Abstract
The prevalence and growth characteristics of glioma tumours in human tissues are often modelled by a parabolic partial differential equation. It is essential to analyse tumour growth factors to establish mathematical benchmarks in understanding cancer progression. In this tumour study, we consider factors such as the tumour proliferation rates and the anisotropy of the spatial diffusion tensor. We aim to solve the resulting model together with its initial condition, to provide realistic biological predictions into the mechanism of cancer invasion, metastasis and life expectancy after diagnosis. The solutions are inspired by transformations that we propose to convert the tumour model into a heat equation. A key component in understanding the physics of cancer phenomena, is through obtaining precise solutions. Lie symmetries provide the mechanism to obtain exact solutions.
1 Introduction
Tumours of the brain cause significant neurological problems and impact life expectancy dramatically. In particular, a glioma is a type of tumour that originates in the glial cells of the brain or spine. They are known to be aggressive, highly invasive, and are among the most common type afflicting human populations [1]. Unfortunately such tumours are heterogeneous and exhibit distinct molecular profiles – they vary widely in terms of growth rate and prognosis. Comprehensive research is ongoing on tumour biology and behaviour. The end goal is to find tools for prevention, a resistance to worsening health, or treatment mechanisms to avoid fatalities.
The mathematical modelling of tumours plays a crucial dynamic role in understanding tumour growth predictions and treatment response [2]. Mathematics offers an inexpensive approach to analyse tumour size and has applications in cancer treatment and surgical planning. Reaction–diffusion (or proliferative–invasive) equations offer an excellent baseline for modelling tumour growth.
It is true to state that mathematical models of tumours have limitations. Some tumour facets may not be accounted for in any given model, for example, the effects of oxygenation and nutrient concentration for cell hypoxia, the advance of necrosis, age, genetics, and/or environmental factors. However, despite these drawbacks, the exact solutions of such models are indispensable [3–8]. We discuss several reaction–diffusion models, mainly concentrating on the spread of untreated gliomas. One sees a general perspective of how parameters are extracted from medical modalities to encompass biological knowledge, and the proposed working models to simulate and optimise tumour investigations.
To our knowledge, a study of our main equation has not appeared elsewhere, in any prior mathematical context. For this reason, a discussion of its place among other tumour models is discussed in Section 2. In fact, despite the model being linear, it is non-trivial to solve it subject to initial data. This is precisely what our work has achieved, in a first and original study. It is also new and noteworthy that we prove that such a model is reducible to the classical heat equation.
Other parabolic equations, have been actively studied by symmetries, for example, the Vasicek model [9], the constant elasticity of variance model [10], the Kolmogorov equations [11], the time-dependent Black-Scholes [12], and many others.
We align our study to the existing literature through comparison with known results in the study of Burgess et al. [2]. Other leading mathematical analysis for tumour growth are the works of Woodward et al. [5,13,14]. Our approach has been cross-validated with these studies, ensuring that the solutions are reliable. We adopted the well-known conventions, such as time data, from the studies by Tracqui et al. [5] and Burgess et al. [2] to capture consistent and valid theoretical predictions, but we extend the existing results, providing insights into grey matter tumours specifically.
An important aspect of analysing problems in physics is deriving exact solutions to differential equations. In this regard, a mathematical framework provides powerful tools to effectively address and solve a wide range of physical problems. For example Shah et al. [15] discussed disease models in the field of physics, while under the mathematics of fractional derivatives.
The organisation of this investigation is as follows. Section 2 defines the basic assumptions of the model. In Section 3, we provide transformations that render the isotropic grey matter glioma model into the one-dimensional parabolic heat equation, followed by the determination of exact solutions by two vital methods. The first method is the standard Lie invariant method which includes the optimal system of one-dimensional subalgebras, and a second approach, is a solution of the initial-value problem. Section 4 provides the mathematical inferences of our study. The conclusion is given in Section 5.
2 The model
Suppose that the cellular flux obeys Fick’s law with proliferation descriptive of an exponential growth, so that we have the reaction–diffusion model [2]
where
Experimental data from rats demonstrated that glioma cells disperse differently depending on its location in the brain matter, that is, grey vs white matter [16,17]. This spatial variation may be encompassed by the model proposed by Swanson et al. [18], which includes the spatial dependence of the diffusion coefficient, i.e. with
The two tissues found in the brain have distinct functions and characteristics. Abnormal growths may develop in either tissue, but this impacts modes of diagnosis and treatment. Gliomas in grey matter show symptoms that include seizures, headaches, and even cognitive issues depending on the tumour grade, location, and size. These factors also influence treatment aspects like surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
The diffusive term in equation (1) exhibits tensor properties, where grey matter is mostly isotropic while white matter is highly anisotropic [19]. Thus, in the case of grey matter, we have the model
where
We may impose the initial condition (IC),
in a three-dimensional unbounded domain. A typical IC includes, say
The primary contribution of this work is that we offer a poignant treatment of an important equation in medical biology. By simplifying a significant glioma model, we are able to find exact solutions and extract important theoretical observations predicted by the model.
3 Transformations and solutions
We prove how to transform (3) to the classical heat equation by an aptly chosen change in variables. This change provides a mathematical tool to solve (3) via interesting features of the classical heat equation. The discovery of such transformations are inspired by Lie’s [20] technique that allows for the classification of some equations to simple equations. However, this scope of his work is not trivial and not well-known. This is our approach below, where we seek simple transformations that are able to incorporate initial values.
But first, we require a meaningful connection between the diffusion and proliferation. Consider a mathematical expression for the diffusion coefficient, subject to the proliferation rate
where
Hence, we prove the following result.
Theorem 1
Eq. (3) is converted to
which is the
coupled with the transformations
followed by
Proof
An application of (7) renders Eq. (3) to the form
Thereafter, the transformation (8) converts (9) to the heat equation (6).□
A simple extension of this theorem and its transformations to the IC (4) yields the following result.
Lemma 2
The invertible transformations of Theorem 1 converts IC (4) to
The above choice for the diffusion parameter is a biologically significant one, as this is generally how diffusion depends on proliferation. There are two possible paths to the solution of (3). First, we solve using the optimal system of subalgebras that provides non-equivalent classes of invariant solutions. Second, we solve the initial value problem by constructing a symmetry that incorporates the IC. Both approaches are important for the mathematical analysis of grey matter gliomas.
3.1 Exact solution via symmetries
The Lie point symmetries of (6) are well established, they are as follows:
The optimal one-dimensional subalgebra based on the above generators are [22] (p. 206)
where
Case (i)
This subalgebra yields the invariants
In this regard, we obtain the exact solution of (6) as
where
Case (ii)
This subalgebra yields the invariants
where
For
and Theorem 1 gives the exact solution for (3), viz.
Case (iii)
The invariants of this case are
where
Case (iv)
The invariants of this case are
Thus, this subalgebra gives us the exact solution of (6), i.e.,
where
In this case, a reversal of the transformations from Theorem 1, gives the exact solution for (3), viz.
For
where
Case (v)
Here the invariants are
where
Finally, a reversal of the transformations of Theorem 1 gives the exact solution for (3), viz.
3.2 Initial-value solution via symmetries
To achieve the desired accuracies of solutions and simulate the complex behaviour of tumour growth over time, IC’s are crucial in solution processes. The heat equation is a perfect choice for study as it admits the heat kernel [23,24]. We demonstrate a technique to solve a Cauchy problem for (6) that involves Lie symmetries [25–28]. The main aim is to solve the original equation (3) subject to IC (4).
We recall that the fundamental solution of (6) is
which is singular at (0,0).
The symmetry generators of the heat Eq. (6) may be written as
so that the invariant surface condition (ISC) [22] is
where it is imposed that
Eq. (29) is an IC (less restrictive) [29]. We now demonstrate a solution – more solutions exist and can be found by the same process.
We emphasise that the function
If one can solve (30), we will find
Let
and
Thus, via the ISC (28), we obtain that the solution to (6) is
We let
Let us consider a specific IC.
Case (vi) Consider the logarithmic growth function
By the procedure described above, we find
and the heat equation’s solution is then
Finally, the equation for grey matter gliomas has solution, subject to (4), as
If we let
4 Mathematical analysis
In this section, we extract significant insights from the exact solutions. In this regard, some assumptions are necessary. First, we analyse high-grade tumours, characterised by high proliferation, at the value
The highest concentration of cells is near the centre
We present selected results from our cases in the figures and tables that follow. Figures 1 and 2 display the behaviour of cell density vs radius, for Cases (i)–(vi), where time of diagnosis is

Tumour cell density vs radius: (a) Case (i) with parameter selection
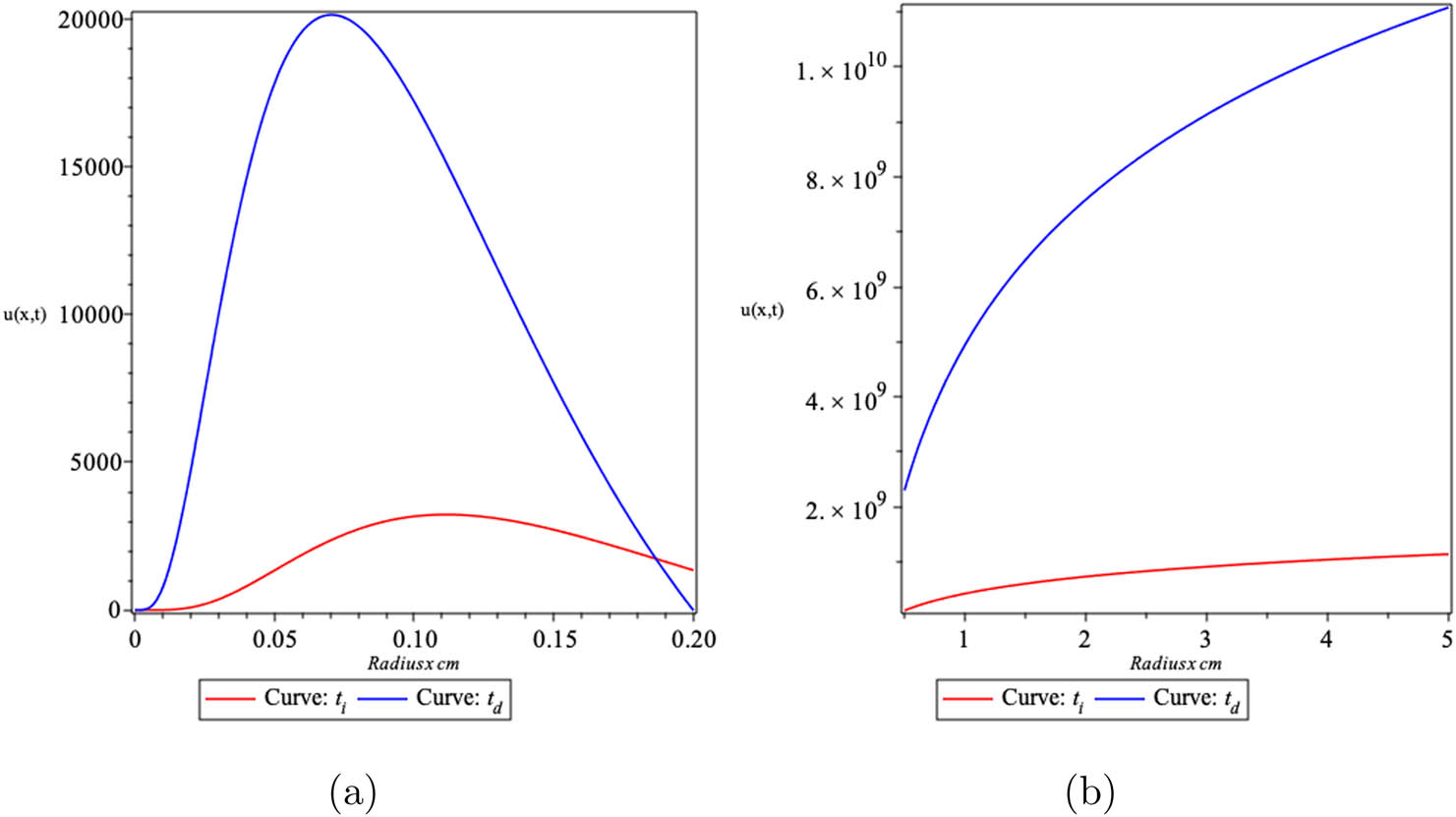
Tumour cell density vs radius: (a) Case (v) with parameter selection
In Table 1, we determine the time of diagnosis and death given the critical cell density and the radii of
Expected survival of an untreated high-grade glioma
| (i) | (ii) | (vi) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
0.65 | 0.47 | 0.36 |
|
|
0.92 | 0.74 | 0.50 |
| Survival (years) | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.14 |
The expected cancer survival rate is vital in determining treatment options: side effects vs quality of life. Knowing the realistic survival can help patients prepare emotionally and realistically for the future.
Patients with a higher likelihood of survival may receive more aggressive treatments, while those with a lower chance of survival might focus on palliative care or supportive therapies.
In Table 2, we report on the tumour cell density under a high-grade glioma. For these results, we again utilise the time of diagnosis
Cell density under time of diagnosis and death
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) | (vi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density at
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Density at
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cell density constitutes vital data in experimental research assisting to replicate the tumour microenvironment more accurately. High cell density in tumours impact oxygen and nutrient levels. These microenvironmental conditions often interact with tumour growth and therapy response.
Some insights observed from the figures and tables are as follows. In Table 1, as expected, the high-grade gliomas have a very short life expectancy. The survival years reported by Tracqui et al. [5] and also applied by Burgess et al. [2], for high-grade gliomas with a constant diffusion coefficient is 0.49 years. Our expected survival is lower under a spatial diffusion coefficient, grey matter tumour model.
We observe from Figures 1 and 2, which provide the spatial profile of tumour cells at the time of diagnosis and death, that the cell densities around the centre approach between 10 and 10,000 times the critical cell density for most cases, with the exception of Cases (iii) and (v). In the former case, density around the centre is close to the critical cell density value but in the latter case, we see lower densities which would increase the difficulty in diagnosis.
From Table 2, we note that Case (iv) has cell density close to the critical cell density value, while most other cases predict 10- to 1,000-fold cell densities. We highlight from Table 1 that imposing the IC has a significant impact – it lowers life expectancy.
5 Conclusion
Gliomas can be challenging to diagnose accurately, especially within early stages. Research into glioma biology and the development of new diagnostic techniques are influenced by cell density studies. Accurate detection impacts treatment interventions and life expectancy.
Exact solutions to tumour models are pivotal in unravelling the complexities of gliomas, with symmetry analysis providing new and significant information in terms of (1) life expectancy/growth and (2) cell density. We highlight the correlation between the outcomes from the symmetry analysis and the underlying physics of diagnosis and tumour growth patterns:
Our contribution provides precise predictions in times of diagnosis, survival, and death for grey matter gliomas. The study’s innovative use of symmetries provides a breakthrough in proving lower life expectancy for isotropic grey matter tumours vs the full brain reported in the study by Tracqui et al. [5].
Symmetry analysis represents a major advancement in the understanding of the diagnosis capability of this model. Cell densities (Table 2) are comparable to findings reported by Burgess et al. [2], indicating grey matter tumours are mostly, as easily diagnosed as white plus grey matter brain tumours.
As a first, the addition of logarithmic growth in the IC of the model offers a reshaping of the way we model growth conditions, with lower survival predicted under this type of growth.
This is the first study of model (3), a grey matter isotropic model, hence it is the benchmark for any subsequent mathematical analysis. Our findings are robust and mathematically sound, as they are derived from a comprehensive analysis, ensuring the reliability of the results. Moreover the conclusions drawn implement Fishers’ approximation for the underlying model, as substantiated in the literature. This work represents some crucial contributions:
The novel approach presented offers a fresh perspective on solution approaches, by introducing new transformations to convert a tumour model to the simple heat equation. The transformations presented are tractable, and therefore, available to wide audiences.
Our conclusions are of practical importance, as they extend current theories and have potential implications for real-world medical theories.
The study of a specialised topic, such as grey matter tumours, is expected to stimulate further research and exploration in new avenues.
Mathematics and physics are deeply interconnected. In future, the theory presented here can be applied to similar models, offering effective methods for solving a broad spectrum of physical problems.
Acknowledgments
Opinions expressed and conclusions arrived at are those of the authors and are not necessarily to be attributed to the CoE-MaSS.
-
Funding information: The author states no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The author states no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Alvord EC. Shaw CM in the pathology of the aging human nervous system. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1991. Search in Google Scholar
[2] Burgess PK, Kulesa PM, Murray JD, Alvord EC. The interaction of growth rates and diffusion coefficients in a three-dimensional mathematical model of gliomas. J Neuropath Exp Neur. 1997;56:704–13. 10.1097/00005072-199706000-00008Search in Google Scholar
[3] Wein L, Koplow D. Mathematical modeling of brain cancer to identify promising combination treatments. Preprint, D Sloan School of Management. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT. 1999. Search in Google Scholar
[4] Moyo S, Leach PGL. Symmetry methods applied to a mathematical model of a tumour of the brain. Proc. Inst. Math. NAS of Ukraine. 2004;50:204–10. Search in Google Scholar
[5] Tracqui P, Cruywagen GC, Woodward DE, Bartooll GT, Murray JD, Alvord EC. A mathematical model of glioma growth: the effect of chemotherapy on spatio-temporal growth. Cell Prolif. 1995;28:17–31. 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1995.tb00036.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Cruywagen GC, Woodward DE, Tracqui P, Bartoo GT, Murray JD, Alvord EC. The modelling of diffusive tumours, J Biol Syst. 1995;3:937–45. 10.1142/S0218339095000836Search in Google Scholar
[7] Jamal S. Prototype gliomas: Invariant solutions and expected survival times. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst - S. 10.3934/dcdss.2024113. Search in Google Scholar
[8] Swanson KR, Bridge C, Murray JD, Alvord EC. Virtual and real brain tumours: Using mathematical modeling to quantify glioma growth and invasion. J Neurol Sci. 2003;216:1–10. 10.1016/j.jns.2003.06.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Sinkala W, Leach PGL, O’Hara JG. Embedding the Vasicek model into the Cox-Ingersoll-Ross model. Math Methods Appl Sci. 2011;34(2):152–9. 10.1002/mma.1342Search in Google Scholar
[10] Bakkaloglu A, Aziz T, Fatima A, Mahomed FM, Khalique CM. Invariant approach to optimal investment-consumption problem: the constant elasticity of variance (CEV) model. Math Methods Appl Sci. 2017;40(5):1382–95. 10.1002/mma.4060Search in Google Scholar
[11] Bluman GW, Shtelen V. Nonlocal transformations of Kolmogorov equations into the backward heat equation. J Math Anal Applic. 2004;291:419–37. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2003.11.028Search in Google Scholar
[12] Naz R, Johnpillai AG. Exact solutions via invariant approach for Black-Scholes model with time-dependent parameters. Math Meth Appl Sci. 2018;41:4417–27. 10.1002/mma.4903Search in Google Scholar
[13] Woodward DE, Cook J, Tracqui P, Cruywagen GC, Murray JD, Alvord EC. A mathematical model of glioma growth: the effect of extent of surgical resection. Cell Prolif. 1996;29(6):269–88. 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1996.tb01580.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Cook J, Woodward DE, Tracqui P, Murray JD. Resection of gliomas and life expectancy. J Neuro-Oncol. 1995;24(4):131–5. Search in Google Scholar
[15] Shah K, Ahmad I, Shafiullah, Mukheimer A, Abdeljawad T, Jeelani MB. On the existence and numerical simulation of Cholera epidemic model. Open Phys. 2024;22:20230165. 10.1515/phys-2023-0165Search in Google Scholar
[16] Chicoine MR, Silbergeld DL. Assessment of brain tumour cell motility in vivo and in vitro. J Neurosurg. 1995;82:615–22. 10.3171/jns.1995.82.4.0615Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Giese A, Kluwe L, Laube B, Meissner H, Berens ME, Westphal M. Migration of human glioma cells on myelin. Neurosurgery 1996;38:755–64. 10.1227/00006123-199604000-00026Search in Google Scholar
[18] Swanson KR, Alvord EC, Murray JD. A quantitative model for differential motility of gliomas in grey and white matter. Cell Prolif. 2000;33:317–29. 10.1046/j.1365-2184.2000.00177.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Martín-Landrove M. Reaction–diffusion models for glioma tumour growth. arXiv:1707.09409v1. Search in Google Scholar
[20] Lie S. On integration of a class of linear partial differential equations by means of definite integrals. Arch Math Naturvidensk 1881;5:328–58. (German) Search in Google Scholar
[21] Fisher RA. The wave of advance of advantageous genes. Ann Eugenics. 1937;7:353–69. 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1937.tb02153.xSearch in Google Scholar
[22] Olver PJ. Applications of lie groups to differential equations. 2nd edition, New York: Springer; 1993. 10.1007/978-1-4612-4350-2Search in Google Scholar
[23] Evans LC. Partial differential equations. Graduate Studies in Mathematics. 2nd ed. Vol 19. Rhode Island: American Mathematical Society; 2010. 10.1090/gsm/019Search in Google Scholar
[24] Tikhonov AN. Uniqueness theorems for the heat equation. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 1935;1:294–300. (In Russian and French)Search in Google Scholar
[25] Champala R, Jamal S, Khan S. Fractional pricing models: transformations to a heat equation and Lie symmetries. Fractal Fract. 2023;7:632. 10.3390/fractalfract7080632Search in Google Scholar
[26] Jamal S, Maphanga R. A progressive approach to solving a CEV model via symmetry invariant surface conditions. AIMS Math. 2024;9(2):4326–36. 10.3934/math.2024214Search in Google Scholar
[27] Maphanga R, Jamal S. A terminal condition in linear bond-pricing under symmetry invariance. J Nonlinear Math Phys. 2023;30:1295–304. 10.1007/s44198-023-00132-6Search in Google Scholar
[28] Jamal S, Champala R, Khan S. Lie symmetries and the invariant solutions of the fractional Black-Scholes equation under time-dependent parameters. Fractal Fract. 2024;8:269. 10.3390/fractalfract8050269Search in Google Scholar
[29] Goard J. Noninvariant boundary conditions. Appl Anal. 2003;82:473–81. 10.1080/0003681031000109639Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- Explicit exact solutions and bifurcation analysis for the mZK equation with truncated M-fractional derivatives utilizing two reliable methods
- Optical and laser damage resistance: Role of periodic cylindrical surfaces
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- Solving an isotropic grey matter tumour model via a heat transfer equation
- Study on the penetration protection of a fiber-reinforced composite structure with CNTs/GFP clip STF/3DKevlar
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- Interpreting optical effects with relativistic transformations adopting one-way synchronization to conserve simultaneity and space–time continuity
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- Dynamic behavior and modulation instability of the generalized coupled fractional nonlinear Helmholtz equation with cubic–quintic term
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- The mechanism of carbon monoxide fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser-induced plasma
- Numerical solution of a nonconstant coefficient advection diffusion equation in an irregular domain and analyses of numerical dispersion and dissipation
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- Impacts of sinusoidal heat flux and embraced heated rectangular cavity on natural convection within a square enclosure partially filled with porous medium and Casson-hybrid nanofluid
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- Solitonic wave solutions of a Hamiltonian nonlinear atom chain model through the Hirota bilinear transformation method
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- Influence of decaying heat source and temperature-dependent thermal conductivity on photo-hydro-elasto semiconductor media
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- Single-step fabrication of Mn(iv) oxide-Mn(ii) sulfide/poly-2-mercaptoaniline porous network nanocomposite for pseudo-supercapacitors and charge storage
- Novel constructed dynamical analytical solutions and conserved quantities of the new (2+1)-dimensional KdV model describing acoustic wave propagation
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- Robust control and preservation of quantum steering, nonlocality, and coherence in open atomic systems
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- Finite element analysis of turbulent thermal enhancement in grooved channels with flat- and plus-shaped fins
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- On solutions of the Dirac equation for 1D hydrogenic atoms or ions
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- Stability analysis, circuit simulation, and color image encryption of a novel four-dimensional hyperchaotic model with hidden and self-excited attractors
- A high-accuracy exponential time integration scheme for the Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson fluid flow with temperature-dependent conductivity
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- Hydraulic fracturing radioactive source tracing technology based on hydraulic fracturing tracing mechanics model
- Numerical solution and stability analysis of non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid flow subject to exponential heat source/sink over a Riga sheet
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- Irreversibility analysis of a bioconvective two-phase nanofluid in a Maxwell (non-Newtonian) flow induced by a rotating disk with thermal radiation
- Hydrodynamic and sensitivity analysis of a polymeric calendering process for non-Newtonian fluids with temperature-dependent viscosity
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- Insights into chemical reactions occurring in generalized nanomaterials due to spinning surface with melting constraints
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- Soliton-like solutions for a nonlinear doubly dispersive equation in an elastic Murnaghan's rod via Hirota's bilinear method
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- Analyzing the role of length and radius of MWCNTs in a nanofluid flow influenced by variable thermal conductivity and viscosity considering Marangoni convection
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- Exact bound state solutions of the radial Schrödinger equation for the Coulomb potential by conformable Nikiforov–Uvarov approach
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- Propagation properties of Airyprime pulses in relaxing nonlinear media
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- PbO-doped K2O–BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–TeO2-glasses: Mechanical and shielding efficacy
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- Numerical modeling of enhanced reactive oxygen plasma in pulsed laser deposition of metal oxide thin films
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- Swirling-annular-flow-induced instability of a micro shell considering Knudsen number and viscosity effects
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- Investigation of thermal conductivity and Raman spectra for HfAlB, TaAlB, and WAlB based on first-principles calculations
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- A new family of Poisson-exponential distributions with applications to cancer data and glass fiber reliability
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- A widespread study of discrete entropic model and its distribution along with fluctuations of energy
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- The influence of scattering correction effect based on optical path distribution on CO2 retrieval
- Anisotropic dissociation and spectral response of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene under static directional electric fields
- Role of tungsten oxide (WO3) on thermal and optical properties of smart polymer composites
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- Novel exact solitons to the fractional modified mixed-Korteweg--de Vries model with a stability analysis
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Single-step fabrication of Ag2S/poly-2-mercaptoaniline nanoribbon photocathodes for green hydrogen generation from artificial and natural red-sea water
- Abundant new interaction solutions and nonlinear dynamics for the (3+1)-dimensional Hirota–Satsuma–Ito-like equation
- A novel gold and SiO2 material based planar 5-element high HPBW end-fire antenna array for 300 GHz applications
- Explicit exact solutions and bifurcation analysis for the mZK equation with truncated M-fractional derivatives utilizing two reliable methods
- Optical and laser damage resistance: Role of periodic cylindrical surfaces
- Numerical study of flow and heat transfer in the air-side metal foam partially filled channels of panel-type radiator under forced convection
- Water-based hybrid nanofluid flow containing CNT nanoparticles over an extending surface with velocity slips, thermal convective, and zero-mass flux conditions
- Dynamical wave structures for some diffusion--reaction equations with quadratic and quartic nonlinearities
- Solving an isotropic grey matter tumour model via a heat transfer equation
- Study on the penetration protection of a fiber-reinforced composite structure with CNTs/GFP clip STF/3DKevlar
- Influence of Hall current and acoustic pressure on nanostructured DPL thermoelastic plates under ramp heating in a double-temperature model
- Applications of the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction–diffusion system: Analytical and numerical approaches
- AC electroosmotic flow of Maxwell fluid in a pH-regulated parallel-plate silica nanochannel
- Interpreting optical effects with relativistic transformations adopting one-way synchronization to conserve simultaneity and space–time continuity
- Modeling and analysis of quantum communication channel in airborne platforms with boundary layer effects
- Theoretical and numerical investigation of a memristor system with a piecewise memductance under fractal–fractional derivatives
- Tuning the structure and electro-optical properties of α-Cr2O3 films by heat treatment/La doping for optoelectronic applications
- High-speed multi-spectral explosion temperature measurement using golden-section accelerated Pearson correlation algorithm
- Dynamic behavior and modulation instability of the generalized coupled fractional nonlinear Helmholtz equation with cubic–quintic term
- Study on the duration of laser-induced air plasma flash near thin film surface
- Exploring the dynamics of fractional-order nonlinear dispersive wave system through homotopy technique
- The mechanism of carbon monoxide fluorescence inside a femtosecond laser-induced plasma
- Numerical solution of a nonconstant coefficient advection diffusion equation in an irregular domain and analyses of numerical dispersion and dissipation
- Numerical examination of the chemically reactive MHD flow of hybrid nanofluids over a two-dimensional stretching surface with the Cattaneo–Christov model and slip conditions
- Impacts of sinusoidal heat flux and embraced heated rectangular cavity on natural convection within a square enclosure partially filled with porous medium and Casson-hybrid nanofluid
- Stability analysis of unsteady ternary nanofluid flow past a stretching/shrinking wedge
- Solitonic wave solutions of a Hamiltonian nonlinear atom chain model through the Hirota bilinear transformation method
- Bilinear form and soltion solutions for (3+1)-dimensional negative-order KdV-CBS equation
- Solitary chirp pulses and soliton control for variable coefficients cubic–quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation in nonuniform management system
- Influence of decaying heat source and temperature-dependent thermal conductivity on photo-hydro-elasto semiconductor media
- Dissipative disorder optimization in the radiative thin film flow of partially ionized non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid with second-order slip condition
- Bifurcation, chaotic behavior, and traveling wave solutions for the fractional (4+1)-dimensional Davey–Stewartson–Kadomtsev–Petviashvili model
- New investigation on soliton solutions of two nonlinear PDEs in mathematical physics with a dynamical property: Bifurcation analysis
- Mathematical analysis of nanoparticle type and volume fraction on heat transfer efficiency of nanofluids
- Creation of single-wing Lorenz-like attractors via a ten-ninths-degree term
- Optical soliton solutions, bifurcation analysis, chaotic behaviors of nonlinear Schrödinger equation and modulation instability in optical fiber
- Chaotic dynamics and some solutions for the (n + 1)-dimensional modified Zakharov–Kuznetsov equation in plasma physics
- Fractal formation and chaotic soliton phenomena in nonlinear conformable Heisenberg ferromagnetic spin chain equation
- Single-step fabrication of Mn(iv) oxide-Mn(ii) sulfide/poly-2-mercaptoaniline porous network nanocomposite for pseudo-supercapacitors and charge storage
- Novel constructed dynamical analytical solutions and conserved quantities of the new (2+1)-dimensional KdV model describing acoustic wave propagation
- Tavis–Cummings model in the presence of a deformed field and time-dependent coupling
- Spinning dynamics of stress-dependent viscosity of generalized Cross-nonlinear materials affected by gravitationally swirling disk
- Design and prediction of high optical density photovoltaic polymers using machine learning-DFT studies
- Robust control and preservation of quantum steering, nonlocality, and coherence in open atomic systems
- Coating thickness and process efficiency of reverse roll coating using a magnetized hybrid nanomaterial flow
- Dynamic analysis, circuit realization, and its synchronization of a new chaotic hyperjerk system
- Decoherence of steerability and coherence dynamics induced by nonlinear qubit–cavity interactions
- Finite element analysis of turbulent thermal enhancement in grooved channels with flat- and plus-shaped fins
- Modulational instability and associated ion-acoustic modulated envelope solitons in a quantum plasma having ion beams
- Statistical inference of constant-stress partially accelerated life tests under type II generalized hybrid censored data from Burr III distribution
- On solutions of the Dirac equation for 1D hydrogenic atoms or ions
- Entropy optimization for chemically reactive magnetized unsteady thin film hybrid nanofluid flow on inclined surface subject to nonlinear mixed convection and variable temperature
- Stability analysis, circuit simulation, and color image encryption of a novel four-dimensional hyperchaotic model with hidden and self-excited attractors
- A high-accuracy exponential time integration scheme for the Darcy–Forchheimer Williamson fluid flow with temperature-dependent conductivity
- Novel analysis of fractional regularized long-wave equation in plasma dynamics
- Development of a photoelectrode based on a bismuth(iii) oxyiodide/intercalated iodide-poly(1H-pyrrole) rough spherical nanocomposite for green hydrogen generation
- Investigation of solar radiation effects on the energy performance of the (Al2O3–CuO–Cu)/H2O ternary nanofluidic system through a convectively heated cylinder
- Quantum resources for a system of two atoms interacting with a deformed field in the presence of intensity-dependent coupling
- Studying bifurcations and chaotic dynamics in the generalized hyperelastic-rod wave equation through Hamiltonian mechanics
- A new numerical technique for the solution of time-fractional nonlinear Klein–Gordon equation involving Atangana–Baleanu derivative using cubic B-spline functions
- Interaction solutions of high-order breathers and lumps for a (3+1)-dimensional conformable fractional potential-YTSF-like model
- Hydraulic fracturing radioactive source tracing technology based on hydraulic fracturing tracing mechanics model
- Numerical solution and stability analysis of non-Newtonian hybrid nanofluid flow subject to exponential heat source/sink over a Riga sheet
- Numerical investigation of mixed convection and viscous dissipation in couple stress nanofluid flow: A merged Adomian decomposition method and Mohand transform
- Effectual quintic B-spline functions for solving the time fractional coupled Boussinesq–Burgers equation arising in shallow water waves
- Analysis of MHD hybrid nanofluid flow over cone and wedge with exponential and thermal heat source and activation energy
- Solitons and travelling waves structure for M-fractional Kairat-II equation using three explicit methods
- Impact of nanoparticle shapes on the heat transfer properties of Cu and CuO nanofluids flowing over a stretching surface with slip effects: A computational study
- Computational simulation of heat transfer and nanofluid flow for two-sided lid-driven square cavity under the influence of magnetic field
- Irreversibility analysis of a bioconvective two-phase nanofluid in a Maxwell (non-Newtonian) flow induced by a rotating disk with thermal radiation
- Hydrodynamic and sensitivity analysis of a polymeric calendering process for non-Newtonian fluids with temperature-dependent viscosity
- Exploring the peakon solitons molecules and solitary wave structure to the nonlinear damped Kortewege–de Vries equation through efficient technique
- Modeling and heat transfer analysis of magnetized hybrid micropolar blood-based nanofluid flow in Darcy–Forchheimer porous stenosis narrow arteries
- Activation energy and cross-diffusion effects on 3D rotating nanofluid flow in a Darcy–Forchheimer porous medium with radiation and convective heating
- Insights into chemical reactions occurring in generalized nanomaterials due to spinning surface with melting constraints
- Influence of a magnetic field on double-porosity photo-thermoelastic materials under Lord–Shulman theory
- Soliton-like solutions for a nonlinear doubly dispersive equation in an elastic Murnaghan's rod via Hirota's bilinear method
- Analytical and numerical investigation of exact wave patterns and chaotic dynamics in the extended improved Boussinesq equation
- Nonclassical correlation dynamics of Heisenberg XYZ states with (x, y)-spin--orbit interaction, x-magnetic field, and intrinsic decoherence effects
- Exact traveling wave and soliton solutions for chemotaxis model and (3+1)-dimensional Boiti–Leon–Manna–Pempinelli equation
- Unveiling the transformative role of samarium in ZnO: Exploring structural and optical modifications for advanced functional applications
- On the derivation of solitary wave solutions for the time-fractional Rosenau equation through two analytical techniques
- Analyzing the role of length and radius of MWCNTs in a nanofluid flow influenced by variable thermal conductivity and viscosity considering Marangoni convection
- Advanced mathematical analysis of heat and mass transfer in oscillatory micropolar bio-nanofluid flows via peristaltic waves and electroosmotic effects
- Exact bound state solutions of the radial Schrödinger equation for the Coulomb potential by conformable Nikiforov–Uvarov approach
- Some anisotropic and perfect fluid plane symmetric solutions of Einstein's field equations using killing symmetries
- Nonlinear dynamics of the dissipative ion-acoustic solitary waves in anisotropic rotating magnetoplasmas
- Curves in multiplicative equiaffine plane
- Exact solution of the three-dimensional (3D) Z2 lattice gauge theory
- Propagation properties of Airyprime pulses in relaxing nonlinear media
- Symbolic computation: Analytical solutions and dynamics of a shallow water wave equation in coastal engineering
- Wave propagation in nonlocal piezo-photo-hygrothermoelastic semiconductors subjected to heat and moisture flux
- Comparative reaction dynamics in rotating nanofluid systems: Quartic and cubic kinetics under MHD influence
- Laplace transform technique and probabilistic analysis-based hypothesis testing in medical and engineering applications
- Physical properties of ternary chloro-perovskites KTCl3 (T = Ge, Al) for optoelectronic applications
- Gravitational length stretching: Curvature-induced modulation of quantum probability densities
- The search for the cosmological cold dark matter axion – A new refined narrow mass window and detection scheme
- A comparative study of quantum resources in bipartite Lipkin–Meshkov–Glick model under DM interaction and Zeeman splitting
- PbO-doped K2O–BaO–Al2O3–B2O3–TeO2-glasses: Mechanical and shielding efficacy
- Nanospherical arsenic(iii) oxoiodide/iodide-intercalated poly(N-methylpyrrole) composite synthesis for broad-spectrum optical detection
- Sine power Burr X distribution with estimation and applications in physics and other fields
- Numerical modeling of enhanced reactive oxygen plasma in pulsed laser deposition of metal oxide thin films
- Dynamical analyses and dispersive soliton solutions to the nonlinear fractional model in stratified fluids
- Computation of exact analytical soliton solutions and their dynamics in advanced optical system
- An innovative approximation concerning the diffusion and electrical conductivity tensor at critical altitudes within the F-region of ionospheric plasma at low latitudes
- An analytical investigation to the (3+1)-dimensional Yu–Toda–Sassa–Fukuyama equation with dynamical analysis: Bifurcation
- Swirling-annular-flow-induced instability of a micro shell considering Knudsen number and viscosity effects
- Numerical analysis of non-similar convection flows of a two-phase nanofluid past a semi-infinite vertical plate with thermal radiation
- MgO NPs reinforced PCL/PVC nanocomposite films with enhanced UV shielding and thermal stability for packaging applications
- Optimal conditions for indoor air purification using non-thermal Corona discharge electrostatic precipitator
- Investigation of thermal conductivity and Raman spectra for HfAlB, TaAlB, and WAlB based on first-principles calculations
- Tunable double plasmon-induced transparency based on monolayer patterned graphene metamaterial
- DSC: depth data quality optimization framework for RGBD camouflaged object detection
- A new family of Poisson-exponential distributions with applications to cancer data and glass fiber reliability
- Numerical investigation of couple stress under slip conditions via modified Adomian decomposition method
- Monitoring plateau lake area changes in Yunnan province, southwestern China using medium-resolution remote sensing imagery: applicability of water indices and environmental dependencies
- Heterodyne interferometric fiber-optic gyroscope
- Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations via homothetic symmetries of non-static plane symmetric spacetime
- A widespread study of discrete entropic model and its distribution along with fluctuations of energy
- Empirical model integration for accurate charge carrier mobility simulation in silicon MOSFETs
- The influence of scattering correction effect based on optical path distribution on CO2 retrieval
- Anisotropic dissociation and spectral response of 1-Bromo-4-chlorobenzene under static directional electric fields
- Role of tungsten oxide (WO3) on thermal and optical properties of smart polymer composites
- Analysis of iterative deblurring: no explicit noise
- Review Article
- Examination of the gamma radiation shielding properties of different clay and sand materials in the Adrar region
- Erratum
- Erratum to “On Soliton structures in optical fiber communications with Kundu–Mukherjee–Naskar model (Open Physics 2021;19:679–682)”
- Special Issue on Fundamental Physics from Atoms to Cosmos - Part II
- Possible explanation for the neutron lifetime puzzle
- Special Issue on Nanomaterial utilization and structural optimization - Part III
- Numerical investigation on fluid-thermal-electric performance of a thermoelectric-integrated helically coiled tube heat exchanger for coal mine air cooling
- Special Issue on Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos in Physical Systems
- Analysis of the fractional relativistic isothermal gas sphere with application to neutron stars
- Abundant wave symmetries in the (3+1)-dimensional Chafee–Infante equation through the Hirota bilinear transformation technique
- Successive midpoint method for fractional differential equations with nonlocal kernels: Error analysis, stability, and applications
- Novel exact solitons to the fractional modified mixed-Korteweg--de Vries model with a stability analysis

