Abstract
Simulation optimization of complex geological bodies is a necessary means to improve inversion accuracy and computational efficiency; thus, inversion of magnetotelluric (MT) based on unstructured grids has become a research hotspot in recent years. This article realizes the three-dimensional (3D) finite element forward modeling of MT based on the magnetic vector potential-electric scalar potential method, using unstructured grids as the forward modeling grid, which improves computational efficiency. The inversion uses the limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (LBFGS) method, and in the process of calculating the objective function gradient, the quasi-forward method is used to avoid solving the Jacobian matrix, which has the advantages of requiring small storage space and fast computational efficiency. Finally, the 3D LBFGS inversion algorithm of MT based on unstructured grids was realized, and the inversion studies of classic and complex models verified the effectiveness and the reliability of the algorithm proposed in this article.
1 Introduction
The magnetotelluric (MT) method is an important geophysical exploration technique that utilizes naturally occurring alternating electromagnetic fields excited by the ionosphere. By measuring the orthogonal components of the electric and magnetic fields at the Earth’s surface, it provides valuable information about subsurface structures [1,2]. The MT method does not require large-scale transmitting equipment and offers advantages such as ease of implementation and a wide detection depth. It finds extensive applications in various geophysical domains [3,4,5,6,7,8].
Samrock et al. [9] proposed a crustal-scale resistivity model based on MT data from a magmatic segment in the East African Rift. The model depicts the storage of melts throughout the crust and their transport controlled by faults, providing new insights into the migration of melts and volatiles in continental rift environments. Wu et al. [10] conducted MT surveys around the Zhangzhou Basin in China, revealing the two-dimensional resistivity structure of the geothermal belt in the basin. The cover layer is mainly composed of Quaternary and late Jurassic volcanic rocks, distributed in the west and east of the basin. The heat source is composed of heat from the crustal granite and the upper mantle. The anomalously low-resistivity zone in the middle crust may affect the distribution of high-temperature hot springs. Yang et al. [11] investigated natural gas hydrates in the permafrost zone of the Juhuanggen mining area in the Qilian Mountains of China. The study showed that thick and high-resistivity near-surface permafrost is a key factor for the existence of underlying natural gas hydrates. The degradation of permafrost may lead to the decomposition of natural gas hydrates. Deng et al. [12] detailed the formation mechanism of the Xiangshan volcanic basin, a large volcanic uranium mineral district in China, based on the results of three-dimensional MT inversion. Bedrosian et al. [13] used three-dimensional MT methods to reveal the important influence of the crustal structure on volcanic arc magmatism at Mount St. Helens. The combined effects of crustal structure inheritance (i.e., channels provided by faults at the edges of the igneous body) and top control (i.e., magma provided by the igneous body) led to the anomalous location and composition of the volcano. Gao et al. [14] revealed the phenomenon of magma recharge in the Wudalianchi volcanic group in the northeast China through three-dimensional resistivity imaging. This provides a powerful tool for studying intraplate volcanic activity and can be used to monitor and predict potential volcanic activity. Wei et al. [15] deployed a dense MT observation network in the Tibetan Plateau and obtained the three-dimensional resistivity structure of the crust below the Tibetan Plateau. The results showed that there are a large number of low-resistivity anomaly zones below the crust of the Tibetan Plateau. These anomaly zones correspond to areas with abundant underground fluids. They are important driving forces for the geological structure, magmatic activity, and seismic activity in the region. Underground fluids can serve as channels for magma ascent or as sliding surfaces for earthquakes.
In the current MT theory, commonly used numerical simulation methods for 3D forward modeling include the finite difference method (FDM) [16,17], the finite element method (FEM) [18], and the integral equation method (IEM) [19,20]. FDM is simple in principle and easy to implement; FEM has advantages in handling complex terrain and geological bodies with complex geometries; IEM has high computational efficiency because it only slices the anomaly, and it has high simulation accuracy for simple models. The traditional way of finite element grid partitioning is to use rectangular grids. Many scholars have done a lot of work and achieved good results in solving the problem of MT forward modeling, but rectangular grids have certain limitations in simulating uneven terrain and complex anomaly boundaries. With the development of computers and the increasing demands on the accuracy of forward simulation and the complexity of models, MT forward simulation based on unstructured grids has been well developed in recent years [21,22,23]. In practical applications, tetrahedral grids are easier to generate and are most widely used in the field of electromagnetics [24,25,26,27]. Some scholars have also achieved good results using unstructured hexahedral grids [26,27].
Thanks to the development of fast, stable, and high-accuracy 3D forward solvers, significant achievements have been made in both theoretical research and practical applications of 3D MT inversion [28,29,30]. The two most mainstream inversion methods are the nonlinear conjugate gradient (NLCG) and OCCAM methods. Mackie and Madden [16] proposed the conjugate gradient inversion algorithm for 3D MT problems, using the conjugate gradient method to incompletely solve the inversion equation based on the maximum likelihood inversion theory. In their inversion strategy, they avoid the direct calculation and storage of the Jacobian matrix (or sensitivity matrix), and save significant computational time and memory requirements by solving pseudo-forward problems to obtain the product of the Jacobian matrix or its transpose with a vector. Newman and Alumbaugh [31] implemented the NLCG inversion of 3D MT data based on the NLCG method improved by Polak and Ribière [32]. The NLCG method, combining gradient direction and conjugacy, makes its convergence method closer to the Newton method and avoids obtaining the Hessian matrix. During the iteration process, it only needs to solve the gradient of the objective function, which requires minimal storage space. However, each iteration process requires multiple searches for the iteration step length, leading to a longer time. The OCCAM method is known for its stability as it searches for the iteration regularization factor at each iteration, and it is not greatly dependent on the initial model. Siripunvaraporn et al. [33] improved the OCCAM method proposed by Constable et al. [34], transferring the solution problem in the model space to the data space, thus achieving the Data Space OCCAM inversion algorithm. In real situations, the number of model parameters usually exceeds the number of observational data, especially in 3D problems. Therefore, the model space OCCAM method, which requires a large amount of memory, is not very suitable for 3D inversion, highlighting the advantages of the Data Space OCCAM algorithm in 3D inversion problems.
The limited-memory Broyden–Fletcher–Goldfarb–Shanno (LBFGS) was proposed by scholars Broyden, Fletcher, Goldfarb, and Shanno in 1970. This method is an improvement on the Newton method, avoiding the calculation of the Hessian matrix and the Jacobian matrix and using a limited number of iteration information to approximate the Hessian matrix, which requires very little storage space. In 2006, Avdeev first used the LBFGS to implement the one-dimensional inversion of MT. Avdeev [28,35] used the LBFGS method to implement the inversion of 3D MT data. The quasi-Newton (QN) method is a numerical optimization method developed from the Newton method. It inherits the good convergence properties of the Newton method, yet avoids the calculation of the second-order derivative of the objective function, i.e., the Hessian matrix. The limited memory method, also known as the LBFGS method, along with the NLCG method, are collectively referred to as the most suitable methods for solving large-scale optimization problems [31].
This article employs the LBFGS inversion method, which is efficient in computation and requires minimal storage space. In the process of calculating the gradient of the objective function, the pseudo-forward method is used to optimize the algorithm. Simultaneously, the unstructured grid is used for numerical simulation, which can effectively simulate complex geological bodies, avoid the deficiencies of structured grids, and improve both computational efficiency and accuracy. Ultimately, the 3D LBFGS inversion algorithm for MT based on unstructured grids was implemented. The inversion research on both classical and complex models validated the effectiveness and reliability of the algorithm proposed in this article.
2 Forward modeling
The theoretical foundation of MT is based on Maxwell’s equations. Starting from these equations and under quasi-static conditions, we derive the boundary value problem of the 3D double curl equation for the electromagnetic field.
2.1 3D Boundary value problem
In the time domain, the electromagnetic field equations must comply with Maxwell’s equations, which consist of the following four equations:
where
By applying the Fourier transform to the time-domain Maxwell equations, we convert them into frequency-domain Maxwell equations. At this point, MT sounding is viewed as a quasi-static electromagnetic field problem. We can ignore the influence of displacement current on the electromagnetic field, and the Maxwell equations are represented as follows:
2.2 Magnetic vector potential–electric scalar potential
From equations (5)–(8), we derive the coupled equations of the electromagnetic field:
where
In 2001, Eugene A. Badea proposed that representing the electromagnetic field in terms of magnetic vector potential–electric scalar potential would yield more stable solutions for equations (9) and (10). Therefore, the method of solving for the magnetic vector potential–electric scalar potential is more stable than directly solving the electromagnetic field, and the solution speed is faster.
Without considering the displacement current, the divergence of the current density is zero, which can be expressed as follows:
Because the magnetic field is divergence free, any divergence-free field can be expressed as the curl of another vector field. Thus, the magnetic field can be expressed as follows:
Substituting equation (12) into equation (9) gives:
Since the curl of the gradient of any scalar field
This can be further transformed into:
Here,
Taking the curl of both sides of equation (9) and incorporating equation (10), we can get the frequency domain electric field equation:
By substituting equation (15) into equation (16) and considering that the divergence of the gradient equals zero, we obtain
For equation (17), after the finite element analysis, the resulting discrete matrix is asymmetric, which may lead to instability in the numerical solution. To avoid this issue, Biro and Preis proposed in 1989 to add
When the Coulomb gauge condition
Equation (18) becomes:
However, equation (20) does not consider the condition that the divergence of current density is zero. Therefore, we add the divergence condition:
Consequently, the boundary value problem for the 3D forward problem in MT, based on magnetic vector potential and electric scalar potential, is represented by equations (20) and (21).
3 Inversion method
3.1 Inversion objective function
Geophysical inversion problems consist of two parts: a data term and a model term. The former ensures that the inversion result can fit the observed data, while the latter ensures that the inversion result has physical properties under a limited amount of data, reducing the multiplicity of geophysical inversion solutions. Therefore, the inversion problem can be expressed as follows:
In the equation,
In geophysical inversion problems, the detailed expression of the data term is given as follows:
In this equation,
In this equation,
In this study, due to the lack of measured data, we use the method of adding Gaussian random error to the forward response of the theoretical model to obtain pseudo-measured data, with the specific algorithm as follows:
In this equation,
In MT inversion, there are multiple choices for measured data, such as apparent resistivity, phase, impedance, etc. In this 3D MT inversion, impedance
In the inversion of unstructured grids, the handling of the model term is a very important issue. It is different from the more mature handling of the model term in structured grids. The relationship between unstructured grids is unknown, so it is necessary to find an unstructured grid-specific model term handling method. First, it should be understood that the model term function has roughly two points: constraint on the model itself and smoothing of the model vector. The former’s significance lies in the constraint of the model itself, and the latter’s significance lies in the interrelation between models. Therefore, in the inversion problem of unstructured grids, the model term is written as follows:
In this equation,
This represents the gradient smooth constraint between models. By approximating equation (29), we can obtain:
In these equations,

Interaction of unstructured grid model vectors.
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of a nonstructured two-dimensional grid model, which explains the handling of the model term in nonstructured grids. The grey grid represents the model unit that needs to be smoothed currently, the black dots represent the centroid of each grid unit, and the distance from each grid centroid to the grey unit is represented by a dashed line. From the schematic diagram, it can be concluded that the distance between the grey grid unit and the surrounding grids is inversely proportional, and it is directly proportional to the volume of the surrounding grids.
3.2 Gradient of the objective function
In the LBFGS inversion, it is not necessary to directly calculate the sensitivity matrix, but only to solve the objective function and the gradient of the objective function. The objective function has been detailed in the previous section. The following introduces the method for solving the gradient of the objective function.
According to the objective function, the gradient of the objective function can be directly expressed as follows:
Among them, the gradient of the model term is very simple, it can be directly expressed as follows:
The gradient of the data term needs to be detailed. According to equation (23), let
At the same time, let the sensitivity matrix be:
Then the gradient of the data term can be expressed as follows:
The initial principle of the LBFGS inversion method is derived from the Newton method, and the LBFGS inversion method is obtained step by step through the optimization of the Newton method. This method has improved some of the shortcomings of the Newton method and the QN method, and has the advantages of fast computing speed and small memory space requirements.
3.3 Newton’s method and QN’s method
In geophysical inversion methods, the purpose of the inversion is the process of taking the limit value of the objective function, that is, the derivative of the objective function is zero. However, the general inversion problems are nonlinear problems, so the QN method uses the Taylor series expansion to approximate nonlinear problems to linear ones and gets closer to the final solution through continuous iteration. Therefore, the derivative of the objective function
By transformation, the iterative equation can be obtained:
Let the second derivative of the objective function (Hessian matrix) be
Equation (39) is the iterative equation of Newton’s method. In 3D inversion problems, it is very difficult to calculate the inverse matrix of a large Hessian matrix, so scholars introduced the idea of the QN method and made various approximate calculations for solving the inverse matrix of the Hessian, thus avoiding the inverse matrix solution of the Hessian matrix.
Therefore, the iterative equation of the QN method is modified based on equation (39):
Among them,
However, in high-dimensional models,
3.4 The limited memory QN method
The LBFGS overcomes the problem of the QN Method requiring a large amount of memory space. Its main idea is to only save a finite amount of gradient information from previous iterations to approximate the inverse of the Hessian matrix. Its iterative equation is the same as the QN method, as shown in equation (40). The operation process is also divided into two steps: solving the inverse of the approximate Hessian matrix and the line search step. Assuming it needs to save the information from the previous m (3–20) iterations, the update equation for the inverse of the Hessian matrix is given as follows:
where
(1) Set
(2) do:
end do;
(3) Set
(4) do:
end do;
(5)
In the aforementioned process, the initial inverse matrix
After updating the inverse of the Hessian matrix
The coefficient

Armijo sufficient descent condition diagram.
Furthermore, the iterative step length also needs to meet the curvature condition:
Where the coefficient
In LBFGS, both of these conditions must be met to achieve the optimal convergence step length. The step length of the first iteration is taken as the reciprocal of the two norms of the gradient to ensure that the direction of descent is not too large. After updating the inverse of the Hessian matrix B, the initial value of the iterative step length is
4 Synthetic data inversion
According to the aforementioned theories, Fortran code is used to implement the 3D inversion of geomagnetic electromagnetic based on unstructured grids. The inversion method uses a LBFGS method. Several models are designed to test the inversion effect.
In the following inversion, the regularization factor is chosen as
4.1 Low-resistivity prismatic model
To verify the feasibility of the 3D inversion of MT based on unstructured grids, a 3D anomaly model was first established. The schematic diagram of the model is as follows, with a burial depth of

Schematic diagram of low-resistivity anomaly and cross-section of unstructured grid.
The information of the unstructured mesh partition is as follows: the number of grid nodes is
As shown in Figure 4, the number of ground observation points is

Schematic diagram of observation point information.
The inversion was performed, and the fitting difference requirement was met after the 29th iteration, which took about
As shown in Figure 5, the average fitting error for the first time is around

Error decrease curve.
Figure 6 shows the slices of the inversion results in three directions, and the wireframes in the figure indicate the actual position of the anomaly. From all three directions, it can be seen that the shape and position of the anomaly are very well recovered in every direction. In terms of numerical values, the anomaly can be recovered to around
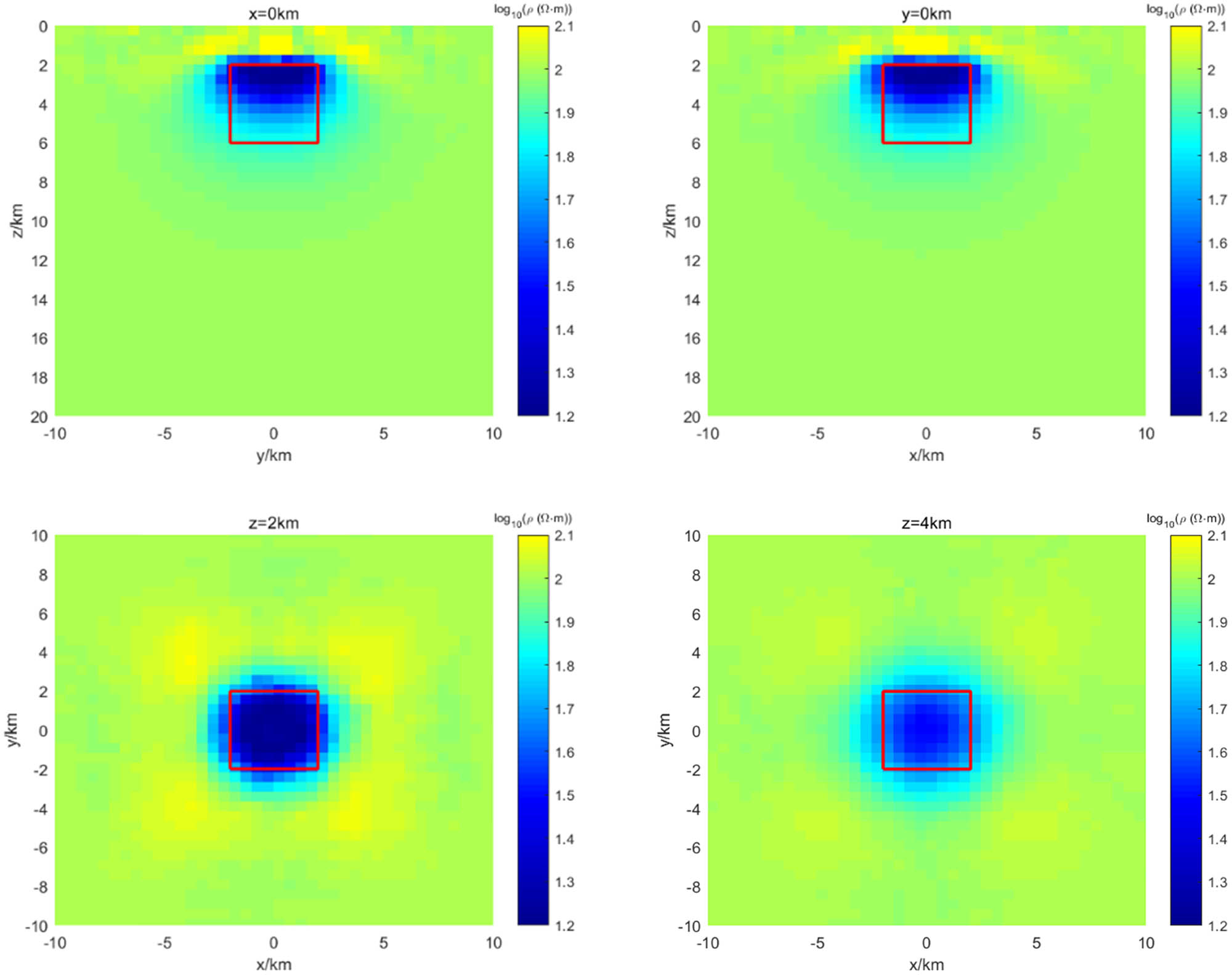
Resistivity inversion results of the low-resistivity anomaly at
4.2 High- and low-resistivity double prism model
To study the lateral resolution of the inversion results under unstructured grids and the inversion effects of multiple anomaly models, a research model with two 3D anomalies was established. As shown in Figure 7, both anomalies are buried at a depth of

Schematic diagram of high and low-resistivity double anomaly model.
The aforementioned model was discretized with an unstructured grid, resulting in the following schematic diagram of the unstructured grid partition.
Figure 8 is a 3D cross-section of the grid partition. This grid has

Cross-section of unstructured grid.
In the entire grid partition, Figure 9 is an enlarged cross-section of the yellow area in Figure 8. A dense encryption was performed around the inversion anomaly in Figure 9 to ensure the accuracy of the forward solution and a more detailed partition of the anomaly.

Cross-section of grid partition in the inversion area.
Next, we introduce the arrangement of the measurement points and the relationship between them and the projection of the anomaly on the surface, as shown in Figure 10.

Observation point information.
The red stars in Figure 10 represent the positions of the measurement points. There are
The inversion results were achieved after the 51th iteration, which took a total of

Error curve.
For the combination of high- and low-resistivity models, the initial error of the error curve is over
The following are the inversion results, showing three slices of the inversion results in the
As can be seen from the figure, both the high- and low-resistivity anomalies are well displayed in the inversion results, and their positions are very well recovered. In terms of numerical values, the low-resistivity anomaly is well recovered to about

Resistivity inversion results of high- and low-resistivity double anomalies at
4.3 Inclined prism model
To study the inversion effect of unstructured grids on complex anomaly models, this section designs an inversion example of a 3D inclined prism, studying the performance of unstructured grid inversion on the inclined body. As shown in Figure 13, the top surface of the inclined prism body is buried

Schematic diagram of the inclined prism model.
The aforementioned model was discretized with an unstructured grid using the Tetgen code, and different areas were marked, resulting in the following schematic diagram of the unstructured grid partition:
Figure 14 is a 3D cross-section of the grid partition. This grid has

Cross-section of unstructured grid.
Figure 15 is an enlarged cross-section of the yellow area in Figure 14 in the

Cross-section of grid partition in partial area: (a)
Next, we introduce the arrangement of the measurement points and the relationship between them and the projection of the anomaly on the surface.
The red points in Figure 16 represent the positions of the measurement points. There are

Relationship between the position of observation points and the projection of the anomaly on the ground.
The inversion results were achieved after the 55th iteration, which took a total of
The initial error of the error curve is close to

Error decrease curve of inversion iteration.
In Figure 18, from the overall inversion effect of the slices from three directions, the inversion result clearly reflects the inclined direction of the anomaly and can basically recover to the theoretical position. In terms of values, the minimum resistivity of the inversion result is recovered to about

Resistivity inversion results of inclined anomaly at
5 Conclusion
This article has implemented a 3D LBFGS inversion for MT based on unstructured grids. Through the inversion research of classic models and complex models, the following conclusions are drawn:
(1) In the inversion process based on unstructured grids, the selection of unstructured grids is very important. It is crucial to find an optimized grid that satisfies both the accuracy of the forward solution and the stability of the inversion iteration direction.
(2) In unstructured inversion, the study of model terms is a relatively cutting-edge topic. This research adopts the method of foreign scholars to divide the model term into two parts for processing, which plays a significant role in the stability of the descent direction and the smoothness of the model during the inversion.
(3) In this inversion, many methods to improve computational efficiency have been adopted. The forward algorithm uses a forward method based on magnetic vector potential-electric scalar potential, which is much more efficient than directly calculating the magnetic field. In inversion, the quasi-forward method avoids solving the Jacobian matrix, and the LBFGS inversion method has the advantages of improving computational efficiency and reducing storage space. Therefore, the inversion code of this article combines many advantages, greatly improving the inversion efficiency.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Tikhonov A. On determining electric characteristics of the deep layers of the Earth’s crust. Doklady. 1950;73:295–7.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Cagniard L. Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting. Geophysics. 1953;18:605–35.10.1190/1.1437915Search in Google Scholar
[3] Farquharson CG, Craven JA. Three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric data for mineral exploration: An example from the McArthur River uranium deposit, Saskatchewan, Canada. J Appl Geophys. 2009;68:450–8.10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.02.002Search in Google Scholar
[4] Zhang K, Wei W, Lu Q, Dong H, Li Y. Theoretical assessment of 3-D magnetotelluric method for oil and gas exploration: Synthetic examples. J Appl Geophys. 2014;106:23–36.10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.04.003Search in Google Scholar
[5] Patro PK. Magnetotelluric studies for hydrocarbon and geothermal resources: Examples from the Asian region. Surv Geophys. 2017;38:1005–41.10.1007/s10712-017-9439-xSearch in Google Scholar
[6] Chandrasekhar E, Fontes SL, Flexor JM, Rajaram M, Anand S. Magnetotelluric and aeromagnetic investigations for assessment of groundwater resources in Parnaiba basin in Piaui State of North-East Brazil. J Appl Geophy. 2009;68:269–81.10.1016/j.jappgeo.2008.12.001Search in Google Scholar
[7] Hanekop O, Simpson F. Error propagation in electromagnetic transfer functions: What role for the magnetotelluric method in detecting earthquake precursors? Geophys J Int. 2006;165:763–74.10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.02948.xSearch in Google Scholar
[8] Meqbel NM, Egbert GD, Wannamaker PE, Kelbert A, Schultz A. Deep electrical resistivity structure of the northwestern US derived from 3-D inversion of USArray magnetotelluric data. Earth Planet Sci Lett. 2014;402:290–304.10.1016/j.epsl.2013.12.026Search in Google Scholar
[9] Samrock F, Grayver AV, Eysteinsson H, Saar MO. Magnetotelluric image of transcrustal magmatic system beneath the Tulu Moye geothermal prospect in the Ethiopian Rift. Geophys Res Lett. 2018;45:12–847.10.1029/2018GL080333Search in Google Scholar
[10] Wu C, Hu X, Wang G, Xi Y, Lin W, Liu S, et al. Magnetotelluric imaging of the Zhangzhou Basin geothermal zone, Southeastern China. Energies. 2018;11:2170.10.3390/en11082170Search in Google Scholar
[11] Yang B, Hu X, Lin W, Liu S, Fang H. Exploration of permafrost with audio-magnetotelluric data for gas hydrates in the Juhugeng Mine of the Qilian Mountains, China. Geophysics. 2019;84:B247–58.10.1190/geo2018-0469.1Search in Google Scholar
[12] Deng J, Yu H, Chen H, Du Z, Yang H, Li H, et al. Ore-controlling structures of the Xiangshan Volcanic Basin, SE China: Revealed from three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric data. Ore Geol Rev. 2020;127:103807.10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103807Search in Google Scholar
[13] Bedrosian PA, Peacock JR, Bowles-Martinez E, Schultz A, Hill GJ. Crustal inheritance and a top-down control on arc magmatism at Mount St Helens. Nat Geosci. 2018;11:865–70.10.1038/s41561-018-0217-2Search in Google Scholar
[14] Gao J, Zhang H, Zhang S, Xin H, Li Z, Tian W, et al. Magma recharging beneath the Weishan volcano of the intraplate Wudalianchi volcanic field, northeast China, implied from 3-D magnetotelluric imaging. Geology. 2020;48:913–8.10.1130/G47531.1Search in Google Scholar
[15] Wei W, Unsworth M, Jones A, Booker J, Tan H, Nelson D, et al. Detection of widespread fluids in the Tibetan crust by magnetotelluric studies. Science. 2001;292:716–9.10.1126/science.1010580Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Mackie RL, Madden TR. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using conjugate gradients. Geophys J Int. 1993;115(1):215–29.10.1111/j.1365-246X.1993.tb05600.xSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Tan HD, Yu QF, Booker J, Wei WB. Magnetotelluric three-dimensional modeling using the staggered-grid finite difference method. Chin J Geophy. 2003;46(5):705–11.10.1002/cjg2.420Search in Google Scholar
[18] Nam MJ, Kim HJ, Song Y, Lee TJ, Son JS, Suh JH. 3D magnetotelluric modelling including surface topography. Geophys Prospect. 2007;55(2):277–87.10.1111/j.1365-2478.2007.00614.xSearch in Google Scholar
[19] Wannamaker PE, Hohmann GW, Sanfilipo WA. Electromagnetic modeling of three-dimensional bodies in layered earths using integral equations. Geophysics. 1984;49(1):60–74.10.1190/1.1441562Search in Google Scholar
[20] Xiong Z. Electromagnetic modeling of 3-D structures by the method of system iteration using integral equations. Geophysics. 1992;57(12):1556–61.10.1190/1.1443223Search in Google Scholar
[21] Franke A, Borner RU, Spitzer K. Adaptive unstructured grid finite element simulation of two-dimensional magnetotelluric fields for arbitrary surface and seafloor topography. Geophys J Int. 2007;171(1):71–86.10.1111/j.1365-246X.2007.03481.xSearch in Google Scholar
[22] Usui Y. 3-D inversion of magnetotelluric data using unstructured tetrahedral elements: applicability to data affected by topography. Geophys J Int. 2015;202(2):828–49.10.1093/gji/ggv186Search in Google Scholar
[23] Liu CS, Ren ZY, Tang JT, Yan Y. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling using edge-based finite-element unstructured meshes. Appl Geophys. 2008;5(3):170–80.10.1007/s11770-008-0024-4Search in Google Scholar
[24] Jahandari H, Farquharson CG. A finite-volume solution to the geophysical electromagnetic forward problem using unstructured grids. Geophysics. 2014;79:E287–E302.10.1190/geo2013-0312.1Search in Google Scholar
[25] Ren ZY, Kalscheuer T, Greenhalgh S, Maurer H. A goal-oriented adaptive finite-element approach for plane wave 3-D electromagnetic modeling. Geophys J Int. 2013;194(2):700–18.10.1093/gji/ggt154Search in Google Scholar
[26] Grayver AV. Parallel three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using adaptive finite-element method. Part I: Theory Synth study Geophys J Int. 2015;202(1):584–603.10.1093/gji/ggv165Search in Google Scholar
[27] Su XB, Li TL, Zhu C, Chai LW, Guan ZW. Study of three-dimensional MT forward modeling using vector finite element method. Prog Geophy. 2015;30(4):1772–8.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Avdeev DB. Three-dimensional electromagnetic modelling and inversion from theory to application. Surv Geophys. 2005;26(6):767–99.10.1007/s10712-005-1836-xSearch in Google Scholar
[29] Börner R. Numerical modelling in geo-electromagnetics: Advances and challenges. Surv Geophys. 2010;31(2):225–45.10.1007/s10712-009-9087-xSearch in Google Scholar
[30] Siripunvaraporn W. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion: An introductory guide for developers and users. Surv Geophys. 2012;33(1):5–27.10.1007/s10712-011-9122-6Search in Google Scholar
[31] Newman GA, Alumbaugh DL. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using non-linear conjugate gradients. Geophys J Int. 2000;140(2):410–24.10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00007.xSearch in Google Scholar
[32] Polak E, Ribière G. Note sur la convergence de méthods de directions conjugées. ESAIM. 1969;3(R1):35–43.10.1051/m2an/196903R100351Search in Google Scholar
[33] Siripunvaraporn W, Egbert GD, Lenbury Y, Uyeshima M. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion: data-space method. Phys Earth Planet Inter. 2005;150(1–3):3–14.10.1016/j.pepi.2004.08.023Search in Google Scholar
[34] Constable S, Parker RL, Constable CG. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics. 1987;52(3):289–300.10.1190/1.1442303Search in Google Scholar
[35] Avdeev D, Avdeeva A. 3D magnetotelluric inversion using a limited-memory quasi-newton optimization. Geophysics. 2009;74(3):F45–57.10.1190/1.3114023Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Theoretical magnetotelluric response of stratiform earth consisting of alternative homogeneous and transitional layers
- The research of common drought indexes for the application to the drought monitoring in the region of Jin Sha river
- Evolutionary game analysis of government, businesses, and consumers in high-standard farmland low-carbon construction
- On the use of low-frequency passive seismic as a direct hydrocarbon indicator: A case study at Banyubang oil field, Indonesia
- Water transportation planning in connection with extreme weather conditions; case study – Port of Novi Sad, Serbia
- Zircon U–Pb ages of the Paleozoic volcaniclastic strata in the Junggar Basin, NW China
- Monitoring of mangrove forests vegetation based on optical versus microwave data: A case study western coast of Saudi Arabia
- Microfacies analysis of marine shale: A case study of the shales of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the western Chongqing, Sichuan Basin, China
- Multisource remote sensing image fusion processing in plateau seismic region feature information extraction and application analysis – An example of the Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022
- Identification of magnetic mineralogy and paleo-flow direction of the Miocene-quaternary volcanic products in the north of Lake Van, Eastern Turkey
- Impact of fully rotating steel casing bored pile on adjacent tunnels
- Adolescents’ consumption intentions toward leisure tourism in high-risk leisure environments in riverine areas
- Petrogenesis of Jurassic granitic rocks in South China Block: Implications for events related to subduction of Paleo-Pacific plate
- Differences in urban daytime and night block vitality based on mobile phone signaling data: A case study of Kunming’s urban district
- Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan
- Integrated geophysical approach for detection and size-geometry characterization of a multiscale karst system in carbonate units, semiarid Brazil
- Spatial and temporal changes in ecosystem services value and analysis of driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta Region
- Deep fault sliding rates for Ka-Ping block of Xinjiang based on repeating earthquakes
- Improved deep learning segmentation of outdoor point clouds with different sampling strategies and using intensities
- Platform margin belt structure and sedimentation characteristics of Changxing Formation reefs on both sides of the Kaijiang-Liangping trough, eastern Sichuan Basin, China
- Enhancing attapulgite and cement-modified loess for effective landfill lining: A study on seepage prevention and Cu/Pb ion adsorption
- Flood risk assessment, a case study in an arid environment of Southeast Morocco
- Lower limits of physical properties and classification evaluation criteria of the tight reservoir in the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Kuqa depression
- Evaluation of Viaducts’ contribution to road network accessibility in the Yunnan–Guizhou area based on the node deletion method
- Permian tectonic switch of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints from magmatism in the southern Alxa region, NW China
- Element geochemical differences in lower Cambrian black shales with hydrothermal sedimentation in the Yangtze block, South China
- Three-dimensional finite-memory quasi-Newton inversion of the magnetotelluric based on unstructured grids
- Obliquity-paced summer monsoon from the Shilou red clay section on the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau
- Classification and logging identification of reservoir space near the upper Ordovician pinch-out line in Tahe Oilfield
- Ultra-deep channel sand body target recognition method based on improved deep learning under UAV cluster
- New formula to determine flyrock distance on sedimentary rocks with low strength
- Assessing the ecological security of tourism in Northeast China
- Effective reservoir identification and sweet spot prediction in Chang 8 Member tight oil reservoirs in Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin
- Detecting heterogeneity of spatial accessibility to sports facilities for adolescents at fine scale: A case study in Changsha, China
- Effects of freeze–thaw cycles on soil nutrients by soft rock and sand remodeling
- Vibration prediction with a method based on the absorption property of blast-induced seismic waves: A case study
- A new look at the geodynamic development of the Ediacaran–early Cambrian forearc basalts of the Tannuola-Khamsara Island Arc (Central Asia, Russia): Conclusions from geological, geochemical, and Nd-isotope data
- Spatio-temporal analysis of the driving factors of urban land use expansion in China: A study of the Yangtze River Delta region
- Selection of Euler deconvolution solutions using the enhanced horizontal gradient and stable vertical differentiation
- Phase change of the Ordovician hydrocarbon in the Tarim Basin: A case study from the Halahatang–Shunbei area
- Using interpretative structure model and analytical network process for optimum site selection of airport locations in Delta Egypt
- Geochemistry of magnetite from Fe-skarn deposits along the central Loei Fold Belt, Thailand
- Functional typology of settlements in the Srem region, Serbia
- Hunger Games Search for the elucidation of gravity anomalies with application to geothermal energy investigations and volcanic activity studies
- Addressing incomplete tile phenomena in image tiling: Introducing the grid six-intersection model
- Evaluation and control model for resilience of water resource building system based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and its application
- MIF and AHP methods for delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques in Tirunelveli, Tenkasi District, India
- New database for the estimation of dynamic coefficient of friction of snow
- Measuring urban growth dynamics: A study in Hue city, Vietnam
- Comparative models of support-vector machine, multilayer perceptron, and decision tree predication approaches for landslide susceptibility analysis
- Experimental study on the influence of clay content on the shear strength of silty soil and mechanism analysis
- Geosite assessment as a contribution to the sustainable development of Babušnica, Serbia
- Using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process for road transportation services management based on remote sensing and GIS technology
- Accumulation mechanism of multi-type unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in Northern China: Taking Hari Sag of the Yin’e Basin as an example
- TOC prediction of source rocks based on the convolutional neural network and logging curves – A case study of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag
- A method for fast detection of wind farms from remote sensing images using deep learning and geospatial analysis
- Spatial distribution and driving factors of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China based on GIS and geodetector
- Physicochemical and mineralogical composition studies of clays from Share and Tshonga areas, Northern Bida Basin, Nigeria: Implications for Geophagia
- Geochemical sedimentary records of eutrophication and environmental change in Chaohu Lake, East China
- Research progress of freeze–thaw rock using bibliometric analysis
- Mixed irrigation affects the composition and diversity of the soil bacterial community
- Examining the swelling potential of cohesive soils with high plasticity according to their index properties using GIS
- Geological genesis and identification of high-porosity and low-permeability sandstones in the Cretaceous Bashkirchik Formation, northern Tarim Basin
- Usability of PPGIS tools exemplified by geodiscussion – a tool for public participation in shaping public space
- Efficient development technology of Upper Paleozoic Lower Shihezi tight sandstone gas reservoir in northeastern Ordos Basin
- Assessment of soil resources of agricultural landscapes in Turkestan region of the Republic of Kazakhstan based on agrochemical indexes
- Evaluating the impact of DEM interpolation algorithms on relief index for soil resource management
- Petrogenetic relationship between plutonic and subvolcanic rocks in the Jurassic Shuikoushan complex, South China
- A novel workflow for shale lithology identification – A case study in the Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin, China
- Characteristics and main controlling factors of dolomite reservoirs in Fei-3 Member of Feixianguan Formation of Lower Triassic, Puguang area
- Impact of high-speed railway network on county-level accessibility and economic linkage in Jiangxi Province, China: A spatio-temporal data analysis
- Estimation model of wild fractional vegetation cover based on RGB vegetation index and its application
- Lithofacies, petrography, and geochemistry of the Lamphun oceanic plate stratigraphy: As a record of the subduction history of Paleo-Tethys in Chiang Mai-Chiang Rai Suture Zone of Thailand
- Structural features and tectonic activity of the Weihe Fault, central China
- Application of the wavelet transform and Hilbert–Huang transform in stratigraphic sequence division of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Structural detachment influences the shale gas preservation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Northern Guizhou Province
- Distribution law of Chang 7 Member tight oil in the western Ordos Basin based on geological, logging and numerical simulation techniques
- Evaluation of alteration in the geothermal province west of Cappadocia, Türkiye: Mineralogical, petrographical, geochemical, and remote sensing data
- Numerical modeling of site response at large strains with simplified nonlinear models: Application to Lotung seismic array
- Quantitative characterization of granite failure intensity under dynamic disturbance from energy standpoint
- Characteristics of debris flow dynamics and prediction of the hazardous area in Bangou Village, Yanqing District, Beijing, China
- Rockfall mapping and susceptibility evaluation based on UAV high-resolution imagery and support vector machine method
- Statistical comparison analysis of different real-time kinematic methods for the development of photogrammetric products: CORS-RTK, CORS-RTK + PPK, RTK-DRTK2, and RTK + DRTK2 + GCP
- Hydrogeological mapping of fracture networks using earth observation data to improve rainfall–runoff modeling in arid mountains, Saudi Arabia
- Petrography and geochemistry of pegmatite and leucogranite of Ntega-Marangara area, Burundi, in relation to rare metal mineralisation
- Prediction of formation fracture pressure based on reinforcement learning and XGBoost
- Hazard zonation for potential earthquake-induced landslide in the eastern East Kunlun fault zone
- Monitoring water infiltration in multiple layers of sandstone coal mining model with cracks using ERT
- Study of the patterns of ice lake variation and the factors influencing these changes in the western Nyingchi area
- Productive conservation at the landslide prone area under the threat of rapid land cover changes
- Sedimentary processes and patterns in deposits corresponding to freshwater lake-facies of hyperpycnal flow – An experimental study based on flume depositional simulations
- Study on time-dependent injectability evaluation of mudstone considering the self-healing effect
- Detection of objects with diverse geometric shapes in GPR images using deep-learning methods
- Behavior of trace metals in sedimentary cores from marine and lacustrine environments in Algeria
- Spatiotemporal variation pattern and spatial coupling relationship between NDVI and LST in Mu Us Sandy Land
- Formation mechanism and oil-bearing properties of gravity flow sand body of Chang 63 sub-member of Yanchang Formation in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin
- Diagenesis of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, China
- Vertical high-velocity structures and seismic activity in western Shandong Rise, China: Case study inspired by double-difference seismic tomography
- Spatial coupling relationship between metamorphic core complex and gold deposits: Constraints from geophysical electromagnetics
- Disparities in the geospatial allocation of public facilities from the perspective of living circles
- Research on spatial correlation structure of war heritage based on field theory. A case study of Jinzhai County, China
- Formation mechanisms of Qiaoba-Zhongdu Danxia landforms in southwestern Sichuan Province, China
- Magnetic data interpretation: Implication for structure and hydrocarbon potentiality at Delta Wadi Diit, Southeastern Egypt
- Deeply buried clastic rock diagenesis evolution mechanism of Dongdaohaizi sag in the center of Junggar fault basin, Northwest China
- Application of LS-RAPID to simulate the motion of two contrasting landslides triggered by earthquakes
- The new insight of tectonic setting in Sunda–Banda transition zone using tomography seismic. Case study: 7.1 M deep earthquake 29 August 2023
- The critical role of c and φ in ensuring stability: A study on rockfill dams
- Evidence of late quaternary activity of the Weining-Shuicheng Fault in Guizhou, China
- Extreme hydroclimatic events and response of vegetation in the eastern QTP since 10 ka
- Spatial–temporal effect of sea–land gradient on landscape pattern and ecological risk in the coastal zone: A case study of Dalian City
- Study on the influence mechanism of land use on carbon storage under multiple scenarios: A case study of Wenzhou
- A new method for identifying reservoir fluid properties based on well logging data: A case study from PL block of Bohai Bay Basin, North China
- Comparison between thermal models across the Middle Magdalena Valley, Eastern Cordillera, and Eastern Llanos basins in Colombia
- Mineralogical and elemental analysis of Kazakh coals from three mines: Preliminary insights from mode of occurrence to environmental impacts
- Chlorite-induced porosity evolution in multi-source tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin
- Predicting stability factors for rotational failures in earth slopes and embankments using artificial intelligence techniques
- Origin of Late Cretaceous A-type granitoids in South China: Response to the rollback and retreat of the Paleo-Pacific plate
- Modification of dolomitization on reservoir spaces in reef–shoal complex: A case study of Permian Changxing Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Geological characteristics of the Daduhe gold belt, western Sichuan, China: Implications for exploration
- Rock physics model for deep coal-bed methane reservoir based on equivalent medium theory: A case study of Carboniferous-Permian in Eastern Ordos Basin
- Enhancing the total-field magnetic anomaly using the normalized source strength
- Shear wave velocity profiling of Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia, utilizing the multi-channel analysis of surface waves method
- Effect of coal facies on pore structure heterogeneity of coal measures: Quantitative characterization and comparative study
- Inversion method of organic matter content of different types of soils in black soil area based on hyperspectral indices
- Detection of seepage zones in artificial levees: A case study at the Körös River, Hungary
- Tight sandstone fluid detection technology based on multi-wave seismic data
- Characteristics and control techniques of soft rock tunnel lining cracks in high geo-stress environments: Case study of Wushaoling tunnel group
- Influence of pore structure characteristics on the Permian Shan-1 reservoir in Longdong, Southwest Ordos Basin, China
- Study on sedimentary model of Shanxi Formation – Lower Shihezi Formation in Da 17 well area of Daniudi gas field, Ordos Basin
- Multi-scenario territorial spatial simulation and dynamic changes: A case study of Jilin Province in China from 1985 to 2030
- Review Articles
- Major ascidian species with negative impacts on bivalve aquaculture: Current knowledge and future research aims
- Prediction and assessment of meteorological drought in southwest China using long short-term memory model
- Communication
- Essential questions in earth and geosciences according to large language models
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan”
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part I
- Spatial-temporal and trend analysis of traffic accidents in AP Vojvodina (North Serbia)
- Exploring environmental awareness, knowledge, and safety: A comparative study among students in Montenegro and North Macedonia
- Determinants influencing tourists’ willingness to visit Türkiye – Impact of earthquake hazards on Serbian visitors’ preferences
- Application of remote sensing in monitoring land degradation: A case study of Stanari municipality (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Optimizing agricultural land use: A GIS-based assessment of suitability in the Sana River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Assessing risk-prone areas in the Kratovska Reka catchment (North Macedonia) by integrating advanced geospatial analytics and flash flood potential index
- Analysis of the intensity of erosive processes and state of vegetation cover in the zone of influence of the Kolubara Mining Basin
- GIS-based spatial modeling of landslide susceptibility using BWM-LSI: A case study – city of Smederevo (Serbia)
- Geospatial modeling of wildfire susceptibility on a national scale in Montenegro: A comparative evaluation of F-AHP and FR methodologies
- Geosite assessment as the first step for the development of canyoning activities in North Montenegro
- Urban geoheritage and degradation risk assessment of the Sokograd fortress (Sokobanja, Eastern Serbia)
- Multi-hazard modeling of erosion and landslide susceptibility at the national scale in the example of North Macedonia
- Understanding seismic hazard resilience in Montenegro: A qualitative analysis of community preparedness and response capabilities
- Forest soil CO2 emission in Quercus robur level II monitoring site
- Characterization of glomalin proteins in soil: A potential indicator of erosion intensity
- Power of Terroir: Case study of Grašac at the Fruška Gora wine region (North Serbia)
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part I
- Qualitative insights into cultural heritage protection in Serbia: Addressing legal and institutional gaps for disaster risk resilience
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Theoretical magnetotelluric response of stratiform earth consisting of alternative homogeneous and transitional layers
- The research of common drought indexes for the application to the drought monitoring in the region of Jin Sha river
- Evolutionary game analysis of government, businesses, and consumers in high-standard farmland low-carbon construction
- On the use of low-frequency passive seismic as a direct hydrocarbon indicator: A case study at Banyubang oil field, Indonesia
- Water transportation planning in connection with extreme weather conditions; case study – Port of Novi Sad, Serbia
- Zircon U–Pb ages of the Paleozoic volcaniclastic strata in the Junggar Basin, NW China
- Monitoring of mangrove forests vegetation based on optical versus microwave data: A case study western coast of Saudi Arabia
- Microfacies analysis of marine shale: A case study of the shales of the Wufeng–Longmaxi formation in the western Chongqing, Sichuan Basin, China
- Multisource remote sensing image fusion processing in plateau seismic region feature information extraction and application analysis – An example of the Menyuan Ms6.9 earthquake on January 8, 2022
- Identification of magnetic mineralogy and paleo-flow direction of the Miocene-quaternary volcanic products in the north of Lake Van, Eastern Turkey
- Impact of fully rotating steel casing bored pile on adjacent tunnels
- Adolescents’ consumption intentions toward leisure tourism in high-risk leisure environments in riverine areas
- Petrogenesis of Jurassic granitic rocks in South China Block: Implications for events related to subduction of Paleo-Pacific plate
- Differences in urban daytime and night block vitality based on mobile phone signaling data: A case study of Kunming’s urban district
- Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan
- Integrated geophysical approach for detection and size-geometry characterization of a multiscale karst system in carbonate units, semiarid Brazil
- Spatial and temporal changes in ecosystem services value and analysis of driving factors in the Yangtze River Delta Region
- Deep fault sliding rates for Ka-Ping block of Xinjiang based on repeating earthquakes
- Improved deep learning segmentation of outdoor point clouds with different sampling strategies and using intensities
- Platform margin belt structure and sedimentation characteristics of Changxing Formation reefs on both sides of the Kaijiang-Liangping trough, eastern Sichuan Basin, China
- Enhancing attapulgite and cement-modified loess for effective landfill lining: A study on seepage prevention and Cu/Pb ion adsorption
- Flood risk assessment, a case study in an arid environment of Southeast Morocco
- Lower limits of physical properties and classification evaluation criteria of the tight reservoir in the Ahe Formation in the Dibei Area of the Kuqa depression
- Evaluation of Viaducts’ contribution to road network accessibility in the Yunnan–Guizhou area based on the node deletion method
- Permian tectonic switch of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Constraints from magmatism in the southern Alxa region, NW China
- Element geochemical differences in lower Cambrian black shales with hydrothermal sedimentation in the Yangtze block, South China
- Three-dimensional finite-memory quasi-Newton inversion of the magnetotelluric based on unstructured grids
- Obliquity-paced summer monsoon from the Shilou red clay section on the eastern Chinese Loess Plateau
- Classification and logging identification of reservoir space near the upper Ordovician pinch-out line in Tahe Oilfield
- Ultra-deep channel sand body target recognition method based on improved deep learning under UAV cluster
- New formula to determine flyrock distance on sedimentary rocks with low strength
- Assessing the ecological security of tourism in Northeast China
- Effective reservoir identification and sweet spot prediction in Chang 8 Member tight oil reservoirs in Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin
- Detecting heterogeneity of spatial accessibility to sports facilities for adolescents at fine scale: A case study in Changsha, China
- Effects of freeze–thaw cycles on soil nutrients by soft rock and sand remodeling
- Vibration prediction with a method based on the absorption property of blast-induced seismic waves: A case study
- A new look at the geodynamic development of the Ediacaran–early Cambrian forearc basalts of the Tannuola-Khamsara Island Arc (Central Asia, Russia): Conclusions from geological, geochemical, and Nd-isotope data
- Spatio-temporal analysis of the driving factors of urban land use expansion in China: A study of the Yangtze River Delta region
- Selection of Euler deconvolution solutions using the enhanced horizontal gradient and stable vertical differentiation
- Phase change of the Ordovician hydrocarbon in the Tarim Basin: A case study from the Halahatang–Shunbei area
- Using interpretative structure model and analytical network process for optimum site selection of airport locations in Delta Egypt
- Geochemistry of magnetite from Fe-skarn deposits along the central Loei Fold Belt, Thailand
- Functional typology of settlements in the Srem region, Serbia
- Hunger Games Search for the elucidation of gravity anomalies with application to geothermal energy investigations and volcanic activity studies
- Addressing incomplete tile phenomena in image tiling: Introducing the grid six-intersection model
- Evaluation and control model for resilience of water resource building system based on fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and its application
- MIF and AHP methods for delineation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing and GIS techniques in Tirunelveli, Tenkasi District, India
- New database for the estimation of dynamic coefficient of friction of snow
- Measuring urban growth dynamics: A study in Hue city, Vietnam
- Comparative models of support-vector machine, multilayer perceptron, and decision tree predication approaches for landslide susceptibility analysis
- Experimental study on the influence of clay content on the shear strength of silty soil and mechanism analysis
- Geosite assessment as a contribution to the sustainable development of Babušnica, Serbia
- Using fuzzy analytical hierarchy process for road transportation services management based on remote sensing and GIS technology
- Accumulation mechanism of multi-type unconventional oil and gas reservoirs in Northern China: Taking Hari Sag of the Yin’e Basin as an example
- TOC prediction of source rocks based on the convolutional neural network and logging curves – A case study of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag
- A method for fast detection of wind farms from remote sensing images using deep learning and geospatial analysis
- Spatial distribution and driving factors of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China based on GIS and geodetector
- Physicochemical and mineralogical composition studies of clays from Share and Tshonga areas, Northern Bida Basin, Nigeria: Implications for Geophagia
- Geochemical sedimentary records of eutrophication and environmental change in Chaohu Lake, East China
- Research progress of freeze–thaw rock using bibliometric analysis
- Mixed irrigation affects the composition and diversity of the soil bacterial community
- Examining the swelling potential of cohesive soils with high plasticity according to their index properties using GIS
- Geological genesis and identification of high-porosity and low-permeability sandstones in the Cretaceous Bashkirchik Formation, northern Tarim Basin
- Usability of PPGIS tools exemplified by geodiscussion – a tool for public participation in shaping public space
- Efficient development technology of Upper Paleozoic Lower Shihezi tight sandstone gas reservoir in northeastern Ordos Basin
- Assessment of soil resources of agricultural landscapes in Turkestan region of the Republic of Kazakhstan based on agrochemical indexes
- Evaluating the impact of DEM interpolation algorithms on relief index for soil resource management
- Petrogenetic relationship between plutonic and subvolcanic rocks in the Jurassic Shuikoushan complex, South China
- A novel workflow for shale lithology identification – A case study in the Gulong Depression, Songliao Basin, China
- Characteristics and main controlling factors of dolomite reservoirs in Fei-3 Member of Feixianguan Formation of Lower Triassic, Puguang area
- Impact of high-speed railway network on county-level accessibility and economic linkage in Jiangxi Province, China: A spatio-temporal data analysis
- Estimation model of wild fractional vegetation cover based on RGB vegetation index and its application
- Lithofacies, petrography, and geochemistry of the Lamphun oceanic plate stratigraphy: As a record of the subduction history of Paleo-Tethys in Chiang Mai-Chiang Rai Suture Zone of Thailand
- Structural features and tectonic activity of the Weihe Fault, central China
- Application of the wavelet transform and Hilbert–Huang transform in stratigraphic sequence division of Jurassic Shaximiao Formation in Southwest Sichuan Basin
- Structural detachment influences the shale gas preservation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation, Northern Guizhou Province
- Distribution law of Chang 7 Member tight oil in the western Ordos Basin based on geological, logging and numerical simulation techniques
- Evaluation of alteration in the geothermal province west of Cappadocia, Türkiye: Mineralogical, petrographical, geochemical, and remote sensing data
- Numerical modeling of site response at large strains with simplified nonlinear models: Application to Lotung seismic array
- Quantitative characterization of granite failure intensity under dynamic disturbance from energy standpoint
- Characteristics of debris flow dynamics and prediction of the hazardous area in Bangou Village, Yanqing District, Beijing, China
- Rockfall mapping and susceptibility evaluation based on UAV high-resolution imagery and support vector machine method
- Statistical comparison analysis of different real-time kinematic methods for the development of photogrammetric products: CORS-RTK, CORS-RTK + PPK, RTK-DRTK2, and RTK + DRTK2 + GCP
- Hydrogeological mapping of fracture networks using earth observation data to improve rainfall–runoff modeling in arid mountains, Saudi Arabia
- Petrography and geochemistry of pegmatite and leucogranite of Ntega-Marangara area, Burundi, in relation to rare metal mineralisation
- Prediction of formation fracture pressure based on reinforcement learning and XGBoost
- Hazard zonation for potential earthquake-induced landslide in the eastern East Kunlun fault zone
- Monitoring water infiltration in multiple layers of sandstone coal mining model with cracks using ERT
- Study of the patterns of ice lake variation and the factors influencing these changes in the western Nyingchi area
- Productive conservation at the landslide prone area under the threat of rapid land cover changes
- Sedimentary processes and patterns in deposits corresponding to freshwater lake-facies of hyperpycnal flow – An experimental study based on flume depositional simulations
- Study on time-dependent injectability evaluation of mudstone considering the self-healing effect
- Detection of objects with diverse geometric shapes in GPR images using deep-learning methods
- Behavior of trace metals in sedimentary cores from marine and lacustrine environments in Algeria
- Spatiotemporal variation pattern and spatial coupling relationship between NDVI and LST in Mu Us Sandy Land
- Formation mechanism and oil-bearing properties of gravity flow sand body of Chang 63 sub-member of Yanchang Formation in Huaqing area, Ordos Basin
- Diagenesis of marine-continental transitional shale from the Upper Permian Longtan Formation in southern Sichuan Basin, China
- Vertical high-velocity structures and seismic activity in western Shandong Rise, China: Case study inspired by double-difference seismic tomography
- Spatial coupling relationship between metamorphic core complex and gold deposits: Constraints from geophysical electromagnetics
- Disparities in the geospatial allocation of public facilities from the perspective of living circles
- Research on spatial correlation structure of war heritage based on field theory. A case study of Jinzhai County, China
- Formation mechanisms of Qiaoba-Zhongdu Danxia landforms in southwestern Sichuan Province, China
- Magnetic data interpretation: Implication for structure and hydrocarbon potentiality at Delta Wadi Diit, Southeastern Egypt
- Deeply buried clastic rock diagenesis evolution mechanism of Dongdaohaizi sag in the center of Junggar fault basin, Northwest China
- Application of LS-RAPID to simulate the motion of two contrasting landslides triggered by earthquakes
- The new insight of tectonic setting in Sunda–Banda transition zone using tomography seismic. Case study: 7.1 M deep earthquake 29 August 2023
- The critical role of c and φ in ensuring stability: A study on rockfill dams
- Evidence of late quaternary activity of the Weining-Shuicheng Fault in Guizhou, China
- Extreme hydroclimatic events and response of vegetation in the eastern QTP since 10 ka
- Spatial–temporal effect of sea–land gradient on landscape pattern and ecological risk in the coastal zone: A case study of Dalian City
- Study on the influence mechanism of land use on carbon storage under multiple scenarios: A case study of Wenzhou
- A new method for identifying reservoir fluid properties based on well logging data: A case study from PL block of Bohai Bay Basin, North China
- Comparison between thermal models across the Middle Magdalena Valley, Eastern Cordillera, and Eastern Llanos basins in Colombia
- Mineralogical and elemental analysis of Kazakh coals from three mines: Preliminary insights from mode of occurrence to environmental impacts
- Chlorite-induced porosity evolution in multi-source tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Shaximiao Formation in western Sichuan Basin
- Predicting stability factors for rotational failures in earth slopes and embankments using artificial intelligence techniques
- Origin of Late Cretaceous A-type granitoids in South China: Response to the rollback and retreat of the Paleo-Pacific plate
- Modification of dolomitization on reservoir spaces in reef–shoal complex: A case study of Permian Changxing Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China
- Geological characteristics of the Daduhe gold belt, western Sichuan, China: Implications for exploration
- Rock physics model for deep coal-bed methane reservoir based on equivalent medium theory: A case study of Carboniferous-Permian in Eastern Ordos Basin
- Enhancing the total-field magnetic anomaly using the normalized source strength
- Shear wave velocity profiling of Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia, utilizing the multi-channel analysis of surface waves method
- Effect of coal facies on pore structure heterogeneity of coal measures: Quantitative characterization and comparative study
- Inversion method of organic matter content of different types of soils in black soil area based on hyperspectral indices
- Detection of seepage zones in artificial levees: A case study at the Körös River, Hungary
- Tight sandstone fluid detection technology based on multi-wave seismic data
- Characteristics and control techniques of soft rock tunnel lining cracks in high geo-stress environments: Case study of Wushaoling tunnel group
- Influence of pore structure characteristics on the Permian Shan-1 reservoir in Longdong, Southwest Ordos Basin, China
- Study on sedimentary model of Shanxi Formation – Lower Shihezi Formation in Da 17 well area of Daniudi gas field, Ordos Basin
- Multi-scenario territorial spatial simulation and dynamic changes: A case study of Jilin Province in China from 1985 to 2030
- Review Articles
- Major ascidian species with negative impacts on bivalve aquaculture: Current knowledge and future research aims
- Prediction and assessment of meteorological drought in southwest China using long short-term memory model
- Communication
- Essential questions in earth and geosciences according to large language models
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Random forest and artificial neural network-based tsunami forests classification using data fusion of Sentinel-2 and Airbus Vision-1 satellites: A case study of Garhi Chandan, Pakistan”
- Special Issue: Natural Resources and Environmental Risks: Towards a Sustainable Future - Part I
- Spatial-temporal and trend analysis of traffic accidents in AP Vojvodina (North Serbia)
- Exploring environmental awareness, knowledge, and safety: A comparative study among students in Montenegro and North Macedonia
- Determinants influencing tourists’ willingness to visit Türkiye – Impact of earthquake hazards on Serbian visitors’ preferences
- Application of remote sensing in monitoring land degradation: A case study of Stanari municipality (Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Optimizing agricultural land use: A GIS-based assessment of suitability in the Sana River Basin, Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Assessing risk-prone areas in the Kratovska Reka catchment (North Macedonia) by integrating advanced geospatial analytics and flash flood potential index
- Analysis of the intensity of erosive processes and state of vegetation cover in the zone of influence of the Kolubara Mining Basin
- GIS-based spatial modeling of landslide susceptibility using BWM-LSI: A case study – city of Smederevo (Serbia)
- Geospatial modeling of wildfire susceptibility on a national scale in Montenegro: A comparative evaluation of F-AHP and FR methodologies
- Geosite assessment as the first step for the development of canyoning activities in North Montenegro
- Urban geoheritage and degradation risk assessment of the Sokograd fortress (Sokobanja, Eastern Serbia)
- Multi-hazard modeling of erosion and landslide susceptibility at the national scale in the example of North Macedonia
- Understanding seismic hazard resilience in Montenegro: A qualitative analysis of community preparedness and response capabilities
- Forest soil CO2 emission in Quercus robur level II monitoring site
- Characterization of glomalin proteins in soil: A potential indicator of erosion intensity
- Power of Terroir: Case study of Grašac at the Fruška Gora wine region (North Serbia)
- Special Issue: Geospatial and Environmental Dynamics - Part I
- Qualitative insights into cultural heritage protection in Serbia: Addressing legal and institutional gaps for disaster risk resilience

