Abstract
In order to improve the experimental demonstration effect of computer technology, this article combines virtual reality technology and intelligent reflective surface-assisted perception and communication technology to build a general computer experiment demonstration platform. Based on sparse code division multiple access, this article proposes an intelligent reflector-assisted joint multi-user information reliable access and environmental reflector sensing scheme. Moreover, this article extracts the information about the environmental reflector in the received signal by means of computational imaging. In addition, this article iteratively optimizes the performance of multi-user information access and environment awareness through the relationship between the information of the environmental reflector and the received signal. The experimental research shows that the augmented reality-based general computer technology experimental demonstration platform proposed in this article has good effects and can effectively promote the computer technology experimental demonstration effect.
1 Introduction
With the rapid development of computer networks and distance education, network virtual laboratory is gradually shown in front of us. At present, many virtual technologies have been used in education systems abroad [1]. By applying information technologies such as computer technology and communication in teaching, it provides solutions for the experimental courses of distance education and builds a virtual laboratory environment in distance teaching. It has become a hotspot of current research to make the previous experiments using real experimental equipment develop toward an intelligent virtual experimental system.
In the virtual experiment platform, “components are software,” the design of the virtual laboratory mainly includes two aspects: the establishment of the component model library and the construction of the virtual experiment platform that can realize the human–computer interaction environment. The object-oriented method is applied to the modeling of the virtual device library, and the simulation model is constructed according to the objects that make up the system and their interaction relationships, so that the model has good independence, scalability, maintainability, and reusability [2]. Components can be divided into three types [3]: prototype atomic components, non-prototype atomic components, and molecular components. Prototype atomic components are provided by the original creator of the experiment (also a programmer), and non-prototype atomic components are dynamically loaded by the experiment creator (such as an experimenter and an experiment instructor) according to the authority of the corresponding component of a certain device product system, and through reflection technology and XML technology. Tteachers or experimenters set the corresponding properties of Beans according to the experimental requirements and generate new components with specific functions through simple configuration and construction, and no longer need to write a component program for each component to achieve; molecular components refer to the mixed packaging of multiple atomic components and molecular components [4].
Some researchers carry out virtual experimental operations on computer terminals to imitate actual experimental operations; the virtual experiment is to use mouse click and drag to assemble various virtual instruments on the microcomputer into a complete experimental system according to the experimental requirements and process and complete it on this system at the same time. The whole experiment includes the addition of raw materials, the change of experimental conditions, the data acquisition, and the simulation and analysis of the experimental results [5]. It highlights the new concept of “software as an instrument.” The virtual laboratory is the carrier of the virtual experiment and the running environment of the virtual experiment. Through the computer network system, researchers or students can use instruments and equipment, share data and computing resources, obtain other information, conduct seminars with peers, or receive remote guidance from teachers without being limited by time and space [6].
Software sharing network virtual laboratory: Its characteristic is that the virtual laboratory simulation software platform of the shared server accepts the experimental request sent by the client, analyzes and processes the experimental parameters, and finally returns the result to the client after calculation and simulation [7].
Network virtual laboratory for data sharing: Its characteristic is that the experimental data already exists in the remote database, and the server receives the client’s request to retrieve the experimental data in the database and return it to the client [8]. The client cannot control it remotely while the experiment is in progress. The study by Haryana et al. [9] is an implementation of this kind of virtual laboratory.
With the continuous development of computer technology, large-scale integrated circuits, and other technologies, the instrument system is closely integrated with computer software technology, which makes the concept of traditional instruments breakthrough, and virtual instruments appear [10]. With the development of virtual instruments for nearly three decades, it has been recognized by industry, academia, and research laboratories, and its application in all walks of life is also increasing. In education and teaching, especially in the teaching of professional courses in colleges and universities, it has an absolute advantage. Higher education, especially higher vocational education, attaches great importance to cultivating students’ professional skills [11]. In order to master these professional skills firmly and quickly, experimental teaching is an ideal way. As we all know, experiment is an indispensable link in teaching activities, and experimental teaching can make boring theoretical knowledge more intuitive and easy to accept. In the process of experiment, students’ practical ability, problem-solving ability, and innovation ability are also well cultivated. In fact, many disciplines are based on experimental courses, such as physics, chemistry, mechanics, computers, electronics, signal detection courses, and so on. However, with the continuous development of science and technology and the continuous popularization of higher education, higher vocational colleges are also facing some new problems in experimental teaching. This has a negative impact on the development of education [12].
The development of a laboratory based on virtual instrument technology can effectively reform the traditional experimental mode and is more conducive to updating the modern experimental teaching concept. In addition, the content and methods of the existing experimental teaching are outdated, the technical force is weak in management, the funds are scattered, the equipment is outdated, and there are still problems with repeated construction. Laboratory utilization is low, and students’ practice time is limited [13]. Virtual experiments can solve these difficult problems very well. It adopts the simulation method and comprehensively uses human–computer interaction, multimedia integration, network, virtual reality, and other technologies to give full play to the integration, visibility, and interactivity of modern information technology, breaking the traditional experimental teaching in time and space limitations, expanding the depth and breadth of experimental content [14].
The design of the virtual experiment is based on the computer, so during the virtual experiment, repeated work can be efficiently carried out, and various possible results can be obtained. Moreover, it can simulate experiments that are impossible in practice and can also demonstrate error conditions through which the staff understands the serious consequences of these problems. Moreover, the virtual experiment can facilitate network communication, so it can also help the exchange of technical information between schools and between schools and society [15]. Since the virtual laboratory is built on the computer platform with virtual instrument software as the core, it can be used to design soft instruments that have the same or even more functions as the traditional instruments in the previous laboratory and can be easily developed. It can also solve the problems of many traditional laboratory experimental equipment, repeated purchase of instruments, low utilization rate, and high damage rate of instruments. It can provide convenient, concise and efficient experimental instruments for experiments, which can greatly save the capital investment of experimental equipment. This kind of virtual laboratory has the characteristics of flexibility, low cost, and high efficiency and will play a great role in teaching and scientific research in higher vocational colleges [16]. Constructing a virtual experimental teaching environment that integrates experimental teaching, operation, guidance, and submission of results will help to achieve teaching reform, improve the experimental environment, increase the utilization rate of teaching resources, realize resource sharing, save the cost of updating experimental equipment, and improve teaching quality. The signal detection course is a very important professional course, and its practical application range is very wide [17].
Virtual instrument technology is an instrument measurement technology developed based on computer technology and is the product of the combination of computer technology and instrument technology. There are several ways to integrate general-purpose PCs with various instruments [18]: one is to install PCs into instruments, such as smart instruments with a high degree of automation. The volume is getting smaller and smaller, and the performance of this type of instrumentation in all aspects is also continuously improved and gradually there is an instrument with an embedded system; the second is to install the instrumentation system in the PC and use the software and hardware of the PC, to complete various required functions. This is actually the case with virtual instruments. The virtual instrument technology relies on software to achieve different detection tasks on the basis of hardware with superior performance. Users can create a visual interface of man–machine dialogue through virtual instrument software to control the instrument and analyze, store, and display data. Such virtual instrument systems can replace traditional instruments.
Intelligent reflective surface (IRS), also known as reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS), has the ability to customize and control the propagation of reflected signals and has therefore been proposed as a candidate technology for the next generation of wireless networks. More specifically, by adjusting the phase and amplitude characteristics of the IRS element plane, the required reflected signals can be controlled and enhanced, and unwanted interference can be reduced to achieve the so-called “smart radio environment,” which can significantly improve the coverage range and spectral efficiency of existing wireless networks [19]. Compared with traditional active relay technology, IRS does not require the use of separate RF links or other high power consumption and high price components. IRS consumes very low power and is much cheaper in price. IRS can be seamlessly integrated into existing wireless communication networks to achieve various goals, including reducing inter-user interference, lowering transmission power consumption, reflecting and propagating signals to avoid communication congestion, and promoting advanced modulation techniques. These advantages of the IRS have led many people to start researching IRS-assisted communication networks. Not only in communication networks, the IRS also has many advantages in perceptual imaging. Each microvan of IRS can independently control the incident signal and alter the propagation environment in space. By continuously adjusting the reflection characteristics of the IRS, the receiver can obtain different echo signals, thereby obtaining more information in the environment [20].
Zhao et al. [21] proposed a robust downlink transmission scheme for multiple IRSs assisted corporate switched telecommunications network. The satellite network adopts a multigroup multicast transmission scheme to serve many earth stations, while the terrestrial network exploits space division multiple access and multi-IRS-enhanced non-orthogonal multiple access technology to communicate with many terrestrial users. Zhao et al. [22] proposed a dual-layer layer division multiplexing (LDM) enhanced scheme for computation and communication co-design (LDM-3 C) to facilitate simultaneous wireless data aggregation and uplink data transmission in unmanned aerial vehicle networks. Specifically, according to distinguishing signal strength, the communication signals are assigned to the upper layer for uplink data transmission, while the computation signals are mapped onto the lower layer, and the over-the-air computation technique is introduced to realize fast wireless data aggregation.
This article combines virtual reality technology and IRS-assisted perception and communication technology to build a general computer test demonstration platform to improve the effect of virtual computer demonstration teaching.
2 Algorithm model of virtual computer demonstration platform
Millimeter wave imaging technology has made significant progress. However, there are still drawbacks such as too many antenna elements, bulky equipment, and long imaging time. This leads to defects in the application conditions of the computer technology experimental demonstration platform.
In practical applications, millimeter wave signals suffer significant attenuation due to their extremely high frequency. Therefore, millimeter waves are almost unusable for long-distance applications. However, this also reduces signal interference and allows millimeter wave transceivers to be deployed very densely in one area without interfering with each other’s operation. These features not only generate high communication rates but also provide a great opportunity to accurately detect the surrounding environment, easily penetrating simple obstacles such as plastics and fabrics. To overcome these challenges, this article proposes a novel millimeter-wave imaging scheme based on IRS. IRS is a promising new technology recently proposed, which can control its own reflection characteristics through software and be used to reconfigure wireless propagation environments. Its application in computer technology experimental demonstration platforms can effectively enhance signal strength and improve imaging performance. This technology can be applied to Sparse Code Multiple Access (SCMA) encoder technology, and after successful application, VR display of computer technology experiments can be achieved.
2.1 Sparse code division multiple access
The process of SCMA coding is the process of mapping the binary bit stream to the complex number domain. The SCMA encoder can also be expressed as follows: f = Vg. Here, V is a binary mapping matrix, which can map N-dimensional constellation points to R-dimensional SCMA codewords. The mapping matrix of each user is different, and the mapping matrix of each user contains M–N all-zero rows. Each user’s mapping matrix is different, and each user’s mapping matrix contains M–N all-zero rows. Because codewords are sparse, not all user codewords will collide in resource block r, and whether user u occupies resource block r is determined by the corresponding mapping matrix

Schematic diagram of sparse code division multiple access (take six users and four channels as an example).
2.2 System model
Based on SCMA, an intelligent reflector-assisted joint multi-user information reliable access and environmental reflector perception scheme is proposed. SCMA is a code domain non-orthogonal multiple access (code NOMA) method. IRS is a promising technology that surpasses 5G wireless networks, enhancing the transmission environment of wireless communication solutions. IRS uses low-cost passive reflective elements to adjust the phase of the incident signal to enhance the signal quality at the receiver end. In uplink communication, both the sparsity of structured signals based on SCMA and the sparsity of reflectors in unstructured environments should be considered simultaneously. For multi-user information access, SCMA signals can be separated at the receiving end through message-passing algorithms due to sparse codebooks. Moreover, through the separated signals, the information about the environmental reflector in the received signal is extracted by calculating the imaging method. By iteratively optimizing the performance of multi-user information access and environmental perception through the relationship between environmental reflector information and received signals. As shown in Figure 2, there is a millimeter-wave access point (AccessPoint, AP) and several users in the wireless environment. In upstream communication, multiple users send signals to the access point at the same time, and our purpose is twofold. The first is to complete the reliable access of multi-user information, that is, to decode the transmitted signals of all users. The second is to complete the perception and imaging of the wireless environment, that is, to obtain all reflector information in the wireless environment. To accomplish these two purposes, we assume that this system uses the SCMA scheme for data transmission; the signals of these users are distributed on R orthogonal resource blocks (ORE).
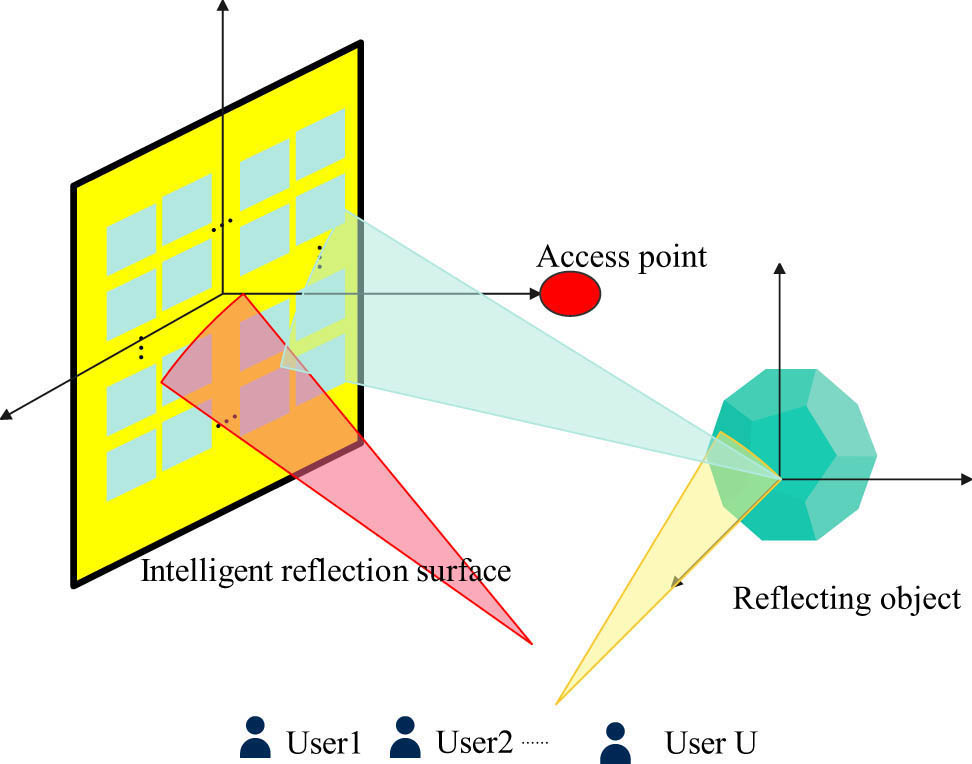
SCMA-IRS system model.
We divide it into pixel blocks of size l
r
, w
r
, and h
r
, the number of pixels is
If it is assumed that the IRS consists of K microfacets, each microfacet of the IRS reflects the incident signal with a set phase offset and amplitude reflection coefficient. We represent the reflection properties of the IRS by the following diagonal matrix:
Among them,
If it is assumed that all signals arriving at the access point need to be reflected by the smart reflective surface, the signals reach the access point through two paths. The first is the path that directly reaches the IRS without being reflected by the reflector, which is called the Light Of Sight (LOS). The second is the path reflected by the reflector, which is called Non-Light Of Sight (NLOS). We denote the NLOS path channel on the r-th ORE from the u-th user to the n-th pixel block to the k-th microfacet of the IRS to the access point by
Among them, x
n
represents the reflection coefficient of the internal reflective surface of the n-th pixel in the room. If this pixel is empty, then
Among them,
Therefore, the received signal received by the access point on the r-th ORE is
Among them,
Among them,
Among them,
The optimal solution for phase
Among them,
2.3 Multi-user information access and environmental awareness
The first goal we want to achieve is to complete the reliable access of multi-user information, that is, to detect the uplink signals of all users. There are U users, and each user has M kinds of codewords. By performing a full search on all (M)U user codeword combinations, a maximum likelihood decoder can provide the theoretical best bit error rate performance. The transmission codewords:
Among them,
The SCMA-IRS-MPA decoder can be represented using a factor graph, as shown in Figure 3. Among them, function nodes (functionnodes, FNs) represent ORE, and variable nodes (variablenodes, VNs) represent users. Through message passing between nodes, the MPA decoder iteratively updates the message probabilities between FNs and VNSs.

SCMA factor graph (take six users and four OREs as an example).
Next, we analyze the computational complexity of the algorithm. We represent the decoding computational complexity of the MPA decoder in terms of the number of addition and multiplication operations required to decode the user codeword. Therefore, the number of additions and multiplications required by the MPA detector are
In the process of multi-user signal detection, we obtain the codeword estimates
Among them,
This is an equation about the target
As the communication process continues, different users send different codeword combinations at different locations, which can generate many different equations. As long as the receiver records all these equations, as the number of obtained equations gets closer and closer to N, it can obtain a better reconstruction effect and obtain x.
The performance of the proposed joint multi-user communication and environment awareness method is gradually improved with the progress of the communication process and the continuous iteration of multi-user communication and environment awareness. As shown in Figure 4, at the beginning, the access point is blind to the wireless environment and has no information about the wireless environment.
Flow chart of an iterative method for joint communication and environment awareness.
The SCMA-IRSMPA decoder may not perform well due to the lack of channel information. However, due to the sparsity of the SCMA codebook, the receiver can still decode certain user signals based on the differences between different codewords themselves. By decoding the user’s transmitted signal, a portion of environmental information can be obtained, which includes channel information. Then pass this channel information to the SCMA-IRS-MPA decoder for user decoding again, obtaining more accurate user codewords, and repeat the previous iteration process through the user codewords. Continuously iterate until the performance reaches the set threshold or the number of iterations reaches the set number, completing the self-loop within a single ORE. After completing the self-loop, the obtained user code-word information, the received signal at the intervention point, and the obtained environmental information will be transmitted to the adjacent ORE. Adjacent ORE can use this information as a starting point to complete their own inner loop and then pass the obtained results to adjacent ORE. After completing its own inner loop, each ORE can wait for more accurate results from adjacent ORE, such as obtaining more information in subsequent time slots and then re decode the user code to obtain more accurate user codewords. This completes the loop between ORE. By continuously iterating between internal loops and ORE loops, as the communication process continues, user information decoding and environmental perception will become better and better.
3 Design of augmented reality (AR)-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
The function items of the remote virtual laboratory system are divided into five relatively independent function modules, namely, experiment customization module, experiment simulation operation module, experiment result visualization module, experiment equipment component module, and component registration module. There is high cohesion and low coupling between modules. Figure 5 shows the functional block diagram of the system.
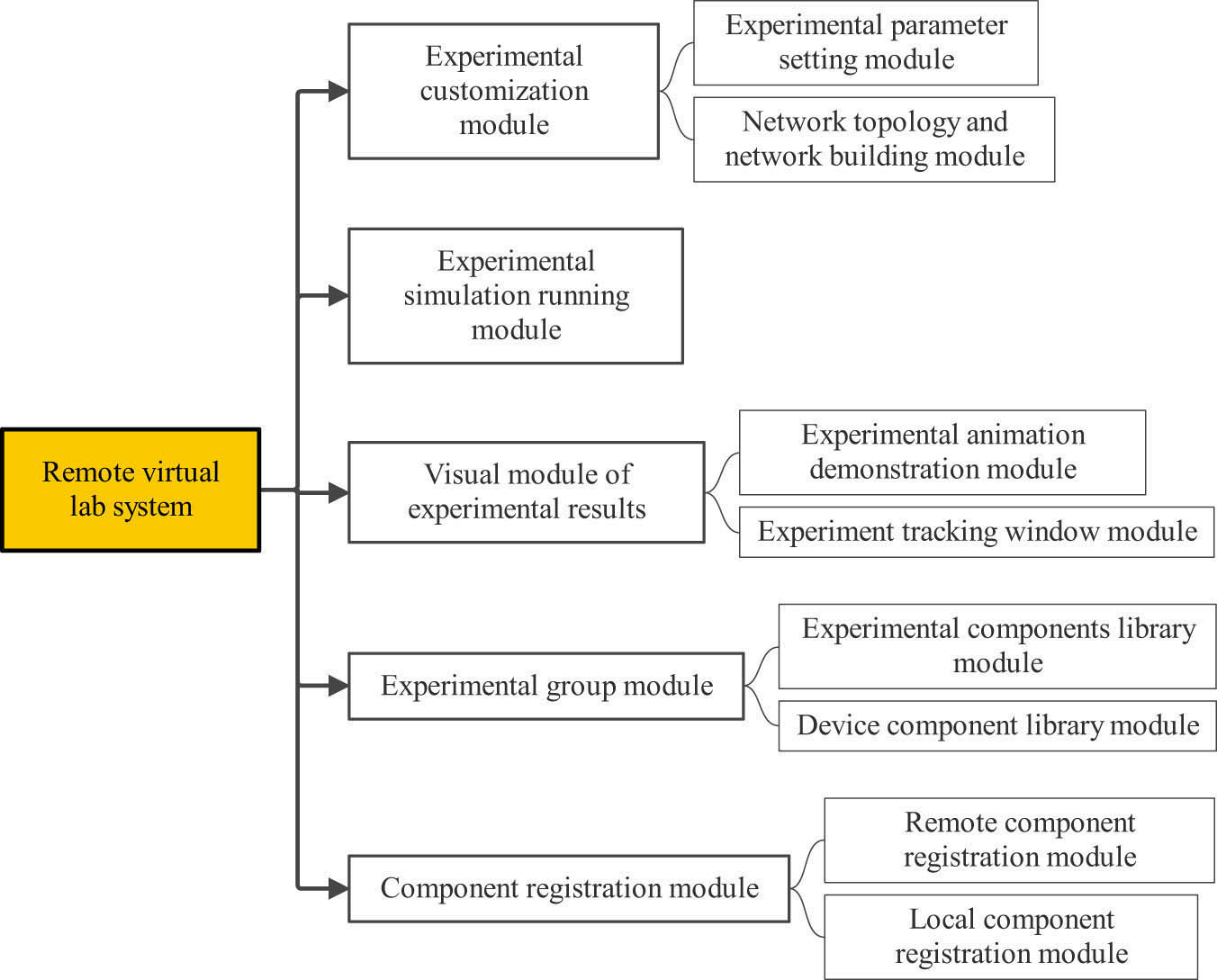
System overall design module diagram.
The design process and design content of each digital signal processor system will vary greatly according to specific requirements. Complex DSP designs can include front-end analog circuit interfaces and digital interfaces to other digital devices and may require algorithm simulation and analysis before design, while simple DSP designs only include digital information processing. The design process of the digital signal processor system is shown in Figure 6.

Design flow of digital signal processor system.
The performance effect of the proposed joint multi-user information access and environment awareness scheme based on the uplink SCMA-IRS system is verified by simulation analysis. We assume the room is 3 m long, wide, and high. The operating frequency band of the system is f c = 60 GHz, and the system bandwidth is B = 1 GHz. There is a mmWave access point inside the room, at the midpoint of an edge from the top of the room. It is assumed that the distribution of reflective surfaces inside the room is randomly generated, as shown in Figure 7. Figure 8 shows the results of environment perception under different SNRs. The number of users is set to 6, which is randomly generated in the environment; the smart reflective surface is composed of 10 × 10 microfacets; and the transmission time is 50 time slots. It can be seen that with the improvement of the SNR, the effect of environmental perception also becomes better when other conditions are the same.

The distribution of reflecting surfaces inside the room.

Environment perception results with different SNRs.
To measure the performance of the proposed SCMA-IRS-based joint multi-user information access and environment awareness scheme, we use two metrics to represent the performance of environment awareness and the performance of multi-user information access, respectively. Among them, the mean square error (MSE) measures the performance of environmental perception. The smaller the MSE, the more accurate the perception of the environment, and vice versa. The symbol error probability (SER) is used to measure the performance of multi-user information access. The smaller the SER, the more accurate the decoding of user information.
Figure 9 shows the performance of the proposed joint communication and sensing scheme as the number of transmitted time slots increases at SNRs of 10, 15, and 20 dB. Figure 9(a) is the change in MSE, and Figure 9(b) is the change in SER. The size of the smart reflective surface is 10 × 10, the number of users is 6, and the location is randomly generated. It can be seen that as the number of time slots increases, that is, as the communication process continues, both the performance of environment perception (MSE) and the performance of multi-user information access (SER) continue to improve. The reason is that with the progress of the communication process, the mutual iteration between environment perception and multi-purpose information decoding makes the obtained channel of access become more and more accurate so that better effect is obtained.
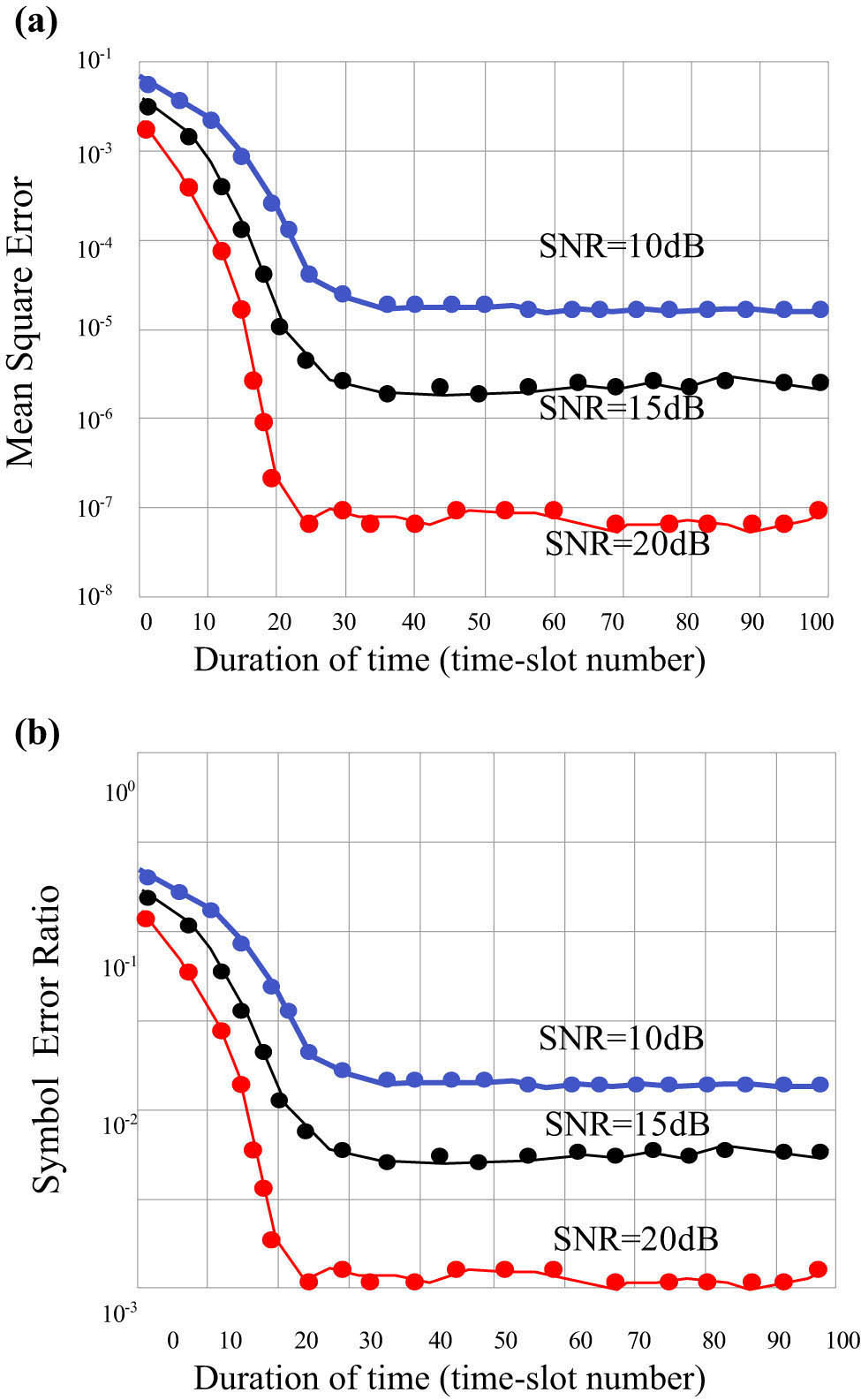
Performance changes as the communication process continues: (a) MSE and (b) SER.
Figure 10 shows the performance change of the proposed joint communication and perception scheme as the number of users changes. Figure 10(a) is the change in MSE, and Figure 10(b) is the change in SER. The SNR is 30 dB, the duration is 50 time slots, and the user location is randomly generated. It can be seen that as the number of users increases, the performance of environment perception (MSE) will continue to get better. The reason is that the increase in the number of users can bring more observation points to environmental perception, and the environmental information in the received signals formed by different user positions can be combined to obtain more accurate environmental information. In the iterative process of perception and communication, better perception will bring more accurate channel information, which will lead to better communication performance.
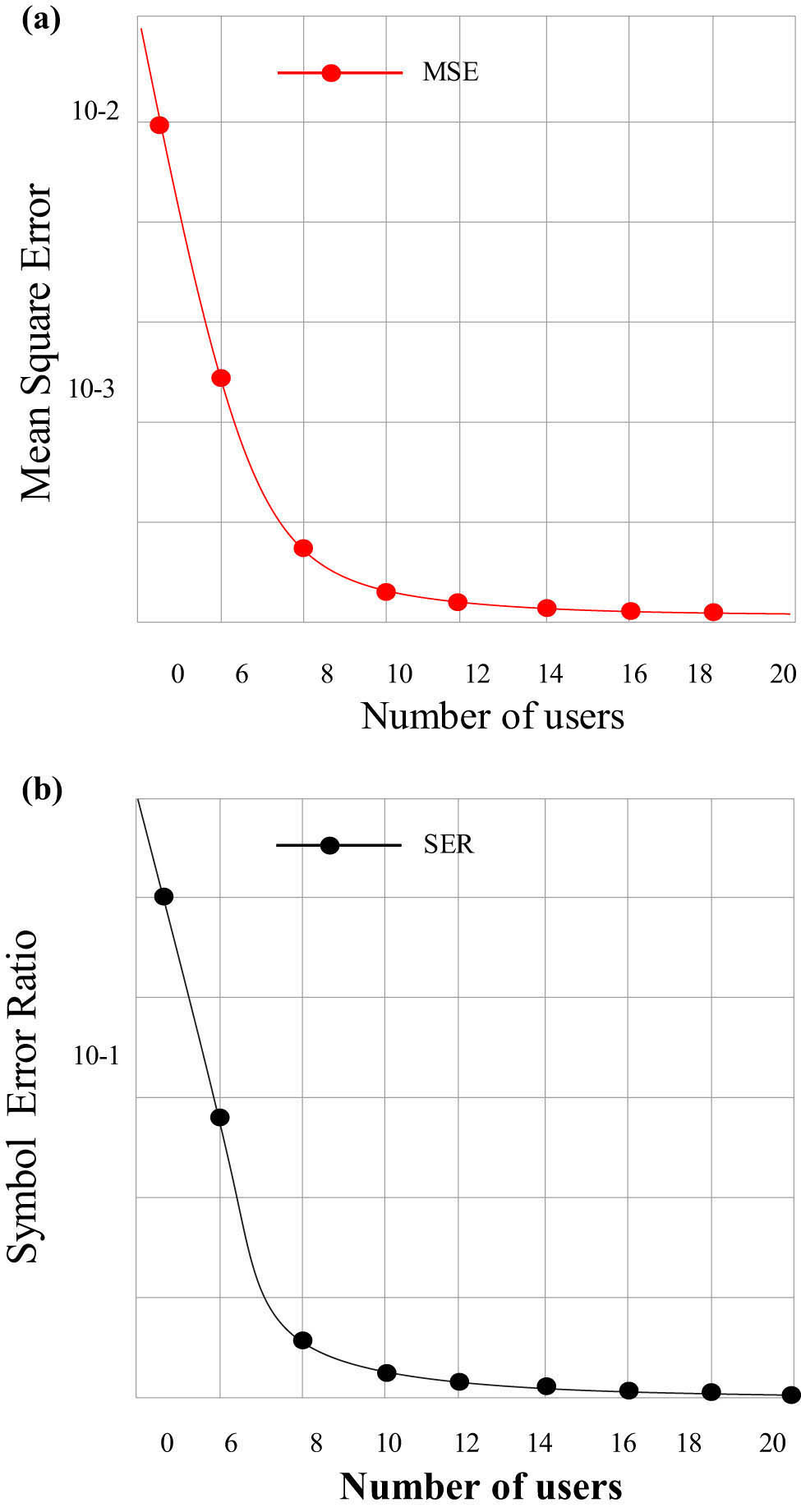
Relationship between the number of users and the proposed joint communication and perception scheme: (a) MSE and (b) SER.
To demonstrate the rationality of the joint multi-user information access and environmental perception scheme introduced by SCMA-IRS in this article’s model, a comparative experiment was conducted between the model with SCMA-IRS and existing models, with SER set at 15 dB. The most widely used hybrid analog digital beamforming (HAD-BF) scheme was selected for comparison, and the MSE and SER of the two were calculated with a duration of 100 s, resulting in Figure 11.

Performance comparison results of different models: (a) MSE and (b) SER.
In Figure 11, compared with HAD-BF, SCMA-IRS has certain advantages in the comparison of MSE and SER parameters. It is verified that introducing SCMA-IRS is a reasonable improvement on existing models.
On this basis, the effect of the AR-based general computer technology experimental demonstration platform proposed in this article is verified, and its practical effects are counted, and the practical results shown in Table 1 are obtained.
Practical effect of AR-based general computer technology experimental demonstration platform
| Number | Teaching practice | Number | Teaching practice | Number | Teaching practice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 86.99 | 21 | 86.62 | 41 | 81.33 |
| 2 | 81.34 | 22 | 81.98 | 42 | 80.18 |
| 3 | 83.29 | 23 | 79.69 | 43 | 79.95 |
| 4 | 83.75 | 24 | 80.99 | 44 | 81.63 |
| 5 | 80.80 | 25 | 79.09 | 45 | 85.40 |
| 6 | 82.83 | 26 | 81.22 | 46 | 82.41 |
| 7 | 81.20 | 27 | 83.20 | 47 | 79.85 |
| 8 | 79.24 | 28 | 83.74 | 48 | 83.88 |
| 9 | 83.41 | 29 | 83.29 | 49 | 82.23 |
| 10 | 85.82 | 30 | 80.12 | 50 | 79.10 |
| 11 | 83.19 | 31 | 84.62 | 51 | 80.37 |
| 12 | 83.95 | 32 | 84.40 | 52 | 82.76 |
| 13 | 82.91 | 33 | 80.95 | 53 | 79.35 |
| 14 | 83.05 | 34 | 83.60 | 54 | 81.66 |
| 15 | 79.86 | 35 | 79.98 | 55 | 79.02 |
| 16 | 85.07 | 36 | 79.04 | 56 | 84.04 |
| 17 | 84.00 | 37 | 86.69 | 57 | 86.94 |
| 18 | 83.15 | 38 | 81.19 | 58 | 81.70 |
| 19 | 83.37 | 39 | 82.97 | 59 | 84.12 |
| 20 | 82.41 | 40 | 79.53 | 60 | 84.72 |
It can be seen from the above research that the AR-based general computer technology experimental demonstration platform proposed in this article has a good effect and can effectively promote the computer technology experimental demonstration effect.
For some theoretical basic courses, due to the fact that the course content is mostly about understanding and analyzing basic theories and algorithm formulas, the experimental projects are mainly focused on verification. When specific hardware (such as course specific experimental boxes) is used for experimental operations, they often cannot be exactly the same as the theoretical results and phenomena described in the book. The target audience for professional basic courses is undergraduate students in their early years. Most students have weak independent hands-on innovation abilities, which can lead to confusion and misunderstanding during the experimental process, which is not conducive to their better grasp of the course content. In addition, for the analysis and processing of some ideal situations in textbooks, hardware experimental boxes also have significant limitations. For example, the most commonly used unit impulse signal in signal analysis cannot be perfectly implemented in experimental boxes. To solve these problems, simulation experimental software needs to be introduced in experimental teaching. In the experiments of basic theoretical courses, simulation software experiments can keep the experimental results highly consistent with what is taught in the textbook and have strong flexibility. Changes in experimental projects can be simplified to only modify a few parameters. The requirements for simulation software experiments on the platform are only a microcomputer and related software. Currently, university computer rooms are relatively abundant, and student experimental venues are no longer limited to designated professional laboratories. This is also conducive to integrating experimental resources and sharing, maximizing laboratory functions, and effectively improving the efficiency of experimental teaching.
4 Conclusion
The popularization of the Internet has provided the possibility for distance education to better understand the concepts learned for students, so it is necessary to provide a learning platform that closely integrates theory and experiment. Traditional experiments are inseparable from experimental equipment, and experiments often require preliminary preparation and regular maintenance of experimental equipment. Moreover, the experimental conditions are limited, which leads to low experimental efficiency, which in turn affects the teaching effect. In addition, the results of the experiments cannot be analyzed in time, and the experimental methods cannot be improved according to the results of the experimental analysis, including the monitoring of the experimental process. This article combines virtual reality technology and IRS-assisted perception and communication technology to build a general computer test demonstration platform. The research shows that the AR-based general computer technology experimental demonstration platform proposed in this article has good effects and can effectively promote the computer technology experimental demonstration effect.
The decoding algorithm for SCMA-IRS multi-user information access is based on message passing algorithm, which has a high computational complexity. How to design a more reasonable decoder. Perception and distributed computing can be combined together. Currently, the perception process is carried out in one terminal, while in communication networks such as the Internet of Things, there are many computing devices, and each device can obtain different information. In the future, it is necessary to further improve the performance of this model by combining distributed IoT technology.
-
Funding information: This work was funded by Key Natural Science Project of Huainan Normal University: “Research on the Design and Experience of Computerized and Non Computerized Children’s Programming Games” (2023XJZD017).
-
Author contribution: Fang Xu: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing-original draft, writing-review & editing. Author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: Author states no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Syed TA, Siddiqui MS, Abdullah HB, Jan S, Namoun A, Alzahrani A, et al. In-depth review of augmented reality: tracking technologies, development tools, AR displays, collaborative AR, and security concerns. Sensors. 2022;23(1):146–56.10.3390/s23010146Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Chiu WK. Pedagogy of emerging technologies in chemical education during the era of digitalization and artificial intelligence: a systematic review. Educ Sci. 2021;11(11):709–20.10.3390/educsci11110709Search in Google Scholar
[3] de Freitas FV, Gomes MVM, Winkler I. Benefits and challenges of virtual-reality-based industrial usability testing and design reviews: a patents landscape and literature review. Appl Sci. 2022;12(3):1755–66.10.3390/app12031755Search in Google Scholar
[4] Kourtesis P, Collina S, Doumas LA, MacPherson SE. Validation of the virtual reality everyday assessment lab (VR-EAL): an immersive virtual reality neuropsychological battery with enhanced ecological validity. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2021;27(2):181–96.10.1017/S1355617720000764Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Burton Q, Lejeune T, Dehem S, Lebrun N, Ajana K, Edwards MG, et al. Performing a shortened version of the Action Research Arm Test in immersive virtual reality to assess post-stroke upper limb activity. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2022;19(1):133–46.10.1186/s12984-022-01114-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Lee H, Woo D, Yu S. Virtual reality metaverse system supplementing remote education methods: based on aircraft maintenance simulation. Appl Sci. 2022;12(5):2667–80.10.3390/app12052667Search in Google Scholar
[7] Wittstein MW, Crider A, Mastrocola S, Gonzalez MG. Use of virtual reality to assess dynamic posturography and sensory organization: instrument validation study. JMIR Serious Games. 2020;8(4):e19580–92.10.2196/19580Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Martirosov S, Bureš M, Zítka T. Cyber sickness in low-immersive, semi-immersive, and fully immersive virtual reality. Virtual Real. 2022;26(1):15–32.10.1007/s10055-021-00507-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Haryana MRA, Warsono S, Achjari D, Nahartyo E. Virtual reality learning media with innovative learning materials to enhance individual learning outcomes based on cognitive load theory. Int J Manag Educ. 2022;20(3):100657–68.10.1016/j.ijme.2022.100657Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wodarski P, Jurkojć J, Polechoński J, Bieniek A, Chrzan M, Michnik R, et al. Assessment of gait stability and preferred walking speed in virtual reality. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2020;22(1):127–34.10.37190/ABB-01490-2019-03Search in Google Scholar
[11] Pietikäinen O, Hämäläinen P, Lehtinen J, Karttunen AJ. VRChem: a virtual reality molecular builder. Appl Sci. 2021;11(22):10767–80.10.3390/app112210767Search in Google Scholar
[12] Mees L, Upadhyaya S, Kumar P, Kotawala S, Haran S, Rajasekar S, et al. Validation of a head-mounted virtual reality visual field screening device. J Glaucoma. 2020;29(2):86–91.10.1097/IJG.0000000000001415Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Varmaghani S, Abbasi Z, Weech S, Rasti J. Spatial and attentional aftereffects of virtual reality and relations to cybersickness. Virtual Real. 2022;26(2):659–68.10.1007/s10055-021-00535-0Search in Google Scholar
[14] Parong J, Mayer RE. Cognitive and affective processes for learning science in immersive virtual reality. J Comput Assist Learn. 2021;37(1):226–41.10.1111/jcal.12482Search in Google Scholar
[15] Wu B, Yu X, Gu X. Effectiveness of immersive virtual reality using head-mounted displays on learning performance: a meta-analysis. Br J Educ Technol. 2020;51(6):1991–2005.10.1111/bjet.13023Search in Google Scholar
[16] Fussell SG, Truong D. Using virtual reality for dynamic learning: an extended technology acceptance model. Virtual Real. 2022;26(1):249–67.10.1007/s10055-021-00554-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Marek N, Pollmann S. Contextual-cueing beyond the initial field of view—a virtual reality experiment. Brain Sci. 2020;10(7):446–57.10.3390/brainsci10070446Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Gao Y, González VA, Yiu TW, Cabrera-Guerrero G, Li N, Baghouz A, et al. Immersive virtual reality as an empirical research tool: exploring the capability of a machine learning model for predicting construction workers’ safety behaviour. Virtual Real. 2022;26(1):361–83.10.1007/s10055-021-00572-9Search in Google Scholar
[19] Yang P, Liu Z. The influence of immersive virtual reality (IVR) on skill transfer of learners: the moderating effects of learning engagement. Int J Emerg Technol Learn. 2022;17(10):62–73.10.3991/ijet.v17i10.30923Search in Google Scholar
[20] Liberatore MJ, Wagner WP. Virtual, mixed, and augmented reality: a systematic review for immersive systems research. Virtual Real. 2021;25(3):773–99.10.1007/s10055-020-00492-0Search in Google Scholar
[21] Zhao B, Lin M, Cheng M, Wang JB, Cheng J, Alouini MS. Robust downlink transmission design in IRS-assisted cognitive satellite and terrestrial networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2023;41(8):2514–29.10.1109/JSAC.2023.3288234Search in Google Scholar
[22] Zhao B, Lin M, Wang Z, Wang JY, Al-Dhahir N. LDM-enhanced computation and communication co-design in unmanned aerial vehicle networks. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst. 2024;60(6):9394–400.10.1109/TAES.2024.3436646Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations

