Abstract
One of the key variables that can affect energy consumption in a building is the shape of the structure. The current study aims to balance the using solar radiation (lighting, heating, and cooling) and energy consumption by analyzing climatic factors’ effect on building formation systems’ standards. The research shows the mechanism of reaching optimal solutions in building performance problems using evolutionary algorithms as a reliable strategy. By examining the formation of compact fabric elements, the mass of the building on the site is compared with the parametric model adapted to the context to find out the negatives and positives according to the heat gain for each. The research relied on analytical and descriptive methods to clarify the determinants. The analysis included three main axes, the urban characteristics, the urban climatic compatibility in the study area, and parametric analysis. According to the results, shaped building blocks can simultaneously enhance indoor daylight levels and energy performance. Using the framework as a reference model can increase the chances of solving complex urban design problems earlier and recommend sustainable building designs.
1 Introduction
Long and scorching summers brought on by the Arabian Desert plateau’s harsh climate result in an interior environment that differs from areas with a temperate climate. Most of the year in Najaf is hot and dry, except for the chilly, dry winter months, frequently interspersed with just a few wet days [1].
In addition, the region’s exposure to monsoon winds is laden with dust and dirt because of its location on the edge of the eastern plateau of the western desert of the Arabian Peninsula [2] (Figure 1). It bypasses the geographical factor to reach the outskirts of major cities with regional influence because of its religious and historical status because it included the remains of Imam Ali[1](PB), in the first place. It also consists of the world’s most significant and oldest cemetery in the second degree. It is also considered the founding center of Islamic Shiite globally, where the religious seminary and religious schools are scattered around Imam Ali’s shrine. The alleys and houses comprise the four lanes Al-Mashreq, Al-Amarah, Al-Huwash, and Al-Buraq [3]. Consequently, the need to develop high-performance buildings and sustainable design has become imperative, mainly because of ongoing renovation projects, including high-rise hotels adhering to the traditional fabric of three floors or less, as identified in field surveys. The negative impact of these new constructions in the context of the traditional fabric concerning urban design underscores the necessity for a boundary model that facilitates the design of buildings aligned with the context while achieving sustainable goals through energy conservation.

Najaf city criteria (collected by researchers).
The research aims to clarify the urban characteristics of the ancient city of Najaf and the extent to which they are affected by the prevailing climatic factors in the region. It also tries to study the time of the suitability of the building style and material for those extreme climate characteristics by creating digital representations. The analysis focuses on obtaining a digital database that helps to know the impact of climatic factors on the morphological composition of buildings to reach the highest possible degree of thermal comfort with traditional fabric [4].
The nature of the region’s climate entailed compact residential units [5]. The streets are narrow and crooked to gain the largest shade area, thus reducing the air temperature applies to the architectural characteristics of buildings, such as the height of the ceilings, the manipulation of the heights, the formation between the closed and the open internal spaces of the residential unit and its relationship to the outer space, and the material used in building the basic structure such as walls and ceilings or the materials used in the finishes [6]. Therefore, developing high-performance buildings and sustainable design has become essential to reducing energy consumption while maintaining occupant satisfaction and well-being in indoor environments. So, it is necessary to compare the metrics to specific reference values. Energy intensity is one of these natural metrics. It is the energy required per square foot per year and is calculated by dividing the total energy consumption of the building by the total floor area. Lower energy consumption implies that the building performs better, which is affected by many internal and external factors, such as weather data, schedules, and building shapes [7].
In earlier research, the parametric technique was utilized to address the outside surfaces of buildings, like their roofs and facades, to increase their overall performance and energy efficiency [8]. In contrast, this study suggests using simulation techniques and the parametric optimization approach to find the best building plans for modifying design parameters. This study demonstrated that the shape of the building mass significantly affects performance and increases energy consumption, particularly in recent years when temperatures have changed more rapidly than in the past. However, more research needs to be done on the impact of digitally integrated mass creation.
2 Literature review
Parametric digital tools have expanded the field of solution exploration for architecture. At the applied level, parametric architecture finds itself in a continuous cycle of innovative adaptation and retooling of the discipline and transformation of the architectural and urban environment to the social and economic age of the information society by finding a new spatial language in the urban fabric context compatible with artistic awareness and orientation toward the age of information and digital technology. All the elements of architecture are subject to parametric adaptation and thus adaptable to each other and the context as multiple systems are linked to each other and the environment, with attention to environmentally effective solutions that impose different types of behaviors. The adaptive potential enables urban forms, especially in the existing fabrics of cities, to create a higher level of conduct in the sphere of activity of the user, residents, or tourists [4]. In this context, the parametric analysis of adapted passive strategies, inspired by traditional architecture in a hot and dry climate in affecting energy demand (cooling and heating loads), is one of the mechanisms for evaluating the energy consumption of buildings according to the formation of their constituent blocks [9].
Strategies such as psychrometric chart, field survey of the site, and dynamic simulation (Energy Plus) are analyzed through a graph to understand its thermal behavior and energy demand through different scenarios of the shape of the building block with passive strategies and modified parameters. This method proved that there is a difference in the temperatures of the internal and external areas with a difference exceedingly more than 10 degrees of heat and change. These differences are based on the analyzed scenarios [10]. At the analytical level, spatial quality criteria are regarded as an analytical hierarchy process. Islamic courtyard’s environment and social and cultural significance are seen as an indication of spatial quality [11] to create criteria for returning to the traditional dwellings with a central courtyard. These criteria were subprinciples when noting the basic concepts of functionality, aesthetics, and ecology. The priority criteria were thus established, considering the spatial quality requirements that served as the basis for defining the essential characteristics of the courtyard in traditional homes [12].
On urban formation as an adaptation strategy to improve external thermal comfort in the urban residential community, hybrid scenarios were developed for the proportions of different external residential canyons by mixing methods of shading and vegetation [5]. Simulation models are developed for several design scenarios, and thermal comfort values for each way based on physiological equivalent temperature (PET) are compared [13]. The result concluded that there was a significant decrease in PET for narrow areas (alleys) compared to that for broad regions (streets). Moreover, the shading process and landscaping affected an almost complete shading of the outer envelope of the facades of residential buildings [14]. This can lead to a decrease in the temperature of outer space and outdoor thermal comfort, and benefit from it in increasing social activities in a hot, dry climate [15].
It is clear from previous studies that the parametric design helps in finding environmental solutions at the level of the building and urban fabric in various regions, especially regarding solar radiation, due to its negative impact in hot and dry areas and positive impact in cold and wet areas to reduce energy consumption in heating and cooling and gain from the traditional strategies in force in the pre-energy era.
3 Methodology
The local microclimate of the compact fabric depends on the temperature, wind speed, and humidity, which vary from city to city. This study used Grasshopper software and Ladybug and Honeybee plug-ins to analyze and simulate the distribution of solar radiation and reduce energy consumption in Al-Buraq district in Najaf. A parametric model was made based on these data to reach the formation of a shape adapted to the surrounding buildings, and based on heat gain, it compares the mass in the site with the environmentally adapted parametric model, and then outlines the pros and cons of each. As a result, the differences between these parameters on the global climate map for each of these four regions of the ancient city cause the local climate region parameters to fit into the sensitive fabric of climate. The difference between the ground level and the sea level may be responsible for this discrepancy. This study will attempt to explain the simulation-based optimization algorithms approach for evaluating optimal modulation in obtaining thermal comfort, which facilitates energy optimization for similar future projects and improves the adequacy of the parametric approach in the early design stage.
4 Case study and field experience
4.1 The characteristics of the urban fabric description
The Najaf ancient city was formed from three prominent landmarks:
The shrine of Imam Ali(PB), peace be upon him, which was the reason for the city’s emergence and transformation from the meeting point of the trade routes leading to Mecca and Yemen to a civilized incubator.
Wadi Al-Salam Cemetery is the cemetery in which burials began from the Babylonian period, at the beginning of history until now.
Al-Najaf Sea, a lake that extends from the low edge of the plateau of the Arabian Peninsula to the desert. It was affected by dry climatic factors and shrank its size today, but it is mentioned in history that it was a great sea in which ships sailed [9].
As for the urban fabric that grew around the shrine at different times, it consists of the following: housing units, religious schools, markets, roads, and the wall. The old Najaf city comprised four residential districts surrounding the shrine mentioned above by Imam Ali(PB) [10]. The town grew circularly around the shrine, and soon houses and religious schools surrounded it from all sides, especially in the eastern and northeastern region (the locality of Al-Mishra). It was considered sacred because it is located between the shrine and Karbala on one side and Al-Sahlah Mosque and Al-Kufa on the other side [11].
Therefore, this area has become the gateway from which expatriates enter and has been used as a market for shopping by visitors. Furthermore, it developed to be the great market of Najaf, which went through various development cases then and until now. Al-Najaf Sea borders the old city from the west, and Wadi Al-Salam cemetery from the northwest, so the city’s growth stopped from these two sides. As for the eastern and southern sides, it grew up to Kufa and the districts surrounding Najaf with a modern residential pattern. At the same time, the old city remained within the boundaries of the old wall, which was replaced by a street after its demolition at different times, to be characterized by a spontaneous urban fabric that is different from the modern urban fabric [10] (Figure 5). Al-Buraq region (the study case covered by the research) is in the southeastern-south part of the old city. This region enjoys the preservation of the urban fabric (Figure 2).
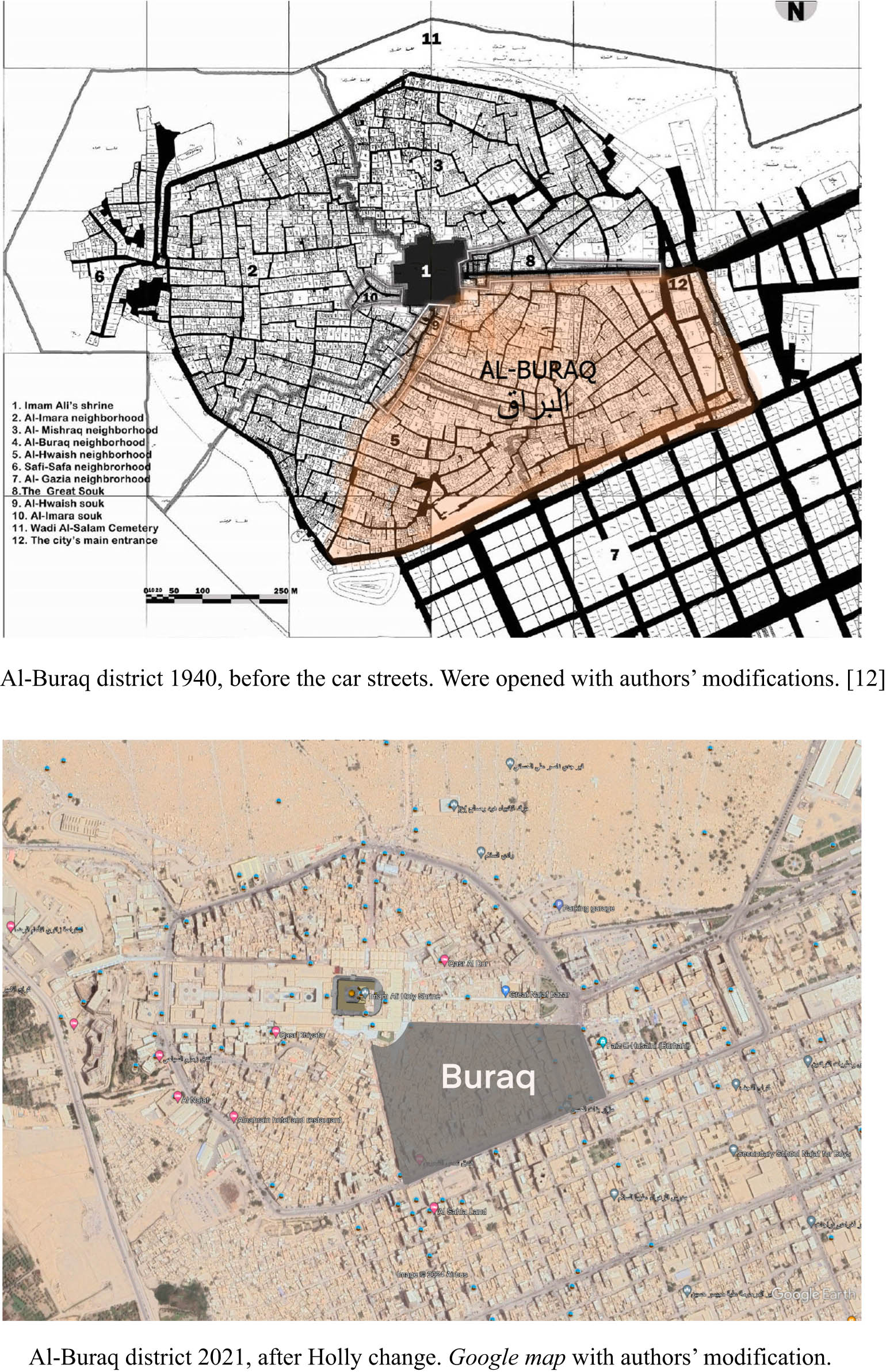

Al-Buraq district 1940 till.
However, in recent times, the fabric was permeated by tall buildings that somehow affected the traditional urban fabric (Figure 3). In this study, first, we will address the impact of these tall buildings on the material in terms of the functional change of land use, as the area is originally residential. The entrance buildings have a commercial function. Second, the height of the building climatically affects the thermal comfort of the area. Hence, the researchers hypothesized that the parametric design would help find a building shape that fits with the contextual morphology of the site.

Exploiting empty spaces in the traditional fabric by placing tall buildings. Source: Drawing by the authors.
The site chosen for the study will be analyzed before and after the block’s signature as a case. Then a block that fits the morphological context of the surrounding buildings will be selected to validate the hypothesis.
4.1.1 Climate information of case study
The case study is a part of the urban fabric of the Al-Buraq area in the old city of Najaf. Its coordinates are 31°59′.08 ″40 N/°44′.54 ″4 E, according to the Köppen climate classification. It was determined as hot, dry weather with an enormous difference in temperature between night and day, summer and winter. The meteorological department was used to obtain climate data for the region (Figure 4), where it was found that the highest temperature in summer for the year 2022 is in the 13 days – it reached 52°C on June 19, while the lowest temperature recorded until the completion of the research was 0–1°C January 19, 22. A lower temperature in December was not expected, according to weather forecasts for the region [13].

Iraq climate. Source File: BW climate.png.
4.2 Site study
The site is considered one of the oldest places in Najaf, whose construction dates back almost a thousand years [3]. Because of the end of the life span of most of the building materials and the lack of maintenance and restoration, the building was eroded and destroyed, and it no longer had a significant importance in this particular area. Its height is eight floors due to its high economic value due to its proximity to the shrine of Imam Ali [11]. Figure 5 shows the study site and its components (Figure 6).

Al-Buraq neighborhood after hotel build. Source: Drawing by the authors.

Al-Buraq neighborhood after hotel build. Source: Drawing by the authors.
4.3 Practical framework
The solar radiation and the percentage of shading in the region will be analyzed to see if recent morphological changes affect the urban fabric in the area negatively or positively. Then, parametric operations are applied through the Rhino-Grasshopper program to obtain a shape (not a design), a form that represents the building supposed to be designed and result obtained from the environmental variables entered as data for the program. The temperature comparison will be made during the highest temperature on July 14, 2022, by default using the Rhino-Grasshopper-Ladybug-Butterfly program and simulating the reality of the situation before and after placing the block. The wind speed was studied on the hottest days. According to the Iraqi Meteorological Authority data, it does not exceed 14.40 toward the northwest, as shown in Figure 7, where it is clear that the wind speed on the hottest days is 11,20,21. The windflower shows that it is faster. It is 14.40 in the northwestern part. Data are based on Ladybug weather file sources (epwmap). In addition, according to the Siple PA, the Passel CF equation measures the effect of wind speed on reducing the temperature [14].

The wind speed on the hottest days is 14.40 on June 11, 20, 21, as appears from the windflower in the northwestern. Researchers’ Analytics in Grasshopper.
where WCI = wind chill index (kg*cal/m2/h), v = wind velocity (m/s), and T a = air temperate.
Since the CFD program is linked with the Butterfly plugins in the Rhino-Grasshopper program, the calculations for the equation will be calculated automatically and not manually.
In this case, the hot winds are considered the poison winds because the northwestern region is a desert region [15]. July 14, 2022, will be taken as the typical day for the climate analysis at the site according to the climate analysis at the site, where it was found that the hottest week is from July 13–19, 2022, as shown in Figure 8 by epwmap.

Import stat shows the hottest week 2022 for 24 h daily. Researchers analytic in Grasshopper.
To measure the maximum air temperature, one must determine a specific hour. Rhino defines the hottest period as hours from 10 am to 4 pm on July 14, 2022, considered the hottest during the year, as shown in Figure 9.

The measurement of the air temperature in the study area, which is 49°C (researchers analytic in Grasshopper).
It was clear from the results that the highest temperature in this period was 16°C, i.e., 4°C in the afternoon, and the air temperature was 45.2°C (without influencing factors). It is noted here that when adding the effect of the building blocks to the area and adding the diversity of the floor, the percentage of reflection of which varies according to the cladding material, ranging from 0 to 1, where the slightest consideration is given for the grassy land until it reaches the highest percentage for the dry land. Here, we assumed the ratio of the sun’s reflection to be 0.75. During the same period and under the same climatic conditions, the temperature increased to 50.59°C. By adding sky exposure, the temperature decreased to 50.36°C (Table 1 and Figure 10).
Marks the effect of factors (GR), (UTCI), and (AT) on the change of temperature in 1 h of the day
| Influencing factor | Embodiment of variables into parameters |
|---|---|
| Air temperature (AT) without any influencing factor |
 |
| UTCI (universal thermal climate index) for 1 h (4 pm) |
 |
| Ground reflection, 0–1; grass, 0.25; soil to dry ground, 1. In our study, 0.75 is a factor reflection | Before adding  |
After adding  |
|
| Sky exposure |
 |

Study of the solar radiation of the site without mass. Source: Drawing by the authors.
It is clear from Figure 11 that the area of the site before the intervention, which consisted of the compact fabric of the traditional houses, enjoyed complete shade at all hours for the hottest day, which is on July 14, 2022, according to climate forecasts in the Global Meteorological Department, with a temperature of 51°C. These results were hypothetically simulated by the site in the Rhino-Grasshopper program. In contrast, the temperature became 54°C when the existing mass was added as a reality after introducing the last changes in the tissue.

The same time as a new building. The area was exposed to direct radiation all day, increasing the temperature from 51 to 52°C. Source: Drawing by the authors.
5 Parametric model
To obtain the height of the ground level in the Buraq area in the Holy City of Najaf, we used CAD Mapper and then analyzed the site climatically using Ladybug in the grasshopper program. It is worth mentioning that the model is a guide for the shape that is supposed to be designed through a set of climatic information for the site, which is embodied in a way that helps the architectural designer decide on the shape of the block that is supposed to be signed at the site. Therefore, multiple possibilities exist for choosing the final form and not being restricted to the state reached as a parametric model. The shape of the model was obtained as a result of the influence of climatic factors, such as temperature, solar radiation, wind speed, and relative humidity in the place as primary factors, and the thermal reflection of the land and surrounding buildings and the thermal diffusion of the sky as secondary factors.
5.1 Design process based on the optimization algorithm
The site has been emptied of the building blocks that are about to fall and are supposed to be removed because they are not permanent on the site. According to a study by Diwan Company, their removal is a foregone conclusion, as they do not contain buildings of heritage or historical value. From eight in the morning, solar radiation falls on the facades at this hour. Where the solar radiation was analyzed in 3 hours according to Table 1; given that the sun at 8 am will have a height of 2 m maximum on the facades, this distance was considered as a threshold for measuring the solar radiation on the faces surrounding the building supposed to be designed. Moreover, after projecting the solar radiation according to the specified daytime hours, considering the height of the building is 24 m, which is the same height as the existing building, which consists of eight floors. One of the contemporary paradigms of thought is the model that helps the architectural designer by embodying climatic factors, especially temperature, and solar radiation, in a tangible way so that it is one of the primary design determinants that the designer relies on while forming the external shape of the block, as in this study (Table 2 and Figure 12).
Shows a set of cases of the parametric model for certain hours of the day
| Situation | Hours |
|---|---|
 |
8 am 14/7/2022 |
 |
2 pm 14/7/2022 |
 |
4 pm 14/7/2022 |
 |
The shape of the mass after setting the sequential algorithm for the hours of the day that the block is exposed to starts at six in the morning |
 |
The mass’s shape after developing the sequential algorithm for the daylight hours the group is exposed to. It turned out that the highest temperature that the collection was exposed to was at 2 o’clock in the afternoon |

The phases of formation of the parametric model shape according to the data on the site (the height of buildings and streets), climatic factors such as solar radiation and the angle of incidence of the rays, and the directions of the sun’s path from east to west and according to the hours of the day. Drawing by the authors.
6 Conclusion
This study proposes a method of morphology generation for the architectural design by integrating the optimization algorithm with external shape and decision-making analysis. The design technique effectively could obtain several structural morphologies for buildings with structural rationality and aesthetic standards, perform the evaluation, and choose the best alternative. The first stage consists of the characteristics of the site (climatic and geographical characteristics of the old city of Najaf) and the features of the solar radiation of the region to create an innovative form for these two elements. This will provide architects with direct guidance when applying parametric modeling to architectural morphology generation. On the other hand, by analyzing the relationship between the mass’s shape and the climatic factors, with the solar radiation and the directions application, it is proved that this sensitive relationship can generate a cluster of alternatives for architectural morphology design. In addition, the morphology generation of mass is investigated through two different design domains. One contains a shell for the structure, and the other is laminates that represent the multiple floors of the building. Organic, distinct, and mechanically logical results show how effective and applicable the suggested process is.
To clarify the whole process from architectural morphology generation to scheme evaluation and selection by the parametric modeling method, the model is applied to complete the performance ranking and selection of evaluation cases by taking several morphological methodology generation results as evaluation cases, as well as the principle of architectural form, as the basic evaluation criteria in this study to simulate the parametric model and compare it to the veritable mass.
7 Result
The parametric model is adaptable according to the context and has morphological specifications that assistance reduces heat acquisition and, thus, its positive thermal impact on the surrounding masses. These results were reached through a comparison between the parametric analysis of the heat gain of the existing block at the site and the results of the parametric analysis of the heat gain of the model, as the results showed that the parametric model reflects the influence of climatic factors on the surrounding buildings, so it is highly adapted to the surrounding buildings.
As for the model itself, it obtains the most significant amount of shading during the day, and thus, it gets the lowest temperature gained during the day. From this, we conclude that the parametric model is a mental orientation rather than a software application. It is a thought, technique, and way of thinking that seeks to express and explore relationships. This allows the parametric design to reshape previous plans in a new way, achieving its diversity.
The parametric model is contextually adaptable and has morphological specifications that help reduce heat acquisition and, thus, its positive thermal impact on the surrounding masses. These results were reached through a comparison between the parametric analysis of heat gain for the mass at the site and the results of the parametric analysis of heat gain for the model, as the results showed that the parametric model reflects the influence of climatic factors on the surrounding buildings, so it adapts greatly to them.
As for the model itself, it gets the most shading during the day and gets the lowest temperature gained during the day. From this, we conclude that the parametric model is a mental orientation rather than a software application. It is an idea, technique, and way of thinking that seeks to express and explore relationships. This allows the parametric design to reconfigure previous plans in a new way, achieving their diversity.
Through the relationship of the site of the proposed block with the existing buildings, the solar radiation falling on the facades of the surrounding buildings was analyzed through two variables: the height of the proposed building (the number of floors required) and the time of falling solar radiation.
Because of the intersection of the continuity of solar radiation with the height of the building, a certain body will be formed for us that will be far from falling solar rays.
The solar radiation was analyzed three times during the day: the first case was at sunrise. The first hours of sunrise do not affect the facades due to the compact texture and low temperature, and the eighth was considered the first hour for the solar analysis. It was found that the sun’s height according to the height of the surrounding buildings is 2 m. This height was considered a threshold for measuring solar radiation on the surrounding facades (Figure 13).

The threshold line for solar radiation on the facades surrounding the proposed site.
The second case is at 2 o’clock in the afternoon, and the third case is at 4 o’clock in the afternoon. The study reached these particular hours using the time change parameter, an algorithm series that gives numerical variables from 1 to 24 h to obtain the appropriate shape for the mass in the times affecting the fall of solar radiation.
This very sensitive relationship produced many shapes at the level of the external building, depending on two algorithms, the height of the building, and the time of solar radiation (Figure 14).

The parametric model after being subjected to the same climatic study of the existing mass, where the model appears wholly shaded from the eastern and northern sides. Notes: The difference in places exposed to solar radiation in the same period.
The operations applied in the primary program are sequential and successive and contain many (totals or groups) to reach an integrated model that can be used in other projects.

The embodiment of geographical characteristics and solar radiation characteristics as algorithms in the first stage of formation.
This process was implemented in two stages. The first stage is to analyze region properties (climatic and geographical characteristics of the old city of Najaf), as well as the solar radiation characteristics of the region (Figure 15).

The application of shadows and solar radiation in the first stage to achieve results for the environmentally integrated model.
The second stage consists of applying shadows and solar radiation to obtain results for the environmentally integrated model according to the details resulting from the mass related to the surrounding (Figure 16).
This study is specialized for a specific site; it can expand future research to include intangible characteristics such as social status, which is crucial in urban areas morphology.
-
Funding information: We declare that the manuscript was done depending on the personal effort of the author, and there is no funding effort from any side or organization.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Most datasets generated and analyzed in this study are in this submitted manuscript. The other datasets are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author with the attached information.
References
[1] Alhilo EA, Kuba SA, Dirweesh AF. Nanotechnology use to preserve the durability of archaeological brick buildings in Al-Najaf city. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 2021;1067:910.1088/1757-899X/1067/1/012044Search in Google Scholar
[2] Kamoona GMI, Shaheen BR. The influence of theremal streeses on housing groupings. J Eng. 2002;8(2):63–82.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Abid S. Representing Najaf: an investigation into the current pressure on the physical and social fabric of Najaf s old town. International Planning History Society Proceedings. 2016;17(1):171–2.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Besbas S, Nocera F, Zemmouri N, Khadraoui MA, Besbas A. Parametric-based multi-objective optimization workflow: Daylight and energy performance study of hospital building in Algeria. Sustainability. 2022;14(19):12652.10.3390/su141912652Search in Google Scholar
[5] Latif A, Shahin B. Structural design according to constructal theory in architecture. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 2021 Mar;1090:12070. 10.1088/1757-899X/1090/1/012070.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Shaheen BR, Al-Ethari AM, Abdul-Mun’em U. The effect of services system in architectural form developments. J Eng. 2014;20(4):2.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Fang Y. Optimization of daylighting and energy performance using parametric design, simulation modeling, and genetic algorithms. North Carolina State University; 2017.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Niama DF, Kammou GM. The effect of cool roofs on the achieving of energy conservation with the administrative building spaces. Assoc Arab Univ J Eng Sci. 2020;27(3):112–24.10.33261/jaaru.2020.27.3.012Search in Google Scholar
[9] Sandes CA, Attiyah AN. Routledge Handbook of Sustainable Heritage. Najaf, Iraq; 2022. p. 213–225.10.4324/9781003038955-19Search in Google Scholar
[10] Al-hiloa IA, Al-Baghdadia AA-S. Promoting the cultural and urban identity of the holy cities: The case study of Al-Najaf, Iraq. Kerbala J Eng Sci. 2022;2(4):192–208.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Farhan SL, Alyasari HI, Akef VS, Zubaidi SL, Hashim KS. Analysing the transformed urban patterns of Al-Najaf historical center: Urgent issues and possible solutions. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 2021;1058(1):12052.10.1088/1757-899X/1058/1/012052Search in Google Scholar
[12] Falah SM. The Shrine that consumed its town: The role of religion and politics in reshaping the Iraqi city of Najaf. University of Cincinnati; 2018.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Kaihoul A, Sriti L, Amraoui K, di Turi S, Ruggiero F. The effect of climate-responsive design on thermal and energy performance: A simulation based study in the hot-dry Algerian South region. J Build Eng. 2021;43:103023.10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103023Search in Google Scholar
[14] Gorman JM, Regnier M, Abraham JP. Heat exchange between the human body and the environment: A comprehensive, multi-scale numerical simulation. Adv Heat Transf. 2020;52:197–247.10.1016/bs.aiht.2020.07.001Search in Google Scholar
[15] Alasadi F, Dewachi M. The role of brick in determining features of Iraqi architecture. IOP Conf Ser: Mater Sci Eng. 2020 Aug;881:12018. 10.1088/1757-899X/881/1/012018.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Methodology of automated quality management
- Influence of vibratory conveyor design parameters on the trough motion and the self-synchronization of inertial vibrators
- Application of finite element method in industrial design, example of an electric motorcycle design project
- Correlative evaluation of the corrosion resilience and passivation properties of zinc and aluminum alloys in neutral chloride and acid-chloride solutions
- Will COVID “encourage” B2B and data exchange engineering in logistic firms?
- Influence of unsupported sleepers on flange climb derailment of two freight wagons
- A hybrid detection algorithm for 5G OTFS waveform for 64 and 256 QAM with Rayleigh and Rician channels
- Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy
- Exploring the potential of ammonia and hydrogen as alternative fuels for transportation
- Impact of insulation on energy consumption and CO2 emissions in high-rise commercial buildings at various climate zones
- Advanced autopilot design with extremum-seeking control for aircraft control
- Adaptive multidimensional trust-based recommendation model for peer to peer applications
- Effects of CFRP sheets on the flexural behavior of high-strength concrete beam
- Enhancing urban sustainability through industrial synergy: A multidisciplinary framework for integrating sustainable industrial practices within urban settings – The case of Hamadan industrial city
- Advanced vibrant controller results of an energetic framework structure
- Application of the Taguchi method and RSM for process parameter optimization in AWSJ machining of CFRP composite-based orthopedic implants
- Improved correlation of soil modulus with SPT N values
- Technologies for high-temperature batch annealing of grain-oriented electrical steel: An overview
- Assessing the need for the adoption of digitalization in Indian small and medium enterprises
- A non-ideal hybridization issue for vertical TFET-based dielectric-modulated biosensor
- Optimizing data retrieval for enhanced data integrity verification in cloud environments
- Performance analysis of nonlinear crosstalk of WDM systems using modulation schemes criteria
- Nonlinear finite-element analysis of RC beams with various opening near supports
- Thermal analysis of Fe3O4–Cu/water over a cone: a fractional Maxwell model
- Radial–axial runner blade design using the coordinate slice technique
- Theoretical and experimental comparison between straight and curved continuous box girders
- Effect of the reinforcement ratio on the mechanical behaviour of textile-reinforced concrete composite: Experiment and numerical modeling
- Experimental and numerical investigation on composite beam–column joint connection behavior using different types of connection schemes
- Enhanced performance and robustness in anti-lock brake systems using barrier function-based integral sliding mode control
- Evaluation of the creep strength of samples produced by fused deposition modeling
- A combined feedforward-feedback controller design for nonlinear systems
- Effect of adjacent structures on footing settlement for different multi-building arrangements
- Analyzing the impact of curved tracks on wheel flange thickness reduction in railway systems
- Review Articles
- Mechanical and smart properties of cement nanocomposites containing nanomaterials: A brief review
- Applications of nanotechnology and nanoproduction techniques
- Relationship between indoor environmental quality and guests’ comfort and satisfaction at green hotels: A comprehensive review
- Communication
- Techniques to mitigate the admission of radon inside buildings
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Effect of short heat treatment on mechanical properties and shape memory properties of Cu–Al–Ni shape memory alloy”
- Special Issue: AESMT-3 - Part II
- Integrated fuzzy logic and multicriteria decision model methods for selecting suitable sites for wastewater treatment plant: A case study in the center of Basrah, Iraq
- Physical and mechanical response of porous metals composites with nano-natural additives
- Special Issue: AESMT-4 - Part II
- New recycling method of lubricant oil and the effect on the viscosity and viscous shear as an environmentally friendly
- Identify the effect of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on mechanical and microstructural characteristics of aluminum matrix composite produced by powder metallurgy technique
- Static behavior of piled raft foundation in clay
- Ultra-low-power CMOS ring oscillator with minimum power consumption of 2.9 pW using low-voltage biasing technique
- Using ANN for well type identifying and increasing production from Sa’di formation of Halfaya oil field – Iraq
- Optimizing the performance of concrete tiles using nano-papyrus and carbon fibers
- Special Issue: AESMT-5 - Part II
- Comparative the effect of distribution transformer coil shape on electromagnetic forces and their distribution using the FEM
- The complex of Weyl module in free characteristic in the event of a partition (7,5,3)
- Restrained captive domination number
- Experimental study of improving hot mix asphalt reinforced with carbon fibers
- Asphalt binder modified with recycled tyre rubber
- Thermal performance of radiant floor cooling with phase change material for energy-efficient buildings
- Surveying the prediction of risks in cryptocurrency investments using recurrent neural networks
- A deep reinforcement learning framework to modify LQR for an active vibration control applied to 2D building models
- Evaluation of mechanically stabilized earth retaining walls for different soil–structure interaction methods: A review
- Assessment of heat transfer in a triangular duct with different configurations of ribs using computational fluid dynamics
- Sulfate removal from wastewater by using waste material as an adsorbent
- Experimental investigation on strengthening lap joints subjected to bending in glulam timber beams using CFRP sheets
- A study of the vibrations of a rotor bearing suspended by a hybrid spring system of shape memory alloys
- Stability analysis of Hub dam under rapid drawdown
- Developing ANFIS-FMEA model for assessment and prioritization of potential trouble factors in Iraqi building projects
- Numerical and experimental comparison study of piled raft foundation
- Effect of asphalt modified with waste engine oil on the durability properties of hot asphalt mixtures with reclaimed asphalt pavement
- Hydraulic model for flood inundation in Diyala River Basin using HEC-RAS, PMP, and neural network
- Numerical study on discharge capacity of piano key side weir with various ratios of the crest length to the width
- The optimal allocation of thyristor-controlled series compensators for enhancement HVAC transmission lines Iraqi super grid by using seeker optimization algorithm
- Numerical and experimental study of the impact on aerodynamic characteristics of the NACA0012 airfoil
- Effect of nano-TiO2 on physical and rheological properties of asphalt cement
- Performance evolution of novel palm leaf powder used for enhancing hot mix asphalt
- Performance analysis, evaluation, and improvement of selected unsignalized intersection using SIDRA software – Case study
- Flexural behavior of RC beams externally reinforced with CFRP composites using various strategies
- Influence of fiber types on the properties of the artificial cold-bonded lightweight aggregates
- Experimental investigation of RC beams strengthened with externally bonded BFRP composites
- Generalized RKM methods for solving fifth-order quasi-linear fractional partial differential equation
- An experimental and numerical study investigating sediment transport position in the bed of sewer pipes in Karbala
- Role of individual component failure in the performance of a 1-out-of-3 cold standby system: A Markov model approach
- Implementation for the cases (5, 4) and (5, 4)/(2, 0)
- Center group actions and related concepts
- Experimental investigation of the effect of horizontal construction joints on the behavior of deep beams
- Deletion of a vertex in even sum domination
- Deep learning techniques in concrete powder mix designing
- Effect of loading type in concrete deep beam with strut reinforcement
- Studying the effect of using CFRP warping on strength of husk rice concrete columns
- Parametric analysis of the influence of climatic factors on the formation of traditional buildings in the city of Al Najaf
- Suitability location for landfill using a fuzzy-GIS model: A case study in Hillah, Iraq
- Hybrid approach for cost estimation of sustainable building projects using artificial neural networks
- Assessment of indirect tensile stress and tensile–strength ratio and creep compliance in HMA mixes with micro-silica and PMB
- Density functional theory to study stopping power of proton in water, lung, bladder, and intestine
- A review of single flow, flow boiling, and coating microchannel studies
- Effect of GFRP bar length on the flexural behavior of hybrid concrete beams strengthened with NSM bars
- Exploring the impact of parameters on flow boiling heat transfer in microchannels and coated microtubes: A comprehensive review
- Crumb rubber modification for enhanced rutting resistance in asphalt mixtures
- Special Issue: AESMT-6
- Design of a new sorting colors system based on PLC, TIA portal, and factory I/O programs
- Forecasting empirical formula for suspended sediment load prediction at upstream of Al-Kufa barrage, Kufa City, Iraq
- Optimization and characterization of sustainable geopolymer mortars based on palygorskite clay, water glass, and sodium hydroxide
- Sediment transport modelling upstream of Al Kufa Barrage
- Study of energy loss, range, and stopping time for proton in germanium and copper materials
- Effect of internal and external recycle ratios on the nutrient removal efficiency of anaerobic/anoxic/oxic (VIP) wastewater treatment plant
- Enhancing structural behaviour of polypropylene fibre concrete columns longitudinally reinforced with fibreglass bars
- Sustainable road paving: Enhancing concrete paver blocks with zeolite-enhanced cement
- Evaluation of the operational performance of Karbala waste water treatment plant under variable flow using GPS-X model
- Design and simulation of photonic crystal fiber for highly sensitive chemical sensing applications
- Optimization and design of a new column sequencing for crude oil distillation at Basrah refinery
- Inductive 3D numerical modelling of the tibia bone using MRI to examine von Mises stress and overall deformation
- An image encryption method based on modified elliptic curve Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol and Hill Cipher
- Experimental investigation of generating superheated steam using a parabolic dish with a cylindrical cavity receiver: A case study
- Effect of surface roughness on the interface behavior of clayey soils
- Investigated of the optical properties for SiO2 by using Lorentz model
- Measurements of induced vibrations due to steel pipe pile driving in Al-Fao soil: Effect of partial end closure
- Experimental and numerical studies of ballistic resistance of hybrid sandwich composite body armor
- Evaluation of clay layer presence on shallow foundation settlement in dry sand under an earthquake
- Optimal design of mechanical performances of asphalt mixtures comprising nano-clay additives
- Advancing seismic performance: Isolators, TMDs, and multi-level strategies in reinforced concrete buildings
- Predicted evaporation in Basrah using artificial neural networks
- Energy management system for a small town to enhance quality of life
- Numerical study on entropy minimization in pipes with helical airfoil and CuO nanoparticle integration
- Equations and methodologies of inlet drainage system discharge coefficients: A review
- Thermal buckling analysis for hybrid and composite laminated plate by using new displacement function
- Investigation into the mechanical and thermal properties of lightweight mortar using commercial beads or recycled expanded polystyrene
- Experimental and theoretical analysis of single-jet column and concrete column using double-jet grouting technique applied at Al-Rashdia site
- The impact of incorporating waste materials on the mechanical and physical characteristics of tile adhesive materials
- Seismic resilience: Innovations in structural engineering for earthquake-prone areas
- Automatic human identification using fingerprint images based on Gabor filter and SIFT features fusion
- Performance of GRKM-method for solving classes of ordinary and partial differential equations of sixth-orders
- Visible light-boosted photodegradation activity of Ag–AgVO3/Zn0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 supported heterojunctions for effective degradation of organic contaminates
- Production of sustainable concrete with treated cement kiln dust and iron slag waste aggregate
- Key effects on the structural behavior of fiber-reinforced lightweight concrete-ribbed slabs: A review
- A comparative analysis of the energy dissipation efficiency of various piano key weir types
- Special Issue: Transport 2022 - Part II
- Variability in road surface temperature in urban road network – A case study making use of mobile measurements
- Special Issue: BCEE5-2023
- Evaluation of reclaimed asphalt mixtures rejuvenated with waste engine oil to resist rutting deformation
- Assessment of potential resistance to moisture damage and fatigue cracks of asphalt mixture modified with ground granulated blast furnace slag
- Investigating seismic response in adjacent structures: A study on the impact of buildings’ orientation and distance considering soil–structure interaction
- Improvement of porosity of mortar using polyethylene glycol pre-polymer-impregnated mortar
- Three-dimensional analysis of steel beam-column bolted connections
- Assessment of agricultural drought in Iraq employing Landsat and MODIS imagery
- Performance evaluation of grouted porous asphalt concrete
- Optimization of local modified metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete by Taguchi method
- Effect of waste tire products on some characteristics of roller-compacted concrete
- Studying the lateral displacement of retaining wall supporting sandy soil under dynamic loads
- Seismic performance evaluation of concrete buttress dram (Dynamic linear analysis)
- Behavior of soil reinforced with micropiles
- Possibility of production high strength lightweight concrete containing organic waste aggregate and recycled steel fibers
- An investigation of self-sensing and mechanical properties of smart engineered cementitious composites reinforced with functional materials
- Forecasting changes in precipitation and temperatures of a regional watershed in Northern Iraq using LARS-WG model
- Experimental investigation of dynamic soil properties for modeling energy-absorbing layers
- Numerical investigation of the effect of longitudinal steel reinforcement ratio on the ductility of concrete beams
- An experimental study on the tensile properties of reinforced asphalt pavement
- Self-sensing behavior of hot asphalt mixture with steel fiber-based additive
- Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete deep beams reinforced by basalt fibers
- Optimizing asphalt binder performance with various PET types
- Investigation of the hydraulic characteristics and homogeneity of the microstructure of the air voids in the sustainable rigid pavement
- Enhanced biogas production from municipal solid waste via digestion with cow manure: A case study
- Special Issue: AESMT-7 - Part I
- Preparation and investigation of cobalt nanoparticles by laser ablation: Structure, linear, and nonlinear optical properties
- Seismic analysis of RC building with plan irregularity in Baghdad/Iraq to obtain the optimal behavior
- The effect of urban environment on large-scale path loss model’s main parameters for mmWave 5G mobile network in Iraq
- Formatting a questionnaire for the quality control of river bank roads
- Vibration suppression of smart composite beam using model predictive controller
- Machine learning-based compressive strength estimation in nanomaterial-modified lightweight concrete
- In-depth analysis of critical factors affecting Iraqi construction projects performance
- Behavior of container berth structure under the influence of environmental and operational loads
- Energy absorption and impact response of ballistic resistance laminate
- Effect of water-absorbent polymer balls in internal curing on punching shear behavior of bubble slabs
- Effect of surface roughness on interface shear strength parameters of sandy soils
- Evaluating the interaction for embedded H-steel section in normal concrete under monotonic and repeated loads
- Estimation of the settlement of pile head using ANN and multivariate linear regression based on the results of load transfer method
- Enhancing communication: Deep learning for Arabic sign language translation
- A review of recent studies of both heat pipe and evaporative cooling in passive heat recovery
- Effect of nano-silica on the mechanical properties of LWC
- An experimental study of some mechanical properties and absorption for polymer-modified cement mortar modified with superplasticizer
- Digital beamforming enhancement with LSTM-based deep learning for millimeter wave transmission
- Developing an efficient planning process for heritage buildings maintenance in Iraq
- Design and optimization of two-stage controller for three-phase multi-converter/multi-machine electric vehicle
- Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of Al1050/Al2O3/Gr composite processed by forming operation ECAP
- Calculations of mass stopping power and range of protons in organic compounds (CH3OH, CH2O, and CO2) at energy range of 0.01–1,000 MeV
- Investigation of in vitro behavior of composite coating hydroxyapatite-nano silver on 316L stainless steel substrate by electrophoretic technic for biomedical tools
- A review: Enhancing tribological properties of journal bearings composite materials
- Improvements in the randomness and security of digital currency using the photon sponge hash function through Maiorana–McFarland S-box replacement
- Design a new scheme for image security using a deep learning technique of hierarchical parameters
- Special Issue: ICES 2023
- Comparative geotechnical analysis for ultimate bearing capacity of precast concrete piles using cone resistance measurements
- Visualizing sustainable rainwater harvesting: A case study of Karbala Province
- Geogrid reinforcement for improving bearing capacity and stability of square foundations
- Evaluation of the effluent concentrations of Karbala wastewater treatment plant using reliability analysis
- Adsorbent made with inexpensive, local resources
- Effect of drain pipes on seepage and slope stability through a zoned earth dam
- Sediment accumulation in an 8 inch sewer pipe for a sample of various particles obtained from the streets of Karbala city, Iraq
- Special Issue: IETAS 2024 - Part I
- Analyzing the impact of transfer learning on explanation accuracy in deep learning-based ECG recognition systems
- Effect of scale factor on the dynamic response of frame foundations
- Improving multi-object detection and tracking with deep learning, DeepSORT, and frame cancellation techniques
- The impact of using prestressed CFRP bars on the development of flexural strength
- Assessment of surface hardness and impact strength of denture base resins reinforced with silver–titanium dioxide and silver–zirconium dioxide nanoparticles: In vitro study
- A data augmentation approach to enhance breast cancer detection using generative adversarial and artificial neural networks
- Modification of the 5D Lorenz chaotic map with fuzzy numbers for video encryption in cloud computing
- Special Issue: 51st KKBN - Part I
- Evaluation of static bending caused damage of glass-fiber composite structure using terahertz inspection

