The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
-
Jingting Dong
, Fenghong Cao
Abstract
Calcium homeostasis is correlated closely with the occurrence and development of various cancers. The role of calcium homeostasis in prostate cancer has remained unclear. The present study aimed to investigate the relationship between transmembrane and crimp-crimp domain 1 (TMCO1) and calreticulin (CALR) in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and the mechanism of action on prostate cancer metastasis. Effects of CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 knockdown on prostate cancer cells were investigated using following methods: cell cloning, Transwell, wound scratch assay, JC-1 assay, Fluo-4 Assay, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) fluorescent probe, mitochondrial fluorescence probe, Western blot and Immunofluorescence. TMCO1 and CALR are overexpressed in prostate cancer and knockdown of TMCO1 significantly inhibited the invasion, migration and cell proliferation. Furthermore, knocking down TMCO1 modulated the intensity of ER probes and mitochondrial fluorescence probes, and affected the levels of intracellular calcium ion and mitochondrial membrane potential. In addition, CALR recombinant protein upregulated the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker, Vimentin, Conversely, knockout of TMCO1 significantly reduced the expression of CALR and Vimentin. Knockout of TMCO1 can reverse the effect of CALR recombinant protein, elucidating the pivotal roles of TMCO1 and CALR in the regulation of prostate cancer metastasis through modulation of calcium homeostasis.
1 Introduction
Globally, prostate cancer (PCa) is the most prevalent malignancy among men, with a pronounced incidence in developed countries [1], and ranks within the top five cancers for both incidence and mortality worldwide, contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality among elderly men [2]. The standard therapeutic approaches for PCa include drug treatment and surgical intervention. However, a substantial proportion of patients face the challenges of recurrence and metastasis [3]. The majority of PCa-related mortalities are attributed to the metastatic spread of tumor cells, which can disseminate to various distant organs such as the lungs, liver, bones, and lymph nodes [4].
Transmembrane and coiled-coil domains 1 (TMCO1), also known as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca2+ Load-Activated Ca2+ Channel, is an ER transmembrane protein [5]. Studies have shown that deletion or downregulation of the TMCO1 gene can perturb intracellular calcium balance, triggering ER stress and aberrant Ca2+ signaling, resulting in tumorigenesis [6]. Calreticulin (CALR) serves as the primary calcium-binding protein in the ER and exhibits multifaceted roles in cellular function [7]. CALR impedes the binding of the androgen receptor to hormone-responsive DNA elements, thereby suppressing the transcriptional activity of retinoic acid receptors. This inhibition also affects the neural differentiation processes induced by retinoic acid [8]. Elevated levels of CALR have been observed in various malignancies, including gastric, lung, and pancreatic cancers [9]. Despite these findings, it is still unclear how the interaction between TMCO1 and CALR influences PCa metastasis.
Therefore, we propose a hypothesis that TMCO1 and CALR influence ER calcium regulation and mediate prostate cancer cell metastasis. Our study delineates the interplay between TMCO1 and CALR, elucidates their association with the pathological characteristics and prognostic indicators of prostate cancer, and lays a theoretical groundwork for the development of targeted therapeutic interventions.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 TCGA data analysis
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/index.html) is a comprehensive database that encompasses a vast array of prostate cancer (PCa) samples coupled with rich clinical data [10]. Leveraging TCGA, we conducted an analysis of the gene expression profiles of TMCO1 and CALR in PCa tissues and normal tissues.
2.2 Clinical sample collection
After obtaining written informed consent, specimens were collected from PCa patients in the Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology. The study was approved by the ethics committees of each participating center. From January 2021 to December 2023, we collected 59 prostate biopsy specimens, electroprostatectomy specimens and total prostatectomy specimens of PCa patients in the Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Science and Technology. And we collected the relevant clinicopathological data.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the Ethical Committee of Affiliated Hospital of North China University of Technology (202103001).
2.3 Cell culture and transfection
Human PCa cell lines (DU145 and PC-3) were come from National Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures. DU145 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium appended with 10% FBS and 1% penicillin–streptomycin. PC-3 cells maintained in F-12K medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% penicillin-streptomycin. All cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air and 5% CO2.
Cells were seeded into six-well plates, and upon reaching a confluence of 70–80%, 150pmol siRNA and Lipofectamine 8000 were added and transfected for 24 h at 37°C according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Small interfering RNAs were purchased from Sangon Biotech Co. Post-transfection efficiency was evaluated using Western blot analysis. The sequences were as follows: TMCO1 siRNA1(Sense: 5′-CAGGCAUAACCUGGGUCCUGGUUUA-3′; antisense: 5′-UAAACCAGGACCCAGGUUAUGCCUG-3′); TMCO1 siRNA2(Sense: 5′-UAGAGAGACAAGAAGAGAAACUGAA-3′; antisense: 5′-UUCAGUUUCUCUUCUUGUCUCUCUA-3′)
TMCO1 siRNA3(Sense: GGGUCCUGGUUUACAGGACAGACAA; antisense: 5′-UUGUCUGUCCUGUAAACCAGGACCC-3′); negative control (Sense: 5′-GGGUCGGUUAUACGGCAGAACUCAA-3′; antisense: 5′-UUGAGUUCUGCCGUAUAACCGACCC-3′).
2.4 Immunofluorescence
Tissues were routinely dehydrated and embedded in paraffin, and serial sections were dewaxed to water; EDTA antigen repair solution was heated. The primary antibody TMCO1 (1:200, ab238768, Abcam, USA;), CALR (1:100, ab92516, Abcam, USA) was incubated overnight at 4°C. After rewarming for 60 min at room temperature, the sections were incubated with a secondary antibody (1:100, ZF-0316, ASGB-BIO, China) at 37°C for 60 min. Add 1–2 drops of fluorescent blocking tablets (including DAPI) to seal the tablets, then observe under a fluorescence microscope.
2.5 Immunohistochemical
Tissues were routinely dehydrated and embedded in paraffin; serial sections were dewaxed to water, and EDTA antigen repair solution was heated. The primary antibody TMCO1 (1:200, ab238768, Abcam, USA;) and CALR (1:100, ab92516, Abcam, USA) was incubated overnight at 4°C. Incubated for 60 min at room temperature for rewarming. Incubation with secondary antibody (PV-9001, ASGB-BIO, China) was at 37°C for 1 h. The newly prepared DAB chromogenic hematoxylin staining solution was dropped and counterstained. Finally, dehydration and sealing were done. Immunohistochemical staining was blindly scored by two pathologists.
2.6 CCK8
Cell Counting Kit-8 was used to evaluate cell viability. Simply, DU145 and PC-3 human PCa cells were seeded in 96-well plates (1,000 cells/well) for 24 h. Subsequently, 10 μL of the CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, and the plates were incubated for 3 h, strictly following the manufacturer’s guidelines. The OD value at 450 nm was measured.
2.7 Transwell
Following a 24-h serum starvation period, DU145 and PC-3 cells were prepared into a cell suspension, and 200 µL of the cell suspension was added to the Transwell upper chamber (50,000 cells/well). The culture was conventionally grown at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 10 min and stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min. Subsequently, the cells were washed twice with PBS and gently wiped with a cotton swab to remove residual cells. Five visual fields were randomly selected from the center and surrounding areas; these fields were then observed, photographed, and counted with an inverted microscope.
2.8 Wound scratch assay
Cells of DU145 and PC-3 in a logarithmic growth phase, at a density of 40,000 cells/well, were plated and cultured until confluence exceeded 90%. On the backside of the 6-well plate, horizontal lines were evenly marked at 1 cm intervals across the well using a marker pen. Pipette tips were used to scratch two parallel lines in the central area where the cells grew. The cells were washed with PBS for 3 times to remove the scratched cells. Samples were taken at 0 h time point, photographed at 100× magnification, and the samples were placed into an incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 for further cultivation. Samples were taken at 24 h time point, and photographs were taken at 100×.
2.9 Cell cloning
DU145 and PC-3 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were harvested at a density of 300 cells per well and resuspended in a culture medium. The cell suspension was then diluted in a series of gradient multiples. The cells were maintained in an incubator for 2 weeks. Subsequently, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min. After fixation, the solution was aspirated, and the cells were stained with a 0.1% crystal violet solution for 20 min. Following staining, the cells were washed twice with PBS and allowed to air dry.
2.10 ER fluorescent probe
Intracellular ER levels were measured utilizing specific ER-Tracker Red fluorescent probes (C1041, Beyotime, https://www.beyotime.com/product/C1041.htm). The cell culture medium was removed, and the ER-Tracker Red working solution, pre-warmed to 37°C, was introduced. The cells were then incubated with the staining solution at 37°C for 25 min. Post incubation, the ER-Tracker Red solution was removed, and the cells were gently washed twice with fresh cell culture fluid. The cells were finally observed under a fluorescence microscope.
2.11 Mitochondrial fluorescence probe
A minute quantity of the 200 μM Mito-Tracker Red CMXRos (C1049B, Beyotime, https://www.beyotime.com/product/C1049B-50%CE%BCg.htm) stock solution was diluted in the cell culture medium at a ratio of 1:10,000, yielding a final concentration of 200 nM. Then, the cells were incubated with this working solution at 37°C for 25 min. Following the incubation period, the Mito-Tracker Red CMXRos working solution was aspirated, and the cells were then replenished with fresh, pre-warmed cell culture medium maintained at 37°C. The cells were subsequently examined under a fluorescence microscope.
2.12 Mitochondrial membrane potential
In accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions for reagent (C2003S, Beyotime, https://www.beyotime.com/product/C2003S.htm), first, the JC-1 staining working solution was prepared by pipetting 5 µL of JC-1 (200×) from the kit and mixing it thoroughly with 1 mL of JC-1 staining buffer. The cells were seeded into a six-well plate, adding 1 mL of the JC-1 staining solution to each well. Then, the cells were incubated with JC-1 staining solution at 37°C for 20 min. After incubation, the staining solution was removed and the cells were washed twice with 1 mL of JC-1 staining buffer per well. The Carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenyl hydrazone (CCCP), supplied at a concentration of 10 mM in the kit, was introduced to the cell culture medium at a dilution ratio of 1:1,000, resulting in a final concentration of 10 μM. Then, CCCP was incubated with cells for 20 min. The application of CCCP served as the positive control in the experiment. Finally, the stained cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope.
2.13 Fluo-4 calcium assay kit
The medium was removed, and the cells were washed three times with HBSS solution. Fluo4-AM (S1060, Beyotime, https://www.beyotime.com/product/S1060.htm) working solution was added, and the amount of solution was subject to the covering cell. The cells were incubated at 37°C for 30 min in a cell incubator. Cells were washed three times with HBSS solution. Then HBSS solution was added to cover the cells. The cells were incubated for approximately 30 min at 37°C in an incubator to ensure to facilitate the complete conversion of Fluo-4 AM into Fluo-4. The cells were visualized under a fluorescence microscope, and representative images were captured.
2.14 Western blot
Cells were washed with PBS, and protein lysate was prepared for lysis. After centrifugation, the supernatant was taken as whole protein extract and stored at −80°C. After quantification of the BCA protein, the protein was denatured, and SDS–PAGE gel electrophoresis was prepared. The separated proteins were transferred to the PVDF membrane. Subsequently, primary antibodies TMCO1 (1:1,000, 27757-1-AP, Proteintech, China), CALR (1:1,000, ab92516, Abcam, USA), Vimentin (1:2,000, ab92547, Abcam, USSA), GAPDH (1:3,000, ab8245, Abcam, USA), and β-actin (1:1,000, ab8226, Abcam, USA) were added and incubated at 4°C overnight. Then, they were incubated with secondary antibodies (1:5,000, ZB-2301, ASGB-BIO, China) or (1:5,000; ZB-2305; ASGB-BIO, China). The images were developed in the gel imaging instrument, and the images were saved.
2.15 Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
Following the protocol of the Immunoprecipitation Kit with Protein A + G Magnetic Beads (P2179, Beyotime), the cells were lysed by the addition of 100 μL of lysis buffer. The lysate was then centrifuged at 10,000 × g at 4°C for 5 min, and the supernatant was collected; 50 μL was reserved as the input control. Both the 3 μg antibody and an equivalent amount of normal IgG, serving as negative controls, were diluted according to the manufacturer’s instructions for the antibodies. These were then incubated with 100 μL of Protein A + G magnetic beads at room temperature for 1 h to allow the beads to bind to the antibody. A volume of 500 μL of cell lysate was added to the Protein A + G magnetic beads that had been bound with either antibodies or normal IgG. This mixture was incubated on a shaker at room temperature overnight at 4°C. After incubation, the mixtures were centrifuged at 1,000g at 4°C for 5 min, and the supernatant was removed; 100 μL of SDS-PAGE Sample Loading Buffer (1×) was added, and the mixture was heated at 95°C for 5 min. The supernatant was then collected for Western detection using the method described in Section 2.14.
2.16 Statistical analysis of data
SPSS 22.0 was used for statistical analysis, and all measurement data were expressed in the form of mean ± standard deviation. Differences between two groups were compared using Student’s t-test analysis of variance. One-way analysis of variance was used to determine the differences between three or more groups. P < 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. All experiments were performed independently at three times.
3 Results
3.1 TMCO1 and CALR may be the key genes affecting PCa metastasis
To determine the expression pattern of TMCO1 and CALR in PCa, we compared its expression in PCa and normal tissues using the TCGA data. As shown in Figure 1a and b, the expression level of TMCO1 and CALR were significantly higher in prostate cancer samples than in normal samples. Furthermore, a correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationship between TMCO1 and CALR, revealing a significant association between these two proteins (Figure 1c).
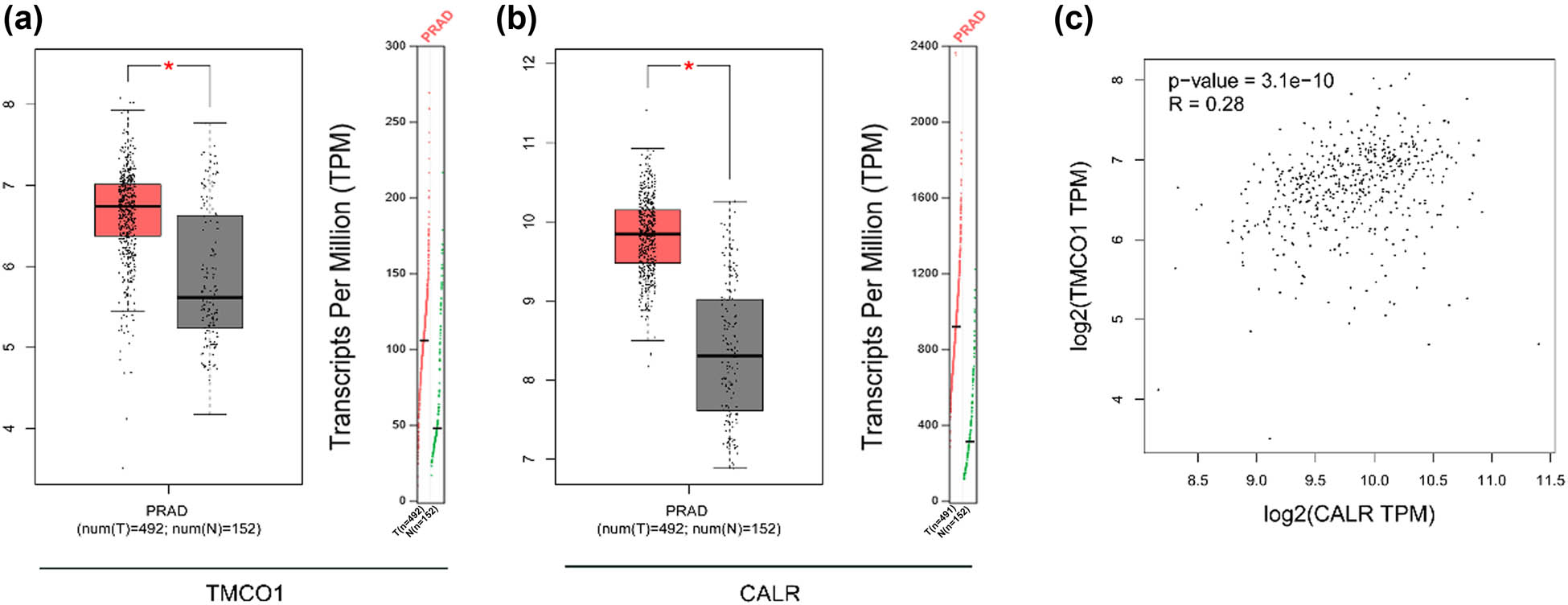
TCGA data analysis TMCO1 and CALR. (a) TCGA data analysis of TMCO1 expression specificity. In the box figure, the red is the expression of TMCO1 in cancer tissue, and the black is the expression of TMCO1 in normal prostate tissue. (b) TCGA data analysis of CALR expression specificity. In the box figure, red is the expression of CALR in cancer tissue, and black is the expression of CALR in normal prostate tissue. (c) Correlation between TMCO1 and CALR expression was analyzed by TCGA data. PRAD is PCa. *P < 0.05.
3.2 TMCO1 and CALR are highly expressed in PCa samples
We collected a total of 59 prostate biopsy specimens, electro prostatectomy specimens, total prostatectomy specimens, and along with pertinent clinicopathological data. Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry showed that TMCO1 and CALR were highly expressed in PCa tissues (Figure 2a–d), a finding that corroborated the analysis of the TCGA database. The expressions of TMCO1 and CALR were correlated with the Gleason score defined by WHO. Based on the analysis of the relationship between clinicopathologic features, TMCO1 was closely related to lymphatic metastasis, invasion depth, clinical stage and survival (Table 1).

Expression of TMCO1 and CALR in PCa. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence showed that CALR and TMCO1 genes were differentially expressed in adjacent and prostatic adenocarcinoma tissues, respectively. (c) and (d) Immunohistochemistry showed that the protein expressions of CALR and TMCO1 genes were different in adjacent and prostatic adenocarcinoma tissues, respectively. Scale bars, 20 μm. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Expression and clinicopathological features of TMCO1 and CALR in Pca
| Characteristics | Total (n = 59) | TMCO1 | CALR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (n = 37) | Negative (n = 22) | Positive (n = 45) | Negative (n = 14) | ||
| Age (year) | |||||
| ≤60 | 24 | 16 | 8 | 18 | 6 |
| >60 | 35 | 21 | 14 | 27 | 8 |
| χ 2 | 0.271 | 0.036 | |||
| P-value | 0.603 | 0.849 | |||
| Gleason score | |||||
| ≤7 | 26 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 11 |
| >7 | 33 | 25 | 8 | 30 | 3 |
| χ 2 | 5.450 | 8.866 | |||
| P-value | 0.020 | 0.003 | |||
| T stage | |||||
| T1–2 | 27 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 11 |
| T3–4 | 32 | 24 | 8 | 29 | 3 |
| χ 2 | 4.515 | 7.960 | |||
| P-value | 0.034 | 0.005 | |||
| Metastasis to lymph nodes | |||||
| Yes | 34 | 26 | 8 | 31 | 3 |
| No | 25 | 11 | 14 | 14 | 11 |
| χ 2 | 6.496 | 9.850 | |||
| P-value | 0.011 | 0.002 | |||
| Invasion to seminal vesicle | |||||
| Yes | 39 | 28 | 11 | 34 | 5 |
| No | 20 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 9 |
| χ 2 | 4.059 | 5.891 | |||
| P-value | 0.044 | 0.015 | |||
| AJCC clinicopathological stage | |||||
| I–IIc | 16 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 8 |
| IIIa–IIIc | 28 | 23 | 5 | 24 | 4 |
| IVa–IVb | 15 | 7 | 8 | 13 | 2 |
| χ 2 | 8.633 | 7.358 | |||
| P-value | 0.013 | 0.026 | |||
| Survival | |||||
| Yes | 32 | 16 | 16 | 21 | 11 |
| No | 27 | 21 | 6 | 24 | 3 |
| χ 2 | 4.832 | 4.379 | |||
| P-value | 0.028 | 0.036 | |||
3.3 Optimal interference sequence of recombinant protein CALR and TMCO1
To determine the optimal concentration of CALR recombinant protein, CCK-8 assay was performed to examine cell proliferation of PC-3 and DU145 cells treated with a series of concentrations of CALR recombinant protein. Our data showed that when the concentration of CALR recombinant protein reached 20 ng/mL, the effect on cell apoptosis was minimal. Hence, 20 ng/mL CALR recombinant protein was chosen for the experimental concentration (Figure 3a and b). Three TMCO1 siRNA were synthesized, and their protein expression levels were observed. The Western blot results showed that the transfection effects of TMCO1 siRNA3 were significantly better than TMCO1 siRNA1 and TMCO1 siRNA2. Therefore, TMCO1 siRNA3 was chosen as the interference sequence for use in subsequent experiments (Figure 3c–e).

(a) and (b) Detection of the effect of CALR human recombinant protein on the proliferation of DU145 and PC-3 human PCa cells. (c)–(e) Screening the optimal interference sequence of TMCO1 in DU145 and PC-3 human PCa cells. (f)–(h) Effects of TMCO1 siRNA, CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 siRNA + CALR recombinant protein on colony formation of DU145 and PC-3 cells. ***P < 0.001 vs NC, ### P < 0.001 vs CALR Recombinant, ▲▲▲ P < 0.001 vs Control.
In a cell cloning experiment, it was found that the proliferation ability of PCa cells was significantly enhanced following the application of CALR recombinant protein. Knockdown of TMCO1 expression significantly inhibited the proliferation ability of prostatic cancer cells, Moreover, the knockdown also mitigated the proliferative impact induced by the CALR recombinant protein (Figure 3f–h).
3.4 Knockout of TMCO1 reversed CALR recombinant protein-induced invasion and migration of PCa cells
Using the scratch and Transwell assays, we observed a significant enhancement in the invasive and migratory capabilities of DU 145 and PC-3 cells following the application of CALR recombinant protein. Furthermore, the knockout of TMCO1 significantly inhibited the invasion and migration ability of DU 145 and PC3 cells. Compared with the CALR recombinant group, the CALR recombinant + TMCO1siRNA group exhibited a significant decrease in the number of invaded cells and a concurrent increase in the migration area (Figure 4a–f).

Effects of TMCO1 and CALR on invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells. (a)–(c) Changes in cell invasion ability after TMCO1 siRNA, CALR recombinant protein, TMCO1 siRNA + CALR recombinant protein in DU145 cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. (d)–(f) Changes in cell migration ability after TMCO1 siRNA, CALR recombinant protein, TMCO1 siRNA + CALR recombinant protein in PC-3 cells. Scale bars, 200 μm. ***P < 0.001 vs NC, ### P < 0.001 vs CALR Recombinant, ▲▲▲ P < 0.001 vs Control.
3.5 TMCO1 and CALR knockdown regulates mitochondrial membrane potential and calcium ion imaging in PCa cells
Mitochondrial membrane potential assays revealed a significant increase in the intensity of the mitochondrial membrane potential in DU145 and PC-3 cells following the application of CALR recombinant protein, as evidenced by a pronounced enhancement in red fluorescence. Compared with the NC group, the knockdown of TMCO1 significantly reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential in DU145 and PC-3 cells. Furthermore, when compared with the group treated with CALR recombinant protein alone, the mitochondrial membrane potential was significantly lower in the group cotreated with CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 siRNA. (Figure 5a–c). Calcium imaging assays demonstrated an increase in intracellular calcium ion levels in DU145 and PC-3 cells following the administration of CALR recombinant protein. In contrast, the knockout of TMCO1 significantly diminished the fluorescence intensity in these cells, indicating a reduced presence of intracellular calcium ions. (Figure 5d–f). These findings suggest that TMCO1 and CALR play roles in calcium regulation in prostate cancer.

Mitochondrial membrane potential and calcium ion imaging results. (a)–(c) Mitochondrial membrane potential observed in each group on prostate cancer cell (DU145 and PC-3) membrane potential, CCCP is a positive control group. (d)–(f) The effect of each group on calcium level of prostate cancer cells (DU145 and PC-3) was observed by the Fluo4 AM experiment. Scale bars, 50 μm. ***P < 0.001 vs NC, ### P < 0.001 vs CALR Recombinant, △△△ P < 0.001 vs CCCP, and ▲▲▲ P < 0.001 vs Control.
3.6 Interfering with TMCO1 and overexpressing CALR regulate ER and mitochondrial function
Fluorescence probe experiments conducted on five groups of cells revealed a significant increase in the fluorescence intensity of both the ER and mitochondrial probes in DU145 and PC-3 cells following the application of CALR recombinant protein (Figure 6a–c). Conversely, interference with TMCO1 substantially reduced the fluorescence intensity of these probes in DU145 and PC-3 cells (Figure 6d–f), thereby diminishing the induction effect of CALR recombinant protein.

Changes of Prostate Cancer Cells by Endoplasmic Reticulum Probe and Mitochondrial Probe. (a)–(c) ER Tracker Red was used to detect the fluorescence intensity of ER in DU145 and PC-3 cells after TMCO1 siRNA, CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 siRNA + CALR recombinant protein. (d)–(f) Mitochondrial Tracker Red was used to detect the mitochondrial fluorescence intensity levels of TMCO1 siRNA, CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 siRNA + CALR recombinant protein in DU145 and PC-3 cells. Scale bars, 50 μm., ***P < 0.001 vs NC, ### P < 0.001 vs CALR Recombinant, ▲ P < 0.05 vs Control, and ▲▲▲ P < 0.001 vs Control.
3.7 Regulation of Vimentin expression by interfering TMCO1 and CALR recombinant proteins
Western blot and immunofluorescence analyses revealed that, compared with NC group, the knockdown of TMCO1 led to a decrease in the expression of CALR and Vimentin. In contrast, the CALR recombinant protein, when compared to the control group, significantly increased the expression levels of TMCO1 and Vimentin. Furthermore, the co-treatment with CALR recombinant protein and TMCO1 siRNA resulted in a decrease in the expression of CALR and Vimentin, as compared to the group treated with CALR recombinant protein alone (Figure 7a–l). Additionally, co-immunoprecipitation experiments confirmed an interaction between TMCO1 and CALR (Figure S1).

The relationship between TMCO1and CALR in prostate cancer cells. (a)–(g) Western blot was used to detect the effects of TMCO1 and CALR recombinant proteins and their combination on the expression of CALR and Vimentin. (h)–(l) Immunofluorescence assay was used to detect the effects of TMCO1 and CALR recombinant proteins and their combination on the expression of CALR. Scale bars, 20 μm. ***P < 0.001 vs NC, # P < 0.05 vs CALR Recombinant, ### P < 0.001 vs CALR Recombinant, ▲ P < 0.05 vs Control, ▲▲▲ P < 0.001 vs Control.
4 Discussion
In the United States alone, over 160,000 new cases of prostate cancer (PCa) are diagnosed annually, with a significant proportion presenting some degree of metastasis [11]. Despite therapeutic interventions, the prognosis for metastatic PCa remains grim, often correlating with a substantial decrease in overall survival [12]. Through analysis of the relationship between TMCO1 and CALR, as well as the pathological characteristics of PCa, and the molecular mechanism affecting its metastasis, we demonstrated that TMCO1 and CALR played vital role in the metastasis of PCa cells, and knockout TMCO1 expression can reverse the effect of CALR recombinant protein. It was discovered that there is a connection between TMCO1 and CALR that influences PCa metastasis via regulating calcium homeostasis.
TMCO1, a transmembrane protein resident in the ER, is recognized as an ER calcium overload-activated calcium channel [13]. It is notably and highly expressed in the thymus, prostate, and testis [14]. TMCO1 plays a critical role in maintaining ER calcium homeostasis by reversibly binding to and releasing calcium ions, thereby detecting and managing excessive calcium levels [5]. Upon encountering an elevation in ER Ca2+ concentration, TMCO1 is activated, transitioning from dimers to tetramers, which facilitates the release of the surplus Ca2+, averting an overaccumulation of intracellular calcium [15]. It has been found that TMCO1 deficiency can compromise mitochondrial function [16]. The deletion or down-regulation of the TMCO1 gene can trigger a cascade of cellular responses that lead to calcium overload, cytosolic calcium imbalance, and aberrant calcium signaling within the ER. Such dysregulation of intracellular calcium homeostasis can precipitate ER stress and disrupt calcium signal transduction pathways, which are recognized as contributing factors to the process of tumorigenesis [17]. Notably, research has indicated a correlation between the downregulation of TMCO1 and an adverse prognosis in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma (UBUC) [18]. In glioma research, the upregulation of TMCO1 has been shown to facilitate epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in U87 and U251 cell lines, thereby enhancing cell migration and invasion [19]. Furthermore, the interaction between iASPP and TMCO1 could offer novel therapeutic strategies for cancer treatment. By specifically suppressing iASPP expression, the levels of TMCO1 protein may be diminished, calcium ion homeostasis could be reestablished, and consequently, tumor progression might be curtailed [20]. Conversely, the knockdown of TMCO1 exerts an inhibitory effect on these processes The relationship between TMCO1 and PCa has not been reported. Research indicates that calcium ion regulation has a “double-sided role” in cancer, with both promoting and inhibiting it. This study indicated that the overexpression of TMCO1 in prostate cancer tissues was closely related to the invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer. These findings underscore the potential of TMCO1 as a diagnostic biomarker and its relevance in the clinical progression of prostate cancer. Interestingly, TMCO1 gene knockout reduced the invasion and migration ability of prostate cancer cells, concurrent with reduced ER stress, mitochondrial membrane potential, and calcium ion levels. The role of TMCO1 in tumor cells is complex and varied, and it may play different roles in different tumor types. In our study, TMCO1 plays an oncogenic role in tumorigenesis, potentially through the modulation of calcium ion homeostasis, which in turn affects the biological behaviors of cancer cells.
CALR, an ER protein with a crucial role in calcium ion binding and protein folding, has been implicated in various cellular processes [9]. Its presence in the nucleus further suggests that it may be involved in transcriptional regulation. CALR binds to the synthetic peptide KLGFKR, which closely resembles an amino acid sequence in the DNA-binding domain of the nuclear receptor superfamily [9]. An bioinformatics analysis of CALR data from public databases reveals that mutations of CALR were widely present in tumors, indicating a broad association with various cancers [21]. Prior research has established an interaction between CALR and the NF-κB signaling pathway. Specifically, elevated CALR expression has been demonstrated to enhance lung cancer cell proliferation by activating the NF-κB signaling [7]. CALR is overexpressed in breast cancer, and its knockdown can affect the spread of the tumor [22]. Evidence suggests that CALR expression is elevated in gastric cancer compared to normal tissue levels, and this increase is associated with lymph node metastasis as well as overall metastatic potential. And the elevated expression of CALR has been demonstrated to enhance the migratory capacity of gastric cancer cells in both in vivo and in vitro studies [23]. Numerous investigations have demonstrated the influence of CALR on the proliferative and metastatic capabilities of PCa. Alur et al. [24] studies showed that CALR is highly expressed in prostate epithelial cells and is regulated by androgens and a downregulation of CALR expression has been observed in certain PCa specimens. Furthermore, Alur proposes that CALR may play an inhibitory role in the growth and metastasis of PCa. Recent studies have shown that CALR modulates the expression of β1-integrin, impacting PCa metastasis through diverse regulatory mechanisms [25]. Additionally, Zhu has suggested that CALR mediates androgen-induced regulation of calcium sensitivity in LNCaP cells [26]. In the study, it was discovered that CALR can regulate the invasion and migration of prostate cancer cells, and can regulate mitochondrial membrane potential, calcium ion level, and ER stress, and the expression of Vimentin. Our study delineates a pivotal role for CALR in the advancement of tumorigenesis. It is speculated that CALR may affect the metastasis of prostate cancer through calcium ion level and ER stress. The experimental outcomes demonstrated that the knockdown of TMCO1 could reverse the effect of CALR in inducing prostate cancer cell metastasis. This study further demonstrated the regulatory mechanism of TMCO1 and CALR in the metastasis of prostate cancer. Furthermore, our analysis of the TCGA database revealed that both TMCO1 and CALR are upregulated in PCa, with a significant correlation observed between their expression levels. Co-immunoprecipitation results demonstrated a significant interaction between the TMCO1 and CALR. The above results indicate that TMCO1 may regulate the invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer cells, as well as mitochondrial membrane potential, calcium level, and Vimentin expression through CALR.
The analysis of clinical specimens showed that TMCO1 and CALR were overexpressed in PCa and correlated with Gleason score, lymphatic metastasis, invasion depth, and clinical stage and survival. After that, we looked at how recombinant protein CALR and TMCO1 knockdown affected human PCa cells and found that the migration, invasion and proliferation abilities of DU145 and PC-3 were significantly enhanced after CALR recombinant protein, and also had an impact on the intensity of intracellular calcium ions, ER probe and mitochondrial fluorescence probe. Knockdown of TMCO1 significantly inhibited these abilities in DU145 and PC-3 cells and reversed the induction effect of CALR recombinant protein. Most importantly, the knockout of TMCO1 dramatically decreased CALR expression.
In summary, our study delineates the multifaceted roles of TMCO1 and CALR in prostate cancer, underscoring the potential of modulating calcium signaling pathways as a novel therapeutic approach. Although we have shown that interfering with TMCO1 can reverse the induction of CALR recombinant protein through cell experiments, more research is required to determine the precise mechanism by which TMCO1 and CALR effect PCa metastasis. Given their roles in calcium ion homeostasis, the influence of TMCO1 and CALR on the tumor immune microenvironment deserves deeper examination. Later on, a PCa cell subcutaneous tumor model in nude mice can be established.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, TMCO1 plays a key role in the metastasis mechanism of prostate cancer. TMCO1 and CALR can regulate mitochondrial membrane potential, ER stress, and calcium ion level can affect PCa metastasis. The inhibition of TMCO1 expression can reverse the effect of CALR induction, providing a theoretical reference for revealing the metastasis mechanism of prostate cancer cells.
-
Funding information: The funding was provided by the Hebei Medical Science Research Project (NO.20221526); basic scientific research projects of colleges and universities in Hebei Province (NO. JQN2020004); and Hebei Medical Applicable Technology Tracking Project (NO.GZ2021089).
-
Author contributions: All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Jingting Dong and Shaosan Kang designed the study and carried them out; Fenghong Cao, Xi Chen, and Xiaofei Wang carried out the experiments and analyzed the data. Lei Wang, Qing Wang, and Yupu Zhai contributed to material preparation and data collection, and interpreted the data and statistical analysis. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca-Cancer J Clin. 2021 May;71(3):209–49.10.3322/caac.21660Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Bergengren O, Pekala KR, Matsoukas K, Fainberg J, Mungovan SF, Bratt O, et al. 2022 Update on prostate cancer epidemiology and risk factors-a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2023 Aug;84(2):191–206.10.1016/j.eururo.2023.04.021Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Akoto T, Saini S. Role of exosomes in prostate cancer metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar;22(7):3528.10.3390/ijms22073528Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Sekhoacha M, Riet K, Motloung P, Gumenku L, Adegoke A, Mashele S. Prostate cancer review: genetics, diagnosis, treatment options, and alternative approaches. Molecules. 2022 Sep;27(17):5730.10.3390/molecules27175730Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Yang KY, Zhao S, Feng H, Shen J, Chen Y, Wang ST, et al. Ca(2+) homeostasis maintained by TMCO1 underlies corpus callosum development via ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2022 Aug;13(8):674.10.1038/s41419-022-05131-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Li J, Liu C, Li Y, Zheng Q, Xu Y, Liu B, et al. TMCO1-mediated Ca(2+) leak underlies osteoblast functions via CaMKII signaling. Nat Commun. 2019 Apr;10(1):1589.10.1038/s41467-019-09653-5Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Gao F, Mu X, Wu H, Chen L, Liu J, Zhao Y. Calreticulin (CALR)-induced activation of NF-ĸB signaling pathway boosts lung cancer cell proliferation. Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6856–65.10.1080/21655979.2022.2040874Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Belčič Mikič T, Pajič T, Zver S, Sever M. The contemporary approach to calr-positive myeloproliferative neoplasms. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar;22(7):3371.10.3390/ijms22073371Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Fucikova J, Spisek R, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Calreticulin and cancer. Cell Res. 2021 Jan;31(1):5–16.10.1038/s41422-020-0383-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Blum A, Wang P, Zenklusen JC. SnapShot: TCGA-analyzed tumors. Cell. 2018 Apr;173(2):530.10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.059Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. Ca-Cancer J. Clin. 2023 Jan;73(1):17–48.10.3322/caac.21763Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Achard V, Putora PM, Omlin A, Zilli T, Fischer S. Metastatic prostate cancer: treatment options. Oncology. 2022;100(1):48–59.10.1159/000519861Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Xin B, Puffenberger EG, Turben S, Tan H, Zhou A, Wang H. Homozygous frameshift mutation in TMCO1 causes a syndrome with craniofacial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and mental retardation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jan;107(1):258–63.10.1073/pnas.0908457107Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Batchelor-Regan H, Xin B, Zhou A, Wang H. From disease description and gene discovery to functional cell pathway: a decade-long journey for TMCO1. Front Genet. 2021 May;12:652400.10.3389/fgene.2021.652400Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Wang QC, Zheng Q, Tan H, Zhang B, Li X, Yang Y, et al. TMCO1 Is an ER Ca(2+) load-activated Ca(2+) channel. Cell. 2016 Jun;165(6):1454–66.10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.051Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Wang X, Wang QC, Sun Z, Li T, Yang K, An C, et al. ER stress mediated degradation of diacylglycerol acyltransferase impairs mitochondrial functions in TMCO1 deficient cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 May;512(4):914–20.10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.115Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Zhang N, Tang M, Wen M, Cao Y, Ouyang B. Expression, purification and characterization of TMCO1 for structural studies. Protein Expr Purif. 2021 Mar;179:105803.10.1016/j.pep.2020.105803Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Li CF, Wu WR, Chan TC, Wang YH, Chen LR, Wu WJ, et al. Transmembrane and coiled-coil domain 1 impairs the AKT signaling pathway in urinary bladder urothelial carcinoma: a characterization of a tumor suppressor. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Dec;23(24):7650–63.10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Gao L, Ye Z, Liu JH, Yang JA, Li Y, Cai JY, et al. TMCO1 expression promotes cell proliferation and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in human gliomas. Med Oncol. 2022 May;39(5):90.10.1007/s12032-022-01687-ySuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Zheng S, Zhao D, Hou G, Zhao S, Zhang W, Wang X, et al. iASPP suppresses Gp78-mediated TMCO1 degradation to maintain Ca(2+) homeostasis and control tumor growth and drug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Feb;119(6):e2111380119.10.1073/pnas.2111380119Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Li Y, Liu X, Chen H, Xie P, Ma R, He J, et al. Bioinformatics analysis for the role of CALR in human cancers. PLoS One. 2021 Dec;16(12):e0261254.10.1371/journal.pone.0261254Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Liu X, Xie P, Hao N, Zhang M, Liu Y, Liu P, et al. HIF-1-regulated expression of calreticulin promotes breast tumorigenesis and progression through Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov;118(44):e2109144118.10.1073/pnas.2109144118Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Wang L, Chen J, Zuo Q, Wu C, Yu T, Zheng P, et al. Calreticulin enhances gastric cancer metastasis by dimethylating H3K9 in the E-cadherin promoter region mediating by G9a. Oncogenesis. 2022 May;11(1):29.10.1038/s41389-022-00405-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Alur M, Nguyen MM, Eggener SE, Jiang F, Dadras SS, Stern J, et al. Suppressive roles of calreticulin in prostate cancer growth and metastasis. Am J Pathol. 2009 Aug;175(2):882–90.10.2353/ajpath.2009.080417Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Lin YC, Huang YL, Wang MH, Chen CY, Chen WM, Weng YC, et al. Calreticulin regulates β1-Integrin mRNA stability in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Biomedicines. 2022 Mar;10(3):646.10.3390/biomedicines10030646Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Zhu N, Wang Z. Calreticulin expression is associated with androgen regulation of the sensitivity to calcium ionophore-induced apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999 Apr;59(8):1896–902.Suche in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?


