Abstract
In recent years, nano-modified asphalt has gained significant attraction from researchers in the design of asphalt pavement fields. The recently discovered Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2) are among the most exciting and promising nanomaterials. This study examines the effect of 1, 3, 5, and 7% of nano-TiO2 by weight of asphalt on some of its rheological and hardened properties. The experimental study included physical and rheological properties. The asphalt penetration, softening point, ductility, and rotational viscometer tests indicate that 5% nano-TiO2 is the ideal amount to be added to bitumen as a modifier. The study of the rotating viscosity test showed that the addition of nano-TiO2 helped to increase viscosity and lessen bituminous sensitivity. Rutting factor in terms of G*/sin δ indicated the addition of 3 to 7% of nano-TiO2 increased the rutting resistance of asphalt against higher temperatures and promoted performance grade by about one grade at 3% and two grades at a range of 5–7% this suggests that nano-TiO2 increased the stiffness of the asphalt and leading to enhance the rutting performance of asphalt. While fatigue parameter, G*.sin δ shows that as nanocontent increases, higher stiffness at 5 and 7% of TiO2 content leads to an increase in complex modulus and a decrease in fatigue parameter. Higher creep stiffness and higher m-values were noted at low temperatures as nano increases in asphalt binder, increasing stiffness and decreasing the m-value at −6 and 12°C. As a result, using 5% nano-TiO2 will improve asphalt’s physical properties and enhance asphalt anit-rutting and fatigue resistance.
1 Introduction
Asphalt binder is considered one of the unique material components in paving construction and industry. Due to the population’s increasing capacity and the demand for cars, the repeated axial loading damage increases on the pavement surface, accompanied by other extrinsic features like hot climate weather and bad construction, which finally lead to the early failure of asphalt pavement. Modifying asphalt binders has been the key solution in recent years to avoid these problems. This is due to the applicability of additives such as polymers, fillers, waste material, and the new generation of nanomaterials. The benefits of nanomaterials include their high-temperature sensitivity, improved extendibility, and higher specific surface area. According to Yao et al. and Li et al. [1,2], adding nanomaterials to asphalt that has already been treated for polymers is more advantageous; as a result, nanomaterials improve the interaction of polymers with the asphalt matrix, decrease polymer segregation, and increase the stability of modified asphalt binder. Numerous studies conducted globally have used nanomaterials to successfully enhance the engineering properties of asphalt binders [3,4,5,6]. Hamedi [7] investigated a binder 60–70 with aggregates coated in nano-Al2O3 and nano-Fe2O3 for an asphalt mixture. Asphalt mixtures with and without nano-additives were tested using a modified Lottman method by the authors. The authors conclude that the nano-additive increased the asphalt mixture’s resistance to moisture. Titanium dioxide appears in nature as rutile, anatase, and brookite. Titanium dioxide at the nanoscale comprises 80% anatase and 20% rutile. It has been demonstrated that, compared to regular TiO2, nano-TiO2 has a very high surface area, a tiny diameter, and a very low opacity. Because of these unique features, some researchers used nano-TiO2 to enhance the performance of modified asphalt. The addition of TiO2 to the asphalt binder increases viscosity [8,9,10] and the G*/sin δ parameter at high temperatures [11]; TiO2 causes a slight reduction in the non-recoverable creep compliance and increases the matrix recovery rate [12]; the aging index is decreased [13]; the more nano-TiO2 is incorporated into the asphalt binder, the greater the mass loss [14]. Other researchers, like Shafabakhsh et al. [15], assessed how nano-TiO2 affected the rutting and fatigue characteristics of the HMA mixture. According to the results, nano-TiO2 improved the rutting and fatigue behavior of the combination. Later, the author examined the impact of nano-TiO2/SiO2 on the effectiveness of a mixture, showing that nano-TiO2/SiO2 improves the binder’s rheological behavior and the mixes’ rutting behavior [16]. The rutting behavior of hot-mix asphalt modified with nano-TiO2 was assessed in a study by Tanzadeh et al. [17]. The wheel-tracking test was used to look into how well the specimens rutted. According to the results, nano-TiO2 improved the rutting performance of the unmodified asphalt mixture. A different combination of nano-TiO2/CaCO3 was used by Zhang et al. [18]; the author conducted a study to assess the asphalt rheological performance with different dosages with the 5% optimal dosage TiO2/CaCO3 content, asphalt viscosity improved and enhanced anti-rutting capacity by increasing its rutting parameter (G*/sin δ). According to Rocha Segundo et al. [19], a transparent binder modified with 0.5, 3.0, 6.0, and 10.0% nano-TiO2 is compared to the transparent base binder, conventional binders, and polymer-modified binders in terms of its physicochemical and rheological characteristics. The addition of nano-TiO2 gradually raised the softening point and reduced penetration by up to 6.0% of modification. Furthermore, TiO2 would shorten the fatigue life of transparent-binder asphalt pavements. Instead, it would make high contents more resistant to rutting. According to the results, the author recommended that 0.5% of TiO2 was the best addition rate without degrading the transparent binder’s fatigue resistance, and 10.0% was the best for permanent deformation. The rheological parameters G*/sin δ improve when the amount of nano-TiO2 and nano-ZnO in the asphalt matrix increases; according to a recent study, the non-recoverable creep compliance caused by stiffness growth at high temperatures increases the resistance to permanent deformations. Filling the porosity of the conventional asphalt binder increases impermeability and decreases the effects of oxidation and volatilization, which lowers the Aging Index values [20]. Both nanoparticles perform better regarding fatigue damage at low deformation amplitudes and worse at large deformation amplitudes. When compared, the binder modified with nano-ZnO exhibits better mechanical and rheological response at high temperatures. In contrast, the binder modified with nano-TiO2 exhibits a higher number of cycles during the assessment of the fatigue damage tolerance. Low-temperature cracking, which results from the asphalt layer shrinking and the creation of tensile strains greater than the asphalt mixture’s fracture strength, is another significant problem with flexible pavements. The likelihood of low-temperature cracks increases due to bitumen’s increased creep stiffness and lower viscous behavior. the fatigue parameter (G*.sin δ) showed that TiO2/CaCO3 would improve fatigue resistance at intermediate-temperature. Other studies [21,22] indicated that nano-TiO2 decreases asphalt binder susceptibility against temperature and reduces its sensitivity towards aging since it affects the physical testing and rheological properties of asphalt, causing an increase in asphalt rutting resistance at higher temperatures and enhancement of the elasticity of asphalt, at intermediate temperature performance of bitumen improves so the fatigue lives increase. Also, Cadorin et al. [23] present how the presence of nano-TiO2 affected the matrix’s susceptibility in their study. The author concludes that nano-TiO2 enhances the matrix’s mechanical and rheological properties, increasing its resistance to persistent at specific stress/strain levels, deformation, stiffness, fatigue damage tolerance, and oxidative aging resistance. Different concentrations of nano-TiO2 were added by Filho et al. to a neat asphalt binder with a penetration grade of 50/70. They discovered that nano-TiO2 might increase fatigue resistance by conventional testing, linear amplitude sweep, and multiple stress creep recovery [24]. Later, they concluded that including nano-TiO2 developed a higher performance in high temperatures than the pure binders by promoting a non-recoverable compliant decrease, leading to an increase in the resistance to permanent deformation besides a growing delay in aging, as evidenced by a lower aging index and reduction in mass loss [25]. According to research, nano-TiO2 in the anatase phase is more effective than the rutile and brookite phase at purifying the environment [26]. The oxidation of a titanium precursor at a high temperature produces nano-TiO2. Most of the literature on using nano-TiO2 for asphalt modification focuses on protecting asphalt pavement from photocatalytic oxidation and removing vehicle pollutants like NOx [14,27,28]. According to published studies, nano-TiO2 has a great potential to reduce atmospheric nitrogen monoxide by maintaining it close to the source of the pollution. Similarly, a few research studies, including nano-TiO2, have been reported to increase the rheological performance of asphaltic mixtures. Some concerns about human health should be addressed when dealing with any nanoparticles. Regarding nanoparticle safety and related potential health dangers, there are some reservations. Since they are tiny, they can easily pass through biological barriers like cell membranes and human skin and build up in unfavorable places to dangerous levels [29]. According to Grassian et al. [30], breathing in nano-TiO2 at a concentration of 8.8 mg/m3 resulted in lung irritation. Although some studies have already been done, there is still much ambiguity about how manufactured nanomaterials may affect the environment and people’s health. More articles have recently been published on this subject due to the widespread use of nanotechnology in various sectors, particularly in packaging and food additives [30,31,32,33,34]. There are several stages where exposure can be significant, including creating nanomaterials and modifying the asphalt binder. Inhalation, ocular contact, and dermal adsorption are the most likely exposure modes [34]. The handling and manipulation of such materials should be treated as possible hazards unless the nanomaterials suppliers provide other information, in which case safety handling procedures should be followed. Crucho [35] stated that modified asphalt binder in a laboratory with a fume hood cabinet and personal protections: gloves made of nitrile that are at least 0.5 mm thick, a mask to protect one’s eyes, a breathing mask with a particle-filter FFP3, and a protective suit (Tychen C – category III). The related studies show that incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles into asphalt binders improves asphalt binders’ toughness, rutting resistance, stiffness, and resilience to aging while lowering the penetration grade and raising the softening point of binders. Besides, its effect promotes NOx and SO2 pollutants from the atmosphere through photocatalytic activity. In this context, there is a definite need for new studies to supplement previously published ones targeted the impact of the addition of nano-TiO2 and how it affects the high-temperature properties of asphalt; changing asphalt binder high-temperature rheology may change the rheology at low and intermediate temperatures. Since more complexity is involved with the fatigue phenomena, less attention has been dedicated to analyzing their impact on the fatigue performance of asphalt. In this article, the effect of adding different content of nano-TiO2 (1, 3, 5, and 7% by weight of mass) was examined via penetration, softening point, ductility, viscosity, and penetration index were evaluated, and dynamic shear rheometer (DSR) and bending beam rheometer (BBR) assessed the asphalt susceptibility with high, intermediate, and low temperatures.
2 Materials and methods
The material in this research is locally available in Iraq and used in paving work, while nano-TiO2 was imported from SkySpring Nanomaterial, Inc.
2.1 Asphalt
Neat asphalt binder graded 40–50 penetration was obtained from the Al Doura refinery southwest of Baghdad province. The main properties of asphalt are presented in Tables 1 and 2.
Physical properties of Al-Doura asphalt
| Property | Designation | Units | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration at 25°C, 100 g, 5 s | AASHTO T 49 | 0.1 mm | 47 |
| Softening point | AASHTO T 53 | °C | 49 |
| Specific gravity at 25°C | ASTM-D70 | — | 1.03 |
| Flash point | AASHTO T 48 | °C | 288 |
| Ductility | AASHTO T 51 | cm | 112 |
| Residue from thin-film oven test AASHTO T 179 | |||
| Retained penetration, % of original | AASHTO T 49 | 0.1 mm | 61 |
| Ductility at 25°C, 5 cm/min | AASHTO T 51 | cm | 87 |
Rheological properties of Al-Doura asphalt
| Property | Designation | Result | Temperature | AASHTO M320 limits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original test on binder | ||||
| Rotational viscosity, Pa s | AASHTO T316 | 0.63 | 135°C | Max. 3 |
| 0.16 | 165°C | — | ||
| DSR, 10 rad/s, G*/sin δ, kPa | AASHTO T315 | 2.34 | 64°C | Min. 1 |
| 0.842 | 70°C | |||
| Rolling thin film oven (RTFO) Binder Residue | ||||
| DSR, 10 rad/s, G*/sin δ, kPa | AASHTO T315 | 3.67 | 64°C | Min 2.2 |
| 1.68 | 70°C | |||
| Mass loss, % | AASHTO T240 | 0.61 | Min. 1 | |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Binder Residue | ||||
| DSR, 10 rad/s, G*.sin δ, kPa | AASHTO T315 | 6980 | 25°C | Max. 5000 |
| 4662 | 28°C | |||
| Creep stiffness, MPa | AASHTO T313 | 177 | −16°C | Min. 300 |
| Slope m-value | 0.393 | −16°C | Max 0.3 | |
2.2 Nano-TiO2
Nano-TiO2 (titanium oxide), shown in Figure 1, is a naturally occurring titanium oxide. Rutile, anatase, and brookite are the most common forms found in nature. Titanium oxide at the nanoscale comprises 80% anatase and 20% rutile. Sky Springs Nanomaterials Inc. sold rutile TiO2 (99.5%, 10–30 nm), employed as a nano-additive in this investigation; SEM image shows the particle shapes in Figure 2, while Table 3 presents physical nanocharacteristics.

Photo of nano-TiO2.

SEM image of nano-TiO2.
Physical properties of nano-Tio2
| Properties | Nano-TiO2 |
| Appearance | White powder |
| Average particle size (nm) | 10–30 |
| Specific surface area: m2/g | 50–100 |
| Bulk density (g/cm3) | 0.08 |
| Purity | 99.5% |
| Solubility | Insoluble |
2.3 Preparation of nano-modified asphalt
In this study, nano-Tio2 was added at 1, 3, 5, and 7% by weight of neat asphalt binder. A high-speed mixer with a jiffy head, as shown in Figure 3, was used to perform the homogenous modified asphalt blend and ensure good nanoparticle dispersion; the basic procedure included heating the asphalt to 160°C for sufficient time and manually stirring. Then, nano-TiO2 was introduced slowly at a rate of 2 gm per minute. Finally, a shearing rate of 6,000 revolutions was performed for 40 min. Figure 4 summarizes the procedure used for asphalt binder modification.

Mixing of nanomaterial with asphalt.

The procedure of asphalt modification.
3 Asphalt test
3.1 Physical and rheological tests
Routine physical testing was established to assess the impact of various nano-modified asphalt concentrations, including a penetration test to measure the consistency of asphalt based on ASTM D5. At the same time, the softening point is conducted based on ASTM D36. Furthermore, ASTM-D113 provides an accurate measure of tensile property for asphalt by a ductility test. The penetration and the softening point result were later used to compute the penetration Index (PI) presented in equation (1) to quantify asphalt temperature sensitivity [36].
3.2 DSR
The DSR test describes the viscous and elastically behavior of asphalt at medium to high temperatures. DSR measures the phase angle (δ) and the shear modulus (G*). Unaged, RTFO aged, and PAV aged bitumen is all done per AASHTO T 315.
3.3 BBR
The BBR test measures bitumen’s stiffness and relaxation characteristics at low temperatures. These variables indicate an asphalt resistance to low-temperature cracking. On PAV-aged bitumen, a BBR test is conducted per AASHTO T 313.
3.4 Rotational viscometer (RV)
The RV test can assess asphalt workability during the mixing and compacting processes. According to the AASHTO TP48 standard, the asphalt RV readings are calculated. The RV Brookfield (DV-III) measures bitumen viscosity at 135°C, and a 165°C test is run. Figure 5 presents the testing setup for identifying neat and nano-modified asphalt’s physical and rheological properties.

The testing device used in this study: (a) penetration test, (b) softening point, (c) ductility, (d) RTFO, (e) rotianle viscometer, (f) DSR, (g) BBR, and (h) PAV.
4 The test result of asphalt
4.1 Physical tests
Figures 6–9 show how different TiO2 concentrations affect the properties of asphalt in terms of penetration, softening point, ductility, and PI values. Nano-modified asphalts show a noticeable decrease in penetration, with the highest difference at 5% TiO2, up to 22% from the neat asphalt. Conversely, the softening point values increased positively at 6,13,16, and 14% for 1, 3, 5, and 7% for adding nano-TiO2, respectively. According to the results, 5% nano-TiO2 causes a decrease in the penetration grade and increases the softening point of binders. This behavior will promote asphalt stiffness and improve the resistance towards higher temperatures. PI value, shown in Figure 9, guaranteed the blend’s stiffness. Increasing the PI value indicated increasing hardness, which improved the TiO2 blend’s temperature susceptibility and vice versa. It has been noted that among asphalt blends, asphalt with 5% TiO2 has the highest hardness and is most closely related to neat asphalt. Furthermore, ductility value increased with increasing Nanocontent in a wide range between 112 and 123 cm for neat and 7% nano-TiO2. Based on penetration, softening point, and ductility tests, it was determined that asphalt’s hardness had increased, improving its susceptibility to temperature changes.

Asphalt penetration modified asphalt with TiO2.

Asphalt softening point modified asphalt with TiO2.

Asphalt ductility modified asphalt with TiO2.

Asphalt PI-modified asphalt with TiO2.
4.2 Rheological test results
4.2.1 Viscosity
Figure 10 indicates that with the increase of nano-TiO2 from 1 to 7%, the viscosity of neat asphalt binder would enhance at both 135 and 165°C temperatures. Viscometer testing result exhibited in Figure 9 shows an increasing rate in the value of viscosity by nearly 29, 42, 56, and 53% at 135°C at increasing content of nano-TiO2 from 1 to 7%, respectively, compared to neat asphalt binder. Meanwhile, the same trend was noted at 165°C with less effective than up to 7% with 0.288 Pa s showing an increase by about 44% as associated with neat asphalt.

The viscosity of nano-modified asphalt.
It can be concluded that after 5% of nano-modified asphalt, the values of viscosity take the lead of the same increase or less; this could be attributed to the broken bond among asphalt particles as a result of utilizing high Shear mixer making asphalt particles separated leading to be replaced by nano-TiO2 particles [37]. It can be inferred that adding nano-TiO2 helped to increase viscosity and lessen bituminous sensitivity. Viscosity variation, meanwhile, revealed a marked upward tendency.
4.2.2 DSR test results
4.2.2.1 Rutting parameter G*/sin δ
The rheological testing used in the current study is to assess the Performance Grade (PG) classification for the upper-critical temperature over a range of temperatures and different nanocontent. The study examined neat asphalt and nano-modified asphalt binder samples regarding original, RTFO, and PAV. Specimen subjected to DSR oscillatory shear at 10 rad/s (1.59 Hz) corresponds to traffic traveling around 90 km/h. With a run-up in 6°C increments, the preliminary temperature values were adjusted to 64°C for unaged and RTFOT-aged samples. The presented result is in Table 4, and Figures 11–15 indicate an enhancement in asphalt binder properties as nano-TiO2 content increased from 1 to 7%. In the case of the original and RTFO binder, the Superpave specifies a minimum amount of 1 and 2.2 kPa, respectively. Generally, a slight increase in rutting parameter G*/sin is shown with 1%, while these values exhibit an increase by about 51% for 3% TiO2 and nearly 64%. When nanocontent is from 5 to 7% at 64°C in the case of the original binder, the same trend at this temperature has been noted, with a slight change for the RTFO binder at the same temperature. It was noted that adding 5% to 7 of nano-TiO2 by weight of neat asphalt increased the value of G*/sin δ beyond the specification limit and survived against high temperatures, reaching a temperature of 76°C with a negligible increase behind 5% of nanocontent. TiO2 can increase PG grading by two grades to 76-16, which could be attributed to the vaporization of light elements and the consequences of change in asphalt nature aromatics and resins to asphaltness [11]. The outcomes of these results indicated that the addition of 3–7% of nano-TiO2 increased the rutting resistance of asphalt against higher temperatures and promoted PG by about one grade at 3% and two grades at a range of 5–7% this suggests that nano-TiO2 increased the stiffness of the asphalt and leading to enhance the rutting performance of asphalt. In conclusion, it can be stated that adding nano-TiO2 by an amount of 5% enabled the asphalt to maintain higher stiffness at a higher temperature than its PG specification. Additionally, the binder was changed into a more advanced “high-temperature PG graded” binder.
Performance-graded asphalt test results
| Temperature, °C | Property | 0% | 1% | 3% | 5% | 7% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test on original binder | ||||||
| 64 | G*/sin δ | 2.34 | 2.71 | 4.85 | 6.57 | 6.66 |
| δ | 84 | 82 | 80 | 77 | 75 | |
| 70 | G*/sin δ | — | — | 1.22 | 2.41 | 2.53 |
| δ | — | — | 82 | 79 | 77 | |
| 76 | G*/sin δ | — | — | — | 1.77 | 1.82 |
| δ | — | — | — | 81 | 80 | |
| Test on RTFO binder | ||||||
| 64 | G*/sin δ | 3.67 | 4.64 | 6.28 | 9.21 | 9.45 |
| δ | 68 | 66 | 63 | 60 | 59 | |
| 70 | G*/sin δ | — | — | 4.22 | 5.58 | 5.80 |
| δ | — | — | 66 | 64 | 62 | |
| 76 | G*/sin δ | — | — | — | 2.05 | 2.21 |
| δ | — | — | — | 65 | 64 | |
| Test on PAV binder | ||||||
| 25 | G*.sin δ | *6980 | *6433 | *5741 | 4850 | 4552 |
| δ | 52 | 51 | 48 | 44 | 43 | |
| 28 | G*.sin δ | 4662 | 4421 | 3951 | 3420 | 3105 |
| δ | 58 | 57 | 56 | 52 | 50 | |
| Actual PG | 64–16 | 64–16 | 70–16 | 76–16 | 76–16 | |
*failed to specify the limit.

Rutting parameter of original nano-modified asphalt, G*/sin δ.

Rutting parameter of original nano-modified asphalt, phase angle δ.

Rutting parameter of RTFO nano-modified asphalt, G*/sin δ.
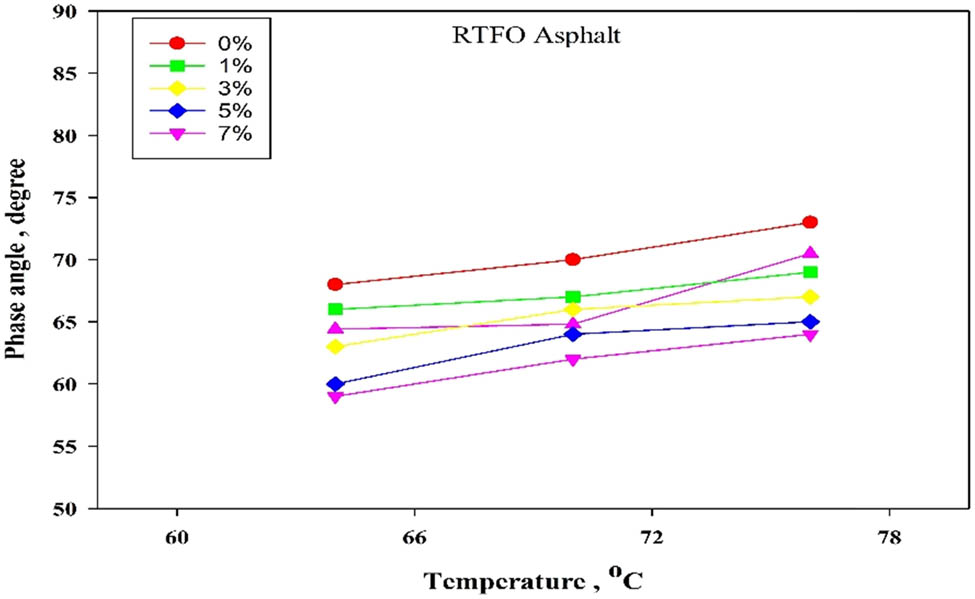
Rutting parameter of RTFO nano-modified asphalt, phase angle δ.

Falling temperature of neat and nano-modified asphalt.
4.2.2.2 Fatigue parameter G*.sin δ
Testing values for Superpave fatigue parameter G*.sin δ and phase angle δ for neat and nano-modified asphalt are listed in Table 4 and compared in Figure 16. It can be noted that δ values decrease with the continuous increase of nano-TiO2 at temperatures 25 and 28°C. A slight difference is seen at 1% nano-TiO2. However, this decrease gradually increases, showing an improvement in the elastic nature of asphalt by about 8, 16, 18% at 25°C and 4, 11, and 14% at 28°C, when nano-TiO2 content increased from 3 to 7%, respectively. Additionally, it can be seen that the δ values difference between changed samples and neat asphalt is lessened at lower temperatures due to the asphalt matrix behaving more elastically as the temperature drops. On the other hand, the behavior of decreasing rate in G*.sin δ values was obtained as nanocontent increased, highlighted with higher stiffness at 5 and 7% of TiO2 content, leading to an increasingly complex modulus and decreasing fatigue parameter by about 30 and 34% from neat asphalt concerning this content of nano at both temperatures 25 and 28°C. These results agree with another researcher [38].

G*.sin δ and δ values of neat and nano-TiO2-modified asphalt.
Although nano-modification also enhanced the elastic behavior of asphalt binder, as evidenced by decreased phase angles, the high complex moduli led to more significant values of G*.sin δ. According to the Superpave fatigue parameter data, the change of asphalt binder with nanoparticles causes a decrease in resistance against fatigue cracking. Keeping in mind that the Superpave fatigue parameter is based on the results of a single loading cycle, it should be noted that there may be some differences between the parameter and the field findings.
4.2.3 BBR stiffness and m-value
The BBR testing result exhibited in Figures 17 and 18 shows that nano-TiO2 particles decreased the elasticity of asphalt at low temperatures. Nano-modified asphalt failed to meet the Superpave criteria for creep stiffness or creep slope at −12°C; instead, at −6°C, the binders achieved the specifications. Incorporating nano-TiO2 into asphalt binder at different contents increased its stiffness and decreased the m-value at both temperatures, showing a higher chance of low-temperature cracking.

m-Value of neat and nano-modified asphalt.

Stiffness value of neat and nano-modified asphalt.
Dealing with samples at −12°C, the phase angle in Figure 16 presented a lower m-value than neat asphalt; 1% nano-TiO2 decreased m-value to 0.363, showing a slight decrease of nearly 7% ad with increasing nanocontent from 3, 5, to 7%, m-value lowered by 14,21 and 23% to neat asphalt that is related to an enhancement in the elastic characteristics of asphalt. Additionally, it can be seen that the phase angle difference between neat and nano-modified asphalt is lessened at lower temperatures. This might be because the asphalt matrix will behave more elastically as the Temperature is lowered. At temperatures as low as −12°C, asphalt nano-modified with 1–7% nano-TiO2 would demonstrate the necessary fatigue resistance. Therefore, it can be concluded that nano-TiO2 addition to PG 64-16 is negligible and has no impact on the base binder’s low-temperature PG. The creep stiffness modulus of neat and nano-TiO2-modified asphalt was presented in Figure 18 at two temperatures, −6 and −12°C. At −6°C, all samples meet the Superpave speciation below 300 MPa When the Temperature dropped to −12°C, a significant increase was noted up to 3% for nano-TiO2 modified asphalt as compared to neat sample, hence beyond threshold limits of 3% higher stiffness observed causes the asphalt to be stiff and less elastic. In addition, nano-modified asphalt with a 3% concentration shows a greater modulus with a lower m-value when compared to neat asphalt, showing that fracture resistance for nano-modified asphalt has been slightly lowered but can still meet specification criteria.
4.3 Evaluation of the cost
Considering the financial effects of utilizing nanomaterials as AC modifiers is essential. Nanotechnology produces nanoparticles in tiny quantities, but asphalt pavement building uses enormous quantities of materials – measured in tons. Due to the intricate processing steps necessary to produce such high purity levels, restricted size range, and high specific surface area, nanomaterials are expensive. Currently, 1 kg of nano-TiO2 costs $188 from Skyspring (the source of imported nano in this study). However, as demand rises, more alternative energy sources are used, and manufacturing technology advances, the cost has been falling over time, and this trend is anticipated to continue. For the addition of modifiers to be cost-effective at current costs, a significant increase in durability must be obtained. Additionally, from an economic perspective, modifiers requiring smaller optimum amounts are more competitive. Adding 5% TiO2 is more cost-effective and improves asphalt rheology at various temperatures.
5 Conclusion
This study examines the effect of 1, 3, 5, and 7% of nano-TiO2 by weight of asphalt on some of its rheological and hardened properties. The physical and rheological properties of nano-modified asphalt were assessed the asphalt susceptibility with high, intermediate, and low temperatures. The following conclusion can be drawn: based on tests for penetration, softening point, viscosity, and ductility, it was determined that asphalt’s hardness had increased, improving its susceptibility to temperature changes. The rutting factor, which measures the binder’s resistance to rutting at high temperatures, showed that whether RTFO was aged or original, increasing the content of nano-TiO2 from 3 to 7% increases the rutting resistance of asphalt against higher temperatures and promoted PG by about one grade at 3% nanolevel and two grades at a range of 5–7%, which suggests that nano-TiO2 increased the stiffness of the asphalt. While at medium Temperature, fatigue factor value for PAV aged asphalt, G*.sin δ shows that higher stiffness at 5 and 7% of TiO2 content increases complex modulus and decreases fatigue parameters as nanocontent increases. Higher creep stiffness and higher m-values were noted at low temperatures as nano increases in asphalt binder, increasing stiffness and decreasing the m-value at both −6 and 12°C, leading to a higher chance of low-temperature cracking. Finally, 5% of nano-TiO2 will improve asphalt’s physical properties and enhance asphalt anit-rutting and fatigue resistance.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Most datasets generated and analyzed in this study are comprised in this submitted manuscript. The other datasets are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author with the attached information.
References
[1] Yao H, Dai, Q, You, Z, Ye, M, Yap, YK. Rheological properties, low-temperature cracking resistance, and optical performance of exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets modified asphalt binder. Constr Build Mater. 2016 Jun 15;113:988–96.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.152Search in Google Scholar
[2] Li R, Xiao F, Amirkhanian S, You Z, Huang J. Developments of nano materials and technologies on asphalt materials–A review. Constr Build Mater. 2017 Jul 15;143:633–48.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.158Search in Google Scholar
[3] Golestani B, Nam BH, Nejad FM, Fallah S. Nanoclay application to asphalt concrete: Characterization of polymer and linear nanocomposite-modified asphalt binder and mixture. Constr Build Mater. 2015 Aug 30;91:32–8.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.05.019Search in Google Scholar
[4] Cheraghian G, Wistuba MP, Kiani S, Behnood A, Afrand M, Barron AR. Engineered nanocomposites in asphalt binders. Nanotechnol Rev. 2022 Mar 2;11(1):1047–67.10.1515/ntrev-2022-0062Search in Google Scholar
[5] Zhang D, Zhang H, Zhu C, Shi C. Synergetic effect of multi-dimensional nanomaterials for anti-aging properties of SBS modified bitumen. Constr Build Mater. 2017 Jul 30;144:423–31.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.205Search in Google Scholar
[6] Aljbouri HJ, Albayati AH. Effect of nanomaterials on the durability of hot mix asphalt. Transp Eng. 2023 Mar 1;11:100165.10.1016/j.treng.2023.100165Search in Google Scholar
[7] Hamedi GH. Investigating the use of nano coating over the aggregate surface on moisture damage of asphalt mixtures. Int J Civ Eng. 2018 Jun;16:659–69.10.1007/s40999-016-0143-xSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Buhari R, Abdullah ME, Ahmad MK, Chong AL, Haini R, Bakar SK. Physical and rheological properties of Titanium Dioxide modified asphalt. In E3S Web of Conferences; 2018. Vol. 34, EDP Sciences. p. 01035.10.1051/e3sconf/20183401035Search in Google Scholar
[9] Günay T, Ahmedzade P. Physical and rheological properties of nano-TiO2 and nanocomposite modified bitumens. Constr Build Mater. 2020 May 20;243:118208.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118208Search in Google Scholar
[10] Chen M, Liu Y. NOx removal from vehicle emissions by functionality surface of asphalt road. J Hazard Mater. 2010 Feb 15;174(1-3):375–9.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.062Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Qian G, Yu H, Gong X, Zhao L. Impact of Nano-TiO2 on the NO2 degradation and rheological performance of asphalt pavement. Constr Build Mater. 2019 Sep 10;218:53–63.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.05.075Search in Google Scholar
[12] Mahali I, Sahoo UC. Rheological characterization of Nanocomposite modified asphalt binder. Int J Pavement Res Technol. 2019 Nov;12:589–94.10.1007/s42947-019-0070-8Search in Google Scholar
[13] Zhang H, Zhu C, Yu J, Shi C, Zhang D. Influence of surface modification on physical and ultraviolet aging resistance of bitumen containing inorganic nanoparticles. Constr Build Mater. 2015 Nov 15;98:735–40.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.138Search in Google Scholar
[14] Hassan MM, Dylla H, Asadi S, Mohammad LN, Cooper S. Laboratory evaluation of environmental performance of photocatalytic titanium dioxide warm-mix asphalt pavements. J Mater Civ Eng. 2012 May 1;24(5):599–605.10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000408Search in Google Scholar
[15] Shafabakhsh GH, Mirabdolazimi SM, Sadeghnejad M. Evaluation the effect of nano-TiO2 on the rutting and fatigue behavior of asphalt mixtures. Constr Build Mater. 2014 Mar 15;54:566–71.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.12.064Search in Google Scholar
[16] Shafabakhsh GH, Ani OJ. Experimental investigation of effect of Nano TiO2/SiO2 modified bitumen on the rutting and fatigue performance of asphalt mixtures containing steel slag aggregates. Constr Build Mater. 2015 Nov 15;98:692–702.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.08.083Search in Google Scholar
[17] Tanzadeh J, Vahedi F, Kheiry PT, Tanzadeh R. Laboratory study on the effect of nano TiO2 on rutting performance of asphalt pavements. Adv Mater Res. 2013 Feb 6;622:990–4.10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.622-623.990Search in Google Scholar
[18] Zhang L, Gao X, Wang W, Wang H, Zheng K. Laboratory evaluation of rheological properties of asphalt binder modified by nano-tio2/caco3. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2021 Feb 12;2021:1–3.10.1155/2021/5522025Search in Google Scholar
[19] Rocha Segundo I, Landi Jr S, Margaritis A, Pipintakos G, Freitas E, Vuye C, et al. Physicochemical and rheological properties of a transparent asphalt binder modified with nano-TiO2. Nanomaterials. 2020 Oct 28;10(11):2152.10.3390/nano10112152Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Staub de Melo JV, Manfro AL, Barra BS, Dell’Antonio Cadorin N, Borba Broering W. Evaluation of the rheological behavior and the development of performance equations of asphalt composites produced with titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2023 Jan 10;13(2):288.10.3390/nano13020288Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Ameli A, Pakshir AH, Babagoli R, Norouzi N, Nasr D, Davoudinezhad S. Experimental investigation of the influence of Nano TiO2 on rheological properties of binders and performance of stone matrix asphalt mixtures containing steel slag aggregate. Constr Build Mater. 2020 Dec 30;265:120750.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120750Search in Google Scholar
[22] Kleizienė R, Paliukaitė M, Vaitkus A. Effect of nano SiO 2, TiO 2 and ZnO modification to rheological properties of neat and polymer modified bitumen. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Asphalt Pavements & Environment (APE) 5 2020. Springer International Publishing; p. 325–36.10.1007/978-3-030-29779-4_32Search in Google Scholar
[23] Cadorin ND, de Melo JV, Broering WB, Manfro AL, Barra BS. Asphalt nanocomposite with titanium dioxide: Mechanical, rheological and photoactivity performance. Constr Build Mater. 2021 Jun 28;289:123178.10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123178Search in Google Scholar
[24] Filho PG, Rodrigues dos Santos AT, Lucena LC, de Sousa Neto VF. Rheological evaluation of asphalt binder 50/70 incorporated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Mater Civ Eng. 2019 Oct 1;31(10):04019235.10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002885Search in Google Scholar
[25] Filho PG, dos Santos AT, Lucena LC, Tenório EA. Rheological evaluation of asphalt binder modified with nanoparticles of titanium dioxide. Int J Civ Eng. 2020 Oct;18:1195–207.10.1007/s40999-020-00525-4Search in Google Scholar
[26] Beeldens A. An environmental friendly solution for air purification and self-cleaning effect: the application of TiO2 as photocatalyst in concrete. Proceedings of transport research arena Europe–TRA. Göteborg, Sweden: 2006 Jun 1. p. 1–9.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Hassan M, Mohammad LN, Asadi S, Dylla H, Cooper III S. Sustainable photocatalytic asphalt pavements for mitigation of nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide vehicle emissions. J Mater Civ Eng. 2013 Mar 1;25(3):365–71.10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000613Search in Google Scholar
[28] Venturini L, Bacchi M. Research, design, and development of a photocatalytic asphalt pavement. In Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Environmentally Friendly Roads: ENVIROAD; 2009 Oct 15.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Ramesh KT. Nanomaterials. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2009.10.1007/978-0-387-09783-1Search in Google Scholar
[30] Grassian VH, O’Shaughnessy PT, Adamcakova-Dodd A, Pettibone JM, Thorne PS. Inhalation exposure study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with a primary particle size of 2 to 5 nm. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Mar;115(3):397–402.10.1289/ehp.9469Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Forbes TZ. Occurrence of nanomaterials in the environment. In Nanomaterials in the environment 2015 179–218.10.1061/9780784414088.ch07Search in Google Scholar
[32] National Research Council. A research strategy for environmental, health, and safety aspects of engineered nanomaterials, 2012.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Haase A, Luch A. Genotoxicity of nanomaterials in vitro: Treasure or trash? Arch Toxicol. 2016 Nov;90:2827–30.10.1007/s00204-016-1825-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Ramachandran G, Ostraat M, Evans DE, Methner MM, O’Shaughnessy P, D’Arcy J, et al. A strategy for assessing workplace exposures to nanomaterials. J Occup Environ Hyg. 2011 Nov 1;8(11):673–85.10.1080/15459624.2011.623223Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Crucho JML. Development of an accelerated asphalt concrete aging method and utilization of nano-modifiers to improve durability of asphalt concrete. Ph.D. thesis. Lisboa, Portugal: Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa; 2018.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Wang W, Cheng Y, Tan G, Liu Z, Shi C. Laboratory investigation on high-and low-temperature performances of asphalt mastics modified by waste oil shale ash. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 2018 Jul;20:1710–23.10.1007/s10163-018-0737-2Search in Google Scholar
[37] Sadeghnejad M, Shafabakhsh G. Experimental study on the physical and rheological properties of bitumen modified with different nano materials(Nano SiO2 & Nano TiO2). Int J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2017 Aug 1;13(3):253–63.Search in Google Scholar
[38] Nejad FM, Nazari H, Naderi K, Karimiyan Khosroshahi F, Hatefi Oskuei M. Thermal and rheological properties of nanoparticle modified asphalt binder at low and intermediate temperature range. Pet Sci Technol. 2017 Apr 3;35(7):641–6.10.1080/10916466.2016.1276589Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection

