Abstract
Aluminum is a highly valuable structural metal utilized in various industrial sectors; particularly, it is utilized in considerable quantities in the nautical, aeronautical, and automotive industries. Aluminum is additionally utilized in small amounts in several other industrial sectors. The composite materials are now extensively utilized in various applications after their introduction. In this research, they prepared composite samples of aluminum with adding hematite nanoparticles with different ratio (2, 4, 6, and 8) wt% by powder metallurgy technology, and the sample preparation conditions was (mixing time reach to 2 h for every sample; the compaction loads is 6 tons and sintering temperature equal to 600°C). The tests conducted were XRD, SEM, EDS, green density, green porosity, microhardness, compression, and wear. The results illustrate that the hardness and wear values increase when increasing the hematite percentage.
1 Introduction
Aluminum and aluminum alloys are generally utilized in different industries, including aerospace, building, cooking utensils, packaging, and electrical wiring [1,2]. Unfortunately, there are limited sources for primary aluminum, which has been mined from ores. As a result, it is essential to recycle aluminum effectively. Thus, the researchers are focusing their efforts on developing aluminum recycling processes that are very effective [3,4]. Aluminum composites are recognized as sophisticated materials because they outperform conventional technical materials in their mechanical, electrical [5], and thermal characteristics [6] while being more cost-effective [7,8,9,10,11]. Because of their strong mechanical qualities, aluminum matrix composites [12,13,14], often known as AMCs, have become more important in various sectors. Aluminum–metallic matrix composites are the material of choice in many industries and applications involving marine, automotive, military, aerospace, and other domestic uses. Enhanced mechanical characteristics are the consequence of combining a variety of reinforcements with aluminum metal matrix composites utilizing powder metallurgy technology. These improvements involve increased wear rate, hardness, compressive strength, and ultimate tensile strength. AMCs are made up of nonmetallic reinforcement (SiC, B4C, Si3N4, AlN, TiC, TiB2, and TiO2) inserted into an aluminum matrix. This combination offers improved qualities compared to alloys made of base metal (Al). Reinforcement in AMCs may be present in the form of discontinuous or continuous fibers, whiskers, or particles in volume fractions ranging from a few percent to 70%. AMCs are examples of sophisticated technical materials, and compared to other standard aluminum alloys, their qualities surpass those of AMCs [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22].
Powder metallurgy, often known as PM, is an important part of many different sectors since it allows for producing high-strength materials at a lower price, and PM alloys have superior mechanical qualities. Powder metallurgy is the manufacturing and usage of powder metallurgy, and powders have been specified as particles that are typically smaller than 1,000 nm in size. The term “powder” refers to these particles. In addition, a powder metallurgy alloy with an aluminum basis has enhanced characteristics like excellent stress resistance for corrosion cracking and high transverse yield strength [23,24]. Utilizing PM is beneficial for several reasons, the most important of which are economic, distinctiveness, and captive application. The powder metallurgical technique offers the additional benefit of manufacturing near-net-shape components while eliminating the need for completed machining procedures. Compared to other metal casting methods, the PM has been illustrated to improve product quality and significantly reduce the number of raw materials utilized [25,26].
Utilizing the powder metallurgy method, there are a few different approaches to manufacturing metal foams based on aluminum [27]. The density, weight, or compaction pressure of the reinforcing and the kind of reinforcement are some of the powder metallurgy process factors that significantly impact the recycling and foaming of aluminum [3]. A significant amount of development and research work was done in AMCs utilizing various reinforcing materials to obtain a material with the needed qualities by strategically utilizing various reinforcing elements inside the aluminum matrix.
Mohammad et al. [28] researched whether adding materials involving aluminum boron carbide and manganese may increase the strength of aluminum composites – the application of powdered metallurgy to accomplish enhanced mechanical functionality. The obtained results show that the alloy is improved at less addition of boron and manganese. This lead to enhance casting capacity and mechanical performance of the alloy and the composites with superior mechanical characteristics. Rojas et al. [29] researched the recyclability of aluminum as waste called chips and typically is not ideal for melting. Sawing procedures combined with powder metallurgy are utilized to obtain the aluminum powder. The grinding process utilized various grinding times and a 55 revolutions/minute rotating speed. A pressure of 800 MPa was utilized while compacting the material. The cylindrical specimens were sintered by argon at a temp of 620°C for 1 h. Based on the findings, it is clear that aluminum chips have reached the optimum state to be processed throughout the powder metallurgy process. Zamani et al. [30] researched mixed metals (MCCs) strengthened with Al + Gr + Al2O3 particles to attain better wear and mechanical characteristics. Powder metallurgy was the approach that was utilized to explore the mechanical characteristics, wear characteristics, and purity of Al + Gr. The results show that the mixed impact of Al2O3 and graphite reinforcing particles leads to improving the mixed mechanical and wear characteristics of the hybrid MMC. Also, the mechanical characteristics have improved while the wear rate and friction decreased significantly.
Zhangab et al. [31] utilized the powder metallurgy process to investigate the effect of SiC-graphene nanosheets (GNSs) and SiC-graphite on the microstructures and characteristics of particulate-reinforced metal matrix composites. The ceramic nanoparticle dispersion is necessary for mixing with aluminum matrix composites [32]. The results show that the thin GNSs enhance the aluminum particle deformation and are distributed more evenly within the composite than graphite. Yu et al. [33] utilized graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) because of their good mechanical characteristics and excellent electrical and thermal characteristics. The process was undertaken with the powder metallurgy by adding 0.5 wt% (GNPs) and pure Al.
In most cases, the microstructure will influence the material’s physical and mechanical characteristics. The GNPs were distributed uniformly throughout the Al matrix, and the tensile yield strength hardness and composite fracture were measured at 73 HV and 248 MPa, respectively. Charan et al. [34] utilized four composite alloy specimens, each consisting of aluminum powder mixed with silicone carbide at 2 and 7 volts and alumina at 3 and 8 volts [35]. The specimens were charged to varying voltages. According to the findings, increased Al/SiC volume reduced the material’s hardness, density, and compressive strength. The physical and mechanical characteristics of the pipeline’s powder metallurgy process have dramatically improved compared to commercial aluminum ones. Albert et al. [36] involve three different volume fractionation to improve the mechanical characteristics of aluminum carbide (TiC) in metal aluminum metal composites. The synthesis of mechanically alloyed by powder metallurgy processes of 0, 5, and 10% TiC. The results suggest that adding TiC increases the composite’s hardness significantly.
Analysis of nanocomposites (MMNCs) made of aluminum–aluminum oxide (Al-Al2O3) by Amierah et al. [37] with varying volumes of reinforcement made of aluminum oxide. Three different kinds of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposite have been generated utilizing a typically pumped metallurgy (PM) approach, with 10, 15, and 20% volume fractions of Al2O3, respectively. The optical micrographs revealed that the nanoparticles were closely connected to the matrix and the Al2O3 reinforcement. Also, when the quantity of reinforcing rises, the mechanical qualities of the reinforcement, involving its compressive power, tensile resistance, and hardness, would increase. Venkatesh et al. [38] enhanced the mechanical behavior of the kaolin-fortified aluminum matrix that was created utilizing the technique of powder metallurgy. The composite samples were produced utilizing powder metallurgy and reinforced with 5, 10, 15, and 20% kaolin. It was demonstrated that A-Kaoline stiffness increases from 77 VHN to 187 VHN when aluminum is reinforced by 20%. Still, the rigidity of aluminum without reinforcement is only 20% higher, involving high-strength ceramic particles into the kaoline reinforcement phase, such as Al2O3 and SiO2, resulting in a tensile and compression strength improvement of the composition ranging from 0 to 20%.
The current work aims to produce composite material from aluminum-added hematite (iron oxide) with 2, 4, 6, 8 wt% and studied the effect of added on mechanical characteristics involving (compression, wear, and hardness tests) physical tests such as apparent density, porosity in addition to investigating the microstructure of aluminum substrate before and after adding iron oxide utilizing X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and energy-dispersive spectroscope (EDS).
2 Experimental part
In this part, we will discuss the tools and resources utilized throughout this project and the order in which operations and assessments have been carried out.
The materials utilized in this work are aluminum and hematite powders of high purity (99.9 wt%). The elemental powders (i.e., Al and Fe2O3) utilized in this research with an average particle size are as follows: for Al = 33 µm and Fe2O3 = 25 nm.
2.1 Plan of work
The following is one possible explanation for the plane of work:
Preparation of several nanocomposite materials as indicated with nano Fe2O3 added as 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 wt% to the aluminum matrix.
Wet-mixing the powders for 2 h.
The addition of powders to the die cavity in a step-by-step, precisely regulated way.
Pressing powders at a pressure of six tons.
Sintering of all prepared specimens in a vacuum oven with Argon inert gas at 350°C for 1 h, then increasing the sintering temp to 600°C for the next 3 h.
After the sintering process, go to the samples tested.
3 Tests
3.1 X-Ray diffraction analysis
The X-ray diffraction examination was done on specimens containing 6 and 8 weight percent of Fe2O3 aluminum composite to detect the already present phases. Lab XRD-6000 from Shimadzu was utilized as the X-ray diffraction instrument. It had a single wavelength of Cu-Kα – 1.54 A° and a nickel filter.
3.2 Physical tests
Many physical tests were performed on sintered specimens, green compacts, and elemental powders. The following are possible components of these examinations:
3.2.1 The apparent density of powders and blended powders
The measure of the weight of a single unit volume of a metal powder in a noncompacted state, expressed in grams per cubic centimeter, is referred to as the apparent density. The determination of apparent density is a crucial characteristic of powdered substances. The volumetric property of loose powder is a crucial factor that influences various process parameters, such as the design of compacting machinery and the extent of press movements required to achieve compaction and densification of the powder.
Pouring powder into standard-graded cubes with a max capacity of 10 ml into the appropriate grade is how apparent density measurements are produced. During the leveling process, extreme caution is required to prevent the powder in the cup from becoming physically denser. A microbalance is utilized to determine, with an accuracy of within ±0.0001 g), the cup’s weight both with and without the powder. The following calculation is then utilized to estimate the material’s apparent density in grams/cubic centimeter.
where
3.2.2 Green density and porosity
The green density of the compact may be represented as the weight of a unit volume of compressed mixed powder in grams/cubic centimeter. The following formula is utilized to determine it based on the assessment of the dimensions and the weight of the compact specimen:
where
The understanding of the theoretical density of mixed powders (mixed), computed by the percent by weight of elements powder multiplied by its theoretical density, is utilized to measure green porosity. The formula for this calculation is as described in the following:
where
The formula may then be utilized to determine the porosity of the green material:
where
3.3 Scanning electron microscope examination
These specimens, which had a diameter of 10 millimeters, were flattened utilizing SiC grinding papers of varying roughness (400, 600, 800, and 1,000 grit size). Samples had a diameter of 10 mm. Throughout the grinding procedure, the water served as a coolant, preventing an increase in temp that the friction between the specimen and the grinding sheets would have otherwise caused. After that, a mirror-like surface that is flat, scratch-free, and reflective was produced by polishing the samples utilizing diamond paste. The grinding and polishing processes were carried out with the help of model polishing equipment (MP-2B grinder polisher). After the samples had been etched utilizing a solution of 0.5% hydrofluoric acid and 99.5% distilled water for fifteen seconds at room temperature [15], they were washed with distilled water and then dried utilizing an electrical drier [39] to determine the microstructure of each sample.
3.4 Microhardness measurements
Microhardness type of the Vickers tester (Digital Display microhardness Tester model Hv-1000). Utilizing a standard 136° Vickers diamond pyramid indenter and optical microscopy to evaluate the diagonal length of Vicker’s impression, this apparatus was utilized to determine the hardness of the specimen by applying a load of 100 g and holding it in place for 20 s on the specimen’s outermost layer. The following is a specification of the microhardness (H.V.) of the Vicker [31]:
where P = applied to the load and
Each specimen has its unique sequence of the three measurements.
3.5 Test of compression
The following are the dimensions of the cylindrical specimens subjected to the compressive load: 1 cm diameter and 2 cm height. In this instance, samples were created by the ASTM standard [34]. The compression tests were conducted at room temp utilizing a computerized conventional test machine (Gunt/Hamburg, China) with a loading proportion of 0.1 mm min−1.
3.6 Wear test
By ASTM (G99-04) [40] specimens with a diameter of 1.3 cm and a height of 0.5 cm were created for each composite sample. To prepare the samples for testing, a surface roughness of 0.8 µm on the mean was achieved by grinding them with SiC sheets. After that, the samples were weighed utilizing a sensitive electric balance model (M254A) with an accuracy of +0.0001. The pin-on-disk idea was utilized in the research of dry wear with several types of wear tester devices (MT-4003, version 10.0). The samples put through the test were pinned vs. a standard disk made of steel with a hardness of (850 HV).
F is the normal force on the pin = 10 N, d is the pin diameter = 1 cm, Disk diameter = 3 cm, R is the radius of wear track = 0.5 cm, and ω is the rotating disk speeding = 250 rpm.
The sample was weighed after 5, 10, 15, and 30 min to calculate how much weight had been lost. The following formula was utilized to translate the total loss in weight to an equivalent loss in volume:
where weight loss = weight before the test − weight after the test.
Furtherance of observing the deterioration of the surface’s microstructure utilizing an optical microscope, the rate of wear was calculated utilizing the results of this test. The experiment was conducted at room temperature and with no lubrication present.
4 Results and discussion
The findings of X-ray diffraction experiments and the microhardness of composite specimens produced of Fe2O3 and aluminum are examined in depth. In addition, the findings of the wear test and the green density of compact specimens are involved in the discussion.
4.1 X-ray diffraction pattern of compacts
X-ray diffraction examinations of all samples were conducted to determine which nanocomposite samples were employed in this investigation. The results of these analyses are displayed in Figure 1. An X-ray diffraction test was conducted on the samples 0, 6, and 8 wt% of Fe2O3 nanopowders implanted in the aluminum matrix to ascertain the phases already present in each sample. The diffraction angle (2θ°) ranges from 30° to 90°, and the phases produced by this range are discussed further down. When compared the XRD results can noted Fe2O3 shifted aluminum peaks.

Demonstrates X-ray diffraction findings for specimens.
4.2 The green density of compacts
Figure 2 illustrates the correlation between compacting pressure and the green density of compacted specimens. The green density will grow as more pressing tension is applied to any compact. This increase will take place from 4 to 7 MPa. According to what is illustrated in Figure 2, the compacting pressure is the foundation for all subsequent investigations of other factors involving the loading rate, the time during which the load is at its most significant, and all other parameters involved in the sintering process [41,42].
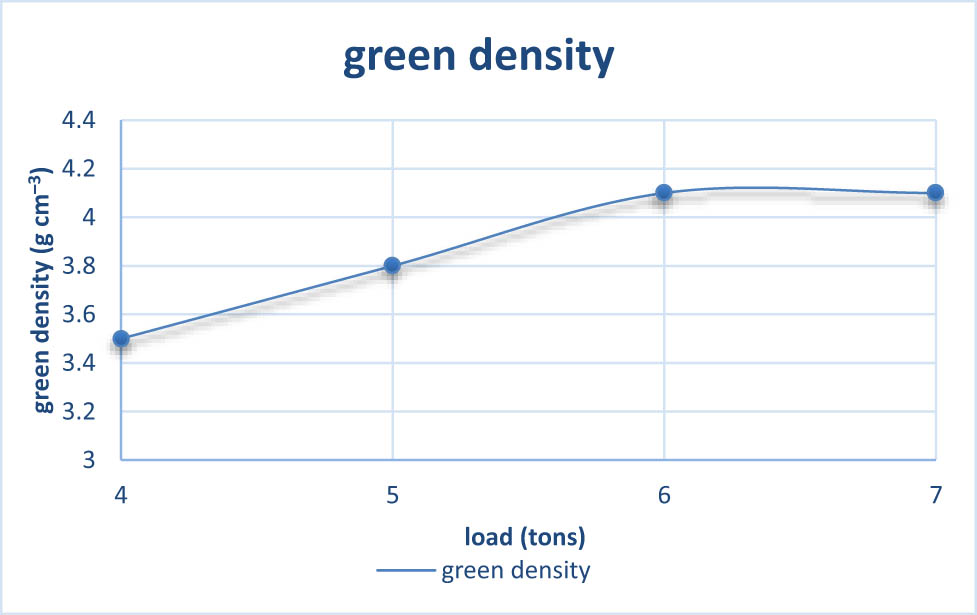
Green density as a function of load.
Another factor that plays a role in determining density is the ratio of the compact to the amount of pressure given to the contact area between the die-side walls and powder. Where there is the most wall friction, which results in the most significant amount of relative motion between particles, the tip of the outside circle has the highest density. The circumference density drops quickly from top to bottom, with the most compact density toward the bottom. Since there is less friction between the powder and die wall, there is less of an impact on the density distribution along the centerline of the compact. This results in a more consistent density distribution.
4.3 Scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive spectroscope
The FESEM images captured at a magnification of 50 µm or 70,000× are depicted in Figure 3. The nanocomposite microstructure incorporating varying weight percentages (2, 4, 6, and 8) of Fe2O3 is depicted in the presented images, which demonstrate the existence of Fe2O3 and uniform dispersion within the Al-matrix. The presence of Fe2O3 within the boundaries of grains of aluminum particles can be attributed to the high energy levels of these boundaries, which serve as attractive sites for foreign particles. The gray light signifies the aluminum matrix. Examining nanocomposite microstructure indicates a homogeneous dispersion of the hybrid nanomaterials and reduced porosity at the interfaces between grains. The Fe2O3 nanoceramic exhibits a white coloration as show in Figure 3, whereas the Al matrix displays a darker hue [43,44].

SEM and EDS patterns for different Fe2O3 ratios.
The energy dispersion spectrum (EDS) analysis was employed to ascertain the composition of the nanocomposite. The outcome commonly derived from the data presented in Figure 3a is depicted in Figure 3b. Due to the relatively larger identification area of the EDS beam in comparison to the mean size of Fe2O3 nanoparticles, the resulting EDS peaks for said nanoparticles will unavoidably contain compositional data about the Al matrix near the particles. Based on the compositional analysis of the matrix, it is apparent that the composition of the nanoparticles is solely responsible for the presence of O and a portion of the Fe peak. The data indicate that the values of Fe and O increase as the percentage of Fe2O3 added increases [45].
4.4 Microhardness measurement
For determining the microhardness of the samples that were created utilizing a powder metallurgy technique (compaction and sintering), the tests were carried out by taking the average of three readings taken at each position. The graphical representation of the obtained findings may be seen in Figure 4.

The microhardness values of hematite percent added to aluminum specimen.
The determined hardness magnitude for the nanocomposite specimens is illustrated in Figure 4. Since it is common knowledge that Fe2O3 has a higher hardness and a higher level of brittleness compared to Al, and since Al has a lower level of strength and a higher level of softness in this system, [20] and since the specimens consist of both Fe2O3 and Al, it can be deduced (based on the hardness magnitudes) that when the amount of Fe2O3 increases, the level of hardness also increases. Because of this, a phase composed entirely of Fe2O3 would have a greater value for its hardness (which is said to have greater strength than the other). The flexibility of the aluminum matrix is anticipated to be maintained, although the strength of aluminum that ceramic nanoparticles have strengthened is anticipated to be significantly increased [46,47,48].
The mechanical [48] properties evaluation reveals an improvement in hardness and tensile strength with the fiber addition without significant loss in ductility. Ultimate tensile strength increased by 65.51 with 6% reinforcement of short basalt fibers. Here, continuous fiber, continuous fiber, and random distribution were compared up to 6% volume distribution only. The effect of the further addition of fibers was not discussed. The microstructure shows a uniform distribution of fibers. Uniform distribution and enhanced mechanical properties were found in a study [47] with 5% rice husk ash where experimental data was compared with simulations.
4.5 Compressive strength test
The compressive strength test findings are illustrated in Figure 4, which involves a list of the magnitudes. Figure 5 also illustrates how the percentage of hematite particles in the aluminum matrix affects the material’s compressive strength.

The compressive strength of hematite percent added to aluminum specimen.
Because of these findings, it is simple to demonstrate that increasing the proportion of hematite in the aluminum base increased the compressive strength. The increase in compressive strength may be attributed to the function that micro iron oxide particles play in the material. These particles acted as impediments that hampered the migration of dislocations, which resulted in the matrix being reinforced. The sample with Al + 8% Fe2O3 showed the most significant increase in compressive strength, 129% compared to the control.
The increases in the compressive resistances of nanocomposites are associated with the introduction of the hard ceramic materials of Fe2O3. However, the increase in Fe2O3 can increase brittleness and decrease compressive strength, and it can then inhibit elastic deformation and prevent failure at the rimmed area on the surface. Nanoparticles of hematite-AMCs impedes dislocation motion and that will cause dislocation rotate around the hematite particles [49].
4.6 Wear tests
They are utilizing the density of every specimen to do a conversion from the loss in weight to a reduction in volume. The outcomes of this test are illustrated in Figure 6 and were carried out under the same settings as those described earlier (F = 10 N; = 300 rpm; t = (5, 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30) min).

The volume loss of specimens.
The data indicate a positive correlation between the applied load and volume loss, with the highest volume loss observed at a load of 10 N and the lowest at lower loads. The maximum volume reduction was observed at a force of 10 N, while the opposite was true for the minimum volume loss. The anticipated outcome was the manifestation of this phenomenon, whereby the augmentation of the load results in a concomitant rise in the level of friction between the surface of the specimen and the rotating disk. In addition, the volume loss was illustrated to grow with time since an increase in the amount of specimen particles lost with increasing friction duration. In addition, these data demonstrate the impact of adding iron oxide particles on wear rates in various situations. The volume loss experienced by the composite fell dramatically as the percentage of iron oxide in the composite increased. It reached its lowest value in the composite, involving the highest amount of iron oxide (8%). This may be due to the function that iron oxide particles play in inhibiting the mobility of dislocations; as a result, material’s hardness was raised, and its resistance to wear was also improved. According to the data presented earlier, the wear rate in the Al specimen is at its peak at 10 N. However, this rate is reduced by 66% in aluminum reinforced with 8% Fe2O3.
The wear volume and wear factors have decreased as the percentage of reinforcement increased. It is due to the fact that hematite is a harder material, and it imparts the hardness property to the composite [50]. The damaged surface has been studied due to the adhesion wear for aluminum and aluminum reinforced by 8% Fe2O3 alloys, and images have been taken by the light microscope as shown in the following figures:
Figure 7a and b shows the light optical microscope for aluminum and aluminum reinforced by 8% Fe2O3 alloys after wear test, These figures illustrated the effect of wear process on the surface of the samples and the grooves are found in the direction of rotation of disk. Due to friction, the increase in temperature is observed.

Microstructure for aluminum and aluminum reinforced by 8% Fe2O3 alloys by use light optical microscope with magnification 100× after wear test under 10 N load and 30 min. (a) Al; (b) Al-8% Fe2O3.
Where the grooves were clearer and deeper in aluminum alloy compared to samples aluminum reinforced by 8% Fe2O3 alloy due to the presence of iron oxide, which increases the hardness and gives relatively high wear resistance (Table 1).
Summary of mechanical tests
| Samples | Micro harness (g mm‒2) | Compression value (MPa) | Volume loss (mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 53 | 110 | 0.72 |
| Al-2% nFe2O3 | 84 | 194 | 0.47 |
| Al-4% nFe2O3 | 112 | 219 | 0.36 |
| Al-6% nFe2O3 | 177 | 245 | 0.26 |
| Al-8% nFe2O3 | 204 | 262 | 0.21 |
5 Conclusion
The following are some possible inferences to make after looking at the findings:
The powder metallurgy (PM) technique is theoretically viable, energetically efficient, and economically cost-effective successfully to fabricate composite samples of aluminum reinforced by Fe2O3 particles.
The experimental results showed that (Fe2O3 + Al2O3) Al composites could be helpful for automotive and aeronautic applications, which can be fabricated without difficulty utilizing the powder technology route.
All the specimens compacted at 6 tons and sintered at (600°C ± 5) for (3 h) of prepared specimens are effective in satisfying sintering completely Al and Fe2O3 into a structure that gained.
Almost all the prepared samples resulted in a two-phase structure (i.e., Al and Fe2O3) at room temperature.
The microstructure analysis reveals that the hybrid nanomaterials Fe2O3 exhibit a homogeneous distribution within the pure aluminum matrix, reducing porosity. This particular factor results in a noteworthy improvement in both tribological and mechanical characteristics.
The Al-Fe2O3 prepared increased the hardness, compression strength, and wear resistance relatively with increasing Fe2O3.
The wear test was conducted utilizing produced nanocomposite cylindrical pins in contact with a steel disc, with a constant load of 10 N and a sliding speed of 300 rpm. The findings indicate that the incorporation of nano Fe2O3 resulted in a decrease in wear rate, weight loss, and coefficient of friction (COF). Notably, the highest reduction in wear was found by adding 8% Fe2O3 wt% as compared to the base metal, with a decrease of 66%.
Acknowledgments
The Ministry of Higher Education, University of Babylon, and Al-Mustaqbal University are gratefully acknowledged (Grant number: MUC-E-0122). This research was carried out in the laboratory at the University of Babylon.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest
-
Data availability statement: Most datasets generated and analyzed in this study are in this submitted manuscript. The other datasets are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author with the attached information.
References
[1] Marini D, Genova V, Marra F, Pulci G, Valente M. Mechanical behaviour with temperatures of aluminum matrix composites with CNTs. Chem Eng Trans. 2017;60:25–30.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Hussain AJ, Al-Khafaji ZS, Hamza WA. An investigation into the distribution of internal residual stresses of aluminum plate subjected to thermal load by using hole drilling technique. J Mech Eng Res Dev. 2021;44:402–11.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Kumar N, Bharti A. Review on powder metallurgy: A novel technique for recycling and foaming of aluminium-based materials. Powder Metall Met Ceram. 2021;60:52–9.10.1007/s11106-021-00214-4Search in Google Scholar
[4] Radhi NS, Al-Khafaji ZS. Preparation and Investigation composite coating (Ni-nano hydroxyapatite) on low carbon steel samples. 6th International Conference on Nanotechnology, Adv. Mater. its Appl.; 2018. 10.13140/RG.2.2.10097.79201 Search in Google Scholar
[5] Radhi NS, Marza M, Al-Khafaji ZS. Modification of nickel-phosphor electroless coatings by adding particles of zirconia. Solid State Technol. 2020;63:1178–86.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Al-Zubaidy B, Radhi NS, Al-Khafaji ZS. Study the effect of thermal impact on the modelling of (titanium-titania) functionally graded materials by using finite element analysis. Int J Mech Eng Technol. 2019;10:776–84.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Moona G, Walia RS, Rastogi V, Sharma R. Aluminium metal matrix composites: A retrospective investigation. Indian J Pure Appl Phys. 2018;56:164–75.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Al-khafaji ZS, Radhi NS, Mohson SA. Preparation and modelling of composite materials (polyester-alumina) as implant in human body. Int J Mech Eng Technol. 2018;9:468–78.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sallal HA, Radhi MS, Mahboba MH, Al-Khafaji Z. Impact of embedded sol-gel synthesized triple composites on polymer’s mechanical properties. Egypt J Chem. 2022;66:197–203. 10.21608/ejchem.2022.154630.6684 Search in Google Scholar
[10] Fahad ND, Radhi NS, Al-Khafaji ZS, Diwan AA. Surface modification of hybrid composite multilayers spin cold spraying for biomedical duplex stainless steel. Heliyon. 2023;9:14103. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14103 Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Radhi NS, Sahi NM, Al-Khafaji Z. Investigation mechanical and biological properties of hybrid PMMA composite materials as prosthesis complete denture. Egypt J Chem. 2022;65:681–8. 10.21608/EJCHEM.2022.110545.5034 Search in Google Scholar
[12] Davim JP. Metal matrix composites: Materials, manufacturing and engineering. De Gruyter; 2014.10.1515/9783110315448Search in Google Scholar
[13] Alma MH, Candan Z, Gonultas O, Salan T, Tozluoglu A, Acharya SK, et al. Green composites: Materials, manufacturing and engineering. Vol. 7. Elsevier, Amsterdam, Netherlands: Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG; 2017.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Shirvanimoghaddam K, Hamim SU, Karbalaei Akbari M, Fakhrhoseini SM, Khayyam H, Pakseresht AH, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced metal matrix composites: Fabrication processes and properties. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf. 2017;92:70–96.10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.10.032Search in Google Scholar
[15] Inegbenebor AO, Bolu CA, Babalola PO, Inegbenebor AI, Fayomi OSI. Aluminum silicon carbide particulate metal matrix composite development via stir casting processing. Silicon. 2018;10:343–7.10.1007/s12633-016-9451-7Search in Google Scholar
[16] Raza M, Alrobei H, Malik RA, Hussain A, Alzaid M, Saleem M, et al. Structural, fatigue behavior, and mechanical properties of zirconium tungstate-reinforced casted A356 aluminum alloy. Metals (Basel). 2020;10:1492.10.3390/met10111492Search in Google Scholar
[17] Aynalem GF. Processing methods and mechanical properties of aluminium matrix composites. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2020;2020:1–19.10.1155/2020/3765791Search in Google Scholar
[18] Abdullahi U, Maleque MA, Ali MY. Characterization of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminium nano-composite using field emission scanning electron microscope. Int J Eng Mater Manuf. 2018;3:63–7.10.26776/ijemm.03.01.2018.08Search in Google Scholar
[19] Meignanamoorthy M, Sakthivelu S, Ravichandran M. A survey of aluminium metal matrix composites using powder metallurgy. IJARTET. 2015;2(3):53–6.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Koli DK, Agnihotri G, Purohit R. Advanced aluminium matrix composites: The critical need of automotive and aerospace engineering fields. Mater Today Proc. 2015;2:3032–41.10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.290Search in Google Scholar
[21] Surappa MK. Aluminium matrix composites: Challenges and opportunities. Sadhana. 2003;28:319–34.10.1007/BF02717141Search in Google Scholar
[22] Srivyas PD, Charoo MS. Aluminum metal matrix composites a review of reinforcement; mechanical and tribological behavior. Int J Eng Technol. 2018;7:117–22.10.14419/ijet.v7i2.4.13020Search in Google Scholar
[23] Abed Janabi ZM, Jaber Alsalami HS, Al-Khafaji ZS, Hussien SA. Increasing of the corrosion resistance by preparing the trivalent nickel complex. Egypt J Chem. 2021;65:193–8. 10.21608/EJCHEM.2021.100733.4683 Search in Google Scholar
[24] Abed KM, Radhi NS, Jasim AH, Al-Khafaji ZS, Radhi S, Hussien SA. Study the effect of adding zirconia particles to nickel–phosphorus electroless coatings as product innovation on stainless steel substrate. Open Eng. 2022;12:1038–45. 10.1515/eng-2022-0364 Search in Google Scholar
[25] Samal P, Newkirk J. Powder metallurgy methods and applications. ASM Handb. Powder Metall. 2015;7:480–7.10.31399/asm.hb.v07.a0006098Search in Google Scholar
[26] Judge W, Kipouros G. Powder metallurgy aluminum alloys: Structure and porosity. New York: Encycl Alum Its Alloy CRC Press Taylor Fr Group; 2018. p. 1977–9510.1201/9781351045636-140000247Search in Google Scholar
[27] Radziejowska A, Sagan J, Sobotka A. Technological and organizational problems in the construction of the radiation shielding concrete and suggestions to solve: A case study. Open Eng. 2021;11:1114–21.10.1515/eng-2021-0082Search in Google Scholar
[28] Zaki MU, Hussain S. Impact of addition of manganese and boron carbide on aluminium metal matrix composites using powder metallurgy process. Mater Today Proc. 2021;44:4364–8.10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.562Search in Google Scholar
[29] Rojas-Díaz LM, Verano-Jiménez LE, Muñoz-García E, Esguerra-Arce J, Esguerra-Arce A. Production and characterization of aluminum powder derived from mechanical saw chips and its processing through powder metallurgy. Powder Technol. 2020;360:301–11.10.1016/j.powtec.2019.10.028Search in Google Scholar
[30] Zamani NABN, Iqbal AKMA, Nuruzzaman DM. Mechanical and tribological behavior of powder metallurgy processed aluminum–graphite composite. Russ J Non-Ferrous Met. 2019;60:274–81.10.3103/S1067821219030179Search in Google Scholar
[31] Zhang J, Liu Q, Yang S, Chen Z, Liu Q, Jiang Z. Microstructural evolution of hybrid aluminum matrix composites reinforced with SiC nanoparticles and graphene/graphite prepared by powder metallurgy. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int. 2020;30:192–9.10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.01.024Search in Google Scholar
[32] Kumar V, Singh A. Polypropylene clay nanocomposites. Rev Chem Eng. 2013;29:439–48.10.1515/revce-2013-0014Search in Google Scholar
[33] Yu H, Zhang SQ, Xia JH, Su Q, Ma BC, Wu JH, et al. Microstructural evolution, mechanical and physical properties of graphene reinforced aluminum composites fabricated via powder metallurgy. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;802:140669.10.1016/j.msea.2020.140669Search in Google Scholar
[34] Nayak KC, Pandey AK, Date PP. Mechanical and physical characterization of powder metallurgy based aluminium metal matrix hybrid composite. Mater Today Proc. 2020;33:5408–13.10.1016/j.matpr.2020.03.134Search in Google Scholar
[35] El-Hageen HM, Alatwi AM, Rashed ANZ. Silicon-germanium dioxide and aluminum indium gallium arsenide-based acoustic optic modulators. Open Eng. 2020;10:506–11. 10.1515/eng-2020-0065 Search in Google Scholar
[36] Albert T, Sunil J, Christopher AS, Jegan R, Prabhu PA, Selvaganesan M. Preparation and characterization of aluminium-titanium carbide (Al-TiC) composite using powder metallurgy. Mater Today Proc. 2021;37:1558–61.10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.155Search in Google Scholar
[37] Zamani NABN, Iqbal AKMA, Nuruzzaman DM. Fabrication and characterization of Al2O3 nanoparticle reinforced aluminium matrix composite via powder metallurgy. Mater Today Proc. 2020;29:190–5.10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.541Search in Google Scholar
[38] Venkatesh VSS, Deoghare AB. Fabrication and mechanical behaviour of Al-Kaoline metal matrix composite fabricated through powder metallurgy technique. Mater Today Proc. 2021;38:3291–6.10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.021Search in Google Scholar
[39] Jabor M, Radh NS, Al-kinani MA, Al-khafaji ZS. Optimization of electro less of nickel base coating for cermet cutting tools substrate. J Mech Eng Res Dev. 2021;44:30–40.Search in Google Scholar
[40] Conshohocken W. ASTM G99-17, standard test method for wear testing with a pin-on-disk apparatus, ASTM International. Wear. 2017;1:1–5.Search in Google Scholar
[41] Jordá JMM. 1 Metal matrix composites for thermal management. Met. Matrix Compos. Berlin, Germany: De Gruyter; 2014. p. 1–38.10.1515/9783110315448.1Search in Google Scholar
[42] Boudjema HL, Bendaikha H, Maschke U. Green composites based on Atriplex halimus fibers and PLA matrix. J Polym Eng. 2020;40:693–702.10.1515/polyeng-2020-0068Search in Google Scholar
[43] Alalkawi HJM, Aziz GA, Aljawad HA. Wear performance and magnetic property of aluminum reinforced with Fe2O3 And Al2O3 hybrid nanocomposite using powder metallurgy P/M method. IRAQI J Mech Mater Eng. 2020;20:322–31.10.32852/iqjfmme.v20i4.531Search in Google Scholar
[44] Srivastava SK, Kotal M. Recent advances on preparation, properties and applications of polyurethane nanocomposites. Davim JP, Charitidis CA, editors. In: Nanocomposites: Materials, Manufacturing and Engineering. Berlin, Germany: De Gruyter; 2013;33–92.10.1515/9783110267426.33Search in Google Scholar
[45] Mazahery A, Ostadshabani M. Investigation on mechanical properties of nano-Al2O3-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. J Compos Mater. 2011;45:2579–86. 10.1177/0021998311401111 Search in Google Scholar
[46] Shankar G, Jayashree PK, Shetty R, Kini A, Sharma SS. Individual and combined effect of reinforcements on stir cast aluminium metal matrix composites-a review. Int J Curr Eng Technol. 2013;3:922–34.Search in Google Scholar
[47] Siddharth D, Mahato N, Rao JB. Synthesis & characterization of RHA (Rice Husk Ash) particulates reinforced A7075 composites. J Manuf Eng. 2017;12:55–61.Search in Google Scholar
[48] Wankhade S, Sanjeevamurthy D, Jamdare P. Synthesis and characterization of Fe2O3 particulate reinforced aluminum alloy: A review. Int J Sci Res. 2022;11:157–60. 10.21275/SR22731184047 Search in Google Scholar
[49] Salman KD, Al-Maliki WAK, Alobaid F, Epple B. Microstructural analysis and mechanical properties of a hybrid Al/Fe2O3/Ag nano-composite. Appl Sci. 2022;12:4730. 10.3390/app12094730 Search in Google Scholar
[50] Phanibhushana MV, Chandrappa CN, Niranjan HB. Study of wear characteristics of hematite reinforced aluminum metal matrix composites. Mater Today Proc. 2017;4:3484–93. 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.02.238 Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection

