomb potential by conformable Nikiforov–Uvarov approach
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- Propagation properties of Airyprime pulses in relaxing nonlinear media
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- PbO-doped K2O–BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–TeO2-glasses: Mechanical and shielding efficacy
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- Numerical modeling of enhanced reactive oxygen plasma in pulsed laser deposition of metal oxide thin films
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- Swirling-annular-flow-induced instability of a micro shell considering Knudsen number and viscosity effects
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- Investigation of thermal conductivity and Raman spectra for HfAlB, TaAlB, and WAlB based on first-principles calculations
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- A new family of Poisson-exponential distributions with applications to cancer data and glass fiber reliability
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- A widespread study of discrete entropic model and its distribution along with fluctuations of energy
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- The influence of scattering correction effect based on optical path distribution on CO2 retrieval
- Anisotropic dissociation and spectral response of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene under static directional electric fields
- Role of tungsten oxide (WO3) on thermal and optical properties of smart polymer composites
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- Novel exact solitons to the fractional modified mixed-Korteweg--de Vries model with a stability analysis
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- Explicit exact solutions and bifurcation analysis for the mZK equation with truncated M-fractional derivatives utilizing two reliable methods
- Optical and laser damage resistance: Role of periodic cylindrical surfaces
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- Solving an isotropic grey matter tumour model via a heat transfer equation
- Study on the penetration protection of a fiber-reinforced composite structure with CNTs/GFP clip STF/3DKevlar
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- Interpreting optical effects with relativistic transformations adopting one-way synchronization to conserve simultaneity and space–time continuity
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- Dynamic behavior and modulation instability of the generalized coupled fractional nonlinear Helmholtz equation with cubic–quintic term
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- The mechanism of carbon monoxide fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser-induced plasma
- Numerical solution of a nonconstant coefficient advection diffusion equation in an irregular domain and analyses of numerical dispersion and dissipation
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- Impacts of sinusoidal heat flux and embraced heated rectangular cavity on natural convection within a square enclosure partially filled with porous medium and Casson-hybrid nanofluid
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- Solitonic wave solutions of a Hamiltonian nonlinear atom chain model through the Hirota bilinear transformation method
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- Influence of decaying heat source and temperature-dependent thermal conductivity on photo-hydro-elasto semiconductor media
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- Single-step fabrication of Mn(iv) oxide-Mn(ii) sulfide/poly-2-mercaptoaniline porous network nanocomposite for pseudo-supercapacitors and charge storage
- Novel constructed dynamical analytical solutions and conserved quantities of the new (2+1)-dimensional KdV model describing acoustic wave propagation
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- Robust control and preservation of quantum steering, nonlocality, and coherence in open atomic systems
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- Finite element analysis of turbulent thermal enhancement in grooved channels with flat- and plus-shaped fins
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- On solutions of the Dirac equation for 1D hydrogenic atoms or ions
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- Stability analysis, circuit simulation, and color image encryption of a novel four-dimensional hyperchaotic model with hidden and self-excited attractors
- A high-accuracy exponential time integration scheme for the Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson fluid flow with temperature-dependent conductivity
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- Hydraulic fracturing radioactive source tracing technology based on hydraulic fracturing tracing mechanics model
- Numerical solution and stability analysis of non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid flow subject to exponential heat source/sink over a Riga sheet
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- Irreversibility analysis of a bioconvective two-phase nanofluid in a Maxwell (non-Newtonian) flow induced by a rotating disk with thermal radiation
- Hydrodynamic and sensitivity analysis of a polymeric calendering process for non-Newtonian fluids with temperature-dependent viscosity
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- Insights into chemical reactions occurring in generalized nanomaterials due to spinning surface with melting constraints
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- Soliton-like solutions for a nonlinear doubly dispersive equation in an elastic Murnaghan's rod via Hirota's bilinear method
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- Analyzing the role of length and radius of MWCNTs in a nanofluid flow influenced by variable thermal conductivity and viscosity considering Marangoni convection
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- Exact bound state solutions of the radial Schrödinger equation for the Coulomb potential by conformable Nikiforov–Uvarov approach
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- Propagation properties of Airyprime pulses in relaxing nonlinear media
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- PbO-doped K2O–BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–TeO2-glasses: Mechanical and shielding efficacy
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- Numerical modeling of enhanced reactive oxygen plasma in pulsed laser deposition of metal oxide thin films
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- Swirling-annular-flow-induced instability of a micro shell considering Knudsen number and viscosity effects
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- Investigation of thermal conductivity and Raman spectra for HfAlB, TaAlB, and WAlB based on first-principles calculations
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- A new family of Poisson-exponential distributions with applications to cancer data and glass fiber reliability
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- A widespread study of discrete entropic model and its distribution along with fluctuations of energy
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- The influence of scattering correction effect based on optical path distribution on CO2 retrieval
- Anisotropic dissociation and spectral response of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene under static directional electric fields
- Role of tungsten oxide (WO3) on thermal and optical properties of smart polymer composites
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- Novel exact solitons to the fractional modified mixed-Korteweg--de Vries model with a stability analysis

