Abstract
T-node tensile specimens, including both rectangular steel pipes and rectangular steel pipe concrete configurations, were developed based on the results of tensile tests conducted on concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe T-nodes. The specimens incorporated Perfobond Leiste (PBL) stiffeners, with concrete-filled rectangular steel pipes used for the main pipes and square steel pipes as the branch (stub) pipes. The fatigue performance of the concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe T-nodes under tensile loading, in-plane bending, and out-of-plane bending was investigated using PBL stiffeners as internal reinforcement. To determine the stress concentration parameters of the branch pipes, a nonlinear finite element analysis was performed using ABAQUS (a finite element analysis software suite developed by Dassault Systèmes) software. The analysis adopted a width-to-thickness ratio of 0.4 for the branch pipe and 27 for the main pipe. The results indicate that the hot spot locations of the PBL-stiffened concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe T-nodes are consistent with those of both the unstiffened rectangular steel pipe nodes and the concrete-filled nodes. Furthermore, the stress concentration factor of the PBL-stiffened node is significantly lower than that of the unstiffened steel pipe node, indicating markedly improved fatigue resistance.
1 Introduction
Open-cell steel plates, also known as Perfobond Leiste (PBL) stiffening ribs, are embedded longitudinally along the inner wall of steel pipes to form PBL-stiffened steel pipe concrete structures, which are subsequently filled with concrete [1,2]. These ribs serve dual functions: providing internal stiffening and acting as shear connectors. Their inclusion enhances the bond strength at the steel–concrete interface, reduces relative slip, and prevents interface spalling in the node area – thereby improving the tensile stiffness and load-carrying capacity of the node.
Previous studies have extensively investigated the stress concentration factors (SCFs) of T-welded rectangular steel pipe nodes [3], offering empirical formulas and identifying likely hot spot locations. It has been shown that filling steel pipes with concrete can significantly reduce SCFs – by 15–80% – and increase fatigue life by approximately 1.7 times compared to hollow steel pipe nodes [4]. Research also suggests that while the S–N curve of steel pipe nodes may still be applicable, hot spot stresses must be carefully managed [5]. Additional tests confirm the superior fatigue performance of steel pipe concrete nodes under axial and bending loads, with more uniform stress distributions than their hollow counterparts [6].
Building on this foundation, this study focuses on T-node stubs for rectangular steel pipe concrete, incorporating PBL stiffeners. Through tensile experiments, we compare stress characteristics among rectangular steel pipe nodes, concrete-filled nodes, and PBL-stiffened nodes. The results reveal that PBL stiffeners significantly reduce axial stress and enhance uniformity of stress distribution at the node root. This article further analyzes changes in hot spot locations and SCFs across different node configurations, and evaluates the fatigue resistance of the proposed PBL-stiffened structure. The findings aim to provide technical support for the application of such nodes in steel pipe concrete bridge engineering [7,8].
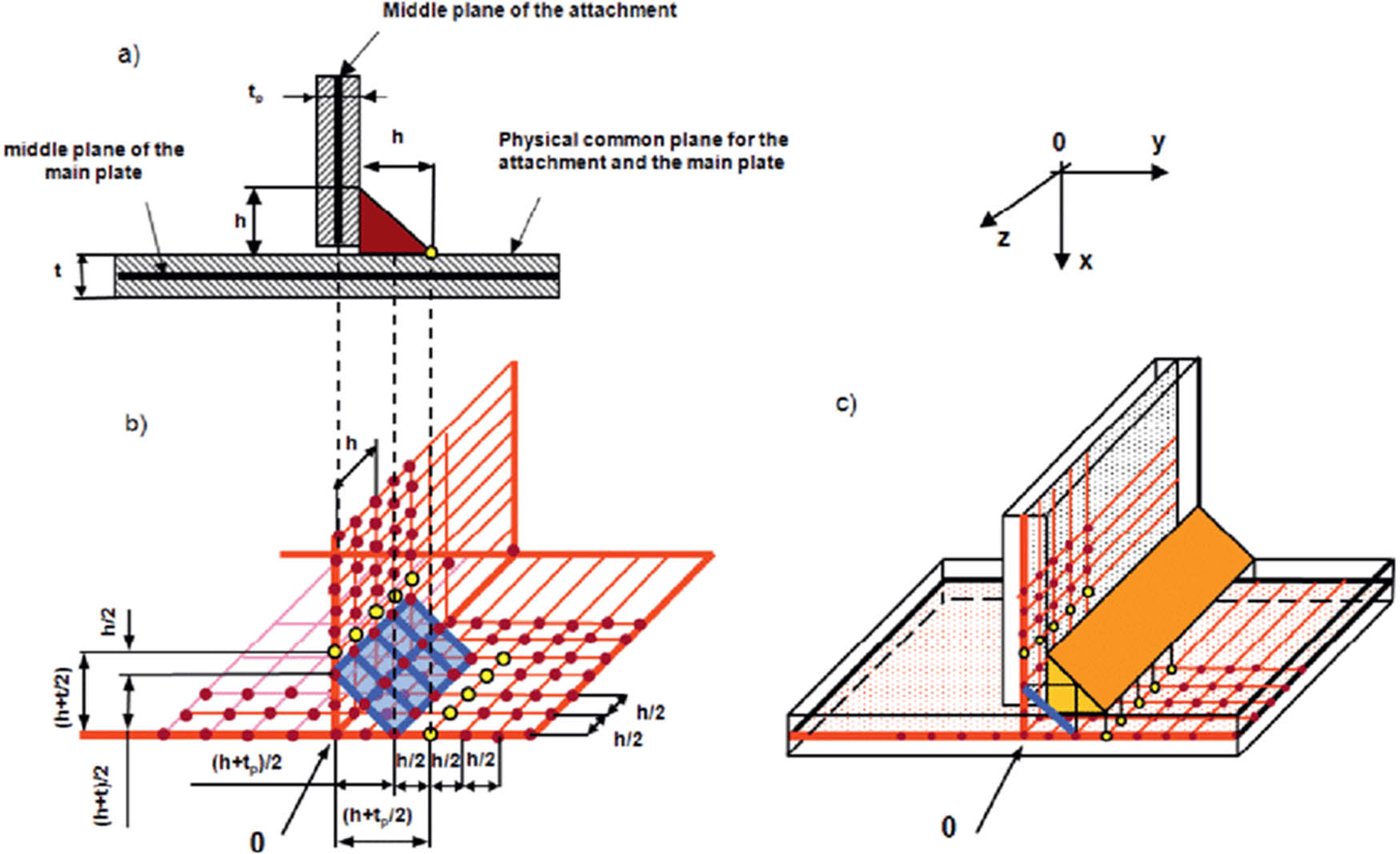
The main steel pipe’s width/thickness ratio, the branch main pipe’s width/thickness ratio, the concrete filling inside the pipe, the positioning of the PBL stiffening ribs, and other factors are some of the many variables that affect the fatigue performance of steel pipe T-nodes [9]. In order to examine the impact of PBL stiffening ribs on the SCF of the uneven width T-node, this study develops the tensile test of PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete node based on the tensile test of T-node designed by Packer. The literature is in agreement with the main pipe’s constructional dimensions, material parameters, and branch pipe width. β = 0.4 is the width ratio of the branch pipe to the main pipe. The test reported in the literature states that the wall thickness of the branch pipe is adjusted to 6.32 mm, which is thicker than the wall thickness of the main pipe (4.74 mm), in order to prevent axial tension damage to the branch pipe [10]. This test is intended to analyze the node’s bearing capacity. The branch pipe wall’s thickness is decreased to 4.74 mm, which, in keeping with the test’s goals as outlined in this document, is the same thickness as the main pipe wall. The yield strength of the main pipe and the branch pipe steel is f y = 400 MPa, the ultimate tensile strength is f u = 544 MPa, and the compressive strength of the concrete cylinder is f c = 30.0 MPa. Figure 1 displays the specimen structure, while Table 1 displays the precise design parameters.
Test piece construction form.
Specimen parameters
| Data sources | Test piece number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [10] | T1 | 125.6 | 174.5 | 4.12 | 50.1 | 52.2 | 4.21 | 0.32 | 25 |
| T1C | 125.6 | 174.5 | 4.12 | 50.1 | 52.2 | 4.21 | 0.32 | 25 | |
| This article | T1PLB | 125.6 | 174.5 | 4.12 | 50.1 | 52.2 | 4.21 | 0.32 | 25 |
Table 1 summarizes the geometric parameters and data sources of different specimens, including T1 and T1C from the referenced literature and T1PLB from this article. All three specimens share identical main geometric dimensions: main steel pipe outer diameter of 125.6 mm, side length of 174.5 mm, wall thickness of 4.12 mm; branch pipe outer diameter of 50.1 mm, side length of 52.2 mm, wall thickness of 4.21 mm; with a width-to-thickness ratio of 0.32; and a PBL stiffening rib spacing of 25 mm. This indicates that the T1PLB specimen in this study maintains consistent geometry with previous research but mainly differs in structural details such as the addition of PBL stiffeners for comparative analysis [11].
2 Numerical simulation
The branch pipe’s connection welds and the contact nonlinearity at the steel–concrete interface are taken into consideration in this work because they have a substantial impact on the node’s stress concentration coefficient. Since the branch pipe of the T-node encounters moderate amounts of stress under tensile, in-plane, and out-of-plane bending when both are in an elastic operating condition, material and geometrical nonlinearities do not need to be taken into consideration in the model.
The loading patterns of specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL are displayed in Figure 2. Figure 2(a) applies an axial tensile load P of 1 MPa to the specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL; Figure 2(b) shows that the specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL experience an in-plane bending moment Min, which results in a tensile stress of 1 MPa in the steel pipe outside the stub’s root; and Figure 2(c) shows that the specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL experience an out-of-plane bending moment that acts on them and produces a tensile stress of 1 MPa in the steel pipe outside the root of the mouth movement.
Specimen loading mode.
2.1 Steel and concrete structures’ relationship
In steel–concrete composite structures, the interaction between steel and concrete components plays a crucial role in determining the overall mechanical behavior and load-bearing capacity. Both steel and concrete materials are typically modeled using the linear elastic stress–strain relationship under service load conditions, which assumes a proportional and reversible response between stress and strain within the elastic limit.
For steel, this linear elastic behavior is characterized by a relatively high modulus of elasticity and a well-defined yield point, allowing for accurate prediction of deformation under applied loads. Concrete, although more brittle and heterogeneous than steel, is often idealized as a linear elastic material before cracking occurs. The linear elastic assumption simplifies the analysis of initial stiffness and stress distribution in composite members.
The compatibility of deformation between steel and concrete is ensured through effective bonding or mechanical connectors, which transfer stresses across the interface. This interaction allows the composite structure to benefit from the high tensile strength and ductility of steel, combined with the compressive strength and stiffness of concrete.
However, it is important to note that beyond the elastic range, concrete exhibits nonlinear behavior due to cracking and crushing, while steel shows plastic deformation. Thus, for ultimate strength or failure analyses, more advanced constitutive models are required to capture the inelastic behavior of both materials and their interaction mechanisms.
In summary, the linear elastic stress–strain relationship provides a fundamental and practical basis for modeling steel and concrete components in composite structures during the initial loading stages, facilitating structural design and preliminary performance evaluation.
2.2 Modeling of the steel–concrete interface contact
The master surface at the steel–concrete interface is represented by the normal contact and tangential bond–slip contact models, which is the concrete, and the slave surfaces, which are the steel pipe and PBL stiffening ribs, which have more stiffness. In the normal contact between the steel box and concrete interface, which adheres to the “hard” contact paradigm, the contact surface transmits the interfacial pressure p. According to the Coulomb friction model, the tangential contact occurs when the interfacial shear stress
Contact model.
2.3 Selection of cell types and model meshing
The ABAQUS simulation model employs different element types for various components: the steel pipe and PBL stiffening ribs are modeled using S4R four-node reduced integration shell elements and C3D8R eight-node reduced integration hexahedral elements, respectively. The concrete filled inside the rectangular steel pipe is also modeled using these element types. However, due to the complexity of meshing hexahedral elements and the relatively minor impact of stress accuracy in the concrete region – attributed to the presence of PBL mortise and tenon connectors within the PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe – this study adopts C3D4 four-node tetrahedral elements for the concrete simulation. The end plates are represented by rigid surfaces. Figure 4 illustrates the meshing of the concrete T-node in the PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe. To minimize mesh transition issues, a sweep meshing technique is applied throughout the model.
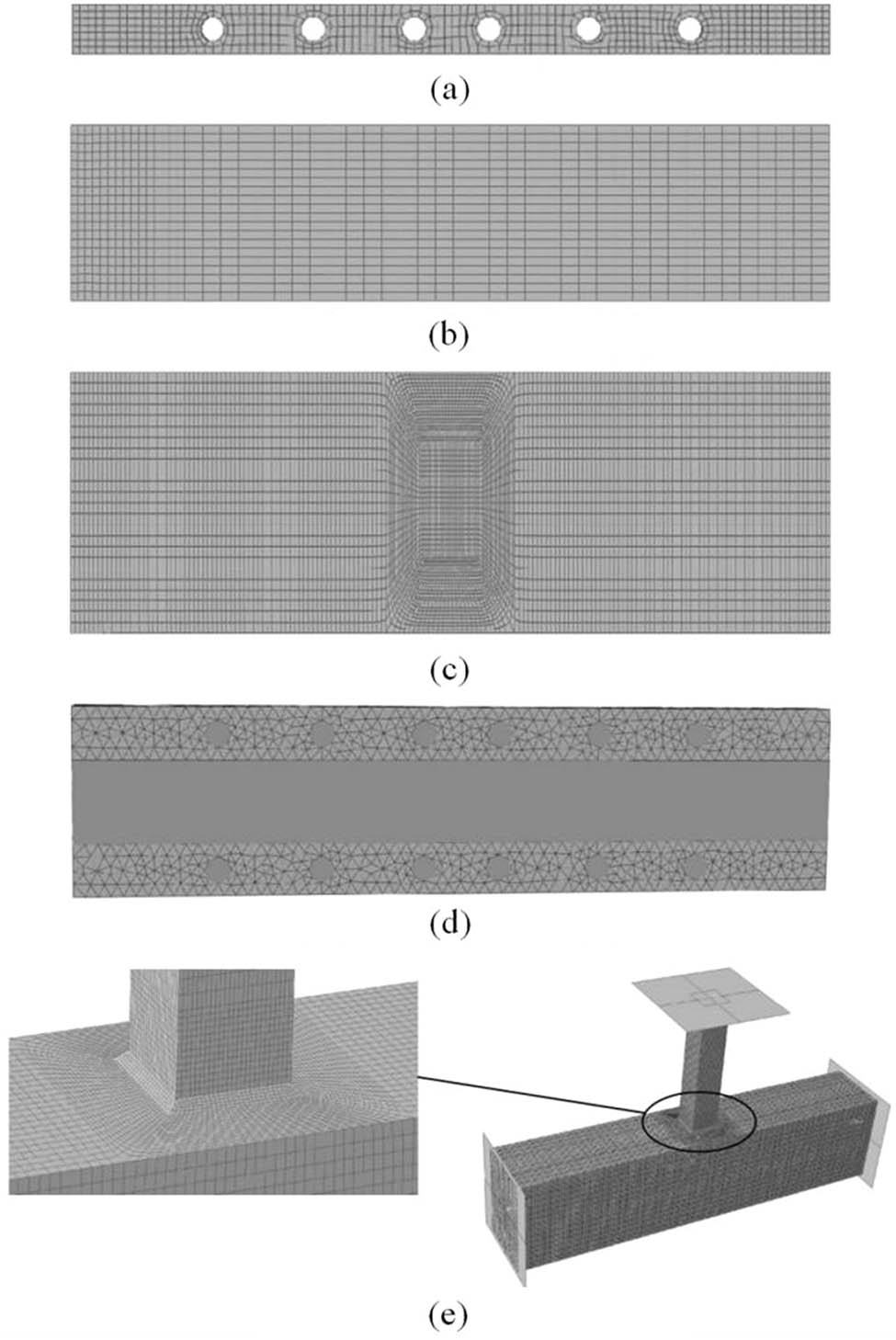
Grid division: (a) PBL stiffener, (b) branch pipe steel pipe, (c) main steel pipe, (d) concrete in the pipe, and (e) junction model.
2.4 Welded seam simulation
Using a S8R6 thick shell unit, the fillet weld on the branch main connection is simulated. The simulation of the weld shell unit is depicted in Figure 5, where
Simulation of the welded shell unit.
2.5 Boundary conditions
The end plate, branch pipe, and main pipe are all bounded. Its center is where the reference points RP-1, RP-2, and RP-3 are located, and they are connected to it. The x, y, and z directions of translational freedom as well as the x and z directions of rotational freedom delimited the RP-1 and RP-2 reference points. The centralized load F is applied to reference point RP-3 in accordance with the force requirements. The following formulas can be used to calculate the equivalent centralized loads for the branch pipe’s axial tensile, in-face bending, and out-of-face bending:
where
3 Results
3.1 Estimating where hot spots are most likely to be
Finding the hot spot’s location is the first step in applying the hot spot stress method to analyze T-nodes’ fatigue performance. The German specification CIDECT 8 provides the potential locations of hot spots in rectangular steel pipe nodes along with the appropriate stress concentration parameters [15]. The location of the hot spot is thought to be consistent with that of the rectangular steel pipe node, when the stress concentration coefficient of the rectangular steel pipe concrete T-node with bending in the branch pipe’s face and axial force in the branch pipe is studied, as shown by the line ABCD in Figure 6. The location of the hot spot of the rectangular steel pipe concrete node of the PBL stiffener can be ascertained through examining the stress distribution law perpendicular to the direction of the weld seam; in other words, the maximum stress perpendicular to the weld direction is considered to be the hot spot stress rather than the maximum primary stress [16].
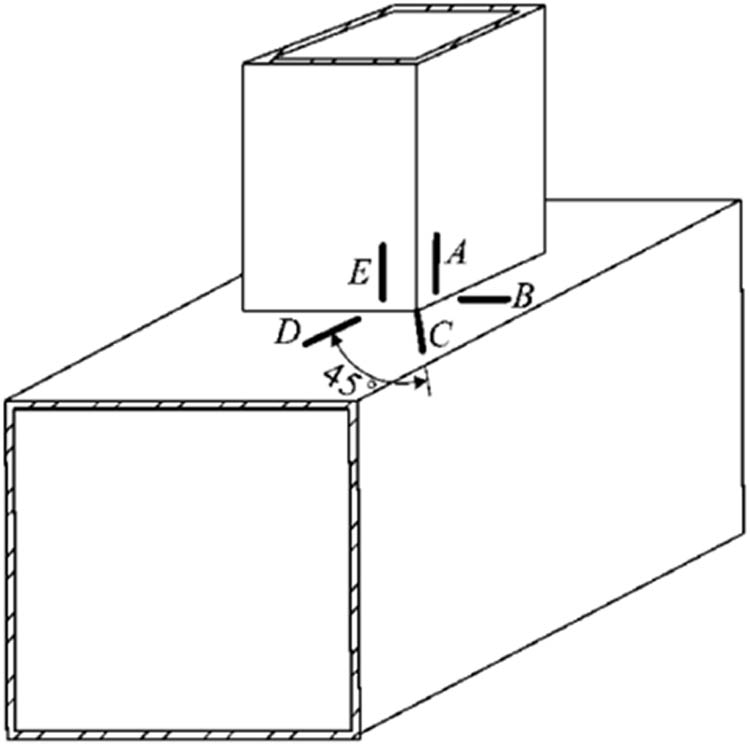
Location of hot spots.
The stress contour distributions are illustrated in Figure 6. When the branch pipe is subjected to tension, the stress distribution in the T-node, evaluated perpendicular to the weld direction, reveals notable differences. By comparing specimens T1 and T2, it is observed that under axial loading on the branch pipe, the stress level on the branch pipe wall plate parallel to the main pipe’s axial direction is higher than that on the wall plate perpendicular to it in specimens T1C and T1PBL. For the main pipe, the highest stresses occur along line segments B or C, whereas for the branch pipe, the maximum stresses are concentrated at line segments A or E.
During in-plane bending of the branch pipe, comparison of specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL shows that the branch pipe’s maximum stresses consistently appear at line segments A or E, while the main pipe’s maximum stresses occur at line segments C or D.
Under out-of-plane bending of the branch pipe, the stress distribution comparison also indicates that the main pipe’s peak stresses are located at line segments B or C, with the branch pipe’s maximum stresses at line segments A or E.
These observations demonstrate that, in PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe nodes, the locations of stress hot spots align closely with those found in both rectangular steel pipe nodes and concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe nodes, confirming a consistent pattern of stress concentration across these node types.
3.2 SCF comparison
The branch pipe in this study has a nominal stress of 1 MPa, and the SCF is the hot spot stress. The hot spot stress of the main and branch pipes divided by their nominal stress is known as the SCF. The rectangular steel pipe and rectangular steel pipe concrete’s hot spot stress concentration coefficient, and PBL reinforced rectangular steel pipe concrete node is determined by using the quadratic extrapolation method [17].
Figure 7 illustrates the SCFs at line segments A, B, C, D, and E for each specimen under axial tension of the stub. The SCF of specimen T1-CIDECT 8 is calculated according to the German CIDECT 8 specification [18].
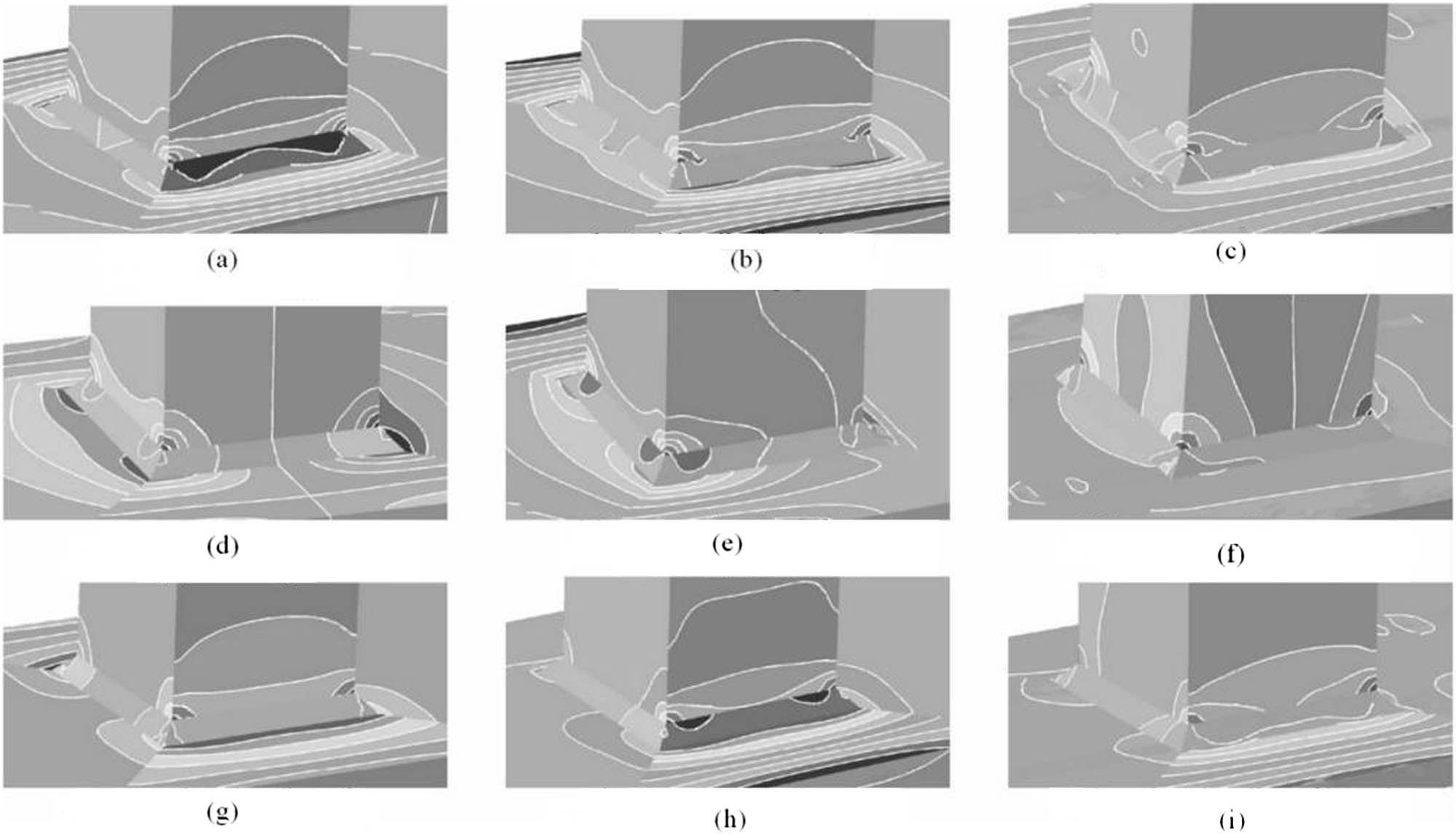
Stress contours: (a) axial pull of specimen T1 branch pipe, (b) axial pull of specimen T1C branch pipe, (c) axial pull of specimen T1PBL branch pipe, (d) in-plane bending of branch pipe T1 of specimen, (e) in-plane bending of branch pipe T1C of specimen, (f) in-plane bending of branch pipe T1PBL of specimen, (g) out-plane bending of branch pipe T1 of specimen, (h) out-plane bending of branch pipe T1C of specimen, and (i) out-plane bending of branch pipe T1PBL of specimen.
Figure 8 presents a comparative analysis of SCFs at various hotspot locations for different pipe configurations during axial loading. Four configurations are included: T1-CIDECT, T1, T1C, and T1PBL. The SCF values for each configuration at different hotspots are summarized as follows:
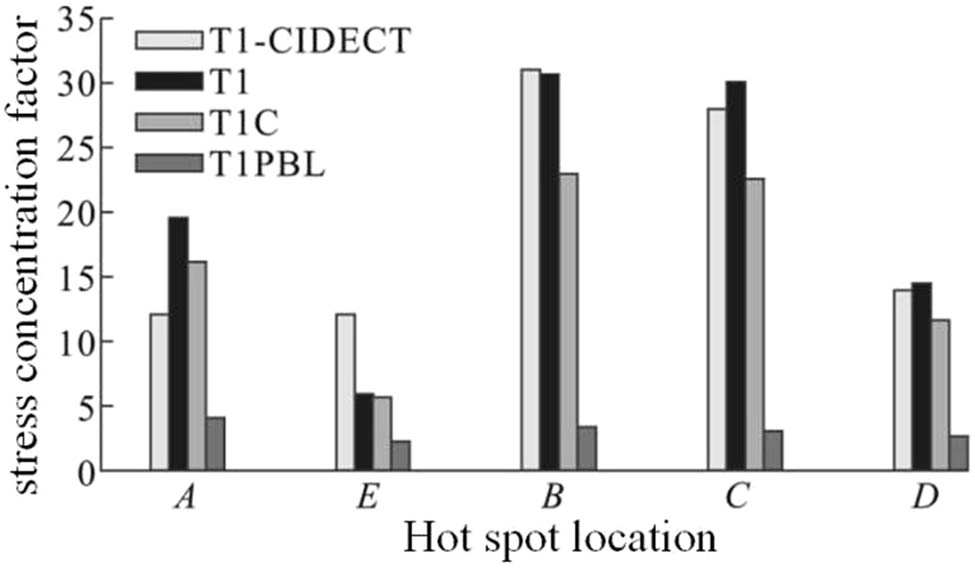
Comparative analysis of SCF in pipe shaft pulling with branches.
Location A: At hotspot A, the SCFs of T1 and T1-CIDECT are relatively high, whereas those of T1C and T1PBL are lower. This indicates that T1 and T1-CIDECT configurations are more prone to stress concentration at this location.
Location E: Only T1-CIDECT exhibits a significant increase in SCF at position E, while the other configurations show comparatively lower values. This suggests that T1-CIDECT experiences greater stress concentration at this point, whereas the other configurations are less affected.
Location B: Position B has the highest SCF among all hotspots. The SCFs for T1 and T1C are significantly higher than those for T1-CIDECT and T1PBL, indicating that this location is especially susceptible to stress concentration in the T1 and T1C configurations and may represent a structural weak point.
Location C: The SCFs at position C are the second highest after position B. At this location, T1 and T1PBL exhibit relatively higher SCFs, while T1-CIDECT and T1C show somewhat lower values. This suggests that T1 and T1PBL configurations may also experience notable stress concentrations here.
Location D: At position D, all configurations display relatively low SCFs, though T1PBL shows a slightly higher value compared to the others. This indicates that the T1PBL configuration may be subjected to slightly greater stress at this location.
The calculated values of the SCF of the main pipe at line segments B, C, and D are close to the numerical simulation results in this article. It demonstrates the accuracy of the numerical simulation approach used in this work. The computed values of the branch pipe’s SCF at line segments A and E, as shown in Figure 8, are quite similar to the average value computed in this work. The SCF of the rectangular steel pipe concrete node is smaller than that of the rectangular steel pipe node, which is consistent with the findings in the literature [6]. The SCF of the PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete node is significantly smaller than that of the rectangular steel pipe concrete node. These results come from comparing the SCFs of specimens T1, T1C, and T1PBL at the hot spot locations. The maximum SCFs for branch pipes of rectangular steel pipe, rectangle steel pipe concrete, and PBL enhanced rectangular steel pipe concrete nodes all appeared at line segment A, but the maximum SCFs for main pipes all showed at line segment B.
Figure 9 shows a comparative analysis of the SCF at different hot spots during pipe bending for three different configurations: T1, T1C, and T1PBL. The stress concentration at different hot spots for each configuration is shown below:
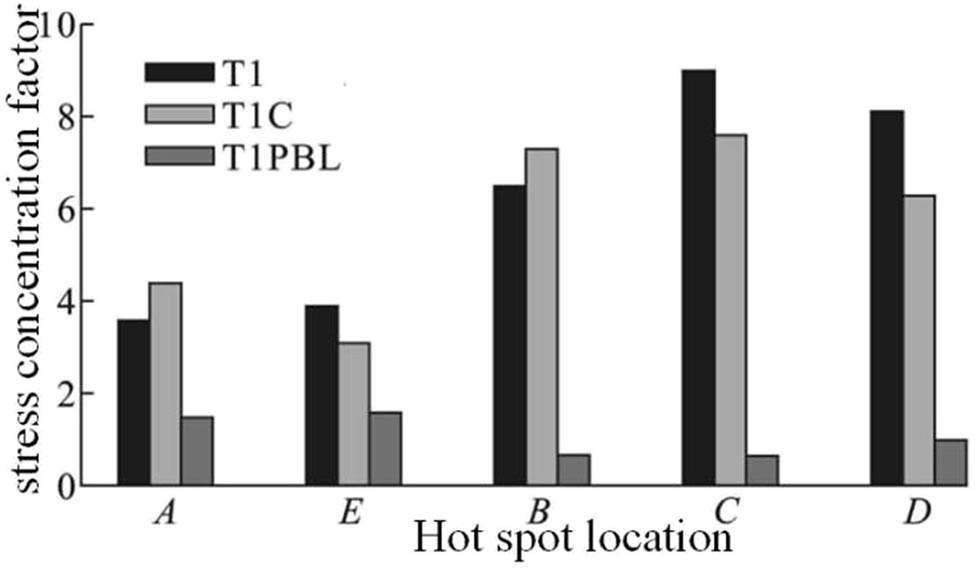
Comparison of stress concentration variables for branch pipe bending in the face.
Position A: At position A, the T1 configuration has the highest SCF, followed by T1C and T1PBL. This indicates that at position A, the T1 configuration is most prone to stress concentration, while the T1PBL configuration has less stress concentration [19].
Position E: At this position, the T1C configuration has a higher SCF than the other two configurations, the T1 has a slightly lower SCF, and the T1PBL has the lowest SCF. This indicates that the T1C configuration has the most significant stress concentration at Position E.
Position B: The SCF values for Position B are relatively high, and the SCFs of the T1 and T1PBL configurations are close to each other, while the SCF of T1C is relatively low, indicating that the T1 and T1PBL configurations have a high degree of stress concentration at this position.
Position C: At position C, the SCF of the T1 configuration is significantly higher than the other configurations, reaching the highest value in the figure, while the SCF of T1C and T1PBL are relatively low. This indicates that at position C, the T1 configuration has the most pronounced stress concentration and is a potential weak point [20–22].
Position D: The SCF value of position D is relatively low, the SCF value of T1C is slightly higher, and the SCF values of T1 and T1PBL are closer, indicating that the stress concentration of each configuration at this position is relatively small.
In summary, Figure 9 shows that there is a significant difference in the distribution of stress concentration at each hot spot in different configurations during pipe bending. In particular, the T1 configuration has the most significant stress concentration at position C and position B, while the T1PBL and T1C configurations have smaller stress concentrations at most positions. These data are helpful in selecting a reasonable configuration to reduce the stress concentration at a particular location.
When the branch pipe is bent out of face, Figure 10 shows the SCFs of each specimen at line segments A, B, C, D, and E. Figure 10 shows that the rectangular steel pipe concrete node’s SCF is lower than the rectangular steel pipe node’s; additionally, the PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete node’s SCF is significantly lower than the rectangular steel pipe node’s. Line segment B displayed the maximum SCF for the rectangular steel pipe main pipe, rectangular steel pipe concrete, and PBL-stiffened rectangle steel pipe concrete nodes. Line segment E displayed the maximum SCF for the branch pipe.
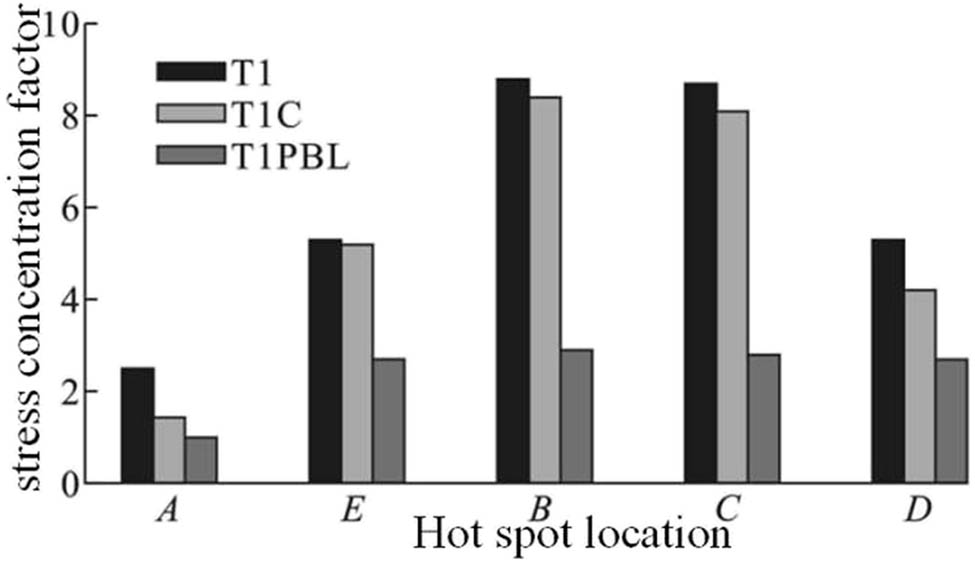
Compares the stress concentration parameters when bending a branch pipe outside of its face.
In conclusion, when the branch pipe is subjected to axial tension – as opposed to in-plane or out-of-plane bending – the SCFs for rectangular steel pipe nodes, concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe nodes, and PBL-stiffened concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe nodes are all significantly increased. However, compared to hollow rectangular steel pipe nodes, the SCF of concrete-filled nodes is notably reduced, indicating that concrete infill helps to alleviate local stress concentration. Furthermore, the incorporation of PBL stiffening ribs in concrete-filled rectangular steel pipe nodes leads to a substantial improvement in fatigue resistance and a further reduction in SCF, thereby enhancing the overall structural performance of the node.
Although these findings are primarily based on nonlinear finite element simulations, they demonstrate clear mechanical advantages of the proposed node configuration. To enhance the credibility and engineering applicability of the results, subsequent physical experiments and validation tests are planned. These future efforts will provide empirical evidence to support the numerical findings, verify the fatigue behavior under real-world loading conditions, and further promote the use of PBL-stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete nodes in structural applications such as bridge engineering and high-performance composite joints.
4 Conclusion
In summary, when the branch pipe is subjected to axial tension, the stress concentration coefficients of the rectangular steel pipe, steel pipe concrete node, and PBL-stiffened steel pipe concrete node increase significantly compared with the in-plane moment and out-of-plane moment conditions. Compared with the hollow rectangular steel pipe node, the filling of concrete can effectively reduce the degree of stress concentration; the further introduction of PBL stiffened ribs is more significant in improving the fatigue performance of the node, effectively reducing the stress concentration coefficient, and improving the overall load carrying capacity and fatigue life of the node.
This study is mainly based on nonlinear finite element simulation analysis, which has shown the advantages of PBL stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete nodes in mechanical properties. In order to verify the reliability of the numerical simulation and improve the engineering applicability, solid tests or validation experiments will be carried out to obtain more convincing empirical data to further promote the application of this node form in practical engineering.
In addition, considering the excellent fatigue performance and structural adaptability of this node form, it is recommended to promote the application of this node form in steel–tube–concrete bridge structures, especially for complex stress members or fatigue-sensitive parts, such as shaped nodes, diagonal nodes, cantilever connection zones, and transition nodes between the bridge deck system and the main structure. Future research can further explore the adaptability and construction optimization strategy of this node form under different structural forms and loading conditions, so as to enhance its application potential and promotion value in bridges and other large-span structural systems.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Chunyan Jia and Mengyang Lu designed the research together. Chunyan Jia conducted the main experiments, collected and analyzed the data, and drafted the initial manuscript. Mengyang Lu assisted in data validation, participated in result interpretation, and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual content. Both authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors have accepted responsibility for the entire content of this manuscript and approved its submission.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Lu T, Li J, Xiao E, Zhong H, Deng J, Ma L, et al. Assemblage of root-associated microbiome contributes to disparate performance of two rice genotypes under aluminum stress. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025;220:109539.10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109539Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Squitti R, Pal A, De Luca A, Rizzo G, Rongioletti M, Tondolo V. Exchangeable copper excess and zinc deficiency in the serum of patients with colorectal cancer. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025;203(7):3548–58.10.1007/s12011-024-04431-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Chunsheng W, Chuanzhong M, Jialei C, Hao QU, Wenchang W, Qinfeng DI. Analysis of secondary makeup characteristics of drill collar joint and prediction of downhole equivalent impact torque of well SDTK1. Pet Explor Dev. 2024;51(3):697–705.10.1016/S1876-3804(24)60498-2Search in Google Scholar
[4] Diao Y, He S, Wang Y, Tu L. Experimental and numerical investigations on stress concentration factors of concrete filled steel tube X-joints. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):11415.10.1038/s41598-024-62312-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Ahmadian V, Aval SBB, Noori M, Wang T, Altabey WA. Comparative study of a newly proposed machine learning classification to detect damage occurrence in structures. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2024;127:107226.10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107226Search in Google Scholar
[6] Takeshita M, Tanaka A, Yoshida H, Nakamura I, Shibata Y, Hata S, et al. Effect of the xanthine oxidase inhibitor, febuxostat, on WBC count in asymptomatic hyperuricemia: subanalysis of the randomized PRIZE study. J Atheroscler Thrombosis. 2024;31(6):864–75.10.5551/jat.64574Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Zhang C, Roh B, Shan G. Poster: Dynamic clustered federated framework for multi-domain network anomaly detection. In Companion of the 19th International Conference on emerging Networking Experiments and Technologies; 2023. p. 71–2.10.1145/3624354.3630086Search in Google Scholar
[8] Karam MS, Nakamura H, Yamamoto Y, Tahir M, Hameed R. Numerical evaluation of the internal fracture mechanism of the single PBL shear connector considering the effects of position and strength of the transverse rebar. Struct Concr. 2024;25(4):2759–83.10.1002/suco.202300473Search in Google Scholar
[9] Xue C, Huang H, Jia Q. Shear mechanism of a novel SFCBs-reinforced composite shear connector: experimental, theoretical investigations and numerical model. Materials. 2024;17(14):3508.10.3390/ma17143508Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Yang S, Hong Y, Pu Q, Ling X, Chen X, Wu K. Mechanical behaviour of steel–concrete joints in railway rigid frame-continuous composite system bridge. J Constr Steel Res. 2024;222:108946.10.1016/j.jcsr.2024.108946Search in Google Scholar
[11] Luo C, Wang X, Xu YJ, Jia S, Liu Z, Mao B, et al. Synergistic identification of hydrogeological parameters and pollution source information for groundwater point and areal source contamination based on machine learning surrogate-artificial hummingbird algorithm. EGUsphere. 2025;2025:1–54.10.5194/egusphere-2025-2083Search in Google Scholar
[12] Noda M, Kikuchi C, Hori E, Iwao T, Nagami C, Takeuchi M, et al. Effect of anagliptin on vascular injury in the femoral artery of type 2 diabetic rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2024;47(1):204–12.10.1248/bpb.b23-00706Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Wang B, Wang C, Yin S, Du J, Yang X. Performance degradation of corrugated steel webs and concrete flange T-PBL connectors under fatigue loading. Int J Civ Eng. 2025;23(3):403–17.10.1007/s40999-024-01055-zSearch in Google Scholar
[14] Du Y, Yu Z, Chen Y, Ma N, Wang R. Experimental study on the force mechanism of internal composite connectors in steel–concrete composite sections of bridge towers. Buildings. 2025;15(13):2284.10.3390/buildings15132284Search in Google Scholar
[15] Kumar P, Kota SR. Machine learning models in structural engineering research and a secured framework for structural health monitoring. Multimed Tools Appl. 2024;83(3):7721–59.10.1007/s11042-023-15853-5Search in Google Scholar
[16] Li A, Fan L, Tian X. Self-cruising environmental ship based on improved ant colony algorithm. In 2024 8th CAA International Conference on Vehicular Control and Intelligence (CVCI). IEEE; 2024. p. 1–6.10.1109/CVCI63518.2024.10830161Search in Google Scholar
[17] Kumar SP, Beenamol M. Multiple layer radial basis neural network with remora regression tree optimum feature extraction for structural health monitoring. Asian J Civ Eng. 2023;24(4):989–99.10.1007/s42107-022-00547-4Search in Google Scholar
[18] Liu D, Miao C, Deng W, Zhang J, Zhang L, Gu J. Shear lag effect of steel–concrete composite girder bridge with steel truss webs: experiment, finite element, and theory. J Struct Eng. 2025;151(10):04025154.10.1061/JSENDH.STENG-14499Search in Google Scholar
[19] Yan B, Li C, Qiu M, Zhu Y, Hu M. Flexural performance of transverse wet joint in steel-UHPC composite beam under negative bending moments. J Constr Steel Res. 2024;223:109029.10.1016/j.jcsr.2024.109029Search in Google Scholar
[20] Wang Q, Li M, Chen C, Xu L, Fu Y, Xu J, et al. Glucose homeostasis controls N-acetyltransferase 10-mediated ac4C modification of HK2 to drive gastric tumorigenesis. Theranostics. 2025;15(6):2428.10.7150/thno.104310Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Vinayagam G, Thaiyan Rajendran R, Mohan MS, Stanislaus Arputharaj B, Jayakumar SS, Baskar S, et al. Multi-perspective investigations of aerosol’s non-linear impact on unmanned aerial vehicle for air pollution control applications under various aerosol working environments. Aerosol Sci Eng. 2024;8(2):213–40.10.1007/s41810-024-00219-7Search in Google Scholar
[22] Wang W. Esg performance on the financing cost of A-share listed companies and an empirical study. Int J Hous Sci Appl. 2024;45(2):1–7.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Generalized (ψ,φ)-contraction to investigate Volterra integral inclusions and fractal fractional PDEs in super-metric space with numerical experiments
- Solitons in ultrasound imaging: Exploring applications and enhancements via the Westervelt equation
- Stochastic improved Simpson for solving nonlinear fractional-order systems using product integration rules
- Exploring dynamical features like bifurcation assessment, sensitivity visualization, and solitary wave solutions of the integrable Akbota equation
- Research on surface defect detection method and optimization of paper-plastic composite bag based on improved combined segmentation algorithm
- Impact the sulphur content in Iraqi crude oil on the mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of carbon steel in various types of API 5L pipelines and ASTM 106 grade B
- Unravelling quiescent optical solitons: An exploration of the complex Ginzburg–Landau equation with nonlinear chromatic dispersion and self-phase modulation
- Perturbation-iteration approach for fractional-order logistic differential equations
- Variational formulations for the Euler and Navier–Stokes systems in fluid mechanics and related models
- Rotor response to unbalanced load and system performance considering variable bearing profile
- DeepFowl: Disease prediction from chicken excreta images using deep learning
- Channel flow of Ellis fluid due to cilia motion
- A case study of fractional-order varicella virus model to nonlinear dynamics strategy for control and prevalence
- Multi-point estimation weldment recognition and estimation of pose with data-driven robotics design
- Analysis of Hall current and nonuniform heating effects on magneto-convection between vertically aligned plates under the influence of electric and magnetic fields
- A comparative study on residual power series method and differential transform method through the time-fractional telegraph equation
- Insights from the nonlinear Schrödinger–Hirota equation with chromatic dispersion: Dynamics in fiber–optic communication
- Mathematical analysis of Jeffrey ferrofluid on stretching surface with the Darcy–Forchheimer model
- Exploring the interaction between lump, stripe and double-stripe, and periodic wave solutions of the Konopelchenko–Dubrovsky–Kaup–Kupershmidt system
- Computational investigation of tuberculosis and HIV/AIDS co-infection in fuzzy environment
- Signature verification by geometry and image processing
- Theoretical and numerical approach for quantifying sensitivity to system parameters of nonlinear systems
- Chaotic behaviors, stability, and solitary wave propagations of M-fractional LWE equation in magneto-electro-elastic circular rod
- Dynamic analysis and optimization of syphilis spread: Simulations, integrating treatment and public health interventions
- Visco-thermoelastic rectangular plate under uniform loading: A study of deflection
- Threshold dynamics and optimal control of an epidemiological smoking model
- Numerical computational model for an unsteady hybrid nanofluid flow in a porous medium past an MHD rotating sheet
- Regression prediction model of fabric brightness based on light and shadow reconstruction of layered images
- Dynamics and prevention of gemini virus infection in red chili crops studied with generalized fractional operator: Analysis and modeling
- Qualitative analysis on existence and stability of nonlinear fractional dynamic equations on time scales
- Review Article
- Haar wavelet collocation method for existence and numerical solutions of fourth-order integro-differential equations with bounded coefficients
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Analysis and Design of Communication Networks for IoT Applications - Part II
- Silicon-based all-optical wavelength converter for on-chip optical interconnection
- Research on a path-tracking control system of unmanned rollers based on an optimization algorithm and real-time feedback
- Analysis of the sports action recognition model based on the LSTM recurrent neural network
- Industrial robot trajectory error compensation based on enhanced transfer convolutional neural networks
- Research on IoT network performance prediction model of power grid warehouse based on nonlinear GA-BP neural network
- Interactive recommendation of social network communication between cities based on GNN and user preferences
- Application of improved P-BEM in time varying channel prediction in 5G high-speed mobile communication system
- Construction of a BIM smart building collaborative design model combining the Internet of Things
- Optimizing malicious website prediction: An advanced XGBoost-based machine learning model
- Economic operation analysis of the power grid combining communication network and distributed optimization algorithm
- Sports video temporal action detection technology based on an improved MSST algorithm
- Internet of things data security and privacy protection based on improved federated learning
- Enterprise power emission reduction technology based on the LSTM–SVM model
- Construction of multi-style face models based on artistic image generation algorithms
- Special Issue: Decision and Control in Nonlinear Systems - Part II
- Animation video frame prediction based on ConvGRU fine-grained synthesis flow
- Application of GGNN inference propagation model for martial art intensity evaluation
- Benefit evaluation of building energy-saving renovation projects based on BWM weighting method
- Deep neural network application in real-time economic dispatch and frequency control of microgrids
- Real-time force/position control of soft growing robots: A data-driven model predictive approach
- Mechanical product design and manufacturing system based on CNN and server optimization algorithm
- Application of finite element analysis in the formal analysis of ancient architectural plaque section
- Research on territorial spatial planning based on data mining and geographic information visualization
- Fault diagnosis of agricultural sprinkler irrigation machinery equipment based on machine vision
- Closure technology of large span steel truss arch bridge with temporarily fixed edge supports
- Intelligent accounting question-answering robot based on a large language model and knowledge graph
- Analysis of manufacturing and retailer blockchain decision based on resource recyclability
- Flexible manufacturing workshop mechanical processing and product scheduling algorithm based on MES
- Exploration of indoor environment perception and design model based on virtual reality technology
- Tennis automatic ball-picking robot based on image object detection and positioning technology
- A new CNN deep learning model for computer-intelligent color matching
- Design of AR-based general computer technology experiment demonstration platform
- Indoor environment monitoring method based on the fusion of audio recognition and video patrol features
- Health condition prediction method of the computer numerical control machine tool parts by ensembling digital twins and improved LSTM networks
- Establishment of a green degree evaluation model for wall materials based on lifecycle
- Quantitative evaluation of college music teaching pronunciation based on nonlinear feature extraction
- Multi-index nonlinear robust virtual synchronous generator control method for microgrid inverters
- Manufacturing engineering production line scheduling management technology integrating availability constraints and heuristic rules
- Analysis of digital intelligent financial audit system based on improved BiLSTM neural network
- Attention community discovery model applied to complex network information analysis
- A neural collaborative filtering recommendation algorithm based on attention mechanism and contrastive learning
- Rehabilitation training method for motor dysfunction based on video stream matching
- Research on façade design for cold-region buildings based on artificial neural networks and parametric modeling techniques
- Intelligent implementation of muscle strain identification algorithm in Mi health exercise induced waist muscle strain
- Optimization design of urban rainwater and flood drainage system based on SWMM
- Improved GA for construction progress and cost management in construction projects
- Evaluation and prediction of SVM parameters in engineering cost based on random forest hybrid optimization
- Museum intelligent warning system based on wireless data module
- Special Issue: Nonlinear Engineering’s significance in Materials Science
- Experimental research on the degradation of chemical industrial wastewater by combined hydrodynamic cavitation based on nonlinear dynamic model
- Study on low-cycle fatigue life of nickel-based superalloy GH4586 at various temperatures
- Some results of solutions to neutral stochastic functional operator-differential equations
- Ultrasonic cavitation did not occur in high-pressure CO2 liquid
- Research on the performance of a novel type of cemented filler material for coal mine opening and filling
- Testing of recycled fine aggregate concrete’s mechanical properties using recycled fine aggregate concrete and research on technology for highway construction
- A modified fuzzy TOPSIS approach for the condition assessment of existing bridges
- Nonlinear structural and vibration analysis of straddle monorail pantograph under random excitations
- Achieving high efficiency and stability in blue OLEDs: Role of wide-gap hosts and emitter interactions
- Construction of teaching quality evaluation model of online dance teaching course based on improved PSO-BPNN
- Enhanced electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding properties of multi-component polymer/graphite nanocomposites prepared by solid-state shear milling
- Optimization of thermal characteristics of buried composite phase-change energy storage walls based on nonlinear engineering methods
- A higher-performance big data-based movie recommendation system
- Nonlinear impact of minimum wage on labor employment in China
- Nonlinear comprehensive evaluation method based on information entropy and discrimination optimization
- Application of numerical calculation methods in stability analysis of pile foundation under complex foundation conditions
- Research on the contribution of shale gas development and utilization in Sichuan Province to carbon peak based on the PSA process
- Characteristics of tight oil reservoirs and their impact on seepage flow from a nonlinear engineering perspective
- Nonlinear deformation decomposition and mode identification of plane structures via orthogonal theory
- Numerical simulation of damage mechanism in rock with cracks impacted by self-excited pulsed jet based on SPH-FEM coupling method: The perspective of nonlinear engineering and materials science
- Cross-scale modeling and collaborative optimization of ethanol-catalyzed coupling to produce C4 olefins: Nonlinear modeling and collaborative optimization strategies
- Unequal width T-node stress concentration factor analysis of stiffened rectangular steel pipe concrete
- Special Issue: Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Control
- Development of a cognitive blood glucose–insulin control strategy design for a nonlinear diabetic patient model
- Big data-based optimized model of building design in the context of rural revitalization
- Multi-UAV assisted air-to-ground data collection for ground sensors with unknown positions
- Design of urban and rural elderly care public areas integrating person-environment fit theory
- Application of lossless signal transmission technology in piano timbre recognition
- Application of improved GA in optimizing rural tourism routes
- Architectural animation generation system based on AL-GAN algorithm
- Advanced sentiment analysis in online shopping: Implementing LSTM models analyzing E-commerce user sentiments
- Intelligent recommendation algorithm for piano tracks based on the CNN model
- Visualization of large-scale user association feature data based on a nonlinear dimensionality reduction method
- Low-carbon economic optimization of microgrid clusters based on an energy interaction operation strategy
- Optimization effect of video data extraction and search based on Faster-RCNN hybrid model on intelligent information systems
- Construction of image segmentation system combining TC and swarm intelligence algorithm
- Particle swarm optimization and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm for the adhesive layer defect detection
- Optimization of student learning status by instructional intervention decision-making techniques incorporating reinforcement learning
- Fuzzy model-based stabilization control and state estimation of nonlinear systems
- Optimization of distribution network scheduling based on BA and photovoltaic uncertainty
- Tai Chi movement segmentation and recognition on the grounds of multi-sensor data fusion and the DBSCAN algorithm

