Abstract
In the last few decades, tyre rubber waste has been considered a risky issue to the ecosystem. A huge amount of used and deformed tyres is disposed of in landfill or recycled into other products. The main goal is to modify 60/70 bitumen grade to achieve 40/50 bitumen results. In this work, tyre rubber waste was added at different weights from 5 to 20% after cutting into small particles to use in the modification process of 60/70 asphalt binder. The modified asphalt was tested to meet the Iraqi standard specifications of roads and bridges. In the experimental work, Central Composite Design was applied to attain mathematical models that describes binder consistency by relating three operating parameters: tyre rubber ratio, mixing temperature and time. The predicted models relate to the penetration and softening point of the modified binder achieved R 2 of 97 and 99%, respectively. The obtained results indicated that the penetration and softening point improved after adding 20% recycled tyre rubber at 170°C and 20 min of mixing time.
1 Introduction
Over few decades, poor road pavement performance has become a widespread issue due to a dramatic increase in the traffic volume and poor maintenance services. In addition, increasing temperatures and axle loadings result in many road surfacedistresses particularly fatigue, rutting and bleeding problems. Therefore, appropriate solutions have been suggested to reduce the structural damages. Different modifiers are added by weight to the bitumen binder before mixing with aggregates. For example, adding styrenebutadiene rubber and styrene butadiene styrene as powders may improve asphalt thermal and mechanical properties. However, adding aforementioned polymers are not always the best choice due to their expensive cost. Therefore, providing other alternatives encouraged researchers as well as industrial companies to find out environmental aspects toward sustainability such as using recycled tyre rubber (RTR).
Annually, over 1 billion scrap tyres are generated worldwide in addition to 4 billion tyres that are accumulated in landfills as well as stockpiles based on a report by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development [1]. To reduce the impact of tyre waste disposal environmentally, crumb rubber (CR) is used as a modifier to produce a homogenous asphalt binder through the common method called “wet process” established by Charles McDonald in 1960s [2]. In this method, CR is added into the bitumen binder before mixing with aggregate composition. Under controlled temperature and mixing time (i.e., 170°C for 45–60 min), the CR melts and the characteristics of asphalt will get improved significantly [3].
A number of investigations and efforts have been conducted on the utilization of the CR in asphalt mixes to examine its effect on asphalt engineering performance. Chemical interaction of the CR and asphalt is affected by their properties in terms of CR size, concentration, source and asphalt characteristics such as penetration, viscosity, source, etc. A high rate of interaction is a result of high CR-specific surface area. In addition, the fast-swelling rate of CR particles is obtained when mixed with low viscous asphalt because there is a significant increase in the asphaltene amount of the residual binder [4]. High compatibility between CR and asphalt was achieved by using CR from scrap truck tyre because of the higher natural content of rubber [5].
Other important factors were taken into consideration when adding CR, such as mixing temperature and speed. The results of previous studies showed that the physical characteristics of modified asphalt enhance at lower interaction circumstances (i.e., 160°C and 10 Hz) which is commonly known as swelling extent. However, the asphalt properties declined after increasing the mixing temperature and time to higher levels [6–8]. This is mostly true due to the fact that polymer swelling is caused by diffusing small molecules of solvent through its structure. As a result, a cleavage of polymeric chains may occur which indicated a reduction in the asphalt molecular weight.
A number of conventional and microscopic tests including dynamic shear, penetration, softening point, tensile strength, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy have been carried out to simulate asphalt resistance to permanent deformation and cracking following the modification process. Previous studies revealed that penetration decreases as the CR content increases up to 20% at 190°C mixing temperature, while the softening point increases to 72°C at the same percentage and mixing condition [9]. Accordingly, the modified asphalt showed good performance in cracking within its service life. Thereby, modifying asphalt with CR shows an advantageous impact in term of water resistance by developing the elasticity of asphalt mixtures as well as decreasing maintenance costs and road noise [10–13].
The current work aims to investigate adding RTR as a modifier to enhance 40/50 bitumen properties since the last is widely used in airports and road constructions. Penetration and softening point tests are usually measures of binder consistency under different temperatures. The key of this research is to find the optimal temperature and mixing time after adding a certain amount of RTR to 60/70 bitumen that achieve 40/50 bitumen penetration and softening point. By applying different contents of RTR (5–20% with an increment of 5%) of asphalt weight and different ranges of mixing time (20–60 min) and temperatures (130–180°C), binder consistency was modelled mathematically using Central Composite Design (CCD). Details of the experimental work and methodology are described in the next section.
2 Methodology
2.1 Materials
Two materials were prepared for achieving the goals of this experimental work. They are locally produced in Iraq as follows.
2.1.1 Asphalt binder
A bitumen of 60/70 penetration grade was used in the current work. This type of bitumen is produced in the Samawah oil refinery in Iraq for use in paving roads and building construction. As mentioned previously, the objective of this study is to modify 60/70 bitumen to reach 40/50 penetration grade. The obtained data of physical properties of these bitumens are presented in Table 1 after conducting the required tests in the Samawah oil refinery [14].
Physical properties of 60/70 versus 40/50 asphalt binders [14]
| Tests | Units | Asphalt grade (60/70) | Asphalt grade (40/50) | ASTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration 100 g at 25°C and 5 s | 1/10 mm | 64 | 43 | D5 |
| Absolute viscosity at 60°C | Poise | 3,380 | 3,268 | D88 |
| Kinematic viscosity at 135°C | C st | 406 | 403 | D88 |
| Ductility at 25°C and 5 cm/min | cm | 153 | 130 | D113 |
| Softening point (ring & ball) | °C | 57.6 | 53.7 | D36 |
| Specific gravity at 25°C | g/cm3 | 1.02 | 1.04 | D70 |
| Flash point (Cleveland Open Cup) | °C | 227 | 235 | D92 |
2.1.2 RTR
It is also known as CR and is obtained by cutting scrap tyres into shreds and then ground into small particle sizes (about 10 mm) after removing reinforcing cords as illustrated in Figure 1. These particles were collected from Diwaniya rubber factory. For this study, the RTR was prepared as 5, 10, 15 and 20% of asphalt binder weight.

RTR particles produced by Diwaniya rubber factory.
2.2 Laboratory tests
Samples of the modified binder were prepared in the laboratory using a mechanical mixer for mixing the RTR particles with 60/70 bitumen. First, about 600 g of binder was heated and then placed on a sand bath above a hot plate. A high-shear radial flow impeller attached to the mixer was placed in the binder for stirring at a speed of 700 rpm. Then, a certain amount of RTR particles (i.e., 5–20% in weight) was added gradually to the binder. The continued mixing time was also varied (i.e., 20–60 min) at each specific quantity of RTR. The temperature of the binder was controlled for a specific range (i.e., 130–180°C). After mixing, each can of modified binder was allowed to cool at room temperature for 24 h before being reheated for testing. The total number of prepared modified asphaltic samples was 15 in the current work. Table 2 shows the range of the operating parameters.
Operating parameters range
| Parameter | Symbol | Minimum value | Maximum value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tyre rubber ratio (wt%) | X 1 | 5 | 20 |
| Temperature (°C) | X 2 | 130 | 180 |
| Mixing time (min) | X 3 | 20 | 60 |
Next, empirical tests of penetration and softening point are used to determine the asphalt consistency in terms of temperature susceptibility after adding the RTR modifier in different contents. Based on ASTM D5, the penetration test of bitumen took place at 25°C. A 100 g prescribed needle is placed on the surface of the asphalt cement for 5 s to measure the penetration depth. The softening point was also tested according to ASTM D36. The test is executed by confining asphalt samples in brass rings and loading the samples with steel balls. The samples are placed in a water bath at a certain height above a metal plate for heating at a specific rate. Following that, the heated steel ball will pull the sample down toward the metal plate. Then, the water temperature is measured and designated as the softening point of the modified asphalt.
2.3 Design of experiments
CCD according to response surface methodology through the Box-Wilson method [15] was used to achieve a mathematical model describing binder consistency by relating three operating parameters. The effect of adding RTR ratio (wt%), temperature (°C) and mixing time (min) on the penetration and softening point of the binder was evaluated in the current study. The number of experiments (N) required to predict these models depends on the number of operating factors (f = 3) tested according to the following equation:
Thus, the required number of experiments for three factors is 15 experiments and the operating parameters in the mathematical model will be represented by a quadratic polynomial second-order equation which has an independent variable of each factor as (X). As shown in Table 2, the symbols X 1, X 2, X 3 denote the amount of tyre rubber ratio, temperature and mixing time, respectively. The predicted responses as a dependent variable of Y which is used to represent the penetration and softening point of the binder are as shown in the following equation:
where A 0 to A 9 represent the constants of the mathematical model that can be estimated by regression analysis. To optimize the operating parameters for getting the best operating values on bitumen consistency, the statistical software program (Minitab version-19) will be used.
Table 3 shows the ranges of three investigated variables by coding based on the experimental design concept.
Coding and range of investigated parameters
| Parameter | Symbol | Level and range | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Tyre rubber ratio (wt%) | X 1 | 5 | 12.5 | 20 |
| Temperature (°C) | X 2 | 130 | 155 | 180 |
| Mixing time (min) | X 3 | 20 | 40 | 60 |
3 Results and discussion
As shown in Table 4, the experimental design of the full factorial design with three levels of coded parameters (X 1, X 2 and X 3) was used to predict approximate values of penetration and softening point of the binder.
Design experiments of coded and real operating variables
| Run | Coded parameters | Real variables | Response 1/Penetration | Response 2/Softening point | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X 1 | X 2 | X 3 | RTR% | Temperature | Mixing time | |||
| 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 5 | 130 | 20 | 52.333 | 47.0 |
| 2 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 20 | 130 | 20 | 49.667 | 47.0 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 5 | 180 | 20 | 52.333 | 48.0 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 20 | 180 | 20 | 49.667 | 49.0 |
| 5 | -1 | −1 | 1 | 5 | 130 | 60 | 54.333 | 48.9 |
| 6 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 20 | 130 | 60 | 59.000 | 49.0 |
| 7 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 180 | 60 | 58.333 | 49.0 |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 20 | 180 | 60 | 48.667 | 50.0 |
| 9 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 155 | 40 | 57.000 | 50.1 |
| 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 155 | 40 | 53.333 | 51.0 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 12.5 | 130 | 40 | 57.000 | 50.0 |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 12.5 | 180 | 40 | 56.482 | 51.04 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 12.5 | 155 | 20 | 57.220 | 51.8 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12.5 | 155 | 60 | 61.326 | 53.3 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12.5 | 155 | 40 | 59.275 | 52.6 |
The experimental results were analysed statistically to conduct the mathematical models that describe the penetration and softening point of the binder with obtained correlation coefficient R 2 and variance explained S as demonstrated in the following equations:
3.1 Effect of temperature and mixing time on bitumen penetration
Figures 2 and 3 illustrate the specific effect of adding 5, 10, 15 and 20% of RTR on bitumen performance in terms of penetration under various mixing times and temperatures. It can be summarized that at lower RTR content and as the temperature increased to 155°C, high penetration was reported particularly when the mixing time is set at 40 min. Next, a gradual increase of RTR% was tested in consistent with raising temperature from 130 to 180°C. As a result, the performance of modified bitumen shows low penetration. It is also worth mentioning that the homogeneity of bitumen becomes better and results in the reduction of penetration less than 50 when the added RTR particles started to melt as the mixing time increased up to 60 min. Similar outcomes were reported by previous works [6–9,16]. Finally, the modified bitumen 60/70 achieves the required penetration grade of bitumen 40/50 according to the Iraqi specifications SORB/R9 [17]. The lowest penetration was 47 which is closed to the obtained result of bitumen 40/50 shown in Table 1 after adding 20% RTR at 180°C and 60 min.
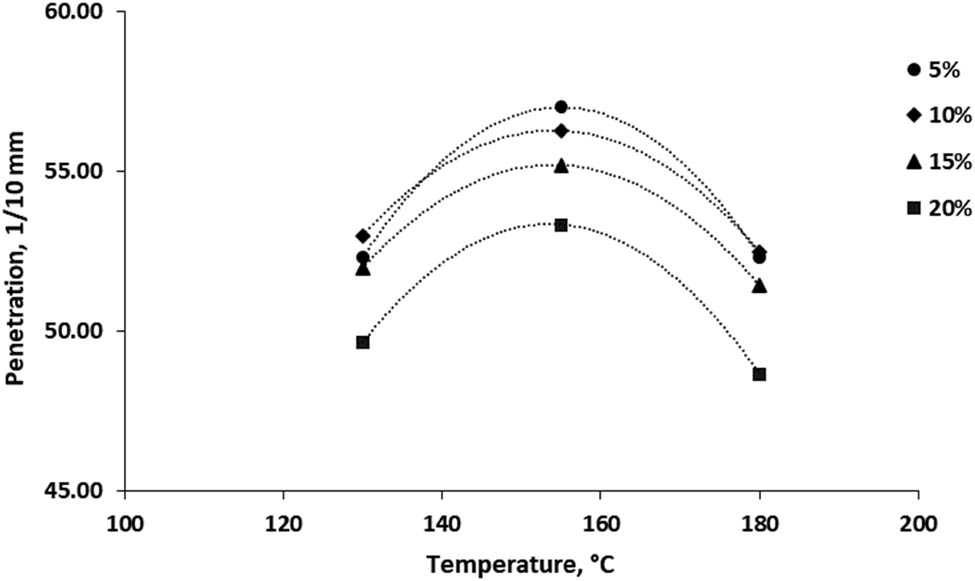
Penetration versus temperature at different RTR ratios.
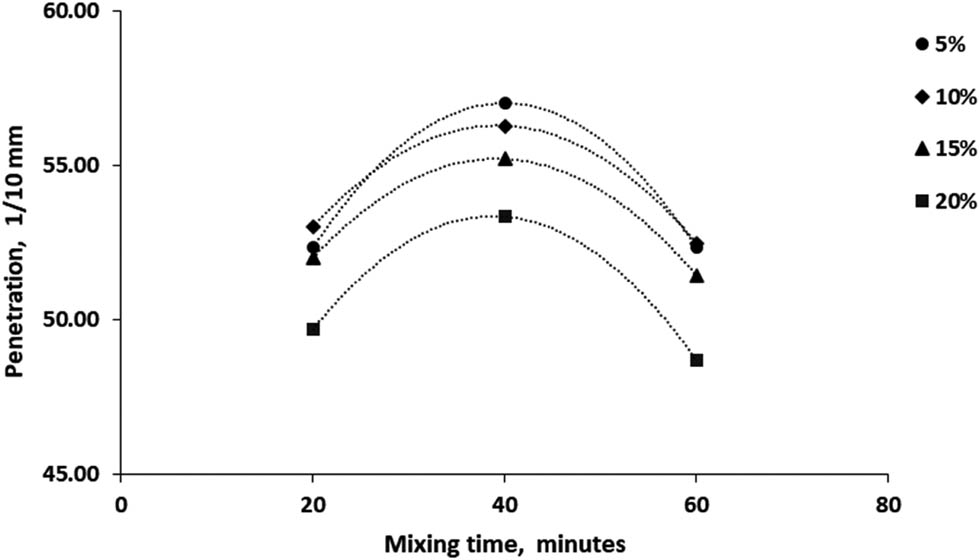
Penetration versus mixing time at different RTR ratios.
3.2 Effect of temperature and mixing time on bitumen softening point
The effect of modifying bitumen with 5–20% RTR on softening point is illustrated in Figures 4 and 5. The results were obtained and analysed at different mixing times and temperatures. It can be explained that various range of softening points (47–51) were obtained when the temperature increased up to 160°C. As a result, it was observed that increasing RTR content leads to increase softening point of the binder which may result in an increase in the viscosity property. It is also necessary to report that the softening point of bitumen shows a significant reduction when the mixing time varied from 40 to 60 min particularly after adding 20% RTR content at 180°C. The obtained softening point of modified bitumen was close to that shown in Table 1 related to 40/50 asphalt. Similar results were stated in previous works [10,16,18,19].
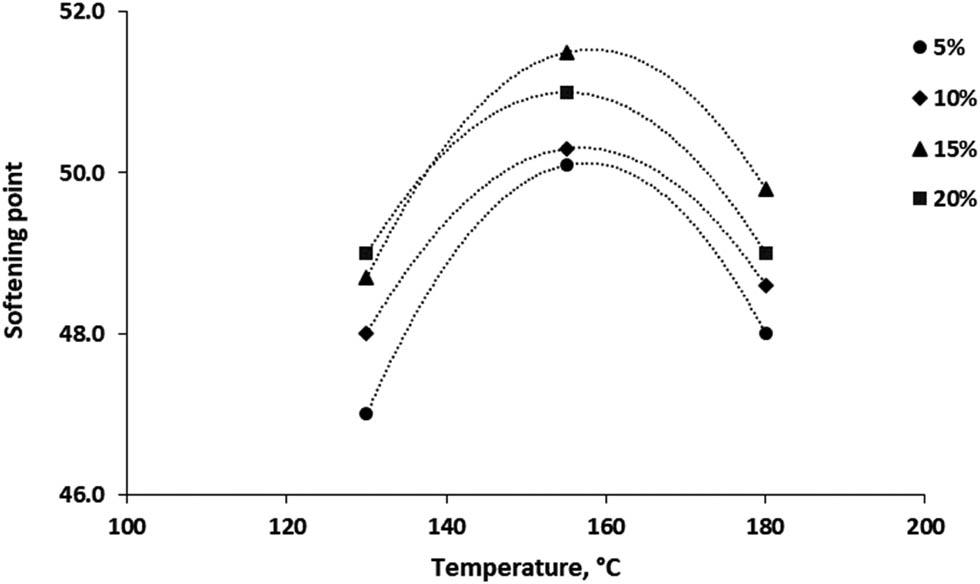
Softening point versus temperature at different RTR ratios.
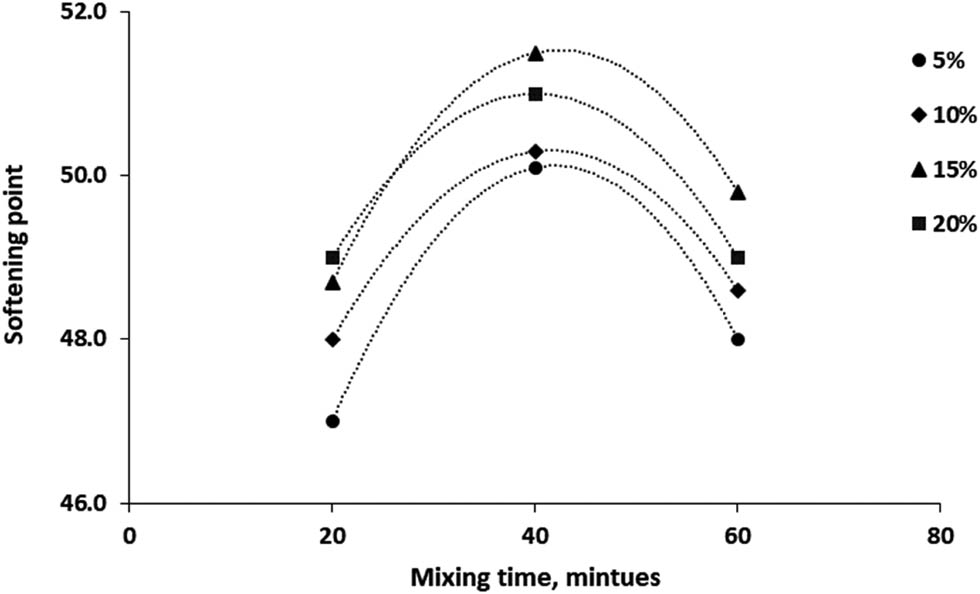
Softening point versus mixing time at different RTR ratios.
3.3 Optimization
Figure 6 shows the optimization of operating variables. It can be concluded that the best result obtained was shown at approximately 20% RTR to achieve approximately 50 mm penetration grade when the mixing time was set at 20 min and the optimal mixing temperature was 170°C. After this point, the RTR swollen and produced gel-like materials that increased the viscosity of bitumen [3]. Finally, the obtained softening point was reported as 50.24 which is close to the obtained value of bitumen 40/50 shown in Table 1.
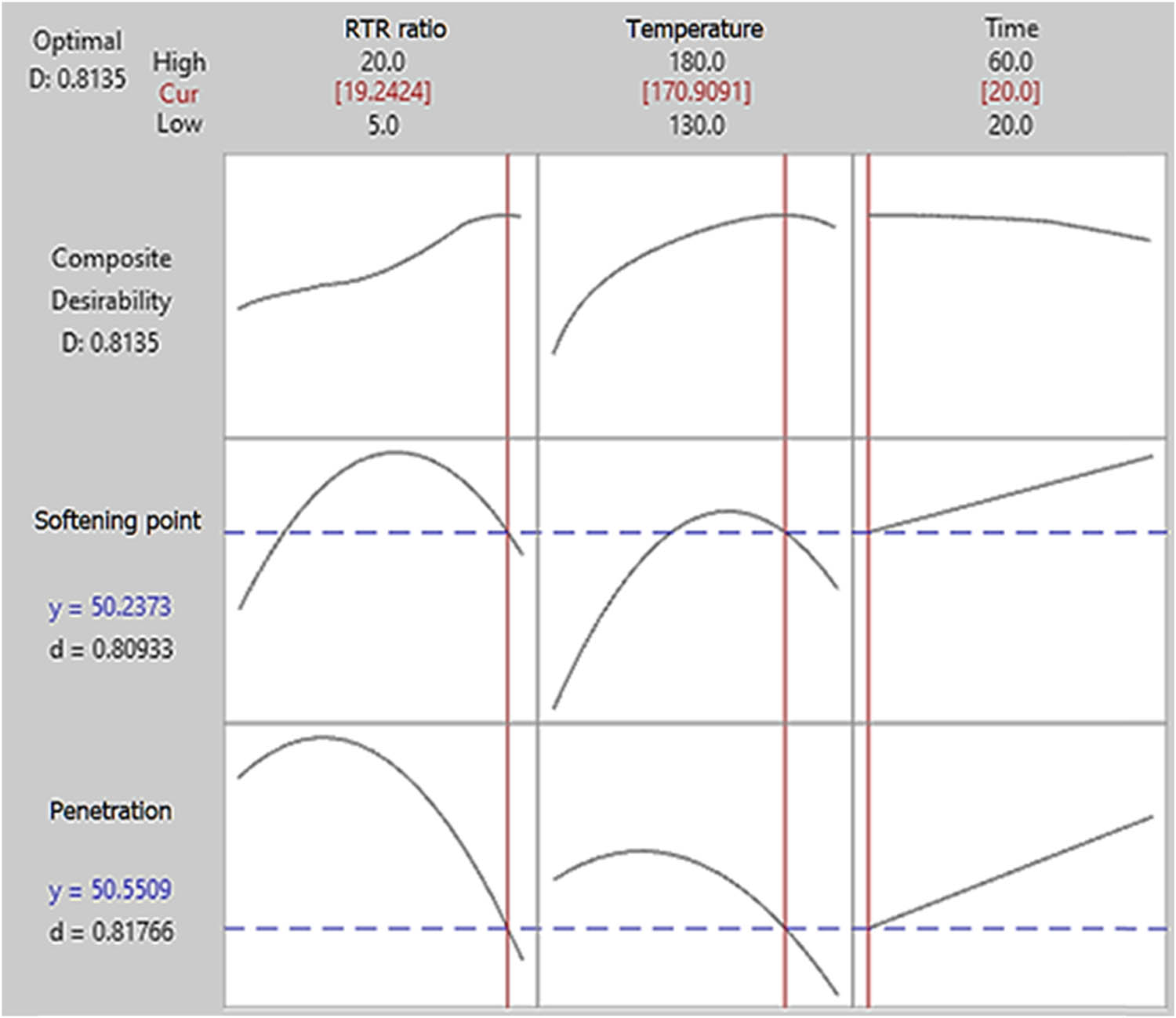
Optimization of operating variables.
4 Conclusions
The re-use of RTR as a modifier of asphalt binder can contribute in reduction of waste tyre rubbers pollution as well as consider an economic solution in minimizing the costs of recycling and manufacture. This work aims to investigate the improvement of 60/70 bitumen to achieve 40/50 bitumen properties by adding RTR contents as a modifier under different ranges of mixing temperature and mixing times. According to the previously conducted studies, the penetration and softening point of modified asphalt binder were improved after adding certain contents of RTR. The optimization reveals that the maximum limit 50 mm penetration can be achieved after adding 20% RTR at 170°C and 20 min mixing time. In conclusion, the obtained results in the current work are in consistent with the requirements of the Iraqi specifications SORB/R9 related to the properties of 40/50 bitumen used in road paving. For future works, it is worth suggesting that the obtained modified asphalt should be tested in asphaltic mix design to investigate mixture performance against different types of cracks such as fatigue and rutting. Other polymers are recommended to mix with RTR in specific percentages to test the penetration and softening point of new binder properties.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Most datasets generated and analysed in this study are in this submitted manuscript. The other datasets are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author with the attached information.
References
[1] Development, W.B.C.f.S. Managing End-of-Life Tires. 2023. Cited 2023. https://www.wbcsd.org/Sector-Projects/Tire-Industry-Project/End-of-Life-Tires-ELTs.Suche in Google Scholar
[2] Heitzman MA. State of the practice: design and construction of asphalt paving materials with crumb-rubber modifier. Final report. Washington, DC (United States): Federal Highway Administration; 1992.Suche in Google Scholar
[3] Presti DL. Recycled tyre rubber modified bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: a literature review. Constr Build Mater. 2013;49:863–81.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.09.007Suche in Google Scholar
[4] Airey GD, Rahman MM, Collop AC. Absorption of bitumen into crumb rubber using the basket drainage method. Int J Pavement Eng. 2003;4(2):105–19.10.1080/1029843032000158879Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Frantzis P. Crumb rubber–bitumen interactions: diffusion of bitumen into rubber. J Mater Civ Eng. 2004;16(4):387–90.10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2004)16:4(387)Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Abdelrahman M. Controlling performance of crumb rubber-modified binders through addition of polymer modifiers. Transp Res Rec. 2006;1962(1):64–70.10.1177/0361198106196200108Suche in Google Scholar
[7] Abdelrahman M, Katti DR, Ghavibazoo A, Upadhyay HB, Katti KS. Engineering physical properties of asphalt binders through nanoclay–asphalt interactions. J Mater Civ Eng. 2014;26(12):04014099.10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001017Suche in Google Scholar
[8] Abdelrahman MA, Carpenter SH. Mechanism of interaction of asphalt cement with crumb rubber modifier. Transp Res Rec. 1999;1661(1):106–13.10.3141/1661-15Suche in Google Scholar
[9] Dakhil IH. Improvement of asphalt binder by recycling of waste tyre rubber. Int J Adv Res. 2016;4(5):414–8.10.21474/IJAR01/388Suche in Google Scholar
[10] Lv Q, Huang W, Zheng M, Hu Y, Yan C, Wang J. Understanding the particle effects and interaction effects of crumb rubber modified asphalt regarding bonding properties. Constr Build Mater. 2022;348:128716.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128716Suche in Google Scholar
[11] Manosalvas-Paredes M, Gallego J, Saiz L, Bermejo JM. Rubber modified binders as an alternative to cellulose fiber–SBS polymers in stone matrix asphalt. Constr Build Mater. 2016;121:727–32.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.028Suche in Google Scholar
[12] Yaacob H, Ali Mughal M, Putra Jaya R, Hainin MR, Jayanti DS, Che Wan CN. Rheological properties of styrene butadiene rubber-modified bitumen binder. UTM Jurnal Teknologi; 2016;78(7–2):121–6.10.11113/jt.v78.9503Suche in Google Scholar
[13] Tan Z, Wang J. Research of the rheological modification mechanism of crumb rubber-modified asphalt containing polyamide 6 additive. Adv Civ Eng. 2020;1–10.10.1155/2020/8877487Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Refinery, S.O., Physical properties of 60/70 and 40/50 asphalt binders. 2023.Suche in Google Scholar
[15] Usman A, Sutanto MH, Napiah MB, Yaro NSA. Optimization in asphalt mixtures: a review. In Response surface methodology in engineering science. UK: IntechOpen; 2021.Suche in Google Scholar
[16] Zhu H, Zhang M, Li Y, Zou Y, Chen A, Wang F, et al. Swelled mechanism of crumb rubber and technical properties of crumb rubber modified bitumen. Materials. 2022;15(22):7987.10.3390/ma15227987Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Housing, M.o.C.a. Standard specifications for roads and bridges – section R9. Iraq. 2003.Suche in Google Scholar
[18] Abdelaziz M, Mohamed Rehan K. Rheological evaluation of bituminous binder modified with waste plastic material. In the 5th International Symposium on Hydrocarbons & Chemistry (ISHC5). Algiers; 2010.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Hainin MR, Aziz MA, Aziz A, Adnan A, Hassan A, Putra Jaya R, et al. Performance of modified asphalt binder with tire rubber powder. J UTM Technol (Sci Eng). 2015;73(4):55–60.10.11113/jt.v73.4288Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection

