Abstract
The Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the Sichuan Basin represents a significant tight gas reservoir, exhibiting marked permeability variations between the southern and northern regions of western Sichuan. This study examines the reservoir characteristics of the Shaximiao Formation, with a focus on the evolution of sandstone porosity under bidirectional provenance conditions and the underlying causes of permeability variations. The insights derived from this research are critical for the effective exploration and development of tight sandstone gas reservoirs. Analysis of core samples and thin sections through X-ray diffraction, cathodoluminescence, scanning electron microscopy, and electron probe microanalysis reveals that the southern region predominantly consists of feldspathic and lithic sandstone, whereas the northern region is characterized by feldspathic lithic and lithic feldspathic sandstone. The average porosity and permeability in the southern region are 10.52% and 0.1334 × 10−3 μm2, respectively, while in the northern region, they are 9.74% and 0.5262 × 10−3 μm2. The primary reservoir spaces are intergranular primary pores and intragranular secondary dissolution pores. Compaction significantly reduces porosity, particularly in the northern region (23.94%) compared to the southern region (22.75%), primarily due to the presence of chlorite coatings. Cementation further reduces porosity, whereas dissolution processes enhance it, elucidating the similar porosity values but differing permeabilities between the regions.
1 Introduction
Sedimentary diagenesis is the geological process through which loose sediments progressively transform into solid sedimentary rocks under specific pressure and temperature conditions. This process typically occurs within strata several kilometers beneath the Earth’s surface and involves various geological actions, including compaction, cementation, recrystallization, and the formation of new minerals [1,2,3,4,5]. As the concluding stage in the formation of sedimentary rocks, diagenesis not only solidifies sediments into rock but also profoundly influences the structure of the Earth’s lithosphere and the distribution of mineral resources [6,7,8]. Additionally, differential sedimentary processes in unconventional oil and gas reservoirs significantly influence the physical properties, fracture development, and organic matter enrichment. These factors are crucial in determining the potential for oil and gas exploration and development [9,10,11].
Globally, tight sandstone oil and gas resources are regarded as possessing substantial exploration value and widespread geographical distribution [12,13,14]. According to a report by the United States Geological Survey, nearly 70 basins worldwide have been identified as containing tight gas resources [15,16,17,18]. In China, the total and technically recoverable volumes of these resources are estimated at 21.9 trillion and 11.3 trillion cubic meters, respectively, with particularly promising prospects in basins such as Sichuan, Ordos, Tarim, and offshore areas [19,20,21,22,23].
In the Sichuan Basin, tight gas resources are predominantly concentrated in Triassic and Jurassic strata, particularly within the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation [24,25,26,27]. The Shaximiao Formation has emerged as a focal point for exploration and development due to its relatively shallow burial depth, low development costs, and rapid return on investment [28,29,30]. The Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan exhibits considerable exploration potential. It contains multiple sets of source rocks, including the Lower Jurassic Ziliujing Formation, Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation dark mudstone, carbonaceous mudstone, and coal seams, all of which contribute to a rich endowment of natural gas resources. The reservoir of the Shaximiao Formation predominantly consists of delta plain sediments, with the rock type primarily being feldspathic lithic sandstone. The reservoir space is characterized by the development of residual primary intergranular pores, intergranular dissolved pores, intragranular dissolved pores, and microcracks [31,32]. These features provide a foundation for the formation of large and medium-sized gas fields. The exploration prospects for tight sandstone oil and gas within the Shaximiao Formation are significantly influenced by geological conditions [33,34]. Key geological parameters include the maturity of the source rocks, as well as the porosity and permeability of the reservoirs, alongside the sealing conditions of the cap rocks [30,35–37].
The Shaximiao Formation in this region displays bidirectional provenance from the north and south. Regarding sedimentary facies, the study area primarily develops delta-lake sedimentary systems [38–40]. The reservoirs are influenced by various diagenetic processes, resulting in significant differences in reservoir properties between the northern and southern regions. Consequently, it is essential to investigate the primary factors driving the differential evolution of these reservoirs [28,41]. This investigation will offer valuable insights for further research on tight sandstone reservoirs in the western Sichuan Basin.
2 Overview of the study area
The study area is situated in the western Sichuan Basin, the major part of which is the Longmenshan foreland basin. It encompasses the low-steep zone of the western Sichuan Depression and the low-gentle zone of the northern Sichuan Depression, which are part of the Jurassic regenerated foreland basin [42–46] (Figure 1a and b). Structurally, the southern region is delineated by the Emei-Washan fault block zone, whereas the northern region is bordered by the front uplift zone of the Micang Mountain. From south to north, the geological features include the southern depression, the southern uplift zone, the central depression, the northern uplift zone, and the northern depression [47–49] (Figure 1c).
![Figure 1
Geological overview map of western Sichuan Basin: (a) location map of the Sichuan Basin, (b) tectonic subdivision map of the Sichuan Basin (modified after Zhang et al. [52]), (c) tectonic subdivision of western Sichuan, and (d) lithological profile of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan.](/document/doi/10.1515/geo-2022-0732/asset/graphic/j_geo-2022-0732_fig_001.jpg)
Geological overview map of western Sichuan Basin: (a) location map of the Sichuan Basin, (b) tectonic subdivision map of the Sichuan Basin (modified after Zhang et al. [52]), (c) tectonic subdivision of western Sichuan, and (d) lithological profile of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan.
The strata of the Shaximiao Formation in the study area belong to the Mesozoic red beds and are characterized by deposits from tropical desert seasonal rivers [33,50,51]. The lithology comprises rhythmically interbedded feldspathic quartz sandstone, mudstone, and shale of varying thicknesses. The Shaximiao Formation exhibits a conformable contact with the underlying Lianggaoshan Formation or Qianfoya Formation, as well as with the overlying Suining Formation. Additionally, it may unconformably overlie the Ziliujing Formation. The formation thickness varies from approximately 650 to 2,500 m, with the first member of the Shaximiao Formation ranging from 120 to 350 m in thickness and the second member spanning 600 to 1,000 m (Figure 1d).
3 Samples and methods
3.1 Sample
This study utilized logging and drilling data from over 30 wells in the western Sichuan region. During sampling, sandstones from southwestern and northwestern Sichuan were specifically selected for a detailed comparative study due to the bidirectional provenance characteristics of the study area. We selected drilling cores and logging data from 13 wells in the southern region and 14 wells in the northern region of the study area. A series of tests and analyses were performed on the collected samples, including thin-section observation, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, electron probe microanalysis (EPMA), image analysis, and fluid inclusion analysis.
3.2 Test methods
All tests and analyses were performed at the Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Development Engineering at Chengdu University of Technology. Thin-section images were obtained using a Nikon LV100POL polarizing microscope. Certain thin sections were treated with alizarin red and blue epoxy resin, following the procedures outlined in SY/T 5913-2004, “Rock Sample Preparation Methods,” and SY/T 5368-2016, “Rock Thin Section Identification.” SEM and energy-dispersive spectroscopy analyses were conducted using a Quanta250 FEG field emission environmental SEM and an Oxford INCAx-max20 spectrometer to capture and analyze the pore structure, composition, and crystal morphology of the samples. Quantitative analysis of whole rock and clay was conducted using a D8 Discover X-ray diffractometer, in accordance with SY/T 5163-2010, under experimental conditions of 45 kV, 35 mA, a scanning speed of 2°/min, and a scanning range of 2°–60°. The EPMA-1720 H Series electron probe microanalyzer, operating at a test voltage of 15 kV, beam current of 10 nA, and a beam diameter of 5 μm, was utilized to quantitatively determine the component content and the contribution of physical properties of diagenetic materials in the reservoir, with a test error of less than 1%. Fluid inclusion homogenization temperatures were measured using a THMSG-600 heating and cooling stage, during which inclusions were identified under the microscope, and their homogenization temperatures were recorded through temperature changes. For nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) experiments, samples were dried and saturated under vacuum and high pressure using a MesoMR23-060H-1 NMR instrument, followed by high-speed centrifugation and NMR analysis. Subsequently, a PoreMaster60 automatic mercury porosimeter was employed to gradually increase the pressure until stabilization, recording mercury intrusion volumes and pressure values to generate curve graphs, thereby accurately characterizing the pore-throat structure and distribution patterns of the reservoir.
3.3 Calculation method
The study area, characterized as a typical low-permeability tight reservoir, employs the following methodologies to, respectively, ascertain the diagenetic intensity in the southwestern and northwestern regions of Sichuan [53].
3.3.1 Restoration of original porosity
Calculation based on the sorting coefficient, the formula is:
where φ 0 represents the initial porosity, and S 0 denotes the sorting coefficient.
3.3.2 Porosity loss due to early-stage compaction
The compaction rate during reservoir evolution is derived from factors such as initial porosity, intergranular pores, clay content, and cementation, with the following formulas:
where φ 1 represents the porosity after early compaction, φ 0 is the initial porosity, W 1 is the compaction rate, φ Inter is the intergranular porosity, φ M is the matrix content, and φ Ce is the cement content.
3.3.3 Porosity loss due to cementation
Through the process of cementation, the porosity of the reservoir further decreases. This is mainly reflected in the increase of infill materials within the voids, which occupy part of the original intergranular pores and the content of clay minerals, as represented by
where φ 1 represents the porosity after early compaction, φ 0 is the initial porosity, W 2 is the cementation rate, and φ Ce is the cement content.
3.3.4 Porosity increase due to dissolution
The porosity generated by dissolution and the intensity of the dissolution process can be expressed as follows:
where φ 2 is the porosity after cementation, φ 0 is the initial porosity, W 3 is the dissolution rate, and φ Dis is the porosity due to dissolution.
4 Results
4.1 Petrology and physical characterization
In the Sichuan region, the Shaximiao Formation predominantly comprises feldspathic sandstone and lithic feldspathic sandstone (Figure 2a). In the southwestern Sichuan area, the sandstone of the Shaximiao Formation displays a quartz mass fraction ranging from 33.3 to 43.25%, a feldspar mass fraction between 28.35 and 43.8%, and a lithic mass fraction of 7.66–14.13%. Conversely, in the northwestern Sichuan area, the sandstone displays a quartz mass fraction ranging from 56.3 to 58.63%, feldspar from 11.88 to 22%, and lithics from 15.91 to 26.41% (Figure 2b). The physical properties of the Shaximiao Formation reservoir sandstone were assessed using MIP. In the southwestern Sichuan area, the porosity of the Shaximiao Formation sandstone ranges from a maximum of 18.76% to a minimum of 0.28%, yielding an average porosity of 10.52%. The porosity distribution reveals two peaks, occurring within the ranges of 1–3% and 9–14% (Figure 2c). The average permeability is 0.1334 × 10−3 μm2, with the majority of permeability values concentrated between 0.987 × 10⁻⁵ and 0.987 × 10−3 μm2, accounting for 59.41% of the total permeability. In the northwestern Sichuan area, the porosity distribution is unimodal, with an average value of 9.74% and an average permeability of 1.2442 × 10−³ μm2 (Figure 2d). The Shaximiao Formation reservoirs in both regions exhibit similar porosity; however, they display significantly different permeability characteristics, with notable microscopic features (Figure 3).
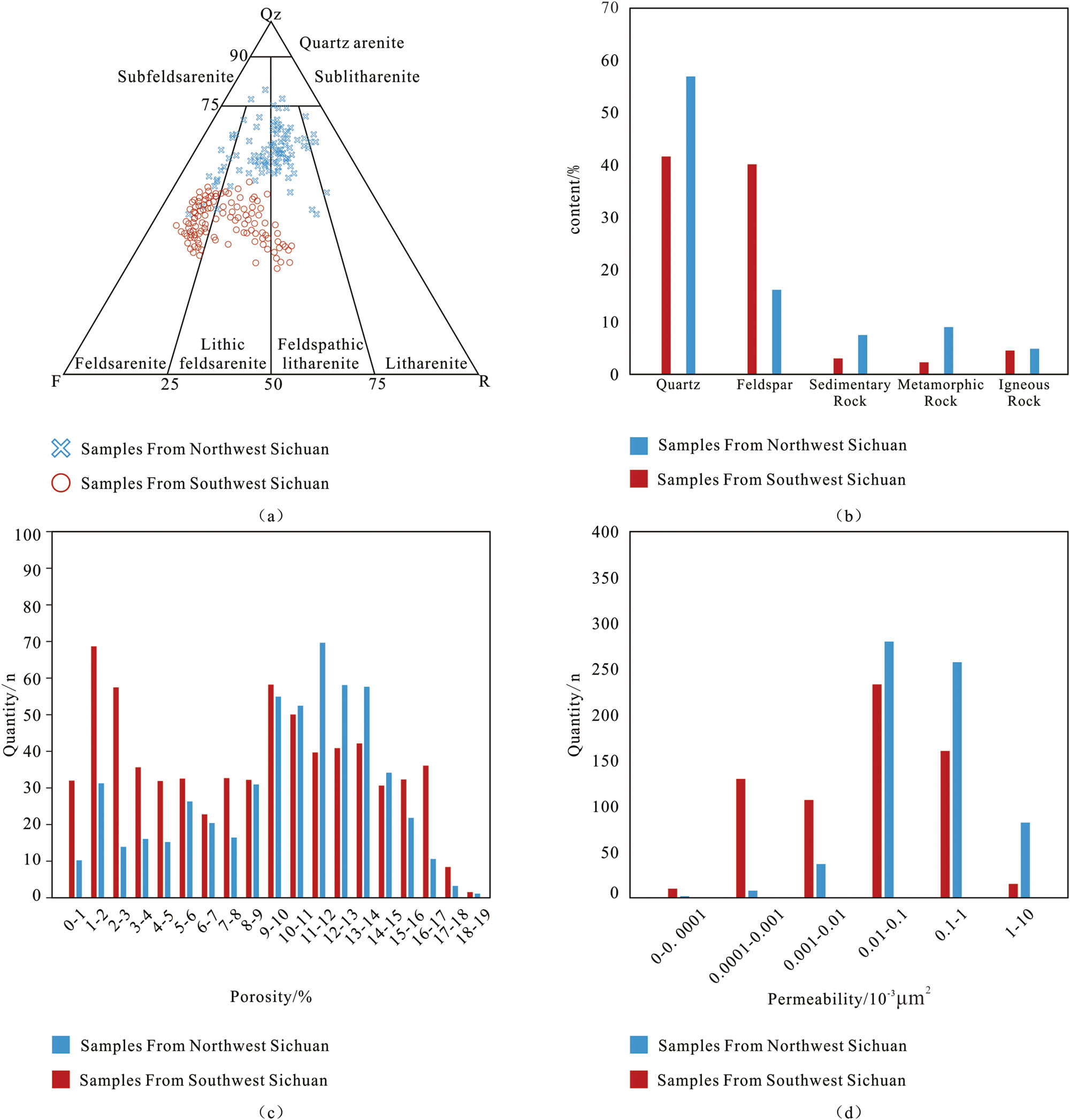
Reservoir petrological characteristics and statistical chart of porosity and permeability of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin: (a) point plot of reservoir sandstone in the Shaximiao Formation in the Sichuan region, (b) statistical chart of mineral components in the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs in the Sichuan region, (c) porosity and permeability statistical chart for the southwestern Sichuan region, and (d) porosity and permeability statistical chart for the northwestern Sichuan region.
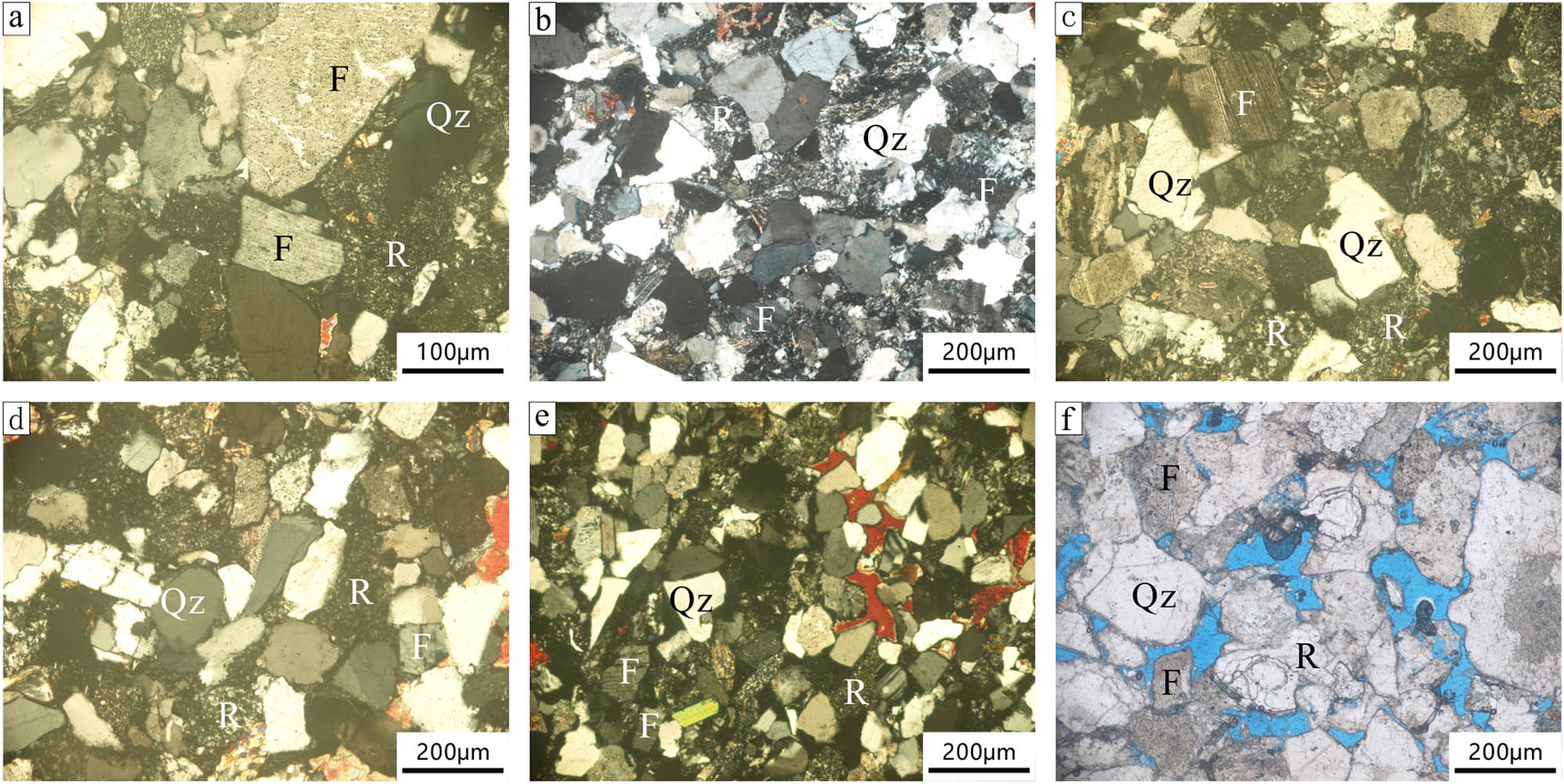
Typical microscopic photos of sandstone in the Shaximiao Formation reservoir in the Western Sichuan Basin: (a) northwestern Sichuan, W1 well, 2,870 m, coarse-grained feldspathic lithic sandstone (+), (b) northwestern Sichuan, ZT6 well, 3,005 m, medium-grained feldspathic lithic sandstone (+), (c) northwestern Sichuan, W1 well, 2,852 m, medium-grained lithic feldspathic sandstone (+), (d) southwestern Sichuan, BQ110 well, 2,052 m, medium-grained lithic feldspathic sandstone (+), (e) southwestern Sichuan, D26 well, 1246.16 m, medium-grained feldspathic sandstone (+), (f) southwestern Sichuan, JT1 well, 1938.37 m, coarse-grained lithic feldspathic sandstone (+); Qz = quartz, R = lithic, F = feldspar, Cal = calcite. (Thin section instrument: Nikon LV100POL polarizing microscope, manufactured in Japan (Nikon), production date: 2010).
4.2 Pore type
The study area exhibits various types of reservoir spaces (Figure 4), including primary pores, intragranular dissolution pores, mold pores, and intercrystalline pores within clay minerals. Primary intergranular pores primarily consist of residual pores resulting from compaction and secondary enlarged intergranular pores within quartz. Intragranular dissolution pores primarily form through the dissolution of unstable lithic fragments, including feldspar and mica. Lithic fragments and feldspar are susceptible to forming mold pores, particularly alkali feldspar, which often undergoes complete dissolution, leaving only the external contours of the grains.
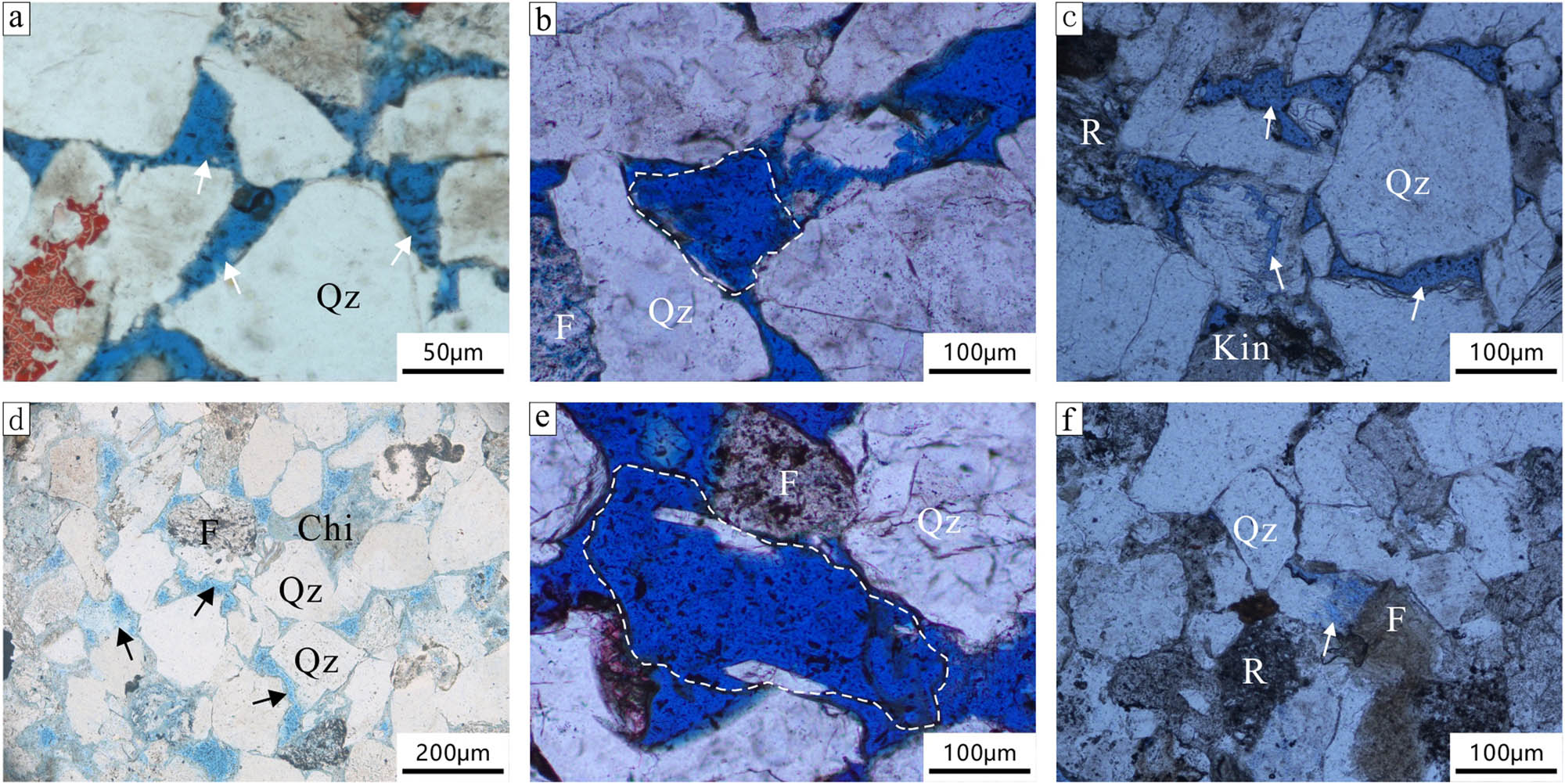
Microscopic characteristics of reservoir pores in the Shaximiao Formation in the western Sichuan Basin: (a) primary pores (indicated by white arrows), JT1 well, 1808.5 m, feldspathic sandstone (−); (b) mold pores (encircled by white dashed lines), QL18 well, 2082.346 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone (−); (c) intragranular dissolution pores and primary intergranular pores (indicated by white arrows), YQ2 well, 2258.04 m, lithic feldspathic sandstone (−); (d) intergranular dissolution pores (indicated by white arrows), D26 well, 1248.33 m, feldspathic sandstone (−); (e) dissolution pores (indicated by black arrows) and primary pores (indicated by white arrows), QL8 well, 1954.60 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone (−); and (f) secondary dissolution pores (indicated by white arrows), YQ2 well, 2,233 m, feldspathic sandstone (−); Qz = quartz, R = lithics, F = feldspar, Chi = chlorite, Mu = mica, Bit = biotite. (Thin section instrument: Nikon LV100POL polarizing microscope, manufactured in Japan (Nikon), production date: 2010).
4.3 Pore-throat characteristics
By combining the analysis of pore-throat structure and physical properties (Figure 5), it is evident that the permeability of the Shaximiao Formation reservoir in the study area is primarily influenced by a small number of pores with the largest radii. The storage capacity of these reservoirs is primarily dictated by the presence of a limited number of larger pores, while smaller pores contribute less significantly to permeability. Therefore, the pore-throat structure remains a crucial factor influencing the storage and permeability characteristics of the Shaximiao Formation sandstone in the study area.

Mercury intrusion curve, pore-throat radius, and permeability contribution diagram of sandstone reservoir in Shaximiao Formation, western Sichuan Basin: (a) pressure-mercury curve in southwest Sichuan, (b) pressure-mercury curve in northwest Sichuan, (c) relationship between borehole radius and permeability contribution in D26 well, southwest Sichuan, (d) relationship between borehole radius and permeability contribution in JH9 well, northwest Sichuan; (e) characteristics of the borehole throat in southwest Sichuan; and (f) characteristics of the borehole throat in northwest Sichuan.
In the southwestern Sichuan area, reservoir permeability is primarily governed by pore throats with radii ranging from 0.05 to 2.2 μm, with the storage space associated with this range of pore throats between 39.36 and 41.69%. In the northwestern Sichuan area, reservoir permeability is primarily governed by pore throats with radii ranging from 0.3 to 3 μm, with the storage space associated with this range of pore throats between 44.60 and 48.02%.
4.4 Characteristics of diagenesis
Overall, the diagenetic processes affecting the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs in the study area are relatively complex, involving compaction, cementation, dissolution, replacement, and alteration (Figure 6).

Typical microscopic photos of diagenesis of Shaximiao Formation reservoir in western Sichuan Basin: (a) southwestern Sichuan, D26 Well, 1254.77 m, feldspathic sandstone, compaction causing grain deformation (indicated by white arrow) (−); (b) northwestern Sichuan, QL1 Well, 2107.88 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, multiple quartz grains compacted (indicated by white arrow) (+); (c) southwestern Sichuan, YQ2 Well, 2230.06 m, feldspathic sandstone, calcite cementation (indicated by white arrow) (+); (d) southwestern Sichuan, JT1 Well, 1924.01 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, siliceous cementation predating calcite cementation (−); (e) southwestern Sichuan, YQ2 Well, 2230.06 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, chlorite film (indicated by green dashed line) (+); (f) southwestern Sichuan, YQ1 Well, 1672.15 m, feldspathic sandstone, feldspar dissolution residue and chlorite film (indicated by green dashed line) (+); (g) southwestern Sichuan, PL9 Well, 1979.18 m, chlorite coating; (h) southwestern Sichuan, MQ8 Well, 1872.15 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, kaolinite cementation (indicated by white arrow) (+); (i) southwestern Sichuan, MQ8 Well, 1877.52 m, platy kaolinite; (j) southwestern Sichuan, D26 Well, 1257.44 m, montmorillonite cementation; (k) southwestern Sichuan, YQ1 Well, 2229.57 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, zeolite cementation (+); (l) southwestern Sichuan, YQ2 Well, 2230.06 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, zeolite cementation (+); (m) southwestern Sichuan, GK2 Well, 1952.95 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, quartz grains dissolved and replaced (indicated by white arrow) (+); (n) northwestern Sichuan, QL18 Well, 2095.27 m, feldspathic lithic sandstone, feldspar dissolution and clay formation (+); and (o) southwestern Sichuan, D26 Well, 1251.82 m, feldspathic sandstone, chlorite replacement (indicated by white arrow) (+). Thin-section Instrument: Nikon LV100POL Polarizing Microscope, Made in Japan (Nikon), Manufactured in 2010; Scanning Electron Microscope: Quanta250 FEG, Made in USA (FEI), Manufactured in 2019.
4.4.1 Compaction
Clastic particles exhibit point–line contacts between grains, with localized regions potentially exhibiting concave–convex contacts (Figure 6a and b). Plastic particles experience compressive deformation, resulting in the formation of pseudo-matrix structures in certain regions. The porosity and number of intergranular pores decrease, while secondary pores form due to the dissolution of clay within these pores.
4.4.2 Cementation
Cementation in the Sichuan region primarily manifests as carbonate, siliceous, and clay mineral cementation, with a minor presence of zeolite cementation.
4.4.2.1 Carbonate cementation
In the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs, carbonate cementation predominantly manifests as multi-phase calcite development (Figure 6c). The content of early calcite cementation ranges from approximately 2 to 12%, exceeding 20% in some instances, forming fine to medium crystals that primarily develop as continuous cementation along pore margins. Thin-section observations indicate that, in addition to calcite, zeolite is identified as a significant product of carbonate cementation in the study area.
4.4.2.2 Siliceous cementation
Siliceous cementation manifests in two forms: secondary quartz overgrowth and intergranular quartz particles (Figure 6d). Early siliceous cementation primarily manifests as first-order overgrowths, which are clearly visible in cast thin sections, exhibiting a gray line between the siliceous overgrowths and clastic quartz particles. In the middle to late diagenetic stages, secondary quartz enlargement predominantly takes the form of silica filling within pores, resulting in sutured contacts in plane view.
4.4.2.3 Clay mineral cementation
Clay mineral cementation is a critical type of cementation in the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs. Microscopic identification, SEM, and XRD analysis reveal that the study area primarily features chlorite (Figure 6e–g), kaolinite (Figure 6h and i), montmorillonite (Figure 6j), and illite cementation. The content and occurrence of clay minerals serve as critical indicators in sandstone studies.
4.4.2.4 Zeolite cementation
The occurrence of zeolite in the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs of western Sichuan significantly influences pore evolution (Figure 6k and l). Zeolite, a prevalent authigenic mineral, commonly acts as a cementing agent during diagenesis, exerting a minor effect on the porosity and permeability of reservoirs.
4.4.3 Dissolution
Dissolution in the study area is primarily characterized by the dissolution of feldspar and lithic fragments, categorized into early diagenetic and middle diagenetic dissolution (Figure 6m and n). Dissolution serves as a major pore-enhancing process during the late diagenetic stages, leading to the formation of dissolution pores within feldspar grains and secondary pores resulting from the dissolution of early calcite cement. Dissolution in the study area occurs in multiple phases, resulting in diverse secondary pore shapes and origins, along with significant changes in pore structure. The intense dissolution of feldspar and lithic fragments underscores the sensitivity of the dissolution process.
4.4.4 Replacement and alteration
The replacement processes manifest in various forms within the study area (Figure 6o). Feldspar grains replaced by kaolinite exhibit distinct pseudomorphic textures indicative of detrital replacement, often containing remnants of organic matter encapsulated within the kaolinite crystals. Additionally, some early diagenetic kaolinite transitions from a cryptocrystalline phase to platy or vermiform structures.
4.5 Diagenetic evolution
Based on the characteristics of authigenic mineral states, clay mineral assemblages, rock structure, and pore space distribution, and in accordance with the Chinese classification standard for clastic rock diagenetic stages (SY/T5477–2003), a diagenetic evolution sequence for the Shaximiao Formation sandstone reservoirs has been established. The diagenetic stage evolution in the study area is classified as middle diagenetic stage A, with specific sequences outlined for southwestern Sichuan (Figure 7a) and northwestern Sichuan (Figure 7b).

Diagenetic evolution sequence of Shaximiao Formation: (a) evolutionary sequence of Shaximiao constituent rocks in southwest area and (b) evolutionary sequence of Shaximiao constituent rocks in northwestern area.
Thin-section observations indicate that during the syn-depositional to early diagenetic stages, pore evolution was primarily influenced by initial compaction and early cementation. In the early diagenetic to middle diagenetic stages, the principal diagenetic processes included dissolution and late cementation. The middle diagenetic stage encompasses various diagenetic processes, including late-stage carbonate and clay mineral cementation.
The overall diagenetic evolution process in the Sichuan region can be summarized as follows: compaction → calcite cementation, early zeolite cementation, early chlorite coating → feldspar dissolution, kaolinite precipitation → illite-montmorillonite mixed-layer coating → late calcite cementation, chlorite filling, late zeolite cementation → zeolite dissolution. The primary distinction between the regions lies in the more pronounced chlorite activity observed in southwestern Sichuan.
5 Discussion
5.1 Multi-source pore evolution process
Employing experimental techniques such as thin-section examination, SEM, and XRD, we have acquired the necessary data for our calculations. Based on calculations, the initial porosity in the southwestern Sichuan region was determined to be 38.8%, whereas in the northwestern Sichuan region, it was 36.92%. The early compaction process resulted in a porosity loss of φ 1 = 16.05% in southwestern Sichuan and 12.98% in northwestern Sichuan. Cementation processes further reduced porosity, with φ 2 = 4.75% in southwestern Sichuan and 3.78% in northwestern Sichuan. Subsequently, dissolution and fracture formation increased porosity, resulting in final porosities of 9.07% in southwestern Sichuan and 8.33% in northwestern Sichuan. The specific diagenetic intensity is illustrated in the accompanying figure (Figure 8).

Diagenesis intensity of reservoir of Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan basin.
By integrating the quantitative study process from Section 3.2 with planar porosity observations from thin sections indicating fractures, we obtained the diagenetic intensity and evolution process for the reservoirs. The diagenetic sequence, processes, and their timings were superimposed on the porosity evolution curves to reconstruct the porosity evolution process of the Shaximiao Formation reservoir (Figure 9).
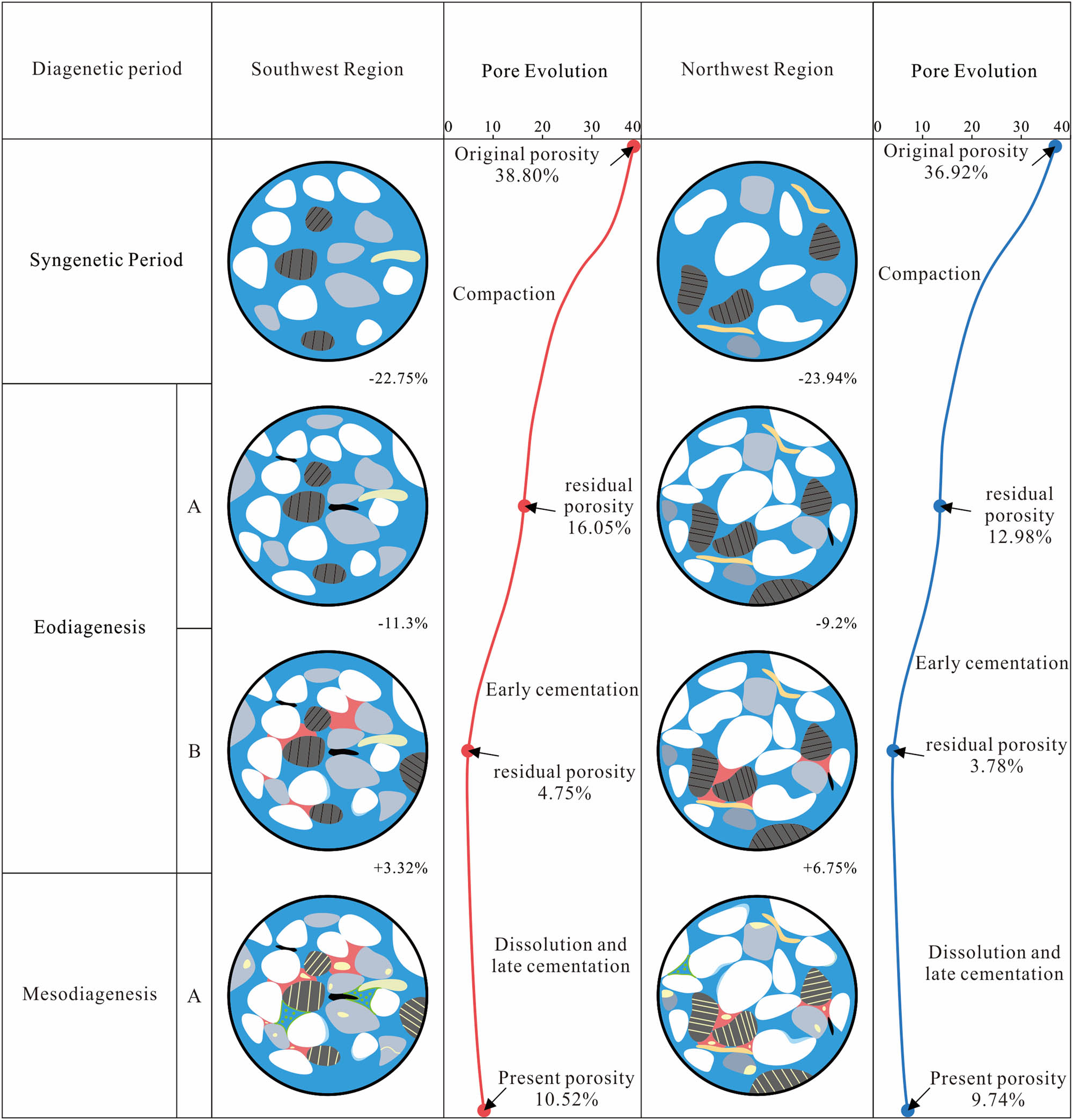
Pore evolution of Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin.
Early compaction was the primary cause of porosity reduction, manifesting as reduced pore space and increased contact area between particles, thereby enhancing reservoir compactness. Calculations indicate that post-early compaction porosity was 16.5% in southwestern Sichuan and 12.98% in northwestern Sichuan. Dissolution was a critical diagenetic process that increased porosity and facilitated the formation of secondary pores. During the subsequent middle diagenetic stage, early secondary pores were refilled, and initial cement was either replaced or further dissolved.
The extent of dissolution varied according to chlorite influence. In the northwestern Sichuan region, extensive dissolution primarily impacted feldspar and lithic fragments. Conversely, in southwestern Sichuan, thick chlorite coatings created a relatively isolated environment, reducing the entry of dissolution agents and consequently lowering the sensitivity of rocks to dissolution. Dissolution primarily occurred in uncoated particles. Additionally, as chlorite coatings thickened, they significantly obstructed pores, explaining why the Shaximiao Formation reservoir exhibits similar porosity but differing permeability between the two regions.
Late-stage cementation was limited. In the northwestern Sichuan region, it involved small quantities of late-stage carbonate and silica cementation. Carbonate cementation remained a key factor in porosity reduction, whereas silica cementation, occurring as quartz overgrowths and granular interstitial quartz, significantly compromised reservoir quality. Research on the Shaximiao Formation indicates that reservoir densification occurred following the peak hydrocarbon generation and expulsion period.
In addition, zeolite is also one of the factors affecting pore evolution. Research has found that its role in the Shaximiao Formation reservoir is double-sided, serving as both a factor for reservoir densification and a potential factor for improving reservoir quality. But it is not the main factor affecting pore size
5.2 Diagenetic differentiation process caused by chlorite
Numerous scholars have proposed varying perspectives on the influence of chlorite on reservoir properties [54–57]. The effect of chlorite on the reservoir in the study area exhibits dual characteristics. On the one hand, chlorite coatings provide a protective role for primary pores. As chlorite content increases, there is a notable increase in the planar porosity of primary pores. However, when chlorite content exceeds 6%, porosity begins to decrease (Figure 10). Conversely, an increase in chlorite content leads to thicker coatings that can obstruct pore throats and pores (Figure 11).
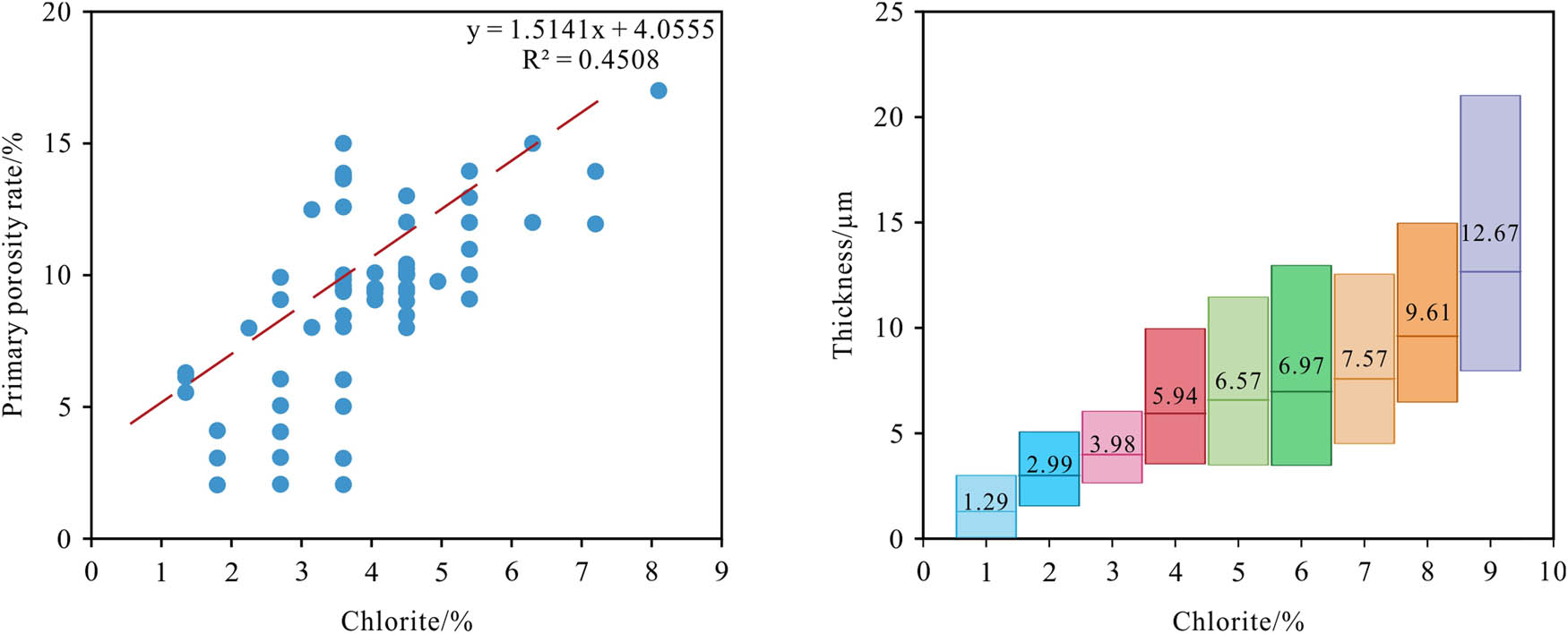
Relationship between chlorite content and primary pore and chlorite envelope thickness.
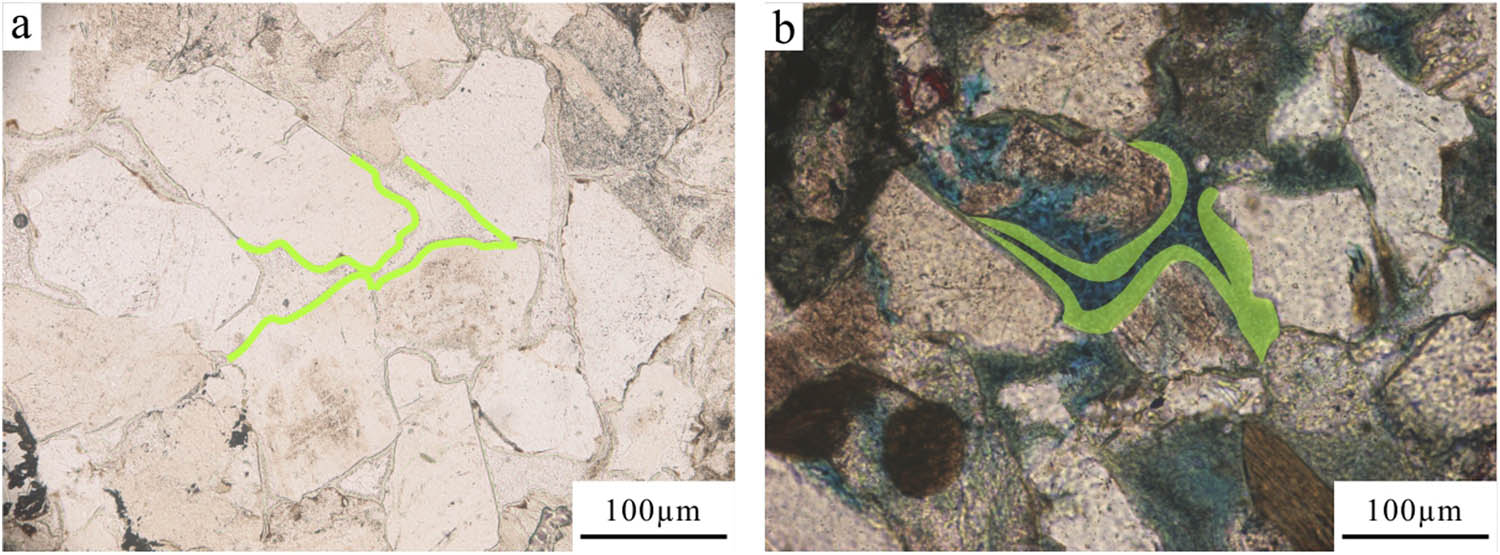
Microscopic characteristics of chlorite envelope: (a) chlorite envelope 8.6–10.5 μm, MQ9 wells, 1709.76 m (−) and (b) chlorite envelope 14.7–20.4 μm, PL9 wells, 1991.21 m.
The content of chlorite was determined using XRD analysis of clay minerals. The thickness of the chlorite coating was estimated through microscopic examination of thin sections and subsequent proportional conversion. Overall, in the study area, chlorite content generally remains below 5%, with an average coating thickness of 7 μm. This low chlorite content supports the preservation of reservoir porosity while still impacting permeability to some degree. This phenomenon accounts for the similar porosity yet differing permeability observed between the southern and northern regions.
Primary pores play a significant role in the formation of high-quality reservoirs. Chlorite coatings, forming as authigenic minerals during early compaction under relatively low pressure, effectively mitigate the adverse effects of subsequent compaction and pressure solution on porosity. The Shaximiao Formation is characterized as a classic tight sandstone reservoir. By the time dissolution fluids penetrate extensively, the reservoir has already become significantly dense. The primary pores preserved by chlorite coatings, along with intercrystalline pores within the chlorite, create pathways for fluid ingress.
Microscopic examination reveals that pores enveloped by chlorite contain fewer cementing materials, indicating that chlorite coatings inhibit secondary quartz overgrowth and late-stage carbonate cementation. This observation underscores that the porosity evolution of Shaximiao Formation reservoirs from different source regions follows a broadly similar trajectory, with significant differences primarily in the degree of chlorite cementation between the southern and northern regions of Western Sichuan. In the southern region, chlorite coatings are more prominent and show a positive correlation with feldspar, mica, and volcanic rock fragments (Figure 12). This correlation suggests that the distribution of chlorite within the Shaximiao sandstones is influenced by both sediment provenance and depositional environment.
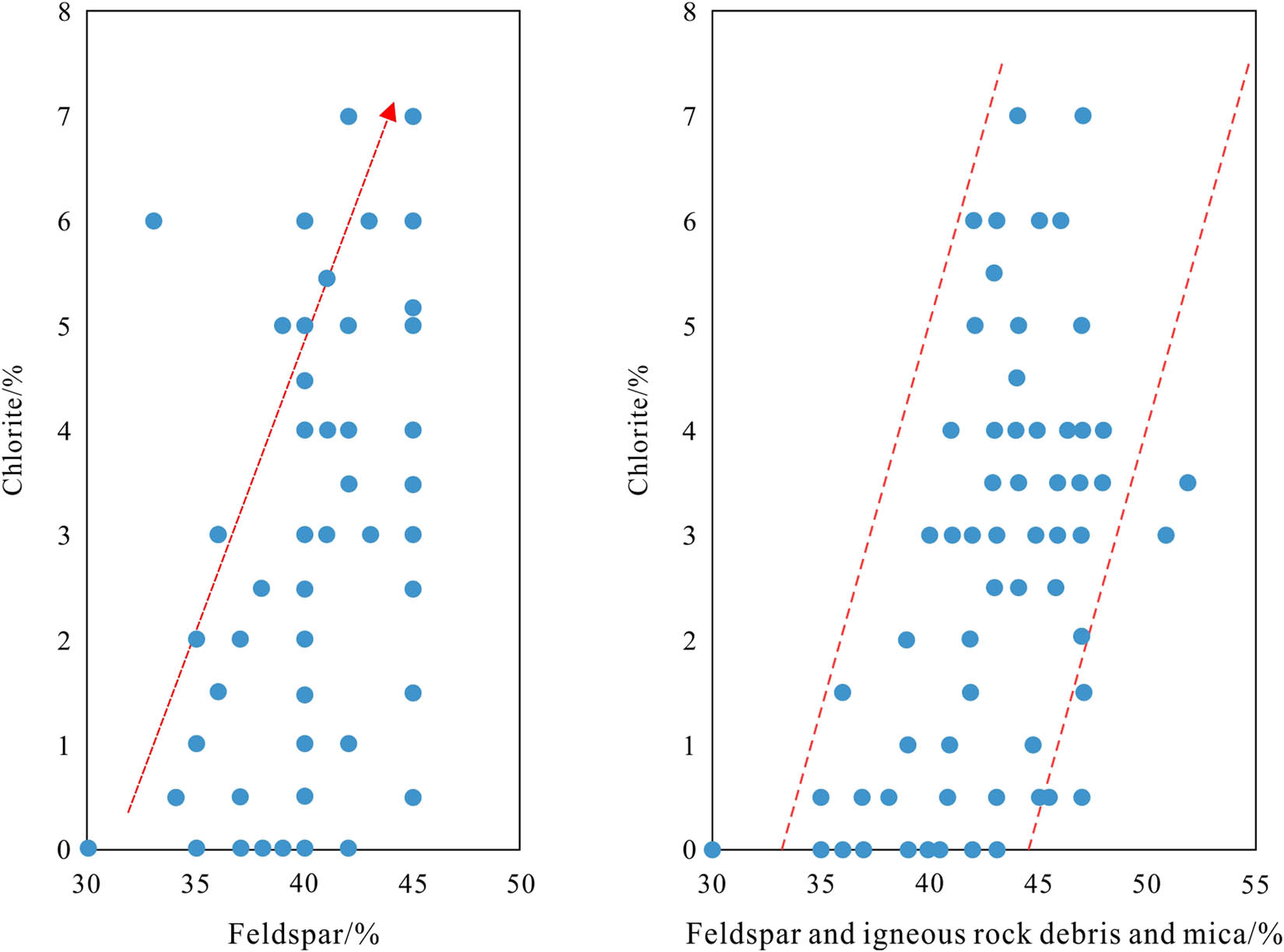
Relationship between chlorite and other components of the Shaximiao Formation in the western Sichuan area.
Additionally, a statistical analysis was performed to examine the relationship between chlorite content and the porosity and permeability of reservoirs in the southern and northern regions of western Sichuan (Figure 13). The results indicate that chlorite content is slightly higher in the southern region than in the northern region. Despite the relatively similar porosity between the two regions, a significant disparity in permeability exists, with the northern region exhibiting markedly higher permeability than the southern region.

Chlorite content correlated with porosity and permeability.
In the study area, chlorite rims demonstrate multi-phase growth characteristics. Early-stage chlorite results from the transformation of clay minerals, while middle to late-stage chlorite forms through precipitation from pore waters. The initial chlorite rims result from the incomplete transformation of primary clay minerals. Substances with intermediate-basic composition, introduced by volcanic activity, readily dissolve in atmospheric water. Changes in fluid pH, Eh values, and salinity induce chemical differentiation, leading to the formation of early-stage iron-rich clay rims, such as ferruginous chlorite. Due to their early formation, these chlorite rims exhibit a lower degree of crystallinity.
Late-stage external linings and pore-filling chlorite form through direct precipitation from pore waters. The chlorite’s sealing effect can reduce the size of intergranular pores, thereby impeding the advancement of dissolution processes and leading to low permeability in reservoirs. This phenomenon is one of the primary factors contributing to the formation of low-permeability reservoirs. Electron probe analysis (Figure 14) indicates that FeO and MgO contents increase progressively from chlorite encrustations and linings near detrital particles to outer pore spaces. This suggests that as burial depth increases, the concentration of Fe and Mg ions in pore water also rises. This phenomenon results from the compactional dewatering of mudstones and the dissolution of iron-rich dark minerals, which release significant amounts of Fe and Mg. Late-stage chlorite is enriched in Na and K, indicating that its formation occurs following the dissolution of feldspar.

Cementation of chlorite in different periods and electron probe data of Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin.
6 Conclusions
Experimental results indicate that the lithology of the Shaximiao Formation in southern western Sichuan is primarily composed of feldspathic sandstone and lithic feldspathic sandstone. In contrast, northern western Sichuan predominantly features lithic feldspathic sandstone and feldspathic lithic sandstone. The primary reservoir spaces include intergranular primary pores and intragranular secondary dissolution pores. The average porosity and permeability in southern western Sichuan are 10.52% and 0.1334 × 10−3 μm2, respectively. In northern western Sichuan, the porosity distribution is unimodal, with an average porosity of 9.74% and an average permeability of 1.2442 × 10−3 μm2, indicating similar porosities but significant differences in permeability between the two regions.
The Shaximiao Formation reservoirs in western Sichuan exhibit various diagenetic processes, including compaction, cementation, dissolution, and metasomatism. Based on experimental results regarding authigenic minerals and inclusions, the diagenetic evolution stage of the Shaximiao Formation reservoirs in the study area is classified as mesodiagenesis stage A.
According to porosity recovery results, the porosity evolution process in southern and northern western Sichuan involves a reduction due to compaction, with porosity changes of 16.05 and 12.98%, respectively; a reduction due to cementation, with changes of 4.75 and 3.78%; and an increase due to dissolution, with changes of 9.07 and 8.33%. Subsequent processes, such as microfracture formation, have led to the current characteristics of low porosity and low permeability in these reservoirs.
Chlorite cementation significantly influences permeability. Different provenance influences in the northern and southern regions result in varying primary components, leading to differential chlorite evolution. This variation causes similar porosities but substantial differences in permeability between the two regions.
-
Funding information: The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study is supported by the open fund of SINOPEC Key Laboratory of Petroleum Accumulation Mechanisms (Project No. 33550007-22-ZC0613-0041).
-
Author contributions: Qingshao Liang: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, bisualization, writing – review & editing. Chunyu Chen: investigation, validation, writing – original draft.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The data involved during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
[1] Bjørlykke K. Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of diagenetic process in sedimentary basins. Sediment Geol. 2014;301:1–14.10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.12.002Search in Google Scholar
[2] Bjørlykke K, Høeg K. Effects of burial diagenesis on stresses, compaction and fluid flow in sedimentary basins. Mar Pet Geol. 1997;14(3):267–76.10.1016/S0264-8172(96)00051-7Search in Google Scholar
[3] Tada R, Siever R. Pressure solution during diagenesis. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci. 1989;17:89.10.1146/annurev.ea.17.050189.000513Search in Google Scholar
[4] Huang Y, Kane IA, Zhao Y. Effects of sedimentary processes and diagenesis on reservoir quality of submarine lobes of the Huangliu Formation in the Yinggehai Basin, China. Mar Pet Geol. 2020;120:104526.10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104526Search in Google Scholar
[5] Henares S, Donselaar ME, Caracciolo L. Depositional controls on sediment properties in dryland rivers: Influence on near-surface diagenesis. Earth-Sci Rev. 2020;208:103297.10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103297Search in Google Scholar
[6] Friedman GM. Deep-burial diagenesis: its implications for vertical movements of the crust, uplift of the lithosphere and isostatic unroofing—a review. Sediment Geol. 1987;50(1–3):67–94.10.1016/0037-0738(87)90028-5Search in Google Scholar
[7] Zhu R, Zou C, Zhang N, Wang X, Cheng R, Liu L, et al. Diagenetic fluids evolution and genetic mechanism of tight sandstone gas reservoirs in Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin, China. Sci China Ser D: Earth Sci. 2008;51:1340–53.10.1007/s11430-008-0102-8Search in Google Scholar
[8] Greve J, Busch B, Quandt D, Knaak M, Hilgers C. The influence of sedimentary facies, mineralogy, and diagenesis on reservoir properties of the coal-bearing Upper Carboniferous of NW Germany. Pet Geosci. 2024;30(1):petgeo2023-020.10.1144/petgeo2023-020Search in Google Scholar
[9] Wang R, Hu Z, Long S, Liu G, Zhao J, Dong L, et al. Differential characteristics of the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi shale reservoir and its implications for exploration and development of shale gas in/around the Sichuan Basin. Acta Geol Sin – Engl Ed. 2019;93(3):520–35.10.1111/1755-6724.13875Search in Google Scholar
[10] Zhao L, Mao W, Liu Z, Cheng S. Research on the differential tectonic-thermal evolution of Longmaxi shale in the southern Sichuan Basin. Adv Geo-Energy Res. 2023;7(3):152–63.10.46690/ager.2023.03.02Search in Google Scholar
[11] Ding C, Chen Z, Guo L, Guo S, Su X, Bai X. Accumulation mechanism of multi-type unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in Northern China: Taking Hari Sag of the Yin’e Basin as an example. Open Geosci. 2024;16(1):507–26.10.1515/geo-2022-0651Search in Google Scholar
[12] Wang X, Li D. Tight sandstone gas: Development and challenges. Adv Resour Res. 2024;4(1):1–28.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Gharavi A, Abbas KA, Hassan MG, Haddad M, Ghoochaninejad H, Alasmar R, et al. Unconventional reservoir characterization and formation evaluation: A case study of a tight sandstone reservoir in West Africa. Energies. 2023;16(22):7572.10.3390/en16227572Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zou C, Zhai G, Zhang G, Wang H, Zhang G, Li J, et al. Formation, distribution, potential and prediction of global conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resources. Pet Explor Dev. 2015;42(1):14–28. 10.1016/S1876-3804(15)60002-7.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Liu S. Review of the development status and technology of tight oil: Advances and outlook. Energ Fuel. 2023;37(19):14645–65.10.1021/acs.energyfuels.3c02726Search in Google Scholar
[16] Hongjun W, Feng MA, Xiaoguang T, Zuodong L, Zhang X, Zhenzhen WU, et al. Assessment of global unconventional oil and gas resources. Pet Explor Dev. 2016;43(6):925–40.10.1016/S1876-3804(16)30111-2Search in Google Scholar
[17] Wenrui H, Jingwei B, Bin H. Trend and progress in global oil and gas exploration. Pet Explor Dev. 2013;40(4):439–43.10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60055-5Search in Google Scholar
[18] Fryklund B, Stark PP. Super basins—New paradigm for oil and gas supply. AAPG Bull. 2020;104(12):2507–19.10.1306/09182017314Search in Google Scholar
[19] Jiang L, Zhao W, Bo D, Hong F, Gong Y, Hao J. Tight sandstone gas accumulation mechanisms and sweet spot prediction, Triassic Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin, China. Pet Sci. 2023;20(6):3301–10.10.1016/j.petsci.2023.07.008Search in Google Scholar
[20] Jia A, Wei Y, Guo Z, Wang G, Meng D, Huang S. Development status and prospect of tight sandstone gas in China. Nat Gas Ind B. 2022;9(5):467–76.10.1016/j.ngib.2022.10.001Search in Google Scholar
[21] Wang W, Li T, Xiao D, Wang B, Yang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Geological conditions and controls on accumulation of tight sandstone gas, deep part of the Shengbei sub-sag, Turpan-Hami basin, NW China. Mar Pet Geol. 2023;158:106513.10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106513Search in Google Scholar
[22] Jianzhong L, Xiaowan T, Bin B, Huang S, Jiang Q, Zhenyu Z, et al. Geological conditions, reservoir evolution and favorable exploration directions of marine ultra-deep oil and gas in China. Pet Explor Dev. 2021;48(1):60–79.10.1016/S1876-3804(21)60005-8Search in Google Scholar
[23] Chen S, Li X, Yang B, Li X, Wang Y, Yang Y, et al. Detailed analysis of seismic reflection characteristics of tight sandstone reservoirs in the upper paleozoic of the ordos basin: A case study of block X. Unconv Resour. 2024;4:100085. 10.1016/j.uncres.2024.100085.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Su N, Chen Z, Yang W, Wang L, Li W, Yang C, et al. Features and favorable exploration direction of normal faults in Jurassic strata in northern central Sichuan Basin, China. J Nat Gas Geosci. 2023;8(6):413–26.10.1016/j.jnggs.2023.11.003Search in Google Scholar
[25] Lu Y, Liang Q, Tian J, Yu Y, Li Y, Chen C, et al. Correlation and response of astronomical forcing in lacustrine deposits of the middle jurassic, sichuan basin, southwest China. Mar Pet Geol. 2024;166:106905.10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.106905Search in Google Scholar
[26] Tan K, Chen J, Yao J, Wu Q, Shi J. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of natural gas in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan Basin. Open Geosci. 2022;14(1):1061–74. 10.1515/geo-2022-0405.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Liu S, Chen A, Shen Z, Lv Z, Zhang X. Fluid-rock interaction and dissolution of feldspar in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe tight sandstone, western Sichuan Basin, China. Open Geosci. 2018;10(1):234–49. 10.1515/geo-2018-0018.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Hengyu L, Mingjie L, Yao X, Qinggao Z, Linke S, Jixiang C, et al. Differential accumulation characteristics and main controlling factors of the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation tight sandstone gas in the central Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosci. 2024;35(6):1014–30.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Tan X, Jiang W, Luo L, Gluyas J, Song L, Liu J, et al. Variations of sedimentary environment under cyclical aridification and impacts on eodiagenesis of tight sandstones from the late Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Central Sichuan Basin. Mar Pet Geol. 2024;161:106699.10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.106699Search in Google Scholar
[30] He Q, Yang T, Cai L, Ren Q, Dai J. Porosity and permeability correction of laumontite-rich reservoirs in the first member of the Shaximiao Formation in the Central Sichuan Basin. Mar Pet Geol. 2023;150:106115. 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106115.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Han XU, Mingjie LIU, Zhang Z, Sujuan YE, Yingtao YA, Ling WU, et al. Diagenesis and porosity evolution of the 3rd member of Xujiahe Formation tight sandstone reservoir in the Western Sichuan Depression, Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Geosci. 2022;33(3):14.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Wu Z, Li T, Ji S, Zhou Q, Tian H. Gas Generation from coal and coal-measure mudstone source rocks of the Xujiahe Formation in the western sichuan depression, Sichuan Basin. J Earth Sci. 2023;34(4):1012–25.10.1007/s12583-022-1627-zSearch in Google Scholar
[33] Ma D, Zhang Z, Zhou C, Cheng D, Hong H, Meng H, et al. Element geochemical characteristics and geological significance of mudstones from the middle jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Sichuan Basin, southwest China. ACS Omega. 2023;8(33):29979–30000.10.1021/acsomega.3c01496Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Wu X, Yang J, Wang P, Li H, Chen Y, Ni C, et al. Gas source of the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the Zhongjiang large gas field of Western Sichuan Depression: Constraints from geochemical characteristics of light hydrocarbons. Energy Geosci. 2024;5(2):100263.10.1016/j.engeos.2023.100263Search in Google Scholar
[35] Zeng J, Zuo Y, Zheng Z, Zhang J, Ge J, Song L, et al. Gas–source comparison and hydrocarbon generation and expulsion histories of the main source rocks of the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation, Western Sichuan Basin. ACS Omega. 2023;8(48):46113–26.10.1021/acsomega.3c07134Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Yang Y, Xie J, Cao Z, Wen L, Wang X, Xiao Y, et al. Forming conditions and key technologies for exploration and development of large tight sandstone gas reservoirs in Shaximiao Formation, Tianfu gas field of Sichuan Basin. Acta Petrol Sin. 2023;44(6):917.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Wang Q, Chen D, Wang F, Gao X, Zou Y, Tian Z, et al. Origin and distribution of an under-pressured tight sandstone reservoir: The Shaximiao Formation, Central Sichuan Basin. Mar Pet Geol. 2021;132:105208.10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105208Search in Google Scholar
[38] Yang T, Li X, Yang Y, Wen L, Cao Z, Wang X, et al. Evolution from shallow‐water deltas to fluvial fans in lacustrine basins: A case study from the Middle Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the central Sichuan Basin, China. Sedimentology. 2024;71(3):1023–55.10.1111/sed.13163Search in Google Scholar
[39] Peng H, Zhou L, Yang J, Peng J, Han H, Gou X, et al. Influence of supercritical CO2 on the formation sensitivity of tight sandstone. Front Energy Res. 2022;10:922941.10.3389/fenrg.2022.922941Search in Google Scholar
[40] Dong H, LiYucong LM, Jiajing Y, Rong B, Zhi Y. Reservoir features and exploration potential of the 1st member of Shaximiao Formation of Middle Jurassic in central Sichuan Basin. China Pet Explor. 2017;22(2):44.Search in Google Scholar
[41] Zhang X, Fu M, Deng H, Li Z, Zhao S, Gluyas JG, et al. The differential diagenesis controls on the physical properties of lithofacies in sandstone reservoirs from the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation, western Sichuan depression, China. J Pet Sci Eng. 2020;193:107413.10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107413Search in Google Scholar
[42] Jia C. Petroleum geology of foreland thrust belts in China. Characteristics of Chinese petroleum geology: Geological features and exploration cases of stratigraphic, foreland and deep formation traps. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media; 2013. pp. 333–421.10.1007/978-3-642-23872-7_9Search in Google Scholar
[43] Liu S, Yang Y, Deng B, Zhong Y, Wen L, Sun W, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Sichuan basin, southwest China. Earth-Sci Rev. 2021;213:103470.10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103470Search in Google Scholar
[44] Chen SF, Wilson C, Luo ZL, Deng QD. The evolution of the western Sichuan foreland basin, southwestern China. J Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1994;10(3–4):159–68.10.1016/0743-9547(94)90016-7Search in Google Scholar
[45] Yong L, Allen PA, Densmore AL, Qiang X. Evolution of the Longmen Shan foreland basin (western Sichuan, China) during the Late Triassic Indosinian orogeny. Basin Res. 2003;15(1):117–38.10.1046/j.1365-2117.2003.00197.xSearch in Google Scholar
[46] Zhu-xin C, Dong J, Guoqi W, Ben-liang LI, Yong-liang L. Meso-Cenozoic sediment transport and tectonic transition in the western Sichuan foreland basin. Geol China. 2008;35(3):472–81.Search in Google Scholar
[47] Hefu L, Huishe L, Liguo C, Fei S. Structural styles of the Longmenshan thrust belt and evolution of the foreland basin in western Sichuan Province, China. Acta Geol Sin-Engl Ed. 1994;7(4):351–72.10.1111/j.1755-6724.1994.mp7004001.xSearch in Google Scholar
[48] Jin W, Tang L, Yang K, Wan G, Lü Z. Segmentation of the Longmen Mountains thrust belt, western Sichuan foreland basin, SW China. Tectonophysics. 2010;485(1–4):107–21.10.1016/j.tecto.2009.12.007Search in Google Scholar
[49] Yong L, Guoshan S. The structural evolution of the middle section of the West Sichuan Depression in the Sichuan Basin controlled the hydrocarbon accumulation in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation. Pet Geol Exp. 2021;43(6):986–95.Search in Google Scholar
[50] Zhang X, Wu D, Fu M, Deng H, Xu Z, Chen C. Controls of sandstone architecture on hydrocarbon accumulation in a shallow-water delta from the Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of the western Sichuan Basin in China. Energy Rep. 2022;8:6068–85.10.1016/j.egyr.2022.04.001Search in Google Scholar
[51] Dong J, Li S, Ye S, Li Q, Wu C. Natural gas geochemistry of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in the Western Sichuan Basin, China: Fault-controlled differentiation in accumulation process. Front Earth Sci. 2022;10:942414.10.3389/feart.2022.942414Search in Google Scholar
[52] Zhang X, He J, Deng H, Fu M, Xiang Z, Peng X, et al. Controls of interlayers on the development and distribution of natural fractures in lacustrine shale reservoirs: a case study of the Da’anzhai member in the Fuling area in the eastern Sichuan Basin. J Pet Sci Eng. 2022;208:109224.10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109224Search in Google Scholar
[53] Sun X, Tan X, Tang Y, Tian J, Lei T, Wang J, et al. Diagenetic-porosity evolution and reservoir evaluation in Multiprovenance Tight Sandstones: Insight from the Lower Shihezi Formation in Hangjinqi Area, Northern Ordos Basin. Lithosphere. 2022;2022(Special 13). 10.2113/2022/6411000.Search in Google Scholar
[54] Golsanami N, Jayasuriya MN, Yan W, Fernando SG, Liu X, Cui L, et al. Characterizing clay textures and their impact on the reservoir using deep learning and Lattice-Boltzmann simulation applied to SEM images. Energy. 2022 Feb;1:240.10.1016/j.energy.2021.122599Search in Google Scholar
[55] Hou LH, Wu ST, Jing ZH, Jiang XH, Yu ZC, Hua G, et al. Effects of types and content of clay minerals on reservoir effectiveness for lacustrine organic matter rich shale. Fuel. 2022;327:125043.10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125043Search in Google Scholar
[56] Zhu S, Wang X, Qin Y, Jia Y, Zhu X, Zhang J, et al. Occurrence and origin of pore-lining chlorite and its effectiveness on preserving porosity in sandstone of the middle Yanchang Formation in the southwest Ordos Basin. Appl Clay Sci. 2017;148:25–38.10.1016/j.clay.2017.08.005Search in Google Scholar
[57] Zhang Y, Qu X, Miao C, Zhu J, Xu W, Wang W. Effect of authigenic chlorite on the pore structure of Tight Clastic Reservoir in Songliao Basin. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(2):1406.10.3390/ijerph20021406Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Theoretical magnetotelluric response of stratiform earth consisting of alternative homogeneous and transitional layers
- The research of common drought indexes for the application to the drought monitoring in the region of Jin Sha river
- Evolutionary game analysis of government, businesses, and consumers in high-standard farmland low-carbon construction
- On the use of low-frequency passive seismic as a direct hydrocarbon indicator: A case study at Banyubang oil field, Indonesia
- Water transportation planning in connection with extreme weather conditions; case study – Port of Novi Sad, Serbia
- Zircon U–Pb ages of the Paleozoic volcaniclastic strata in the Junggar Basin, NW China
- Monitoring of mangrove forests vegetation based on optical versus microwave data: A case study western coast of Saudi Arabia
- Microfacies analysis of marine shale: A case study of the shales of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the western Chongqing, Sichuan Basin, China
- Multisource remote sensing image fusion processing in plateau seismic region feature information extraction and application analysis – An example of the Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022
- Identification of magnetic mineralogy and paleo-flow direction of the Miocene-quaternary volcanic products in the north of Lake Van, Eastern Turkey
- Impact of fully rotating steel casing bored pile on adjacent tunnels
- Adolescents’ consumption intentions toward leisure tourism in high-risk leisure environments in riverine areas
- Petrogenesis of Jurassic granitic rocks in South China Block: Implications for events related to subduction of Paleo-Pacific plate
- Differences in urban daytime and night block vitality based on mobile phone signaling data: A case study of Kunming’s urban district
- Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan
- Integrated geophysical approach for detection and size-geometry characterization of a multiscale karst system in carbonate units, semiarid Brazil
- Spatial and temporal changes in ecosystem services value and analysis of driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta Region
- Deep fault sliding rates for Ka-Ping block of Xinjiang based on repeating earthquakes
- Improved deep learning segmentation of outdoor point clouds with different sampling strategies and using intensities
- Platform margin belt structure and sedimentation characteristics of Changxing Formation reefs on both sides of the Kaijiang-Liangping trough, eastern Sichuan Basin, China
- Enhancing attapulgite and cement-modified loess for effective landfill lining: A study on seepage prevention and Cu/Pb ion adsorption
- Flood risk assessment, a case study in an arid environment of Southeast Morocco
- Lower limits of physical properties and classification evaluation criteria of the tight reservoir in the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Kuqa depression
- Evaluation of Viaducts’ contribution to road network accessibility in the Yunnan–Guizhou area based on the node deletion method
- Permian tectonic switch of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints from magmatism in the southern Alxa region, NW China
- Element geochemical differences in lower Cambrian black shales with hydrothermal sedimentation in the Yangtze block, South China
- Three-dimensional finite-memory quasi-Newton inversion of the magnetotelluric based on unstructured grids
- Obliquity-paced summer monsoon from the Shilou red clay section on the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau
- Classification and logging identification of reservoir space near the upper Ordovician pinch-out line in Tahe Oilfield
- Ultra-deep channel sand body target recognition method based on improved deep learning under UAV cluster
- New formula to determine flyrock distance on sedimentary rocks with low strength
- Assessing the ecological security of tourism in Northeast China
- Effective reservoir identification and sweet spot prediction in Chang 8 Member tight oil reservoirs in Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin
- Detecting heterogeneity of spatial accessibility to sports facilities for adolescents at fine scale: A case study in Changsha, China
- Effects of freeze–thaw cycles on soil nutrients by soft rock and sand remodeling
- Vibration prediction with a method based on the absorption property of blast-induced seismic waves: A case study
- A new look at the geodynamic development of the Ediacaran–early Cambrian forearc basalts of the Tannuola-Khamsara Island Arc (Central Asia, Russia): Conclusions from geological, geochemical, and Nd-isotope data
- Spatio-temporal analysis of the driving factors of urban land use expansion in China: A study of the Yangtze River Delta region
- Selection of Euler deconvolution solutions using the enhanced horizontal gradient and stable vertical differentiation
- Phase change of the Ordovician hydrocarbon in the Tarim Basin: A case study from the Halahatang–Shunbei area
- Using interpretative structure model and analytical network process for optimum site selection of airport locations in Delta Egypt
- Geochemistry of magnetite from Fe-skarn deposits along the central Loei Fold Belt, Thailand
- Functional typology of settlements in the Srem region, Serbia
- Hunger Games Search for the elucidation of gravity anomalies with application to geothermal energy investigations and volcanic activity studies
- Addressing incomplete tile phenomena in image tiling: Introducing the grid six-intersection model
- Evaluation and control model for resilience of water resource building system based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and its application
- MIF and AHP methods for delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques in Tirunelveli, Tenkasi District, India
- New database for the estimation of dynamic coefficient of friction of snow
- Measuring urban growth dynamics: A study in Hue city, Vietnam
- Comparative models of support-vector machine, multilayer perceptron, and decision tree predication approaches for landslide susceptibility analysis
- Experimental study on the influence of clay content on the shear strength of silty soil and mechanism analysis
- Geosite assessment as a contribution to the sustainable development of Babušnica, Serbia
- Using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process for road transportation services management based on remote sensing and GIS technology
- Accumulation mechanism of multi-type unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in Northern China: Taking Hari Sag of the Yin’e Basin as an example
- TOC prediction of source rocks based on the convolutional neural network and logging curves – A case study of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag
- A method for fast detection of wind farms from remote sensing images using deep learning and geospatial analysis
- Spatial distribution and driving factors of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China based on GIS and geodetector
- Physicochemical and mineralogical composition studies of clays from Share and Tshonga areas, Northern Bida Basin, Nigeria: Implications for Geophagia
- Geochemical sedimentary records of eutrophication and environmental change in Chaohu Lake, East China
- Research progress of freeze–thaw rock using bibliometric analysis
- Mixed irrigation affects the composition and diversity of the soil bacterial community
- Examining the swelling potential of cohesive soils with high plasticity according to their index properties using GIS
- Geological genesis and identification of high-porosity and low-permeability sandstones in the Cretaceous Bashkirchik Formation, northern Tarim Basin
- Usability of PPGIS tools exemplified by geodiscussion – a tool for public participation in shaping public space
- Efficient development technology of Upper Paleozoic Lower Shihezi tight sandstone gas reservoir in northeastern Ordos Basin
- Assessment of soil resources of agricultural landscapes in Turkestan region of the Republic of Kazakhstan based on agrochemical indexes
- Evaluating the impact of DEM interpolation algorithms on relief index for soil resource management
- Petrogenetic relationship between plutonic and subvolcanic rocks in the Jurassic Shuikoushan complex, South China
- A novel workflow for shale lithology identification – A case study in the Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin, China
- Characteristics and main controlling factors of dolomite reservoirs in Fei-3 Member of Feixianguan Formation of Lower Triassic, Puguang area
- Impact of high-speed railway network on county-level accessibility and economic linkage in Jiangxi Province, China: A spatio-temporal data analysis
- Estimation model of wild fractional vegetation cover based on RGB vegetation index and its application
- Lithofacies, petrography, and geochemistry of the Lamphun oceanic plate stratigraphy: As a record of the subduction history of Paleo-Tethys in Chiang Mai-Chiang Rai Suture Zone of Thailand
- Structural features and tectonic activity of the Weihe Fault, central China
- Application of the wavelet transform and Hilbert–Huang transform in stratigraphic sequence division of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Structural detachment influences the shale gas preservation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Northern Guizhou Province
- Distribution law of Chang 7 Member tight oil in the western Ordos Basin based on geological, logging and numerical simulation techniques
- Evaluation of alteration in the geothermal province west of Cappadocia, Türkiye: Mineralogical, petrographical, geochemical, and remote sensing data
- Numerical modeling of site response at large strains with simplified nonlinear models: Application to Lotung seismic array
- Quantitative characterization of granite failure intensity under dynamic disturbance from energy standpoint
- Characteristics of debris flow dynamics and prediction of the hazardous area in Bangou Village, Yanqing District, Beijing, China
- Rockfall mapping and susceptibility evaluation based on UAV high-resolution imagery and support vector machine method
- Statistical comparison analysis of different real-time kinematic methods for the development of photogrammetric products: CORS-RTK, CORS-RTK + PPK, RTK-DRTK2, and RTK + DRTK2 + GCP
- Hydrogeological mapping of fracture networks using earth observation data to improve rainfall–runoff modeling in arid mountains, Saudi Arabia
- Petrography and geochemistry of pegmatite and leucogranite of Ntega-Marangara area, Burundi, in relation to rare metal mineralisation
- Prediction of formation fracture pressure based on reinforcement learning and XGBoost
- Hazard zonation for potential earthquake-induced landslide in the eastern East Kunlun fault zone
- Monitoring water infiltration in multiple layers of sandstone coal mining model with cracks using ERT
- Study of the patterns of ice lake variation and the factors influencing these changes in the western Nyingchi area
- Productive conservation at the landslide prone area under the threat of rapid land cover changes
- Sedimentary processes and patterns in deposits corresponding to freshwater lake-facies of hyperpycnal flow – An experimental study based on flume depositional simulations
- Study on time-dependent injectability evaluation of mudstone considering the self-healing effect
- Detection of objects with diverse geometric shapes in GPR images using deep-learning methods
- Behavior of trace metals in sedimentary cores from marine and lacustrine environments in Algeria
- Spatiotemporal variation pattern and spatial coupling relationship between NDVI and LST in Mu Us Sandy Land
- Formation mechanism and oil-bearing properties of gravity flow sand body of Chang 63 sub-member of Yanchang Formation in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin
- Diagenesis of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, China
- Vertical high-velocity structures and seismic activity in western Shandong Rise, China: Case study inspired by double-difference seismic tomography
- Spatial coupling relationship between metamorphic core complex and gold deposits: Constraints from geophysical electromagnetics
- Disparities in the geospatial allocation of public facilities from the perspective of living circles
- Research on spatial correlation structure of war heritage based on field theory. A case study of Jinzhai County, China
- Formation mechanisms of Qiaoba-Zhongdu Danxia landforms in southwestern Sichuan Province, China
- Magnetic data interpretation: Implication for structure and hydrocarbon potentiality at Delta Wadi Diit, Southeastern Egypt
- Deeply buried clastic rock diagenesis evolution mechanism of Dongdaohaizi sag in the center of Junggar fault basin, Northwest China
- Application of LS-RAPID to simulate the motion of two contrasting landslides triggered by earthquakes
- The new insight of tectonic setting in Sunda–Banda transition zone using tomography seismic. Case study: 7.1 M deep earthquake 29 August 2023
- The critical role of c and φ in ensuring stability: A study on rockfill dams
- Evidence of late quaternary activity of the Weining-Shuicheng Fault in Guizhou, China
- Extreme hydroclimatic events and response of vegetation in the eastern QTP since 10 ka
- Spatial–temporal effect of sea–land gradient on landscape pattern and ecological risk in the coastal zone: A case study of Dalian City
- Study on the influence mechanism of land use on carbon storage under multiple scenarios: A case study of Wenzhou
- A new method for identifying reservoir fluid properties based on well logging data: A case study from PL block of Bohai Bay Basin, North China
- Comparison between thermal models across the Middle Magdalena Valley, Eastern Cordillera, and Eastern Llanos basins in Colombia
- Mineralogical and elemental analysis of Kazakh coals from three mines: Preliminary insights from mode of occurrence to environmental impacts
- Chlorite-induced porosity evolution in multi-source tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin
- Predicting stability factors for rotational failures in earth slopes and embankments using artificial intelligence techniques
- Origin of Late Cretaceous A-type granitoids in South China: Response to the rollback and retreat of the Paleo-Pacific plate
- Modification of dolomitization on reservoir spaces in reef–shoal complex: A case study of Permian Changxing Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Geological characteristics of the Daduhe gold belt, western Sichuan, China: Implications for exploration
- Rock physics model for deep coal-bed methane reservoir based on equivalent medium theory: A case study of Carboniferous-Permian in Eastern Ordos Basin
- Enhancing the total-field magnetic anomaly using the normalized source strength
- Shear wave velocity profiling of Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia, utilizing the multi-channel analysis of surface waves method
- Effect of coal facies on pore structure heterogeneity of coal measures: Quantitative characterization and comparative study
- Inversion method of organic matter content of different types of soils in black soil area based on hyperspectral indices
- Detection of seepage zones in artificial levees: A case study at the Körös River, Hungary
- Tight sandstone fluid detection technology based on multi-wave seismic data
- Characteristics and control techniques of soft rock tunnel lining cracks in high geo-stress environments: Case study of Wushaoling tunnel group
- Influence of pore structure characteristics on the Permian Shan-1 reservoir in Longdong, Southwest Ordos Basin, China
- Study on sedimentary model of Shanxi Formation – Lower Shihezi Formation in Da 17 well area of Daniudi gas field, Ordos Basin
- Multi-scenario territorial spatial simulation and dynamic changes: A case study of Jilin Province in China from 1985 to 2030
- Review Articles
- Major ascidian species with negative impacts on bivalve aquaculture: Current knowledge and future research aims
- Prediction and assessment of meteorological drought in southwest China using long short-term memory model
- Communication
- Essential questions in earth and geosciences according to large language models
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan”
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part I
- Spatial-temporal and trend analysis of traffic accidents in AP Vojvodina (North Serbia)
- Exploring environmental awareness, knowledge, and safety: A comparative study among students in Montenegro and North Macedonia
- Determinants influencing tourists’ willingness to visit Türkiye – Impact of earthquake hazards on Serbian visitors’ preferences
- Application of remote sensing in monitoring land degradation: A case study of Stanari municipality (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Optimizing agricultural land use: A GIS-based assessment of suitability in the Sana River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Assessing risk-prone areas in the Kratovska Reka catchment (North Macedonia) by integrating advanced geospatial analytics and flash flood potential index
- Analysis of the intensity of erosive processes and state of vegetation cover in the zone of influence of the Kolubara Mining Basin
- GIS-based spatial modeling of landslide susceptibility using BWM-LSI: A case study – city of Smederevo (Serbia)
- Geospatial modeling of wildfire susceptibility on a national scale in Montenegro: A comparative evaluation of F-AHP and FR methodologies
- Geosite assessment as the first step for the development of canyoning activities in North Montenegro
- Urban geoheritage and degradation risk assessment of the Sokograd fortress (Sokobanja, Eastern Serbia)
- Multi-hazard modeling of erosion and landslide susceptibility at the national scale in the example of North Macedonia
- Understanding seismic hazard resilience in Montenegro: A qualitative analysis of community preparedness and response capabilities
- Forest soil CO2 emission in Quercus robur level II monitoring site
- Characterization of glomalin proteins in soil: A potential indicator of erosion intensity
- Power of Terroir: Case study of Grašac at the Fruška Gora wine region (North Serbia)
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part I
- Qualitative insights into cultural heritage protection in Serbia: Addressing legal and institutional gaps for disaster risk resilience
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Theoretical magnetotelluric response of stratiform earth consisting of alternative homogeneous and transitional layers
- The research of common drought indexes for the application to the drought monitoring in the region of Jin Sha river
- Evolutionary game analysis of government, businesses, and consumers in high-standard farmland low-carbon construction
- On the use of low-frequency passive seismic as a direct hydrocarbon indicator: A case study at Banyubang oil field, Indonesia
- Water transportation planning in connection with extreme weather conditions; case study – Port of Novi Sad, Serbia
- Zircon U–Pb ages of the Paleozoic volcaniclastic strata in the Junggar Basin, NW China
- Monitoring of mangrove forests vegetation based on optical versus microwave data: A case study western coast of Saudi Arabia
- Microfacies analysis of marine shale: A case study of the shales of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the western Chongqing, Sichuan Basin, China
- Multisource remote sensing image fusion processing in plateau seismic region feature information extraction and application analysis – An example of the Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022
- Identification of magnetic mineralogy and paleo-flow direction of the Miocene-quaternary volcanic products in the north of Lake Van, Eastern Turkey
- Impact of fully rotating steel casing bored pile on adjacent tunnels
- Adolescents’ consumption intentions toward leisure tourism in high-risk leisure environments in riverine areas
- Petrogenesis of Jurassic granitic rocks in South China Block: Implications for events related to subduction of Paleo-Pacific plate
- Differences in urban daytime and night block vitality based on mobile phone signaling data: A case study of Kunming’s urban district
- Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan
- Integrated geophysical approach for detection and size-geometry characterization of a multiscale karst system in carbonate units, semiarid Brazil
- Spatial and temporal changes in ecosystem services value and analysis of driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta Region
- Deep fault sliding rates for Ka-Ping block of Xinjiang based on repeating earthquakes
- Improved deep learning segmentation of outdoor point clouds with different sampling strategies and using intensities
- Platform margin belt structure and sedimentation characteristics of Changxing Formation reefs on both sides of the Kaijiang-Liangping trough, eastern Sichuan Basin, China
- Enhancing attapulgite and cement-modified loess for effective landfill lining: A study on seepage prevention and Cu/Pb ion adsorption
- Flood risk assessment, a case study in an arid environment of Southeast Morocco
- Lower limits of physical properties and classification evaluation criteria of the tight reservoir in the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Kuqa depression
- Evaluation of Viaducts’ contribution to road network accessibility in the Yunnan–Guizhou area based on the node deletion method
- Permian tectonic switch of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints from magmatism in the southern Alxa region, NW China
- Element geochemical differences in lower Cambrian black shales with hydrothermal sedimentation in the Yangtze block, South China
- Three-dimensional finite-memory quasi-Newton inversion of the magnetotelluric based on unstructured grids
- Obliquity-paced summer monsoon from the Shilou red clay section on the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau
- Classification and logging identification of reservoir space near the upper Ordovician pinch-out line in Tahe Oilfield
- Ultra-deep channel sand body target recognition method based on improved deep learning under UAV cluster
- New formula to determine flyrock distance on sedimentary rocks with low strength
- Assessing the ecological security of tourism in Northeast China
- Effective reservoir identification and sweet spot prediction in Chang 8 Member tight oil reservoirs in Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin
- Detecting heterogeneity of spatial accessibility to sports facilities for adolescents at fine scale: A case study in Changsha, China
- Effects of freeze–thaw cycles on soil nutrients by soft rock and sand remodeling
- Vibration prediction with a method based on the absorption property of blast-induced seismic waves: A case study
- A new look at the geodynamic development of the Ediacaran–early Cambrian forearc basalts of the Tannuola-Khamsara Island Arc (Central Asia, Russia): Conclusions from geological, geochemical, and Nd-isotope data
- Spatio-temporal analysis of the driving factors of urban land use expansion in China: A study of the Yangtze River Delta region
- Selection of Euler deconvolution solutions using the enhanced horizontal gradient and stable vertical differentiation
- Phase change of the Ordovician hydrocarbon in the Tarim Basin: A case study from the Halahatang–Shunbei area
- Using interpretative structure model and analytical network process for optimum site selection of airport locations in Delta Egypt
- Geochemistry of magnetite from Fe-skarn deposits along the central Loei Fold Belt, Thailand
- Functional typology of settlements in the Srem region, Serbia
- Hunger Games Search for the elucidation of gravity anomalies with application to geothermal energy investigations and volcanic activity studies
- Addressing incomplete tile phenomena in image tiling: Introducing the grid six-intersection model
- Evaluation and control model for resilience of water resource building system based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and its application
- MIF and AHP methods for delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques in Tirunelveli, Tenkasi District, India
- New database for the estimation of dynamic coefficient of friction of snow
- Measuring urban growth dynamics: A study in Hue city, Vietnam
- Comparative models of support-vector machine, multilayer perceptron, and decision tree predication approaches for landslide susceptibility analysis
- Experimental study on the influence of clay content on the shear strength of silty soil and mechanism analysis
- Geosite assessment as a contribution to the sustainable development of Babušnica, Serbia
- Using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process for road transportation services management based on remote sensing and GIS technology
- Accumulation mechanism of multi-type unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in Northern China: Taking Hari Sag of the Yin’e Basin as an example
- TOC prediction of source rocks based on the convolutional neural network and logging curves – A case study of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag
- A method for fast detection of wind farms from remote sensing images using deep learning and geospatial analysis
- Spatial distribution and driving factors of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China based on GIS and geodetector
- Physicochemical and mineralogical composition studies of clays from Share and Tshonga areas, Northern Bida Basin, Nigeria: Implications for Geophagia
- Geochemical sedimentary records of eutrophication and environmental change in Chaohu Lake, East China
- Research progress of freeze–thaw rock using bibliometric analysis
- Mixed irrigation affects the composition and diversity of the soil bacterial community
- Examining the swelling potential of cohesive soils with high plasticity according to their index properties using GIS
- Geological genesis and identification of high-porosity and low-permeability sandstones in the Cretaceous Bashkirchik Formation, northern Tarim Basin
- Usability of PPGIS tools exemplified by geodiscussion – a tool for public participation in shaping public space
- Efficient development technology of Upper Paleozoic Lower Shihezi tight sandstone gas reservoir in northeastern Ordos Basin
- Assessment of soil resources of agricultural landscapes in Turkestan region of the Republic of Kazakhstan based on agrochemical indexes
- Evaluating the impact of DEM interpolation algorithms on relief index for soil resource management
- Petrogenetic relationship between plutonic and subvolcanic rocks in the Jurassic Shuikoushan complex, South China
- A novel workflow for shale lithology identification – A case study in the Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin, China
- Characteristics and main controlling factors of dolomite reservoirs in Fei-3 Member of Feixianguan Formation of Lower Triassic, Puguang area
- Impact of high-speed railway network on county-level accessibility and economic linkage in Jiangxi Province, China: A spatio-temporal data analysis
- Estimation model of wild fractional vegetation cover based on RGB vegetation index and its application
- Lithofacies, petrography, and geochemistry of the Lamphun oceanic plate stratigraphy: As a record of the subduction history of Paleo-Tethys in Chiang Mai-Chiang Rai Suture Zone of Thailand
- Structural features and tectonic activity of the Weihe Fault, central China
- Application of the wavelet transform and Hilbert–Huang transform in stratigraphic sequence division of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Structural detachment influences the shale gas preservation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Northern Guizhou Province
- Distribution law of Chang 7 Member tight oil in the western Ordos Basin based on geological, logging and numerical simulation techniques
- Evaluation of alteration in the geothermal province west of Cappadocia, Türkiye: Mineralogical, petrographical, geochemical, and remote sensing data
- Numerical modeling of site response at large strains with simplified nonlinear models: Application to Lotung seismic array
- Quantitative characterization of granite failure intensity under dynamic disturbance from energy standpoint
- Characteristics of debris flow dynamics and prediction of the hazardous area in Bangou Village, Yanqing District, Beijing, China
- Rockfall mapping and susceptibility evaluation based on UAV high-resolution imagery and support vector machine method
- Statistical comparison analysis of different real-time kinematic methods for the development of photogrammetric products: CORS-RTK, CORS-RTK + PPK, RTK-DRTK2, and RTK + DRTK2 + GCP
- Hydrogeological mapping of fracture networks using earth observation data to improve rainfall–runoff modeling in arid mountains, Saudi Arabia
- Petrography and geochemistry of pegmatite and leucogranite of Ntega-Marangara area, Burundi, in relation to rare metal mineralisation
- Prediction of formation fracture pressure based on reinforcement learning and XGBoost
- Hazard zonation for potential earthquake-induced landslide in the eastern East Kunlun fault zone
- Monitoring water infiltration in multiple layers of sandstone coal mining model with cracks using ERT
- Study of the patterns of ice lake variation and the factors influencing these changes in the western Nyingchi area
- Productive conservation at the landslide prone area under the threat of rapid land cover changes
- Sedimentary processes and patterns in deposits corresponding to freshwater lake-facies of hyperpycnal flow – An experimental study based on flume depositional simulations
- Study on time-dependent injectability evaluation of mudstone considering the self-healing effect
- Detection of objects with diverse geometric shapes in GPR images using deep-learning methods
- Behavior of trace metals in sedimentary cores from marine and lacustrine environments in Algeria
- Spatiotemporal variation pattern and spatial coupling relationship between NDVI and LST in Mu Us Sandy Land
- Formation mechanism and oil-bearing properties of gravity flow sand body of Chang 63 sub-member of Yanchang Formation in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin
- Diagenesis of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, China
- Vertical high-velocity structures and seismic activity in western Shandong Rise, China: Case study inspired by double-difference seismic tomography
- Spatial coupling relationship between metamorphic core complex and gold deposits: Constraints from geophysical electromagnetics
- Disparities in the geospatial allocation of public facilities from the perspective of living circles
- Research on spatial correlation structure of war heritage based on field theory. A case study of Jinzhai County, China
- Formation mechanisms of Qiaoba-Zhongdu Danxia landforms in southwestern Sichuan Province, China
- Magnetic data interpretation: Implication for structure and hydrocarbon potentiality at Delta Wadi Diit, Southeastern Egypt
- Deeply buried clastic rock diagenesis evolution mechanism of Dongdaohaizi sag in the center of Junggar fault basin, Northwest China
- Application of LS-RAPID to simulate the motion of two contrasting landslides triggered by earthquakes
- The new insight of tectonic setting in Sunda–Banda transition zone using tomography seismic. Case study: 7.1 M deep earthquake 29 August 2023
- The critical role of c and φ in ensuring stability: A study on rockfill dams
- Evidence of late quaternary activity of the Weining-Shuicheng Fault in Guizhou, China
- Extreme hydroclimatic events and response of vegetation in the eastern QTP since 10 ka
- Spatial–temporal effect of sea–land gradient on landscape pattern and ecological risk in the coastal zone: A case study of Dalian City
- Study on the influence mechanism of land use on carbon storage under multiple scenarios: A case study of Wenzhou
- A new method for identifying reservoir fluid properties based on well logging data: A case study from PL block of Bohai Bay Basin, North China
- Comparison between thermal models across the Middle Magdalena Valley, Eastern Cordillera, and Eastern Llanos basins in Colombia
- Mineralogical and elemental analysis of Kazakh coals from three mines: Preliminary insights from mode of occurrence to environmental impacts
- Chlorite-induced porosity evolution in multi-source tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin
- Predicting stability factors for rotational failures in earth slopes and embankments using artificial intelligence techniques
- Origin of Late Cretaceous A-type granitoids in South China: Response to the rollback and retreat of the Paleo-Pacific plate
- Modification of dolomitization on reservoir spaces in reef–shoal complex: A case study of Permian Changxing Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Geological characteristics of the Daduhe gold belt, western Sichuan, China: Implications for exploration
- Rock physics model for deep coal-bed methane reservoir based on equivalent medium theory: A case study of Carboniferous-Permian in Eastern Ordos Basin
- Enhancing the total-field magnetic anomaly using the normalized source strength
- Shear wave velocity profiling of Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia, utilizing the multi-channel analysis of surface waves method
- Effect of coal facies on pore structure heterogeneity of coal measures: Quantitative characterization and comparative study
- Inversion method of organic matter content of different types of soils in black soil area based on hyperspectral indices
- Detection of seepage zones in artificial levees: A case study at the Körös River, Hungary
- Tight sandstone fluid detection technology based on multi-wave seismic data
- Characteristics and control techniques of soft rock tunnel lining cracks in high geo-stress environments: Case study of Wushaoling tunnel group
- Influence of pore structure characteristics on the Permian Shan-1 reservoir in Longdong, Southwest Ordos Basin, China
- Study on sedimentary model of Shanxi Formation – Lower Shihezi Formation in Da 17 well area of Daniudi gas field, Ordos Basin
- Multi-scenario territorial spatial simulation and dynamic changes: A case study of Jilin Province in China from 1985 to 2030
- Review Articles
- Major ascidian species with negative impacts on bivalve aquaculture: Current knowledge and future research aims
- Prediction and assessment of meteorological drought in southwest China using long short-term memory model
- Communication
- Essential questions in earth and geosciences according to large language models
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan”
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part I
- Spatial-temporal and trend analysis of traffic accidents in AP Vojvodina (North Serbia)
- Exploring environmental awareness, knowledge, and safety: A comparative study among students in Montenegro and North Macedonia
- Determinants influencing tourists’ willingness to visit Türkiye – Impact of earthquake hazards on Serbian visitors’ preferences
- Application of remote sensing in monitoring land degradation: A case study of Stanari municipality (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Optimizing agricultural land use: A GIS-based assessment of suitability in the Sana River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Assessing risk-prone areas in the Kratovska Reka catchment (North Macedonia) by integrating advanced geospatial analytics and flash flood potential index
- Analysis of the intensity of erosive processes and state of vegetation cover in the zone of influence of the Kolubara Mining Basin
- GIS-based spatial modeling of landslide susceptibility using BWM-LSI: A case study – city of Smederevo (Serbia)
- Geospatial modeling of wildfire susceptibility on a national scale in Montenegro: A comparative evaluation of F-AHP and FR methodologies
- Geosite assessment as the first step for the development of canyoning activities in North Montenegro
- Urban geoheritage and degradation risk assessment of the Sokograd fortress (Sokobanja, Eastern Serbia)
- Multi-hazard modeling of erosion and landslide susceptibility at the national scale in the example of North Macedonia
- Understanding seismic hazard resilience in Montenegro: A qualitative analysis of community preparedness and response capabilities
- Forest soil CO2 emission in Quercus robur level II monitoring site
- Characterization of glomalin proteins in soil: A potential indicator of erosion intensity
- Power of Terroir: Case study of Grašac at the Fruška Gora wine region (North Serbia)
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part I
- Qualitative insights into cultural heritage protection in Serbia: Addressing legal and institutional gaps for disaster risk resilience

