Abstract
The aim of this study is to analyze scientific literature to investigate the current research status, focus areas, and developmental trends in nanoparticle systems for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy. To do that, Research articles published from 2003 to 2023 were retrieved from the Web of Science database, and analysis included quantitative output, distribution by country/region, collaborative publishing data, influential authors, high-yield institutions, keywords, hotspots, and development trends. Visual knowledge maps were generated using VOSviewer and Citespace. Findings reveal a steady increase in publications related to nanoparticle systems for RA therapy, indicating growing global interest. China leads with 487 papers (37.433%), followed by the United States (233, 17.909%), India (179, 13.759%), South Korea (89, 6.841%), and Egypt (50, 3.843%). Active collaboration is observed, particularly between the United States and countries such as China, Germany, Saudi Arabia, India, England, and Pakistan. The Chinese Academy of Sciences ranks first in total articles published (55), with Liu Y from China being the most prolific author. The Journal of Controlled Release emerges as a primary outlet in this field. Primary keyword clusters include “Drug delivery systems,” “Gold nanoparticles,” “Transdermal delivery,” “Angiogenesis,” “Collagen-induced arthritis,” “Rheumatoid arthritis,” “Oxidant stress,” “Dendritic cells,” and “pH sensitive.” Research hotspots with great development potential include “Immunopathological Mechanisms,” “Novel drugs,” and “Smart delivery system.” In conclusion, research on nanoparticle systems for RA therapy has significantly expanded over the past two decades, with a focus on elucidating pathogenetic mechanisms and advancing novel drug delivery strategies anticipated to be prominent in the foreseeable future.
1 Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic synovitis, which leads to joint inflammation, synovial hyperplasia, pannus formation, and the destruction of bones and cartilage [1,2]. It affects approximately 1% of the world’s population, with a higher prevalence among females. The epidemiological data on RA based on geographic region and ethnicity is limited, though the female-to-male ratio is around 2:1 [3–7], and the estimated annual incidence is 12 per 100,000 patient-years in East Asia [8]. RA’s prevalence and disease burden vary across geographic regions, generally higher in industrialized countries and urban settings. Common clinical manifestations include persistent arthritis pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential complications such as cardiovascular, pulmonary, psychological, and bone diseases [9,10]. RA is a persistent, progressive, systemic pathology, often associated with autoantibodies like rheumatoid factor and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies [11]. The pathogenesis of RA is believed to involve fibroblasts and cytokines, leading to chronic inflammation, bone erosion, and tissue destruction in the synovial tissue, resulting in various clinical symptoms and injuries [12,13]. Moreover, systemic inflammation can affect multiple organ systems, including the heart, vascular system, kidneys, lungs, and nervous system.
The current therapies for RA are categorized into four mainstream management options: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), glucocorticoids, nonbiological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biological DMARDs [14]. However, each drug grouping faces significant challenges, including limited bioavailability, high clearance, and varying degrees of toxicity to normal tissues. While medications like NSAIDs and corticosteroids effectively relieve stiffness and pain, they do not slow disease progression. Over the past 20 years, DMARDs have garnered attention for their effectiveness in reducing disease activity and joint deformity [15]. These include traditional synthetic drugs, biological DMARDs, and novel small molecules. Established DMARDs such as gold onofin, minocycline, azathioprine, and cyclosporine are rarely used in modern therapies. Recent years have seen the emergence of several biological DMARDs, including TNF inhibitors, anti-CD20 antibodies, IL-6 receptor antibodies, RANKL antibodies, and JAK inhibitors [16]. Despite the growing number of treatment options, achieving complete long-term disease remission remains challenging for many patients. While most patients can achieve clinical remission after treatment, some develop refractory RA, requiring lifelong medication. Moreover, RA treatments not only delay the disease but also cause significant adverse effects that can be financially and physically burdensome for patients. Given RA’s chronic nature and its need for new therapeutic approaches, there is a pressing need to explore innovative treatments.
In addition to conventional treatments, structured nanoparticle delivery systems can enhance therapeutic efficacy by prolonging the residence time of the drug [17,18]. Nanotechnology offers advanced carrier systems, notably impacting the delivery of various therapeutic agents, including small molecules, RNA, genes, peptides, and diagnostic imaging agents, thereby improving drug stability and pharmacokinetics [19,20]. Hybridized nanoparticles represent the latest generation of delivery systems, integrating lipid-based and polymeric nanocarriers to combine benefits such as incorporating hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, improving stability, and enhancing efficacy [21–23]. In a study published in Nature Nanotechnology, Fang and Zhang reported a multifunctional biosynthesized hybridized nanoparticle formulation with promising potential for treating RA [24]. This formulation, known as Ce-MSCNV, consists of small cerium nanoparticles attached to mesenchymal stem cell nanovesicles [24,25]. Cerium nanoparticles exhibit antioxidant properties, scavenging excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) associated with pathologic inflammation [26,27]. The formulation effectively reduces RA-induced ROS production and modulates macrophage polarization, providing immediate relief from inflammation. Stem cell vesicles deliver immunomodulatory cytokines, promoting immune tolerance and durable disease resolution [28,29]. The combined action of cerium nanoparticles and stem cell vesicles creates a synergistic effect, rapidly treating damaged joints, modulating immune responses, and rebalancing the TH17/Treg cell ratio [30–32]. Overall, as a nano-hybrid therapeutic system with detailed immunomodulation, Ce-MSCNV offers an effective multifactorial approach to treating RA compared to monotherapy.
Chen et al. synthesized macrophage mimetic nanoparticles (M@P-siRNAsT/I) and utilized macrophage mimetic vesicles (MMV) as a delivery vehicle for polymeric biodegradable nanoparticles (PBNPs) and small interfering RNAs targeting tumor necrosis factor (siRNAsT/I) to investigate their potential in treating RA under imaging observation. In their study, they discovered that PBNPs possess catalase functionality, facilitating the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide while simultaneously generating oxygen [33]. The specific gene silencing ability of siRNAsT/I enables M@P-siRNAsT/I to significantly inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 in a statistically significant manner [34]. Incorporation of PBNPs and siRNAsT/I into MMV improved its stability and biocompatibility. Both photoacoustic (PA) imaging and fluorescence imaging demonstrated effective targeting of RA by M@P-siRNAsT/I, both in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, label-free multispectral PA imaging, micro-CT, and histological analysis indicated that M@P-siRNAsT/I induced statistically significant therapeutic effects for RA, including joint erosion improvement, hypoxia inhibition, and anti-inflammatory effects. Additionally, M@P-siRNAsT/I exhibited a favorable biosafety profile in both in vitro and in vivo evaluations. These findings suggest that M@P-siRNAsT/I may have potential in PA image-guided therapy for RA.
Despite the considerable research conducted on therapeutic aspects of RA, there remains a noticeable absence of comprehensive and meaningful analyses regarding published trends in the field. Therefore, it is crucial to integrate the current focus and frontiers in nanoparticle systems for RA therapy before pursuing additional basic and clinical research. Bibliometrics employs quantitative analysis using mathematical and statistical methods to review published research findings, offering researchers objective scientific indicators to monitor quantitative changes, distributions, and patterns in existing literature [35,36]. Currently, the extent and depth of nanoparticle research in RA therapy are largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, a dedicated study is underway to compile the current status of joint distraction in RA therapy research, predict prospective keywords and frontiers, and assist researchers in identifying prevailing research trends and frontiers in this emerging field.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data acquisition and search strategies
Publications pertaining to nanoparticle research in RA treatment were retrieved using the SCI Extension database within the Web of Science Core Collection by Clarivate Analytics. Subsequently, studies related to nanoparticle systems for RA therapy were identified, and bibliometric and visualization analyses were conducted following established methodologies from previous studies. The search parameters were set from January 1, 2003, to December 31, 2023, with the search formula structured as follows: TS = (rheumatoid arthritis) AND TS = (nanoparticles OR nanospheres OR nanospheres OR nanoparticles OR Spherical nanoparticles OR Spherical nanoparticle OR Nanoscale particles OR Nanoscale particle). Additionally, the publication criteria included: [1] publications primarily focused on nanoparticles in RA therapeutics, [2] literature types limited to articles and reviews, and [3] papers written in English. The exclusion criteria included: [1] publications that were not related to immunology research in the context of RA; [2] articles classified as meeting abstracts, conference proceedings, corrections, book chapters, letters, news articles, or similar non-peer-reviewed content (Figure 1). For the included studies, we extracted comprehensive data, including the publication year, title, authorship, nationalities, affiliations, abstract, keywords, and journal names. This information was saved in .txt format for subsequent analysis. Data extraction was carried out independently by coauthors Xie and Liao. Any disagreements were resolved through consultation with experts to reach a consensus. The final dataset was imported into CiteSpace and VOSviewer for visualization and bibliometric analysis, ensuring a robust and transparent approach toward data handling and analysis in accordance with PRISMA guidelines.
Flowchart depicting the literature selection process.
The authors extracted basic information regarding the publications, including details such as journals, titles, authors, keywords, institutions, countries/regions, publication dates, as well as comprehensive statistics such as total citations, H-index, and average citation counts. This information was then imported into Excel 2021. Subsequently, bibliometric analyses and visualizations were conducted using a suite of software applications, including GraphPad Prism 8, Origin 2021, and VOSviewer (version 1.6.14, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands) [37], and CiteSpace (version 6.2.4) [38]. These tools played a pivotal role in dissecting and visualizing the intricate landscape of publications related to nanoparticle systems for RA therapy, offering a comprehensive perspective on the scholarly contributions in this domain.
2.2 Bibliometric analysis and visualization
Bibliometrics entails studying interconnected bodies of literature. It involves analyzing and visualizing links between research topics, researchers, affiliations, or journals. Initially, annual publication trends and relative research interest (RRI) were graphically represented using the curve-fitting function in GraphPad Prism 8. RRI is calculated as the number of papers in a specific field divided by the total number of papers in all fields in a given year, offering insights into the prominence of the field relative to others. For the world map analysis, a methodology based on previous research was utilized [39]. Furthermore, the total number of publications for the top ten countries between 2003 and 2023, along with global trend projections, were analyzed using Origin 2021 software.
An in-depth examination of pertinent studies was undertaken utilizing VOSviewer and Citespace software tools to elucidate collaborations (co-authors), themes (terminology co-occurrence), and citation patterns (bibliographic coupling). This entailed scrutinizing country/region and institution collaborations, overlaying journal biplots, analyzing author collaborations, investigating co-cited authors, and performing cluster analyses. Furthermore, co-cited references and keywords were meticulously identified and assessed to highlight those with significantly higher citations. By configuring relevant parameters as described above, the analysis ensured robust and precise exploration of a substantial volume of literature data pertaining to nanoparticle systems for RA therapy.
Moreover, this investigation utilized VOSviewer to construct and visualize the bibliometric network, facilitating the acquisition of more comprehensive insights, including (1) co-citation analysis of journals and references, and (2) keyword co-occurrence analysis. In the graphical representation produced by VOSviewer, each node corresponds to an entity containing co-cited references and keywords. The node’s size corresponds to the number of publications associated with it, while its color denotes the corresponding publication year. The thickness of the connecting lines between nodes indicates the strength of collaborative or co-citation relationships, offering an intuitively visual portrayal of the intricate interconnections within bibliographic data. This approach enhances the depth of understanding regarding thematic and conceptual associations within the realm of nanoparticle systems for RA therapy.
3 Results
3.1 Global contribution to the field
Based on a meticulously crafted publication search strategy (outlined in Figure 1), a total of 1,301 publications met the established criteria and were included in the final analysis. The number of publications per year from 2003 to 2023 exhibited a gradual and fluctuating trend, surging from a modest 4 articles to an impressive 215+ articles (as depicted in Figure 2a). Concurrently, the RRI demonstrated a relatively stable trend around the baseline level over the same period (as illustrated in Figure 2a). Overall, contributions in the field of RA therapeutic research involving nanoparticles emanated from 73 different countries/regions. Remarkably, China led the way with the largest share of 487 publications, constituting 37.43% of the total. This was followed by the USA (233 publications, 17.91%), India (179 publications, 13.76%), and South Korea (89 publications, 6.84%) (depicted in Figure 2b and c). Furthermore, Figure 2d underscores the evolving landscape of publication contributions, with China taking the lead from 2015 to 2023 by surpassing the United States, continually achieving new highs and forging ahead. However, in recent years, other countries have also made significant strides and remain competitive in advancing research endeavors.
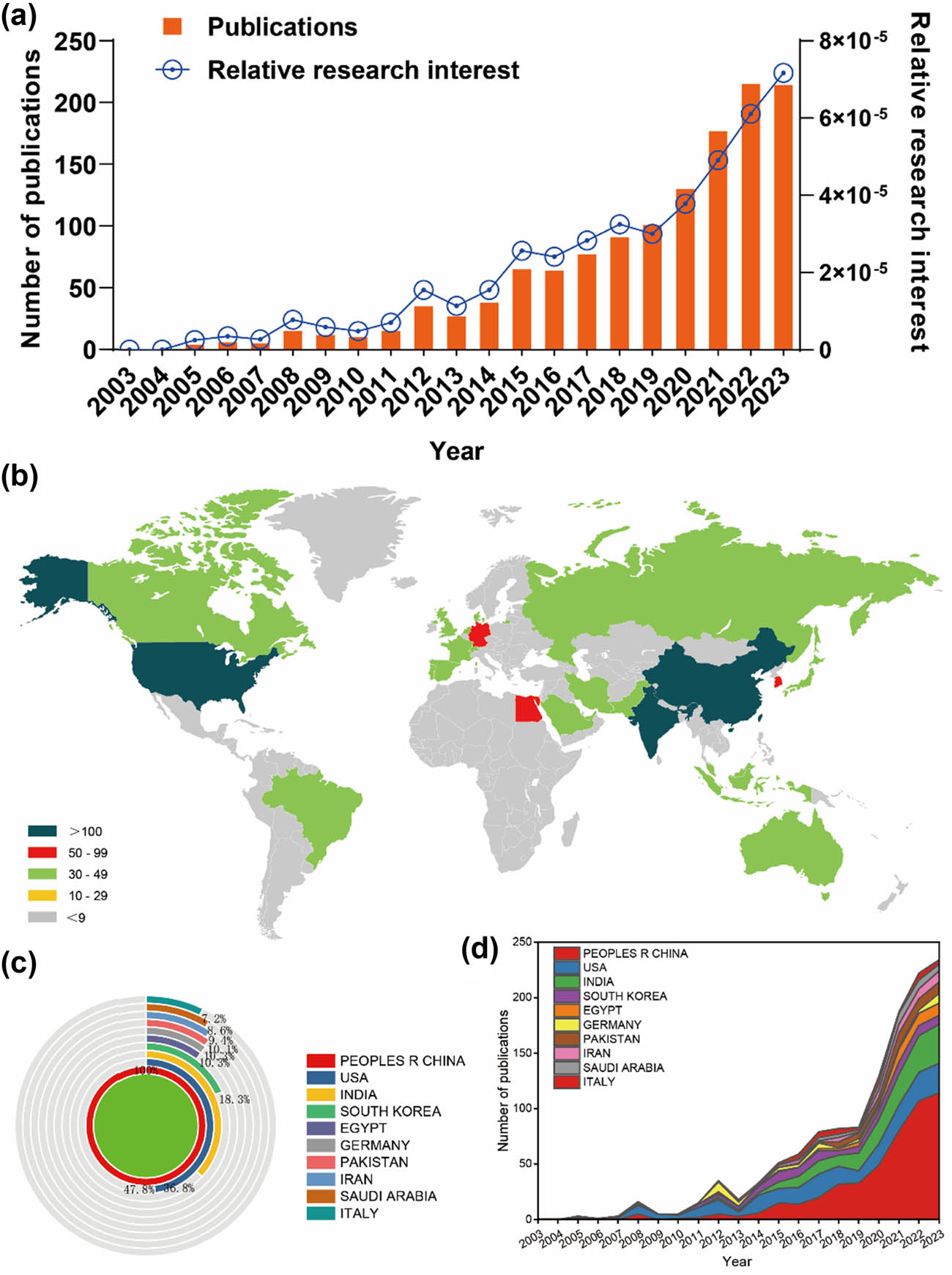
Global trends and the geographical landscape of research on nanoparticles in RA. (a) Annual publication statistics concerning nanoparticles in RA research. (b) A global map illustrating the dispersion of such research. The cumulative (c) and yearly (d) publication counts across the top ten most prolific countries between 2013 and 2023.
3.2 Distribution of countries/regions and institutions
All 1,301 publications originated from a diverse array of 73 countries and engaged 1,760 distinct organizations. Notably, the top ten countries/regions exhibit extensive global distribution, primarily spanning North America, Asia, and Western Europe (Figure 2b). China emerges as a particularly formidable contributor, representing over one-third of the total publications, markedly surpassing other nations. Furthermore, Figure 3 illustrates that the USA garners the highest total number of citations (12,496) and boasts a notable H index of 56, surpassing all other countries. With the highest average citation rate (53.63), the USA, along with Germany and South Korea, solidifies their pivotal positions in publications. Together, these three countries account for more than 27% of the total publications, underscoring their considerable influence in the field. Subsequently, the collaborative patterns between countries/regions are depicted in Figure 4a, with China demonstrating robust collaboration, as evidenced by the size of its node.
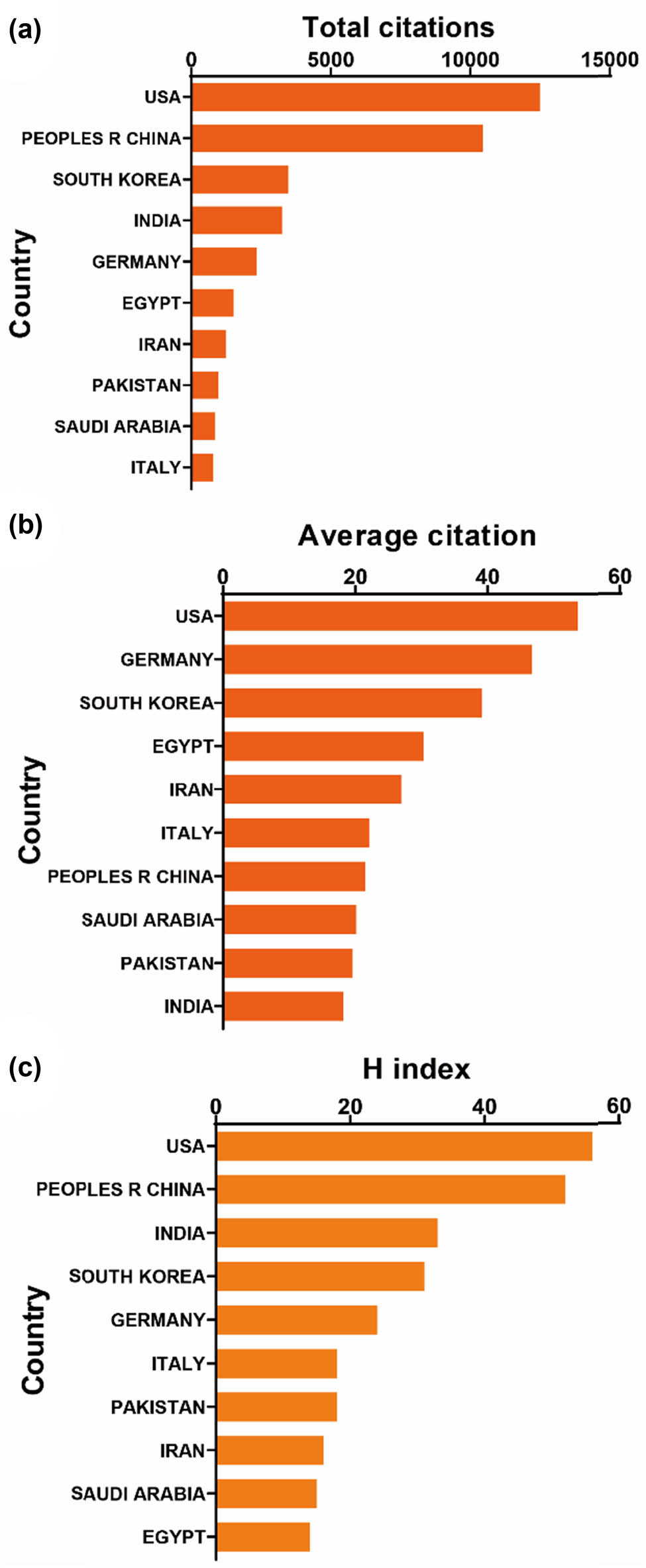
(a) The top ten countries/regions with the highest total citations in research on nanoparticles for RA. (b) The top ten countries/regions with the highest average citations per publication in research on nanoparticles for RA. (c) The top ten countries/regions with the highest publication H-index in research on nanoparticles for RA.
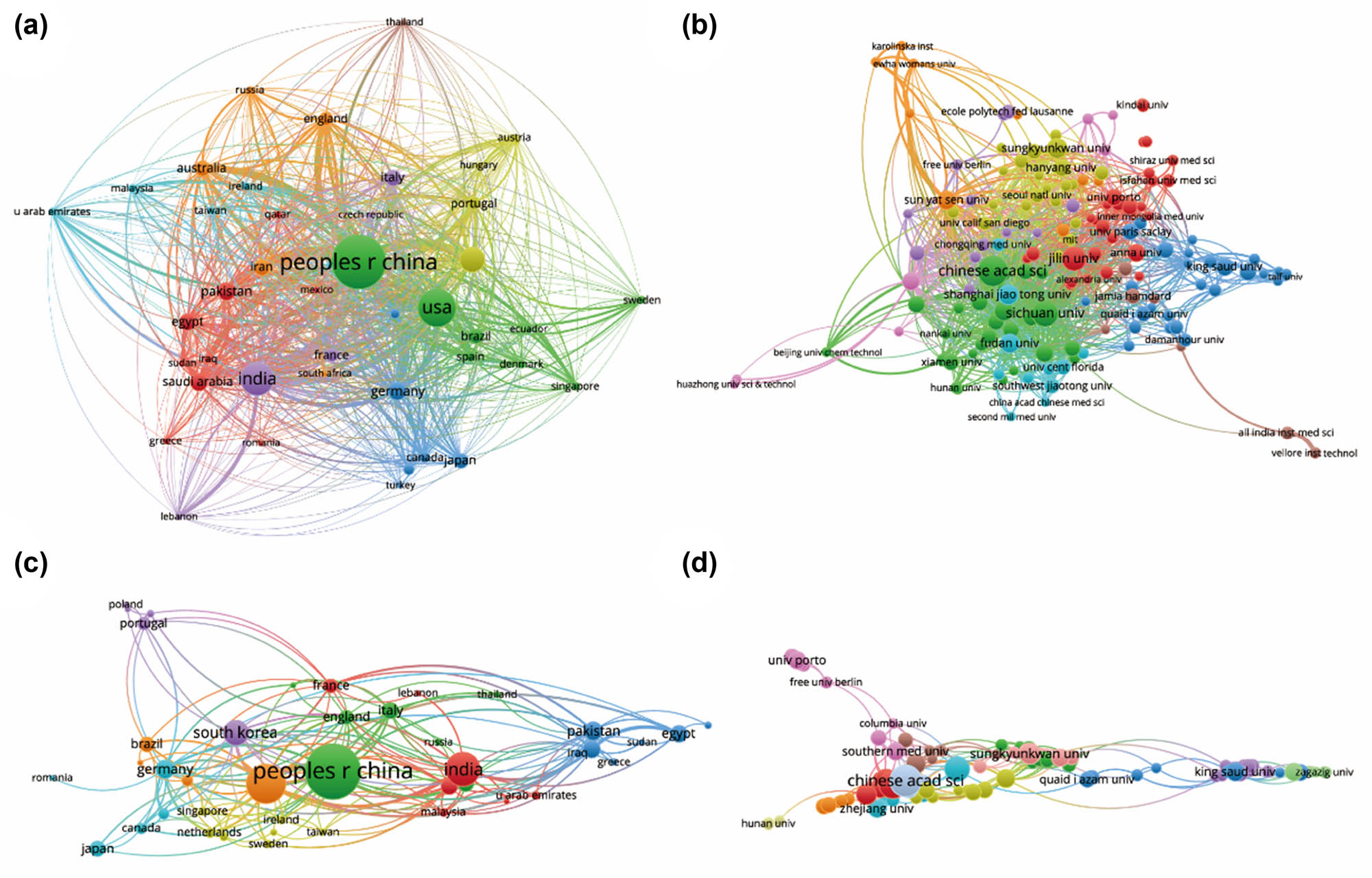
Mapping the involvement of countries, regions, and institutions in research on nanoparticles for RA. (a) Examination of country and regional collaborations utilizing VOSviewer. (b) Assessment of institutional collaborations using VOSviewer. (c) Analysis of authorship-country collaborations via VOSviewer. (d) Evaluation of authorship-institution collaborations via VOSviewer. Node sizes represent countries/regions, scaled by their publication counts. Connecting lines indicate collaboration, with thickness reflecting the strength of cooperation; thicker lines denote closer collaboration.
As demonstrated in Table 1, the top ten most productive institutions are prominently situated in China, Egypt, France, America, and South Korea. It is noteworthy that despite not leading in total publications, Harvard University boasts a significantly higher average citation rate compared to other institutions. Moreover, the analysis of institutional collaborations, as depicted in Figure 4b, highlights Sichuan University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences as leaders in collaborations with other research entities.
Top ten institutions published literature related to nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Institution | Article counts | Percentage (%) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 55 | 4.228 | China |
| 2 | Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB) | 50 | 3.843 | Egypt |
| 3 | Sichuan University | 36 | 2.767 | China |
| 4 | Jilin University | 27 | 2.075 | China |
| 5 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique | 23 | 1.768 | France |
| 6 | Shanghai Jiao Tong University | 23 | 1.768 | China |
| 7 | Harvard University | 21 | 1.614 | |
| 8 | Southern Medical University China | 20 | 1.537 | China |
| 9 | Fudan University | 19 | 1.46 | China |
| 10 | Sungkyunkwan University | 19 | 1.46 | South Korea |
Table 2 delineates the top ten funders in terms of the number of articles published in the field of nanoparticles in RA studies, with the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) clinching the top spot with a substantial number of 313 articles, accounting for 24.06%. This is followed by the National Institutes of Health (USA) and the United States Department of Health and Human Services, both with 94 articles (7.23%). Subsequent to these, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation follows closely with 42 articles (3.23%). Support from these relevant organizations has significantly contributed to the advancement of research in this area.
Top ten funds related to nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Journal | Article counts | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | National Natural Science Foundation of China | 313 | 24.058 |
| 2 | National Institutes of Health (USA) | 94 | 7.225 |
| 3 | United States Department of Health Human Services | 94 | 7.225 |
| 4 | China Postdoctoral Science Foundation | 42 | 3.228 |
| 5 | European Union | 39 | 2.998 |
| 6 | National Research Foundation of Korea | 34 | 2.613 |
| 7 | National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province | 25 | 1.922 |
| 8 | Fundamental Research Funds for The Central Universities | 24 | 1.845 |
| 7 | National Science Foundation | 23 | 1.768 |
| 10 | Fundacao Para A Ciencia E a Tecnologia Fct | 20 | 1.537 |
3.3 Analysis of journals and research areas
Between 2003 and 2023, a total of 1,301 articles were published across 443 journals. Table 3 highlights the top ten journals with the highest number of publications alongside their most recent impact factors (IF). Leading the pack is the Journal of Controlled Release with 47 publications, constituting 3.613% of all articles, followed by the International Journal of Pharmaceutics (41 publications, 3.151%), International Journal of Nanomedicine (30 articles, 2.306%), Pharmaceutics (28 articles, 2.152%), and Biomaterials (27 articles, 2.075%). Remarkably, among these top ten journals, ACS Nano boasted the highest IF of 17.1, trailed closely by Biomaterials (14.0) and Journal of Controlled Release (10.8). The distribution of articles across various journals focusing on nanoparticles in RA research is depicted in Figure 5a–d.
Top ten most productive journals related to nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Journal | Articles count | Percentage (%) | IF (2023) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Journal of Controlled Release | 47 | 3.613 | 10.8 |
| 2 | International Journal of Pharmaceutics | 41 | 3.151 | 5.8 |
| 3 | International Journal of Nanomedicine | 30 | 2.306 | 8.0 |
| 4 | Pharmaceutics | 28 | 2.152 | 5.4 |
| 5 | Biomaterials | 27 | 2.075 | 14.0 |
| 6 | Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology | 24 | 1.845 | 5.0 |
| 7 | ACS Nano | 18 | 1.384 | 17.1 |
| 8 | Journal of Materials Chemistry B | 18 | 1.384 | 7.0 |
| 9 | ACS Applied Materials Interfaces | 17 | 1.307 | 9.5 |
| 10 | Drug Delivery | 17 | 1.307 | 6.0 |
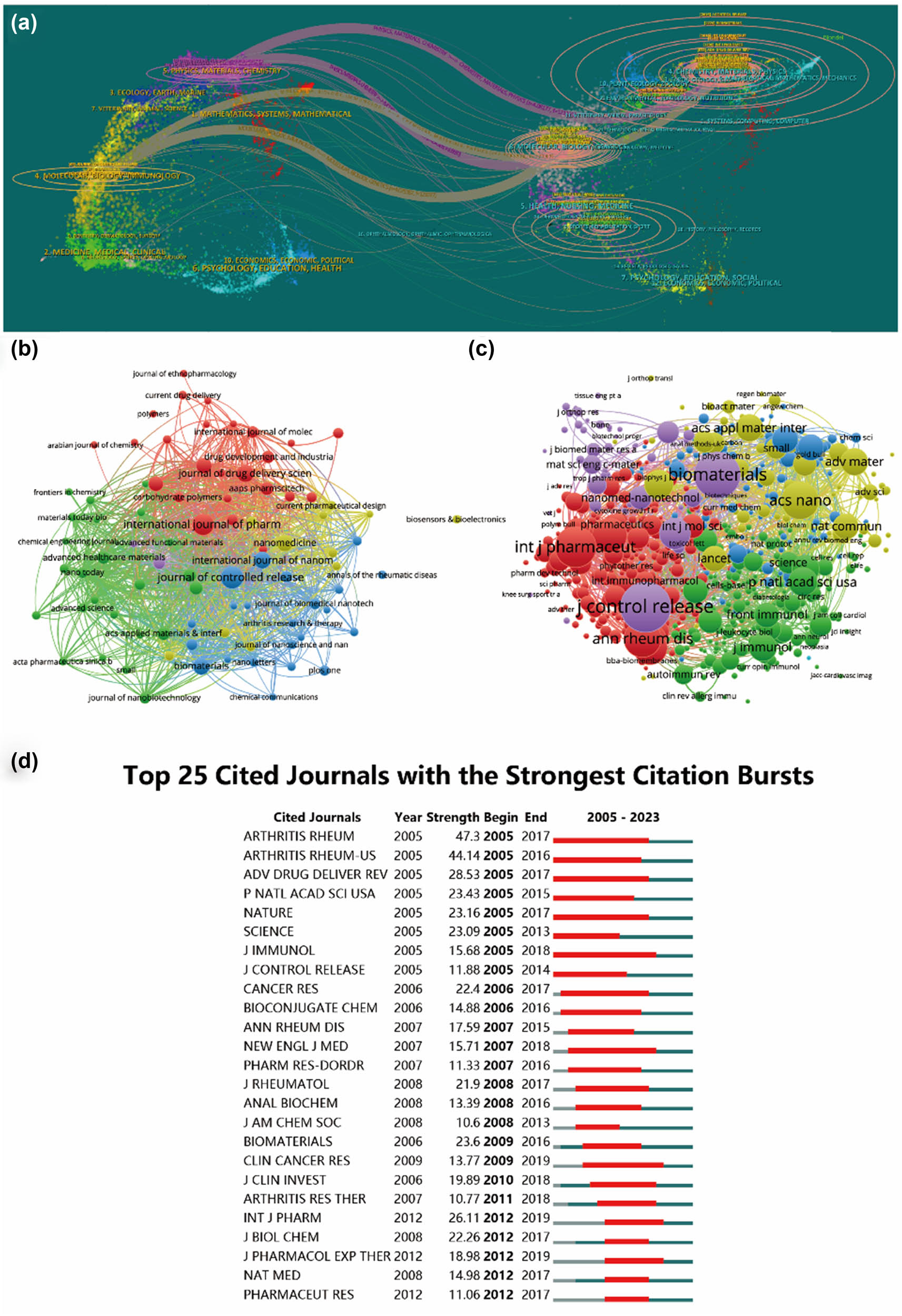
Articles published in various journals on nanoparticles in RA research. (a) Dual-map overlay showcasing journals relevant to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine for rotator cuff injuries. (b) Bibliographic analysis of journals using VOSviewer. (c) Network map illustrating journals that were co-cited, as analyzed by VOSviewer. (d) Presentation of the top 25 cited journals exhibiting the most significant citation bursts in related publications.
Moreover, the identified publications were categorized into 62 different research areas. Among the top ten most represented research areas, Pharmacology Pharmacy accounted for the majority with 455 records, comprising 34.973% of all articles, followed by Chemistry (350 or 26.902%) and Materials Science (347 or 26.672%) (as illustrated in Table 4). Additionally, Figure 5a features a bi-map overlay of journals to demonstrate those related to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine for rotator cuff injuries.
Top ten well-represented research areas
| Rank | Research areas | Records | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pharmacology pharmacy | 455 | 34.973 |
| 2 | Chemistry | 350 | 26.902 |
| 3 | Materials science | 347 | 26.672 |
| 4 | Science technology and other topics | 303 | 23.29 |
| 5 | Engineering | 119 | 9.147 |
| 6 | Biochemistry and molecular biology | 104 | 7.994 |
| 7 | Research experimental medicine | 93 | 7.148 |
| 8 | Physics | 81 | 6.226 |
| 9 | Biotechnology applied microbiology | 70 | 5.38 |
| 10 | Immunology | 62 | 4.766 |
3.4 Authors analysis
Table 5 enumerates the top ten authors who have made noteworthy contributions in the realm of nanoparticles in RA research. Foremost among them is Liu Y, with 20 publications, closely trailed by Park JH, Wang Q, and Zhang Y, each with 17 publications. Furthermore, to visually depict collaborative relationships between researchers, author collaborations were analyzed and presented in Figure 6. Additionally, a co-cited author network visualization graph (Figure 6b and c) was generated. In these visualizations, nodes represent authors, with their size corresponding to the number of collaborations, while lines between nodes signify collaboration connections. Figure 6d showcases the top 25 cited authors, all of whom have significantly influenced research in their respective fields.
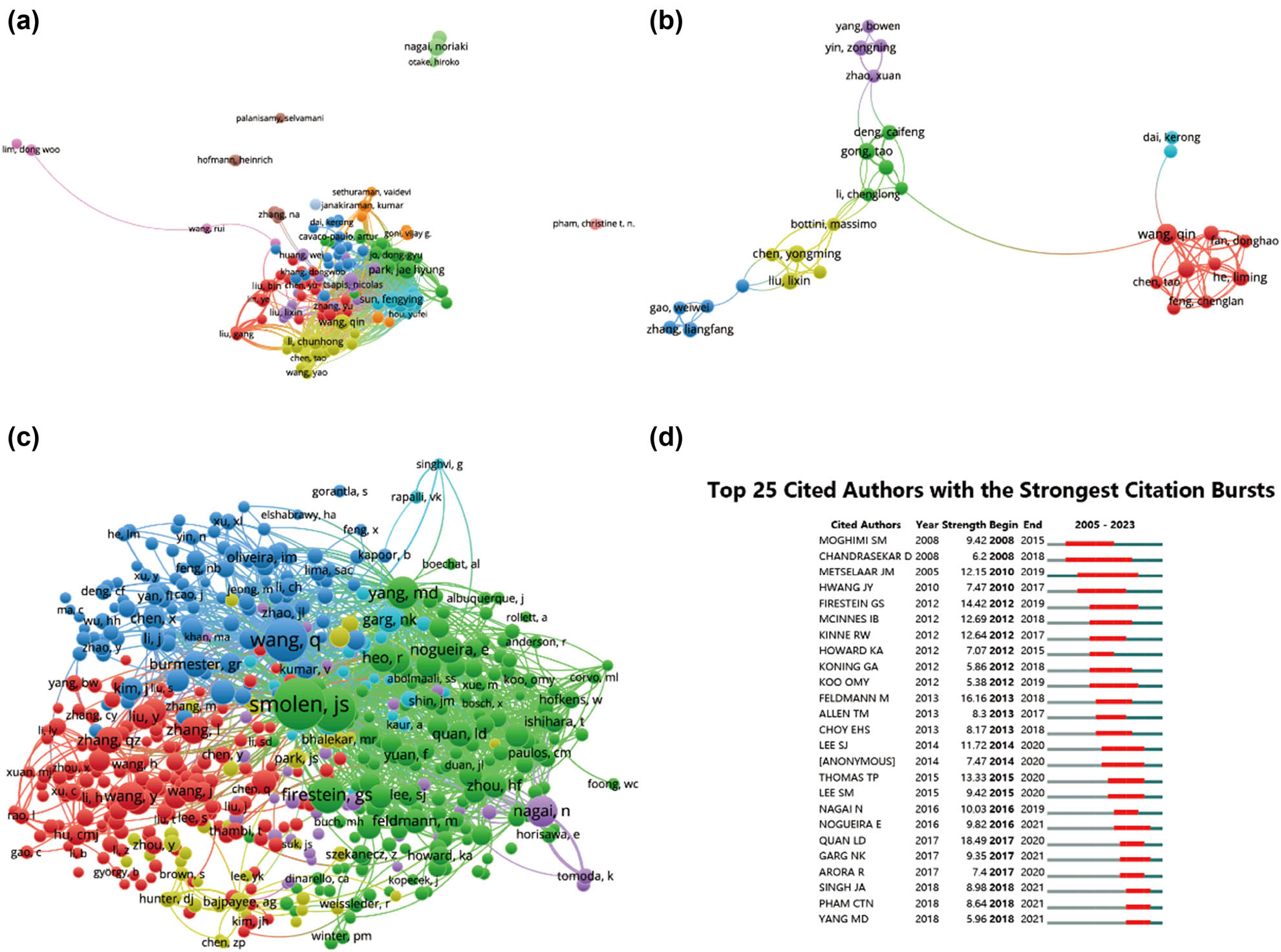
Network visualization of author collaboration in nanoparticle research for RA. (a) Author collaboration analysis conducted using VOSviewer. (b) Network visualization diagram illustrating authorship–author relationships according to VOSviewer analysis. (c) Network visualization diagram depicting co-cited-author relationships based on VOSviewer analysis. (d) Presentation of the top 25 cited authors exhibiting the most significant citation bursts in publications related to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine for rotator cuff injuries. Author collaborations are represented by nodes, with node size proportional to the number of collaborations. Collaboration connections are depicted by lines between nodes.
3.5 Citation and co-citation analysis of reference
We conducted a thorough analysis of the literature in the field, focusing on papers with over 25 citations, totaling 106 articles, which were then visualized using VOSviewer (as depicted in Figure 7a). Table 6 provides details of the top ten cited research papers. Topping the list is “In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags,” which amassed the highest number of citations at 1,972. Following closely is “Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles inhibit synovial inflammation and alleviate joint damage in inflammatory arthritis,” securing second place with 516 citations. In third place is “Antiangiogenic properties of gold nanoparticles,” garnering 378 citations. Additionally, Table 7 outlines the top ten cited review articles. Both “Impact of albumin on drug delivery - New applications on the horizon” and “Biological properties of ‘naked’ metal nanoparticles” received the highest number of citations, each accumulating 650. Subsequently, “Clinical impact of serum proteins on drug delivery” secured third place with 292 citations. The fourth most cited paper was “Cell penetrating peptides: a concise review with emphasis on biomedical applications,” with 222 citations. Moreover, references with citation bursts can serve as valuable indicators of frequently cited literature in a specific field over time [40]. In this study, Figure 7b illustrates the top 25 references that demonstrated the most significant citation bursts, along with the corresponding duration of these bursts. Notably, the article “Targeted delivery of low-dose dexamethasone using PCL- PEG micelles for effective treatment of rheumatoid arthritis,” published in 2016, topped the list with an intensity of 15.53.
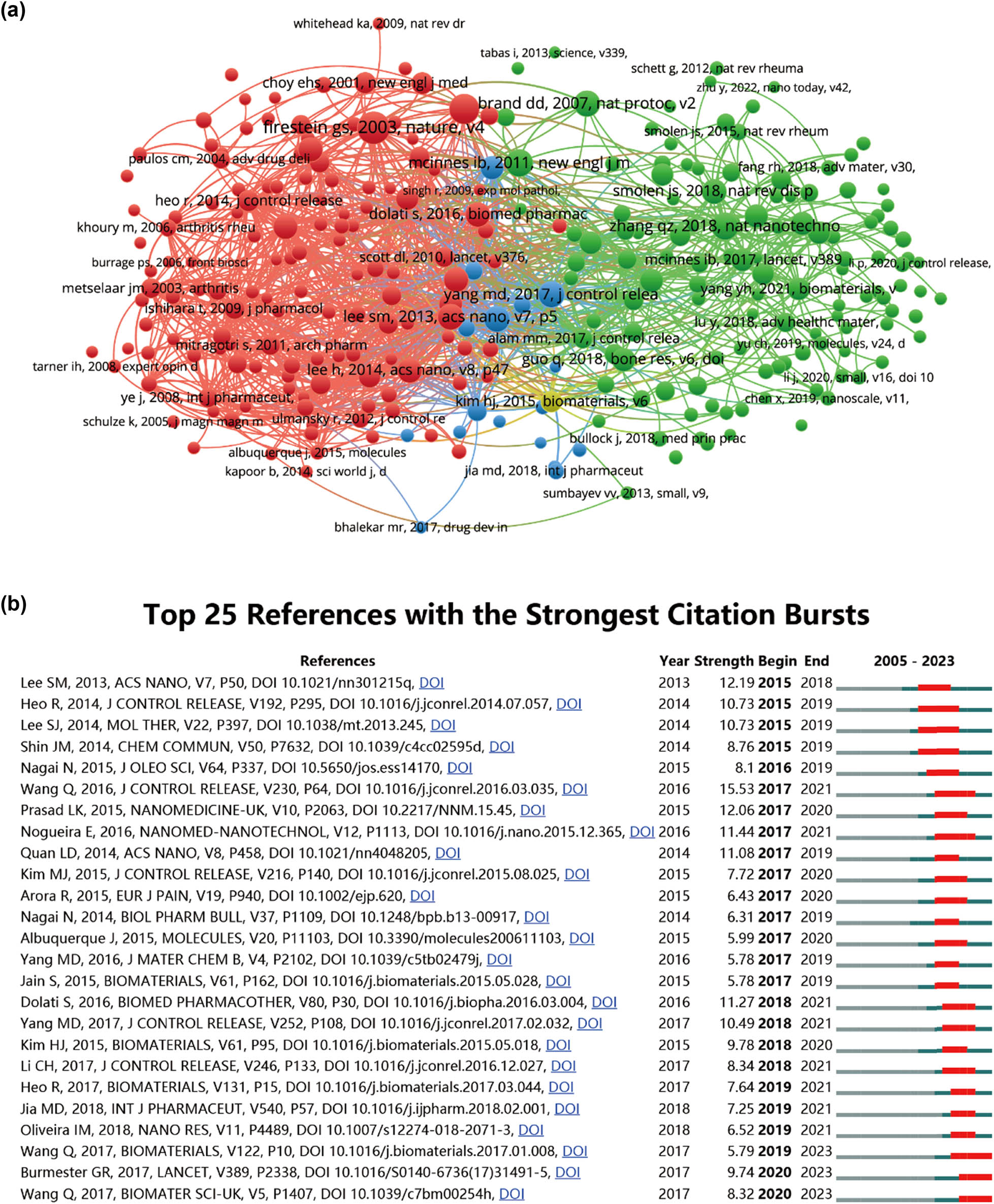
Mapping of references in nanoparticle research for RA. (a) Network map illustrating reference analysis conducted using VOSviewer. (b) Presentation of the top 25 references exhibiting the most significant citation bursts in related publications.
Top ten review articles with the most citations in the field of nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Title | First author | Journal | IF (2023) | Publication year | Total citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Impact of albumin on drug delivery – New applications on the horizon | Elsadek, B | Journal of Controlled Release | 10.8 | 2012 | 650 |
| 2 | Biological properties of “naked” metal nanoparticles | Bhattacharya, R | Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews | 16.1 | 2008 | 650 |
| 3 | Clinical impact of serum proteins on drug delivery | Kratz, F | Journal of Controlled Release | 10.8 | 2012 | 292 |
| 4 | Cell penetrating peptides: A concise review with emphasis on biomedical applications | Derakhshankhah, H | Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy | 7.5 | 2018 | 222 |
| 5 | Delivery of drugs and biomolecules using carbon nanotubes | Vashist, SK | Carbon | 10.9 | 2011 | 216 |
| 6 | Biomimetic nanoparticles for inflammation targeting | Jin, K | Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B | 14.5 | 2018 | 198 |
| 7 | Nanomaterials for nanotheranostics: tuning their properties according to disease needs | Wong, XY | ACS Nano | 17.1 | 2020 | 194 |
| 8 | Recent advances in design of functional biocompatible hydrogels for bone tissue engineering | Xue, X | Advanced Functional Materials | 19.0 | 2021 | 179 |
| 9 | A review of therapeutic challenges and achievements of methotrexate delivery systems for treatment of cancer and RA | Abolmaali, SS | Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology | 3.0 | 2013 | 174 |
| 10 | Methotrexate: a detailed review on drug delivery and clinical aspects | Khan, ZA | Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery | 6.6 | 2012 | 168 |
3.6 Co-occurrence analysis of keywords
In this study, Figure 8 illustrates the co-occurrence cluster analysis of keywords using CiteSpace and VOSviewer to capture the research frontiers in the field. Initially, VOSviewer constructed a network map to analyze the distribution of keywords based on their average year of publication, where dark blue indicates earlier years and yellow indicates later years (as depicted in Figure 8b). A total of 311 keywords were identified, with the five most frequent keywords being: inflammation (total link strength: 1,044), drug-delivery (total link strength: 839), delivery (total link strength: 793), methotrexate (total link strength: 756), and collagen-induced arthritis (total link strength: 714). Most keywords were published before 2020, while terms such as green synthesis and extracellular vesicles emerged relatively recently after 2021. Subsequently, these clusters were divided into 11 different aspects, as shown in Figure 8c, including drug delivery systems, gold, transdermal delivery, gold nanoparticles, angiogenesis, collagen-induced arthritis, RA, oxidative stress, dendritic cells, drug delivery, and pH-sensitive.
Furthermore, Figure 9a illustrates the temporal dynamic evolution of the keyword clusters as depicted by CiteSpace. In total, 11 clusters were identified, all of which represent current research hotspots. Moreover, CiteSpace’s algorithm was utilized to scrutinize keyword bursts and identify the top 25 keywords with the most pronounced citation bursts (as shown in Figure 9b). Notably, “in vivo” exhibited the strongest citation burst with an intensity of 11.66, followed by “poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid (PLGA) nanoparticles” (intensity = 6.08) and “antigen-induced arthritis” (intensity = 1.78). “Activated macrophages” showed the longest burst duration, spanning 12 years from 2007 to 2019. Additionally, keywords such as “tumor necrosis factor-alpha” (2014–2015), “atherosclerosis” (2016–2018), “glucocorticoids” (2017–2019), “inhibition” (2018–2020), and “formulation” (2019–2021), among others, also exhibited significant burst periods. Interestingly, “mesenchymal stem cells,” “extracellular vesicles,” “curcumin,” “drug delivery system,” etc., are keywords that have recently experienced a surge in citations, indicating that research in these areas may represent future research hotspots.
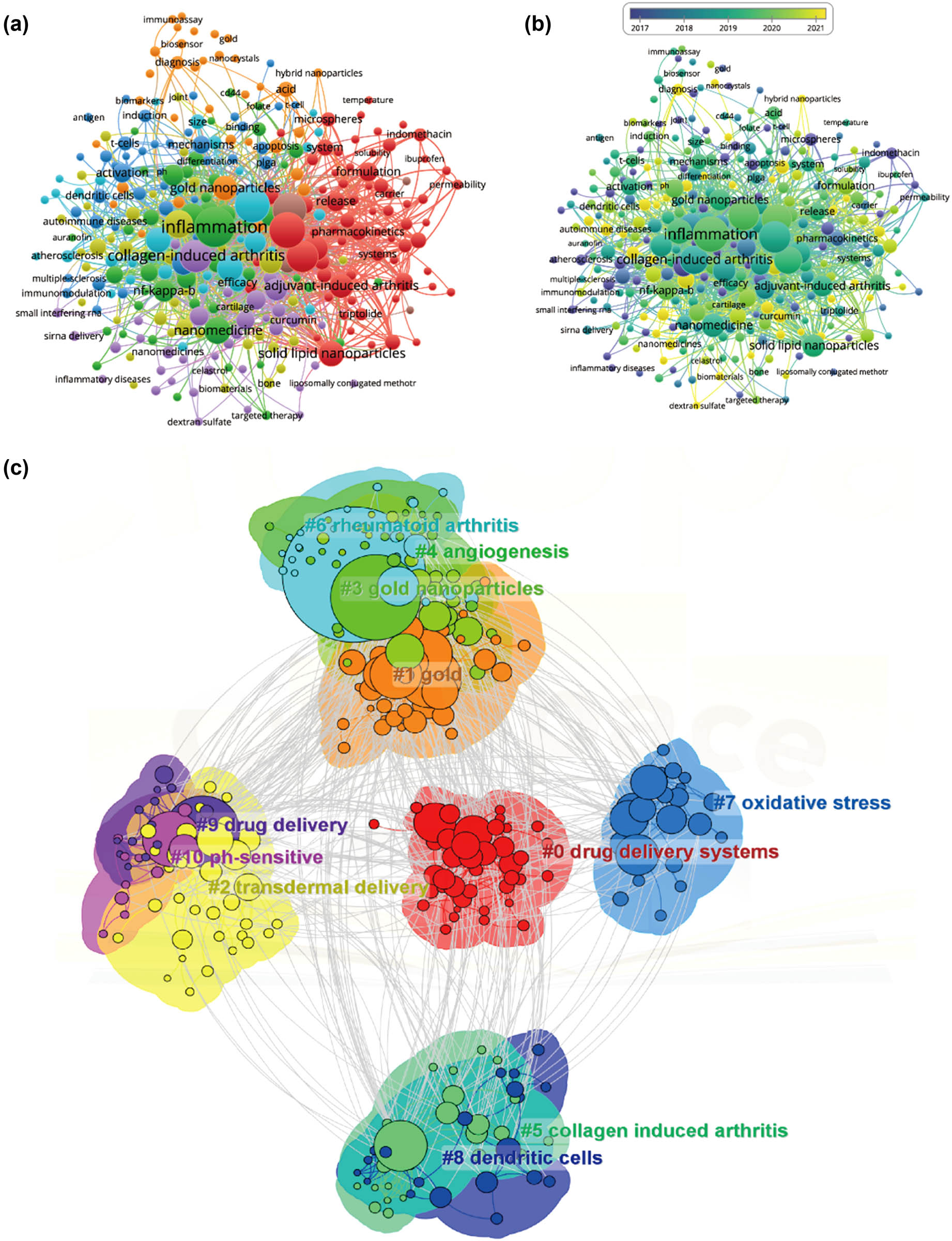
Mapping of keywords in studies concerning nanoparticles in RA research. (a) Network visualization of keywords using VOSviewer, with point size representing frequency. (b) Distribution of keywords based on mean frequency of appearance; keywords in yellow emerged later than those in blue. (c) Visualization of keyword clustering from 2003 to 2023.
4 Discussion
4.1 Trends of nanoparticle system for RA therapy research
Our research spanning from January 1, 2003, to December 31, 2023, reveals a consistent increase in the annual publication count, accompanied by a slight uptick in relative research interest (RRI) in recent years. A diverse pool of approximately 70 countries has contributed to this field of study, with China leading the pack with 487 publications, representing 37.43% of the total output. Notably, Figure 3a underscores the USA’s prominence, leading in total citations, boasting the highest H-index, and exhibiting the highest average citation rate, thus underscoring its pivotal role and exceptional quality contributions to the field. Interestingly, Germany and South Korea trail closely behind in average citations. In the realm of research institutions, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Egyptian Knowledge Bank (EKB), and Sichuan University emerge as dynamic entities propelling the frontiers of research. It is noteworthy that the top ten institutions predominantly hail from developed nations. Collectively, these findings signal an imminent surge in studies offering profound insights and comprehensive understanding of nanoparticle systems in RA therapeutic research.
4.2 Status and quality of authors, journals, and studies publications
In addition to the institutional analysis, our examination extended to the realm of journals, with findings presented in Table 3. Notably, Journal of Controlled Release, International Journal of Pharmaceutics, and International Journal of Nanomedicine emerged as the most prolific publishers in this domain. When considering IF, ACS Nano, Biomaterials, and Journal of Controlled Release garnered the highest IF values, indicating their significance in disseminating high-quality research. It is foreseeable that these top ten journals will continue to serve as primary platforms for cutting-edge research, given their combined quantitative and qualitative prowess. Moreover, a journal-based co-citation analysis was conducted to gauge publication impact and quantify total citations. Figure 5a illustrates that Journal of Controlled Release has made the most substantial contribution to the field. Among the top ten research directions, diverse domains such as clinical, biological, and chemical research were identified, highlighting prevalent interdisciplinary synergies within the field.
Shifting focus to authors, we present the most prolific authors in Table 5. These top-ranked authors have authored numerous studies that are anticipated to drive future research in RA therapeutic applications of nanoparticle systems. Furthermore, collaboration analysis depicted in Figure 6a reveals relatively frequent collaborations among authors within the same country, suggesting the importance of bolstering international academic connections and exchanges. Noteworthy is the emergence of Smolen JS, Wang Q, Mcinnes IB, and Yang MD as highly cited distinguished authors, as shown in Figure 6c. This reflects the international acclaim and recognition garnered by these researchers within the field.
Top ten authors with the most publications on nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Highly published authors | Article counts | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Liu Y | 20 | 1.537 |
| 2 | Park JH | 17 | 1.307 |
| 3 | Wang Q | 17 | 1.307 |
| 4 | Zhang Y | 17 | 1.307 |
| 5 | Zhang N | 16 | 1.23 |
| 6 | Wang Y | 14 | 1.076 |
| 7 | Li CH | 13 | 0.999 |
| 8 | Li J | 13 | 0.999 |
| 9 | Nagai N | 12 | 0.922 |
| 10 | Chen X | 11 | 0.846 |
Top ten research articles with the most citations in the field of nanoparticles in RA research
| Rank | Title | First author | Journal | IF | Publication year | Total citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags | Qian, XM | Nature Biotechnology | 46.9 | 2008 | 1,972 |
| 2 | Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles inhibit synovial inflammation and alleviate joint damage in inflammatory arthritis | Zhang, QZ | Nature Nanotechnology | 38.3 | 2018 | 516 |
| 3 | Antiangiogenic properties of gold nanoparticles | Mukherjee, P | Clinical Cancer Research | 11.5 | 2005 | 378 |
| 4 | Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles | Mu, JY | Molecular Nutrition & Food Research | 5.2 | 2014 | 363 |
| 5 | Gold nanoparticles: A revival in precious metal administration to patients | Thakor, AS | Nano Letters | 10.8 | 2011 | 358 |
| 6 | Synergistic Oxygen generation and ROS scavenging by manganese ferrite/ceria co-decorated nanoparticles for RA treatment | Kim, J | Acs Nano | 17.1 | 2019 | 286 |
| 7 | Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle-mediated TNF-α knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model | Howard, KA | Molecular Therapy | 12.4 | 2009 | 236 |
| 8 | Clearance of pathological antibodies using biomimetic nanoparticles | Copp, JA | Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 11.1 | 2014 | 206 |
| 9 | Targeted silver nanoparticles for RA therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization | Yang, YH | Biomaterials | 14.0 | 2021 | 194 |
| 10 | Targeted chemo-photothermal treatments of RA using gold half-shell multifunctional nanoparticles | Lee, SM | Acs Nano | 17.1 | 2013 | 194 |
The impact of published literature was evaluated through citation analysis of documents (depicted in Figure 5a) and same-citation network analysis (illustrated in Figure 5c). Notably, the most cited article originated from NATURE, presenting a comprehensive nanoparticle-based anti-inflammatory strategy for the treatment of RA [41]. The review by Qiang Guo et al. meticulously dissects the etiology and pathology across specific stages: the (i) trigger, (ii) maturation, (iii) target, and (iv) fulminant phases, elucidating synovial hyperplasia, cartilage damage, bone erosions, and systemic consequences. It delves into recent advancements in understanding RA pathogenesis, disease-modifying medications, and provides insights into next-generation RA treatments. Among the top five most cited articles, the majority focus on clinically oriented topics, emphasizing clinical treatments, systematic evaluations, and experimental clinical studies in sports medicine. Additionally, in the co-citation analysis of references, the pivotal publication authored by Smolen et al. warrants considerable attention.
4.3 Strengths and limitations
While this study offers valuable insights and direction regarding nanoparticle systems in RA therapy, it is essential to recognize its limitations. First, delving into intricate details of nanoparticle design and application, including particle characteristics, treatment duration, drug release efficiency, nanoparticle degradation mechanisms, and their impact on RA treatment outcomes, presents challenges. Second, the selection of publications may be biased due to constraints of chosen databases and languages. For instance, publications from reputable sources like Cochrane, Embase, and non-English journals may have been overlooked. Finally, the latest high-quality papers may not have garnered sufficient citations yet, potentially creating a gap between bibliometric analyses and real-world advancements. Therefore, researchers are encouraged to stay vigilant for the latest publications, particularly those in non-English languages, to ensure a comprehensive and current understanding of the field.
5 Research hotspots and frontiers
The co-occurrence analysis of keywords, coupled with outbreak analysis, yielded valuable insights into the prevailing and emerging focus of joint dispersion in osteoarthritis research. As depicted in Figure 8, the keyword “inflammation” exhibited the highest frequency of citation bursts, underlining its foundational role in this domain of study. Figure 8c delineates prominent research clusters, encompassing key terms such as drug delivery systems, gold, and transdermal delivery. Furthermore, the comprehensive analysis reveals that nanoparticle research for RA therapy spans multiple research areas, indicative of its interdisciplinary nature. These findings serve as a gauge of current trajectories and frontiers in the field. The construction of the keyword co-occurrence network was predicated on the identification of keywords in the titles and abstracts of all amalgamated publications. Our findings are categorized into four principal sections: immunopathological mechanisms, novel drugs, interaction of nanoparticles with joint cells, pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles in joints, and novel nanoparticle-based drug delivery system design and evaluation. These results not only align with promising hotspots in the realm of nanoparticle research for RA therapy but also offer insights into prospective avenues for future research endeavors in this domain (Figure 10).
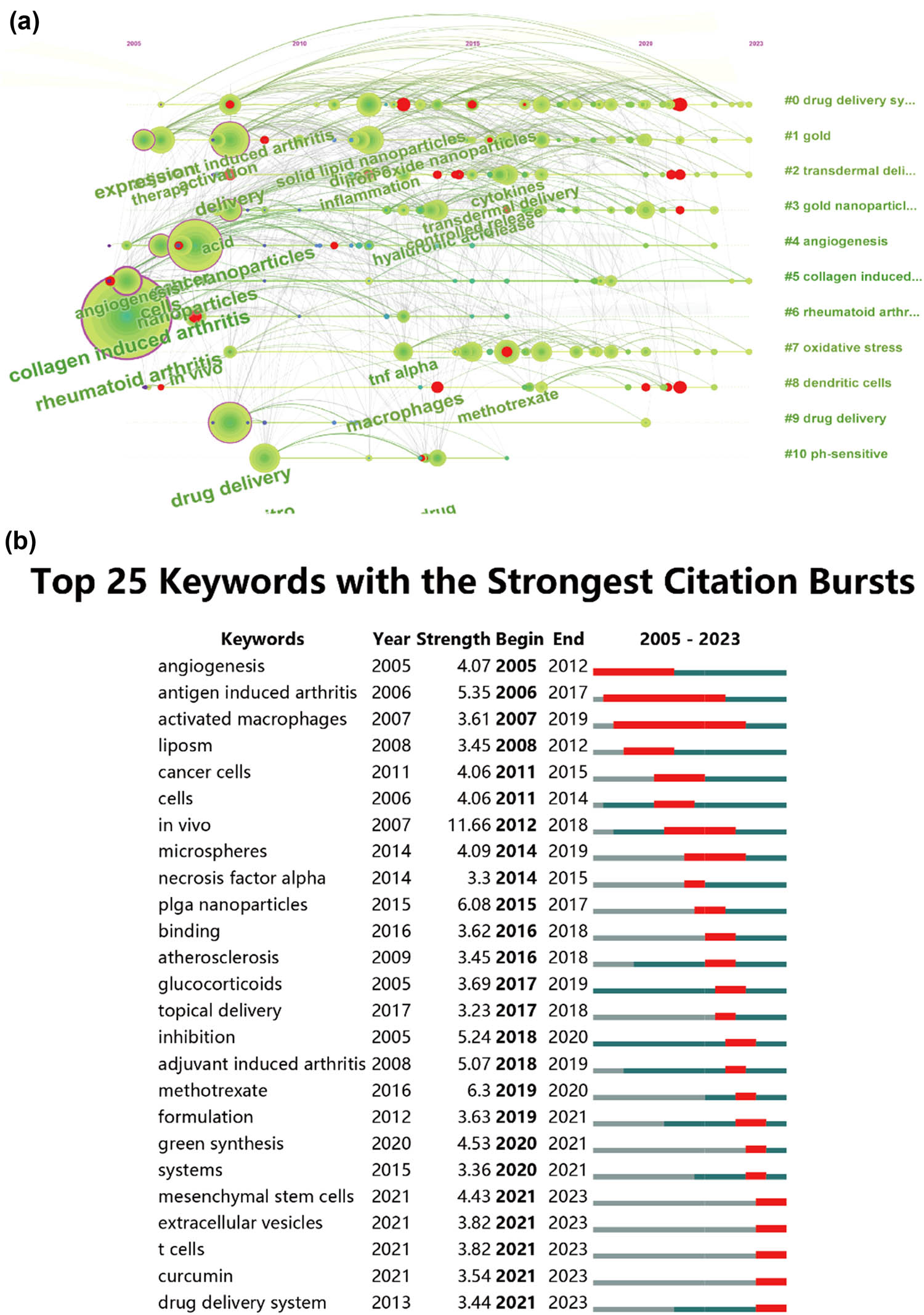
(a) Visualization of keyword timeline from 2013 to 2023. (b) Presentation of the top 25 keywords displaying the most significant citation bursts in publications.
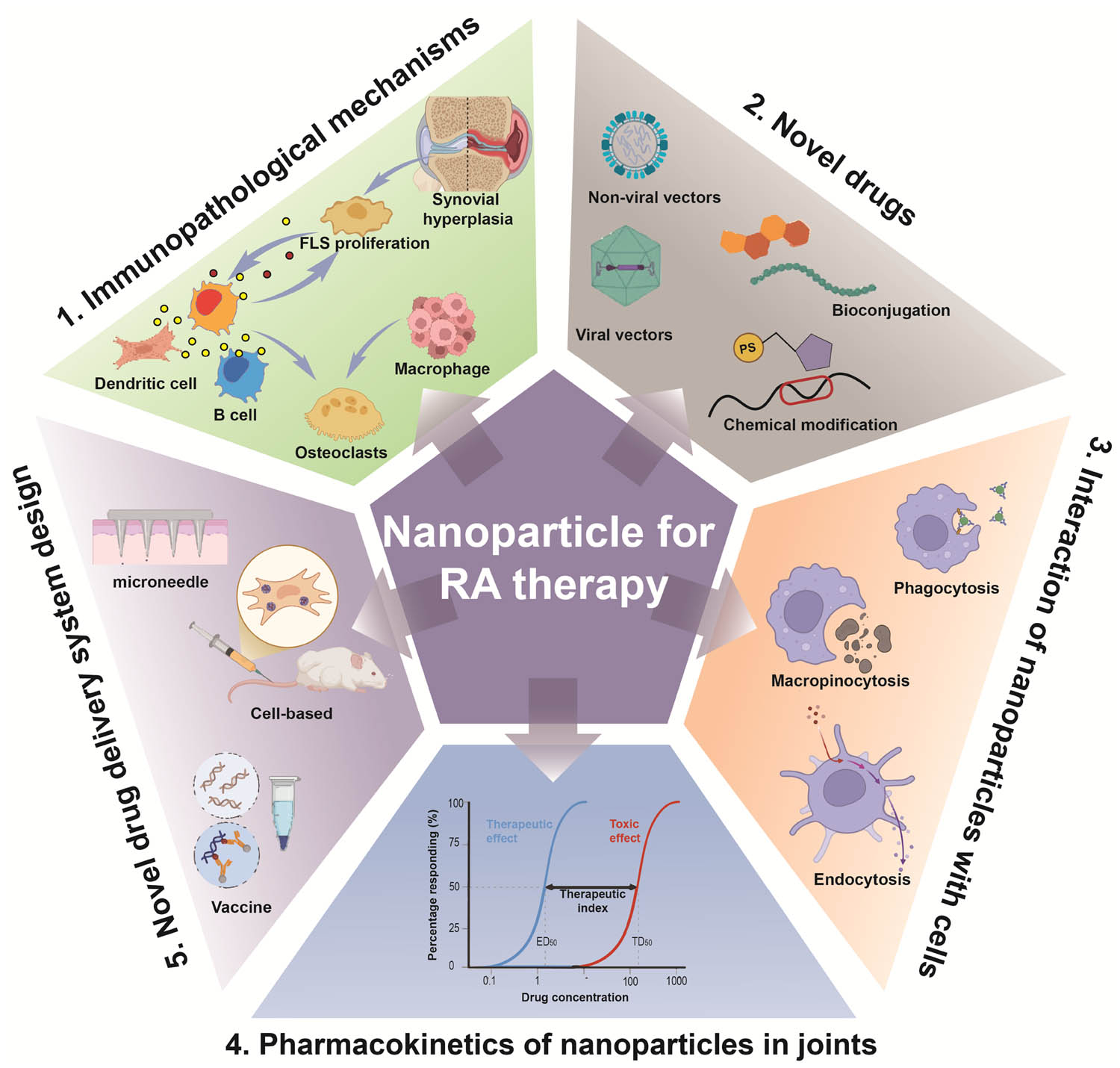
Representative research hotspots and frontiers in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for RA.
5.1 Immunopathological mechanisms
The co-occurrence analysis of keywords has identified four pivotal areas warranting further investigation: oxidative stress, dendritic cells, angiogenesis, and activated macrophages. These immunopathological mechanisms of RA serve as prime targets for nanoparticle systems, enabling precise drug delivery and system design. In a study conducted by Gravandi et al., an animal model of Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA)-induced RA was constructed. The researchers demonstrated that FCA injection prolonged the immobility time of rats, as assessed by various tests including the open field test, acetone drop test, hot plate test, and Von Frey test. Additionally, they measured levels of glutathione (GSH), peroxidase, nitric oxide (NO), and activities of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 [42]. In RA, there is a notable elevation in NO alongside a reduction in GSH and catalase levels. The experimental group in the study focused on rutin nanoparticles, which effectively regulated the oxidative stress milieu and cytokine levels. Furthermore, it inhibited MMP-9 activity while activating MMP-2, thus facilitating treatment. In another study, Prosperi et al. conducted a retrospective analysis to explore the advantages of nanoparticle systems in autoimmune diseases [43]. Nanoparticles represent a cutting-edge approach to drug delivery, leveraging precise target selectivity and enhanced drug-carrying capabilities within specific cells and tissues. This engineering finesse leads to optimized pharmacokinetics and heightened bioavailability of therapeutic agents, with a particular focus on innate immune cells such as macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils. Given their inherent affinity for phagocytosis, nanoparticles hold promise as an immunotherapeutic platform for combating inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, potentially impeding processes like angiogenesis and macrophage activation.
5.2 Novel drugs
Leveraging the high efficiency of nanoparticle systems as carriers, we have engineered novel therapeutic drugs that exhibit superior efficacy when combined. Methotrexate, while a staple in the foundational treatment of RA, faces limitations due to the side effects and rapid drug efflux from the joint area. To address this challenge, Zykova et al. devised an emulsion comprising 50 nm phospholipid nanoparticles stabilized by glycyrrhizic acid [44]. The optimization of conditions for maximal methotrexate incorporation into phospholipid nanoparticles, controlled through HPLC, has significantly bolstered the therapeutic efficacy against RA compared to free methotrexate. Moreover, Diana et al. [45] showcased the anti-arthritic potential of NPs-CM by elucidating its role in inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and curtailing the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines through comparative analysis. Additionally, the oral bioavailability of CM saw a substantial increase when formulated into Solutol-HS 15-stabilized nanoparticles, enabling the transition of CM-based RA therapy from intravenous to oral administration.
5.3 Interaction of nanoparticles with joint cells
The management of RA is directed toward pain relief, slowing disease progression, and enhancing joint mobility and function. While pharmacological strategies focus on symptom alleviation and improving quality of life, a definitive cure remains elusive. Intra-articular injections present several advantages for joint therapy, including heightened bioavailability and minimized systemic adverse effects [46]. Indeed, while this method enables swift clearance of the drug from the joint through capillary and lymphatic drainage, the dense extracellular matrix network in the cartilage may impede drug uptake and hinder the diffusion of drugs administered intra-articularly into target cells and sites. Consequently, this can impact the efficacy of drug utilization [47]. On the contrary, employing nanoparticles stabilizes the encapsulated drug, facilitating controlled drug release. This results in prolonged drug retention and mitigated site-specific toxicity, diffusion, and penetration into the extracellular matrix (ECM) and articular tissues. Additionally, nanoparticle-based delivery systems can actively or passively target specific sites, thereby amplifying therapeutic efficacy while diminishing the side effects associated with the loaded drug [48]. Within the joint, injected nanoparticles have the capacity to interact with cells such as immune cells, synoviocytes, and chondrocytes by either entering these cells or releasing loaded therapeutic agents. This intricate process is influenced by several factors, including nanoparticle size, shape, charge, surface functionalization, and composition, as well as the biological and pathological microenvironment within the joints [49].
Protein corona formation is a phenomenon wherein proteins from the biological environment competitively bind to the surface of nanoparticles, forming a “corona” layer [50,51]. This can alter the nanoparticles’ physicochemical properties, including size, charge, and surface characteristics, and subsequently affect their interactions with biological tissues and cells [52]. In the context of RA, this issue is particularly relevant as the protein corona can influence the behavior of nanoparticles within inflamed joint tissues. Specifically, disorders like autoimmune hemolytic anemia, commonly associated with RA, may alter the binding affinity of proteins to nanoparticle surfaces, resulting in changes in nanoparticle stability, cellular uptake, and drug delivery efficiency [53]. Furthermore, such modifications could impact the immunological response, potentially affecting the therapeutic outcomes of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems [54]. Understanding the dynamics of protein corona formation is crucial for optimizing the design and effectiveness of nanoparticles used in RA therapy, ensuring their targeting accuracy, and minimizing off-target effects [55,56].
5.4 Pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles in joints
Lymphatic drainage facilitates the rapid clearance of drugs from the joint, a process largely influenced by the size of the molecule. Nanoparticles, being larger in size compared to free drug molecules, tend to be retained in the joint for a longer period of time, thereby potentially extending their therapeutic effects [57].
Furthermore, the physical and chemical properties of nanoparticles, including size, shape, and surface properties, play a crucial role in determining their residence time within the joint. Research by Rothenfluh et al. has shown that nanoparticles with tissue-specific targeting abilities exhibit enhanced residence time in the joint space [58]. Indeed, extending the joint retention of nanoparticles is achievable through biomolecule targeting, such as collagen type II. For instance, by incorporating a collagen II-binding peptide into the nanoparticles, their retention in the joint can be prolonged significantly. Studies have shown that nanoparticles modified with a collagen II-binding peptide can remain in the joint for up to 7 days, whereas those with a scrambled peptide are typically cleared within 6–8 h [59]. The principal degradation pathways of nanoparticles encompass chelation, hydrolysis, redox reactions, and enzymolysis [48]. Lymphatic and capillary drainage through the synovium beneath the periarticular joint aids in the elimination of nanoparticles and their encapsulated drugs from the joint cavity. While small particles tend to exit the joint via capillaries, the lymphatic pathway clears nanoparticles and their degradation products regardless of their size. In patients with RA, enhanced synovial lymphatic blood flow due to systemic inflammation and autoimmune dysfunction leads to increased clearance of large particles or molecules, although further confirmation of the nanoparticle removal mechanism is warranted. Given the limited skin permeability of methotrexate (MTX), Amarji et al. [60] devised the microemulsions nanoparticle system to target the drug to specific areas within the stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis of the skin, thereby reducing systemic absorption. This underscores its potential as a novel vehicle for the topical delivery of MTX in therapeutic and safety applications.
5.5 Novel nanoparticle-based drug delivery system design and evaluation
The advancement of biocompatible nanoparticles for in vivo molecular imaging and targeted therapies has garnered significant interest across various scientific, engineering, and biomedical disciplines, including the realm of RA therapy. Recent studies highlight that pegylated gold nanoparticles, which involve colloidal gold coated with a protective layer of polyethylene glycol (PEG), demonstrate exceptional in vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetic properties following systemic injection [61,62]. In contrast to cadmium-containing quantum dots and other nanoparticles that may pose toxicity or elicit immune responses, gold colloids exhibit minimal to no long-term toxicity or adverse effects in vivo [63]. Since certain genes within a drug delivery system have the potential to inhibit undesired gene expression in specific target cells, Stephen et al. encapsulated dexamethasone into PLGA nanoparticles [63]. The drug-loaded PLGA nanoparticles were complexed with polyethyleneimine/siRNA to suppress the expression of undesirable genes and proteins linked to arthritis. The transfection of dexamethasone-loaded and COX-2 siRNA-complexed PLGA nanoparticles was investigated to assess their impact on the expression of arthritis-related genes and the reduction in protein expression. Effective treatment of RA faces challenges due to the scarcity of drugs that specifically target inflamed joints. Liposomes, nanoparticles, and conventional micelles containing limited drug amounts may exhibit instability in circulation, resulting in uncontrolled drug release kinetics. Li et al. introduced a novel drug delivery system comprising pH-sensitive polymeric micelles built on an acid-labile hydrazone bond. Amphiphilic conjugates of a PEG-based derivative and the hydrophobic drug prednisolone (PD) self-assembled into PD micelles with a drug loading of 19.29%. Upon encountering the acidic environment of the synovial fluid, hydrolysis ensued, liberating free PD. The enhancement of joint concentration, based on the area under the concentration-time curve, was 4.63-fold, underscoring the potential of PD micelles for targeted drug delivery in inflammatory diseases [64].
5.6 Impact of work instability (WI) on RA patients
As highlighted in recent studies, WI can have significant consequences for individuals with RA [65]. WI refers to the risk of continuing employment being threatened due to a mismatch between an individual’s functional abilities and the demands of their job. This is especially relevant for RA patients, who often experience fluctuating physical abilities that may affect their ability to meet the demands of their job roles. A study developed the Work Instability Scale (WIS), which provides a tool for assessing the levels of WI in individuals with RA [66]. This scale classifies WI into three bands – low, medium, and high risk – offering a practical method for identifying those at risk of work-related disability.
In RA patients, the consequences of WI are multifaceted [67]. On the one hand, it can exacerbate the physical and psychological burden of the disease, leading to increased stress, decreased morale, and reduced productivity. On the other hand, addressing WI through targeted management strategies can play a crucial role in improving the patient’s overall well-being, job retention, and treatment outcomes. This aligns with findings in organizational behavior research, which emphasizes the importance of authentic leadership and the role of job fit in fostering positive employee outcomes. Authentic leadership has been shown to significantly enhance employee organizational identification and felt obligation, creating a supportive work environment that can buffer against the adverse effects of WI [68].
Leaders who foster an environment of understanding, support, and job flexibility can significantly enhance the mental and physical health of employees with RA. Proper job fit, as discussed in both the RA WI study and leadership literature, emerges as a crucial factor that can help employees navigate the challenges of WI while minimizing the risk of work-related disability [68]. Incorporating strategies for identifying and addressing WI, such as using the WIS for RA patients, along with promoting authentic leadership and ensuring appropriate job fit, could substantially improve the overall work experience for RA patients, as well as their job retention and health outcomes [69].
5.7 Role of nanomaterials in degradation of chemical drugs for autoimmune diseases
Nanomaterials have shown promise in RA therapy and in the degradation of various pharmaceutical agents used to treat autoimmune diseases, including RA [70]. They have demonstrated effectiveness in the photocatalytic degradation of analgesics, mucolytics, and anti-inflammatory drugs commonly prescribed for managing autoimmune conditions like RA. One study highlights how nanomaterials can efficiently degrade drugs used in treating diseases like SARS-CoV-2 and autoimmune disorders, preventing environmental contamination [71].
Pharmaceuticals such as painkillers, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs persist in the environment, contaminating both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, posing risks to wildlife. Nanomaterials can address this issue by enabling the safe and efficient degradation of these drugs, thus contributing to environmental conservation [72–74]. This research underscores the dual benefits of nanomaterials: their potential in RA treatment and their role in sustainable pharmaceutical waste management. By degrading drugs that enter ecosystems through wastewater, nanomaterials offer a sustainable solution to mitigating pharmaceutical contamination. These findings highlight the broader significance of nanomaterials in both healthcare and environmental sustainability.
5.8 Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) and its impact on oral health in RA patients
SS is an autoimmune disorder frequently associated with RA, in which chronic inflammation damages exocrine glands, primarily the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to reduced secretions and severe oral and ocular dryness [75,76]. The resultant xerostomia (dry mouth) not only impairs the ability to chew, swallow, and speak but also significantly increases the risk of dental caries, periodontal disease, and oral infections [77]. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral homeostasis by neutralizing acids, washing away food debris, and providing antimicrobial peptides; therefore, its depletion predisposes individuals to a heightened risk of oral pathology [78]. Furthermore, recent studies highlight that SS in RA patients is often underdiagnosed due to its overlapping symptoms with other autoimmune conditions. Advanced imaging techniques, such as Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT), have demonstrated superior sensitivity in detecting glandular abnormalities compared to traditional physical examinations [79]. In particular, CBCT enables precise assessment of salivary gland calcifications, while power Doppler ultrasound can visualize real-time inflammation in the affected glands, making these tools invaluable for early detection and targeted treatment [80,81].
Beyond oral health deterioration, SS-related salivary gland dysfunction may contribute to dysphagia, which can exacerbate nutritional deficiencies and further compromise patient well-being [82]. Current therapeutic approaches focus on symptom management, including artificial saliva substitutes, systemic secretagogues (e.g., pilocarpine), and localized treatments like low-level laser therapy to enhance salivary gland function [83,84]. The effectiveness of alcohol-free mouthwashes (e.g., Biotene) and fluoride rinses in alleviating xerostomia symptoms is well-documented, along with sugar-free lozenges or gum to stimulate residual salivation [85,86]. Given the increasing recognition of the role of SS in RA, more comprehensive patient education and interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists, dentists, and oral medicine specialists are crucial. Regular dental visits, rigorous oral hygiene routines, and early imaging-based diagnostics should be incorporated into routine RA management to mitigate the long-term consequences of SS-induced oral complications [87,88].
5.9 Impact of cancer and occupational risks on RA patients
RA patients are at higher risk of occupational cancers due to prolonged exposure to environmental and occupational hazards [89]. The WHO estimates that over 200,000 deaths annually are linked to workplace cancer exposures, including air pollution, toxic chemicals, pesticides, heavy metals, and radiation. Given RA’s potential to weaken the immune system, patients may be more susceptible to these carcinogens. Workers in industries with heavy metals or chemicals face an increased cancer risk due to carcinogenic exposures [90,91]. Given cancer’s multifactorial nature, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, early detection through regular screenings is vital for reducing cancer risks in RA patients. Preventive measures should include occupational safety audits, proper personal protective equipment use, and minimizing harmful exposures. Public health strategies to reduce environmental pollution can lower cancer risks for both RA patients and the general population [92]. Therefore, a comprehensive healthcare approach should address the combined impact of rheumatic diseases and environmental/occupational exposures, with public health initiatives focusing on cancer risk reduction.
6 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis of nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for RA from 2003 to 2023. By analyzing quantitative outputs, collaborative networks, and key research themes, we identified global trends and emerging hotspots, such as drug delivery systems, joint cell interactions, and nanoparticle pharmacokinetics. Notably, China has become a dominant player in publications, while the United States stands out for its high impact in terms of H index and citations. The findings underscore the significant progress in understanding immunopathological mechanisms and the development of novel nanoparticle-based therapies. This study highlights the growing importance of nanoparticles in RA treatment, offering a foundation for future research and innovation in the field. The insights presented here not only aid researchers in navigating the evolving landscape but also emphasize the potential of nanoparticle systems to transform RA therapy.
-
Funding information: This study was supported by Hunan Provincial Department of Education Outstanding Youth Project (24B1089); the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ40428); the Planned Science and Technology Project of Huaihua (2020YJ011735); and the Clinical Medical Technology Demonstration Base for Rheumatological Immunology of Huaihua (2022N2403).
-
Author contributions: XYC and LS contributed to conception and design of the study. SWX and PL organized the database. SWX, PL, and LS performed the statistical analysis. SWX and PL wrote the first draft of the manuscript. SM wrote sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Liu L, Hu F, Wang H, Wu X, Eltahan AS, Stanford S, et al. Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine mediated biomimetic delivery of methotrexate by albumin-based nanomedicines for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13(5):5036–48.10.1021/acsnano.9b01710Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Withrow J, Murphy C, Liu Y, Hunter M, Fulzele S, Hamrick MW. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):1–12.10.1186/s13075-016-1178-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Safiri S, Kolahi AA, Hoy D, Smith E, Bettampadi D, Mansournia MA, et al. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990–2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(11):1463–71.10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215920Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Rossini M, Rossi E, Bernardi D, Viapiana O, Gatti D, Idolazzi L, et al. Prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in Italy. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34:659–64.10.1007/s00296-014-2974-6Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Englund M, Jöud A, Geborek P, Felson DT, Jacobsson LT, Petersson IF. Prevalence and incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in southern Sweden 2008 and their relation to prescribed biologics. Rheumatology. 2010;49(8):1563–9.10.1093/rheumatology/keq127Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Eriksson JK, Neovius M, Ernestam S, Lindblad S, Simard JF, Askling J. Incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in Sweden: a nationwide population‐based assessment of incidence, its determinants, and treatment penetration. Arthritis Care Res. 2013;65(6):870–8.10.1002/acr.21900Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Kerola AM, Sexton J, Wibetoe G, Rollefstad S, Crowson CS, Mars N, et al. Incidence, sociodemographic factors and treatment penetration of rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis in Norway. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. WB Saunders, Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2021.10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.08.006Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Finckh A, Gilbert B, Hodkinson B, Bae S-C, Thomas R, Deane KD, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(10):591–602.10.1038/s41584-022-00827-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Shaji J, Lal M. Nanocarriers for targeting in inflammation. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2013;6(3):3–12.Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Nogueira E, Gomes AC, Preto A, Cavaco-Paulo A. Folate-targeted nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(4):1113–26.10.1016/j.nano.2015.12.365Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Zhao J, Guo S, Schrodi SJ, He D. Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Front immunology. 2021;12:790122.10.3389/fimmu.2021.790122Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(1):10–8.10.1038/s41590-020-00816-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Smolen JS. Insights into the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a paradigm in medicine. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102425.10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102425Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Liu Y, Cao F, Sun B, Bellanti JA, Zheng SG. Magnetic nanoparticles: A new diagnostic and treatment platform for rheumatoid arthritis. J Leucoc Biol. 2021;109(2):415–24.10.1002/JLB.5MR0420-008RRSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Bizzaro N, Bartoloni E, Morozzi G, Manganelli S, Riccieri V, Sabatini P, et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer predicts time to rheumatoid arthritis onset in patients with undifferentiated arthritis: results from a 2-year prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15:1–9.10.1186/ar4148Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Olofsson T, Petersson I, Eriksson J, Englund M, Nilsson J, Geborek P, et al. Predictors of work disability after start of anti-TNF therapy in a national cohort of Swedish patients with rheumatoid arthritis: does early anti-TNF therapy bring patients back to work? Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(7):1245–52.10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210239Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Aman RM, Zaghloul RA, Elsaed WM, Hashim IIA. In vitro–in vivo assessments of apocynin-hybrid nanoparticle-based gel as an effective nanophytomedicine for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Delivery Transl. Res. 2023;13:1–27.10.1007/s13346-023-01360-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Ayazi H, Akhavan O, Raoufi M, Varshochian R, Motlagh NSH, Atyabi F. Graphene aerogel nanoparticles for in-situ loading/pH sensitive releasing anticancer drugs. Colloids Surf, B. 2020;186:110712.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110712Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Jangde R, Elhassan GO, Khute S, Singh D, Singh M, Sahu RK, et al. Hesperidin-loaded lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles for topical delivery of bioactive drugs. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(2):211.10.3390/ph15020211Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Rabiee N, Akhavan O, Fatahi Y, Ghadiri AM, Kiani M, Makvandi P, et al. CaZnO-based nanoghosts for the detection of ssDNA, pCRISPR and recombinant SARS-CoV-2 spike antigen and targeted delivery of doxorubicin. Chemosphere. 2022;306:135578.10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135578Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Shah S, Famta P, Raghuvanshi RS, Singh SB, Srivastava S. Lipid polymer hybrid nanocarriers: Insights into synthesis aspects, characterization, release mechanisms, surface functionalization and potential implications. Colloid Interface Sci Commun. 2022;46:100570.10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100570Suche in Google Scholar
[22] Anwer MK, Iqbal M, Muharram MM, Mohammad M, Ezzeldin E, Aldawsari MF, et al. Development of lipomer nanoparticles for the enhancement of drug release, anti-microbial activity and bioavailability of delafloxacin. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(3):252.10.3390/pharmaceutics12030252Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Massadeh S, Omer ME, Alterawi A, Ali R, Alanazi FH, Almutairi F, et al. Optimized polyethylene glycolylated polymer–lipid hybrid nanoparticles as a potential breast cancer treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(7):666.10.3390/pharmaceutics12070666Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Fang RH, Zhang L. Biohybrid nanoparticles for treating arthritis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2023;18(12):1387–8.10.1038/s41565-023-01503-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Koo S, Sohn HS, Kim TH, Yang S, Jang SY, Ye S, et al. Ceria-vesicle nanohybrid therapeutic for modulation of innate and adaptive immunity in a collagen-induced arthritis model. Nat Nanotechnol. 2023;18(12):1502–14.10.1038/s41565-023-01523-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Kim CK, Kim T, Choi IY, Soh M, Kim D, Kim YJ, et al. Ceria nanoparticles that can protect against ischemic stroke. Angew Chem, Int Ed. 2012;51(44):11039–43.10.1002/anie.201203780Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Soh M, Kang DW, Jeong HG, Kim D, Kim DY, Yang W, et al. Ceria–Zirconia nanoparticles as an enhanced multi‐antioxidant for sepsis treatment. Angew Chem. 2017;129(38):11557–61.10.1002/ange.201704904Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Jiang W, Xu J. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(1):e12712.10.1111/cpr.12712Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Suryaprakash S, Lao Y-H, Cho H-Y, Li M, Ji HY, Shao D, et al. Engineered mesenchymal stem cell/nanomedicine spheroid as an active drug delivery platform for combinational glioblastoma therapy. Nano Lett. 2019;19(3):1701–5.10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04697Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Lu K, He C, Guo N, Chan C, Ni K, Lan G, et al. Low-dose X-ray radiotherapy–radiodynamic therapy via nanoscale metal–organic frameworks enhances checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018;2(8):600–10.10.1038/s41551-018-0203-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Shahir M, Mahmoud Hashemi S, Asadirad A, Varahram M, Kazempour‐Dizaji M, Folkerts G, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stem cell‐derived exosomes on the induction of mouse tolerogenic dendritic cells. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(10):7043–55.10.1002/jcp.29601Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Nguyen L, Bang S, Noh I. Tissue regeneration of human mesenchymal stem cells on porous gelatin micro-carriers by long-term dynamic in vitro culture. Tissue Eng Regener Med. 2019;16:19–28.10.1007/s13770-018-00174-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Chen J, Zeng S, Xue Q, Hong Y, Liu L, Song L, et al. Photoacoustic image-guided biomimetic nanoparticles targeting rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(43):e2213373119.10.1073/pnas.2213373119Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Boehnke N, Straehla JP, Safford HC, Kocak M, Rees MG, Ronan M, et al. Massively parallel pooled screening reveals genomic determinants of nanoparticle delivery. Science. 2022;377(6604):eabm5551.10.1126/science.abm5551Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Zhao H, Liu J-B, Bao Z-F, Xu Y-X, Wang Z-Q. Global research trends in dental stem cells: A bibliometric and visualized study. Tissue Eng Part B: Rev. 2022;28(4):733–44.10.1089/ten.teb.2021.0080Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Yuan J, Feng T, Guo Y, Luo K, Wu Q, Yu S, et al. Global scientific trends update on macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: A bibliometric and visualized analysis from 2000 to 2022. Heliyon. 2023;9(9):19761.10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19761Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. Measuring scholarly impact: Methods and practice. Cham: Springer; 2014. p. 285–320.10.1007/978-3-319-10377-8_13Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Chen C. CiteSpace: a practical guide for mapping scientific literature. Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers; 2016.Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Zhang ZZ, Chen YR, Wang SJ, Zhao F, Wang XG, Yang F, et al. Orchestrated biomechanical, structural, and biochemical stimuli for engineering anisotropic meniscus. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(491):eaao0750.10.1126/scitranslmed.aao0750Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Ma L, Ma J, Teng M, Li Y. Visual analysis of colorectal cancer immunotherapy: a bibliometric analysis from 2012 to 2021. Front Immunology. 2022;13:1386.10.3389/fimmu.2022.843106Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Zhang Q, Dehaini D, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Chen X, Zhang L, et al. Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles inhibit synovial inflammation and alleviate joint damage in inflammatory arthritis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2018;13(12):1182–90.10.1038/s41565-018-0254-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Gravandi MM, Pourmanouchehri Z, Behbood L, Fakhri S, Mohammadi-Noori E, Zhaleh M, et al. Rutin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles alleviated Freund’s adjuvant induced rheumatoid arthritis via modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory parameters in Wistar rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023;397:4771–90.10.1007/s00210-023-02902-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Prosperi D, Colombo M, Zanoni I, Granucci F. Drug nanocarriers to treat autoimmunity and chronic inflammatory diseases. Semin Immunol. 2017;34:61–7.10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.010Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Zykova MG, Prozorovskiĭ VN, Ipatova OM, Torkhovskaia TI, Glazatov VV. [Antirheumatoid activity of methotrexate in phospholipid nanoparticles (Phosphogliv)]. Biomed Khim. 2007;53(4):435–41.Suche in Google Scholar
[45] Crisan D, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Crisan M, Schatz S, Hainzl A, Olenic L, et al. Topical silver and gold nanoparticles complexed with Cornus mas suppress inflammation in human psoriasis plaques by inhibiting NF-κB activity. Exp Dermat. 2018;27(10):1166–9.10.1111/exd.13707Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[46] Jones IA, Togashi R, Wilson ML, Heckmann N, Vangsness Jr CT. Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(2):77–90.10.1038/s41584-018-0123-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Larsen C, Ostergaard J, Larsen SW, Jensen H, Jacobsen S, Lindegaard C, et al. Intra-articular depot formulation principles: role in the management of postoperative pain and arthritic disorders. J Pharm Sci. 2008;97(11):4622–54.10.1002/jps.21346Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Wen J, Li H, Dai H, Hua S, Long X, Li H, et al. Intra-articular nanoparticles based therapies for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis management. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100597.10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100597Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Li X, Dai B, Guo J, Zheng L, Guo Q, Peng J, et al. Nanoparticle-cartilage interaction: pathology-based intra-articular drug delivery for osteoarthritis therapy. Nanomicro Lett. 2021;13(1):149.10.1007/s40820-021-00670-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Hajipour MJ, Raheb J, Akhavan O, Arjmand S, Mashinchian O, Rahman M, et al. Personalized disease-specific protein corona influences the therapeutic impact of graphene oxide. Nanoscale. 2015;7(19):8978–94.10.1039/C5NR00520ESuche in Google Scholar
[51] Walkey CD, Chan WC. Understanding and controlling the interaction of nanomaterials with proteins in a physiological environment. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(7):2780–99.10.1039/C1CS15233ESuche in Google Scholar
[52] Mishra RK, Ahmad A, Vyawahare A, Alam P, Khan TH, Khan R. Biological effects of formation of protein corona onto nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;175:1–18.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.152Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Liang Z, Yu H, Lai J, Wen L, Chen G. An easy-to-prepare microshotgun for efficient transmembrane delivery by powering nanoparticles. J Controlled Release. 2020;321:119–31.10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[54] Braunová A, Kostka L, Sivák L, Cuchalová L, Hvězdová Z, Laga R, et al. Tumor-targeted micelle-forming block copolymers for overcoming of multidrug resistance. J Controlled Release. 2017;245:41–51.10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.11.020Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Kopac T. Protein corona, understanding the nanoparticle–protein interactions and future perspectives: A critical review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;169:290–301.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.108Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Warne NM, Nowell CJ, Tran MP, Finnegan JR, Feeney OM, Kempe K. Impact of drug conjugation site and corona chemistry on the therapeutic activity of polymer nanorod–drug conjugates. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13:2402029.10.1002/adhm.202402029Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Aulin C, Harris HE, Klareskog L. A8.27 Intraarticular drug delivery of anti-HMGB1 in hyaluronan gels for osteoarthritis treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(Suppl 1):A92.10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207259.212Suche in Google Scholar
[58] Rothenfluh DA, Bermudez H, O’Neil CP, Hubbell JA. Biofunctional polymer nanoparticles for intra-articular targeting and retention in cartilage. Nat Mater. 2008;7(3):248–54.10.1038/nmat2116Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[59] Hu HY, Lim NH, Ding-Pfennigdorff D, Saas J, Wendt KU, Ritzeler O, et al. DOTAM derivatives as active cartilage-targeting drug carriers for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015;26(3):383–8.10.1021/bc500557sSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Amarji B, Garg NK, Singh B, Katare OP. Microemulsions mediated effective delivery of methotrexate hydrogel: more than a tour de force in psoriasis therapeutics. J Drug Target. 2016;24(2):147–60.10.3109/1061186X.2015.1058804Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] James WD, Hirsch LR, West JL, O’Neal PD, Payne JD. Application of INAA to the build-up and clearance of gold nanoshells in clinical studies in mice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2007;271(2):455–9.10.1007/s10967-007-0230-1Suche in Google Scholar
[62] Qian X, Peng X-H, Ansari DO, Yin-Goen Q, Chen GZ, Shin DM, et al. In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat Biotechnol. 2008;26(1):83–90.10.1038/nbt1377Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Stephen BJ, Chokriwal A, Sharma MM, Jain D, Saxena J, Dhaliwal H, et al. Dexamethasone encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles for the treatment of neuroinflammation. Bioinspired, Biomim and Nanobiomaterials. 2022;11(2):72–85.10.1680/jbibn.21.00059Suche in Google Scholar
[64] Guo Q, Wang Y, Xu D, Nossent J, Pavlos NJ, Xu J. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018;6:15.10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Revicki D, Ganguli A, Kimel M, Roy S, Chen N, Safikhani S, et al. Reliability and validity of the work instability scale for rheumatoid arthritis. Value Health. 2015;18(8):1008–15.10.1016/j.jval.2015.09.2941Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Gilworth G, Chamberlain MA, Harvey A, Woodhouse A, Smith J, Smyth MG, et al. Development of a work instability scale for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2003;49(3):349–54.10.1002/art.11114Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[67] Schmidt W, Tąpolska M, Pawlak-Buś K, Owczarek M, Leszczyński P. Work instability and associated factors among patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Greater Poland. Reumatologia. 2020;58(4):208–12.10.5114/reum.2020.98432Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Eslamdoust S, Borhani T, Dorri R, Karandish M. Authentic leadership’s impact on employees felt obligation: moderated mediation model; 2024. 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5118661/v1.Suche in Google Scholar
[69] Crain TL, Schonert-Reichl KA, Roeser RW. Cultivating teacher mindfulness: Effects of a randomized controlled trial on work, home, and sleep outcomes. J Occup Health Psychol. 2017;22(2):138.10.1037/ocp0000043Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[70] Song Y, Li J, Wu Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):263.10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[71] Ebrahimi M, Akhavan O. Nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradations of analgesic, mucolytic and anti-biotic/viral/inflammatory drugs widely used in controlling SARS-CoV-2. Catalysts. 2022;12(6):667.10.3390/catal12060667Suche in Google Scholar
[72] Tao L, Zhang H, Li G, Liao C, Jiang G. Photocatalytic degradation of pharmaceuticals by pore-structured graphitic carbon nitride with carbon vacancy in water: identification of intermediate degradants and effects of active species. Sci Total Environ. 2022;824:153845.10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153845Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[73] He S, Wang X, Tang L, Wang J, Chen J, Zhang Y. A novel G‐C3N4 modified biogenic mackinawite mediated by SRB for boosting highly efficient adsorption and catalytic degradation of antibiotics in photo–fenton process. Small. 2024;e2408723. 10.1002/smll.202408723.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[74] Sharafudheen SB, Vijayakumar C, Anjana P, Bindhu M, Alharbi NS, Khaled JM, et al. Biogenically synthesized porous TiO2 nanostructures for advanced anti-bacterial, electrochemical, and photocatalytic applications. J Environ Manag. 2024;366:121728.10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.121728Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[75] Beydon M, McCoy S, Nguyen Y, Sumida T, Mariette X, Seror R. Epidemiology of Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2024;20(3):158–69.10.1038/s41584-023-01057-6Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] Gandolfo S, Bombardieri M, Pers J-O, Mariette X, Ciccia F. Precision medicine in Sjögren’s disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 2024;6:e636–47.10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00039-0Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[77] Dental Tips for the Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient Johns Hopkins Arthritis Center 2016. Available from: https://www.hopkinsarthritis.org/arthritis-news/5-dental-tips-for-the-ra-patient/.Suche in Google Scholar
[78] Lundtorp-Olsen C, Nygaard N, Massarenti L, Constancias F, Damgaard C, Kahraman Gursoy U, et al. Supragingival microbiota, cytokines, and proteins in individuals with different trajectories in experimental gingivitis. J Oral Microbiology. 2024;16(1):2372861.10.1080/20002297.2024.2372861Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[79] Schulze R, Couso–Queiruga E, Katsaros C. Accuracy of cone–beam computed tomography in imaging the components of the periodontal phenotype. Periodontology 2000. 2024;1–11.10.1111/prd.12556Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[80] Krithika C, Sreedevi J, Sivapathasundharam B, Nithya V. Benign lymphoepithelial lesion of the minor salivary gland–A rare presentation as a palatal swelling. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2020;24(Suppl 1):S33–6.10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_17_20Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Thomas N, Kaur A, Reddy SS, Nagaraju R, Nagi R, Shankar VG. Three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomographic sialography in the diagnosis and management of primary Sjögren syndrome: Report of 3 cases. Imaging Sci Dent. 2021;51(2):209.10.5624/isd.20200313Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[82] Grundmann O, Fillinger JL, Victory KR, Burd R, Limesand KH. Restoration of radiation therapy-induced salivary gland dysfunction in mice by post therapy IGF-1 administration. BMC cancer. 2010;10:1–9.10.1186/1471-2407-10-417Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[83] Harley RJ, Bowers E, Li J, Bisignani M, Nilsen ML, Johnson JT. Biotène versus hydrasmile for radiation‐induced xerostomia: randomized double‐blind cross‐over study. OTO Open. 2025;9(1):e70038.10.1002/oto2.70038Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[84] Saraux A, Pers J-O, Devauchelle-Pensec V. Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(8):456–71.10.1038/nrrheum.2016.100Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[85] Plummer EL, Maddaford K, Murray GL, Fairley CK, Pasricha S, Mu A, et al. The impact of mouthwash on the oropharyngeal microbiota of men who have sex with men: a substudy of the OMEGA trial. Microbiol Spectr. 2022;10(1):e01757-21.10.1128/spectrum.01757-21Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[86] Nie E, Jiang R, Islam R, Li X, Yu J. Evaluation of caries risk assessment practices among dental practitioners in Guangzhou, China: a cross-sectional study. Front Oral Health. 2024;5:1458188.10.3389/froh.2024.1458188Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[87] Christ L, Kissling S, Finckh A, Fisher BA, Adler S, Maurer B, et al. Concomitant Sjögren’s disease as a biomarker for treatment effectiveness in rheumatoid arthritis-results from the Swiss clinical quality management cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;26(1):68.10.1186/s13075-024-03302-zSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[88] Vivino FB, Carsons SE, Foulks G, Daniels TE, Parke A, Brennan MT, et al. New treatment guidelines for Sjögren’s disease. Rheum Dis Clin. 2016;42(3):531–51.10.1016/j.rdc.2016.03.010Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[89] Daniel R, Ellis R. The cancer prevention book: the holistic plan to reduce your risk of cancer and revolutionize your life. New York, NY: Simon and Schuster; 2001.Suche in Google Scholar
[90] Vuorela J, Sokka T, Pukkala E, Hannonen P. Does yttrium radiosynovectomy increase the risk of cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis. 2003;62(3):251–3.10.1136/ard.62.3.251Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[91] Mertens RT, Gukathasan S, Arojojoye AS, Olelewe C, Awuah SG. Next generation gold drugs and probes: chemistry and biomedical applications. Chem Rev. 2023;123(10):6612–67.10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00649Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[92] Khojasteh A, Mirjalili MH, Alcalde MA, Cusido RM, Eibl R, Palazon J. Powerful plant antioxidants: A new biosustainable approach to the production of rosmarinic acid. Antioxidants. 2020;9(12):1273.10.3390/antiox9121273Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Mechanism of triptolide regulating proliferation and apoptosis of hepatoma cells by inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway
- Maslinic acid improves mitochondrial function and inhibits oxidative stress and autophagy in human gastric smooth muscle cells
- Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT
- Post-pandemic insights on COVID-19 and premature ovarian insufficiency
- Proteome differences of dental stem cells between permanent and deciduous teeth by data-independent acquisition proteomics
- Optimizing a modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide protocol for fungal DNA extraction: Insights from multilocus gene amplification
- Preliminary analysis of the role of small hepatitis B surface proteins mutations in the pathogenesis of occult hepatitis B infection via the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced UPR-ERAD pathway
- Efficacy of alginate-coated gold nanoparticles against antibiotics-resistant Staphylococcus and Streptococcus pathogens of acne origins
- Battling COVID-19 leveraging nanobiotechnology: Gold and silver nanoparticle–B-escin conjugates as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors
- Neurodegenerative diseases and neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis
- Impact of fracture fixation surgery on cognitive function and the gut microbiota in mice with a history of stroke
- COLEC10: A potential tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma through modulation of EMT and PI3K-AKT pathways
- High-temperature requirement serine protease A2 inhibitor UCF-101 ameliorates damaged neurons in traumatic brain-injured rats by the AMPK/NF-κB pathway
- SIK1 inhibits IL-1β-stimulated cartilage apoptosis and inflammation in vitro through the CRTC2/CREB1 signaling
- Rutin–chitooligosaccharide complex: Comprehensive evaluation of its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties in vitro and in vivo
- Knockdown of Aurora kinase B alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast cells damage and inflammation during gestational diabetes
- Calcium-sensing receptors promoted Homer1 expression and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- ABI3BP can inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells
- Changes in blood glucose and metabolism in hyperuricemia mice
- Rapid detection of the GJB2 c.235delC mutation based on CRISPR-Cas13a combined with lateral flow dipstick
- IL-11 promotes Ang II-induced autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial dysfunction in atrial fibroblasts
- Short-chain fatty acid attenuates intestinal inflammation by regulation of gut microbial composition in antibiotic-associated diarrhea
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of pathogens in patients with diabetes complicated by community-acquired pneumonia
- NAT10 promotes radiotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating KPNB1-mediated PD-L1 nuclear translocation
- Phytol-mixed micelles alleviate dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis in zebrafish: Activation of the MMP3–OPN–MAPK pathway-mediating bone remodeling
- Association between TGF-β1 and β-catenin expression in the vaginal wall of patients with pelvic organ prolapse
- Primary pleomorphic liposarcoma involving bilateral ovaries: Case report and literature review
- Effects of de novo donor-specific Class I and II antibodies on graft outcomes after liver transplantation: A pilot cohort study
- Sleep architecture in Alzheimer’s disease continuum: The deep sleep question
- Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments – electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis in an adult patient with upper jaw and pulmonary involvement: A case report
- Inhibition of mast cell activation by Jaranol-targeted Pirin ameliorates allergic responses in mouse allergic rhinitis
- Aeromonas veronii-induced septic arthritis of the hip in a child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Clusterin activates the heat shock response via the PI3K/Akt pathway to protect cardiomyocytes from high-temperature-induced apoptosis
- Research progress on fecal microbiota transplantation in tumor prevention and treatment
- Low-pressure exposure influences the development of HAPE
- Stigmasterol alleviates endplate chondrocyte degeneration through inducing mitophagy by enhancing PINK1 mRNA acetylation via the ESR1/NAT10 axis
- AKAP12, mediated by transcription factor 21, inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and glycolysis in lung squamous cell carcinoma
- Association between PAX9 or MSX1 gene polymorphism and tooth agenesis risk: A meta-analysis
- A case of bloodstream infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Case of nasopharyngeal tuberculosis complicated with cervical lymph node and pulmonary tuberculosis
- p-Cymene inhibits pro-fibrotic and inflammatory mediators to prevent hepatic dysfunction
- GFPT2 promotes paclitaxel resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells via activating NF-κB signaling pathway
- Transfer RNA-derived fragment tRF-36 modulates varicose vein progression via human vascular smooth muscle cell Notch signaling
- RTA-408 attenuates the hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in mice possibly by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- Decreased serum TIMP4 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- Sirt1 protects lupus nephritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 signaling pathway in human glomerular mesangial cells
- Sodium butyrate aids brain injury repair in neonatal rats
- Interaction of MTHFR polymorphism with PAX1 methylation in cervical cancer
- Convallatoxin inhibits proliferation and angiogenesis of glioma cells via regulating JAK/STAT3 pathway
- The effect of the PKR inhibitor, 2-aminopurine, on the replication of influenza A virus, and segment 8 mRNA splicing
- Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans
- Small cell lung cancer with small intestinal metastasis: Case report and literature review
- GRB14: A prognostic biomarker driving tumor progression in gastric cancer through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by interacting with COBLL1
- 15-Lipoxygenase-2 deficiency induces foam cell formation that can be restored by salidroside through the inhibition of arachidonic acid effects
- FTO alleviated the diabetic nephropathy progression by regulating the N6-methyladenosine levels of DACT1
- Clinical relevance of inflammatory markers in the evaluation of severity of ulcerative colitis: A retrospective study
- Zinc valproic acid complex promotes osteoblast differentiation and exhibits anti-osteoporotic potential
- Primary pulmonary synovial sarcoma in the bronchial cavity: A case report
- Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection
- Uterine tumor resembling ovarian sex cord tumor with extensive rhabdoid differentiation: A case report
- Genomic analysis of a novel ST11(PR34365) Clostridioides difficile strain isolated from the human fecal of a CDI patient in Guizhou, China
- Effects of tiered cardiac rehabilitation on CRP, TNF-α, and physical endurance in older adults with coronary heart disease
- Changes in T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with colorectal cancer before and after acupoint catgut embedding acupuncture observation
- Modulating the tumor microenvironment: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in improving lung cancer treatment
- Alterations of metabolites related to microbiota–gut–brain axis in plasma of colon cancer, esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, and lung cancer patients
- Research on individualized drug sensitivity detection technology based on bio-3D printing technology for precision treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors
- CEBPB promotes ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer by stimulating tumor growth and activating the NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway
- Oncolytic bacteria: A revolutionary approach to cancer therapy
- A de novo meningioma with rapid growth: A possible malignancy imposter?
- Diagnosis of secondary tuberculosis infection in an asymptomatic elderly with cancer using next-generation sequencing: Case report
- Hesperidin and its zinc(ii) complex enhance osteoblast differentiation and bone formation: In vitro and in vivo evaluations
- Research progress on the regulation of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases by chemokines
- Anti-arthritic, immunomodulatory, and inflammatory regulation by the benzimidazole derivative BMZ-AD: Insights from an FCA-induced rat model
- Immunoassay for pyruvate kinase M1/2 as an Alzheimer’s biomarker in CSF
- The role of HDAC11 in age-related hearing loss: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- Evaluation and application analysis of animal models of PIPNP based on data mining
- Therapeutic approaches for liver fibrosis/cirrhosis by targeting pyroptosis
- Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Ruellia tuberosa leaf extract induces apoptosis through P53 and STAT3 signalling pathways in prostate cancer cells
- Haplo-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and immunoradiotherapy for severe aplastic anemia complicated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A case report
- Modulation of the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway by Erianin: A novel approach to reduce psoriasiform inflammation and inflammatory signaling
- The expression of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and clinical pathological features in breast cancer patients
- Innovations in MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Bridging modern diagnostics and historical insights
- BAP1 complexes with YY1 and RBBP7 and its downstream targets in ccRCC cells
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome with elevated IgG4 and T-cell clonality: A report of two cases
- Electroacupuncture alleviates sciatic nerve injury in sciatica rats by regulating BDNF and NGF levels, myelin sheath degradation, and autophagy
- Polydatin prevents cholesterol gallstone formation by regulating cholesterol metabolism via PPAR-γ signaling
- RNF144A and RNF144B: Important molecules for health
- Analysis of the detection rate and related factors of thyroid nodules in the healthy population
- Artesunate inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through OGA-mediated O-GlcNAcylation of ZEB1
- Endovascular management of post-pancreatectomy hemorrhage caused by a hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm: Case report and review of the literature
- Efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in patients with relapsed refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A meta-analysis
- SATB2 promotes humeral fracture healing in rats by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway
- Overexpression of the ferroptosis-related gene, NFS1, corresponds to gastric cancer growth and tumor immune infiltration
- Understanding risk factors and prognosis in diabetic foot ulcers
- Atractylenolide I alleviates the experimental allergic response in mice by suppressing TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signalling
- FBXO31 inhibits the stemness characteristics of CD147 (+) melanoma stem cells
- Immune molecule diagnostics in colorectal cancer: CCL2 and CXCL11
- Inhibiting CXCR6 promotes senescence of activated hepatic stellate cells with limited proinflammatory SASP to attenuate hepatic fibrosis
- Cadmium toxicity, health risk and its remediation using low-cost biochar adsorbents
- Pulmonary cryptococcosis with headache as the first presentation: A case report
- Solitary pulmonary metastasis with cystic airspaces in colon cancer: A rare case report
- RUNX1 promotes denervation-induced muscle atrophy by activating the JUNB/NF-κB pathway and driving M1 macrophage polarization
- Morphometric analysis and immunobiological investigation of Indigofera oblongifolia on the infected lung with Plasmodium chabaudi
- The NuA4/TIP60 histone-modifying complex and Hr78 modulate the Lobe2 mutant eye phenotype
- Experimental study on salmon demineralized bone matrix loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: In vitro and in vivo study
- A case of IgA nephropathy treated with a combination of telitacicept and half-dose glucocorticoids
- Analgesic and toxicological evaluation of cannabidiol-rich Moroccan Cannabis sativa L. (Khardala variety) extract: Evidence from an in vivo and in silico study
- Wound healing and signaling pathways
- Combination of immunotherapy and whole-brain radiotherapy on prognosis of patients with multiple brain metastases: A retrospective cohort study
- To explore the relationship between endometrial hyperemia and polycystic ovary syndrome
- Research progress on the impact of curcumin on immune responses in breast cancer
- Biogenic Cu/Ni nanotherapeutics from Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seeds for the treatment of lung cancer
- Dapagliflozin attenuates atrial fibrosis via the HMGB1/RAGE pathway in atrial fibrillation rats
- Glycitein alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in keratinocytes via ROS-associated PI3K–Akt signalling pathway
- ADH5 inhibits proliferation but promotes EMT in non-small cell lung cancer cell through activating Smad2/Smad3
- Apoptotic efficacies of AgNPs formulated by Syzygium aromaticum leaf extract on 32D-FLT3-ITD human leukemia cell line with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- Novel cuproptosis-related genes C1QBP and PFKP identified as prognostic and therapeutic targets in lung adenocarcinoma
- Bee venom promotes exosome secretion and alters miRNA cargo in T cells
- Treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a chronic kidney disease patient with roxadustat: A case report
- Comparative bioinformatics analysis of the Wnt pathway in breast cancer: Selection of novel biomarker panels associated with ER status
- Kynurenine facilitates renal cell carcinoma progression by suppressing M2 macrophage pyroptosis through inhibition of CASP1 cleavage
- RFX5 promotes the growth, motility, and inhibits apoptosis of gastric adenocarcinoma cells through the SIRT1/AMPK axis
- ALKBH5 exacerbates early cardiac damage after radiotherapy for breast cancer via m6A demethylation of TLR4
- Phytochemicals of Roman chamomile: Antioxidant, anti-aging, and whitening activities of distillation residues
- Circadian gene Cry1 inhibits the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular carcinoma by the BAX/BCL2-mediated apoptosis pathway
- The TNFR-RIPK1/RIPK3 signalling pathway mediates the effect of lanthanum on necroptosis of nerve cells
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Optimization and comparative study of Bacillus consortia for cellulolytic potential and cellulase enzyme activity
- The complete mitochondrial genome analysis of Haemaphysalis hystricis Supino, 1897 (Ixodida: Ixodidae) and its phylogenetic implications
- Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors analysis of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among tuberculosis population in Huzhou City, Eastern China
- Indices of human impacts on landscapes: How do they reflect the proportions of natural habitats?
- Genetic analysis of the Siberian flying squirrel population in the northern Changbai Mountains, Northeast China: Insights into population status and conservation
- Diversity and environmental drivers of Suillus communities in Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forests of Inner Mongolia
- Global assessment of the fate of nitrogen deposition in forest ecosystems: Insights from 15N tracer studies
- Fungal and bacterial pathogenic co-infections mainly lead to the assembly of microbial community in tobacco stems
- Influencing of coal industry related airborne particulate matter on ocular surface tear film injury and inflammatory factor expression in Sprague-Dawley rats
- Agriculture
- Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958
- Variation in flower frost tolerance among seven apple cultivars and transcriptome response patterns in two contrastingly frost-tolerant selected cultivars
- Heritability of durable resistance to stripe rust in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)
- Animal Science
- Effect of sex ratio on the life history traits of an important invasive species, Spodoptera frugiperda
- Plant Sciences
- Hairpin in a haystack: In silico identification and characterization of plant-conserved microRNA in Rafflesiaceae
- Widely targeted metabolomics of different tissues in Rubus corchorifolius
- The complete chloroplast genome of Gerbera piloselloides (L.) Cass., 1820 (Carduoideae, Asteraceae) and its phylogenetic analysis
- Field trial to correlate mineral solubilization activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and biochemical content of groundnut plants
- Correlation analysis between semen routine parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation index in patients with semen non-liquefaction: A retrospective study
- Plasticity of the anatomical traits of Rhododendron L. (Ericaceae) leaves and its implications in adaptation to the plateau environment
- Effects of Piriformospora indica and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on growth and physiology of Moringa oleifera under low-temperature stress
- Effects of different sources of potassium fertiliser on yield, fruit quality and nutrient absorption in “Harward” kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa)
- Comparative efficiency and residue levels of spraying programs against powdery mildew in grape varieties
- The DREB7 transcription factor enhances salt tolerance in soybean plants under salt stress
- Food Science
- Phytochemical analysis of Stachys iva: Discovering the optimal extract conditions and its bioactive compounds
- Review on role of honey in disease prevention and treatment through modulation of biological activities
- Computational analysis of polymorphic residues in maltose and maltotriose transporters of a wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
- Optimization of phenolic compound extraction from Tunisian squash by-products: A sustainable approach for antioxidant and antibacterial applications
- Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota
- Toxicological qualities and detoxification trends of fruit by-products for valorization: A review
- Polyphenolic spectrum of cornelian cherry fruits and their health-promoting effect
- Optimizing the encapsulation of the refined extract of squash peels for functional food applications: A sustainable approach to reduce food waste
- Advancements in curcuminoid formulations: An update on bioavailability enhancement strategies curcuminoid bioavailability and formulations
- Impact of saline sprouting on antioxidant properties and bioactive compounds in chia seeds
- The dilemma of food genetics and improvement
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Impact of hyaluronic acid-modified hafnium metalorganic frameworks containing rhynchophylline on Alzheimer’s disease
- Emerging patterns in nanoparticle-based therapeutic approaches for rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis spanning two decades
- Application of CRISPR/Cas gene editing for infectious disease control in poultry
- Preparation of hafnium nitride-coated titanium implants by magnetron sputtering technology and evaluation of their antibacterial properties and biocompatibility
- Preparation and characterization of lemongrass oil nanoemulsion: Antimicrobial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and anticancer activities
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells”
- Corrigendum to “Effects of Ire1 gene on virulence and pathogenicity of Candida albicans”

