Abstract
University libraries are one of the important places to cultivate talents and conduct scientific research, but with the invasion of big data on the Internet, traditional library services cannot accurately understand readers’ needs, leading to a decline in library attendance. To solve this problem, the study proposes to combine multi-view K-mean clustering algorithm with reader behavior analysis to build a college library user portrait system to serve readers. When the enhanced K-mean clustering algorithm from the research was put to the test, the results showed that it performed better than the other two comparison algorithms, with accuracy and loss values of 97 % and 4.3 %, respectively. The user profile method that was suggested in the study was then empirically examined. The findings revealed that, when utilised with university students, the system was effective in raising the attendance rate of students by up to 75 %. In conclusion, it is clear that the method suggested in the study may accurately depict user profiles and offer readers good services, increasing the likelihood that readers will visit university libraries and lowering the waste of educational resources.
1 Introduction
In the age of big data, all types of information have enormous potential worth. By gathering and analyzing these data and information, the demands can be better understood and the speedy solutions to issues can be found [1], 2]. On college campuses, the library acts as the institution’s hub for sharing resources, and as such, the university devotes a significant amount of resources there each year. To find learning resources, students can now more quickly and conveniently utilize the Internet thanks to the quick development of Internet technology and tailored recommendations based on big data, and usage is rising. It is worth noting that library use is not determined solely by user behavior characteristics. For example, an intensive course period may cause students to focus on using study spaces, while the organization of campus cultural activities may temporarily divert users. Traditional library services not only struggle to accurately identify reader needs, but also lack the ability to dynamically respond to external environments such as course schedules, academic cycles, and campus activities. This results in a continuous decline in reader attendance rates. Some universities use traditional methods such as questionnaires and opinion books [3]. Such methods are not only heavy and inefficient, but also have disadvantages such as not being comprehensive and professional enough. To address this situation, the study constructs a university library user portrait system by improving the multi-view clustering algorithm (CA), namely K-means CA, and then combining it with the behavioral analysis of readers in university libraries [4], 5]. It is expected that the system will improve the university library’s understanding of its readers. Therefore, the library can provide more accurate learning resources and personalised services to its readers, and thus improve the attendance rate of the university library. The study’s first section provides an overview of recent domestic and international research on K-mean clustering techniques and user profiling. The second section describes how the K-mean CA was improved, applies behavioral analysis, and creates a system for user profiling in university libraries. The third section tests the performance of the improved algorithm and analyses the practical effects of the user profiling system. The fourth section provides an analytical summary of the whole research results.
2 Related works
With the rapid development of information technology, there are various important multi-feature data in life, which can be collected, analyzed and summarized by multi-perspective CAs. The K-means CA has the advantages of simplicity and efficiency, and is widely used in various fields. Huang et al. proposed a moving window detection algorithm based on K-mean clustering for the problem of difficult detection of valve static friction, and compared the test with the traditional algorithm. The results showed that the algorithm not only detected valve static friction performance better than the traditional algorithm, but also provided static friction band estimation and detects unexpected valve closure [6]. Xiong et al. proposed a learning model based on K-mean clustering and neural networks to address the problem of low average prediction accuracy of wafer reflectance in complex etching environments. A comparative experimental analysis of the model showed that the average prediction accuracy of wafer reflectance improved by 9.38 % and the mean square error was reduced by 21.64 % when the model was used [7]. Zhang et al. proposed a practical protocol model for K-mean clustering that incorporated a collaborative approach to clustering to address the problem of user privacy leakage during clustering [8]. Zhang et al. proposed a recognition system incorporating self-applicable fuzzy dynamics, K-mean clustering and sparse representation classification to address the problem of difficult weed identification in fields. Moreover, it analyzed the system in a comparative experiment. The outcomes demonstrated that the new approach could significantly increase the accuracy of field weed identification and classification compared to the conventional identification technique [9]. Jiang et al. proposed a K-mean clustering-based edge computing node deployment algorithm for the problem of high latency of smart devices in smart manufacturing environments, which was empirically analyzed. The results demonstrated that the proposed algorithm outperformed conventional methods in terms of network latency and computational resource deployment. These results validated the algorithm’s validity and efficacy [10].
In the era of big data, various industries pay much attention to user profiling to provide better services to users, and expect to understand the real needs of users through user profiling to provide more reasonable and humane services. The proposed algorithm is empirically analyzed. The results show that the algorithm can evaluate and summarize the actual circumstances of the use of guides by different users. Moreover, the algorithm can improve the accuracy and comprehensibility of guides and the user profile of the library, thus improving the satisfaction of library users [11]. Han et al. proposed a network user profiling system based on communication behavior to solve the problem that general network traffic cannot distinguish proxy users from normal users, and compared the system with the traditional system in a test. Based on the results, the system can increase the accuracy of detecting real network environments by 85 % and the accuracy of identifying proxy users by 95 %. This can lead to accurate proxy user detection [12]. Li et al. proposed an intelligent management framework based on the user portrait framework to address the problem that the traditional context-aware framework lacked the cold chain logistics and distribution domain, and empirically analyzed the framework. The findings demonstrated that the framework could successfully improve the management capabilities of cold chain logistics and distribution by reducing the root mean square error by 19.9 and the average error of the cold chain information dataset by 8.37 [13].
In summary, various algorithms have been used in the field of user profiling, and the superiority of the K-means algorithm (KmA) has been demonstrated in many industries, and the combination of the two has great potential value. To fill the data gap in this area of research, a user profiling system based on an improved KmA combined with patron behavior analysis is proposed for university libraries. It is hoped that this system will help university libraries understand the real needs of their student patrons and provide them with more targeted assistance and services, thereby increasing their usage rates.
3 User profiling in university libraries incorporating improved KmA and reader behavior analysis
As big data technology becomes more widely used and traditional university library services fail to accurately understand readers’ needs, more and more university students are using the internet to look up study materials. This has led to a gradual decrease in university library attendance rates. Based on this research background, this chapter will improve the KmA and combine it with reader behavior analysis to build a user profiling system suitable for libraries.
3.1 Improvements to the KmA
In the field of data analysis, KmA and mean shift clustering (MSC) are two common clustering methods that partition datasets based on the similarity between data points. However, KmA has high computational efficiency, simple implementation, and is suitable for large-scale datasets. However, MSC has a high computational complexity and may perform poorly on high-dimensional data. Additionally, KmA centers on clustering to attract similar data objects, whereas MSC focuses on discovering mean patterns in the data. Considering the high dimensionality and large amount of reader behavior data in university libraries, this study uses KmA for cluster analysis. When performing a clustering analysis, a lot of data are grouped together into classes according to common criteria. A user portrait system for university libraries will be built on the basis of the study’s clustering of multi-feature data with the aid of CAs. A similarity matrix will be constructed in the classification process based on data similarity, and its expression is shown in equation (1).
In equation (1), i means that there are i data objects, and j means that each data object has j features. The similarity matrix A is a two-dimensional matrix, with rows representing data objects and columns representing features. The element x ij in the matrix represents the value of the j-th feature of the i-th data object. Similarity between different data objects is measured by calculating their distances. The smaller the distance, the greater the similarity. The larger the distance, the greater the difference. In selecting the stability conditions, the study considers two aspects. First, initial clustering centers are selected using a method based on data distribution density to reduce the risk of local optima. The second is the termination condition for CAs iteration. To ensure the stability of the clustering results, the iteration is stopped when the change in the cluster center is less than a certain threshold or the maximum number of iterations is reached. The degree of similarity between different objects can be reflected by the distance between objects, the smaller the distance means that the objects are more similar, and vice versa means that the objects are more different. In equations (2)–(4), there are three distance calculation equations commonly used in clustering, and their mathematical expressions.
In equation (2), D 1 denotes the Euclidean distance between objects a and b. a ij denotes the coordinates of the object a. b ij denotes the coordinates of object b. n denotes the dimension of the object point.
In equation (3), D 2 denotes the city block distance between objects a and b.
In equation (4), D 3 represents the Chebyshev distance between objects a and b. The similarity coefficient, derived from equation (5), can estimate the degree of similarity between objects in the CA. The distance function can also express similarity between objects.
In equation (5),
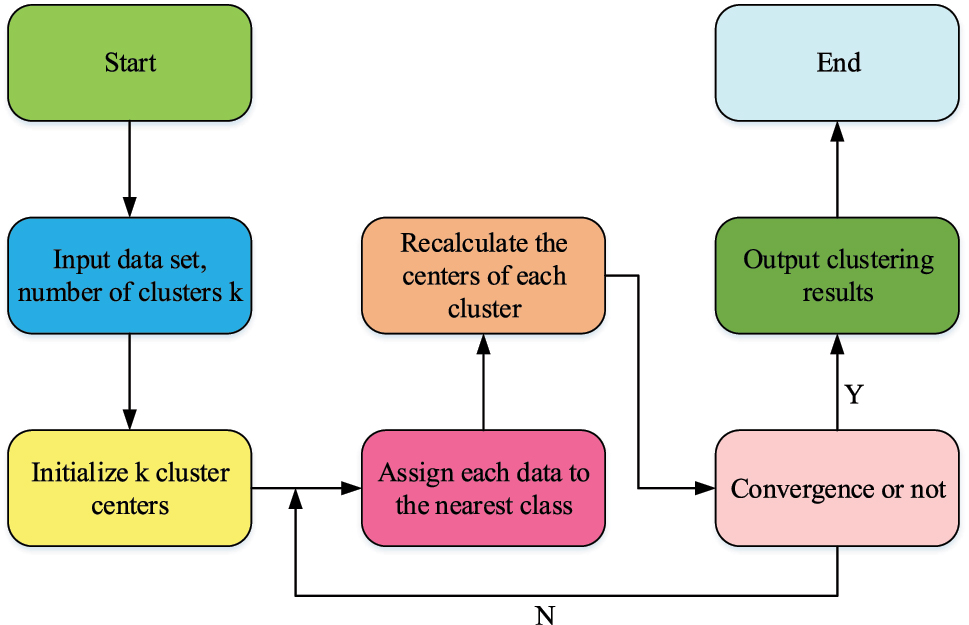
Flow diagram of the KmA.
In Figure 1, the KmA is calculated by setting the number of clusters K. Subsequently, K data are selected as clustering centers in all data ensembles, and the remaining data are classified into K categories by using the distance equation. When the new cluster centroids are the same as the previous ones, the clustering result will be output, and if not, the data will be reclassified. If the new cluster centroids are still not the same, the process is repeated again. The clustering result will not be output until the centroids of the two clusters are the same. Because the centroids used in classic KmA clustering are selected at random, this could produce unstable clustering results that are vulnerable to local optimal solutions. The study improves the conventional KmA to somewhat overcome this flaw. By treating the data ensemble as a cluster and clustering it with a cluster number of 2, the improved KmA operates. As a result, the two clusters that are closest to the cluster center and the smallest cluster are selected and returned to the cluster ensemble. Then, one cluster is selected from the ensemble for clustering with cluster number of 2. The aforementioned procedure is repeated up until K total clusters make up the cluster ensemble. Equation (6) illustrates the formula for this improved algorithm’s cluster center calculation.
In equation (6), u denotes the cluster center vector, S denotes the data ensemble, m denotes the total number in the B data ensemble. The corresponding mathematical formulations are provided by equations (7)–(10), which use the martingale distance to measure the distance between data objects in the improved KmA.
In equation (7), μ denotes the mean,
In equation (8), G denotes the autocorrelation matrix.
In equation (9), Σ denotes the covariance matrix.
In equation (10),
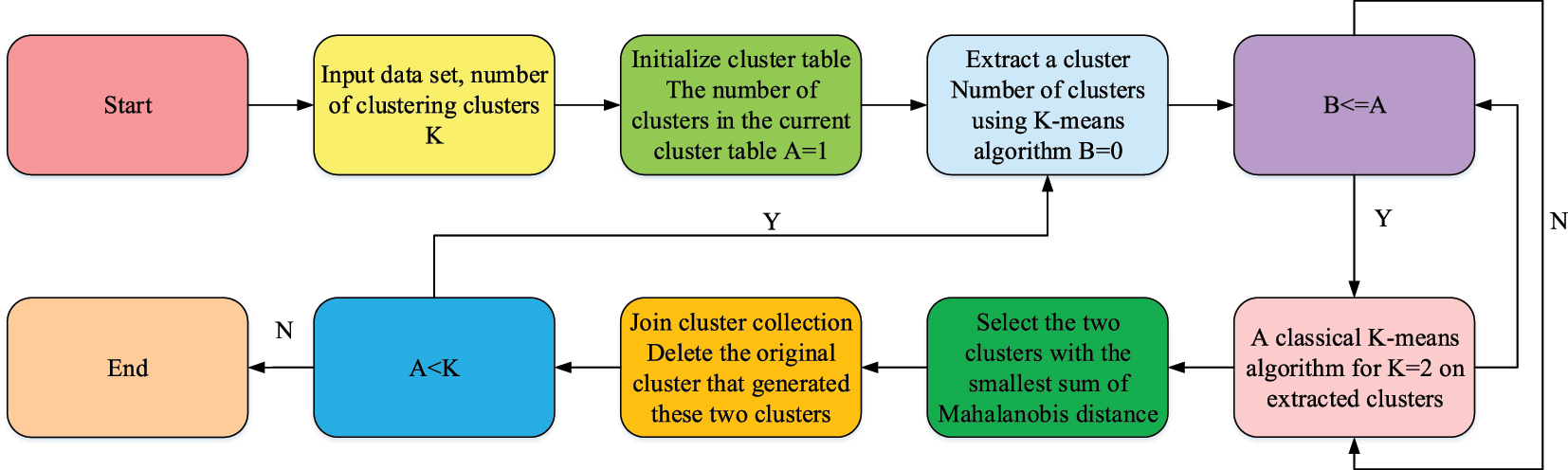
Working flow chart of the modified KmA.
In Figure 2, the improved KmA sets clear iteration termination conditions to ensure the convergence of the algorithm. Specifically, the algorithm stops iterating when either the change in the cluster center is less than a certain threshold or the maximum number of iterations is reached. This ensures the algorithm does not run indefinitely and can converge on stable clustering results within a reasonable number of iterations. Furthermore, the enhanced KmA mitigates the occurrence of local optima by meticulously selecting initial cluster centers based on the density of the data distribution. This initial clustering center selection method, which is based on data distribution density and the gradual updating process of clustering centers, helps improve the stability of the clustering results. This ensures the convergence of the algorithm. The combined multi view KmA can integrate multi-source behavioral data of university library readers, mine complementary information between views, construct accurate user profiles, and support dynamic updates and personalized recommendations. In practical applications, this algorithm can assist libraries in optimizing resource allocation, improving service quality, better meeting reader needs, and thereby increasing library resource utilization and reader satisfaction.
3.2 Building a user profile system for university libraries combined with reader behavior analysis
Behavioral analysis is proposed by the American psychologist Hunter [15]. A lot of useful information can be reflected from various behavioral activities in people’s lives, and by mining and analyzing this information, habits and preferences in people’s lives can be derived [16]. The study will provide some scientific basis for the portrayal of user portraits by mining and analyzing the behavior of student patrons in university libraries [17]. The basic structure of the behavioral analysis is shown in Figure 3.
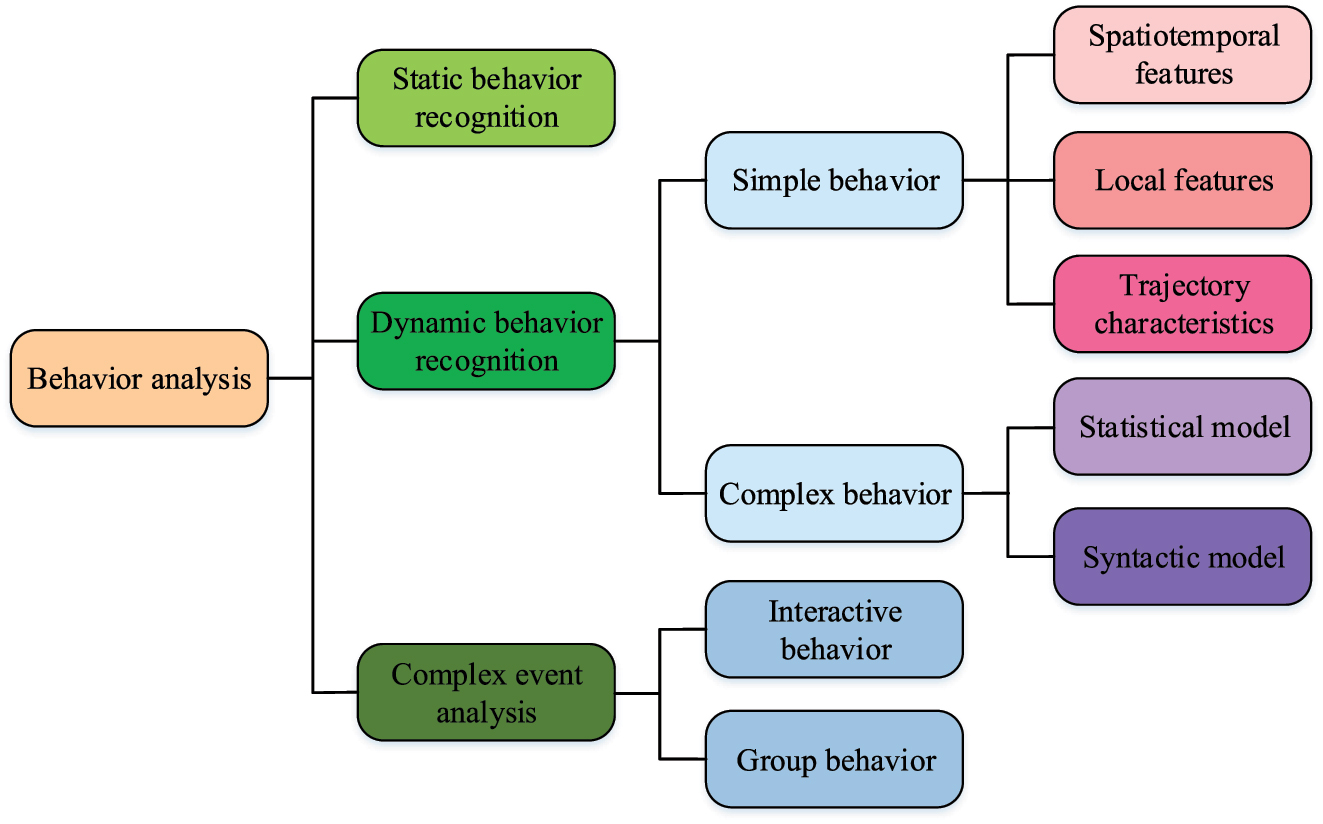
Schematic representation of the behavioral analysis structure.
In Figure 3, behavioral analysis contains static behavior, dynamic behavior and the analysis of occurring events, etc. Through behavioral analysis, a multi-dimensional and multi-perspective feature system can be constructed. For the behavioral analysis of library patrons, the following five perspectives can be analyzed. First, the reader activity rate, whose calculation equation is shown in equation (11).
In equation (11), RA denotes reader activity. N denotes the number of times readers visit the library during the time interval. F denotes the number of days readers visit the library during the time interval. The second angle of analysis is the usage rate of electronic resources, which is calculated by the equation shown in equation (12).
In equation (12), LR denotes the rate of readers’ books borrowed. L denotes the number of times readers borrowed books during the time interval. The third angle of analysis is the characteristics of the books borrowed by readers, and the computational analysis is shown in equation (13).
In equation (13),
In equation (14), PR denotes the usage rate of public resources in the library. pt, st, rt, and vt are the number of bookings for study rooms, reading rooms, seats and self-service printers in the library respectively. The last angle of analysis is the usage of electronic resources in the library, which is calculated as shown in equation (15).
In equation (15), the usage rate of e-resources in library IR. e denotes the collection of e-book repositories. d x denotes the number of downloads in e-book library x. s x denotes the number of down views in e-book library x. The analysis of the reader’s behavior allows the construction of a multi-perspective and multi-characteristic system, which helps to provide an accurate portrayal of the user profiling system. User profiling is based on real user data, abstracting information about the user’s characteristics, based on this information to understand the user’s real needs. Labeling is the core work of user profiling. The research will use design and thinking as a method to construct user portraits. Combined with the research, a user portrait system based on improved KmA and reader behavior analysis for university libraries is proposed, which works as shown in Figure 4.
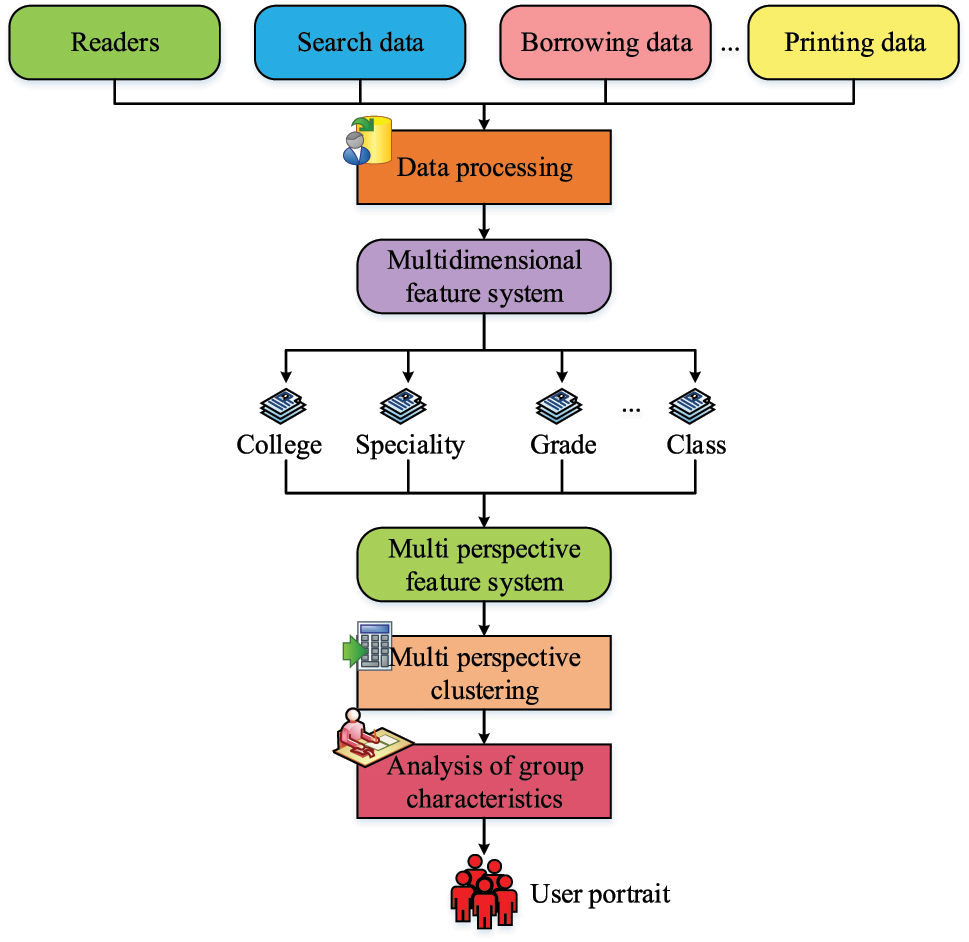
Schematic diagram of the working principle of the user portrait system.
In Figure 4, there are many types of data involved in this process of data collection and processing, and the workload is huge. Student arrival patterns are often highly correlated with course density, homework deadlines, and exam cycles. By integrating user behavior data with structured data such as course schedules, exam schedules, and homework submission cycles, prediction accuracy and strategic flexibility can be further improved. To this end, research has used web crawling technology to capture data from educational systems, gate card swipes, self-service systems, and campus activity announcement platforms. External data and user behavior data are aligned through timestamps to form a multidimensional dataset [18]. The journey of this technique to obtain data information is shown in Figure 5.
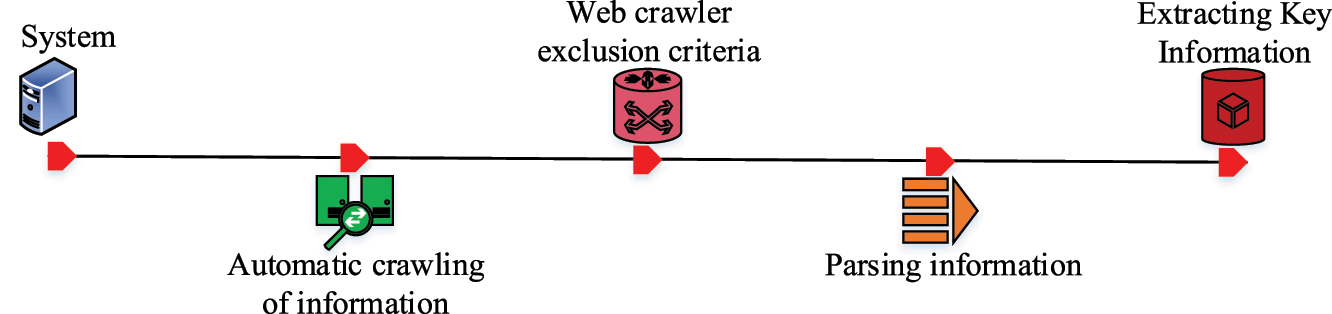
Workflow of web crawler technology.
In Figure 5, the web crawler technology is the first to initiate an access request to the system, crawling the system page information and then extracting the required information according to the web crawler exclusion criteria. This selected information is then parsed and the key information data is finally extracted. However, in the process of crawling and transmitting information data, abnormalities in the data are inevitable. Therefore, processing is required to enhance the quality of the data after it has been collected using web crawler technology. The study uses extraction-transformation-loading (ETL) technology to process and load the data into a data ensemble [19], 20]. ETL work includes data extraction, cleaning, transformation and loading. Data extraction is the use of data interfaces to extract data from the source data. The user profiling system needs to choose incremental extraction for the library where the patron behavior data changes over time, and specific extraction frequencies can be set for different types of data. Once the data has been extracted, it needs to be cleaned. Data cleansing means that missing parts of the data are filled in, incorrect parts are corrected, duplicate parts are removed, etc. A fault-tolerant mechanism can be constructed using RBF neural networks to correct sensor errors and transmission noise in behavioral data, thereby improving the reliability of feature extraction [21]. After cleaning, the data remains in its original format, so the format of the data varies between types. The ETL process is shown in Figure 6.
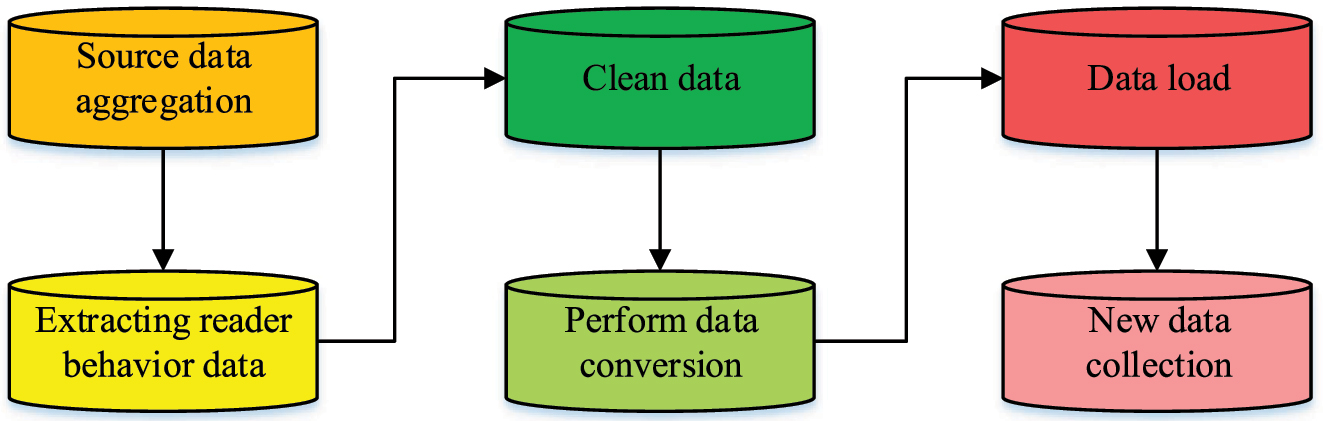
Schematic diagram of the ETL technical workflow.
Ultimately, the system completes the user portrait representation by analyzing the processed reader behavior data, building a multi-dimensional and multi-view reader characteristics system, and using the improved KmA for cluster analysis.
4 Performance testing of modified algorithms and empirical analysis of pictorial systems
The study will construct the algorithm in the computer programming language java in order to test the effectiveness of employing the improved KmA it has suggested. Moreover, the Balance-scale dataset will be selected as the dataset for the algorithm comparison test, and the accuracy rate, loss value, PR curve, and accuracy-recall curve will be used as the evaluation index of the test results. Three majors with comparable numbers in a university will be randomly chosen for the comparison test with the goal to assess the usefulness of the user profiling method suggested by the study. The system usage satisfaction, perceived usefulness, and patron arrival rate will also be used as evaluation indicators.
4.1 Improved KmA performance comparison test
The study uses the conventional KmA, partitioning around medoid (PAM) CA, as a control method and examined the improved KmA’s performance [22]. The test dataset is clustered using the improved algorithm, KmA, and PAM algorithms. On the balance scale dataset, each algorithm is run 30 times independently, randomly initializing the cluster centers each time and recording the accuracy and loss values of each run. The accuracy and loss value results for each algorithm are displayed in Figure 7.
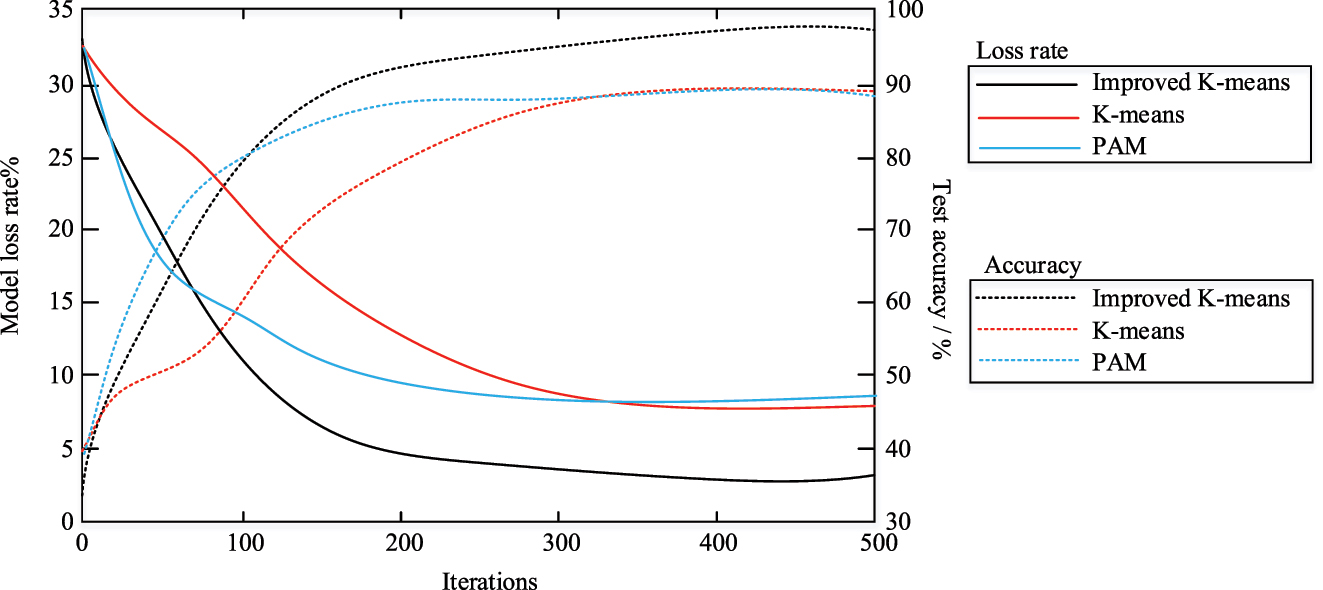
Accuracy and loss value curves of the three algorithms.
At around 100 iterations, the accuracy and loss value curves of the KmA exhibit a variety of accuracy changes, but the loss value is unaffected. At around 300 iterations, both accuracy and loss values begin to stabilize. The above curves of the PAM algorithm also show a fast convergence rate, with both accuracy and loss value starting to stabilize at around 200 iterations. After 500 iterations, the KmA has an accuracy and a loss value of 89 % and 6.7 %, respectively, while the PAM method has an accuracy and a loss value of 88 % and 7.7 %, respectively. After 500 iterations, the accuracy of the improved algorithm is about 8 % higher than that of K-means and PAM algorithms. Moreover, the loss value of the improved algorithm remains stable at 4.3 %, lower than K-means and PAM algorithms. Compare the accuracy differences between improved KmA and KmA and between improved KmA and PAM using paired t-test. Using the Bonferroni correction adjust the significance level to α = 0.025. The test results show that the accuracy of improved KmA is significantly higher than that of KmA (t = 15.34, p < 0.001) and PAM algorithm (t = 16.78, p < 0.001). In addition, Figure 7 shows that the accuracy and loss value curves of the improved KmA remain relatively stable during multiple independent runs and stabilize after 300 iterations. This indicates that the clustering results are stable during the iteration process. In contrast, the KmA experiences significant changes in accuracy after about 100 iterations. This is because traditional KmA tends to get stuck in local optima due to its random selection of initial clustering centers. This results in significant fluctuations in clustering results under different running times. Figure 8 displays the accuracy-recall curves and PR curves for the three techniques.
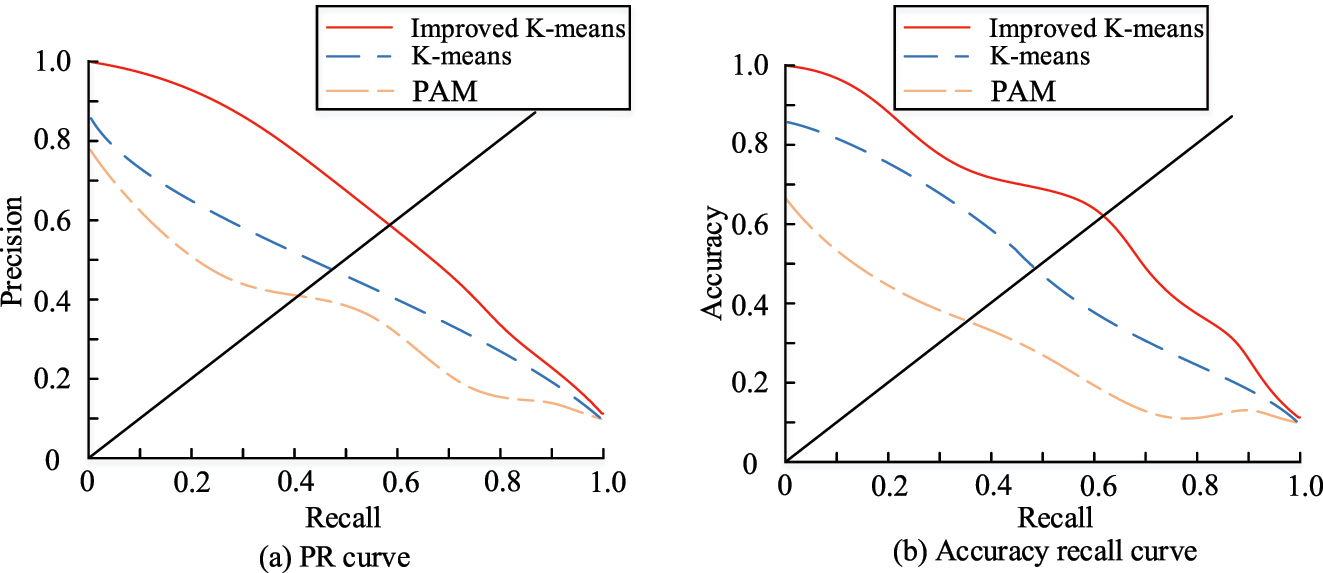
The PR curves and the accuracy-recall curves of the three algorithms.
Figure 8(a) depicts the PR curves for the improved algorithm, the KmA, and the PAM algorithms, all of which exhibit a steadily declining trend. The better algorithm’s area enclosed under the curve is the greatest, followed by the KmA and the PAM algorithm. From Figure 8(b), the accuracy-recall curves of all three algorithms show a gradually decreasing trend, with the area contained under the curve of the improved algorithm being larger than the other two algorithms. In conclusion, the modified algorithm clearly outperforms the KmA and PAM techniques. Using the enhanced algorithm increases the accuracy of clustering. Figure 9 displays the outcomes of the trials that additionally examined the KmA and PAM algorithms’ running times and the sum of their martingale distances in the data set.
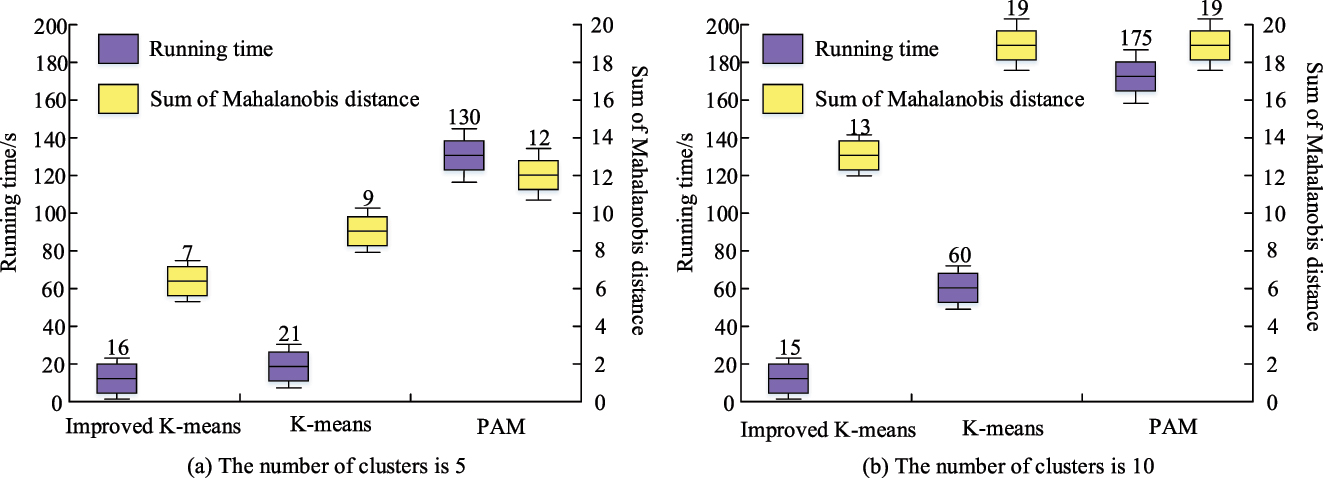
Time-consuming and Mahalanobis distance sum for the three algorithms.
When there are 5 clusters, as shown in Figure 9(a), the modified algorithm outperforms the comparison algorithm with a running duration of 16s and a sum of Marcian distances of 7. As shown in Figure 9(b), when there are 10 clusters, the running time of the improved algorithm is 15 s, and the total of the Marcian distances is 13, both of which are noticeably faster than the times of the other two techniques. Comprehensive Figure 9(a) and (b) shows that when the number of clusters increases, the running time of the improved algorithm remains stable and the speed is significantly higher than the other two algorithms. Moreover, the sum of the martingale distance is still lower than that of the comparison algorithm, i.e. It reflects the advantages of the algorithm in terms of high computational efficiency and accuracy. Figure 10 displays the test results for experiments to ascertain the impact of altering the threshold parameter on the correct rate of the improved algorithm, the KmA, and the PAM algorithm. These experiments are set up in three sets of trials with respective cluster counts of 4, 5, and 6.
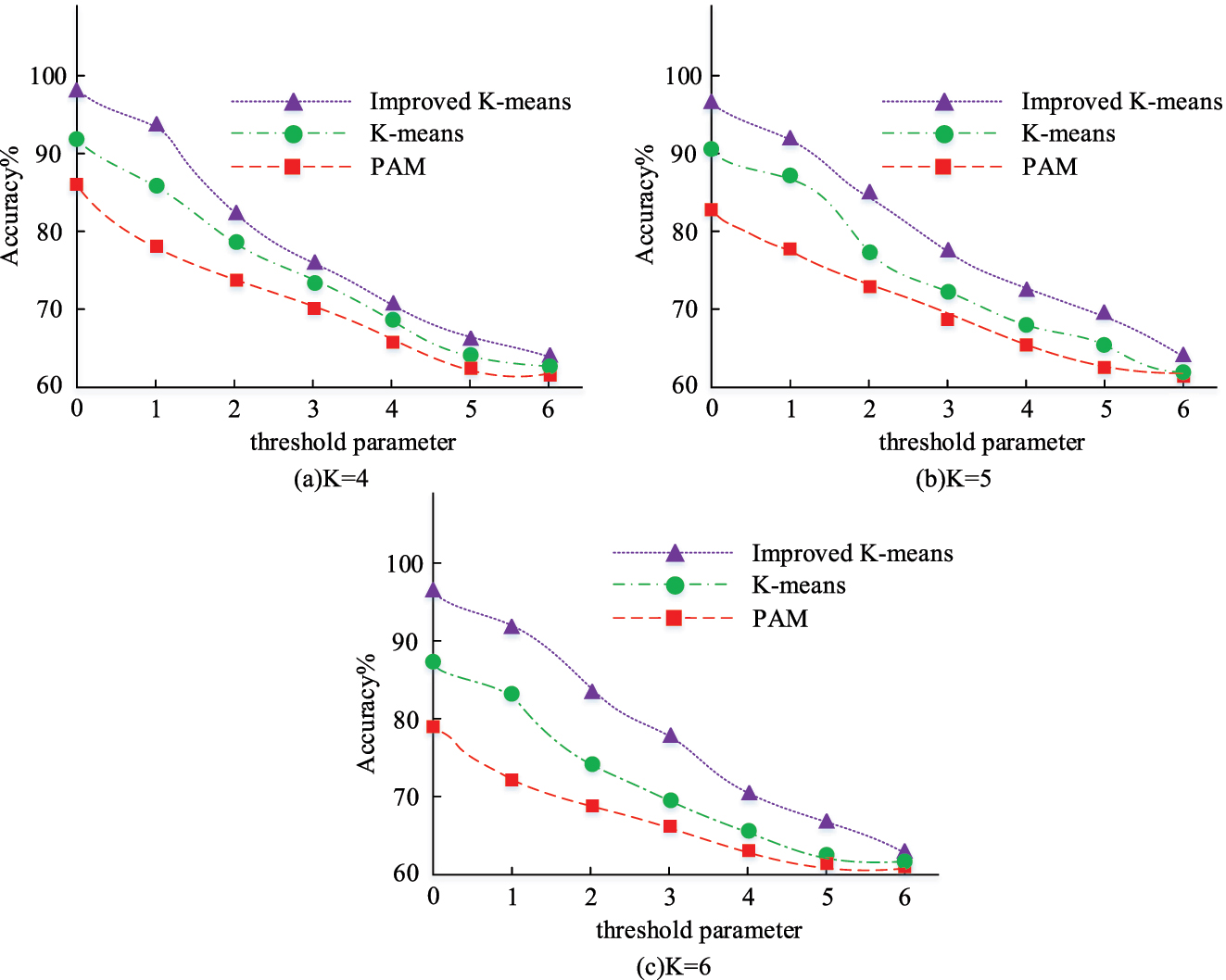
Effect of threshold parameters on accuracy.
In Figure 10, the accuracy of all three algorithms decreases as the threshold parameter increases, but the accuracy stabilizes as it approaches 60 %. The revised algorithm has a greater accuracy rate than the other two algorithms in all three sets of experiments, even when accuracy is declining. In conclusion, the modified algorithm outperforms the KmA and the PAM method in all evaluation indicators. This is demonstrated by testing its performance. The application of the algorithm to the user profiling system of university libraries can improve the accuracy and efficiency of the system carving.
4.2 Empirical analysis of user profiling system in university libraries based on improved algorithm and reader behavior analysis
In the comparison trial, majors that do not use a user profiling system are designated Major 1, majors that used the traditional user profiling system are designated Major 2, and majors that used the proposed system are designated Major 3. The comparison study lasts 67 days, and students from the three majors are surveyed on days 30 and 60 of the study regarding their satisfaction and perceived usefulness of using the system.
In Figure 11(a), after 30 days of the experiment, the student satisfaction and perceived usefulness of Major 3 are 8.3 and 8.1, respectively, both higher than the other two majors. This means that the user profiling system proposed in the study had the highest satisfaction and perceived usefulness. This result also shows that the user profile system has the highest satisfaction and perceived usefulness. Combining Figure 11(a) and (b), it can be concluded that the satisfaction and perceived usefulness of students who did not use any of the user profiling systems remained largely unchanged. Students who used the user profile system shows an increase in satisfaction and perceived usefulness. The students who used the system proposed in the study shows the greatest increase in satisfaction and perceived usefulness. This suggests that the proposed system is superior for real-life applications. The number of students visiting the library is recorded on days 30 and 60 of the trial and the results are shown in Figure 12.
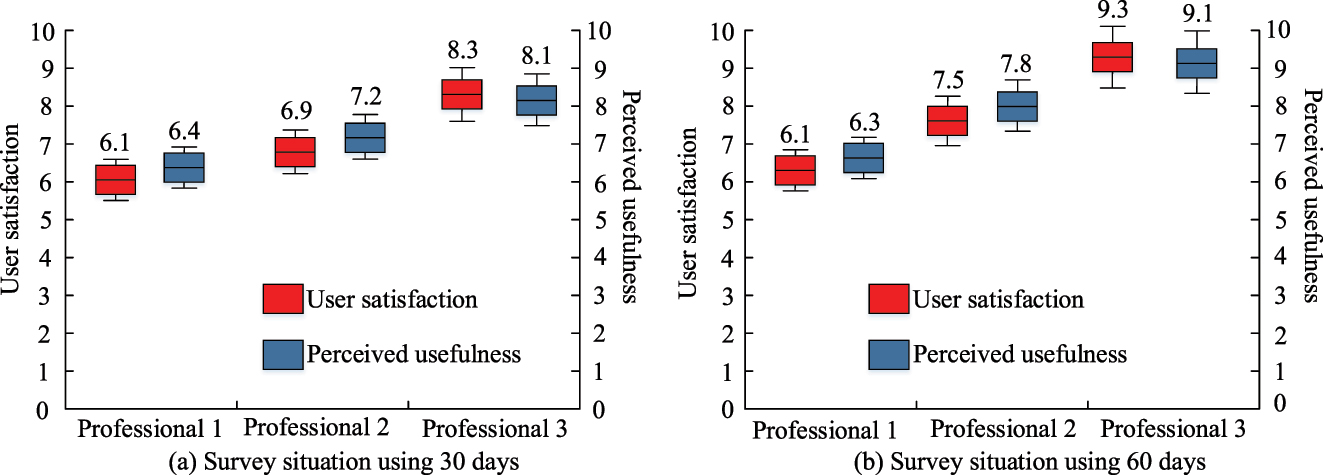
Comparison of the results of the three professional questionnaires.
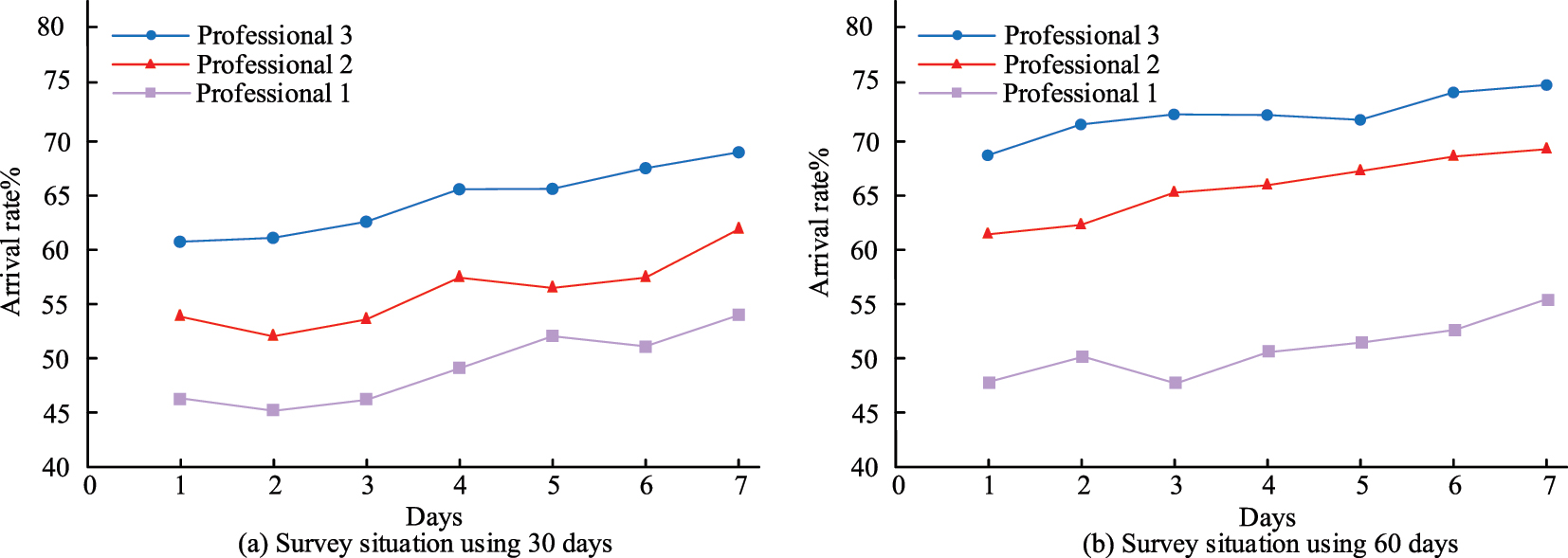
Admission rate of students in the three majors.
In Figure 12(a), after the 30-day trial, students in all three majors visits the library more often than the other two majors each day for a week, with the highest attendance rate of 70 %. In Figure 12(b), after the 60-day trial, students of the three majors visits the library the most times a day within a week, with the highest attendance rate of 75 % for major 3, which is an increase from the 30-day trial. That is, the study proposes that the user profiling system can effectively improve the attendance rate of university libraries and provide better services to patrons. To further validate the performance differences of the proposed improved KmA in different student demographics, this study separates undergraduate and graduate students from the original student data of the three majors and constructs sub-datasets for each. Moreover, the improved KmA is compared with density based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN), hierarchical clustering (HC), and Gaussian mixture model (GMM). The clustering performance of the four algorithms on different groups of students is shown in Table 1.
The clustering performance of four algorithms in different student groups.
| Student group | Index | DBSCAN | HC | GMM | Improved KmA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Undergraduate | Accuracy/% | 76.69 | 80.55 | 87.42 | 96.42 |
| Contour coefficient | 0.46 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.68 | |
| Postgraduate | Accuracy/% | 70.57 | 73.26 | 80.32 | 94.17 |
| Contour coefficient | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.60 |
Table 1 shows that the improved KmA algorithm performs well in both undergraduate and graduate populations. It has an accuracy rate of over 90 % and a contour coefficient of over 0.60. These values are higher than those of the DBSCAN, HC, and GMM algorithms. The results indicate that the improved KmA performs well with various student demographic data and is stable and superior.
4.3 Discussion
Although the manuscript focuses on the characteristics and needs of university libraries, the improved K-means CA and the reader behavior analysis method adopted by the system are universal techniques in the fields of data mining and user analysis. Moreover, different types of libraries have certain similarities in data collection. Therefore, manuscripts still have a certain degree of adaptability in other types of libraries. However, there are significant differences in library management systems, resource types, and reader behavior patterns among different educational institutions. And while the system improves the KmA, it also increases the complexity of the algorithm, which may limit its application in environments with limited computing resources. Therefore, future research should promote cross-institutional data standardization protocols, develop unified data interface specifications, and ensure the compatibility of multi-source data to ensure that the proposed system can be applied on a large scale in different educational institutions. Further optimization of the algorithm’s resource consumption should be carried out to eliminate unnecessary computing steps or migrate computing tasks to cloud platforms that can dynamically adjust computing resources. In addition, this study constructs user profiles based on CAs without considering the influence of time series. In the future, further exploration can be conducted on the modeling ability of neural networks for nonlinear behavior patterns. For example, time-delay recurrent neural networks can capture the temporal dependence of behavioral data through attention mechanisms. These mechanisms can enhance the dynamic response capability of portraits by identifying the lag correlation between job submission cycles and arrival behavior [23], 24].
5 Conclusions
As information technology advances, people are relying more and more on accurate recommendations from big data, while traditional learning resource libraries, such as university libraries, are experiencing a gradual decline in usage. To solve this problem, the study proposed to combine the improved KmA with reader behavior analysis and build a university library user profiling system based on this. Comparing the enhanced KmA to the conventional KmA and the PAM algorithm was examined. According to the test findings, the upgraded KmA had an accuracy and loss value of 97 % and 4.3 %, whereas the KmA’s accuracy and loss value were 89 % and 6.7 %, respectively. Moreover, the PAM algorithm’s accuracy and loss value were 88 % and 7.7 %, respectively. The improved KmA outperformed the other two algorithms used for comparison. The improved KmA was able to consistently outperform the comparison algorithm in terms of accuracy with the influence of the threshold parameter. The running time of the improved KmA was 16s and 15s when the number of clusters was 5 and 10 respectively, which were both lower than the running time of the KmA and the PAM algorithm, i.e. the algorithm had the highest computational efficiency and large computational capacity. An empirical analysis of the proposed user profiling system showed that it was effective in increasing student attendance. Student attendance increased to 70 % after 30 days and 75 % after 60 days of using the system. In summary, the study proposes that the system can accurately portray user profiles, provide good services to readers and achieve the purpose of increasing the attendance rate of university libraries.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Yuping Gao: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing-original draft, Writing-review & editing. Wei Gao: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing-review & editing. All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
1. McArthur, B, Isenor, A. Applying spatial mutual information to AIS data. J Navig 2022;75:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0373463321000734.Search in Google Scholar
2. Song, Y. Optimization of quantitative research methods in social sciences in the era of big data. Acta Inform Malays 2023;7:92–6. https://doi.org/10.26480/aim.02.2023.92.96.Search in Google Scholar
3. Castagna, PJ, Babinski, DE, Pearl, AM, Waxmonsky, JG, Waschbusch, DA. Initial investigation of the psychometric properties of the Limited Prosocial Emotions Questionnaire (LPEQ). Assessment 2021;28:1882–96. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191120927782.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
4. Chen, X, Qiu, Y. A combined clustering algorithm based on ESynC algorithm and a merging judgement process of micro-clusters. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowledge-Based Syst 2021;29:463–95. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0218488521500203.Search in Google Scholar
5. Onunka, O, Onunka, T, Fawole, AA, Adeleke, IJ, Daraojimba, C. Library and information services in the digital age: opportunities and challenges. Acta Inform Malays 2023;7:113–21. https://doi.org/10.26480/aim.02.2023.113.121.Search in Google Scholar
6. Zheng, D, Sun, X, Damarla, SK, Shah, A, Amalraj, J, Huang, B. Valve stiction detection and quantification using a K-means clustering based moving window approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 2021;60:2563–77. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05609.Search in Google Scholar
7. Xiong, WQ, Qiao, Y, Bai, LP, Ghahramani, M, Wu, NQ, Hsieh, PH, et al.. Wafer reflectance prediction for complex etching process based on K-means clustering and neural network. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 2021;34:207–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsm.2021.3068974.Search in Google Scholar
8. Zhang, E, Li, H, Huang, Y, Hong, S, Zhao, L, Ji, C. Practical multi-party private collaborative k-means clustering. Neurocomputing 2022;467:256–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.09.050.Search in Google Scholar
9. Zhang, S, Huang, W, Wang, Z. Combing modified Grabcut, K-means clustering and sparse representation classification for weed recognition in wheat field. Neurocomputing 2021;452:665–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.140.Search in Google Scholar
10. Jiang, C, Wan, J, Abbas, H. An edge computing node deployment method based on improved k-means clustering algorithm for smart manufacturing. IEEE Syst J 2020;15:2230–40. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsyst.2020.2986649.Search in Google Scholar
11. Su, W, Lu, Z, Sun, Y, Liu, G. Let eyes tell: experimental research on university library signage system and users’ wayfinding behavior. Lib Hi Tech 2021;40:198–221. https://doi.org/10.1108/lht-01-2020-0007.Search in Google Scholar
12. Han, ZH, Chen, XS, Zeng, XM, Zhu, Y, Yin, MY. Detecting proxy user based on communication behavior portrait. Comput J 2019;62:1777–92. https://doi.org/10.1093/comjnl/bxz065.Search in Google Scholar
13. Li, X, Wang, Z, Gao, S, Hu, R, Zhu, Q, Wang, L. An intelligent context-aware management framework for cold chain logistics distribution. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 2019;20:4553–66. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2018.2889069.Search in Google Scholar
14. Rajchakit, G, Sriraman, R, Boonsatit, N, Hammachukiattikul, P, Lim, CP, Agarwal, P. Global exponential stability of Clifford-valued neural networks with time-varying delays and impulsive effects. Adv Differ Equ 2021;2021:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-021-03367-z.Search in Google Scholar
15. Sharma, V, Meena, M, Kumar, M, Patnaik, A. Mechanical and three-body abrasive wear behavior analysis of glass and basalt fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. Polym Compos 2020;41:3717–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25670.Search in Google Scholar
16. Wang, L, Zhen, Z, Wo, T, Jiang, B, Sun, H, Long, X. A scalable operating system experiment platform supporting learning behavior analysis. IEEE Trans Educ 2020;63:232–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/te.2020.2975556.Search in Google Scholar
17. Atanassov, K. New topological operator over intuitionistic fuzzy sets. J Comput Cogn Eng 2022;1:94–102. https://doi.org/10.47852/bonviewjcce2202197.Search in Google Scholar
18. Dong, Y. Application of artificial intelligence software based on semantic web technology in English learning and teaching. J Internet Technol 2022;23:143–52.10.53106/160792642022012301015Search in Google Scholar
19. Cheng, H, Yu, C. Automatic data cleaning system for large-scale location image databases using a multilevel extractor and multiresolution dissimilarity calculation. IEEE Intell Syst 2021;36:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1109/mis.2020.3021704.Search in Google Scholar
20. Muller, M, Perry, K, Micheli, L, Almonacid, F, Fernández, EF. Automated detection of photovoltaic cleaning events: a performance comparison of techniques as applied to a broad set of labeled photovoltaic data sets. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 2022;30:567–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3523.Search in Google Scholar
21. Wang, B, Jahanshahi, H, Volos, C, Bekiros, S, Khan, MA, Agarwal, P, et al.. A new RBF neural network-based fault-tolerant active control for fractional time-delayed systems. Electronics 2021;10:1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10121501.Search in Google Scholar
22. Wahengbam, K, Singh, M, Nongmeikapam, K, Singh, A. A group decision optimization analogy based deep learning architecture for multiclass pathology classification in a voice signal. IEEE Sens J 2021;21:8100–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2021.3049277.Search in Google Scholar
23. Rajchakit, G, Sriraman, R, Boonsatit, N, Hammachukiattikul, P, Lim, CP, Agarwal, P. Exponential stability in the Lagrange sense for Clifford-valued recurrent neural networks with time delays. Adv Differ Equ 2021;2021:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-021-03415-8.Search in Google Scholar
24. Boonsatit, N, Rajchakit, G, Sriraman, R, Lim, CP, Agarwal, P. Finite-/fixed-time synchronization of delayed Clifford-valued recurrent neural networks. Adv Differ Equ 2021;2021:276. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13662-021-03438-1.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations

