Abstract
With the widespread application of smart grids, their economic scheduling and operational decisions need to meet the requirements of large-scale network data and improve the transmission performance of communication resources. Therefore, a distributed network architecture is proposed to analyze the scheduling and management of power systems. A distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm based on communication strategies is applied to analyze the power generation allocation and economic operation of grid nodes. The simulation testing and strategy analysis showed that the distributed optimization algorithm achieved a total output power of 850 MW for the power grid and stabilized the regional electricity load. In the verification of the economic dispatch problem, the total output power of the distributed optimization algorithm reached 13594.87 MW, and the economic cost was reduced by about 23%. The designed method is feasible for economic dispatch, and its contribution lies in using the distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm to provide scientific and reasonable communication strategy solutions for smart grid operation, thereby improving information transmission efficiency and reducing the loss of communication resources. However, the scale and scheduling management of the power grid have not yet been explored. It is necessary to strengthen communication and resource allocation in practical applications.
1 Introduction
At present, the smart grid system is mainly responsible for two parts: power transmission and communication networks. Power transmission meets the electricity needs of users, while communication networks maintain smooth information flow between infrastructures, thereby ensuring a win–win situation for both the electricity supply and demand sides [1]. To achieve optimal energy allocation for both users and generators, the economic dispatch problem (EDP) can solve this requirement while maximizing power generation efficiency [2]. Traditional power grids usually use centralized methods to calculate all data and control decisions in scheduling schemes, which consumes much time and cost for communication networks when facing information transmission. As the scale of the power grid expands, traditional centralized scheduling schemes have been unable to meet different supply demands and resource allocation in various regions, making it difficult to operate in large-scale complex communication transmission. For example, regarding the communication data transmission and prediction of vehicle flow, Chandramohan et al. established a traffic volume prediction model. According to the current situation of the city and traffic congestion, unpredictable traffic led to more vehicles driving on the roads. The transportation network and transportation needs of citizens enhanced the predictive ability of traffic flow, thereby improving traffic conditions and achieving green traffic flow communication transmission [3]. Therefore, the distributed optimization strategy can utilize the communication network to exchange adjacent information with each generator in the smart grid by splitting the communication topology structure, thus simplifying large and complex problems and improving the flexibility and convenient operability of smart grids [4,5]. Recently, scholars have completed extensive research on the economic dispatch and operation of smart grids. In response to power grid load attacks and economic dispatch, Chu et al. considered network elastic economic dispatch and attack detection to form a network resilience enhancement framework. The recursive linearization method was used to calculate the minimum error and improve the reliability of the bus system [6]. Ji et al. proposed a distributed economic dispatch algorithm based on event triggering and timing consistency for power grid economic dispatch. By calculating communication frequency and supply–demand balance, the algorithm effectively reduced the interaction information of generators and improved the robustness of the communication network topology [7]. Chen and Liu developed a distributed economic dispatch based on an autonomous consistency algorithm for privacy protection in smart grids and achieved optimal power dispatch under physical constraints. This algorithm demonstrated the feasibility of smooth transitions and privacy protection in grid patterns [8].
In terms of energy generation, the power and utilization of electric energy have been improved, and there are good economic dispatch schemes. Roy et al. considered an adaptive neural model inference system to design the state of charge in the economic dispatch of wind power generation. This model improved the accuracy of power prediction and evaluated the economy of power dispatch [9]. In response to the serious dependence of enterprises on electricity supply, Serat et al. used PV system software to focus on analyzing grid-connected solar rooftop photovoltaic systems. It was shown that this system had accurate energy prediction for the power grid and high economic returns [10]. In addition, the communication strategy of the smart grid could improve the supply and demand allocation of power generation resources and promote the intelligent development of the power grid. Regarding wireless optical communication networks, Rajammal used a grid-based communication protocol and elephant optimization to synthesize the communication network capacity strategy, thereby proving the algorithm's superiority [11]. Gu et al. proposed a thermoelectric collaborative network attack to analyze communication infrastructure and energy systems, which could significantly reduce economic losses through a time window matching strategy [12].
In summary, some studies have developed reliable algorithms and system operations for the economic dispatch of power grids, but there is a lack of specific parameter calculations for the operation strategies and economic costs of smart grids, which cannot meet the effective operation and management of power and communication information. Therefore, this study aims to improve the resource allocation of the power grid by adopting a distributed structure in the power node testing system. This research innovatively combines a virtual communication strategy and distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm, providing better strategic solutions for generator node output and grid economic operation. Therefore, the proposed communication network and distributed optimization algorithm aim to provide reliable economic dispatch solutions, exhibiting technical references for the stable operation of smart grids.
2 Methods and materials
Targeting the economic dispatch and operation problems of the smart grid, a distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm based on communication strategy is proposed by combining the power system bus model and communication network topology diagram. The designed method is to achieve stable operation of smart grid economy through algorithm inference and optimization.
2.1 Distributed structure and economic dispatch of the smart grid
The smart grid utilizes advanced control technology and communication technology to achieve extensive and high-speed bidirectional communication between devices and sensors in various links of the power system, achieving efficient scheduling and operation management of the power system. Various links in the power system are interconnected, and information can be received and transmitted through adjacent generators. However, the close connection between nodes can affect the overall operation. Therefore, this study adopts the 30-node testing system developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), as shown in Figure 1.
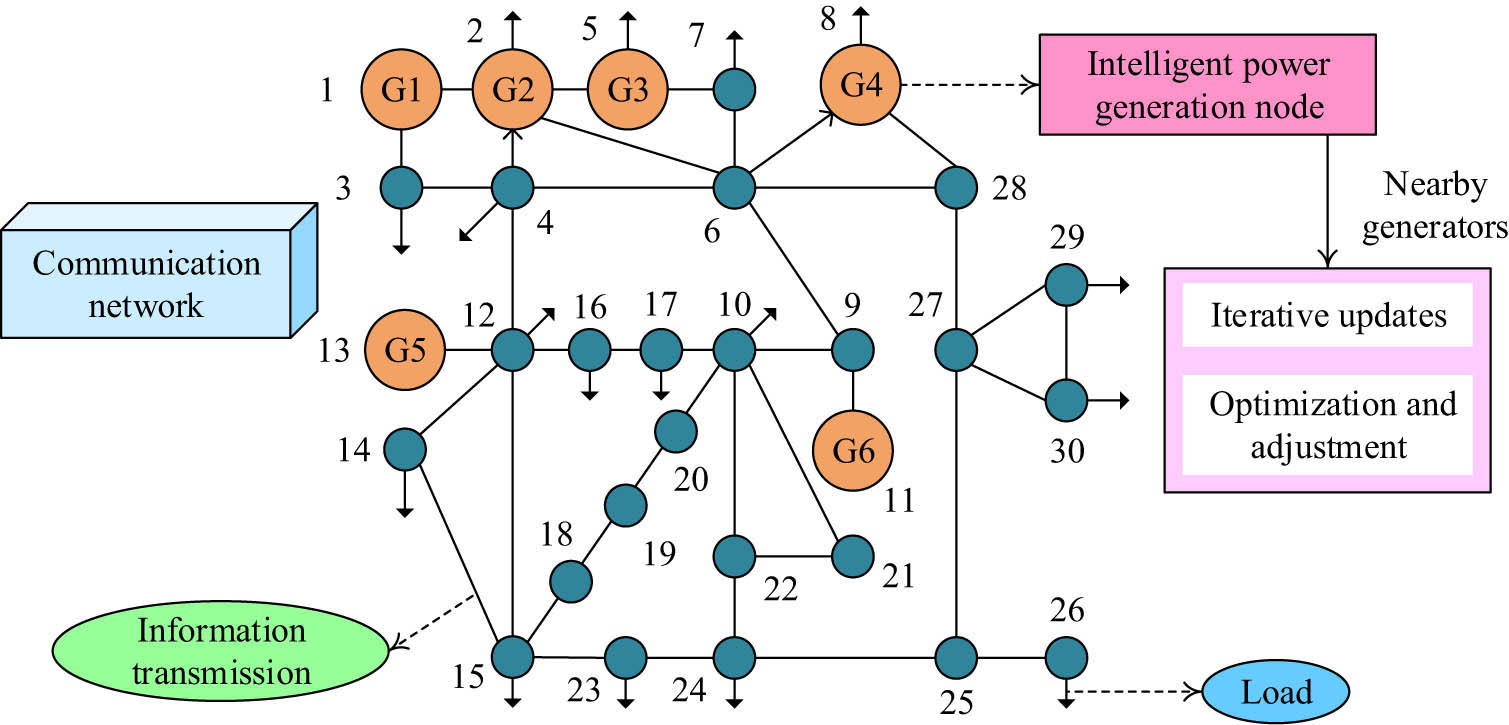
The structure of the IEEE 30-node testing system.
From Figure 1, the distributed strategy of the smart grid in power system generator nodes can achieve information exchange and transmission at any time through adjacent smart generators. The output power of the system is continuously optimized in information updates, thereby reducing power generation costs. Therefore, the distributed structure fully leverages the resource advantages of each region, allocates power supply demand and communication resources reasonably, and effectively improves resource utilization and system robustness.
When implementing economic dispatch, the power system not only needs to meet the overall load requirements but also fully understands the power generation allocation and constraints in each region to achieve the optimal power generation allocation problem at the minimum cost [13,14]. The objective function of EDP is shown in Eq. (1):
In Eq. (1),
In Eq. (2),
In Eq. (3),
In Eq. (4),
In Eq. (5),
In Eq. (6),
In Eq. (7),
2.2 Distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm based on communication strategy
Due to the distributed node structure of the smart grid, the transmission and control of its communication resources need to meet optimization objectives. Therefore, the communication strategy not only meets the power generation demand but also adopts continuous time sampling and communication resource control to improve utilization [15,16]. The function that occurs at a node within a continuous time period is shown in Eq. (8):
In Eq. (8),
In Eq. (9),
In Eq. (10),
In Eq. (11),
In Eq. (12),
In Eq. (13),
In Eq. (14),
In Eq. (15),
2.3 Operation strategy of smart grid economic dispatch
By reasoning the distributed optimization algorithm, a systematic structural analysis is conducted on the balance between the actual power generation applications and user demands to ensure that the accuracy and speed of solving EDP are not disturbed. The virtual communication strategy of the smart grid can effectively adjust the information transmission mode. The generator output power limitation condition in the algorithm is shown in Figure 2.
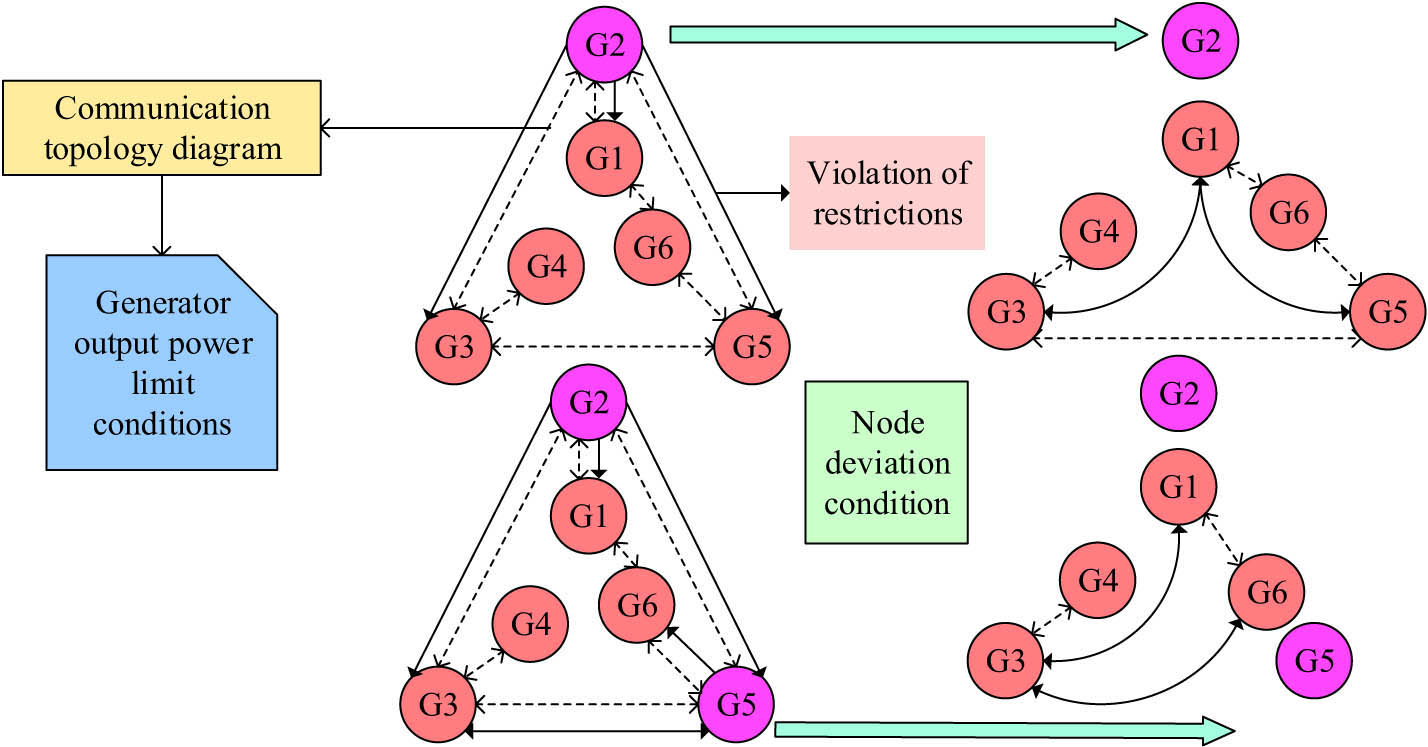
Communication topology diagram of generator deviation from restriction conditions.
From Figure 2, taking the communication topology diagram of the IEEE30 bus testing system as an example, there are constraints on the structure and output power among the six generators to ensure a balance between the supply and demand of distributed generator units in the smart grid. When generator 2 deviates from the output power limit condition, the bus connected to its nodes will be disconnected, which does not affect the connection of other nodes. New circuit connections are added to complete information transmission. Similarly, when generator 5 does not comply with the restriction constraints, the adjacent information transmission will change. The IEEE30 bus testing system is a standard power system testing model widely used to validate various analysis and optimization techniques for power systems. In practical applications, the bus controller module undergoes strict quality control and reliability testing to ensure the long-term stable operation of the system. The system also supports multiple communication protocols and interfaces, and can seamlessly integrate with existing communication systems. Overall, the communication resources of the IEEE30 bus testing system are not only available but also highly reliable. However, in larger power grid systems, when the operation strategy of economic dispatch is not suitable for the IEEE30 node system, the number of nodes and line parameters in the IEEE30 node system are adjusted to accommodate larger network scales. This is because the IEEE 30-node system is typically used for power system standard test cases. Therefore, when dealing with power systems with large network scales, nodes and lines need to be adjusted, taking into account the actual network topology results in order to achieve economic dispatch under larger network scales.
Due to the fact that the IEEE30 node system belongs to the testing standard model for small- and medium-sized power systems, its scale and complexity are suitable for verifying the scheduling, optimization, and fault analysis of power systems. Compared with larger-scale node systems, the power flow distribution of the IEEE30 node system is more susceptible to faults and has a higher load rate, making it suitable for testing the effectiveness of application algorithms. Therefore, this scale makes the node system a widely used benchmark model in the field of power systems. In DDTOA inference based on communication strategy, the algorithm flow and parameter adjustment are performed to address the economic dispatch in smart grids. The DDTOA iteratively obtains the output power of the generator to meet the detection conditions and constraints. The total load demand and optimal output power of the power system under the virtual communication strategy are obtained, as shown in Figure 3.
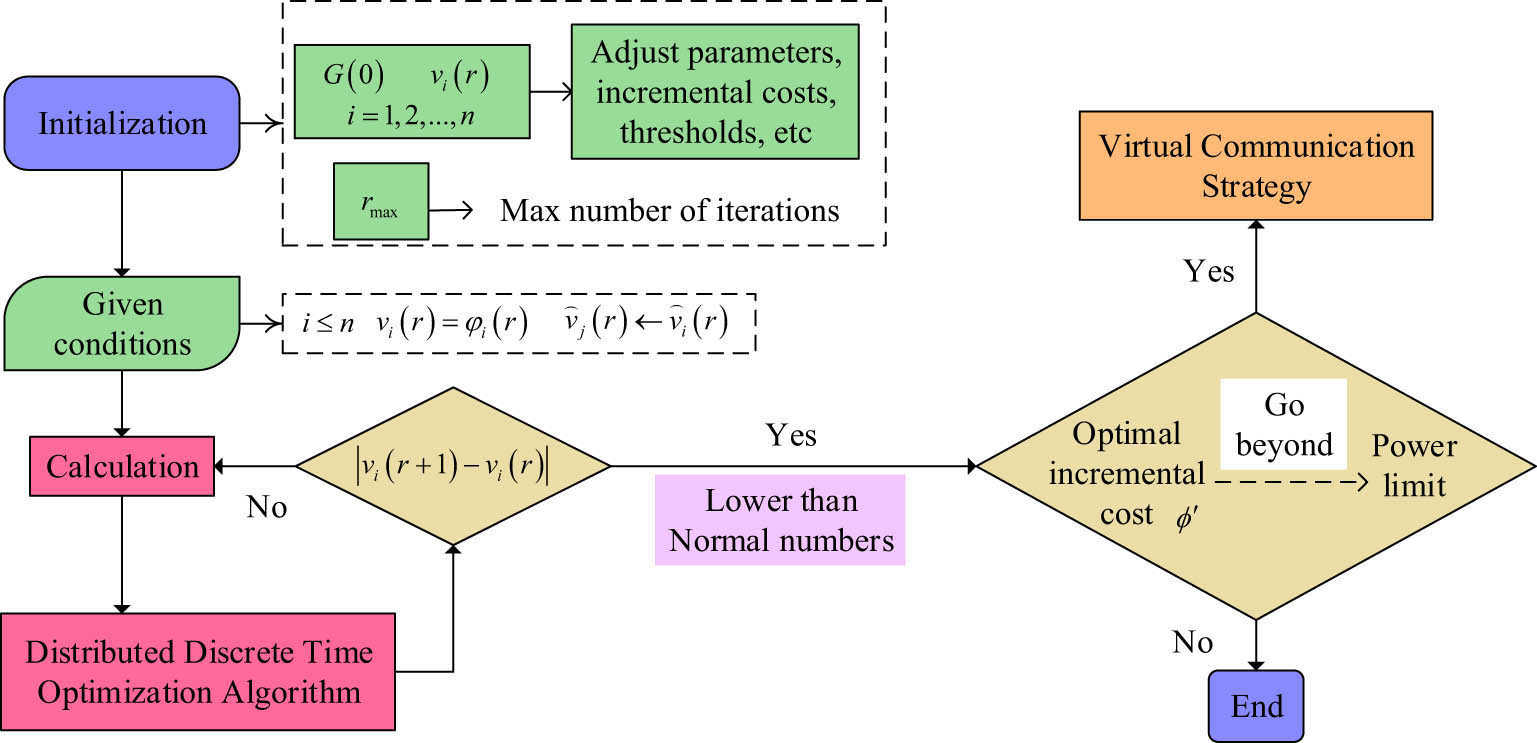
Flow chart of the distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm based on event-driven communication.
In Figure 3, the distributed generator units in the power grid are initialized with parameters, and the limitations of adjusting parameters and iteration times are explained. Then, the calculation is made based on the DDTOA formula. Based on the constraints of the power generation cost function, whether to calculate the output power is determined. The output power also needs to be lower than the optimal incremental cost value to calculate and adjust the entire power grid EDP in combination with the virtual communication strategy.
The connection circuits and node devices of distributed power grids and communication networks are important links in data information transmission. The introduced false data may alter sensor devices or communication line data to transmit incorrect information, thereby affecting the decision-making and operation status of smart grid economic dispatch, as shown in Figure 4.
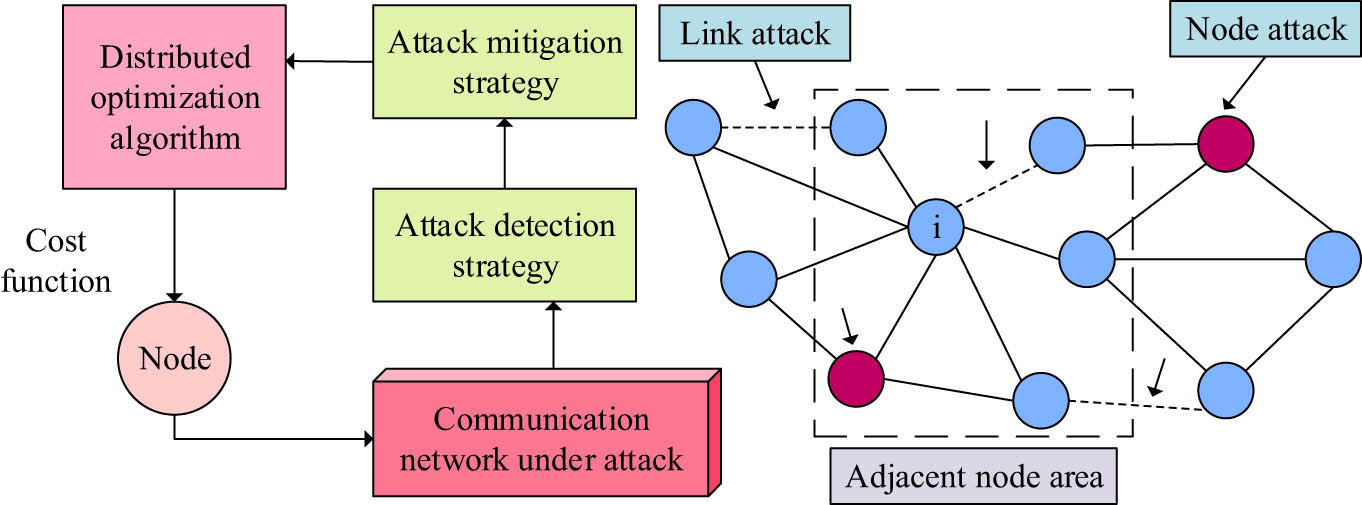
Distributed system of the smart grid and its attack strategy.
From the distributed system of the smart grid displayed in Figure 4, under local attacks, blue nodes represent normal generator nodes, while red and related arrows indicate the attacked nodes. Dashed boxes represent the neighboring nodes of specific nodes. Some communication links and nodes are subjected to discontinuous attacks, which affect the economic dispatch and operation of the power grid system. Subsequently, based on distributed optimization algorithms and attack strategies, internal optimization adjustments are made to the generator node to further optimize the algorithm and improve the reliability of power grid operation.
3 Results
By calculating communication strategies and distributed optimization algorithms, this study applies them to the communication topology of six generator nodes and conducts simulation numerical calculations to analyze the feasibility of economic dispatch and optimization strategies for the power grid.
3.1 Economic dispatch analysis of the power grid based on the distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm
In the simulation of a smart grid dispatching system, the MATLAB/Simulink platform is often used for modeling and simulation; therefore, this study adopts the MATLAB/Simulink platform for simulation experiments. Based on the topology diagram of the communication network and the total load demand of the power system, the constraints on the generator output power are analyzed to maintain the normal operation and economic dispatch of the smart grid. The constraint on the output power of the six generators and the economic dispatch optimization in the DDTOA based on event-driven communication can be set by simulating the numerical values of the smart grid system, as displayed in Table 1.
Generator generation cost function and the system initial value setting results
| Identification device | Total system load demand | Tune parameter | Event-driven parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 850 MW | 5 | 0.31 |
| Generator node | Cost coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a i | b i | c i | |
| 1 | 0.04 | 2 | 561 |
| 2 | 0.03 | 3 | 310 |
| 3 | 0.035 | 4 | 78 |
| 4 | 0.03 | 4 | 561 |
| 5 | 0.04 | 1 | 310 |
| 6 | 0.035 | 3 | 78 |
As shown in Table 1, the smart grid system is composed of six generator nodes. Under the total system load demand and power generation cost function, the output power of the generator met the electricity demand of the users. The parameter settings did not consider the conditional limitations of the output power, and the incremental cost calculation was performed on the distributed optimization algorithm to achieve economic scheduling problems. In the application of smart grid systems, communication strategies play an important role in distributed discrete-time optimization algorithms. Scientific and reasonable communication strategies can significantly reduce communication overhead and improve the system training speed. Moreover, the communication optimization strategy of the smart grid is applicable to larger-scale distributed training, emphasizing the convenience and scalability of concentricity between devices. Therefore, distributed optimization algorithms and their communication strategies can significantly improve the performance and robustness of the system.
By setting the above parameters, the total output power and cost control of the simulated smart grid generator are shown in Figure 5.

Generator output power and cost results without considering constraints. (a) Result of generator output power. (b) The result of the total cost letter value.
From Figure 5(a), the calculated generator power varied frequently between 0 and 20 under different cost functions and then stabilized at around 150 MW. To meet the electricity demand of the users, the total output power of the generator was 850 MW and an economic dispatch strategy for the 125–160 MW power grid was formulated. In Figure 5(b), the minimum cost of these six generator cost functions obtained from Eq. (2) was 8,493, and the optimal solution obtained from the incremental cost was 13. Therefore, the simulation data can meet the electricity demand in the region without considering any constraints on its output power.
Under the same conditions, the auxiliary variables of the distributed time optimization algorithm and the information exchange results between neighboring nodes are related to measurement errors, threshold changes, and other factors. The results are shown in Figure 6.
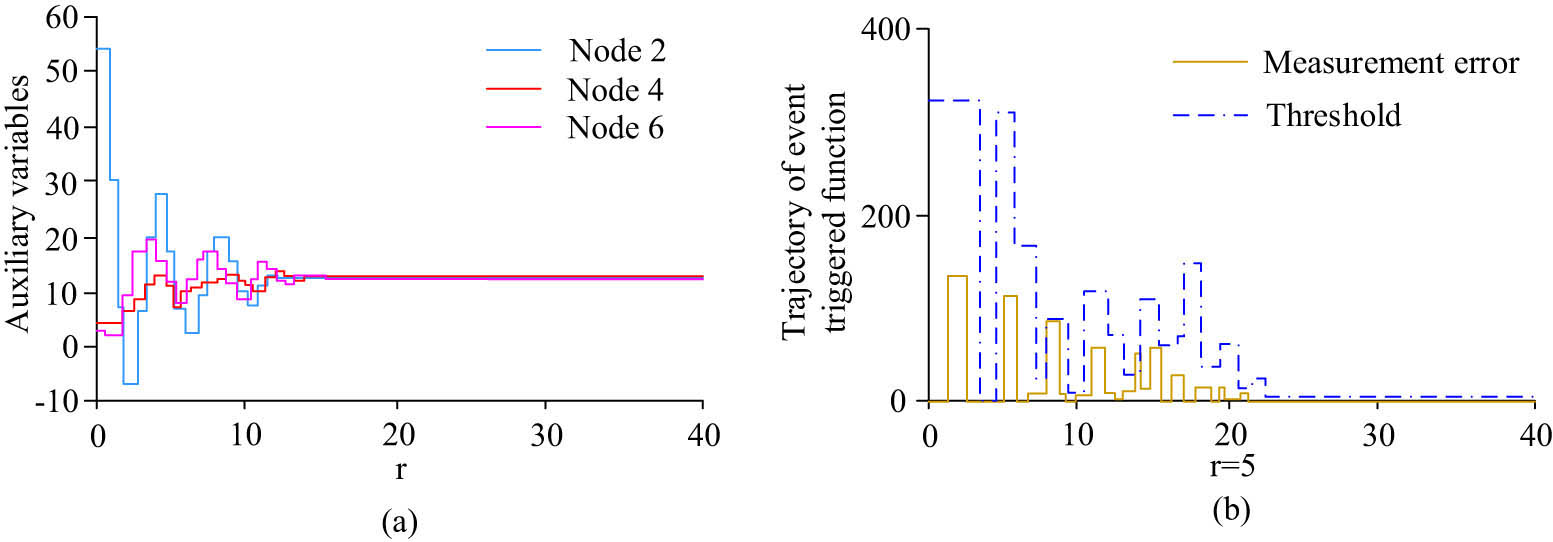
Unrestricted node auxiliary variables and trajectory results. (a) Simulation results of auxiliary variables. (b) Error and threshold results of sudden events at node 5.
According to Figure 6(a), the auxiliary variables of motors 2, 4, and 6 were calculated using Eq. (8). The initial result of node 2 was 53, and the lowest result was −8, with significant fluctuations and subsequent stability at 12. The fluctuation amplitude of node 5 was relatively small, and the auxiliary variable value was below 12. In Figure 6(b), when there was a sudden event in generator 5, the distance between the measurement error calculated by the function and the threshold was relatively small, at around 20. It can be concluded that without considering the limitation of generator output power, information transmission in the communication network only occurs in the contact link, which can easily lead to resource waste in communication networks.
However, distributed time optimization algorithms and communication strategies can effectively filter communication information, ensuring the total load demand of the power system while removing unnecessary information. The generator output power limit constraint is included in the detection conditions, and six generator output power limit ranges are added based on parameter settings. The results are shown in Figure 7.
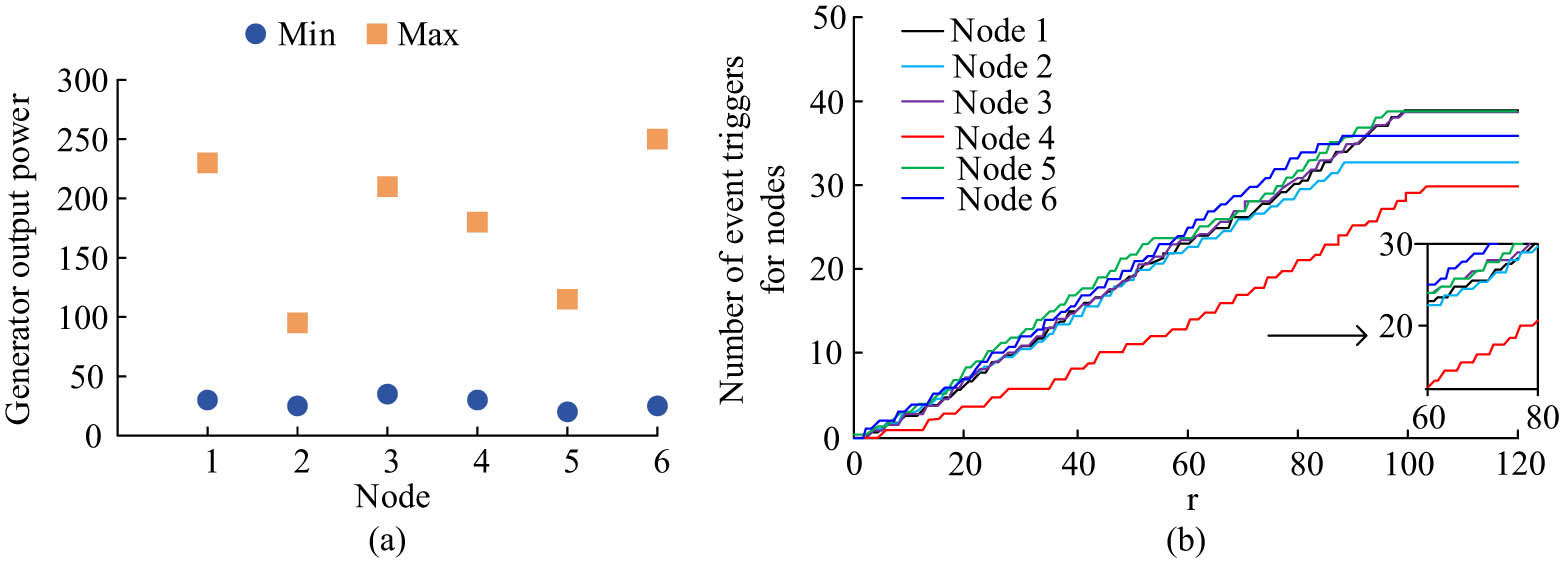
Generator output power limit and drive communication frequency. (a) Limitation result of generator output power. (b) The number of times the generator event drives communication results.
From Figure 7(a), the output power limit range of different generators was generally within 200, and the output power of generator 2 was limited to 25 and 95 MW, respectively. The difference in the output power limit was 95 MW, and the difference in the output power limit of generator 6 was the largest, at 225 MW. In Figure 7(b), the frequency of communication nodes in the power grid under event-driven conditions continued to increase. Generator 4 drove the lowest communication frequency among all nodes and then stabilized at 30 times. The drive frequency of nodes 1, 3, and 5 was relatively high. The frequency increased rapidly with the increase of communication information in the early stage.
Under these conditions, the output power of the generator deviates from the constraint. The optimal economic dispatch output power changes are shown in Figure 8.
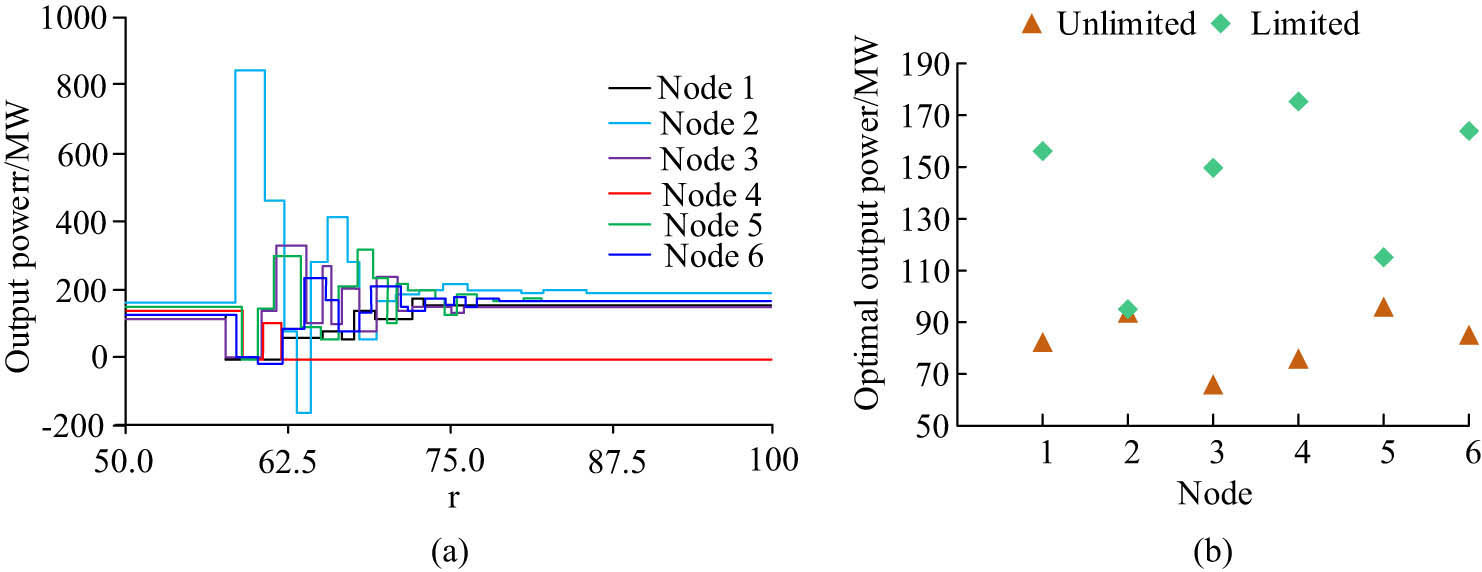
Comparison of output power results and constraints for different nodes. (a) Limitation result of generator output power. (b) Optimal output power results of the generator before and after restriction.
From Figure 8(a), when r was 56, the maximum output power of generator node 4 after deviating from the constraint was 196.15 MW. Among all generators, node 4 performed the lowest on output power, and other generators also met the total load demand by compensating for the power of sudden events at node 4. Figure 8(b) displays the optimal solution before and after the output power limitation constraint. The minimum difference of node 2 was 1.4 MW. The node with the largest difference was node 4, which deviated from the constraint at 99.37 MW. The comprehensive results indicate that the limitation of generator output power can reduce communication information transmission, improve efficiency, and have strong adaptability.
3.2 Analysis of optimization strategies for the economic operation of the smart grid
Based on communication strategies and event-driven distributed optimization algorithms, this study aims to verify and analyze the cost and consumption of economic operations to achieve policy optimization. In distributed power grids and communication networks, when nodes and links are subject to external interference or malicious attacks, the nodes or links of their mathematical models change to compensate for information transmission. When a generator node is attacked, supported by DDTOA, attack detection, and mitigation strategies can effectively reflect the trajectory. The results are shown in Figure 9.
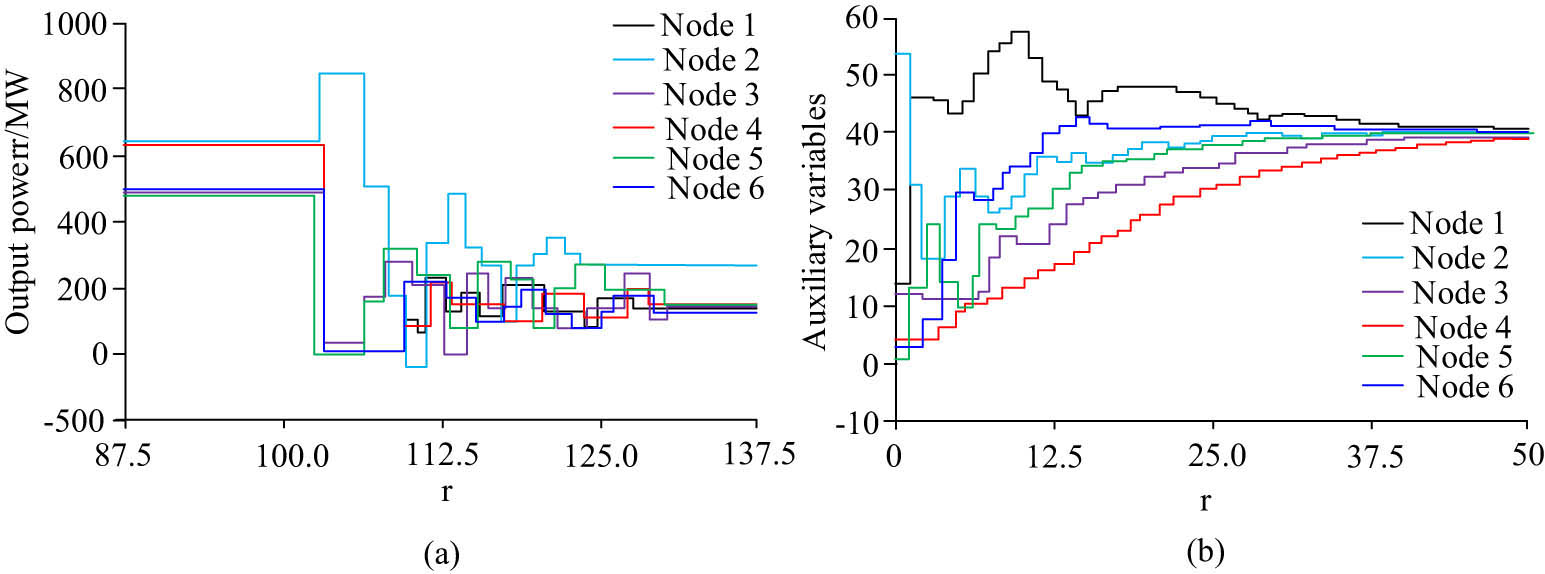
Output power and auxiliary variable results of the generator node under attacks. (a) Generator output power result. (b) Generator node auxiliary variable result.
From Figure 9(a), the output power of the generator node changed significantly when attacked. Earlier, r was 100, and the change in output power was consistent with the model. However, the cost function of the generator showed significant fluctuations, reaching up to 2,000 MW. Afterward, when r was between 100 and 137.5, the output power of each node decreased, and the minimum output basically reached below 0 MW. In Figure 9(b), when r was between 0 and 50, the auxiliary variables of each node continuously increased and stabilized at 40. When a node attack occurred, the subsequent auxiliary variables decreased to a maximum of 30.
In addition, when the links of the communication network are attacked, the results of the related generator output power, measurement error, and threshold are shown in Figure 10.
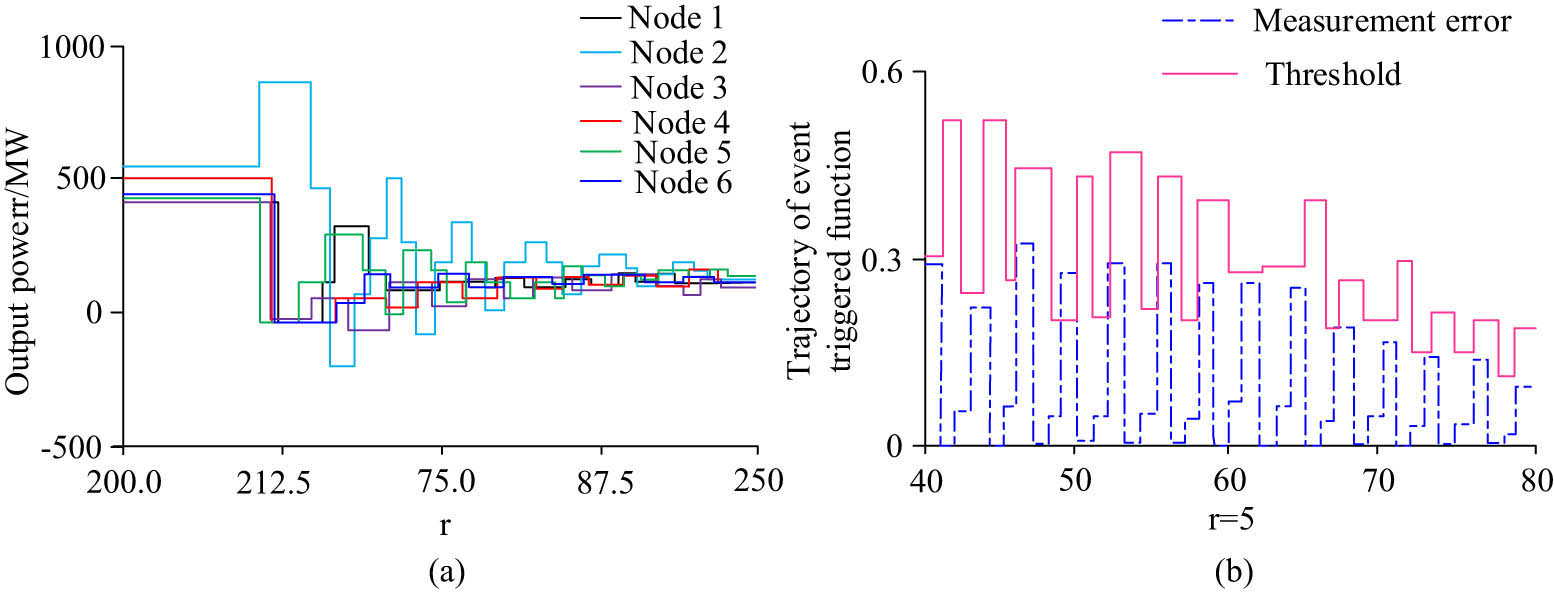
Simulation results of the power grid for communication link attack. (a) Output power result of the generator under attack. (b) Measurement errors and threshold results under attack.
From Figure 10(a), when the communication link was attacked, the output power of the generator started to fluctuate again after r reached 200, which was basically consistent with the initial value. The highest value was 850 MW, the lowest value was − 200 MW, and the stable value decreased by 500 MW compared with the former. In Figure 10(b), the measurement error and threshold trajectory analysis of node 4 indicated that the measurement error was mostly higher than 0.3, with the highest being 0.55 and the lowest being 0.1. The threshold trajectory was much lower than the trajectory with the measurement error, basically below 0.3, and the highest value was 0.31, indicating that the node trajectory under attack changes frequently, causing the event-driven communication to be adjusted to meet the total load demand.
When distributed power grids and communication networks are attacked, the economic operation of smart grids uses optimization strategies to handle measurement errors, dynamically adjust the output power and auxiliary variables of each node to cope with supply and demand fluctuations uncertainty, and balance costs and demand. Optimizing the strategy not only ensures the economic dispatch of the smart grid but also reduces the risks brought by electricity prices and market supply and demand. Therefore, the distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm proposed in the study not only considers the economic efficiency of the power grid but also reduces the impact of uncertainty on the power system.
Finally, optimization strategies and comprehensive analysis are carried out for the EDP of the smart grid. Different algorithms are used to detect indicators such as power generation costs, load demands, and information exchange frequency of the power grid economy to prove the efficacy of the power grid economic operation. The outcomes are shown in Table 2.
Comparison of results of different algorithms for economic dispatch of the power grid
| Method | Total output power/MW | Daily operating cost/10,000 RMB | Daily environmental cost/10,000 RMB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved pigeon swarm optimization algorithm [17] | 1667.25 | 16.731 | 18.386 |
| Improved the raccoon optimization algorithm [18] | 15379.04 | 15.984 | 17.219 |
| Particle swarm optimization algorithm [19] | 14767.15 | 14.591 | 15.264 |
| Parameter improvement particle swarm algorithm [20] | 14655.03 | 14.016 | 14.732 |
| The algorithm | 13594.87 | 13.597 | 13.069 |
From Table 2, different algorithms performed 200 iterations on the same power grid system to obtain different power generation costs and economic operation results. The improved pigeon swarm algorithm had an output power of 1667.25 MW in the power grid, and the environmental cost per unit was 1,838,600 RMB. However, the total output power of the particle swarm algorithm was 14767.15 MW, and the total economic cost was 298,550 RMB. In the economic operation process of a smart grid, the operating cost and environmental cost are related to the economic efficiency of the grid. A low value indicates a better economic dispatch plan. The proposed method had a daily operating cost of 135,900 RMB in the power grid system, which is 23.05% lower than the improved pigeon swarm optimization algorithm. The daily operating costs of the particle swarm optimization algorithm and parameter improvement particle swarm algorithm were relatively close, at 1,459,100 RMB and 1,401,600 RMB, respectively. In the calculation of environmental cost, the daily environmental cost of improving the raccoon optimization algorithm was 172,190 RMB, an increase of 31.75% compared with this research method. Overall, this research method effectively reduces economic operating costs in power grid scheduling and dynamically adjusts the output power of power equipment to balance power supply, demand, and load demand. The minimum output power provided by DDTOA for the power grid was 13594.87 MW, which met the total load demand of the regional power system. The economic operating cost reached 2,666,600 RMB, which was much lower than other economic dispatch schemes. Therefore, it demonstrates the superiority and environmental friendliness of the research method.
The current power system still operates, transmits, and distributes electricity in a centralized, long-distance, and interconnected manner with the main grid, providing high efficiency and convenience for centralized power supply. However, in centralized operation, regional power grid accidents can lead to the collapse of the entire power grid, and the complex and variable peaks of the power load curve may reduce the stability of the regional power grid. Meanwhile, the lack of control over transmission and distribution costs resulted in long-term idle equipment in some areas, causing serious resource waste in investment, construction, and power supply. Therefore, the distributed discrete-time optimization algorithm proposed in this study provides a more scientific and reasonable way for energy utilization and supply. While improving the utilization rate of electricity, favorable adjustments should be made to transmission lines, power generation equipment, and their losses. User loads and power equipment consumption should be reasonably allocated to reduce economic losses and environmental costs caused by equipment consumption.
4 Discussion
A communication strategy based-DDTOA is proposed for analyzing and adjusting the EDP to achieve economic dispatch and operational strategies. According to the optimization algorithm, the numerical calculation of the simulated smart grid showed that the cost function had a basic output power of around 150 MW for six generators and varied frequently. The minimum economic cost to meet regional electricity demand without considering generator output power limitations was 84.93 million RMB. The parameter settings were constrained by the generator output power limit, resulting in frequent changes in the power grid communication nodes and an increase in the information exchange frequency before stabilizing. To ensure the total load demand of the power system and achieve optimal economic dispatch, the maximum output power was 196.15 MW to reduce the communication information transmission and optimize the efficiency of power grid operation. Finally, when an attack occurred on the smart grid, the power output decreased and then stabilized at the total load demand. This is because when communication nodes or lines are attacked, the distributed power grid will adjust the virtual communication strategy of the attacked nodes and lines to compensate for the lost information transmission. The economic benefits of the brown bear optimization algorithm proposed by Ojha et al. for frequency control of renewable energy loads were far lower than those of the distributed time optimization algorithm proposed in this study [21]. Compared with the proposed brown bear optimization algorithm, the method proposed in this study had superiority in meeting the load demand of regional power systems and could promote the economic operation of the power grid.
5 Conclusion
In the development process of a smart grid, the transmission and utilization of communication resources have become important links in the grid operation. This study utilized the economic dispatch and communication network strategies of smart grids to conduct node testing on IEEE models. A distributed strategy was adopted to allocate communication resources reasonably, thereby improving the system's robustness. Afterward, the system development allocation function calculation and discrete-time node calculation were used to provide algorithm improvements for the operation cost and economic dispatch of the power grid to optimize the information transmission and economic operation. When the output power of the generator was between 30 and 180 MW, its driving communication frequency gradually increased and then remained at 30 to promote the communication resource interaction. In the operation strategy of the smart grid, there were significant fluctuations in the measurement error and threshold trajectory of nodes, with the highest measurement error value being 0.55 and the highest threshold point being 0.31. The distributed time optimization algorithm better controlled the economic cost of the power grid, with an economic operating cost of 135,970 RMB, which is far lower than other methods. The above results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed communication network and distributed optimization algorithm in the economic operation of the power grid. However, there is a lack of in-depth analysis of the operating speed of the power system and the quality of communication information. There is no correlation analysis between the efficiency of EDP and the communication resource transmission. Meanwhile, the proposed algorithm lacks validation with real data in actual operating power grids and only analyzes the strategic results of economic dispatch. Therefore, subsequent research not only needs to explore in-depth the actual scheduling problems of larger power grids but also needs to explore practical applications such as communication technology and resource allocation for operating smart grids.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to this manuscript.
-
Funding information: The author states no funding involved.
-
Author contribution: Zhifei Yi: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing-original draft, and writing-review & editing. The author has accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: The author states no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Jebri S, Amor AB, Zidi S. Reliable low-cost data transmission in smart grid system. Comput Commun. 2024;214(1):174–83.10.1016/j.comcom.2023.12.006Search in Google Scholar
[2] Ji L, Shen M, Yang S, Li H. Distributed event-triggering algorithm with uncoordinated step sizes for economic dispatch problem over unbalanced directed network. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst. 2023;145(2):108601–11.10.1016/j.ijepes.2022.108601Search in Google Scholar
[3] Chandramohan D, Dumka A, Dhilipkumar V, Loganathan J. Data dissemination for green-VANETs communication: an opportunistic optimization approach. Int J Pervasive Comput Commun. 2020;17(1):89–108.10.1108/IJPCC-04-2020-0030Search in Google Scholar
[4] Abishek R, Chandra DD. Design of gorilla troops optimizer-tuned 2DOF-PID controller to improve the frequency response of centralized-control technical virtual power plant. Optim Control Appl Methods. 2023;44(6):3257–81.10.1002/oca.3037Search in Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y, Zhao C, Wierman LA. An energy sharing mechanism considering network constraints and market power limitation. IEEE Trans Smart Grid. 2023;14(2):1027–41.10.1109/TSG.2022.3198721Search in Google Scholar
[6] Chu Z, Lakshminarayana S, Chaudhuri B, Teng F. Mitigating load-altering attacks against power grids using cyber-resilient economic dispatch. IEEE Trans Smart Grid. 2022;14(4):3164–75.10.1109/TSG.2022.3231563Search in Google Scholar
[7] Ji L, Xu Z, Yang S, Guo X, Li H. Distributed economic dispatch control in smart grid based on fixed-time dynamic event-triggered algorithm. Electr Power Syst Res. 2024;572(3):1–14.10.1016/j.neucom.2023.127178Search in Google Scholar
[8] Chen W, Liu GP. Privacy-preserving consensus-based distributed economic dispatch of smart grids via state decomposition. IEEE/CAA J Autom Sin. 2024;11(5):1250–61.10.1109/JAS.2023.124122Search in Google Scholar
[9] Roy P, Liao Y, He JB. Economic dispatch for grid-connected wind power with battery-supercapacitor hybrid energy storage system. IEEE Trans Ind Appl. 2023;59(1):1118–28.10.1109/TIA.2022.3203663Search in Google Scholar
[10] Serat Z, Fatemi SAZ, Shirzad S. Design and economic analysis of on-grid solar rooftop PV system using PVsyst software. Arch Adv Eng Sci. 2023;1(1):63–76.10.47852/bonviewAAES32021177Search in Google Scholar
[11] Rajammal SB. Augmentation of spectral efficiency in optical wireless communication networks using grid-based elephant swarm optimization protocol. Int J Commun Syst. 2023;36(16):e5590–616.10.1002/dac.5590Search in Google Scholar
[12] Gu W, Ding S, Lu S, Zhao P, Zou D, Qiu Y, et al. Coordinated heat and power cyber-attacks with time window matching strategy. IEEE Trans Smart Grid. 2023;14(4):2747–61.10.1109/TSG.2023.3273710Search in Google Scholar
[13] Saffar KG, Driss S, Ajaei FB. Impacts of current limiting on the transient stability of the virtual synchronous generator. IEEE Trans Power Electron. 2023;38(2):1509–21.10.1109/TPEL.2022.3208800Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Q, Wang S, Zhang JDY. Scalable and fault-tolerant selection method of verification and accounting nodes for permissionless blockchain. Comput Network. 2023;228(6):109757–70.10.1016/j.comnet.2023.109757Search in Google Scholar
[15] Lv D, Yu Q, Wang X, Wei Y, Liu L, Zhang P, et al. Operational status monitoring of smart grid and power communication network coupling and collaboration based on multi-head attention mechanism. Electr Power Syst Res. 2024;228(3):1–8.10.1016/j.epsr.2023.110013Search in Google Scholar
[16] Flr VBB, Filho MBDC, Souza JCSD, Vergara PP. Critical data visualization to enhance protection schemes for state estimation. IEEE Trans Smart Grid. 2023;14(2):1249–61.10.1109/TSG.2022.3203404Search in Google Scholar
[17] Wang K, Ge P, Duan N, Wang J, Lv J, Liu M, et al. The multi-objective optimal scheduling of the water–wind–light complementary system based on an improved pigeon flock algorithm. Energies. 2023;16(19):1–18.10.3390/en16196787Search in Google Scholar
[18] Bourebia NEH, Li C. A novel raccoon optimization algorithm with multi-objective clustering strategy based routing protocol for WSNs. Peer-to-Peer Network Appl. 2023;16(4):1624–40.10.1007/s12083-023-01479-9Search in Google Scholar
[19] Chen Q, Jun S, Palade V. A hybrid quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization solution to non-convex economic load dispatch with multiple fuel types and valve-point effects. Intell Data Anal. 2023;27(5):1503–22.10.3233/IDA-220415Search in Google Scholar
[20] Lu Q, Ma G, He M. Research on economic distribution strategy of unit combination load based on robust optimization. J Electr Eng Technol. 2023;18(6):4105–17.10.1007/s42835-023-01499-8Search in Google Scholar
[21] Ojha SK, Maddela CO. Load frequency control of a two-area power system with renewable energy sources using brown bear optimization technique. Electr Eng. 2024;106(3):3589–613.10.1007/s00202-023-02143-4Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Fractional-order super-twisting sliding mode active disturbance rejection control for electro-hydraulic position servo systems
- Analytical exploration and parametric insights into optical solitons in magneto-optic waveguides: Advances in nonlinear dynamics for applied sciences
- Bifurcation dynamics and optical soliton structures in the nonlinear Schrödinger–Bopp–Podolsky system
- User profiling in university libraries by combining multi-perspective clustering algorithm and reader behavior analysis
- Exploring bifurcation and chaos control in a discrete-time Lotka–Volterra model framework for COVID-19 modeling
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Research and application of interactive digital twin monitoring system for photovoltaic power station based on global perception
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Optimization design and research of mechatronics based on torque motor control algorithm
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
- Special Issue: Dynamic Engineering and Control Methods for the Nonlinear Systems - Part III
- Generalized numerical RKM method for solving sixth-order fractional partial differential equations

