Abstract
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a challenging malignancy characterized by intricate biology and clinical characteristics. Despite advancements in treatment strategies, the molecular mechanisms underlying ccRCC initiation, progression, and therapeutic resistance remain elusive. Inflammasomes, multi-protein complexes involved in innate immunity and inflammation, have emerged as potential regulators in cancers. However, their involvement and mechanisms in ccRCC remain poorly understood. In this study, we conducted a systematic investigation into the expression patterns and clinical significance of inflammasome complexes in ccRCC. We found the perturbation of inflammasome complexes genes was related to patient’s prognosis and other clinical characteristics. By developing an Inflammasome Complexes (IFC) score and identifying IFC subtypes with distinct clinical characteristics and oncogenic roles, our study suggested that inflammasome activation could impact tumorigenesis and modulate the tumor immune landscape, particularly its positive correlations with immunosuppressive macrophages. Furthermore, our study revealed the potential of inflammasome complex genes as predictive markers for patient responses to various anti-tumor drugs, including Osimertinib, Ulixertinib, Telomerase Inhibitor IX, and GSK2578215A. These findings have significant clinical implications and offer opportunities for guiding treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes of ccRCC.
1 Introduction
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is one of the most prevalent malignant renal tumors, posing a significant challenge due to its intricate biology and clinical characteristics [1,2]. Given its complex nature and global clinical impact, ccRCC has become a critical focal point for researchers and clinicians [3]. The ccRCC exhibits distinct histological traits that underlie its propensity for high metastatic potential, aggressiveness, and inherent resistance to conventional therapeutic interventions [4,5]. Despite the advancement of clinical treatment strategies, a comprehensive understanding of the precise molecular mechanisms governing ccRCC initiation, progression, and the development of therapeutic resistance remains elusive.
The inflammasome, a multifaceted multi-protein complex [6], stands as a key player in the coordination of inflammation and innate immunity, serving as a vital component in host defense against pathogenic microorganisms. Upon activation, these complexes drive the maturation and subsequent secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [7,8]. This activation process not only facilitates a robust immune response but also contributes to the resolution of infections [9]. Intriguingly, inflammasome complexes extend beyond immune cells and are detected in various non-immune cell types, including cancer cells [10,11]. Recent years have unveiled compelling evidence showcasing the connection between inflammasome signaling dysregulation and the genesis of multiple malignant tumors [12,13]. However, the involvement and mechanism of the inflammasome in clear cell renal cell carcinoma remains unclear.
Tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) has gained popularity recently as a critical factor influencing cancer progression and treatment response [14]. In this complex environment, inflammatory complexes exert various significant effects on the TIME [15,16]. The activation of these inflammasome complexes within tumor cells stimulates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and manipulates the modulation of the immune landscape, thus having a widespread impact on several aspects of tumorigenesis [17,18]. The efficacy of immunotherapy has achieved remarkable success across certain cancers [19,20]. Inflammasome complex participation is a particularly interesting topic in the realm of cancer therapies [21]. Moreover, research efforts have focused on the interplay between inflammatory signaling and the response to chemotherapy and target therapy [16]. Certain anti-tumor drugs have demonstrated the ability to incite inflammasome activation within tumor cells [22]. This activation of the inflammasome might subsequently increase tumor susceptibility to specific drugs. Elucidating the mechanisms by which the inflammasome complex regulates the interaction between the tumor and immune microenvironment, as well as any possible implications for therapeutic responses, is critical to the development of effective treatments for ccRCC.
In this study, we provided a comprehensive analysis of the expression patterns and clinical implications of inflammasome complexes in ccRCC. By generating an Inflammasome Complex (IFC) score and identifying IFC subtypes, we gained insights into the immune microenvironment of ccRCC, particularly its associations with immunosuppressive macrophages. Furthermore, our findings revealed the potential of IFC genes as predictive markers for patients’ responses to immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and target-therapy. These results helped to clarify the role of inflammasome complexes in ccRCC, and have the potential to direct therapeutic approaches and enhance patient outcomes of ccRCC.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Data collection and integration
A total of 15 IFC genes were collected from a previous study [23], including NLRP1, NLRP3, CASP4, CASP5, NLRC5, NLRP6, NLRP12, NLRP7, NAIP, NLRC4, AIM2, IFI16, MEFV, NLRP2, and PYCARD. FPKM-UQ normalized RNA-Seq expression profile of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) kidney renal clear cell carcinoma patients was downloaded from UCSC Xena (https://xenabrowser.net/) platform [24], including 535 tumorous samples and 72 adjacent non-tumorous tissues. The expression value of genes was log-transformed for further analysis. Clinical information of patients, including age, gender, overall survival (OS), progression-free interval (PFI), histological grade, and pathological stages, was also obtained from the Xena platform.
2.2 Immunohistochemistry
In order to evaluate the expression of inflammatory complex in ccRCC, we selected NLRP family members, NLRP1, NLRP3, and NLRP, for experiments, and detected the expression of these three proteins in ccRCC and adjacent tissues. A total of 30 patients with ccRCC were collected from the urological department of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University from January 2016 to June 2017. Meanwhile, adjacent tissues were routinely retained 2 cm away from the tumor margin. All tissues were routinely embedded in paraffin wax and confirmed by pathology. Five white slices of each paraffin-embedded tissue block were cut continuously with a thickness of 4 μm, and immunohistochemical staining was performed. NLRP1 and NLRP3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), both in 1:100 dilution. NLRP6 (Millipore), diluted in 1:1,000. Each group of slices was incubated with diluted NLRP1/NLRP3/NLRP6 at 4°C overnight. Sections were coupled with horseradish peroxidase-coupled antibodies (Abcam) at 1:500 dilution at room temperature for 2 h. Then 3,3-diaminobenzidine is added. The staining was observed under optical microscope (ZEISS). Immunohistochemical scores were determined by two pathologists with diagnostic experience. The scoring method was the combination of staining intensity and proportion of positive staining area. The scoring criteria of staining intensity were negative score 0; weak positive marks 1 point; medium positive score 2 points; strong positive score 3 points. The number of stained cells was scored according to the proportion of positive cells in each section, and the percentage of positively stained cells in the total number of cells was taken as the average number of each field score: the score of no positive staining was 0; positive staining of 0–20% was l; positive staining of 20–75% was 2; positive staining greater than 75% was 3. Total score = positive percentage score × staining intensity score. A score of 0–4 was low expression, and a score of 5–9 was high expression.
-
Informed consent: Informed consent has been obtained from all individuals included in this study.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to human use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations, institutional policies and in accordance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration, and has been approved by the authors’ institutional review board or equivalent committee.
2.3 Mutation analysis
The mutation annotation format files of somatic mutation data of ccRCC patients were obtained from the TCGA MC3 project [25]. We used the R package “maftools” to calculate the tumor mutation burden (TMB) for ccRCC samples [26].
2.4 Survival analysis
We used R package “survival” and “survminer” to apply uni- and multi-variate Cox regression models based on the expression level of IFC genes. Kaplan–Meier (KM) curves were used to compare the survival differences between distinct patient groups.
2.5 Calculation of the IFC score and identification of IFC groups
Single-sample GSEA (ssGSEA) algorithm was applied using R package “GSVA” [27] to calculate the IFC score in each ccRCC sample based on the expression level of 15 IFC genes. Next, all samples were divided into two groups (high and low) based on the median value of IFC scores.
2.6 Differential expression analysis of protein-coding genes
The annotation of protein-coding genes was obtained from GENCODE v22 [28] (https://www.gencodegenes.org/). We used the R package “limma” to identify dysregulated genes between distinct sample groups [29]. Genes with empty expression values in more than 50% of samples were filtered out for further analysis. Genes with Benjamini and Hochberg (BH) generated false discovery rate (FDR) values less than 0.01 and were identified as differentially expressed.
2.7 Functional enrichment analysis
Ten oncogenic pathways and ten cancer hallmark gene sets were collected from previous studies [30,31]. We downloaded the hallmark gene sets representing various biological processes from MSigDB [32] (https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb). The ssGSEA algorithm was applied to calculate the enrichment level of each oncogenic pathway and hallmark gene set across ccRCC samples. Metascape platform (https://metascape.org/) was used to perform Gene ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway, and Reactome gene set enrichment analysis [33].
2.8 Identification of the IFC-based subtypes of ccRCC patients
Using the expression of 15 IFC genes, we performed unsupervised non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) [34] clustering on ccRCC patients. R package “NMF” was used to stratify ccRCC samples into two subtypes according to the cophenetic correlation coefficient [35]. Other parameters were set as follows: method = “brunet”, cluster number k = 2:10, nrun = 50.
2.9 The tumor immune microenvironment patterns of ccRCC
We applied Estimation of Stromal and Immune cells in Malignant Tumor tissues using the Expression data (ESTIMATE) method using the R package “estimate” to evaluate the immune cell abundance, stromal cell abundance, tumor purity, and overall tumor immune microenvironment of ccRCC samples [36]. A previous study defined 29 gene signatures representing tumor microenvironment. We collected these signatures and calculated the enrichment level of these signatures using the ssGSEA algorithm. Unsupervised clustering was performed on ccRCC by TIME signatures to define distinct immune clusters. Immune cell infiltration estimation of TCGA ccRCC samples generated by various methods [37,38,39] was downloaded from TIMER 2.0 [40] (http://timer.cistrome.org/). The marker genes of various immune cell types were collected from CellMarker 2.0 [41] (http://bio-bigdata.hrbmu.edu.cn/CellMarker).
2.10 Prediction of immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and target-therapy responses
Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE, http://tide.dfci.harvard.edu/) defined “Dysfunction scores” and “Exclusion scores” representing the dysfunction of T cell and prevention of T cell infiltration, respectively [42]. These two scores could evaluate primary mechanisms of tumor immune evasion, thus representing the possibility of immunotherapy response. The gene expression profile of ccRCC cell lines and drug sensitivity data of chemotherapy were downloaded from the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer [43] (https://www.cancerrxgene.org/) database. Based on the median value of ln(IC50) value of each drug, we divided ccRCC cells into two groups (sensitive and resistant), and then we identified dysregulated IFC genes between two groups and considered them as potential drug targets.
2.11 Statistical analysis
The statistical tests employed to analyze data in this study include the Mann–Whitney U test was utilized to compare the non-normally distributed variables between two groups. The Kruskal–Wallis test was employed to assess the association between the IFC score and different pathological stages of ccRCC. Pearson’s correlation coefficient and Spearman’s correlation coefficient were computed to explore the potential relationships between two variables. Fisher’s exact test was employed to perform overlap analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using R statistical software.
3 Results
3.1 Dysregulated IFC genes were correlated with different clinical outcomes in ccRCC
All of the IFC genes were found to be differentially expressed in tumor samples (Figure 1a). All IFC genes, except for NLRP2, showed significant elevated levels in tumor samples than in normal samples (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05) (Figure S1a). A clear separation was found between ccRCC and normal samples based on the expression levels of IFC genes, suggesting a potential perturbated expression pattern during tumorigenesis. The results from IHC showed that the expression rate of NLRP1, NLRP3, and NLRP6 in ccRCC tissues was significantly higher than that in adjacent non-tumorous tissues (Figure 1b, Table S1). Next, survival analysis revealed significant correlations between IFC gene expression and ccRCC clinical outcomes. Higher level of NLRP6 expression was associated with a prolonged OS. However, higher level of PYCARD, NLRP7, NLRP2, NLRP1, NLRP5, MEFV, IFI16, CASP5, CASP4, and AIM2 might lead to worse OS (Figure 1c). Additionally, some of these IFC genes were also found to have an impact on patients’ PFI (Figure 1d). In order to identify independent prognostic factors, we also performed a multi-Cox regression analysis. Results showed that NLRP6 could serve as a protective factor for both OS and PFI, whereas NLRP1, IFI16, and PYCARD served as risky factors for OS and PFI, respectively (Figure 1e). In summary, our results revealed significant dysregulation of inflammasome complexes genes, suggesting their potential roles in ccRCC development and patient prognosis.

Expression pattern and survival relevance of inflammasome complex (IFC) genes. (a) Heatmap illustrates the expression levels of IFC genes in ccRCC samples compared to normal samples. The color scale represents gene expression levels, with red indicating upregulation and blue indicating downregulation. (b) Expression of NLRP1, NLRP3, and NLRP6 in ccRCC and adjacent tissues (IHC 200 times magnification). (c and d) Forest plots of uni-variate Cox regression model for OS and PFI in ccRCC patients. The plot displays hazard ratios and corresponding 95% confidence intervals for each IFC gene. Red bars are associated with worse survival outcomes, while green bars are associated with better survival outcomes. (e) Forest plots of multi-variate Cox regression model.
3.2 Significant correlations were revealed between IFC score and clinical features
Here, we calculated the IFC score across ccRCC cancer samples using the ssGSEA algorithm based on the expression level of 15 IFC genes. The samples were ranked and divided into high and low IFC groups according to the median value of IFC scores (Figure 2a). KM curves showed that patients from the low IFC group had a prolonged OS and PFI than patients from the high IFC group (Figure 2b). We further explored the clinical associations of distinct IFC groups. Results showed a significant increase in the IFC score as the pathologic stages and grades advanced (Figure 2c). However, no significant differences in the IFC score were observed across different genders and age groups. In addition, we collected genes with a high-frequency somatic mutation in ccRCC and calculated the TMB of the samples (Figure 2d, Figure S1b and c). Subsequently, we investigated the association between the IFC score and gene mutations. We observed an elevated tumor mutational burden in the high IFC group. Moreover, the IFC score was higher in BAP1-mutant samples than in BAP1-wild-type samples (Figure 2e). Previous research has concentrated on the significance of BAP1 mutation status in ccRCC [44,45,46]; our results suggest that inflammasome complexes genes might exert an impact on the interplay between BAP1 and ccRCC development. In summary, our findings revealed a significant correlation between IFC scores, increased TMB, and certain clinical characteristics in ccRCC.
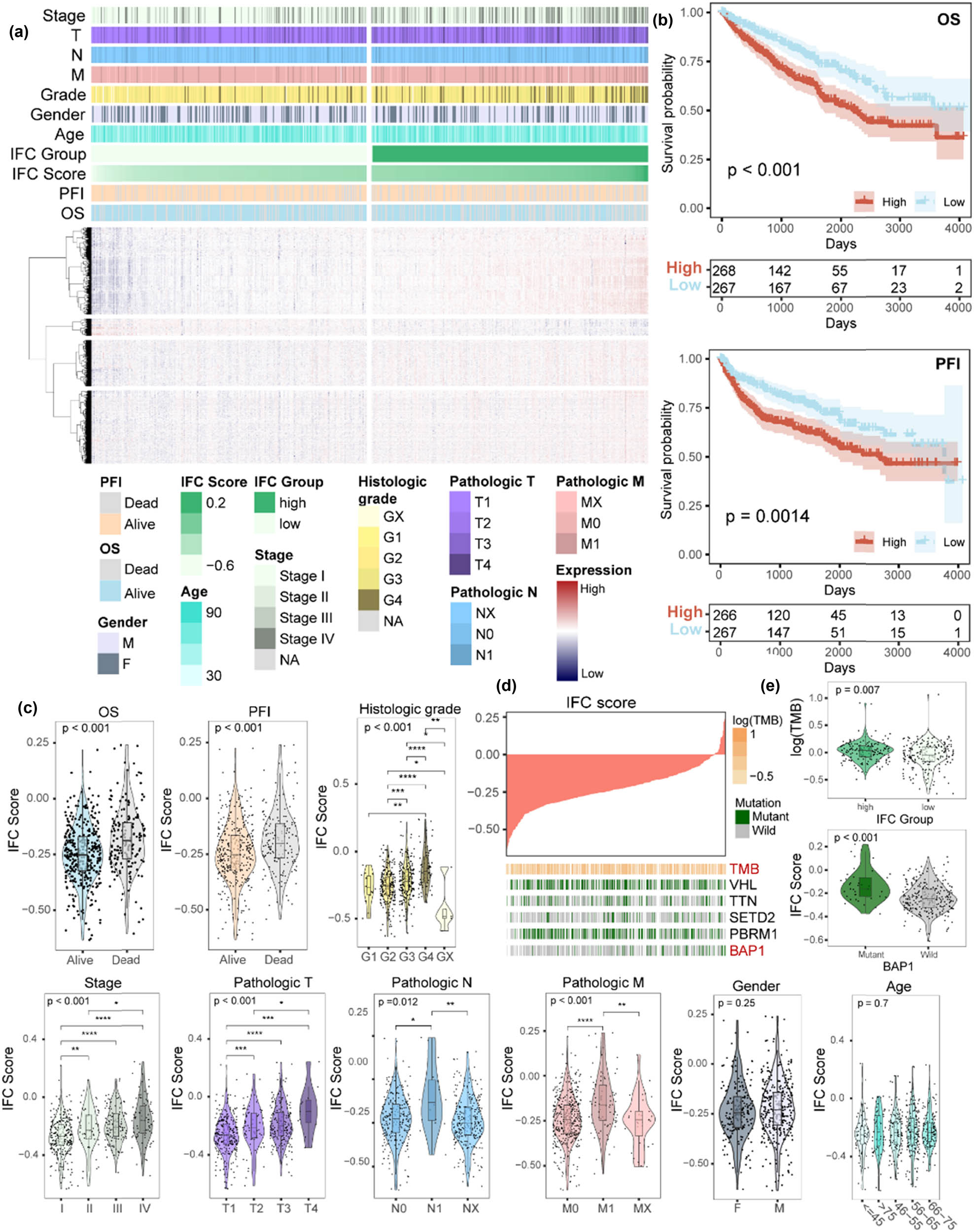
The clinical features associated with the IFC score in ccRCC patients. (a) Heatmap illustrates the expression patterns of dysregulated protein-coding genes between the high and low IFC groups, along with the corresponding clinical characteristics of the samples. (b) KM survival curves demonstrate the differences in OS and PFI between the high and low IFC groups. (c) Violin plots show the distribution of IFC scores among different clinical groups, including gender, age, survival status, pathological stages, and histologic grades (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05; Kruskal–Wallis test p < 0.05). (d) An overview of the association between IFC score and mutation status of the genes with high-frequency somatic mutation and TMB. (e) Violin plots show the TMB differences between high and low IFC groups and the distribution of IFC scores among BAP1 mutant and wild-type samples.
3.3 Dysregulated genes between high and low IFC groups were involved in distinct biological functions
We performed differential expression analysis and identified dysregulated protein-coding genes (110 down-regulated genes and 1361 up-regulated genes, fold change > 2 and FDR < 0.01) between high and low IFC groups (Figure 2a). Dysregulated genes were divided into four clusters by an unsupervised hierarchical clustering method. Then, we performed functional enrichment analysis on the four gene clusters, respectively (Figure 3a). Cluster 1 genes were enriched in tumor invasion, metastasis, and proliferation-related process, including epithelial cell differentiation, positive regulation of nuclear division, and GPCR ligand binding. Cluster 2 genes were involved in biological processes regarding tumor immune response, immune regulation, and formation of tumor microenvironment. Cluster 3 genes were related to abnormal renal function and metabolic regulation. Cluster 4 genes were enriched in terms that were related to various aspects, including renal dysfunction, metabolic regulation, tumor biological behavior, and immune regulation. The results from functional enrichment analysis implied the potential relationship among inflammasome signaling, immune landscape, renal development and tumorigenesis of ccRCC. In addition, we collected ten oncogenic pathways and ten cancer hallmark gene sets and quantified the enrichment level of these gene sets. As a result, we found that Hippo, NRF2, PI3K, TP53, and WNT pathways showed a dysregulated pattern between high and low IFC groups (Figure 3b). Seven cancer hallmark gene sets were significantly up-regulated in the high IFC group (Figure 3c), further suggesting the oncogenic roles of inflammasome signaling. In summary, our finding suggested a potential involvement of the inflammasome complex genes in the pathogenesis and progression of ccRCC.
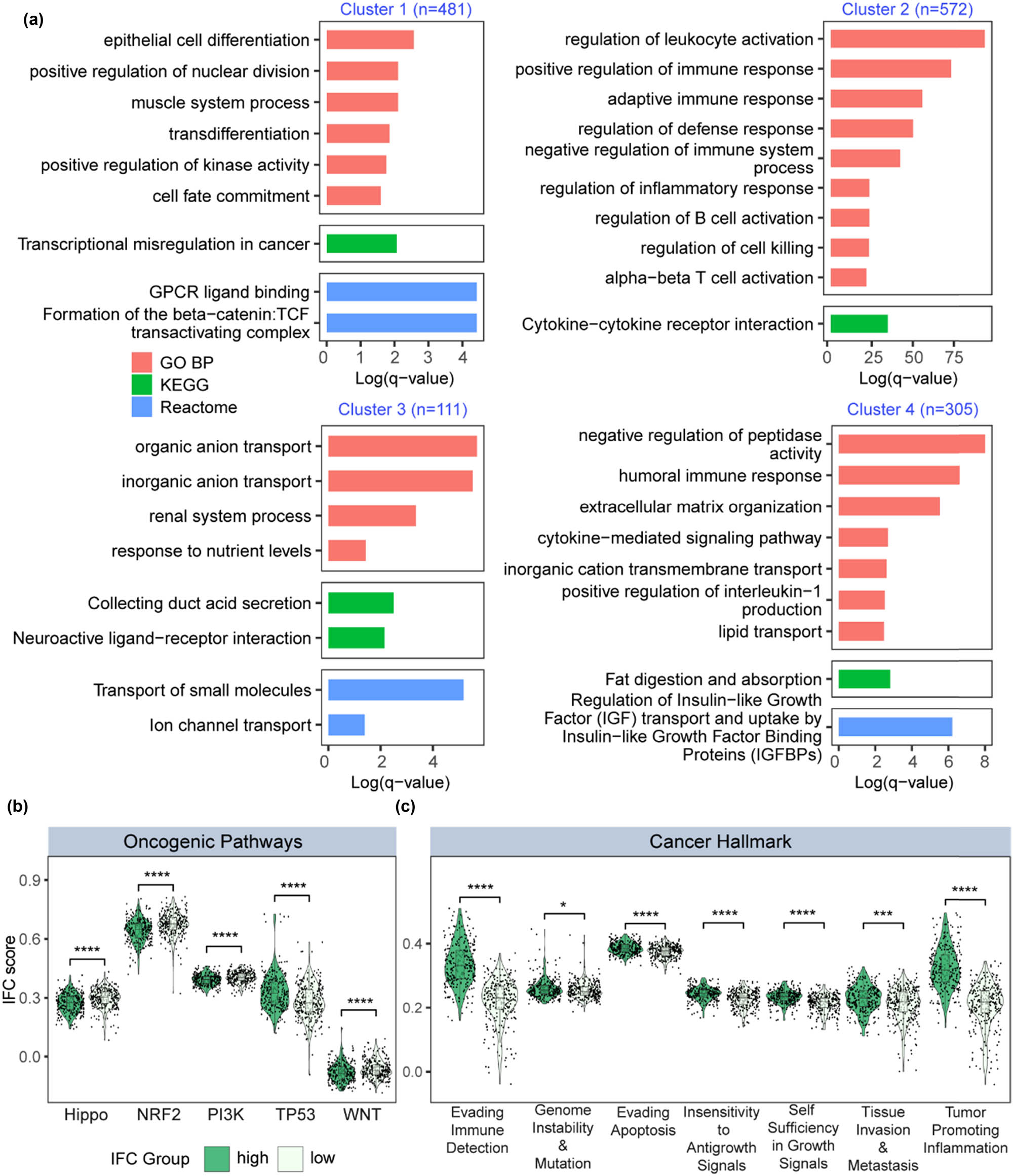
Functional enrichment analysis of high and low IFC groups. (a) Barplot illustrates the results of enrichment analysis for GO, KEGG, and Reactome gene sets. (b) Violin plots demonstrate the differences in oncogenic pathway activation levels between the high and low IFC groups (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05). (c) Violin plots depict the differential expression of cancer hallmark gene sets between the high and low IFC groups (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05; Kruskal–Wallis test p < 0.05).
3.4 Patients’ stratification revealed correlations with distinct clinical features and immunotherapy response
Here, we sought to stratify ccRCC samples into clinically relevant molecular subtypes based on IFC genes. Applying NMF clustering, two IFC subtypes were identified through iterative analysis, including subtype 1 (n = 230) and subtype 2 (n = 305) (Figure 4a and c, Figure S1d). Patients from subtype 1 had better OS and PFI than patients from subtype 2 (Figure 4e). Moreover, we found that subtype 1 patients had relatively lower IFC scores than subtype 2 patients (Figure 4b). Then, we performed an overlap analysis to explore the clinical associations of distinct IFC subtypes. Results showed that patients with advanced pathologic stages and histologic grade were significantly enriched in subtype 2 (Figure 4b), suggesting a potential association between subtype 2 and more aggressive disease characteristics. To further characterize the subtypes, we performed differential expression analysis and identified 839 dysregulated genes, including 10 up-regulated and 829 down-regulated genes (fold change > 2 and FDR < 0.01) (Figure S1e). Next, we quantified various functional gene sets and compared the expression levels between two subtypes (Figure 4d). As a result, oncogenic and immune pathways showed significant up-regulation in subtype 2. Considering the strong associations between IFC subtypes, high/low IFC groups, and tumor immunity, we hypothesized that different patients may exhibit varying responses to immunotherapy. Thus, we calculated the Dysfunction score and Exclusion score of ccRCC samples using TIDE. Results showed that patients from subtype 1 and patients with lower IFC scores exhibited lower Dysfunction levels of score and higher levels of Exclusion scores, suggesting a worse chance to respond to immunotherapy (Figure 4f). In summary, our results demonstrate a strong correlation between IFC-based subtypes and the tumor immune characteristics.
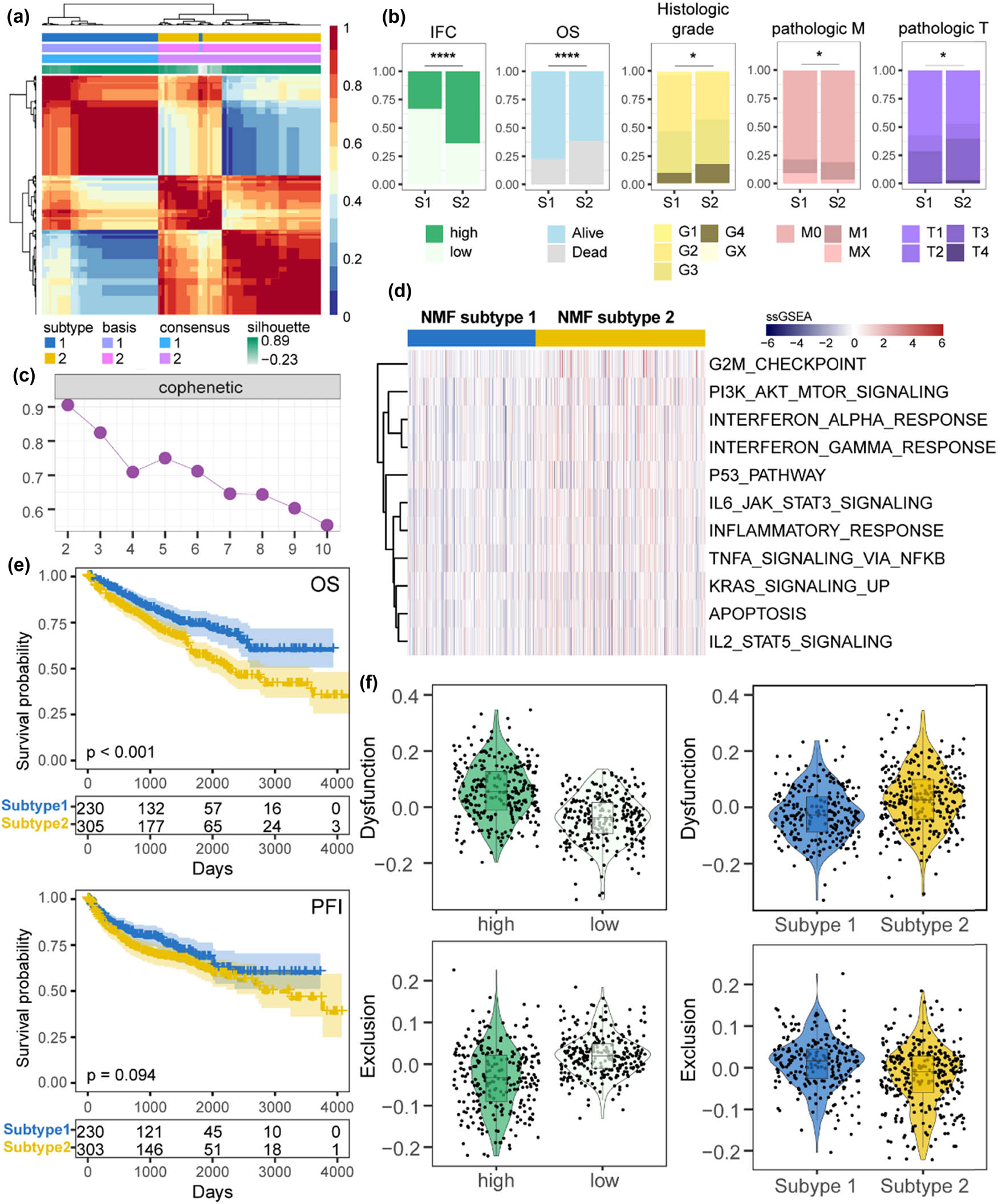
Identification and characterization of NMF-defined IFC subtypes. (a) Heatmap displays the results of NMF clustering (k = 2), which defined distinct IFC subtypes based on gene expression patterns. (b) The barplot illustrates the differences in clinical characteristics between the two IFC subtypes (Fisher’s exact test p < 0.05). (c) Cophenetic plot visualizing the quality of the NMF clustering results. (d) Heatmap shows the expression perturbations of functional gene sets between the two IFC subtypes. (e) KM curves demonstrate the differences in OS and PFI between the two IFC subtypes. (f) Violin plots display the differences in Exclusion score and Dysfunction score between the high and low IFC groups, as well as between the two IFC subtypes (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05).
3.5 IFC scores were positively correlated with immunosuppressive macrophages
Here, we sought to further explore the relationship between IFC and TIME patterns. First, we evaluated ccRCC TIME using the ESTIMATE algorithm, and results showed that IFC scores were positively correlated with ESTIMATE, immune, and stromal scores, whereas they negatively correlated with tumor purity, suggesting increased infiltration levels of immune cells in high IFC score samples (Figure 5a). Next, we collected 29 immune signatures from a previous study and quantified their expression levels across ccRCC samples. ccRCC samples were divided into three immune clusters (high-immunity Cluster 1 n = 236, medium-immunity Cluster 2 n = 263, low-immunity Cluster 3 n = 36) by unsupervised hierarchical clustering method (Figure 5b). As shown in Figure 5c, Cluster 1 samples were enriched in NMF subtype 2 and high IFC Score group, whereas Cluster 3 samples showed a significant overlap with NMF subtype 1 and low IFC score group, suggesting a distinct immune landscape. In addition, we explored the relationship between IFC scores and various immune cell abundance. The strongest correlation was found between IFC scores and macrophage abundances (Figure 5e), suggesting a potential immunosuppressive microenvironment in ccRCC patients with high IFC scores. Thus, we constructed a co-expression network and found intense interplay between macrophage marker genes and IFC genes (Figure 5d), suggesting a potential functional relationship and shared regulatory mechanisms between macrophages and the inflammasome signaling in ccRCC. The relationship between changes in macrophage abundance and the immunotherapy response of patients might be explained by our findings from the standpoint of inflammatory complexes genes.
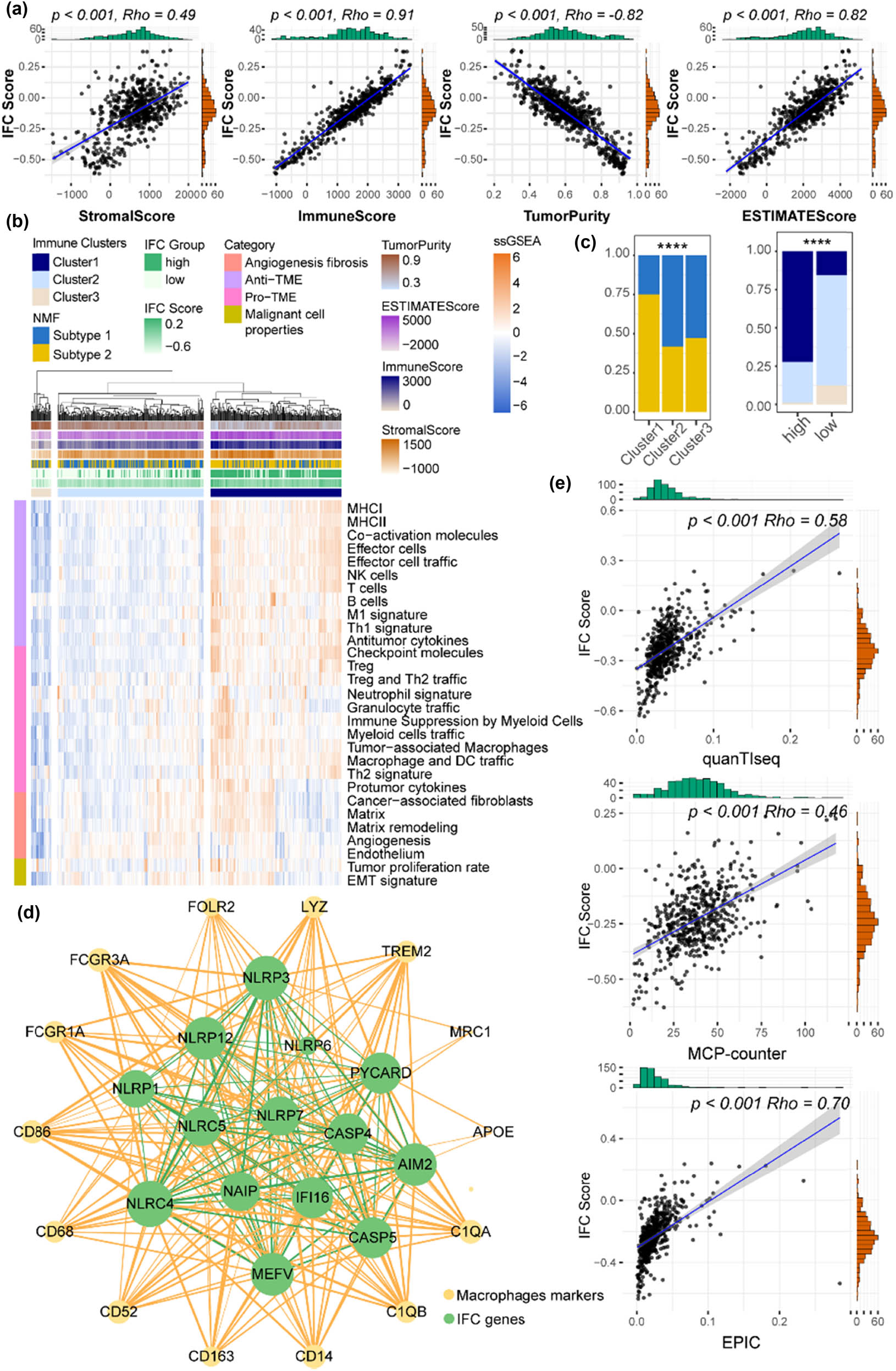
IFC scores were positively correlated with macrophage abundance. (a) Correlation curves display the correlation between the ESTIMATE score, immune score, stromal score, tumor purity, and IFC score. (b) TIME signatures defined three immune clusters. The heatmap displays the expression levels of 29 signatures across ccRCC samples. (c) Barplots illustrate the overlap among the three immune clusters, the high and low IFC groups, and the two IFC subtypes (Fisher’s exact test p < 0.05). (d) Co-expression network between IFC genes and macrophage marker genes. The network visualizes the co-expression relationships within IFC genes (shown in green edges), as well as between IFC and macrophage marker genes (shown in yellow edges). (e) Correlation curves show the correlation between the IFC score and the abundance of macrophages derived from three different data sources.
3.6 Increased expression of IFC genes could sensitize ccRCC patients to anti-tumor drugs
Here, we aimed to predict potential drug targets for ccRCC treatment by IFC genes. Therefore, we explored the correlation between drug sensitivity information and the expression of IFC genes in ccRCC cell lines, constructing a network of drug–target interactions (Figure 6). Through this investigation, we found that the expression perturbation of IFC genes could lead to the resistance of several drugs which have been used for renal cell carcinoma treatment in clinical trials including targeted therapy drugs Axitinib [47,48,49,50], Sorafenib [51], Pazopanib [52,53], Sunitinib [54], and immunotherapy drugs Bevacizumab [55,56], Interleukin-2 [57,58], Pembrolizumab [47], Nivolumab [59,60]. Additionally, we identified several potential anti-tumor drugs for ccRCC treatment, including Osimertinib, Ulixertinib, Telomerase Inhibitor IX, and GSK2578215A (Figure 6a and b). Osimertinib is a chemotherapy drug which has been widely used for metastatic EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer treatment [61]. Ulixertinib is an ERK1/2 inhibitor that has been clinically tested effective for patients with advanced solid tumors [62,63]. Telomerase Inhibitor IX has the potential to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells because of the abnormally high telomerase activity in cancer cells [64]. GSK2578215A is an LRRK2 inhibitor that could affect the sensitivity of ovarian cancer treatment by suppressing homologous recombination [65]. Our results suggested the potential of these anti-tumor drugs in ccRCC treatment by targeting inflammasome signaling. Among IFC genes, we found that MEFV and PYCARD were predicted to be the targets of most drugs in the network. The increased expression level of these two IFC genes could sensitize ccRCC cells to various therapy methods (Figure 6c). In summary, our results indicated a potential role of the inflammasome pathway in modulating ccRCC patients’ response to these specific drugs.
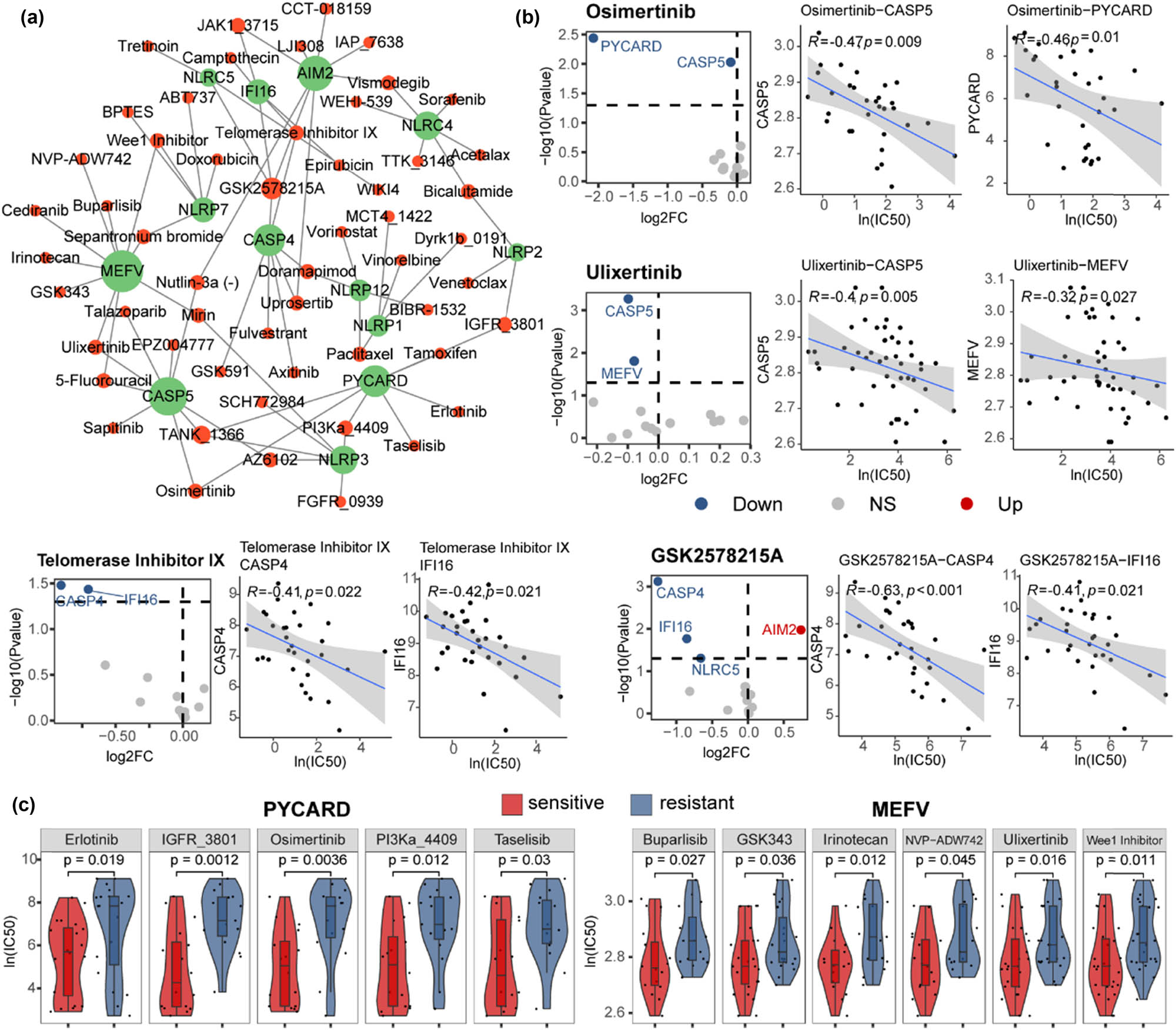
Increased expression of IFC genes could sensitize ccRCC patients to anti-tumor drugs. (a) Network shows the interactions between anti-tumor drugs and predicted target IFC genes. (b) Volcano plots show the expression variation of IFC genes between sensitive and resistant groups of each drug. Red nodes represent IFC genes that were up-regulated in drug-sensitive groups, while blue nodes represent down-regulated. Correlation curves depicting the relationship between the expression levels of IFC genes and drug sensitivity IC50 value in cancer cell lines. (Spearman’s correlation analysis, p < 0.05, |Rho| > 0.3). (c) Violin plots of gene expression between sensitive and resistant groups (Mann–Whitney U test p < 0.05).
4 Discussion
ccRCC is a multifaceted cancer with complicated biological and clinical features. As a key hallmark of cancer, inflammation has been shown to be closely related to the progression and prognosis of various tumors. In some cases, inflammation can promote the occurrence and development of tumors, which supports the therapeutic potential of targeting inflammation for cancer [66]. As the core of inflammation, the inflammasome, a multiprotein complex within cells, plays a vital role in initiating and regulating inflammatory responses, and the precise regulation of its function is significant for maintaining the body’s immune homeostasis [67]. The activation of inflammasome complexes is an important regulatory node in the inflammatory response. It can sense a variety of abnormal signals and regulate the intensity and duration of the inflammatory response through downstream signaling pathways [68]. In this study, we comprehensively investigated the expression patterns and clinical significance of inflammasome complexes in ccRCC, providing insight into their role in tumorigenesis, prognosis, and therapeutic response.
We found that most inflammasome complexes genes showed a significantly up-regulated pattern in ccRCC samples, which was further validated by immunohistochemistry (Figure 1b). Previous studies have established a positive correlation between high levels of inflammasome complexes and the development of cancer; the overactivation of inflammasome signaling in some cancer types is linked to the persistence of inflammatory responses, thereby promoting tumor formation and progression [10,11]. Our results further suggested the role of inflammasome complexes during the tumorigenesis of ccRCC. Moreover, our results showed that perturbations in inflammasome complex genes were associated with patient prognosis and other clinical characteristics by developing an IFC score and identifying IFC subtypes. Therefore, we provided evidence of inflammasome complexes genes’ clinical relevance in ccRCC and highlighted the potential of inflammasome complexes as prognostic markers for patient outcomes.
In addition, we found that there was a positive correlation between inflammasome signaling and immunosuppressive macrophages (Figure 5), indicating that inflammasome activation might contribute to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, thereby facilitating tumor immune evasion and progression. These findings further validated the hypothesis that patients with lower IFC scores would be more likely to respond to immunotherapy (Figure 4f). Our study provided insights into the interplay between inflammasome complexes and the immune response in ccRCC. Significantly, our research also revealed the potential of inflammasome complex genes as predictive markers for patient responses to different anti-tumor drugs, such as GSK2578215A, Ulixertinib, Osimertinib, and Telomerase Inhibitor IX (Figure 6). This suggested that inflammasome activation may have implications for treatment selection and personalized medicine in ccRCC, which also implied the potential mechanisms by which inflammasome complexes modulate therapeutic response.
In summary, the results of our study demonstrated the clinical significance of inflammasome complexes genes in ccRCC and their potential as prognostic indicators and therapeutic targets. Our findings highlighted the importance of understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying inflammasome activation and its impact on tumorigenesis, the immune landscape, and treatment response in ccRCC.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: A.L.Z. and F.C.Y. designed the study and performed analysis. A.L.Z. supervised research and provided critical advice on the study. F.C.Y. and F.L. collected clinical and online data, developed the methodology, and performed experiments. F.C.Y. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12–49. 10.3322/caac.21820.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Dizman N, Philip EJ, Pal SK. Genomic profiling in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(8):435–51. 10.1038/s41581-020-0301-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Stolpa W, Stręk-Cholewińska A, Mizia-Malarz A. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, diagnostic and therapeutic difficulties, case report and literature review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(10):1329. 10.3390/medicina58101329.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Shuch B, Amin A, Armstrong AJ, Eble JN, Ficarra V, Lopez-Beltran A, et al. Understanding pathologic variants of renal cell carcinoma: distilling therapeutic opportunities from biologic complexity. Eur Urol. 2015;67:85–97. 10.1016/j.eururo.2014.04.029.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Abu-Ghanem Y, Powles T, Capitanio U, Beisland C, Järvinen P, Stewart GD, et al. The impact of histological subtype on the incidence, timing, and patterns of recurrence in patients with renal cell carcinoma after surgery-results from RECUR consortium. Eur Urol Oncol. 2021;4(3):473–82. 10.1016/j.euo.2020.09.005.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Amin J, Boche D, Rakic S. What do we know about the inflammasome in humans? Brain Pathol. 2017;27:192–204. 10.1111/bpa.12479.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Christgen S, Place DE, Kanneganti TD. Toward targeting inflammasomes: insights into their regulation and activation. Cell Res. 2020;30(4):315–27. 10.1038/s41422-020-0295-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Fu J, Schroder K, Wu H. Mechanistic insights from inflammasome structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024;24(7):518–35. 10.1038/s41577-024-00995-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Yao J, Sterling K, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Song W. The role of inflammasomes in human diseases and their potential as therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):10. 10.1038/s41392-023-01687-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Sundaram B, Tweedell RE, Prasanth Kumar S, Kanneganti TD. The NLR family of innate immune and cell death sensors. Immunity. 2024;57(4):674–99. 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.03.012.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Deng Z, Lu L, Li B, Shi X, Jin H, Hu W. The roles of inflammasomes in cancer. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1195572. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1195572.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Okin D, Kagan JC. Inflammasomes as regulators of non-infectious disease. Semin Immunol. 2023;69:101815. 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101815.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Liang Q, Wu J, Zhao X, Shen S, Zhu C, Liu T, et al. Establishment of tumor inflammasome clusters with distinct immunogenomic landscape aids immunotherapy. Theranostics. 2021;11:9884–903. 10.7150/thno.63202.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Bagaev A, Kotlov N, Nomie K, Svekolkin V, Gafurov A, Isaeva O, et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2021;39(845-65):e7. 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.014.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Kantono M, Guo B. Inflammasomes and cancer: The dynamic role of the inflammasome in tumor development. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1132. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01132.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Guo H, Callaway JB, Ting JP. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med. 2015;21:677–87. 10.1038/nm.3893.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: Triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity. 2019;51:27–41. 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC, Clarke SJ. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:e493–503. 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70263-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Gu D, Ao X, Yang Y, Chen Z, Xu X. Soluble immune checkpoints in cancer: production, function and biological significance. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):132. 10.1186/s40425-018-0449-0.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Ribas A, Wolchok JD. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science. 2018;359:1350–5. 10.1126/science.aar4060.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Karki R, Kanneganti TD. Diverging inflammasome signals in tumorigenesis and potential targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019;19:197–214. 10.1038/s41568-019-0123-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Huang Y, Wang H, Hao Y, Lin H, Dong M, Ye J, et al. Myeloid PTEN promotes chemotherapy-induced NLRP3-inflammasome activation and antitumour immunity. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22:716–27. 10.1038/s41556-020-0510-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Li YF, Nanayakkara G, Sun Y, Li X, Wang L, Cueto R, et al. Analyses of caspase-1-regulated transcriptomes in various tissues lead to identification of novel IL-1beta-, IL-18- and sirtuin-1-independent pathways. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:40. 10.1186/s13045-017-0406-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Goldman MJ, Craft B, Hastie M, Repecka K, McDade F, Kamath A, et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:675–8. 10.1038/s41587-020-0546-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Zhang Y, Kwok-Shing Ng P, Kucherlapati M, Chen F, Liu Y, Tsang YH, et al. A pan-cancer proteogenomic atlas of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway alterations. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:820–32.e3. 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.04.013.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C, Koeffler HP. Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018;28:1747–56. 10.1101/gr.239244.118.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Hanzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinforma. 2013;14:7. 10.1186/1471-2105-14-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Frankish A, Diekhans M, Ferreira AM, Johnson R, Jungreis I, Loveland J, et al. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:D766–73. 10.1093/nar/gky955.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW, Shi W, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:e47. 10.1093/nar/gkv007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila WK, Luna A, La KC, et al. Oncogenic signaling pathways in the cancer genome atlas. Cell. 2018;173(321-37):e10. 10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.035.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdottir H, Ghandi M, Mesirov JP, Tamayo P. The molecular signatures database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015;1:417–25. 10.1016/j.cels.2015.12.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 2019;10:1523. 10.1038/s41467-019-09234-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Brunet JP, Tamayo P, Golub TR, Mesirov JP. Metagenes and molecular pattern discovery using matrix factorization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:4164–9. 10.1073/pnas.0308531101.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Gaujoux R, Seoighe C. A flexible R package for nonnegative matrix factorization. BMC Bioinforma. 2010;11:367. 10.1186/1471-2105-11-367.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martinez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2612. 10.1038/ncomms3612.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Finotello F, Mayer C, Plattner C, Laschober G, Rieder D, Hackl H, et al. Molecular and pharmacological modulators of the tumor immune contexture revealed by deconvolution of RNA-seq data. Genome Med. 2019;11:34. 10.1186/s13073-019-0638-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Becht E, Giraldo NA, Lacroix L, Buttard B, Elarouci N, Petitprez F, et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016;17:218. 10.1186/s13059-016-1070-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Racle J, de Jonge K, Baumgaertner P, Speiser DE, Gfeller D. Simultaneous enumeration of cancer and immune cell types from bulk tumor gene expression data. Elife. 2017;6:e26476. 10.7554/eLife.26476.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Li B, Severson E, Pignon JC, Zhao H, Li T, Novak J, et al. Comprehensive analyses of tumor immunity: implications for cancer immunotherapy. Genome Biol. 2016;17:174. 10.1186/s13059-016-1028-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Hu C, Li T, Xu Y, Zhang X, Li F, Bai J, et al. CellMarker 2.0: an updated database of manually curated cell markers in human/mouse and web tools based on scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:D870–6. 10.1093/nar/gkac947.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Jiang P, Gu S, Pan D, Fu J, Sahu A, Hu X, et al. Signatures of T cell dysfunction and exclusion predict cancer immunotherapy response. Nat Med. 2018;24:1550–8. 10.1038/s41591-018-0136-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Yang W, Soares J, Greninger P, Edelman EJ, Lightfoot H, Forbes S, et al. Genomics of drug sensitivity in cancer (GDSC): a resource for therapeutic biomarker discovery in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41:D955–61. 10.1093/nar/gks1111.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Hakimi AA, Ostrovnaya I, Reva B, Schultz N, Chen YB, Gonen M, et al. Adverse outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with mutations of 3p21 epigenetic regulators BAP1 and SETD2: a report by MSKCC and the KIRC TCGA research network. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:3259–67. 10.1158/1078-0432.Search in Google Scholar
[45] Niersch J, Vega-Rubin-de-Celis S, Bazarna A, Mergener S, Jendrossek V, Siveke JT, et al. A BAP1 synonymous mutation results in exon skipping, loss of function and worse patient prognosis. iScience. 2021;24:102173. 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102173.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Wu XH, Zhu JM, Lin BH, Qiu QR, Ruan ZT, Wei Y, et al. Semantic computed tomography features for predicting BRCA1-associated protein 1 and/or tumor protein p53 gene mutation status in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023;116:666–75. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.12.023.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, Gafanov R, Hawkins R, Nosov D, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1116–27. 10.1056/NEJMoa1816714.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, Rini B, Albiges L, Campbell MT, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:1103–15. 10.1056/NEJMoa1816047.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Motzer RJ, Escudier B, Tomczak P, Hutson TE, Michaelson MD, Negrier S, et al. Axitinib versus sorafenib as second-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: overall survival analysis and updated results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:552–62. 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70093-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Tomita Y, Motzer RJ, Choueiri TK, Rini BI, Miyake H, Uemura H, et al. Efficacy and safety of avelumab plus axitinib in elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101. ESMO Open. 2022;7:100450. 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100450.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Rini BI, Pal SK, Escudier BJ, Atkins MB, Hutson TE, Porta C, et al. Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (TIVO-3): a phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:95–104. 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30735-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[52] Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1061–8. 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.9764.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J, Hawkins R, Guo J, et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:722–31. 10.1056/NEJMoa1303989.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[54] Motzer RJ, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Shah AY, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma (CheckMate 9ER): long-term follow-up results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23:888–98. 10.1016/S1470-2045(22)00290-X.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] McDermott DF, Huseni MA, Atkins MB, Motzer RJ, Rini BI, Escudier B, et al. Clinical activity and molecular correlates of response to atezolizumab alone or in combination with bevacizumab versus sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 2018;24:749–57. 10.1038/s41591-018-0053-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Motzer RJ, Powles T, Atkins MB, Escudier B, McDermott DF, Alekseev BY, et al. Final overall survival and molecular analysis in IMmotion151, a phase 3 trial comparing atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs sunitinib in patients with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8:275–80. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.5981.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Raeber ME, Sahin D, Karakus U, Boyman O. A systematic review of interleukin-2-based immunotherapies in clinical trials for cancer and autoimmune diseases. EBioMedicine. 2023;90:104539. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104539.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[58] Hannan R, Mohamad O, Diaz de Leon A, Manna S, Pop LM, Zhang Z, et al. Outcome and immune correlates of a phase II trial of high-dose interleukin-2 and stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(24):6716–25. 10.1158/1078-0432.Search in Google Scholar
[59] Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, et al. Long-term outcomes with nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2022;40:127–37. 10.1200/JCO.21.02229.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[60] Choueiri TK, Powles T, Albiges L, Burotto M, Szczylik C, Zurawski B, et al. Cabozantinib plus nivolumab and ipilimumab in renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:1767–78. 10.1056/NEJMoa2212851.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Remon J, Steuer CE, Ramalingam SS, Felip E. Osimertinib and other third-generation EGFR TKI in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:i20–7. 10.1093/annonc/mdx704.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Mendzelevski B, Ferber G, Janku F, Li BT, Sullivan RJ, Welsch D, et al. Effect of ulixertinib, a novel ERK1/2 inhibitor, on the QT/QTc interval in patients with advanced solid tumor malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018;81:1129–41. 10.1007/s00280-018-3564-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[63] Sullivan RJ, Infante JR, Janku F, Wong DJL, Sosman JA, Keedy V, et al. First-in-class ERK1/2 inhibitor ulixertinib (BVD-523) in patients with MAPK mutant advanced solid tumors: Results of a phase I dose-escalation and expansion study. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:184–95. 10.1158/2159-8290.Search in Google Scholar
[64] Li Y, Gu J, Ding Y, Gao H, Li Y, Sun Y, et al. A small molecule compound IX inhibits telomere and attenuates oncogenesis of drug-resistant leukemia cells. FASEB J. 2020;34:8843–57. 10.1096/fj.201902651RR.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[65] Chen L, Hou J, Zeng X, Guo Q, Deng M, Kloeber JA, et al. LRRK2 inhibition potentiates PARP inhibitor cytotoxicity through inhibiting homologous recombination-mediated DNA double strand break repair. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e341. 10.1002/ctm2.341.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[66] Wang M, Chen S, He X, Yuan Y, Wei X. Targeting inflammation as cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2024;17(1):13. 10.1186/s13045-024-01528-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Zhang WJ, Li KY, Lan Y, Zeng HY, Chen SQ, Wang H. NLRP3 inflammasome: A key contributor to the inflammation formation. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023;174:113683. 10.1016/j.fct.2023.113683.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[68] Chen Y, Ye X, Escames G, Lei W, Zhang X, Li M, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: contributions to inflammation-related diseases. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):51. 10.1186/s11658-023-00462-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?

