Abstract
In response to the issues of insufficient clarity and data processing capabilities in the current face model construction process, a method for constructing multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms is proposed. The new method incorporates the image decomposition and normalization model to enhance the algorithm’s ability to process image data. Subsequently, receptive fields, core attention modules, multi-scale attention modules, and dynamic selection attention modules are introduced to enhance the algorithm’s handling of details and model clarity in the process of constructing face data. The research results indicated that the new algorithmic model could improve the data metrics of face models. The incorporation of distinct modules has the potential to enhance various algorithmic metrics. However, the multi-scale attention module emerged as a pivotal component, demonstrating superior stability compared to numerous alternative algorithms. When dealing with face images of different styles, the performance of the new algorithm was better compared to that of other algorithms. Therefore, the new algorithm can enhance the numerical values of face models to a certain extent, improve parameters such as facial texture clarity, and have important research significance in the direction of constructing multi-style face models.
1 Introduction
In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, generative models have shown tremendous potential in image generation [1]. Facial artistic image generation is an artistic representation form that describes detailed facial features and can present traditional facial drawings through modeling [2]. Traditional face generation methods mainly rely on the learning and feature extraction of large-scale facial databases, but the generated facial images often lack innovation and artistic expression. Due to the advancement of intelligent networks, the construction of facial images has gradually shifted toward intelligent networks [3]. The use of computers enables machines to possess artistic drawing capabilities similar to humans [4]. Simultaneously, the construction of facial models can also assist in other fields, such as aiding in the apprehension of criminals in criminal cases through the construction of facial images. Although current cameras can address this issue, there are still challenges with insufficient clarity and unclear images. Therefore, research in this direction becomes increasingly important. Based on this, this study proposes a facial model construction algorithm based on artistic image generation algorithms. To enhance the descriptive ability of facial details, new attention modules have been added. This module not only utilizes dynamic data feature distribution to learn more feature data but also controls the artistic style of facial images. Additionally, receptive fields are incorporated into the algorithm to improve the clarity of facial images. This research is divided into four sections. The first section describes the research in this direction domestically and internationally. The second section focuses on the construction of algorithm structure and system. The third section tests the algorithm’s performance, and the fourth section summarizes the content of the article.
2 Related works
The construction of multi-style facial models involves not only the simple processing of model data but also the resolution of various issues throughout the process. Many experts and scholars have conducted extensive research and made discoveries in this direction. Kirchner and Eric explored the image painting representation from ancient times to the twentieth century and proposed an analysis method for high-resolution photos of artistic works. The research results indicated that until the nineteenth century, painters did not adhere to contemporary color theory when depicting rainbows, and individual choices of color played a decisive role [5]. Fu et al. aimed to study the generation of important floral art in Chinese paintings and introduced a floral generative adversarial network (GAN) framework. They built a dataset containing three classic Chinese painting styles: line drawing, meticulous brushwork, and ink wash, to generate various styles of Chinese floral art. The research showed that this method could produce better and multi-styled Chinese floral art while addressing the issues of artifacts and blurriness present in existing methods [6]. Kaveh et al. proposed a new physics-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving constrained optimization problems, specifically in plasma generation optimization. To assess the performance and capability of the proposed method compared to other optimization techniques, numerical studies were conducted on two sets of test problems. The results demonstrated that the performance of the proposed method was competitive with other state-of-the-art optimization methods [7]. To compare the accuracy of face recognition when replacing the grayscale of each pixel in face images with gradients and surface normals, Koc conducted experiments on different recognition methods. Well-known face recognition methods such as the general vector method and support vector machine were employed, and comparisons were made using the AR and Yale databases. Additionally, a new method, the Pixel Slope Similarity Summation approach, was introduced. The experimental findings suggested that utilizing surface normals as an alternative to gradient vectors for each pixel, without implementing additional processing of its elements, resulted in enhanced recognition rates [8].
Heravi and Farnaz Majid Zadeh proposed a three-dimensional reverse modeling method to digitize the aging process of adult faces into childlike faces. The research extended from a two-dimensional model to a three-dimensional model, allowing for the digital rejuvenation of facial appearance within the age range of 75 to 3 years. The results of the study indicated that faces generated using the new model were perceptually satisfactory, and there was an improvement in system performance [9]. Liao et al. aimed to enhance the accuracy of face pose recognition and introduced a novel multi-view face pose recognition model based on canonical correlation analysis algorithm. The research results showed a significant improvement in recognition accuracy compared to traditional models, with an average accuracy of 96.334%, demonstrating superior recognition performance [10]. Ferrari et al. addressed the precise analysis of three-dimensional facial deformations by proposing a comprehensive framework. They constructed a three-dimensional deformable shape model of the face for fitting target images. The results indicated that the method could accurately capture facial deformations, including local and asymmetrical deformations [11]. To accurately track faces in video sequences, Zheng and Xu presented an efficient face detection and tracking framework based on deep learning. This framework included a SENResNet face detection model and a face tracking model based on regression networks. The research results demonstrated that the proposed model outperformed state-of-the-art comparison methods in terms of accuracy and performance [12].
In summary, there are still many challenges in the research on art and face models, such as the accuracy of face recognition data and the processing of image generation data. Therefore, this study will analyze the construction of facial models and develop a new art generation algorithm for face model construction and data processing. By utilizing dynamic activation functions and neuron activation, the goal is to enhance the ability to adjust the local details of the current face image. Simultaneously, the use of algorithm modules aims to improve the clarity of the current face image’s contours.
3 Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
This section primarily focuses on the exploration of the framework of artistic image generation algorithms. It involves the construction of an algorithmic model based on face features and aims to enhance the performance of the existing algorithm by optimizing the model and incorporating modules such as receptive fields. Finally, a system framework for face model construction is designed.
3.1 Face model generation based on artistic generation algorithms
The process of building face models revolves around capturing detailed information from facial images, including facial features, structural details, and line textures. With the application of computer algorithms, significant success has been achieved in face model construction technology. Generally, there are several methods for generating face models for artistic paintings. First, the construction involves local three-dimensional structures, utilizing facial shadows and abstract contours to build a three-dimensional facial model. Second, for the two-dimensional details of the face, different line densities and model line colors are analyzed to capture details. Multi-style faces refer to data in different styles, such as oil painting-style facial images and pen drawing-style facial images. Constructing faces in different styles requires the application of various artistic techniques, representing the same face features using different textures [3].
The construction of multi-style face models is based on the input face information in the system, producing data for different face styles, and subsequently building face models. Therefore, the artistic image generation algorithm based on face construction mainly involves recognizing and three-dimensional reconstruction of current face model data. The overall structure of its algorithmic model is illustrated in Figure 1.
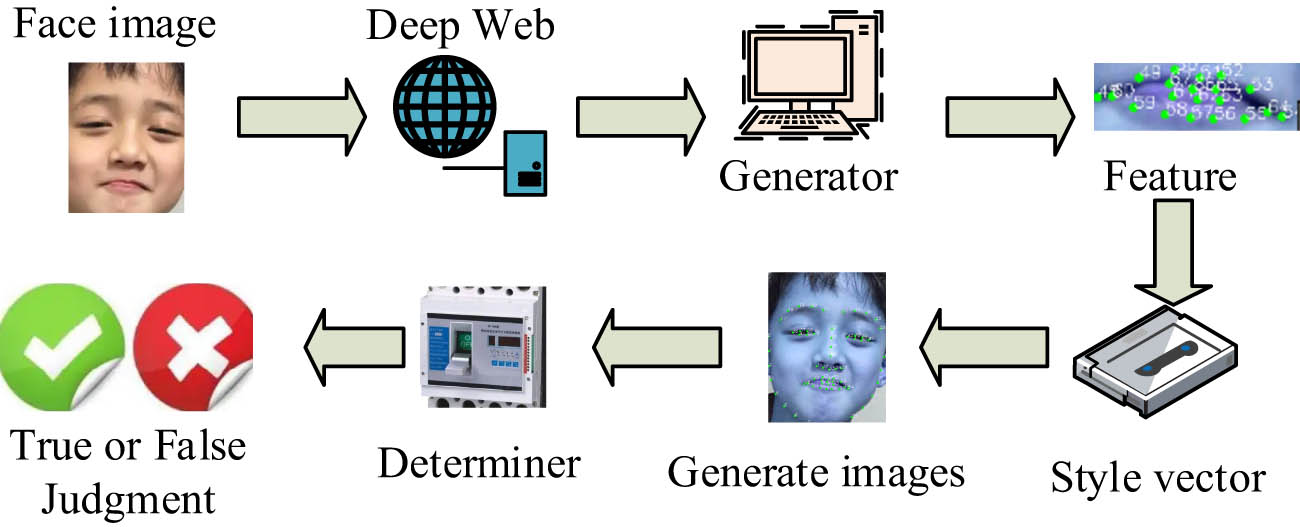
Overall model of art generation algorithm.
As shown in Figure 1, the algorithmic model comprises three structures: a generator, a discriminator, and a detector. During the training of face data, the discriminator can generate more realistic facial data for evaluation, identifying the authenticity of the current data. The generator is primarily responsible for generating diverse face images in different styles. In addition to generating deeper image data, the algorithmic model can construct deep images, completing the three-dimensional structural reconstruction of current face image data through this approach. The model includes a generator consisting of an eight-layer encoder and an eight-layer decoder, where both the encoder and decoder use a 3 × 3 standard convolutional kernel and a discriminator with a five-layer convolutional structure. Each layer of convolution is followed by batch normalization and LeakyReLU activation functions, and finally outputs the true/false judgment through a sigmoid-activated fully connected layer. In addition, the model includes a three-layer feature extractor, two-layer pooling layer, and a detector with one-layer classification layer.
The generator structure of the algorithm includes a decoder and an encoder. When the layers of the current decoder and encoder reach
In Eq. (1), the parameters are the same as described previously. Finally, the output of the decoding layer is obtained through residual connections, as shown in Eq. (2):
where
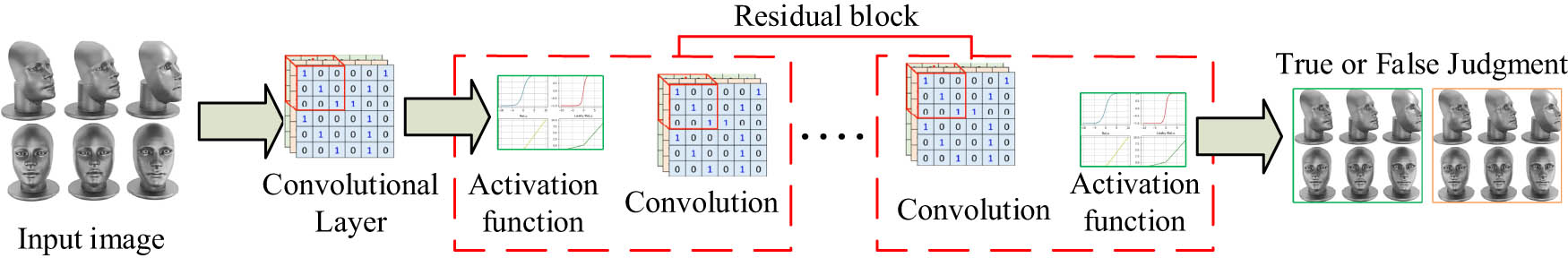
Structure of the art picture generation algorithm judgor.
From Figure 2, the structure of the discriminator model includes multiple convolutional layers, activation layers, and modules for normalizing image data. After inputting facial data, multiple convolution and activation operations are performed in different modules to judge the current face image data, determining whether the image data is real and inputting the real value of facial data. Therefore, the feature set expression at point
where
In Eq. (4), the parameters are consistent with the expressions described earlier. The standard deviation expression is shown in Eq. (5):
where the parameters are consistent with the expressions described earlier. The expression of scaling and bias parameters for image data is achieved through the deep learning information data of the face, encoding information data, and face style information data, implemented by modulating network parameters. To enhance the modulation capability of the modules, an activation function is introduced in the global model training, as shown in Eq. (6) [15]:
where
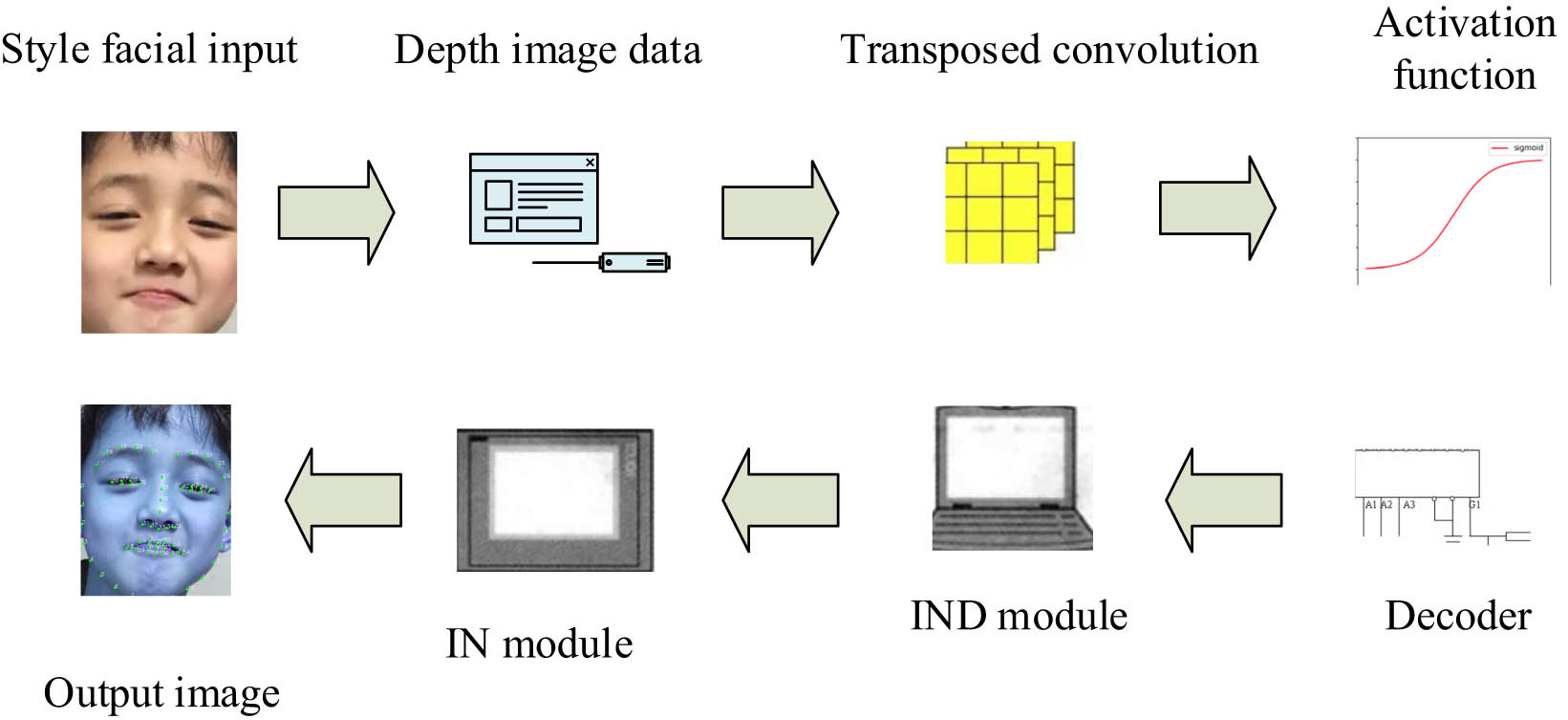
IDN model flowchart.
As shown in Figure 3, when style images and facial data are input, the deep encoding of image data is completed through the convolution and dynamic activation encoding process. In this process, transpose convolution and activation functions are incorporated to process the deep image. The processed data undergoes upsampling through the decoder, and then data parameter addition and multiplication are performed using the IDN module and IN module, ultimately outputting a feature set. In addition to the existing adversarial loss function and pixel loss function used for the algorithm’s loss function calculation, the algorithm’s image generation is hindered by the deep reconstruction loss of the image and the texture loss of the face. The deep reconstruction loss measures the difference between the generated depth information and the ground-truth depth, ensuring accurate reconstruction of facial depth details, as shown in Eq. (7):
where
where
where
where
where the parameter expression is consistent with the above. The final loss function value is given by Eq. (12) [17]:
where
3.2 Algorithm optimization and face model generation system construction
To improve the generalization ability and robustness of the face model generation algorithm, Mixup data enhancement technique is used in the study. Mixup generates new training samples by linearly interpolating a mixture of two images and their labels. This method improves the model’s ability to adapt to input changes and reduces overfitting. There are some unclear aspects in the detailed description of the face model in the current algorithm, requiring further improvement of the algorithm. Accurate depiction of facial details at a large scale is necessary to obtain a relatively realistic face model. Additionally, consideration of detailed face features such as eyebrows and nose is crucial, as ignoring these details will fail to capture the three-dimensional facial features. Therefore, to address these issues, a receptive field is introduced into the algorithm for model improvement and optimization. The receptive field consists of two main components: an attention selection module and an attention gating unit. Attention modules typically use channel attention and self-attention to gather more data information, primarily by controlling the size of the receptive field. The size of the perceptual field varies with the size of the convolution kernel. If the size of the first layer convolution kernel is 3 × 3 and no padding is used, then the perceptual field of the first layer is 3 × 3. By changing the size of the convolution kernel, the size of the perceptual field can be changed. The larger the convolution kernel, the larger the perceptual field, and the wider the range of images captured by the network. The step size determines the interval at which the convolutional kernel moves. The larger the step size of the model, the less overlap there is in the receptive field, and the larger the receptive field will be. The model facilitates the network’s ability to capture information at varying scales by employing feature maps at different scales. Consequently, this dynamic adjustment of the receptive fields at various levels enables the network to adapt to its environment. However, these modules may not capture local information and long-term dependencies in the data. To overcome this limitation, a multi-scale mechanism module is built upon the traditional attention module, including the CAM, MAM, and DSAM. The CAM focuses more on local features, whereas the MAM considers both local and global features. The MAMs, which integrate features across different scales to improve the model’s adaptability to various image complexities, provide a more comprehensive feature representation by fusing features from different scales. In contrast, the CAMs, which focus on enhancing the processing of local details, may be more focused on digging deeper into single-scale features. The ability of the MAM to adapt to image features at different scales makes it more flexible in dealing with images of different sizes and complexity. Therefore, the study uses the MAM for analysis. The features extracted by the CAM are first fed into the MAM, where they are fused through different scales to enhance feature representation. Second, the output of the MAM is further processed by the DSAM, which in turn dynamically adjusts the features according to the current image requirements. Finally, during the training process, the three modules are jointly optimized to ensure that the network works synergistically and the network performance is enhanced through the back propagation algorithm update of the parameters. The CAM is represented by Eq. (13) [18]:
where
In the control of multi-style generation of face images, it is necessary to differentiate the styles of the current face model. Even if the style information in the normalization module of the current decoding layer is removed, modulation is applied only to the depth-encoding information of the current module to create a multi-style control model for the face. To integrate this algorithm into the design and construction of face models, a face model generation system has been developed on this basis. The system framework structure is illustrated in Figure 4.
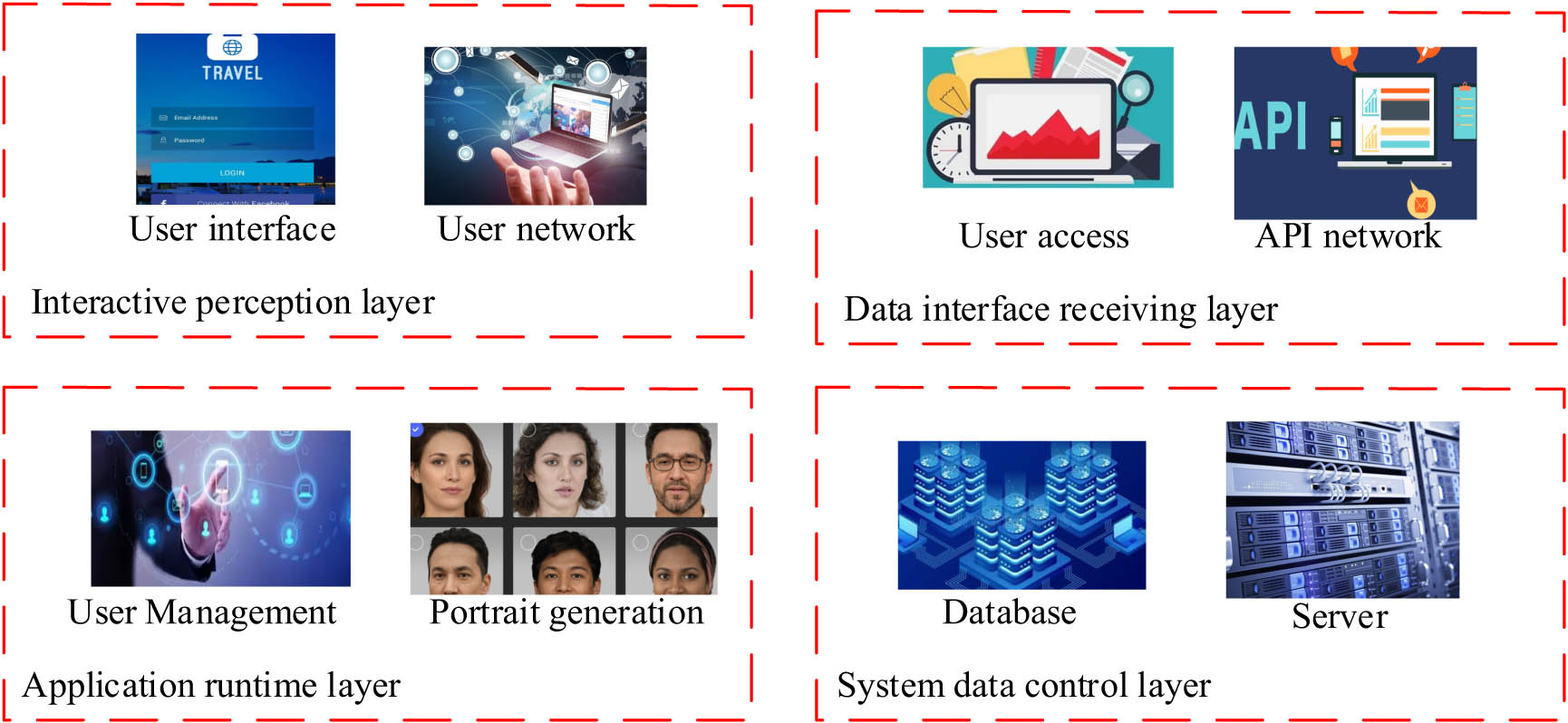
System framework structure.
According to Figure 4, the system modules are divided into four parts: the Interactive Perception Layer, Data Interface Reception Layer, Application Program Execution Layer, and System Data Control Layer. The Interactive Perception Layer primarily provides a visual analysis interface for the current user, such as login, information modification, and data generation. The Data Interface Reception Layer includes the reception and output of data within the system. The Application Program Execution Layer manages the current system’s applications. The System Data Control Layer is responsible for controlling the storage of system algorithms and input/output data. The User Management Module requires control over user information data, usage permissions, account information, etc., as shown in Figure 5.

User management module process diagram.
As illustrated in Figure 5, when users interact with the system modules, they first check whether they have logged into the current data system. If the login is complete, they verify the existence of existing data account information. If there is no account information, they proceed with registration. If there is account information, they go through the password modification process before completing the login. Administrators and regular users have different information management capabilities. Administrators can perform operations such as deleting, viewing, adding information data, and using platform programs. Regular users can only use the current platform program. The generation of multi-style facial images constitutes a pivotal focal point of the present system module, encompassing sketch facial images, pen facial images, and optimized facial images, among others. The specific process is depicted in Figure 6.
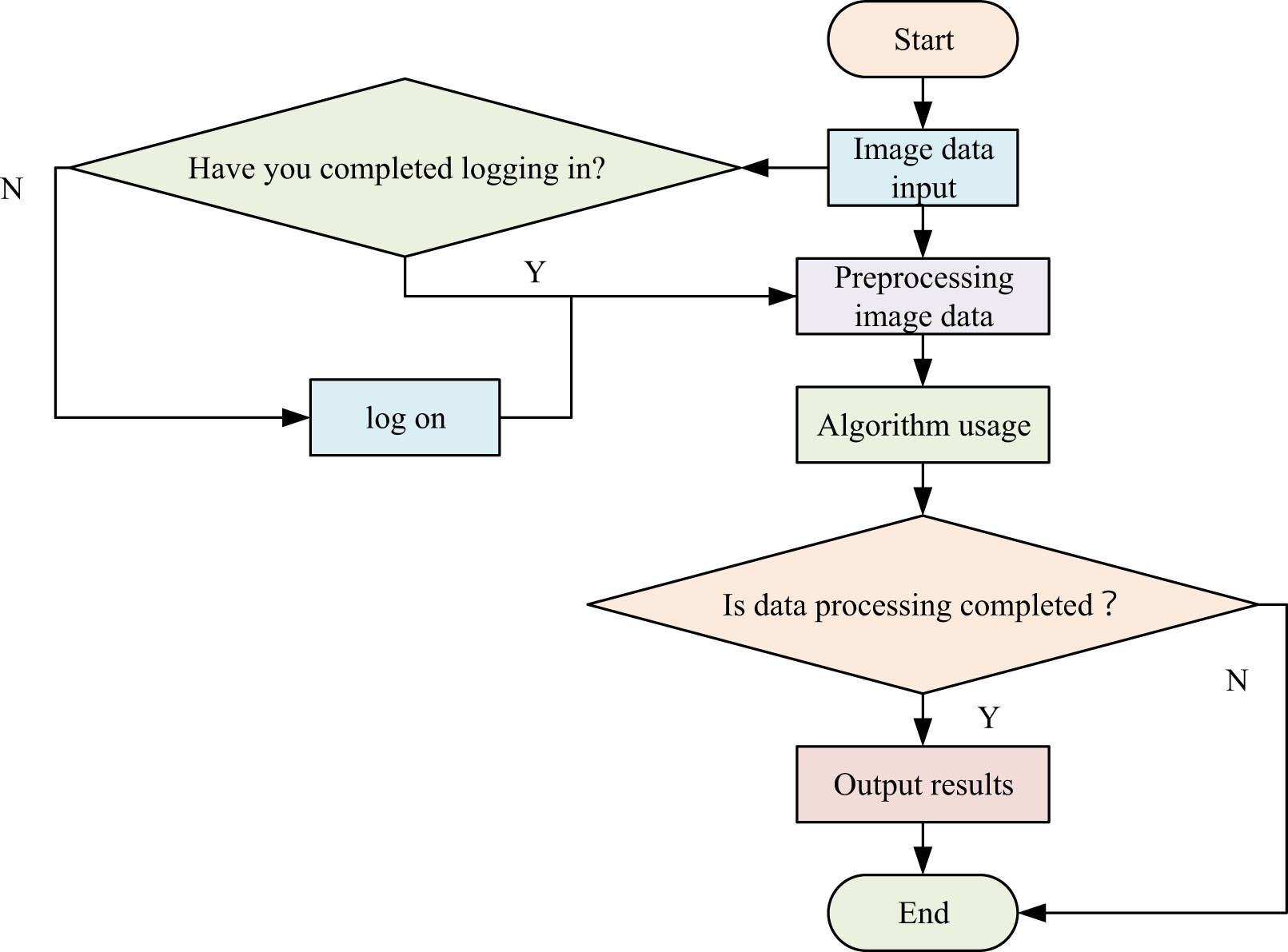
Process of building multi-style face models.
Figure 6 demonstrates that when users utilize the multi-style face module, they need to upload face image information. The system checks the current login status, and if logged in, it preprocesses the image data, stores the image data information, and analyzes the image information using algorithmic data. It checks whether the process is complete and generates the reading results if it is. If the process is not complete, the workflow is terminated. To avoid insufficient memory in the current algorithm module, the system automatically cleans up data over a period to ensure the smooth operation of the current system. In DSAMs, reinforcement learning is used to optimize the feature selection process to improve the model’s adaptability to images of different styles and complexity. The reinforcement learning framework includes intelligence, environments, actions, states, and rewards. The reward function can take into account the amount of information or the contribution of the selected feature map to the task. If a feature map contributes more to the generation or classification task, a higher reward is given. The reward function can contain a sparsity penalty term. If the number of feature maps selected is less, the reward is higher. The fluctuation of reward value is reduced by normalizing the reward value to a stable range such as [0, 1]. The soft update strategy is used to update the strategy of the intelligent body gradually to avoid drastic changes. Finally, a certain amount of randomness is introduced into the environment so that the model can adapt to different input conditions. The stability of training can be improved by the aforementioned ways.
4 The construction results of multi-style face models based on artistic painting generation algorithms
In the overall model construction, data metrics are used to analyze the current research method and generated face data. Fréchet Inception Distance (FID) measures the realism of generated textures compared to real images. Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS) measures the visual similarity between generated and real images. Feature Similarity Index Measure (FSIM) evaluates the similarity of face features in generated and real images. Similarity of Contours and Outline Texture (SCOOT) assesses the realism of facial contours and textures in the generated images. The initial learning rate is set to 0.0002 and is multiplied by 0.95 after each epoch to gradually reduce the learning rate. The batch size for model training is set to 16. The Adam optimizers, whose hyperparameters include β1 and β2, are kept at their default values of 0.9 and 0.999. A smaller value for FID and LPIPS indicates a better generated face model, while larger values for FSIM and SCOOT indicate a better generated face model. The analysis was conducted on two datasets, Dataset 1 and Dataset 2, both of which were collections of existing face image datasets. Multiple algorithms that currently exist in this field were compared with the algorithms used in current research, such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), GAN, Eigenface Algorithm (EA), Fisher Face Algorithm (FFA), Swin Transformers, and StyleGAN2, as shown in Table 1. FID is a measure of the performance of the generated model, the lower the FID, the higher the quality of the generated image and the greater the sense of realism. LPIPS is a measure of image similarity. The lower the LPIPS value, the less the difference between the generated image and the real image in visual perception. SCOOT is a measure of the quality of the generated image. The higher the SCOOT value, the closer the generated image is to the real image in terms of its features. FSIM is a measure of image feature similarity. The higher the FSIM value, the more similar the generated image is to the real image in terms of its features.
Comparison of image index parameters of five algorithm models
| Algorithm | FID | LPIPS | SCOOT | FSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 32.03 | 0.502 | 0.497 | 0.368 |
| GAN | 34.88 | 0.305 | 0.367 | 0.348 |
| EA | 20.67 | 0.483 | 0.422 | 0.498 |
| FFA | 49.87 | 0.302 | 0.500 | 0.532 |
| StyleGAN2 | 17.52 | 0.275 | 0.512 | 0.542 |
| Swin Transformers | 18.68 | 0.298 | 0.536 | 0.500 |
| Research algorithm | 15.07 | 0.259 | 0.579 | 0.554 |
In Table 1, bold values represent the optimal results and are highlighted. Table 1 revealed that, when comparing the five algorithm models, the values of FID and LPIPS for the algorithm used in the study were the smallest. The difference between these values and the lowest values among the four other algorithms was 5.6 and 0.043, respectively. Furthermore, when comparing with the metrics of other algorithm models, the values for FID and LPIPS for the research algorithm were smaller. When comparing FSIM and SCOOT metrics, the research algorithm had the highest values, differing by 0.022 and 0.079, respectively, from the other algorithms. This indicated that the face model metrics of the research algorithm were superior to those of other algorithm models, possibly due to the incorporation of receptive fields and other modules in the algorithm. A comparison of StyleGAN2, Swin Transformers, and the research algorithm revealed a minimal disparity in the metrics of the former two, with the research algorithm exhibiting marginal superiority in the evaluation of the four metrics for face model processing. This finding suggested that the research model demonstrated enhanced performance. To compare the parameter variations of the current algorithm in different datasets, the five algorithms were compared with the current algorithm model using the FID metric, as shown in Figure 7.
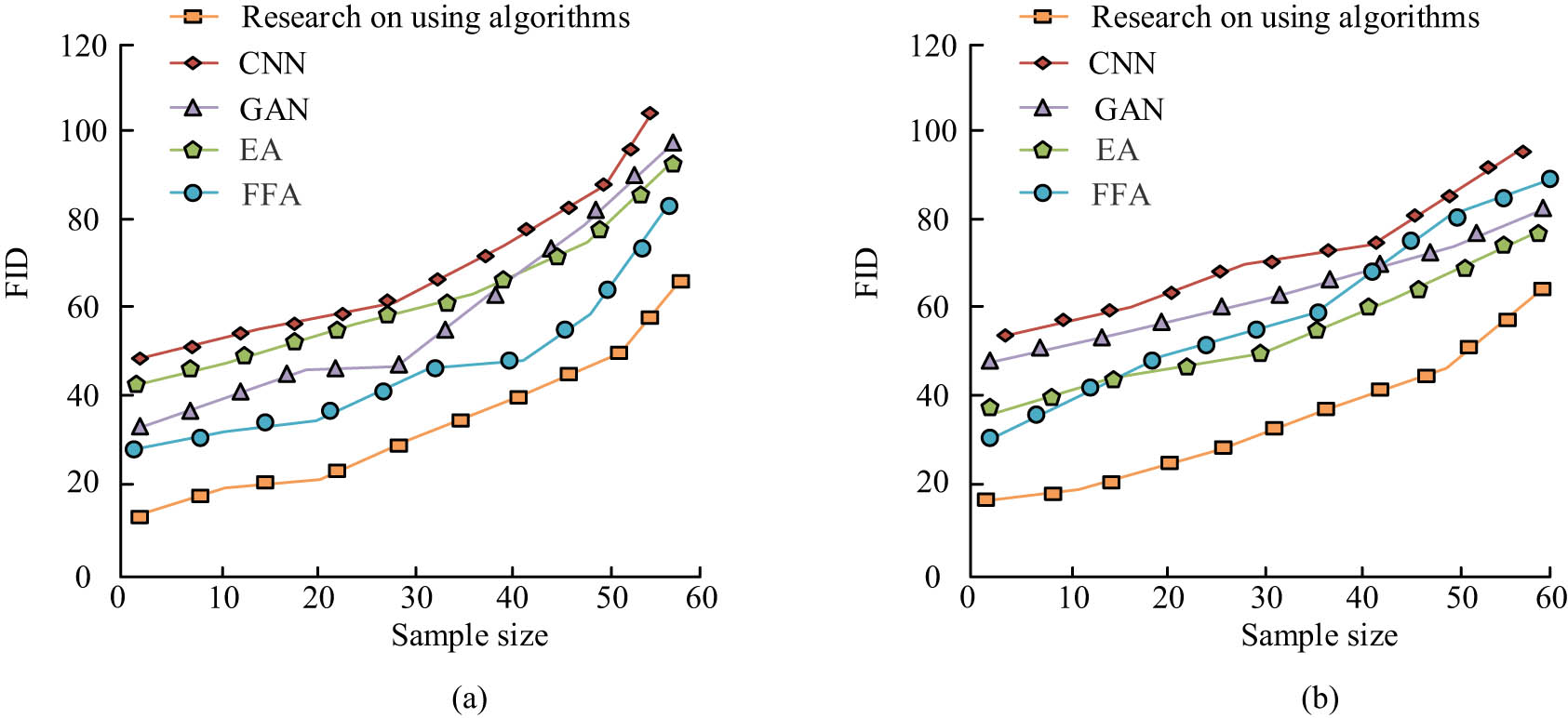
Comparison of FID metrics for different datasets and algorithms: (a) dataset 1 and (b) dataset 2.
In Figure 7, as shown in different datasets, the values of the FID metric for the research algorithm were smaller than the other four algorithms. The trends of several algorithms were similar, with an increase in FID values as the sample size increased. This could be attributed to the algorithm’s slower processing and generation of face data as the sample size increased, leading to fitting issues and an upward trend in the metric values. However, among these changes, the research algorithm showed smaller FID values, indicating that its performance is more stable when processing facial images. For a comparative analysis of the differences in face image data across different styles, the study contrasted the five algorithms in dataset 1 using FID and LPIPS metrics, as illustrated in Figure 8.
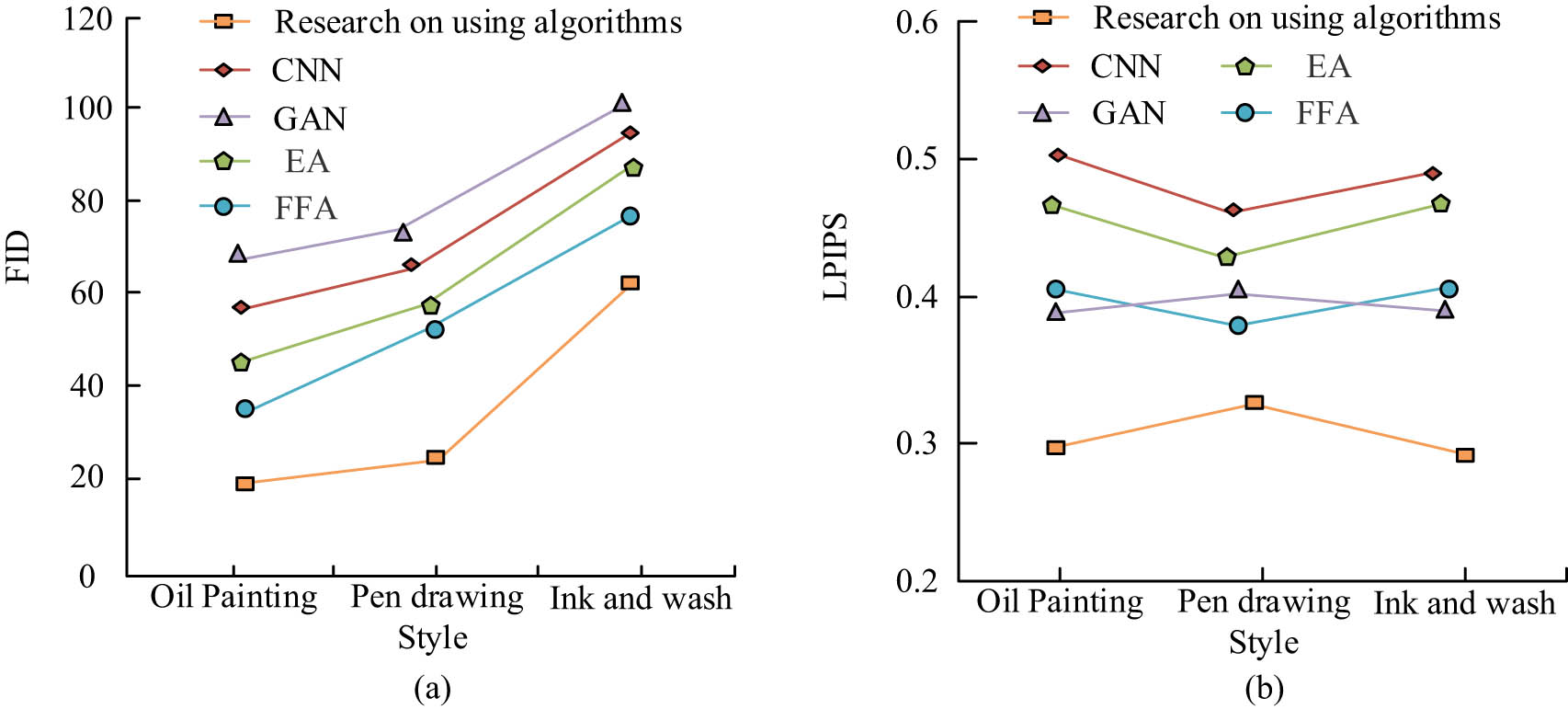
Comparison of FID and LPIPS metrics in dataset 1: (a) FID and (b) LPIPS.
In Figure 8(a), the FID values of the research algorithm varied for different styles. For example, in the ink painting style, the FID value reached a maximum of 58.25, while in the oil painting style, it reached a minimum of 20.31. Comparing the five algorithms, the research algorithm consistently exhibited a smaller FID value. In Figure 8(b), the LPIPS values of the research algorithm were consistently the smallest among the five algorithms, further indicating superior performance across different face image styles. To assess the performance variation after incorporating different modules into the current algorithm model, the study presented the results in Table 2. In Table 2, bold values represent the optimal results and are highlighted.
Parameter changes by adding different modules
| Added modules | FID | LPIPS | SCOOT | FSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAM | 20.040 | 0.302 | 0.498 | 0.542 |
| MAM | 19.480 | 0.352 | 0.445 | 0.516 |
| DSAM | 18.500 | 0.289 | 0.487 | 0.530 |
| CAM + MAM | 19.250 | 0.364 | 0.486 | 0.521 |
| MAM + DSAM | 18.620 | 0.299 | 0.458 | 0.498 |
| CAM + DSAM | 17.410 | 0.291 | 0.493 | 0.536 |
| DSAM + MAM | 18.300 | 0.298 | 0.479 | 0.539 |
| Research algorithm | 15.070 | 0.259 | 0.579 | 0.554 |
The table revealed that introducing various data modules led to changes in different performance metrics. However, the combined and mixed metrics varied, and no single module outperformed the current algorithm model. When CAM was used alone, the FID was 20.040, the LPIPS was 0.302, the SCOOT was 0.498, and the FSIM was 0.542. The CAM mainly focused on the local features, which enhanced the ability to process the face details but may be insufficient in integrating the global features. The MAM had a FID of 19.480, a LPIPS of 0.352, a SCOOT of 0.445, and a FSIM of 0.516. MAM effectively integrated different scales of features and improved the processing of local and global information, which significantly improved the image quality. Its performance was further improved when used in combination with DSAM, which highlighted its advantages in multi-scale feature integration. When using DSAM, the value of FID was 18.500, while the LPIPS was 0.289, SCOOT was 0.487, and FSIM was 0.530. DSAM could dynamically select features according to the image content and adjust the feature weights to enhance the adaptability and flexibility of the model. Combining these modules together can improve the performance in different degrees. Different module combinations yielded diverse metric data, emphasizing the adaptability of different modules in face data processing and model construction.
In Figure 9(a) and (b), the FID and LPIPS metrics were compared across different datasets, demonstrating similar trends in metric changes. However, in dataset 2, both metrics had relatively smaller values, possibly due to the simplicity of face data in that dataset. When introducing different data modules, the study observed variations in parameter metrics. The MAM achieved smaller values in both FID and LPIPS compared to the research algorithm, indicating the module’s capability to enhance image metrics before optimization. If there are currently face models A and B, and model A has higher FID and LPIPS values, it indicates that the generated facial images have significant differences in overall distribution compared to real face images. Although the LPIPS value was also high, it still indicates that the generated images are visually significantly different from the real images. This indicates that the face generated by Model A may not match the real face in terms of overall features such as skin color and proportion of features, and also appears unnatural in terms of visual effect. Model B has lower FID and LPIPS values, indicating that the generated face image is very close to the real face image in terms of overall distribution and visual perception. This means that Model B not only captures the diversity of real faces but also generates results that are more natural and closer to real images in terms of visual effects. To test the stability of the current algorithm, the research compared the algorithm model with four algorithms, as shown in Figure 10.
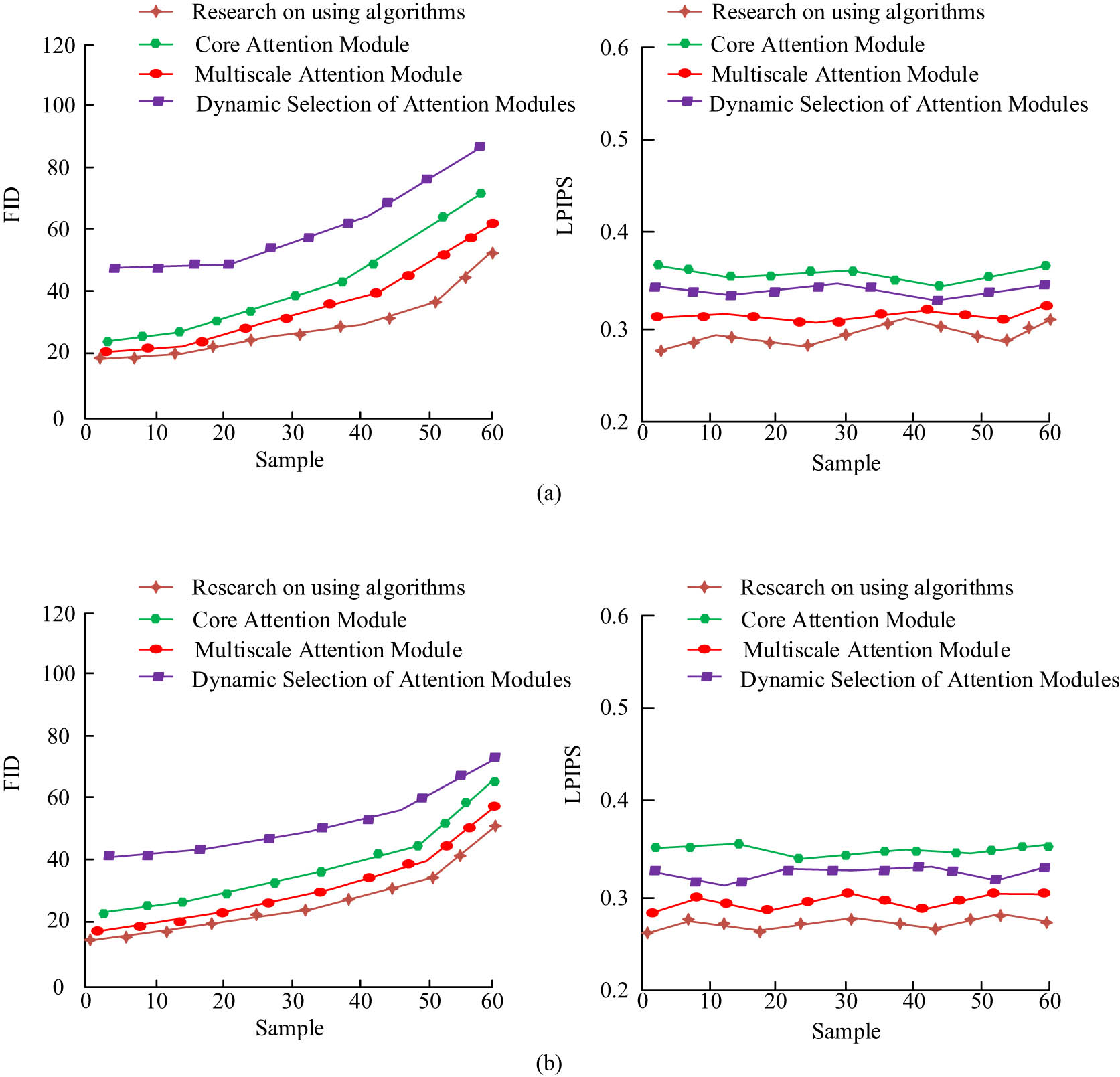
Comparison of algorithm indicators for adding different models to different: (a) dataset 1 and (b) dataset 2.
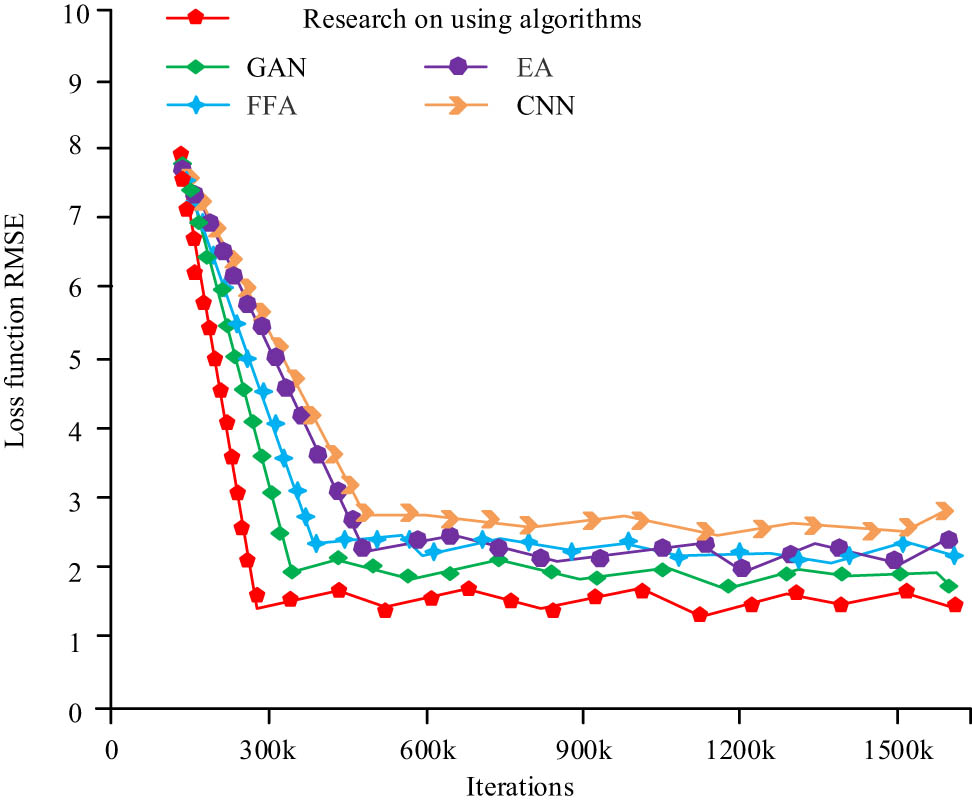
Comparison of loss functions for four algorithms.
To evaluate the stability of the current algorithm, the study compared the research algorithm with four other algorithms in Figure 10. It showed that, with an increase in iteration count, the loss function values of all algorithms decreased and stabilized after reaching a certain point. The study’s algorithm exhibited a relatively smaller loss function value, stabilizing around 1.5, which was lower than the GAN (0.5), EA (0.6), FFA (0.7), and CNN (1.0). This suggested that the stability of the research algorithm was superior to the other four algorithms.
5 Conclusion
This study primarily analyzed face image data of different styles and subsequently constructed a facial image model based on artistic generation algorithms. Initially, the face modeling algorithm was analyzed, establishing the basic model and framework for artistic generation algorithms. Subsequently, different styles of face data were analyzed, optimizing the algorithm model by introducing different data modules. This process resulted in the construction of face models for various styles. To address the research needs, a system framework for different styles of face models was designed. Finally, the algorithm’s performance and practical effects were tested on different datasets. The research findings indicate that the algorithm used in the study achieved lower FID and LPIPS values compared to four other algorithms, with a decrease of 5.6 and 0.043, respectively. Furthermore, the algorithm’s performance in FSIM and SCOOT metrics surpassed other algorithms by 0.022 and 0.079. In the case of a face model with an oil painting style, the FID index reached a minimum of 20.31, while the LPIPS index for an ink painting style was minimized to 0.286. The inclusion of different modules enhanced various image metrics, with the MAM outperforming others in terms of performance. Additionally, the algorithm’s stability was found to be higher when using the MAM. In summary, the research algorithm outperformed other algorithms in terms of constructing face models and algorithm performance. The MAM is identified as a crucial component for enhancing the current algorithm model. While the study has achieved significant results, there are some limitations, such as the use of a relatively small dataset. Future work will involve analyzing larger datasets, and further research on the MAM in this field will be conducted. Face image generation algorithms have a range of applications, including the creation of paintings and graphic design patterns in various styles. Additionally, these algorithms find use in entertainment and game development, facilitating the generation of diverse characters and animations in real time. However, it should be noted that these algorithms are constrained in terms of real-time capabilities and adaptability. Furthermore, their high computational complexity can pose challenges in meeting the demands of real-time applications. Therefore, future research needs to optimize the algorithm to reduce the computational burden and enhance the adaptability to different image types.
-
Funding information: This work is supposed by Xinjiang Institute of Engineering doctor scientific research start fund project, Research on the Innovative Path of Digital Media Art in the Context of AIGC (2024XGYBQJ03).
-
Author contributions: Zhaoyi Xu: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The author states no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Shakrani KV, Kanyangarara NM, Parowa PT, Gupta V, Kumar R. A deep learning model for face recognition in presence of mask. Acta Inform Malays. 2022;6(2):43–6.10.26480/aim.02.2022.43.46Search in Google Scholar
[2] Mikawa M, Lyu J, Fujisawa M. Previous announcement method using 3D CG face interface for mobile robot. J Robot Mech. 2020;32(1):97–112.10.20965/jrm.2020.p0097Search in Google Scholar
[3] Sukumaran A, Brindha T. Nature-inspired hybrid deep learning for race detection by face shape features. Int J Intell Comput Cybern. 2020;13(3):365–88.10.1108/IJICC-03-2020-0020Search in Google Scholar
[4] Shao Z, Zhu H, Tan X, Hao Y, Ma L. Deep multi-center learning for face alignment. Neurocomputing. 2020;396(2):477–86.10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.108Search in Google Scholar
[5] Kirchner E, Koken P. The art of painting rainbows—between color science and painter’s practice. Color Res Appl. 2022;47(6):1372–91.10.1002/col.22810Search in Google Scholar
[6] Fu F, Lv J, Tang C, Mao L. Multi-style Chinese art painting generation of flowers. IET Image Process. 2020;15(3):746–62.10.1049/ipr2.12059Search in Google Scholar
[7] Kaveh A, Akbari H, Hosseini SM. Plasma generation optimization: a new physically-based metaheuristic algorithm for solving constrained optimization problems. Eng Comput. 2020;38(4):1554–606.10.1108/EC-05-2020-0235Search in Google Scholar
[8] Koc M, Ergin S, Gulmezoglu MB, Gupta P. Use of gradient and normal vectors for face recognition. IET Image Process. 2020;14(10):2121–9.10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.1128Search in Google Scholar
[9] Heravi FMZ, Nait-Ali A. Adult-child 3D backward face aging model (3D B-FAM). J Vis Commun Image Represent. 2020;72:10–22.10.1016/j.jvcir.2020.102803Search in Google Scholar
[10] Liao R, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Dai D. Multi-view face pose recognition model construction based on a typical correlation analysis algorithm. Int J Biom. 2021;13(2–3):289–304.10.1504/IJBM.2021.114654Search in Google Scholar
[11] Ferrari C, Berretti S, Pala P, Del Bimbo A. Measuring 3D face deformations from RGB images of expression rehabilitation exercises. Virtual Real Intell Hardw. 2022;4(4):306–23.10.1016/j.vrih.2022.05.004Search in Google Scholar
[12] Zheng G, Xu Y. Efficient face detection and tracking in video sequences based on deep learning. Inf Sci. 2021;568(2):265–85.10.1016/j.ins.2021.03.027Search in Google Scholar
[13] Khayam KN, Mehmood Z, Chaudhry HN, Usman Ashraf M, Tariq U, Nawaf Altouri M, et al. Local-Tetra-Patterns for face recognition encoded on spatial pyramid matching. Comput Mater Contin. 2022;20(3):5039–58.10.32604/cmc.2022.019975Search in Google Scholar
[14] Li Q, Xu L, Yang X. 2D multi-person pose estimation combined with face detection. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell. 2022;36(2):10–33.10.1142/S021800142256002XSearch in Google Scholar
[15] Zhang J, Di L, Liang J. Face alignment based on fusion subspace and 3D fitting. IET Image Process. 2021;15(1):16–27.10.1049/ipr2.12002Search in Google Scholar
[16] Yoganand AV, Devi DR, Kavida AC. Pose and occlusion invariant face recognition system for video surveillance using extensive feature set. Int J Biomed Eng Technol. 2020;33(3):222–39.10.1504/IJBET.2020.10029988Search in Google Scholar
[17] Devi PRS, Baskaran R. SL2E-AFRE: Personalized 3D face reconstruction using autoencoder with simultaneous subspace learning and landmark estimation. Appl Intell. 2021;51(4):2253–68.10.1007/s10489-020-02000-ySearch in Google Scholar
[18] Pal S, Roy A, Shivakumara P, Pal U. Adapting a Swin Transformer for license plate number and text detection in drone images. Artif Intell Appl. 2023;1(3):145–54.10.47852/bonviewAIA3202549Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations

