Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
-
Vahideh Hashemzadeh
, Reza Gharari Arefi
und Mohammad Ehsan Taghavizadeh Yazdi
Abstract
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have unique features that might lead to the development of a new class of diabetic medicines. AuNPs were biosynthesized utilizing sodium-alginate. UV-Vis-spectroscopy, Fourier transforms infrared, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and energy dispersive X-ray were used to examine the particles. The potential of AuNPs for improving the diabetes condition was examined along with swimming in rats. FESEM image revealed the spherical morphology with an average particle size of 106.6 ± 20.8 nm. In the diabetic group, serum glucose, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, cholesterol, and triglyceride (TG) levels were significantly higher than the control group. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) was significantly higher and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) was significantly lower in the diabetic group compared to the control group. Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were also significantly higher in the D group. However, in the groups treated with swimming and gold, these parameters were significantly improved. Specifically, serum-glucose, BUN, creatinine, cholesterol, and TG levels were significantly reduced, while LDL was significantly decreased in the diabetic + swimming + AuNPs group and HDL was significantly increased in the diabetic + AuNPs group. MDA levels were significantly decreased in the treated groups, and other antioxidants were significantly improved in the diabetic + swimming + AuNPs group. Catalase levels were also significantly improved in the D + gold group. It can be concluded that both AuNPs and swimming can decrease diabetic complications.
Graphical Abstract

1 Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of individuals across the world. Diabetes can cause retinopathy, neuropathy, renal failure, and cardiovascular disease, among other complications [1,2]. Type 1 diabetes is brought on by the body’s immune system attacking the pancreatic cells that produce insulin and insulin treatment must last throughout one’s life. When the body develops insulin resistance and the pancreas is unable to generate enough insulin to maintain blood glucose levels within normal ranges, type 2 diabetes develops [3]. Type 2 diabetes is frequently linked to obesity and inactivity [4]. Today, for people with type 1 diabetes and, maybe, some people with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is the cornerstone of diabetes care. Blood sugar levels must be regularly assessed during insulin therapy to adjust the dosage. To increase insulin sensitivity and reduce the amount of glucose in the blood, it is required to change lifestyle with regular physical activity and a nutritious diet [5]. The diet should be rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, but low in saturated and Tran’s fats, which can help regulate blood sugar levels more effectively. Physical exercise also lowers the likelihood of heart failure, which is a major diabetic consequence. The drugs metformin sulfonylureas and DPP-4 inhibitors are examples of oral drugs that can reduce blood glucose levels by boosting insulin production or strengthening insulin sensitivity [6]. The agonists of the GLP-1 receptor and SGLT2 blockers are two recent kinds of drugs that could assist in reducing levels of blood glucose by boosting insulin production or decreasing its absorption in the kidneys. These drugs may also help lower the possibility of cardiovascular disease. To achieve optimal blood sugar management, effective diabetes treatment necessitates a collaborative approach involving the patient and the medical professionals [7,8].
Swimming is a type of aerobic activity that has been found to provide a variety of health advantages, including a lower risk of chronic illnesses like diabetes [9–11]. Swimming can help people with diabetes minimize oxidative stress by increasing insulin sensitivity [12]. Insulin resistance, which is related to increased oxidative stress, is a fundamental characteristic of type 2 diabetes. Swimming has been proven to enhance insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetics, which may aid in the reduction of oxidative stress [13,14]. Swimming has been demonstrated in studies to reduce anxiety-like behavior and oxidative stress in several animal models, as well as to reduce brain oxidative stress, enhance glucose levels, and reduce insulin resistance [15–17]. Swimming may also help to lower oxidative stress by boosting the body’s production of nitric oxide (NO). NO is a chemical that aids in blood flow regulation and inflammation reduction, both of which can contribute to oxidative stress. Swimming has been demonstrated to boost NO generation in people, which may aid in the reduction of oxidative stress and general health [18–20]. Swimming, in addition to reducing oxidative stress, can improve cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and promote weight loss in people with diabetes, making it an ideal form of exercise for people with diabetes who may have mobility issues or other health concerns [21,22].
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) have demonstrated distinct optical, electrical, and chemical features that enable them to be used in a wide range of applications, including biological studies [23,24]. AuNPs have recently emerged as a viable contender for the treatment of diabetes and might be employed as a novel class of diabetic treatments. AuNPs are particularly capable of interacting with biological molecules due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio [25,26]. AuNPs demonstrated biocompatibility, stability, and ease of modification [27,28]. Due to their anti-inflammatory properties, AuNPs may decrease inflammation in diabetes. Numerous diabetes-related issues, such as nerve damage and renal failure, are greatly influenced by inflammation. By lowering inflammation, AuNPs may be able to help avoid or postpone them. AuNPs were also shown that could decrease blood glucose levels in diabetic rats while having no notable adverse effects [29,30].
AuNPs were able to improve glucose uptake in cells and increase insulin sensitivity [31]. Unlike other antioxidants such as vitamin C or E, AuNPs do not oxidize and do not form toxic byproducts. AuNPs’ morphology and size can also be changed to boost their antioxidant capacity. It has been demonstrated that AuNPs increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes including glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), which reduce oxidative damage. In addition, it was found that AuNPs could stop lipid peroxidation, a process that can injure cells [32–34].
In general, AuNPs have special qualities that make them an appealing option for biomedical applications, implying that AuNPs have the potential to be employed as an efficient diabetes therapy, while additional study is required to fully appreciate their potential. Herein, alginate-coated AuNPs were prepared in one step and fully characterized. The alginate-coated AuNPs were also tested in a diabetic animal model.
2 Materials and methods
The materials used for the synthesis of nanoparticles were procured from Sigma Chemical Group. The synthesized AuNPs were characterized using UV-Vis spectroscopy, Fourier transforms infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy. Also, biochemical assessment kits are purchased from the ParsAzmoon, IR.
2.1 Synthesis of AuNPs
In a 250 mL round-bottom flask, 1 g of sodium alginate was dissolved in 90 mL of deionized water. To ensure consistency, the solution was continuously agitated and mixed for a duration of 24 h at room temperature (approximately 20–25°C). Once the alginate was completely dissolved, 2 mL of a 1% gold(iii) chloride trihydrate solution was diluted until the volume reached 10 mL. The gold chloride solution was added dropwise to the flask while being stirred for approximately 5 min. Subsequently, the reaction mixture was heated to facilitate the reduction of gold ions until it reached 80°C. The reaction was continued for 30 min at this temperature. The color of the solution changed from yellow to violet, indicating the formation of AuNPs. Finally, the solution was allowed to cool to room temperature over 2 h. For the supplemental dose, 20 mg/l was orally administered by gavage to rats 1 h before exercise.
2.2 Animals
In this research, 35 male Wistar rats aged 8–10 weeks weighing 220 ± 60 g were used. The rats were kept in the animal house of Torbat-e heydarieh University of Medical Sciences. The maintenance conditions included 12 h of light and 12 h of darkness and an ambient temperature of 20–24 degrees. Animals had free access to drinking water during the experimental period. From five days before the start of the experiment and throughout the entire period of the experiment, the rats were fed individually with normal food in separate cages.
Rats were, using a random number table, divided into five experimental groups including the following groups: control, diabetic, diabetic + swimming, diabetic + AuNPs and diabetic + swimming + AuNPs who were treated 8 weeks after diabetes induction. Control group and diabetic group were used as a baseline for comparison, which did not receive any treatment. Diabetic + swimming group has been exercised (swimming exercise). Diabetic + AuNPs group received AuNPs’ supplement. Diabetic + swimming + AuNPs group has been exercised (swimming) and received AuNPs’ supplement.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals and has been approved by the regional Animal Research Ethics Committee of Working Group of Ethics in Sports Science Research Institute (IR.SSRI.REC.1401.1725).
2.3 Diabetes induction
To induce diabetes, one dose (90 mg/kg, BW) of streptozotocin (STZ) (Merck company, Germany) with 0.9% saline solution and under 12-h fasting conditions was administered intraperitoneally to diabetes groups. After administration of STZ injection after 72 hours, to diagnose diabetes of the animals, a few drops of blood were taken from the sinus of the eye in the fasting state, and blood glucose concentration of more than 250 mg/dL was considered diabetic [35].
2.4 Swimming method
In the swimming method, 3 h before the experiment, rats were placed in the water tank for 3 min to swim for some time [36].
In the experiment, diabetic and nondiabetic rats after receiving the necessary treatments (20 mg/kg/day, P.O, 1 h before training) individually from the height of 20 cm were placed gently in the water. In these conditions, animals will swim in the water to maintain their stability [37,38]. Then the tested rats were subjected to swimming exercise regularly for 1 h a day during 8 weeks for 5 days [39]. After each exercise, the rats were dried with a soft towel and placed in a storage box near an electric heater for 20 s [40,41].
2.5 Measurement of biochemical parameters
Biochemical parameters including serum glucose, cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and creatinine were measured by relevant kits (ParsAzmoon, IR) at the end of the experiment (day 56).
2.6 Determination of malondialdehyde (MDA)
To analyze for MDA, 0.5 mL of sample was mixed to 1 mL of trichloroacetic acid (10%), 2 ml of HCl, and 1.5 mL of TBA (0.67%). It was then placed in a water bath and boiled for 40 min. A total of 1.5 ml of l-butanol and 0.025 ml of HCl were added to the samples after they had cooled. The following stage involved centrifuging the solution at 1,000 g for 10 min and measuring the supernatant absorbance at 535 nm. The MDA concentration was calculated according to the following equation.
Our MDA data were expressed per gram of renal tissue.
2.7 Measurement of thiol contents
To determine the total thiol concentration, 50 µL of rat renal tissue homogenate was gently mixed in 1 ml Tris-EDTA buffer (pH = 8.6) and the absorbance was read at 412 nm against Tris-EDTA buffer alone (A1). Then, 20 µL of 10 mM solution of DTNB was added to the solution, and it was kept at room temperature for 15 min and the absorbance was read for the second time (A2). The absorbance of the DTNB reagent was also read as blank (B) [42]. The thiol levels were determined by a spectrophotometric method based on the use of Ellman’s reagent, and the results are expressed as per gram of tissue.
2.8 Catalase (CAT) activity
CAT activity was measured by the Aebi method (1983). This method is based on detection of the rate constant (k) (dimension: s − 1, k) of hydrogen peroxide destruction by evaluating the reduction in absorbance at 240 nm per minute, and the activity of this enzyme was determined as K (rate constant) per liter.
2.9 SOD activity
SOD activity was evaluated by the Madesh and Balasubramanian procedure. A colorimetric assay involving generation of superoxide by pyrogallol auto-oxidation and the inhibition of superoxide-dependent reduction of the tetrazolium dye, MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl) 2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide), to its Formosan by SOD was measured at 570 nm. An unit of SOD activity was defined based on the amount of enzyme causing 50% inhibition in the MTT reduction rate [43].
2.10 Statistical analysis
The data were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to determine whether the distribution of the data was normal, and after that, the one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test were used to evaluate the normal data and Mann–Whitney for anormal data. A difference with a p-value of 0.05 was taken into account. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v11.5.
3 Results
3.1 UV-Vis spectroscopy and FTIR spectroscopy
The alginate-coated AuNPs’ UV-Vis spectra are shown in Figure 1. The strong absorbance peaks for the alginate-coated AuNPs at 534 nm demonstrated the existence or formation of AuNps.

The UV-Vis spectrum of the as-synthesized alginate-coated AuNPs.
The potential functional groups in alginate-coated AuNPs were investigated using FTIR spectroscopy. AuNPs show no adsorption bands in FTIR curves. Hence, the appeared absorption bands were associated with the existing chemical bonds of alginate coating. Figure 2 displays an adsorption band at 3,418 cm−1, which was corresponded to the hydroxyl group (−OH). The C–H absorption band appeared at 2,925 cm−1. The carboxyl group stretching vibrations, the asymmetric and symmetric absorption bands, are observed at 1,645 and 1,418 cm−1, respectively. The C–O–C vibration also appeared at 1,035 cm−1.

FTIR spectrum of the as-synthesized alginate-coated AuNPs.
3.2 FESEM
FESEM was used to analyze the morphology and average particle sizes of the alginate-coated AuNPs. It was shown that particles were spherical, and possibly there was a coating of alginate polymer. EDX analyses displayed the purity of the prepared alginate-coated AuNPs, containing gold, carbon, and oxygen. The particle size distribution was also determined by using ImageJ software and SPSS. The mean particle size was 106.6 ± 20.8 nm, indicating a narrow particle size distribution (Figure 3).

FESEM images (a and b), the EDX analysis (c), and the particle size distribution of the alginate-coated AuNPs (d).
3.3 Biochemical parameters
Serum glucose in the D group significantly boosted in comparison with the control (p < 0.001), while this condition improved in treated groups with exercise and gold (p < 0.001) (Figure 4).

The glucose level in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared to control, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
Serum BUN and creatinine significantly increased in the D group compared to the control (p < 0.001), while these parameters in the treated groups with exercise and gold significantly reduced (p < 0.01 to p < 0.001) (Figures 5 and 6).

The creatinine level in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared to control, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
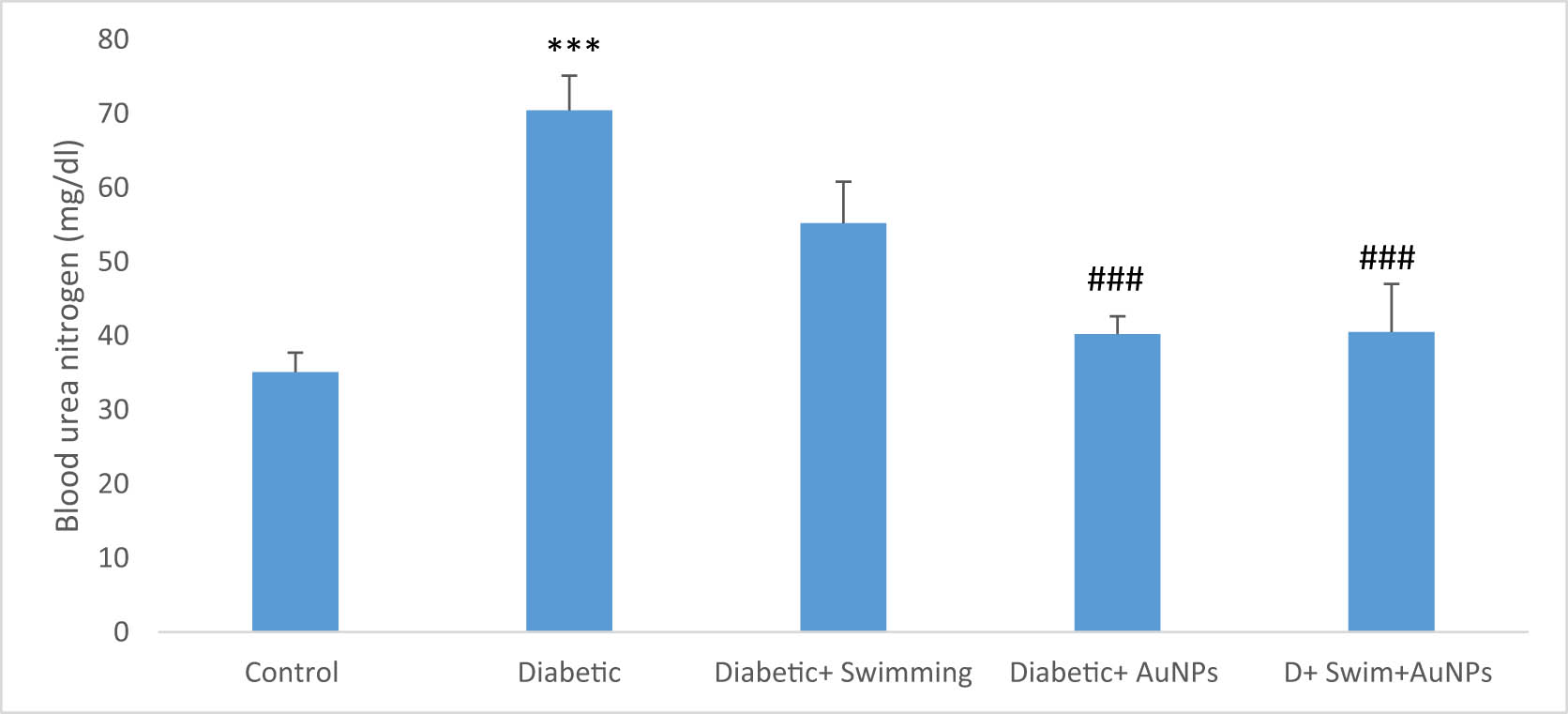
The BUN level in all groups. Data presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared to control, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
Also, the cholesterol and TG significantly enhanced in the D group compared to the control (p < 0.001), while in treated groups with exercise and gold except D + EX, this condition improved (p < 0.001) (Figure 7).

The TG and cholesterol levels in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared to control, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
Both LDL and HDL significantly changed in the D group than the control (p < 0.001) while the LDL significantly decreased in the D + Gold + Ex (p < 0.001) and the HDL significantly increased in the D + Gold group (p < 0.001) (Figure 8).
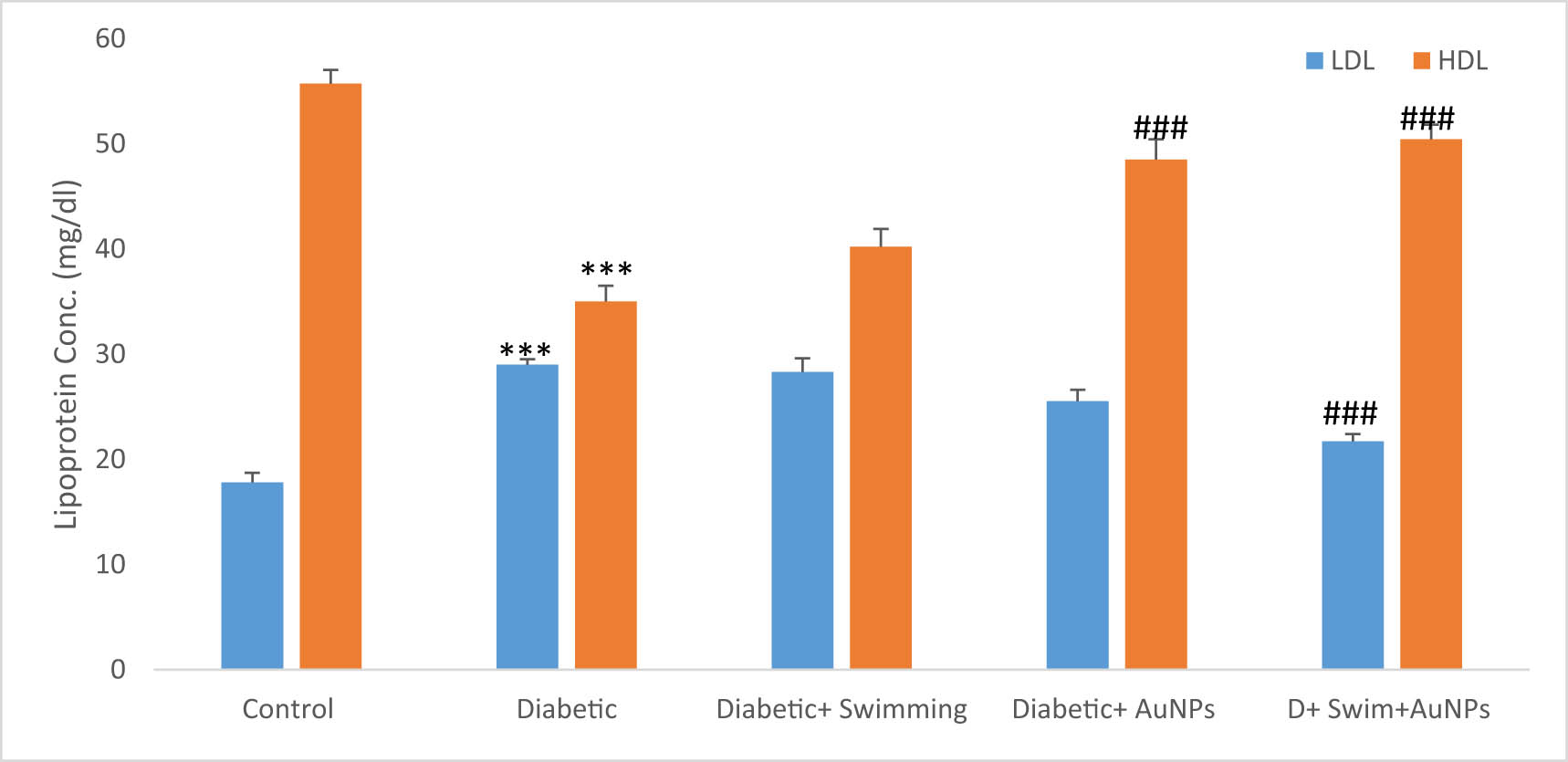
The lipoprotein levels in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.001 compared to control, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
MDA in the D group significantly increased than the control (p < 0.001), while in treated groups with exercise and gold decreased (p < 0.001). Other antioxidants including thiol, SOD, and CAT significantly decreased in the D group than the control (p < 0.001), while these reductions were improved in the D + Gold + Ex group. About CAT, improvement also was significant in the D + Gold group than the D group (p < 0.001) (Table 1).
Redox levels in all groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM
| Groups | Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA | Thiol | SOD | CAT | |
| Control | 0.39 ± 0.02 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | 0.61 ± 0.06 | 54.2 ± 4.9 |
| Diabetic | 1.43 ± 0.16*** | 0.09 ± 0.02*** | 0.07 ± 0.01*** | 10.3 ± 1.7*** |
| Diabetic + swimming | 0.82 ± 0.09### | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 32.8 ± 4.5 |
| Diabetic + AuNPs | 0.54 ± 0.06### | 0.2 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 46.7 ± 10.5### |
| D + Swim + AuNPs | 0.4 ± 0.03### | 0.5 ± 0.06### | 0.5 ± 0.03### | 41.9 ± 3## |
***p < 0.001 compared to control, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to diabetic group.
4 Discussion
Following the successful production and stabilization of AuNPs using alginate, the potential applications of these nanoparticles in the treatment of diabetes along with the effect of swimming exercise. The alginate-coated AuNPs displayed could enhance biocompatibility, making them suitable for use in biological systems. AuNPs were prepared in deionized water in alginate solutions with the presence of gold(iii) chloride trihydrate. The UV-Vis absorption of Au NPs prepared in alginate has revealed the characteristic peak at 534 nm, suggesting the formation of colloidal AuNPs. The addition of alginate can stabilize small-sized AuNPs and slow down the precipitation rate of large-sized AuNPs. The low stability of AuNPs can complicate their use in biological environments and complicate manufacturing and shipping processes. To counter this, a strategy of drying and dispersion was adopted based on cavities formed by alginate chains to prevent Au NPs from contacting each other. FESEM images showed a spherical shape and an even dispersion of AuNPs with the particle size distribution of 106.6 ± 20.8 nm. The average particle size of 106.6 ± 20.8 nm in AuNPs holds immense potential for biomedical applications. The particle size of AuNPs plays a crucial role in their cellular interactions. Smaller AuNPs (such as those around 106.6 nm) exhibit rapid distribution and renal clearance due to their small size, allowing them to efficiently interact with cells [24,44–46]. These interactions influence cellular uptake, intracellular trafficking, and potential toxicity. The size of AuNPs affects their biocompatibility. Smaller particles may have reduced nonspecific organ accumulation, minimizing potential toxicity [44]. This is crucial for long-term therapeutic applications. The compositional studies (EDX analysis) also showed the purity of the prepared AuNPs. The magnified images of AuNPs show that the particles were bud like and spherical in shape and most probably with a layer of alginate, where AuNPs were contained and protected. The FTIR spectrum also confirmed the presence of alginate in the composition of prepared AuNPs.
The toxicity of metallic nanomaterials is induced by the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which causes oxidative stress [47–49]. AuNPs operate as antioxidants by inhibiting the release of ROS, scavenging free radicals, and increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes [50,51]. AuNPs exhibit anti-oxidative and anti-hyperglycemic properties, according to in vivo investigations. Nano gold with a diameter of 21 nm boosts antioxidant capacity in the blood and liver while decreasing blood glucose levels [52]. AuNPs may induce significant anti-oxidative reactions in biomolecules, such as the introduction into free SH groups, resulting in a reduced antioxidant enzyme profile. The recent study has demonstrated that antioxidants suited to neutralize ROS are effective in reducing experimentally induced diabetes and the degree of diabetic effects [53]. Because of their antioxidant and anti-hyperglycemic effects, AuNPs may be effective in treating diabetes [52,54]. Recently, the inhibitory role of AuNPs on the d-ribose glycation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) revealed that AuNPs of varied sizes and concentrations prevented AGE production in BSA, with a sense of the largest total surface area producing the greatest inhibition. This shows that gold colloidal particles might be used to treat diabetes and hyperglycemia [55]. AuNPs can greatly increase antioxidant production in STZ-induced diabetic rats, a well-known model of type 1 diabetes mellitus. The potential of AuNPs to regulate hyperglycemic situations in diabetic rats was examined in four groups including controls, diabetic group, diabetic group treated with AuNPs, and healthy rats treated with AuNPs. It was discovered that glucose levels in diabetic rats were substantially higher than in controls. Both diabetic and nondiabetic rats have impaired kidney and liver function following AuNP treatment. The results indicated that AuNPs can boost antioxidant activity in STZ-induced diabetic rats [56]. A study also investigated the modulating influence of AuNPs on protective antioxidant mechanism in male Wistar diabetic rats with autism spectrum disorder. Normal littermates that had been fed by control mothers only received injections of citrate buffer [57]. STZ was injected intraperitoneally once into the overnight starved autistic pups to cause diabetes mellitus. In comparison to other metrics, AuNPs at 2.5 mg/kg b. wt. improved several of the stress-related indices (SOD, GPX, and CAT), blood antioxidant capacity, and lipid profile [58]. In another study, diabetic nephropathy exposed human proximal renal tubular epithelial cells HK-2 to glyco-oxidative damage. Antioxidant activity has been demonstrated in AuNPs with a diameter of 30 nm. At physiological pH, the produced AuNPs demonstrated colloidal stability, which reduced high glucose-induced cytotoxicity. The inhibitory effects of AuNPs were blocked by 3-TYP (3-(1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl) pyridine), a SIRT3 (sirtuin 3) inhibitor. AuNPs could be employed to minimize the risk of diabetic nephropathy development [54]. AuNPs produced using Gymnema Sylvester R. Br have shown a considerable reduction in blood glucose levels in diabetic rats as well as an anti-inflammatory activity, which was measured by serum levels of TNF-, IL-6, and C-reactive protein [59]. Sambucus nigra L. (SN) extract-functionalized AuNPs have been found to reduce the amount of glycated hemoglobin while having an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect. In an experimental rat model of diabetes, the antidiabetic effects of AuNPs functionalized with SN extract demonstrated that AuNPs lowered MDA levels, COX-2 expression, and proMMP-2 activity while increasing the GSH/GSSG ratio in the muscles and throughout the body and histopathology revealed no morphological abnormalities [52]. AuNPs display strong antioxidant properties that may be used to fight oxidative stress and lessen cellular damage [60–62]. It is possible that they might be used as effective antioxidants in diabetes, where it was observed to reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in animal models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease [63–65]. In addition, AuNPs have been used as drug delivery systems in the treatment of cancer, where they may target cancer cells, release therapeutic compounds in a controlled manner [66].
Swimming can assist to lower oxidative stress by boosting the body’s production of antioxidants, which are molecules that neutralize ROS and keep them from causing harm. Swimming exercise has been demonstrated to improve oxidative stress indicators such as MDA, glutathione disulfide (GSSG), and glutathione (GSH) in type 2 diabetic patients [67–69].
An investigation has demonstrated swimming exercise might lessen inflammation and depressive-like behavior in type 2 diabetic mice. Male C57BL6 mice were given a high-fat diet, STZ, and swimming exercises for a period of 4 weeks. According to the findings, mice with type 2 diabetes exhibited considerably more depressive and anhedonia-like behaviors. In type 2 diabetic mice, swimming exercise reduced anhedonia and depressive-like behaviors and also lowered the levels of glucose and inflammatory mediators in the mice’s blood [70]. In another study, the effects of a 6-week swimming program and fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) seed extract on cardiac antioxidant enzyme activity and plasma glucose were examined in STZ-induced diabetic rats [71]. The results indicated that all groups significantly decreased their body weight. Plasma glucose levels were decreased, while cardiac antioxidant enzyme activity significantly increased [72]. Swimming training and Plantago psyllium co-administration for 12 weeks improved memory deficit in STZ-nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetic rats, probably via hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effects. Another study examined the impact of Aloe vera extract and swimming exercise on the lipid profile of rats suffering from diabetes. Results indicated that compared to swimming exercise alone, swimming exercises with A. vera extract had a greater impact on changing the lipid profile of rats suffering from diabetes. In addition, compared to swimming training alone, swimming exercise with A. vera extract showed a greater effect in improving VLDL, TC, and TG in diabetic rats [73]. Also, swimming exercises with Dysphania ambrosioides extract changed the lipid profile of diabetic rats [74]. The goal of our study was to synthesize, identify, and provide AuNPs supplements for measuring antioxidant activities during exercise activities (swimming) in the recovery of rats with type 2 diabetes. It should be highlighted that this was most likely the first time AuNPs’ supplements combined with swimming have been employed in the treatment of type 2 diabetes in an animal model. In this regard, AuNPs with exercise (swimming) in diabetes have benefited the treatment group. As it was anticipated from the aforementioned studies, we expect synergistic effects in the therapy if the AuNPs were used with swimming exercise simultaneously. In this study, the effects of combined swimming and AuNPs on various parameters in STZ-induced diabetic rats have showed that serum glucose levels were significantly higher in the diabetic group compared to the control group, but improved in diabetic + swimming + AuNPs. Diabetes patients are more likely to develop renal disease, which can result in excessive BUN and creatinine levels. This is due to the fact that high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, resulting in a disease known as diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic nephropathy can impair the kidneys’ capacity to filter waste materials from the blood, resulting in elevated BUN and creatinine levels. It is critical for diabetics to frequently assess their kidney function to detect any symptoms of renal impairment early on [75–82]. The result showed that BUN and creatinine levels were likewise considerably higher in the diabetic group, but substantially lower in the groups treated with both swimming and AuNPs, showing the lower possibility of kidney diseases.
Type 2 diabetic patients are more likely to acquire high levels of TGs and cholesterol, which can lead to diabetic dyslipidemia [83–85]. A lack of “good” cholesterol, or HDL, and elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol, or LDL, and TGs describe this syndrome. Diabetic dyslipidemia raises the likelihood of stroke and cardiovascular disease in diabetics. High levels of TGs can also indicate insulin resistance, a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body grow resistant to insulin’s actions, resulting in high blood sugar levels. This can stimulate the pancreas to generate more insulin, resulting in elevated TG levels [86–88]. Diabetic patients should periodically assess their cholesterol and TG levels and collaborate with their healthcare practitioner to build a treatment plan to maintain these levels. The analyses have revealed that cholesterol and TG levels were higher in the diabetic group, but improved in treatment groups. LDL and HDL values were considerably reduced in the diabetic + swimming + AuNPs group and increased in the diabetic + swimming group. As mentioned, high glucose levels in diabetes can cause oxidative stress and cell damage, leading to consequences such as retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy [89–91]. Hence, the assessment of antioxidant indicators is crucial in diabetes because diabetes is associated with increased oxidative stress, which can cause cell and tissue damage. In this study, MDA levels were greatly reduced in the diabetes group, but higher in the diabetes + swimming + AuNPs group. Other antioxidants, such as total thiol, SOD, and CAT, were also shown to be considerably lower in diabetics. These findings imply that combining swimming with AuNPs has potential therapeutic effects for treating diabetes and its consequences. These findings can be applicable in the real world. Diabetic patients can benefit from swimming for control the diabetic complications. Also, various studies related to the nanoparticle’s applications can open a window to the bright horizon of diabetes treatment. Our study also has some limitations, which are better to considered them in future works including pathological evaluation in various tissues, using different nanoparticle doses for evaluation of the dose dependency manner and assessment of the gene expressions and molecular studies.
5 Conclusion
Results of the study indicated the synergic effects of the AuNPs administration in swimmer diabetic rats. Oxidative stress is an important mechanism involved in diabetes in swimmer diabetic rats received AuNPs reduced synergically. Therefore, it can be concluded that both AuNPs and swimming can decrease diabetic complications including biochemical and oxidative markers.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: R.M. and M.E.T.Y. designed the work. M.E.T.Y. synthesized the nanoparticle. V.H. and A.H. performed the study and analyzed data. R.G.A., M.E.T.Y., and R.M. approve the data. R.M. and M.E.T.Y. drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approve the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Goldney J, Sargeant JA, Davies MJ. Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy. Diabetologia. 2023;66:1–14.10.1007/s00125-023-05988-3Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Yazhen Yuan CS, Guan Y, Lu H, Wang D, Zhang S. Association between the VEGFR-2 -604T/C polymorphism (rs2071559) and type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Open Life Sci. 2023;18:20220081.10.1515/biol-2022-0081Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Coomans de Brachène A, Scoubeau C, Musuaya AE, Costa-Junior JM, Castela A, Carpentier J, et al. Exercise as a non-pharmacological intervention to protect pancreatic beta cells in individuals with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2023;66(3):450–60.10.1007/s00125-022-05837-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Banwari M, Kawathekar N, Jain G. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Review. J Coast Life Med. 2023;11:1171–93.Suche in Google Scholar
[5] Firnanda BJ, Nuzil DQ, Salsabila AF, Khoiriyah RA. A review article: The combination of physical activity and healthy diet in adolescents to prevent diabetes mellitus. International Conference on Halal Food and Health Nutrition. Indonesia; 2022.10.29080/ichafohn.v1i1.1130Suche in Google Scholar
[6] Scheen AJ. Metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 DM. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. America: Springer; 2023. p. 895–921.10.1007/978-3-031-13177-6_32Suche in Google Scholar
[7] American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 16. Diabetes care in the hospital: Standards of medical care in diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45:S244–S53.10.2337/dc22-S016Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Diabetes technology: Standards of medical care in diabetes−2021. Diabetes Care. 2021;44:S85–99.10.2337/dc21-S007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Alipour MR, Yousefzade N, Bavil FM, Naderi R, Ghiasi R. Swimming impacts on pancreatic inflammatory cytokines, mir-146a and NF-кB expression levels in type-2 diabetic rats. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2020;16(8):889–94.10.2174/1573399815666191115154421Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Haghani K, Bakhtiyari S, Doost Mohammadpour J. Alterations in plasma glucose and cardiac antioxidant enzymes activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: Effects of Trigonella foenum-graecum extract and swimming training. Can J Diabetes. 2016;40(2):135–42.10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.08.012Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Teixeira De Lemos E, Pinto R, Oliveira J, Garrido P, Sereno J, Mascarenhas-Melo F, et al. Differential effects of acute (extenuating) and chronic (training) exercise on inflammation and oxidative stress status in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mediators Inflamm. 2011;2011:253061.10.1155/2011/253061Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Ghiasi R, Naderi R, Sheervalilou R, Alipour MR. Swimming training by affecting the pancreatic Sirtuin1 (SIRT1) and oxidative stress, improves insulin sensitivity in diabetic male rats. Hormone Mol Biol Clin Investigation. 2019;40:20190011.10.1515/hmbci-2019-0011Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Asif AH, Nanjundan PK, Basavarajappa GM, Sreeharsha N, Chandur U, Roopashree TS. Insulin resistance modulation with lifestyle modification- proof-of-concept study in rats. Indian J Pharm Educ Res. 2020;54(4):999–1006.10.5530/ijper.54.4.173Suche in Google Scholar
[14] Rahman MM, Kwon HS, Kim MJ, Go HK, Oak MH, Kim DH. Melatonin supplementation plus exercise behavior ameliorate insulin resistance, hypertension and fatigue in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;92:606–14.10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.035Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Matinfar P, Peeri M, Azarbayjani MA. Swimming exercise attenuates anxiety-like behavior by reducing brain oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic mice. Physiol Behav. 2021;237:113449.10.1016/j.physbeh.2021.113449Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Pereira MM, de Morais H, dos Santos Silva E, Corso CR, Adami ER, Carlos RM, et al. The antioxidant gallic acid induces anxiolytic-, but not antidepressant-like effect, in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Metab Brain Dis. 2018;33(5):1573–84.10.1007/s11011-018-0264-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Zhu X, Zhang YM, Zhang MY, Chen YJ, Liu YW. Hesperetin ameliorates diabetes-associated anxiety and depression-like behaviors in rats via activating Nrf2/ARE pathway. Metab Brain Dis. 2021;36(7):1969–83.10.1007/s11011-021-00785-6Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Chis IC, Micu CM, Toader A, Moldovan R, Lele L, Clichici S, et al. The beneficial effect of swimming training associated with quercetin administration on the endothelial nitric oxide-dependent relaxation in the aorta of rats with experimentally induced type 1 diabetes mellitus. Metabolites. 2023;13(5):586.10.3390/metabo13050586Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Jahanabadi S, Tafti SD. Evaluation of the antidepressant effects of pioglitazone in ovariectomized mice through nitric oxide pathway. Tehran Univ Med J. 2022;80(1):24–31.Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Zhou XY, Zhang F, Ying CJ, Chen J, Chen L, Dong J, et al. Inhibition of iNOS alleviates cognitive deficits and depression in diabetic mice through downregulating the NO/sGC/cGMP/PKG signal pathway. Behav Brain Res. 2017;322:70–82.10.1016/j.bbr.2016.12.046Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Qadir KJ, Zangana KO. Effect of swimming program on glycemic control in male adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Sports Med Phys Fit. 2020;60(2):302–7.10.23736/S0022-4707.19.10053-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Rilstone S, Spurway P, Oliver N, Hill NE. Nutritional support for a person with type 1 diabetes undertaking endurance swimming. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:1038294.10.3389/fendo.2022.1038294Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Lee KX, Shameli K, Yew YP, Teow SY, Jahangirian H, Rafiee-Moghaddam R, et al. Recent developments in the facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their biomedical applications. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:275–300.10.2147/IJN.S233789Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Patil T, Gambhir R, Vibhute A, Tiwari AP. Gold nanoparticles: Synthesis methods, functionalization and biological applications. J Clust Sci. 2023;34(2):705–25.10.1007/s10876-022-02287-6Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Ghorani-Azam A, Mottaghipisheh J, Amiri MS, Mashreghi M, Hashemzadeh A, Haddad-Mashadrizeh A, et al. Resveratrol-mediated gold-nanoceria synthesis as green nanomedicine for phytotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Bioscience-Landmark. 2022;27(8):227.10.31083/j.fbl2708227Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Shakerimanesh K, Bayat F, Shahrokhi A, Baradaran A, Yousefi E, Mashreghi M, et al. Biomimetic synthesis and characterisation of homogenouse gold nanoparticles and estimation of its cytotoxity against breast cancer cell line. Mater Technol. 2022;37:1–8.10.1080/10667857.2022.2081287Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Darroudi M, Yazdi MET, Amiri MS. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles. 21st Century Nanoscience–A Handbook. USA: CRC Press; 2020. p. 1–18.10.1201/9780429351525-1Suche in Google Scholar
[28] Taghavizadeh Yazdi ME, Qayoomian M, Beigoli S, Boskabady MH. Recent advances in nanoparticles applications in respiratory disorders, A review. Front Pharmacology. 2023;14:1059343.10.3389/fphar.2023.1059343Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Alghamdi J, El-Refaei MF. Effects of gold and cerium oxide nanoparticles on type 1 diabetes in experimental mice. Pak J Biol Sci. 2020;23(7):959–67.10.3923/pjbs.2020.959.967Suche in Google Scholar
[30] Al-Shwaheen A, Aljabali AAA, Alomari G, Al Zoubi M, Alshaer W, Al-Trad B, et al. Molecular and cellular effects of gold nanoparticles treatment in experimental diabetic myopathy. Heliyon. 2022;8(9).10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10358Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Sharma VK, Prateeksha, Gupta SC, Singh BN, Rao CV, Barik SK. Cinnamomum verum-derived bioactives-functionalized gold nanoparticles for prevention of obesity through gut microbiota reshaping. Mater Today Bio. 2022;13:100204.10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100204Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Sasidharan S, Pottail L. Biodegradable polymers and gold nanoparticle–Decorated skin substitutes: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro biological activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021;193:3232.10.1007/s12010-021-03600-1Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] K Abdelhalim MA, Qaid HAY, Al-Mohy YH, Ghannam MM. The protective roles of vitamin E and α-lipoic acid against nephrotoxicity, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory damage induced by gold nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:729–34.10.2147/IJN.S192740Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Abdelhalim MAK, Moussa SAA, Qaid HAY, Al-Ayed MS. Effect of melanin on gold nanoparticle-induced hepatotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats. Int J Nanomed. 2018;13:5207–13.10.2147/IJN.S170758Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Habibian M, Saghafi MR, Farzanegi P. The effect of regular swimming exercise on the levels of renal matrix mettaloproteinase-2 and transforming growth factor-β1 in rats with diabetes. J Kerman Univ Med Sci. 2016;23(4):446–56.Suche in Google Scholar
[36] Zavvari F, Karimzadeh F. A review on the behavioral tests for learning and memory assessments in rat. Neurosci J Shefaye Khatam. 2017;5(4):110–24.10.18869/acadpub.shefa.5.4.110Suche in Google Scholar
[37] Farzin D, Fathiazad F, Fazellian M. Antidepressant effect of methanolic ginger extract in diabetic mice using forced-swim test. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. 2013;22(98):208.Suche in Google Scholar
[38] Abdel-Rahman MA, Hamad HH, Eltamany EH, Al-Sherbini A-S. Blending and characterization of gold nanoparticles with omega-3 oils induces antidiabetic, and antioxidant activities in-vivo. Egypt J Chem. 2020;63(7):2419–33.Suche in Google Scholar
[39] Singh AV, Kishore V, Santomauro G, Yasa O, Bill J, Sitti M. Mechanical coupling of puller and pusher active microswimmers influences motility. Langmuir. 2020;36(19):5435–43.10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03665Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Bonyadi MR, Badalzadeh R, Poozesh S, Iraj S, Mohammadi M. Effect of regular swimming exercise on pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in healthy and diabetic rats. Med J Tabriz Univ Med Sci. 2010;32(2):19–24.Suche in Google Scholar
[41] Mohammadi M, Salaei I, Sa F. Effect of swimming exercise on oxidative stress in Hippocampus of diabetic male rats. Med J Tabriz Univ Med Sci. 2009;30(2):111–8.Suche in Google Scholar
[42] Sharma J, Sharma A, Bahadur A, Vimala N, Satyam A, Mittal S. Oxidative stress markers and antioxidant levels in normal pregnancy and pre‐eclampsia. Int J Gynecol & Obstet. 2006;94(1):23–7.10.1016/j.ijgo.2006.03.025Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Madesh M, Balasubramanian K. Microtiter plate assay for superoxide dismutase using MTT reduction by superoxide. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 1998;35(3):184–8.Suche in Google Scholar
[44] Sang D, Luo X, Liu J. Biological interaction and imaging of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023;16(1):44.10.1007/s40820-023-01266-4Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Gurunathan S, Han J, Park JH, Kim J-H. A green chemistry approach for synthesizing biocompatible gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2014;9(1):248.10.1186/1556-276X-9-248Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Dheyab MA, Aziz AA, Moradi Khaniabadi P, Jameel MS, Oladzadabbasabadi N, Mohammed SA, et al. Monodisperse gold nanoparticles: A review on synthesis and their application in modern medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7400.10.3390/ijms23137400Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Alabyadh T, Albadri R, Es-Haghi A, Yazdi MET, Ajalli N, Rahdar A, et al. ZnO/CeO2 nanocomposites: Metal-organic framework-mediated synthesis, characterization, and estimation of cellular toxicity toward liver cancer cells. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(3):139.10.3390/jfb13030139Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Khalil Abad MH, Nadaf M, Taghavizadeh Yazdi ME. Biosynthesis of ZnO. Ag2O3 using aqueous extract of Haplophyllum obtusifolium: Characterization and cell toxicity activity against liver carcinoma cells. Micro Nano Lett. 2023;18(6):e12170.10.1049/mna2.12170Suche in Google Scholar
[49] Bagherian MS, Zargham P, Zarharan H, Bakhtiari M, Mortezaee Ghariyeh Ali N, Yousefi E, et al. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm properties of selenium-chitosan-loaded salicylic acid nanoparticles for the removal of emerging contaminants from bacterial pathogens. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024;40(3):86.10.1007/s11274-024-03917-zSuche in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Bednarski M, Dudek M, Knutelska J, Nowiński L, Sapa J, Zygmunt M, et al. The influence of the route of administration of gold nanoparticles on their tissue distribution and basic biochemical parameters: In vivo studies. Pharmacol Rep. 2015;67(3):405–9.10.1016/j.pharep.2014.10.019Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Zarharan H, Bagherian M, Rokhi AS, Bajgiran RR, Yousefi E, Heravian P, et al. The anti-angiogenesis and antioxidant activity of chitosan-mediated synthesized selenium-gold nanostructure. Arab J Chem. 2023;16(7):104806.10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104806Suche in Google Scholar
[52] Opris R, Tatomir C, Olteanu D, Moldovan R, Moldovan B, David L, et al. The effect of Sambucus nigra L. extract and phytosinthesized gold nanoparticles on diabetic rats. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;150:192–200.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.11.033Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Singh K, Yadav VB, Yadav U, Nath G, Srivastava A, Zamboni P, et al. Evaluation of biogenic nanosilver-acticoat for wound healing: A tri-modal in silico, in vitro and in vivo study. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 2023;670:131575.10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.131575Suche in Google Scholar
[54] Yu Y, Gao J, Jiang L, Wang J. Antidiabetic nephropathy effects of synthesized gold nanoparticles through mitigation of oxidative stress. Arab J Chem. 2021;14(3):103007.10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103007Suche in Google Scholar
[55] Liu W, Cohenford MA, Frost L, Seneviratne C, Dain JA. Inhibitory effect of gold nanoparticles on the D-ribose glycation of bovine serum albumin. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9:5461–9.10.2147/IJN.S70777Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Selim ME, Hendi AA, Alfallaj E. The possible counteractive effect of gold nanoparticles against streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes in young male albino rats. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2016;29(3):823–36.Suche in Google Scholar
[57] Singh V, Kashyap S, Yadav U, Srivastava A, Singh AV, Singh RK, et al. Nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots demonstrate no toxicity under in vitro conditions in a cervical cell line and in vivo in Swiss albino mice. Toxicol Res. 2019;8(3):395–406.10.1039/C8TX00260FSuche in Google Scholar
[58] Selim ME, Abd-Elhakim YM, Al-Ayadhi LY. Pancreatic response to gold nanoparticles includes decrease of oxidative stress and inflammation in autistic diabetic model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(2):586–600.10.1159/000369721Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[59] Karthick V, Kumar VG, Dhas TS, Singaravelu G, Sadiq AM, Govindaraju K. Effect of biologically synthesized gold nanoparticles on alloxan-induced diabetic rats-an in vivo approach. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;122:505–11.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.07.022Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Kumari S, Kamboj VK, Rajpoot D, Teotia AK, Verma PK, Singh GN. The unprecedented role of gold nanomaterial in diabetes management. Recent Pat Drug Delivery Formulation. 2019;13(3):219–27.10.2174/1871526518666181114165352Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] Mobaraki F, Momeni M, Yazdi MET, Meshkat Z, Toosi MS, Hosseini SM. Plant-derived synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles: Investigation of its antioxidant and anticancer activity against human testicular embryonic carcinoma stem cells. Process Biochem. 2021;111:167–77.10.1016/j.procbio.2021.09.010Suche in Google Scholar
[62] Li M-B. Gold nanocluster triggering near-infrared photocatalytic oxidations. Gold Bull. 2022;55(2):145–7.10.1007/s13404-022-00315-xSuche in Google Scholar
[63] Zhang J, Liu R, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Xu L, et al. Neuroprotective effects of maize tetrapeptide-anchored gold nanoparticles in Alzheimer’s disease. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2021;200:111584.10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111584Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[64] Hou K, Zhao J, Wang H, Li B, Li K, Shi X, et al. Chiral gold nanoparticles enantioselectively rescue memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4790.10.1038/s41467-020-18525-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Liu L, Li M, Xu M, Wang Z, Zeng Z, Li Y, et al. Actively targeted gold nanoparticle composites improve behavior and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease mice. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;114:111028.10.1016/j.msec.2020.111028Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Mousavi-Kouhi SM, Beyk-Khormizi A, Mohammadzadeh V, Ashna M, Es-haghi A, Mashreghi M, et al. Biological synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using Verbascum speciosum Schrad. and cytotoxicity properties toward HepG2 cancer cell line. Res Chem Intermed. 2022;48(1):167–78.10.1007/s11164-021-04600-wSuche in Google Scholar
[67] Santos GR, Cunha MR, Caldeira EJ, Galdeano EA, Prudente RCS, Pinto CAL. Effect of antioxidant treatment with n-acetylcysteine and swimming on lipid expression of sebaceous glands in diabetic mice. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):11924.10.1038/s41598-021-91459-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Stechyshyn I, Pavliuk B, Demchuk M, Chubka M. Changes in mass measurement indices, cardiointervalogram parameters and duration of swimming in animals with experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with drugs exerting antioxidant properties. Romanian J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 2020;27(2):146–52.Suche in Google Scholar
[69] Zolfalipor M, Farzanegi P, Habibian M. Combined effect of swimming training and arbutin supplementation on kidney total oxidant and antioxidant status in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Modares J Med Sci: Pathobiol. 2015;18(2):85–95.Suche in Google Scholar
[70] Gilak-Dalasm M, Peeri M, Azarbayjani MA. Swimming exercise decreases depression-like behaviour and inflammatory cytokines in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Exp Physiol. 2021;106(9):1981–91.10.1113/EP089501Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[71] Dwivedi C, Pandey H, Pandey AC, Patil S, Ramteke PW, Laux P, et al. In vivo biocompatibility of electrospun biodegradable dual carrier (antibiotic + growth factor) in a mouse model—Implications for rapid wound healing. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(4):180.10.3390/pharmaceutics11040180Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[72] Arshadi S, Bakhtiyari S, Haghani K, Valizadeh A. Effects of fenugreek seed extract and swimming endurance training on plasma glucose and cardiac antioxidant enzymes activity in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(2):87–93.10.1016/j.phrp.2014.12.007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Khajehlandi A, Abednatanzi H, Nikbakht H. The effect of swimming training and aloe Vera extract on lipid profile of male diabetic rats. J Isfahan Med Sch. 2017;34(411):1515–22.Suche in Google Scholar
[74] Paudel N, Rai M, Adhikari S, Thapa A, Bharati S, Maharjan B, et al. Green extraction, phytochemical profiling, and biological evaluation of Dysphania ambrosioides: An in silico and in vitro medicinal investigation. J Herbs, Spices Med Plants. 2023;30:1–18.10.1080/10496475.2023.2267467Suche in Google Scholar
[75] Amini N, Sadeghi A, Afif AH. The effect of eight-week caffeine supplementation and high-intensity interval training on the serum urea and creatinine levels and morphological changes of glomerular unit in diabetic rats. J Kerman Univ Med Sci. 2020;27(6):520–36.Suche in Google Scholar
[76] Giribabu N, Karim K, Kilari EK, Salleh N. Phyllanthus niruri leaves aqueous extract improves kidney functions, ameliorates kidney oxidative stress, inflammation, fibrosis and apoptosis and enhances kidney cell proliferation in adult male rats with diabetes mellitus. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;205:123–37.10.1016/j.jep.2017.05.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[77] Guo Y, Du J, Jiang M, Guo W. Full composition granules of Huanglian (Rhizoma Coptidis) decrease the serum monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and connective tissue growth factor levels and inhibit kidney nuclear factor-κB expression in rats with high-fat diet-induced diabetes. J Tradit Chin Med. 2021;41(3):424–31.Suche in Google Scholar
[78] Hadi A, Arab A, Hajianfar H, Talaei B, Miraghajani M, Babajafari S, et al. The effect of fenugreek seed supplementation on serum irisin levels, blood pressure, and liver and kidney function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A parallel randomized clinical trial. Complementary Ther Med. 2020;49:102315.10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102315Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[79] Lim J, Sanders RA, Snyder AC, Eells JT, Henshel DS, Watkins JB. Effects of low-level light therapy on streptozotocin-induced diabetic kidney. J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol. 2010;99(2):105–10.10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.03.002Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[80] Ma N, Xu N, Yin D, Zheng P, Liu W, Wang G, et al. Levels of circulating GRP78 and CHOP in endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways in Chinese type 2 diabetic kidney disease patients. Medicine (United States). 2021;100(33):e26879.10.1097/MD.0000000000026879Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Salvador LG, Carolina GF, Jesús RD, Virgilia SAM, Susana RA, Jonathan CÍ, et al. A low BUN/creatinine ratio predicts histologically confirmed acute interstitial nephritis. BMC Nephrol. 2023;24(1):75.10.1186/s12882-023-03118-0Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[82] Suhariningsih S, Glory S, Khaleyla F, Kusumawati HN, Septriana M, Susilo Y, et al. Ameliorative and renoprotective effect of electrical stimulation on blood sugar, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine levels, and the islets of langerhans weight in diabetic mice. Vet Med Int. 2022;2022. 10.1155/2022/7922892.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[83] Gharib AF, Askary AE, Almehmadi M, Allam HH, Elsayyad LK, Althobaiti BB, et al. Association of vitamin D deficiency, dyslipidemia, and obesity with the incidence of coronary artery diseases in type 2 diabetic Saudi patients. Clin Laboratory. 2022;68(10):1999–2009.10.7754/Clin.Lab.2022.211104Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[84] Hermans MP, Valensi P. Elevated triglycerides and low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level as marker of very high risk in type 2 diabetes. Curr OpEndocrinology, Diabetes Obes. 2018;25(2):118–29.10.1097/MED.0000000000000398Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[85] Khan SR, Ayub N, Nawab S, Shamsi TS. Triglyceride profile in dyslipidaemia of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Coll Phys Surg Pak. 2008;18(5):270–3.Suche in Google Scholar
[86] De Silva NMG, Freathy RM, Palmer TM, Donnelly LA, Luan J, Gaunt T, et al. Mendelian randomization studies do not support a role for raised circulating triglyceride levels influencing type 2 diabetes, glucose levels, or insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2011;60(3):1008–18.10.2337/db10-1317Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[87] Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE. Skeletal muscle triglyceride: marker or mediator of obesity-induced insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Curr Diabetes Rep. 2002;2(3):216–22.10.1007/s11892-002-0086-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[88] Kwanbunjan K, Panprathip P, Phosat C, Chumpathat N, Wechjakwen N, Puduang S, et al. Association of retinol binding protein 4 and transthyretin with triglyceride levels and insulin resistance in rural thais with high type 2 diabetes risk. BMC Endocr Disord. 2018;18(1):26.10.1186/s12902-018-0254-2Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[89] Czajka A, Malik AN. Hyperglycemia induced damage to mitochondrial respiration in renal mesangial and tubular cells: Implications for diabetic nephropathy. Redox Biol. 2016;10:100–7.10.1016/j.redox.2016.09.007Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[90] Nie P, Bai X, Lou Y, Zhu Y, Jiang S, Zhang L, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce oxidative damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):450.10.1186/s13287-021-02447-xSuche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[91] Li K, Shi X, Luo M, Wu P, Zhang M, Zhang C, et al. Taurine protects against myelin damage of sciatic nerve in diabetic peripheral neuropathy rats by controlling apoptosis of schwann cells via NGF/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(2):111557.10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111557Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?

