Abstract
Evaluating the mechanical properties of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is essential to measure its resistance to permanent deformation from an applied force. These mechanical ePTFE properties must be comparable to the properties of real tissue. Various hydrophilic comonomers 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAM), and N-vinylcaprolactam were used individually for copolymerization with acrylic acid (AA) to be grafted onto ePTFE using the gamma irradiation-induced grafting method. After surface modification, the hydrophobic and mechanical properties of ePTFE were altered. The water uptake and contact angle measurement showed that the modified ePTFE was less hydrophobic (∼500%, θ < 90°) than the unmodified ePTFE (0%, θ = 140°). Moreover, the mechanical properties of ePTFE changed after the modification process due to the polymer grafted onto the ePTFE surface. The data from mechanical tests, such as Young’s modulus (74–121 MPa), ultimate tensile strength (5–9 MPa), and elongation at break (56–121%), obtained for the sample AA-co-HEMA and AA-co-NIPAAM remain within the ranges and are considered desirable for use as a biomaterial. The mechanical strength correlates well with the percentage of the grafting yield after the modification process and is dependent on the parameters used, such as irradiation dose and type of comonomer.
Graphical abstract
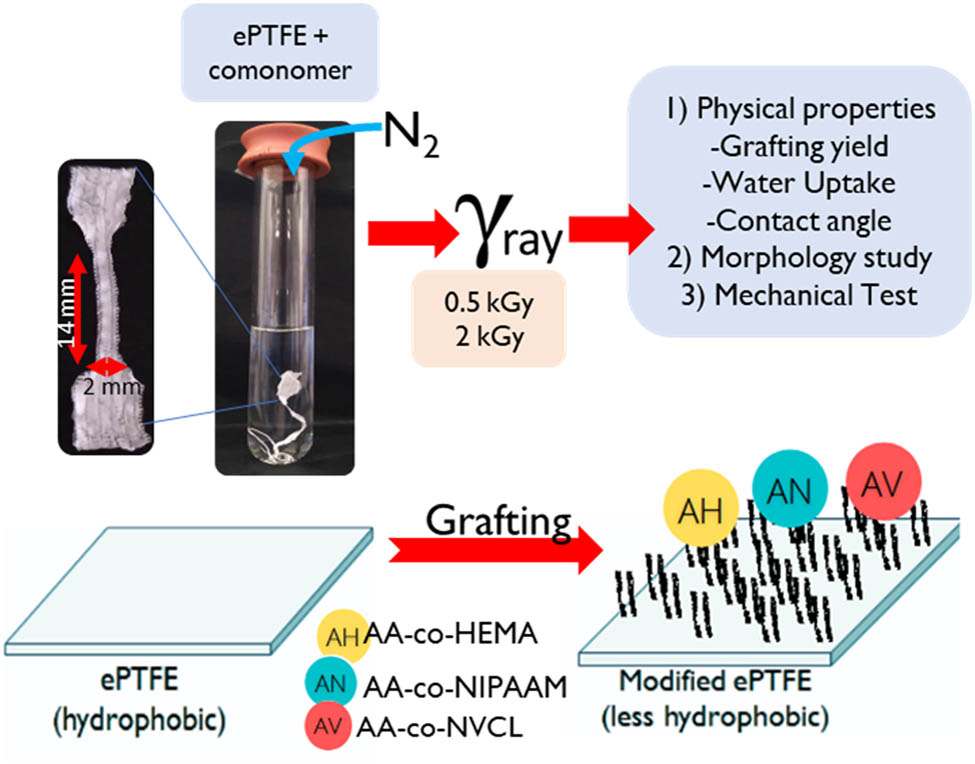
1 Introduction
Polymeric biomaterials have a wide variety of applications for implantation as they are resilient to changes in the body environment after implantation as well as being easily fabricated in various desired properties for specific medical applications [1,2]. Nevertheless, producing polymeric biomaterials that can mimic actual tissue in soft tissue replacement is still a great challenge because no known surgical implant materials ever been shown to be completely free of adverse reactions in the human body [3].
Polymeric biomaterials that are commonly used are polyamides, polyethylene, polyacrylates, and fluoropolymers. One of the synthetic fluoropolymers that are considered to have “gold” properties is expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE). This expanded version of PTFE has a multiple micropore structure that allows tissue at the soft tissue replacement site to grow inside the pores, thus promoting a faster healing process and proper integration with the tissue [4]. ePTFE was first used as a vascular graft in cardiovascular surgery and is currently used in the same application [5,6,7]. ePTFE is also used in other medical applications, such as guided bone generation [8], stent grafts, and surgical meshes [9]. Despite its wide usage in medical applications due to its inertness and nontoxic properties, ePTFE is extremely hydrophobic, which reduces its biocompatibility. As a characteristic of biomaterials, “biocompatibility” refers to materials showing good mechanical, chemical, pharmacological, and surface properties as well as beneficial interactions among cells, tissues, or muscles [1]. The standard specifications for implantable PTFE that may be used for implant products are provided by ASTM F754 [3].
Much research has been conducted on modifying ePTFE to enhance its biocompatibility. Functional groups are introduced to the ePTFE surfaces to reduce the extreme hydrophobicity without changing the bulk polymer’s properties. Surface modification using radiation-induced grafting is a one-port synthesis grafting method compared to other methods such as chemical treatment, which requires multiple chemicals, an initiator, and heat to initiate the radical formation. Fluoropolymers are particularly susceptible to postradiation degradation in which radicals produced during the scission processes can be used to tailor the molecular weight in the fabricating polymer with desired characteristics [10,11]. Grafting through the irradiation method in the presence of monomers with desired functional groups is a simple method to improve ePTFE surface properties [12]. After the modification process, the extreme hydrophobicity of ePTFE can be reduced. This outcome can be seen in previous research using the same method with a different monomer, such as acrylic acid (AA) [13] or N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAM) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) [4].
After the modification process, any polymeric materials will experience changes in physical or chemical properties. The polymeric biomaterials used for biomaterials applications should have the desired balance of biological and mechanical properties to perform as expected in a specific function. The specific optimization of properties, such as elasticity, yield stress, and ultimate strength, depends on the type and functionality of the specific implant. Although there will be some tissue reaction due to the introduction of a foreign substance, any resulting changes in mechanical, physical, and chemical properties within the localized environment should not lead to deleterious local changes and harmful systemic effects.
Mechanical performance is one of the most important biomaterial criteria to be analyzed in modified ePTFE. This property is crucial when handling mechanical stress on the healing of the soft tissue. Increasing mechanical stress potentially causes an increase in the cellular activity, which varies with the cells under study and the methodology used. As an example, soft tissue such as tendons and ligaments displays tissue homeostasis dependent on mechanical stress and motion.
The mechanical properties of ePTFE investigated in studies by Catanese et al. (1999) highlight the linear density of manufactured ePTFE. These studies offer a general view on medical-grade ePTFE used in real implant applications [5]. Additionally, Zhu et al. reported the mechanical properties of modified ePTFE using a thermal treatment [14]. Studies on single monomers using the gamma irradiation-induced grafting method have also been reported [4,13]. Until now, a lack of research has been reported on the mechanical properties of ePTFE modified with a grafting method using dual monomers. Therefore, this article aims to promote an understanding of the mechanical properties of ePTFE after modification using a gamma irradiation-induced grafting method with dual monomers. The monomers used in this research are hydrophilic monomers, namely HEMA, NIPAAM, and N-vinylcaprolactam (NVCL), which were copolymerized with AA and grafted onto ePTFE. The physical and mechanical properties of the upgraded grafted comonomers were evaluated through percentage of water uptake, contact angle measurement, and a tensile test.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
AA, HEMA, NIPAAM, and NVCL were all obtained from Sigma-Aldrich. The comonomers used were a mixture of comonomer AA and HEMA, AA and NIPAAM, and AA and NVCL, and the samples were labeled as AH, AN, and AV, respectively. In this study, the ePTFE used is from the Pall Corporation and has a thickness of 0.3 mm, different from the 0.22 mm-thick ePTFE used in our previous study [15]. The total concentration of comonomer used is 1 M.
2.2 Grafting method
For tensile analysis, the ePTFE was cut into dumbbell-shaped pieces of 14 mm length and 2 mm width using a cutter according to ISO-37. The cut sample was first washed with hot methanol at 40°C to remove any contaminant inside the pores and then dried in a desiccator jar. The sample was immersed in a 1 M total concentration comonomer solution and degassed with nitrogen [15]. Sample AH was irradiated at an irradiation dose of 0.5 kGy, whereas 2 kGy for sample AN and AV with gamma cell (0.78 kGy/h; MDS Nordion). ePTFE samples were also irradiated at 2 kGy with no comonomer present, and the sample was labeled as ePTFE(2). After irradiation, the grafted samples were washed with hot methanol for 1 h to remove any ungrafted homopolymer attached to the ePTFE surface. Then, the samples were washed with deionized water and left immersed for 24 h and dried. The additional weight difference after the grafting procedure was measured as the grafting yield percentage.
2.3 Characterization
The amount of water uptake by the modified sample was measured by the increase of ePTFE-g-AAHEMA/AANIPAAM/AANVCL sample weight, which was soaked in deionized water for 24 h. The percentage of water uptake was calculated using the following formula [15]:
where W s is the weight of the swollen sample (ePTFE/modified ePTFE immersed in deionized water), W d is the weight of the dry sample (ePTFE/modified ePTFE), and W P is the mass of p(AAHEMA/AANIPAAM/AANVCL).
The contact angle measurement was performed using the sessile drop method at 25°C (Surface Analyser LSA100, LAUDA Scientific). A total of 3 µL deionized water was dropped by syringe on the samples, and the contact angle was measured. Five measurements were taken for each sample and the standard deviation was recorded.
Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (Merlin Compact, ZEISS) was performed on the samples under a high vacuum with a standard mode voltage at 3 kV. To make the material conductive, the samples were coated with platinum for 5 min until an 8 nm-thick layer had formed before the analysis. A magnification of 5k× was used for the morphology analysis of the samples [16].
For the tensile test, samples were prepared in dry and wet conditions, and the test was carried out at room temperature. The measurement was conducted using an Instron testing machine (Universal Testing Machine 5564, Instron) at a constant crosshead speed of 10 mm/min under a 50 N load [17]. The wet sample was immersed in deionized water for 24 h before testing. The Young’s modulus, E (MPa), elongation at break, ε (percentage of tensile strain), and ultimate tensile strength (UTS; maximum tensile strength in MPa) were evaluated, and five replicates were taken for all readings. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad PRISM software (GraphPad Software, Inc). Statistical analysis was conducted using the one-way analysis of variance method. The significant difference was defined as p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001, and p < 0.0001 and noted as *, **, ***, and **** in the following results, respectively. If no asterisks are used, p > 0.05 shows no significant difference.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Physical properties of modified ePTFE
The physical changes of the modified samples (AH, AN, and AV) can be observed in Figure 1 either in dry or in wet conditions. After 24 h immersed in deionized water, the modified sample AH, AN, and AV shows that the initial white color of the samples turns colorless. Initially, all sample length was 3.1 mm. After modification, all samples (dry condition) of AH, AN, and AV were reduced in dimension in the range of 1–2 mm after the grafting process (Table 1). An approximately 6% reduction was found for samples AH and AN, whereas sample AV was 3% compared to the original dimension. However, in a wet condition, the modified samples extended their lengths to the original dimensions before the modification process.
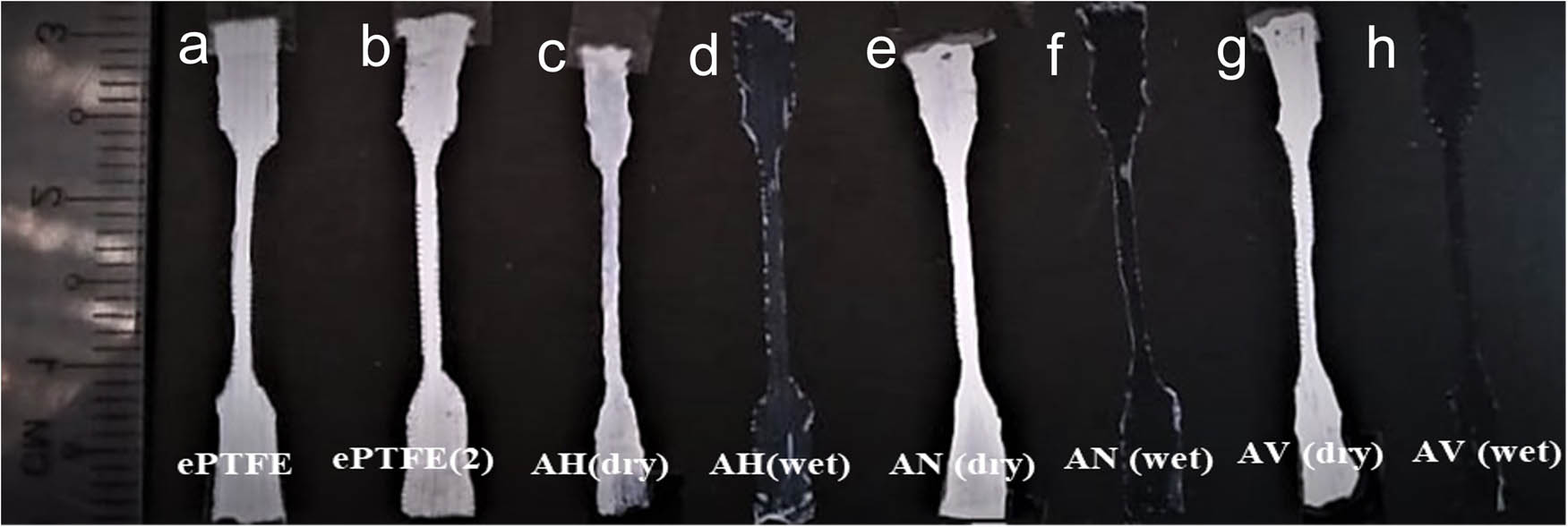
Physical appearance and lengths of samples: (a) unmodified ePTFE, (b) ePTFE(2), (c) sample AH (dry), (d) sample AH (wet), (e) sample AN (dry), (f) sample AN (wet), (g) sample AV (dry), and (h) sample AV (wet).
Length, grafting yield, and water uptake of unmodified and modified ePTFE
| Sample | Length (±1 mm) | Grafting yield (%) | Water uptake (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | |||
| ePTFE | 30.1 | — | — | 0 |
| ePTFE(2) | 3.1 | — | — | 0 |
| AH | 20.9 | 3.1 | 35 ± 3 | 540 ± 40 |
| AN | 20.9 | 3.1 | 36 ± 3 | 552 ± 61 |
| AV | 30 | 3.1 | 16 ± 3 | 378 ± 68 |
The grafting yield (measured by percent of weight increase) and the water uptake of the modified samples are shown in Table 1. Results show that the grafting yield and water uptake of the modified samples were seen to correlate because a higher grafting yield is accompanied by a higher water uptake. Samples AH and AN, with an almost similar grafting yield, were shown to have a higher water uptake compared to the AV sample, which had a smaller grafting yield.
A previous study by Hidzir et al. reported that exposing ePTFE to gamma irradiation at 10 kGy – although without the presence of a monomer – reduced the length of the irradiated ePTFE approximately 9% compared to its original condition due to a scission process that lowered the stress of the polymer chain [13]. In contrast, the observation in this study on a sample ePTFE(2) irradiated without the presence of any monomers at 2 kGy does not show any changes in length. This finding indicates that the scission occurring at a lower irradiation dose, that is, 2 kGy, is probably not excessive, thus resulting in a similar length of the sample ePTFE(2) with unirradiated ePTFE. Grafting the hydrophilic comonomer onto the ePTFE surfaces allows the water to be absorbed on the surface, thus extending its length. The hydrophilic functional groups of the comonomer allow for the formation of H-bonds with water molecules.
The degree of grafting is affected by parameters such as irradiation doses and the type of comonomer used [18]. The parameters used in this study to obtain the optimum grafting include irradiation doses of 0.5 kGy for the sample AH and 2 kGy for samples AN and AV. Above that desired irradiation dose, a homopolymer formed, thus reducing the grafting yield (data not shown).
3.2 Wettability and contact angle
The contact angle analysis (Figure 2(a) and (b)) demonstrated that after the modification process, the hydrophobicity of the ePTFE was altered. In Figure 2(a), the contact angle of all samples was observed for 6 min to determine its wettability because each comonomer grafted onto ePTFE (AH, AN, and AV) had different wettabilities. At t = 0 min, sample AH showed the highest wettability (≤90°) spontaneously (88 ± 12°) after the liquid interacted with the modified surface. This result is followed by both samples AN and AV, showing low wettability (≥90°) with contact angle values of 127 ± 4° and 126 ± 3°, respectively. Sample AN started to display its high wettability properties (90 ± 10°) at t = 2 min. Meanwhile, for sample AV, the contact angle lessens at a slower rate compared to samples AH and AV as the contact angle value was 109 ± 13° after 6 min.
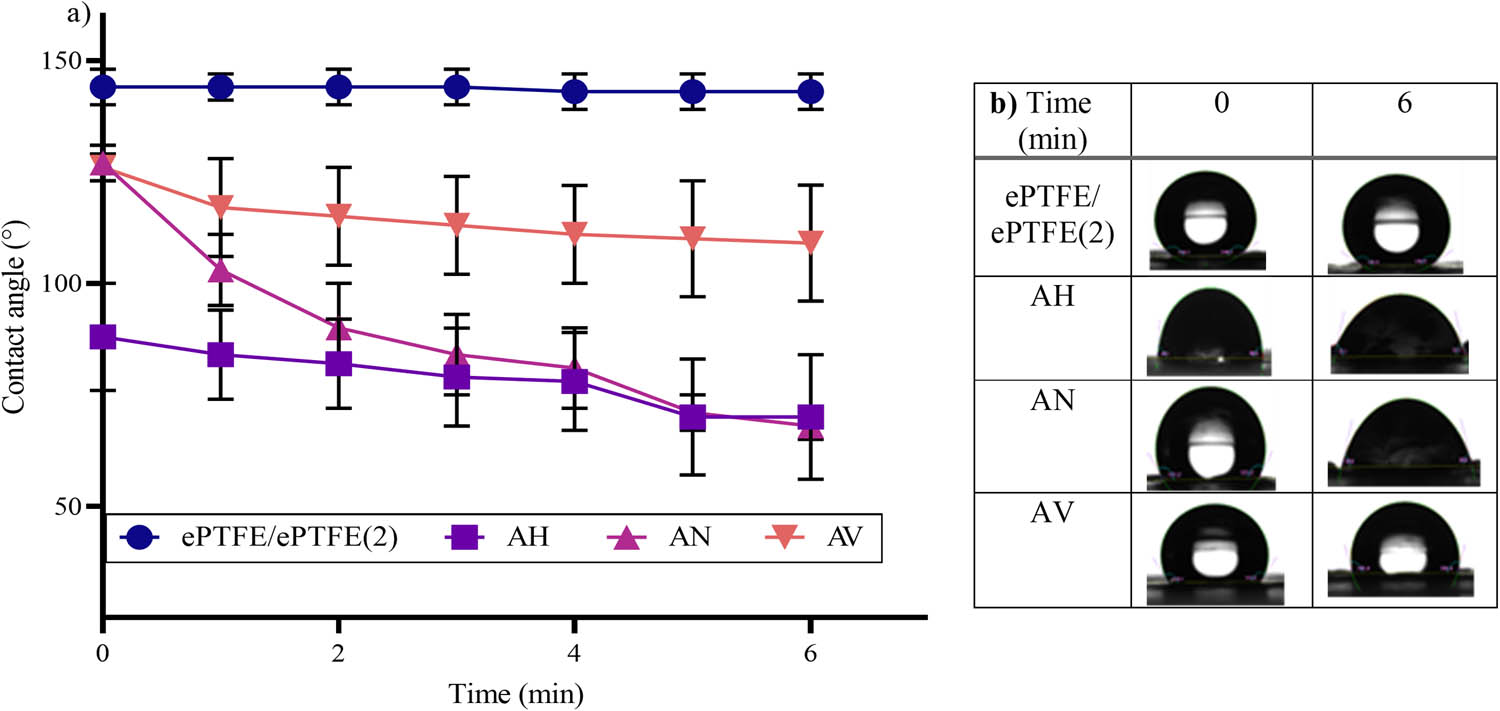
(a) Graph of contact angle for unmodified and modified ePTFE and (b) image of contact angle for unmodified and modified ePTFE.
The contact angle value correlates well with the grafting yield of the modified sample. Sample AH shows a lower contact angle value compared to sample AN although the grafting value was comparable and higher than the sample AV. The contact angle depends on the wettability of the polymeric materials and is time dependent. The wettability of HEMA is faster than NIPAAM, consequently resulting in a shorter measured time, and the contact angle of HEMA was smaller than AN. The contact angle for unmodified ePTFE and ePTFE(2) shows that without the presence of monomers, the hydrophobic properties of ePTFE are changeless. Therefore, no water uptake was observed for both samples: ePTFE and ePTFE(2). Likewise, the water uptake (%) of both AH and AN was comparable after 24 h immersed in deionized water, which resulted in 540 ± 40% and 552 ± 6%, respectively. The value of the water uptake also agrees with the percentage of the grafting yield as the sample AV shows the lowest water uptake, with only 378 ± 68%.
3.3 Field-emission scanning electron microscope morphology of modified ePTFE
Figure 3 shows FESEM images of ePTFE surface samples. The microstructure of the unmodified ePTFE is characterized by many pores and island-like fractions called nodes that are interconnected by fibrils (Figure 3a). Initially, the fibrils were approximately 2–4 µm, and the nodes were about 1 µm. Each node connects from three to five fibrils. After modification, the node structure was seen to form a larger area than the fibrils, and the fibrils were seen to shorten for samples AH, AN, and AV (Figure 3), which was an indicator of successful grafting.
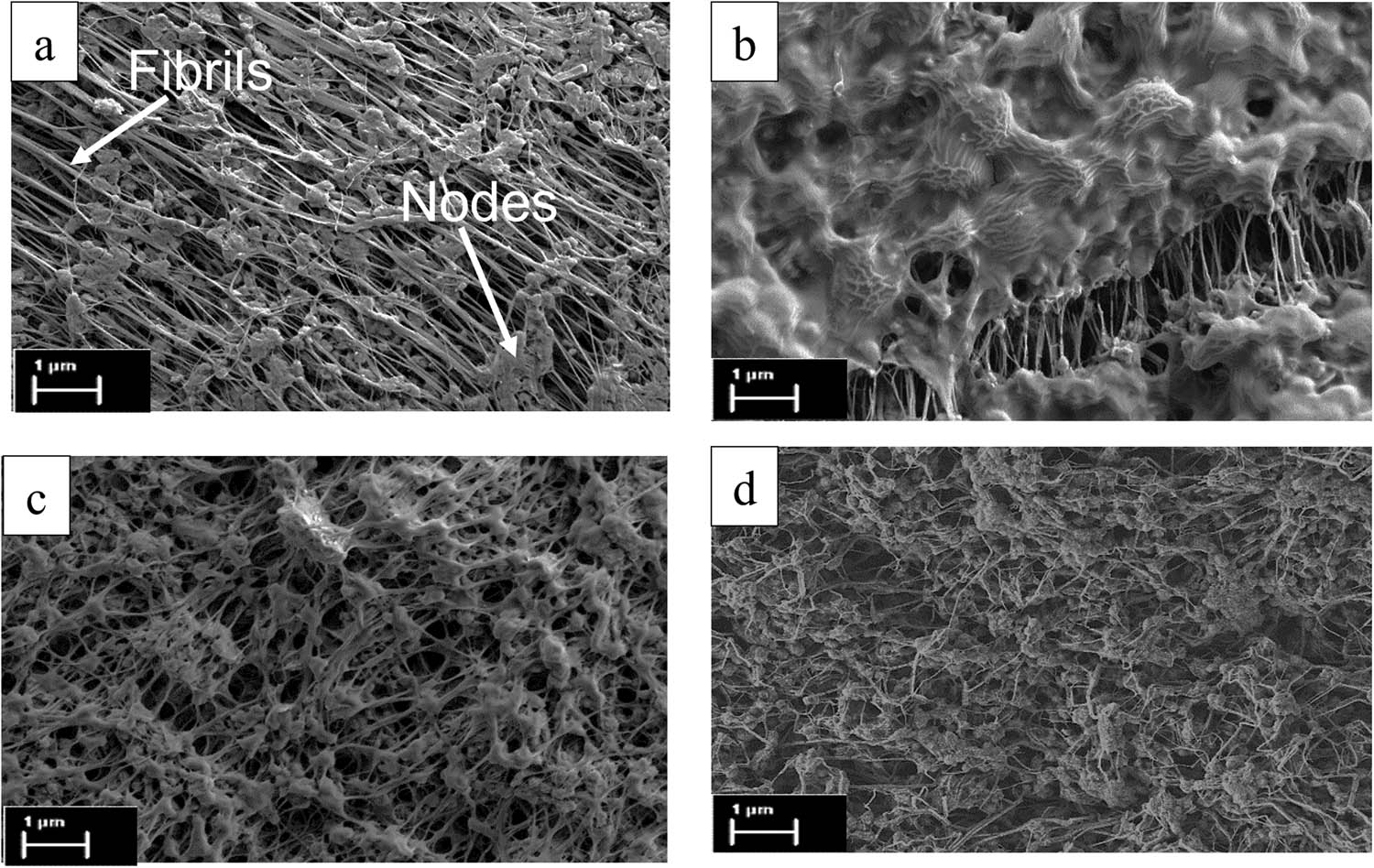
Morphology of (a) unmodified ePTFE, (b) sample AH, (c) sample AN, and (d) sample AV.
The node structures appear interconnected, forming groups of nodes due to the comonomer grafted onto the ePTFE, therefore creating extended structures that concurrently cover most fibrils [19,20]. More nodes were observed depending on the degree of grafting, thus explaining why fewer islands were observed for the AV sample compared to samples AH and AN.
The morphology of sample AH in dry conditions, which consists of more nodes (Figure 3b), tends to shrink more in length compared to samples AN and AV, which consist of fewer nodes (Figure 1 and Table 1).
3.4 Mechanical properties of ePTFE and modified ePTFE
The mechanical test analysis shown in Figure 4 was performed in dry and wet conditions, and three parameters were observed: Young’s modulus (E), UTS, and elongation at break (ε). Statistical analysis was conducted to observe the differences between the unmodified and modified samples. ePTFE is a flexible polymer, and it is commonly susceptible to radiation-induced damage (scission). These properties do affect the mechanical properties and decreased with an increase in irradiation dose [10]. The effect of grafting, where slight crosslinking may also occur during the irradiation process, increased ePTFE rigidity at the same time reducing ductility. Further increases in the irradiation dose in grafting usually will lead to a brittle sample, which is one of the drawbacks of the grafting process [21]. This effect does not just happen to polymer ePTFE. For example, a study conducted by Jiang and Hui examining grafting isoprene onto polyhydroxy butyrate also experienced a similar characteristic after the modification process [22]. Nevertheless, the selection of an optimum irradiation dose and concentration of monomers as well as the introduction of Mohr’s salts to reduce the homopolymer formation in this study can prevent the sample becoming brittle.
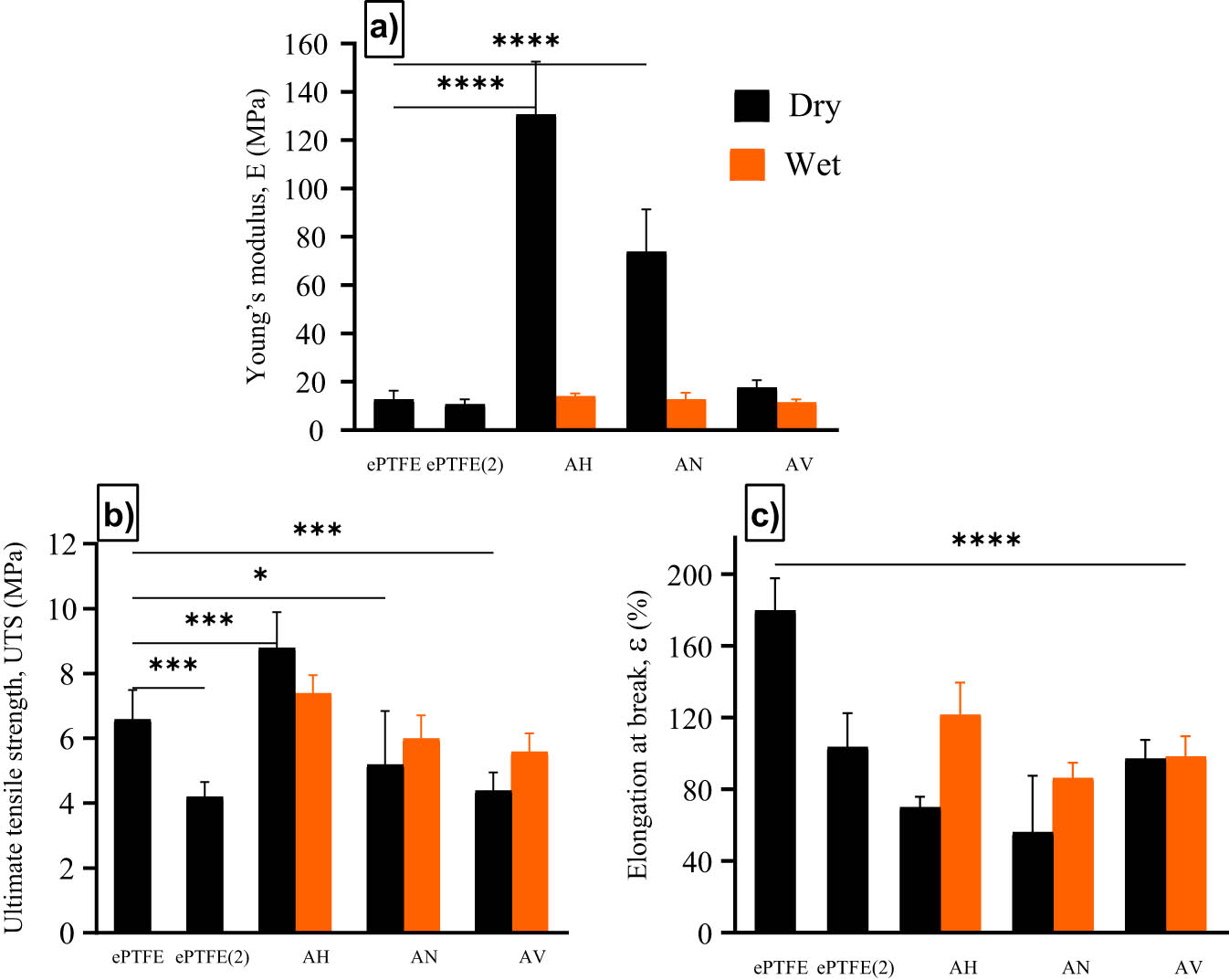
Statistical analysis and mechanical properties ePTFE and modified ePTFE for (a) Young’s modulus (E), (b) UTS, and (c) elongation at break (ε).
The E value (Figure 4(a)) for the ePTFE(2) is 10.8 ± 1.7 MPa without a monomer shows no significant changes (p = 0.8) compared to the unmodified ePTFE (12.8 ± 3.1 MPa). The E of the modified samples grafted with comonomers AH, AN, and AV shows a higher value in dry conditions than wet conditions. Sample AH (130.8 ± 19.5 MPa) shows the highest E value followed by sample AN (74.0 ± 15.6 MPa) with significance values of p < 0.00001 and p < 0.00001 in dry conditions compared to wet conditions, which represents the stiffness of the sample. The result shows a substantial increase in E value for dry samples (i.e., AH and AN) with 10- and 6-fold increases compared to unmodified ePTFE, respectively. In contrast, the E value for the sample AV (17.8 ± 2.6 MPa) in dry conditions was observed to slightly increase (p = 0.4) compared to unmodified ePTFE. For wet samples, the value of E for all modified samples AH, AN, and AV did not show any significant differences, with values of 14.4 ± 1.2, 12.9 ± 2.2, and 11.6 ± 1.2 MPa, respectively.
For the UTS value (Figure 4(b)), a significant difference was observed for all dry samples, namely AH (p = 0.0004), AN (p = 0.0018), AV (p = 0.0004), and ePTFE(2) (p = 0.0002), respectively, compared to the unmodified ePTFE. The UTS for ePTFE(2), AN, and AV shows a lower value with 4.2 ± 0.4, 5.2 ± 1.4, and 4.4 ± 0.4 MPa, respectively, compared to unmodified ePTFE (6.6 ± 0.7 MPa). In contrast, the UTS values for wet samples show no significant differences (p > 0.05) compared to the unmodified ePTFE. Sample AH shows the highest UTS value 8.8 ± 0.9 MPa.
The percentage of ε (Figure 4(c)) shows a significant decrease for all modified samples in both dry and wet conditions, as well as in sample ePTFE(2) (p < 0.00001) compared to the unmodified ePTFE (ε = 179.8 ± 15.7%). Sample AN in dry conditions shows the least value of ε, followed by sample AH and ePTFE(2) with a value of 56.2 ± 28.1%, 70.2 ± 5.1%, and 103.6 ± 16.5%, respectively. The elongation for modified samples AH and AN in wet conditions show a higher ε value compared to dry conditions with ε of 121.6 ± 16.0% and 86.4 ± 7.2%, respectively. Finally, the ε values for sample AV in dry or wet conditions were almost similar, at 97.2 ± 8.9 and 98.4 ± 10.0%, respectively.
The E values in this study show analogous patterns to a study conducted by Yan et al., where the value of ePTFE modified with silk fibroin and salicin also showed an increasing value, however, insignificant compared to the unmodified sample tested in dry condition [8].
The decrease in ε value for sample ePTFE(2) shows that the chain scission of the polymer due to gamma irradiation resulted in exposure damage in the trunk polymer [11]. This result (sample ePTFE(2)) was found to have a similar pattern to that reported by Hidzir et al., where the ePTFE irradiated at a higher dose (10 kGy) was used [13]. The tensile test performed on the ePTFE(2) sample shows that the irradiation process does not affect physical but mechanical properties, such as UTS, and the ε value shows a significant difference. The ε value for modified ePTFE (samples AH and AN) in the wet condition was higher than that of samples in the dry condition. Conversely, the ε value for AV in both dry and wet conditions showed no significant difference and correlated well with the lower grafting yield of AV obtained in this study (16 ± 3%). Previous research by Zhu et al. for ePTFE modification using thermal treatment also shows a decrease in value [14].
A comparison between the mechanical properties of the modified ePTFE with previous research and application of ePTFE as biomaterials is summarized in Table 2. The mechanical properties obtained in the current study are within acceptable ranges for E, UTS, and ε compared to the previous studies and are comparable with ePTFE biomaterials available in the market. Therefore, these results indicate the modified ePTFE in current study remains ideal for biomechanical characteristics.
Comparison of modified ePTFE in this study with previous study and ePTFE available in the market
| Study | Modification method/application | Brand | E (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | ε (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified ePTFE in this study compared with other studies | ||||||
| This study | Radiation | Pall Corporation | 12–131 | 4–9 | 56–121 | — |
| Yan et al. (2021) | Chemical | Daikin | — | 2–3 | ∼40–150 | [8] |
| Zhu et al. (2015) | Thermal | Gore Tex® | 43–59 | — | ∼60–110 | [14] |
| ePTFE biomaterials available in the market | ||||||
| Park et al. (2020) | Vascular graft | Advanta™ VXT | — | ∼17 | — | [23] |
| Zhu et al. (2015) | Pericardial membrane | Gore Tex® | 34 | — | ∼110 | [14] |
| Mun et al. (2012) | Vascular graft | Gore Tex® | 32 | 14 | 28 | [24] |
The grafting yield is an indicator of the measured amount of comonomer grafted onto ePTFE, and the hydrophilicity usually correlates proportional to the grafting yield value. Less grafting yields for the AV sample resulted in the less-functional group attaching to the hydrophobic ePTFE. Therefore, similar properties for wet and dry sample conditions were observed for this sample. In contrast, the higher grafting yields obtained for samples AH and AN (35 ± 3% and 36 ± 3%) resulted in more nodes in the samples, thus affecting their elasticity (with more rigidity observed) compared to the unmodified ePTFE.
4 Conclusion
In sum, the mechanical behavior of ePTFE after modification with various comonomer by gamma radiation showed changes in the tensile performance (e.g., young’s modulus, UTS, and elongation at break). The morphological changes after modification of ePTFE as well as the percentage of the grafting yield play a role in the tensile performance obtained. The mechanical data also proved that the irradiation dose can affect the mechanical performance of the polymeric material without the presence of monomers. The data from mechanical tests in this study, however, remain within acceptable ranges. Thus, ePTFE is considered desirable for use as a biomaterial. More studies are needed for further understanding of the mechanical properties of biomaterials.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia (UKM) Microelectronics Semiconductor Packaging Lab and the UKM Polymer Research Center for the tensile testing facilities, the Department of Physics UKM for contact angle measurement and the Centre for Research and Instrumentation UKM for the FESEM analysis.
-
Funding information: Funded by grant FRGS/1/2019/STG02/UKM/02/6 from Malaysia Ministry of Higher Education.
-
Author contributions: N.A.M.R. – conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing original draft, and visualization; N.M.H. – supervision, conceptualization, methodology, validation, resources, and funding acquisition; I.A.R. – supervision, conceptualization, validation, and formal analysis; and A.K.M. – conceptualization and formal analysis.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Park J, Lakes RS. Biomaterials: an introduction. 3rd ed. New York: Springer; 2007.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Dominique CL, Pascal A. Martine BM. Biocompatibility of elastomers. In: Dumitriu S, Popa V, editors. Polymeric biomaterials: structure and function. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2013. p. 416–478.Search in Google Scholar
[3] ASTM International. Standard specification for implantable polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sheet. Tube, and rod shapes fabricated from granular molding powders. ASTM F754. West Conshohocken, PA; 2015. p. 1–4.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Hidzir NM, Radzali NAM, Rahman IA, Shamsudin SA. Gamma irradiation-induced grafting of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) onto ePTFE for implant applications. Nucl Eng Tech. 2020;52(10):2320–7. 10.1016/j.net.2020.03.016.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Catanese JIII, Cooke D, Maas C, Pruitt L. Mechanical properties of medical grade expanded polytetrafluoroethylene: the effects of internodal distance, density, and displacement rate. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;48(2):187–92.10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(1999)48:2<187::AID-JBM13>3.0.CO;2-MSearch in Google Scholar
[6] Cassady AI, Hidzir NM, Grøndahl L. Enhancing expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (ePTFE) for biomaterials applications. J Appl Polym Sci. 2014;131(15):1–14. 10.1002/app.40533.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Chang TI, Hsu KH, Li SJ, Chuang MK, Luo CW, Chen YJ, et al. Evolution of pulmonary valve reconstruction with focused review of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene handmade valves. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021 Apr 19;32(4):585–92. 10.1093/icvts/ivaa302.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Yan S, Li Y, Jiang Y-C, Xu Y, Wang D, Zhang X, et al. Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene/silk fibroin/salicin vascular graft fabrication for improved endothelialization and anticoagulation. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;542(148610):1–11. 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148610.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Kim J, Lee JM, Yi NJ, Hong SK, Choi Y, Hong K, et al. Long-term outcomes of abdominal wall reconstruction with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene mesh in pediatric liver transplantation. J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 2;10(7):3–9. 10.3390/jcm10071462.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Mathieu HJ, Chevolot Y. Engineering and characterization of polymer surfaces for biomedical applications. In: Kausch H. et al. editors. Radiation effects on polymers for biological use. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2003.10.1007/3-540-45668-6_1Search in Google Scholar
[11] Alkan Gürsel S, Gubler L, Gupta B, Scherer GG. Radiation grafted membranes. In: G GS, editor. Fuel cells I advances in polymer science. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2008.10.1007/12_2008_153Search in Google Scholar
[12] Bhattacharya A. Grafting: a versatile means to modify polymers techniques, factors and applications. Progress in Polymer Science. 2004;29(8):767–814. 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.05.002.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Hidzir NM, Hill DJT, Darren M, Grøndahl L. Radiation-induced grafting of acrylic acid onto expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) membranes. Polymer. 2012;53(26):6063–71. 10.1016/j.polymer.2012.10.042.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Zhu G, Yuan Q, Hock Yeo J, Nakao M. Thermal treatment of expanded polytetraflu-oroethylene (ePTFE) membranes for reconstruction of a valved conduit. Biomed Mater Eng. 2015;26(1):S55–62. 10.3233/BME-151289.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Radzali NAM, Hidzir NM, Mokhtar AK, Rahman IA, editors. 60Co-Induced grafting of dual polymer (Acrylic Acid-co-HEMA) onto expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) membranes. AIP Conference Proceedings, Feb 3–7, 2020. Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. New York: AIP Publishing; 2020.10.1063/5.0031519Search in Google Scholar
[16] Hidzir NM, Lee Q, Hill DJT, Rasoul F, Grøndahl L. Grafting of acrylic acid-co-itaconic acid onto ePTFE and characterization of water uptake by the graft copolymers. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;132(7):1–12. 10.1002/app.41482.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Hidzir NM, Hill DJT, Taran E, Martin D, Grøndah L. Argon plasma treatment-induced grafting of acrylic acid onto expanded poly(tetrafluoroethylene) membranes. Polymer. 2013;54(24):6536–46. 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.10.003.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Hegazy ESA, Taher NH, Ebaid AR, RabieT A-G, Kamal H. Radiation-initiated graft copolymerization of individual monomer and comonomer onto polyethylene and polytetrduoroethylene films. J Appl Polym Sci. 1990;39:1029–43.10.1002/app.1990.070390502Search in Google Scholar
[19] Xu B, Li Y, Fang X, Thouas GA, Cook WD, Newgreen DF, et al. Mechanically tissue-like elastomeric polymers and their potential as a vehicle to deliver functional cardiomyocytes. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013 Dec;28:354–65. 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2013.06.005.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Liu F, Grainger DW. Fluorinated biomaterials. In: Ducheyne P, editor. Comprehensive biomaterials. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2011. p. 514–525.10.1016/B978-0-08-055294-1.00040-4Search in Google Scholar
[21] David A, Meimoun J, Delaunay T, Wiatz V, Saint-Loup R, Parcq J, et al. Structural characterization and mechanical properties of dextrin-graft-poly(butyl acrylate-co-styrene) copolymers. Express Polym Letters. 2019;13(3):235–47. 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2019.20.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Jiang T, Hu P. Radiation-induced graft polymerization of isoprene onto polyhydroxybutyrate. Polym J. 2001;33(9):647–53. 10.1295/polymj.33.647.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Park C, Park S, Kim J, Han A, Ahn S, Min S-K, et al. Enhanced endothelial cell activity induced by incorporation of nano-thick tantalum layer in artificial vascular grafts. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;508(10):144801. 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144801.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Mun CH, Jung Y, Kim SH, Lee SH, Kim HC, Kwon IK, et al. Three-dimensional electrospun poly(lactide-co-varepsilon-caprolactone) for small-diameter vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012 Aug;18(15–16):1608–16. 10.1089/ten.TEA.2011.0695.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2021 Nur Ain Mohd Radzali et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation

