Abstract
In this study, a model to improve the degradability of methylene blue (MB) dye using graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation is investigated. The effect of operative parameters comprising catalyst concentration, initial dye concentration, and pH on the photocatalytic batch during removal of MB is studied. Fractional factorial design (FFD) and response surface methodology (RSM) are used to design the experiment layout. Graphene oxide (GO)/TiO2/SiO2 nanoparticles are synthesized through sonication and sol–gel methodologies. In the experiments, three levels of catalyst varied in the percentage of TiO2 pointed as (I) TiO2:GO (100%), (II) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (50%), and (III) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (25%) are used. The irradiation interval was 7 h at solar radiation energy 6.35–5.00 kW h/m2/day. In the experiments, three levels of catalyst varied in the percentage of TiO2 pointed as (I) TiO2:GO (100%), (II) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (50%), and (III) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (25%) are used. The synthesized catalysts are characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. ANOVA under 23 FFD is conducted to evaluate the effect of independent factors depending on the value of F as pH of solution, weight of catalyst, and concentration of MB. The adsorption kinetics, experimental design with FFD, and RSM are investigated in this study. The Surface Adsorption kinetics were statistically analyzed, the model that best described the results of each experiment was determined out of the two evaluated kinetics (pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order), for the three photocatalyst composites I, II, and III with the parameters; weight of the catalyst, pH, and initial MB concentration, also percentage degradation is evaluated. RSM results are consistent with the kinetic model; first, the pH is considered as the most significant parameter affecting the removal of the organic pollutant, and second, catalyst II gives the highest percentage removal efficiency of MB. FFD results are consistent with both models where the effect of the independent factor depending on the value of F was pH of solution > weight of catalyst > initial concentration of MB. The percentage removal was in the range from 30 to 99%.
1 Introduction
Treatment of wastewater becomes essential and mandatory because they contain many contaminated compounds (organic and inorganic) that cause risk to the living beings and environment if released without treatment. Many of these compounds are stable and pass through conventional wastewater treatment systems, without major changes in their chemistry [1]. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs)are known as being operative for the degradation of many biotic recalcitrant compounds, these processes are technologies that generally use the hydroxyl radicals for oxidizing organic molecules (breaking them down), and can be enhanced by catalysts and/or light [2].
The heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation involves three main steps: adsorption on the surface, surface reaction, and finally desorption of reacted product from the pores. The adsorption mechanism and the reactions put in place have been widely studied, according to the objective of each work, different models, and characterization techniques used. Nevertheless, the common point is the optimization of the process. Optimization of the adsorption process was usually performed in a routine and conventional way [3].
TiO2 is considered as a unique photocatalyst comparing to the other metal oxieds were used, but to remove its limitations some advanced approaches were used, such as adding metal oxides (transition or rare metals) also nonmetal was added to its bulk. Photocatalytic degradation mechanism is highly affected and enhanced by the modifications made on it [4,5,6].
There are many kinds of nanomaterials, which carried a large potential to treat wastewater (containing organic and inorganic pollutants and metal toxin substances) very effectively because of their properties like a greater surface area. The nano photocatalyst-based approaches to remove pollutants from wastewater are eco-friendly and efficient, but they require more energy and more investment to purify the wastewater [7].
Yet, the catalyst most used is TiO2 photocatalysis, and the simplified Langmuir–Hinshelwood kinetic model is used to explain the photocatalytic processes.
Ateia and his colleagues used models of reaction kinetics to define time-dependent relation between the operating conditions of the system and the degradation rate of organic contaminants [4]. The photocatalytic degradation rate depends on the water chemistry factors (e.g., pH, temperature, contaminant concentration, natural organic matter, dissolved oxygen, and inorganic species) and the system factors (e.g., light intensity, light wavelength, catalyst type, and catalyst loading) [8]. Several researchers make efforts to improve models that can describe and estimate the photocatalytic degradation kinetics [1,9,10].
Moreover, photocatalytic experiments provide different results. Therefore, it is challenging to form effective models to optimize photocatalytic activity. Artificial neural networks are used to model photocatalytic efficiency [11], and response surface methodology (RSM) is used for experimental design and to improve (optimize) operational conditions [11,12]. RSM is a statistical method based on the multivariate nonlinear model and allowed the design of mathematical models with a better match with the data obtained by the experimental design. Using an elaborate model with the statistical analysis of factors, it gives the chance to evaluate the interactions between factors and explain the relations very will [3,11,12].
Several adsorption kinetic models are used among them the Langmuir model, which is the most fitting for the experimental results found by Udrea and Ion in removing methylene blue (MB) dye present in wastewater by using adsorbent materials obtained from vegetable waste [13].
This study aimed to apply mathematical modeling on MB dye photodegradation results to find the optimized conditions and the most effective variable. Three modeling systems were investigated in this study, experimental design with FFD (ANOVA under 23), RSM and surface adsorption kinetics. And the factors contain; pH of solution, weight of catalyst (with three % composites), and the amount of MB dye at time t (q t ).
2 Methods
2.1 Synthesis and characterization
Three types of photocatalysis were under study, which varied in the percentage of TiO2 pointed as (I) TiO2:GO (100%), (II) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (50%), and (III) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (25%). The synthesis was by sol–gel method under sonication (sonicating with a probe sonicator for 20 min impulse mode with 2s on and 5s off at 35% amplitude). The modification was confirmed by X-ray diffraction, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscope, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis. Details for both the synthesis and full characterization are given in the previous study [14]. The catalysis is chosen as models for the mathematical modeling study.
Weight/weight percentage for the three prepared catalyzes I, II, and III out of the total weight of the catalyst:
| Catalyst | GO% | Ti% | Si% |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1.96 | 98 | 0 |
| II | 1.29 | 45.5 | 50 |
| III | 0.966 | 24.15 | 74.9 |
2.2 Experiment procedure
The assessment of MB removal is handled in a specific time. The absorbance is measured on UV-Vis spectrophotometer at several wavelengths according to MB charge. 100 mL of DW is spiked with a mixture of MB (with the desired concentration).
The absorption spectrum of MB generally is characterized by an absorption band at high energy (π–π* of benzene ring) and a band at low energy around 580–741 nm (affecting correspondent to the pH of the solution) and corresponding to the n–π* transitions (n is the free doublet on the nitrogen atom of the C═N bond and free doublet of S atom on S═C bond) [15,16].
For establishing adsorption equilibrium, the spiked samples were placed in the dark for around an hour, and then the degradation undergo sunlight irradiation. The irradiation interval was 7 h at solar radiation energy 6.35–5.00 kW h/m2/day. The measured temperature ranged from 35 to 45°C in summer season. At an interval of 30 min, an aliquot of 10 mL was collected, and then the absorbance of MB was measured on UV-Vis spectrophotometer.
Three variables were studied: first, catalyst loading (weight of catalyst) 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, and 0.30 g with fixing pH of solution at pH 6, and the initial concentration of MB at 20 ppm. The second variable was the pH of the solution (the pH were; 2,4,6,8, and 10) with fixing the initial concentration of MB at 20 ppm, with catalyst weight 0.15 g. The last variable was the initial concentration of MB 0.50, 1.00, 3.00, 5.00, 10.00 ppm fixing the pH of solution at pH 6 and 0.15 g weight of catalyst.
2.3 Mathematical modeling
Three modeling systems were investigated in this study, experimental design with FFD (ANOVA under 23), RSM and surface adsorption kinetics. And the factors contain; pH of solution, weight of catalyst (with three % composites), and the amount of MB dye at time t (q t ). An experimental design is performed using SPSS (16.0 package) with FFD to assess the effect of the independent factors under study. RSM was performed on the parameters using Minitab [19] package.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Adsorption kinetics
The heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation involves three main steps: adsorption on the surface, surface reaction, and finally desorption of reacted product from the pores. When studying the mechanism of removing pollutants from water, a set of models explaining the adsorption between the pollutant and the active sites in the catalyst are used. Several adsorption kinetic models are used, among them the Langmuir model, which is the most fitting for the experimental results, two fitting model plotted with experimental data under different conditions the pseudo-first-order model (log(q e − q t ) vs t) and the pseudo-second-order model (t/q t vs t) [2,4].
3.1.1 Effect of initial solution pH on the adsorption efficiency
The pH of the aqueous solution is an important controlling parameter in the adsorption process as it is related to the ionization state of the surface for the catalyst and the pollutant [2,17]. The pH range was chosen to adopt the whole pH ranges of wastewater (industrial, domestic, and pharmaceutical wastewater). The pH plays a critical character both in the characteristics of dye wastes and in the generation of hydroxyl radicals [18]. The effect of pH on the removal of MB is studied in the range of 2–10. Figure 1 shows the plotting of q t vs time for pH ranges [2/4/6/8/10] for the three composites % I (100%), II (50%) and III (25%).
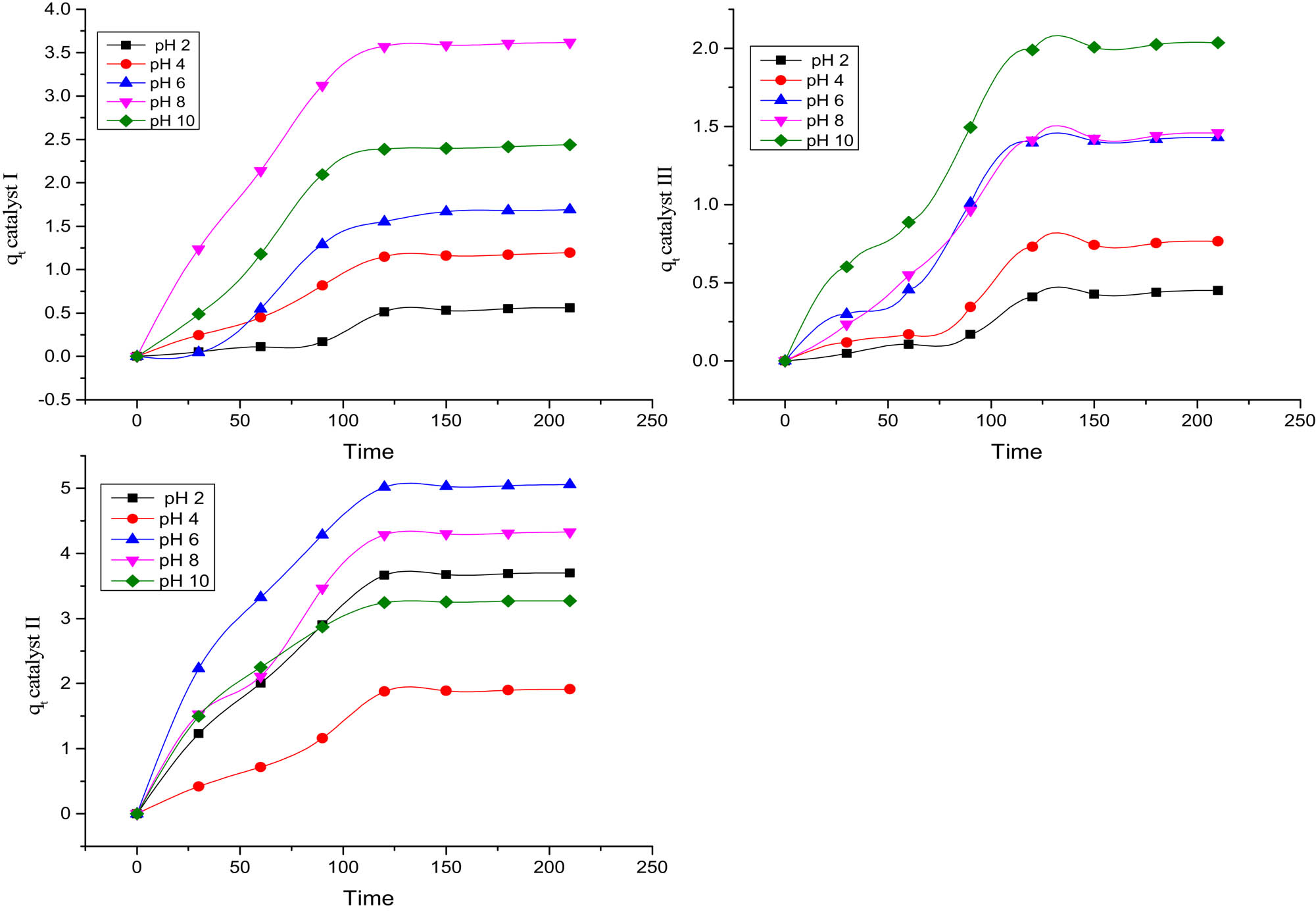
pH ranges (2/4/6/8/10) of catalysts I, II, and III plotting of q t (mg/g) vs time in minutes.
For the composite % I (100%) and III (25%), the basic media is favored in the removal of MB (pH 8 and 10, respectively); meanwhile pH of catalyst composite % II (50%) is 6, which is almost neutral. The results are consistent with [17] and others where the quantities of MB adsorbed increase with pH and that the disappearance of MB is favored at basic pH [17].
The influence of pH on the ionization state of the TiO2 surface becomes positively charged, and MB adsorption is favored in alkaline solution because it has a cationic configuration [17].
The experimental data fitted with a pseudo-second-order (equation 1) adsorption model with regression (R 2) ranged 0.99917–0.9961 (Figures 2 and 3).
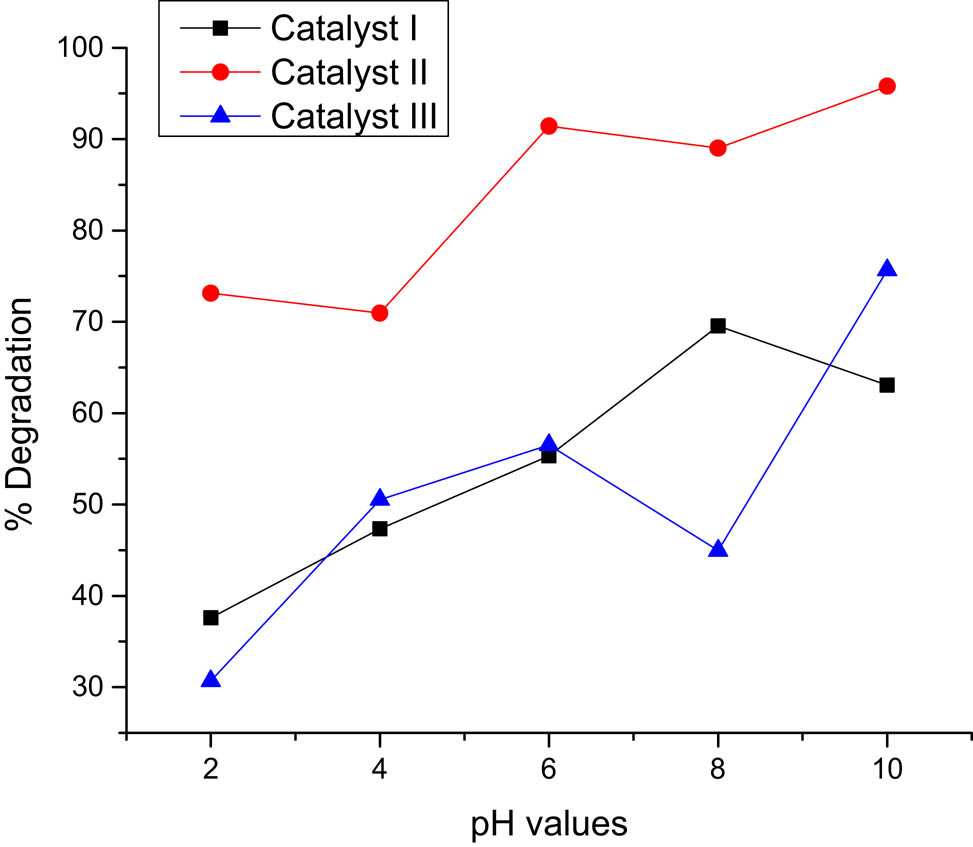
Percentage degradation to pH values.
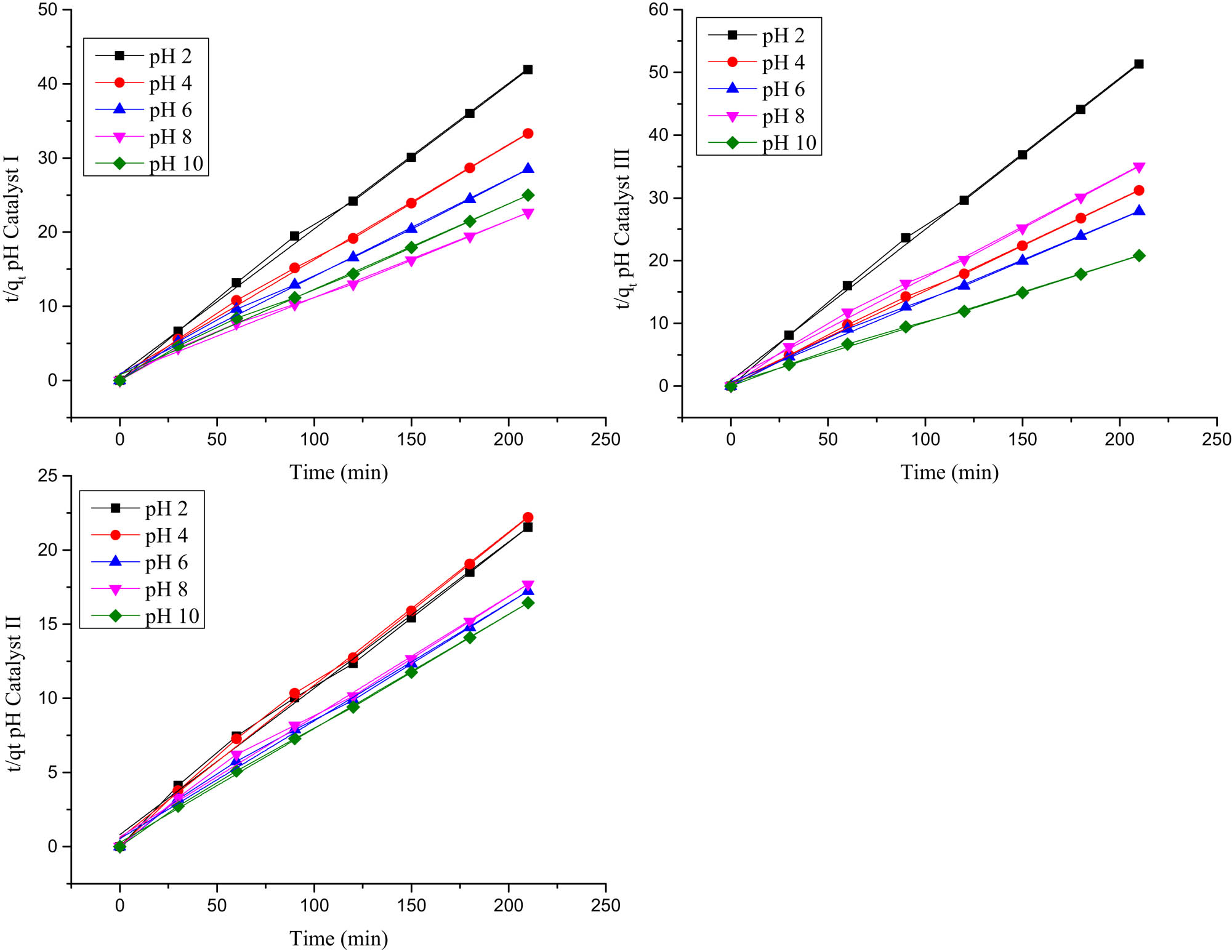
The applicability of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model to pH parameter for catalysts I, II, and III.
3.1.2 Effect of weight of catalyst dosage on the adsorption efficiency
Obtaining the optimal quantity of catalyst loading is a major stage in scaling up the photocatalytic process. It affects the financial side of the process and the downstream processing to separate the photocatalyst from the reaction medium. Catalyst dosage effect on the removal of MB varied as 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, and 0.30 g with fixing pH 6, and the initial concentration of MB at 20 ppm for the three composites (I, II, and III).
The catalyst’s loading effect on the decolorization efficiency is shown in Figure 4. The amount of catalyst added to the reaction medium is significant in the process effectiveness.
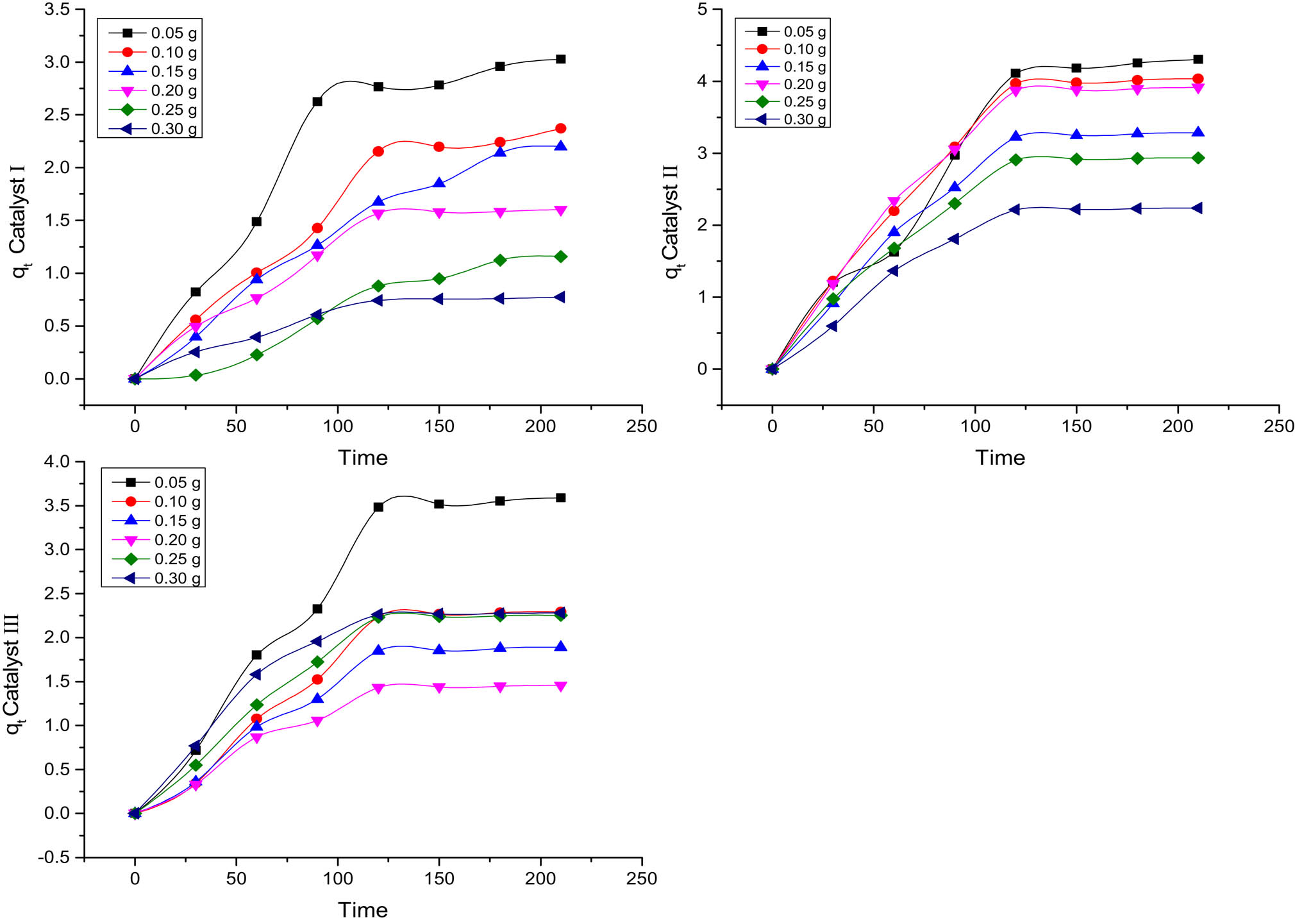
Weight ranges (0.05/0.10/0.15/0.20/0.25/0.30 g) of catalysts I, II, and III q t (mg/g) vs time in minutes.
Figure 5 shows the degradation of efficiency for the catalysts. The maximum % degradation for catalyst I (100%) was at 0.15 g, catalyst II (50%) at 0.30 g, and catalyst III (25%) at 0.25 g. The obtained increase in the decolorization efficiency is designated by the increase in the number of the catalyst’s active sites, which results in the creation of more active radicals (hydroxyl and superoxide) that initiate the degradation reaction. At higher catalyst loading, the TiO2 particles act as a barrier for the incident UV irradiation and prevent their arrival to some particles. A second possibility is the agglomeration of the catalyst nanoparticles, which is preferred by high surface energy and surface area. Therefore, the operative surface area of the catalyst decreases, and the decolorization efficiency is expected to reduce [19].
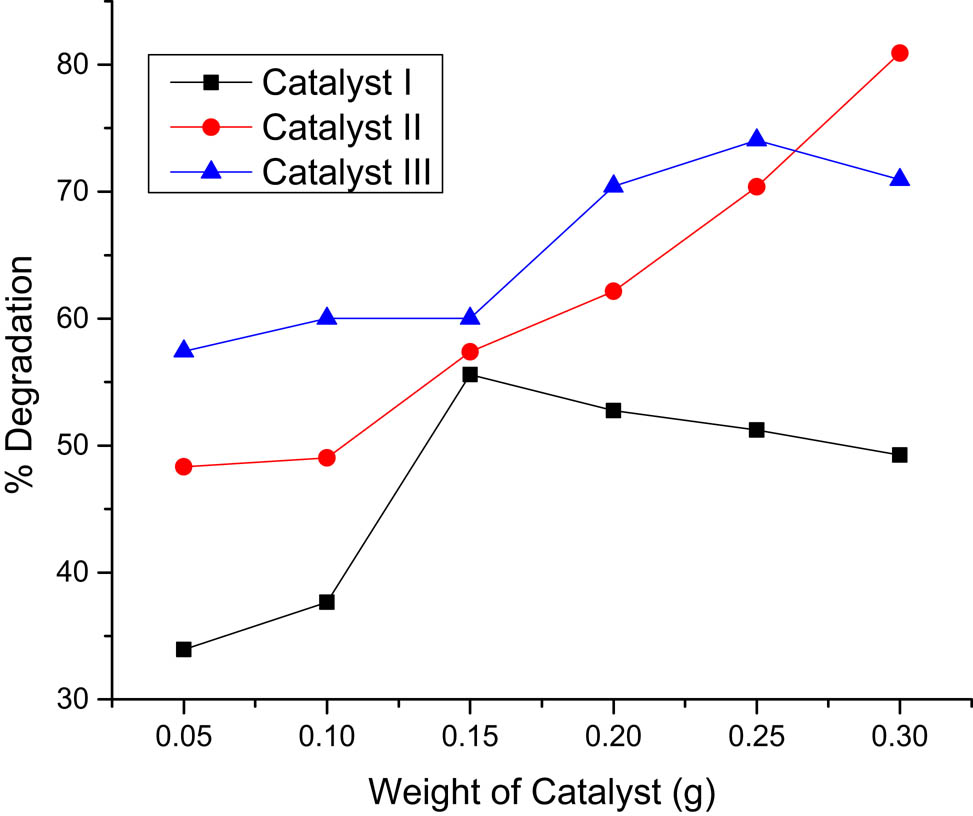
Percentage degradation of MB for the catalysts composites I (100%/), II (50%), and III (25%) versus catalyst weight.
The experimental data fitted with pseudo-second-order (Figure 6) adsorption model with regression (R 2) ranged between 0.998 and 0.987.
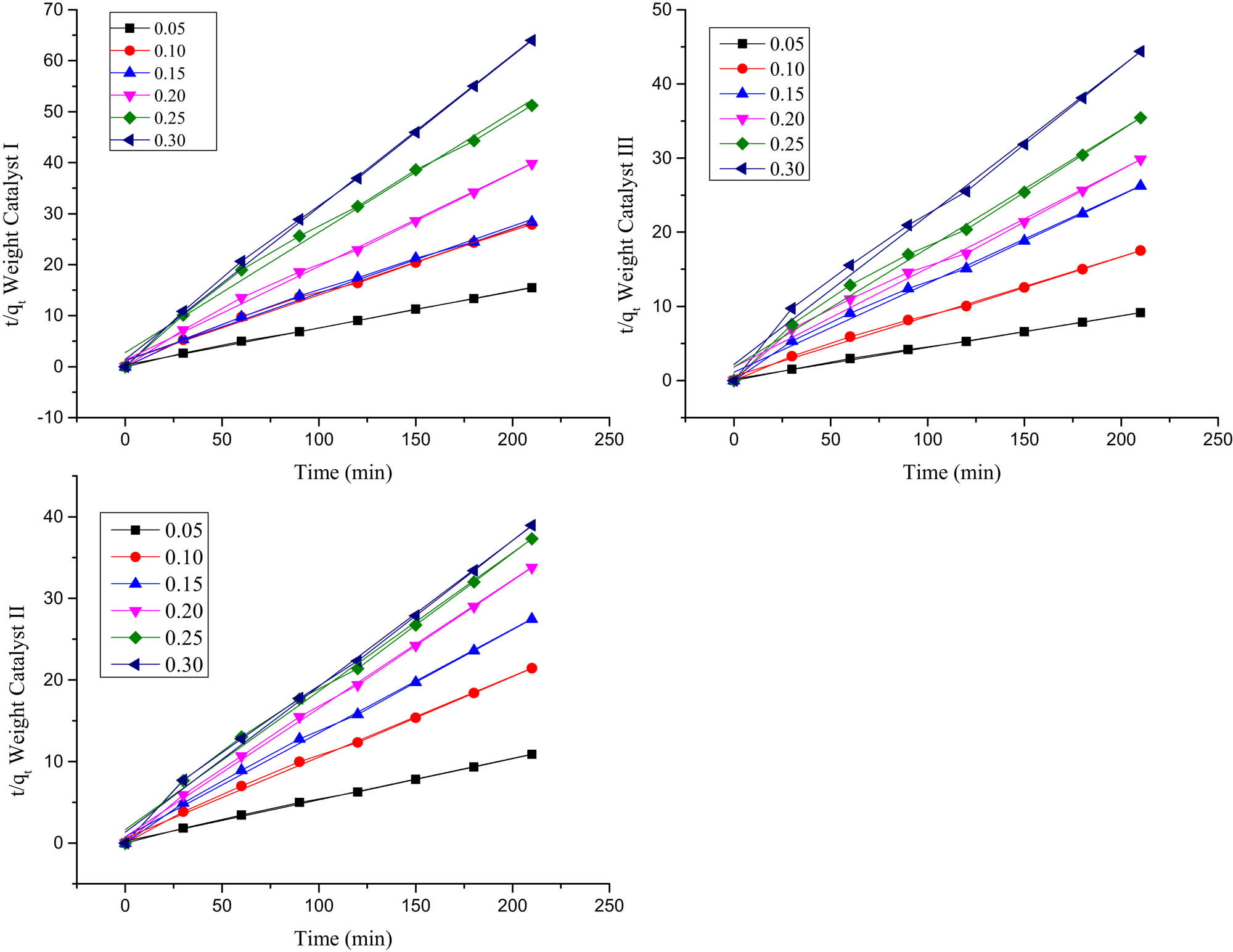
The applicability of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model to catalyst weight parameter for catalysts I, II, and III.
3.1.3 Effect of initial concentration of MB on the adsorption efficiency
The disparity in the color intensity (dye concentration) influences the intensity of light transitory through the reaction medium to reach the surface of the photocatalyst. Therefore, examining the effect of dye concentration on the photocatalytic process is of great importance [19]. The effect of the initial dye concentration on the decolorization of MB is investigated between a wide range of concentrations (0.50, 1.00, 3.00, 5.00, and 10.00 ppm). Figure 6 illustrates the q t vs time for the catalyst composites at the concentration range.
The influence of initial MB concentration on degradation efficiency is shown in Figure 7. A significant reduction in the percentage of degradation is observed with an increase in the initial MB concentration. This is because of the coverage of the catalyst’s active sites with higher adsorption of MB molecules. This is because of the coverage of the catalyst's active sites (suppress the generation of active OH˙ radicals) at higher concentration of MB (adsorption) [19].
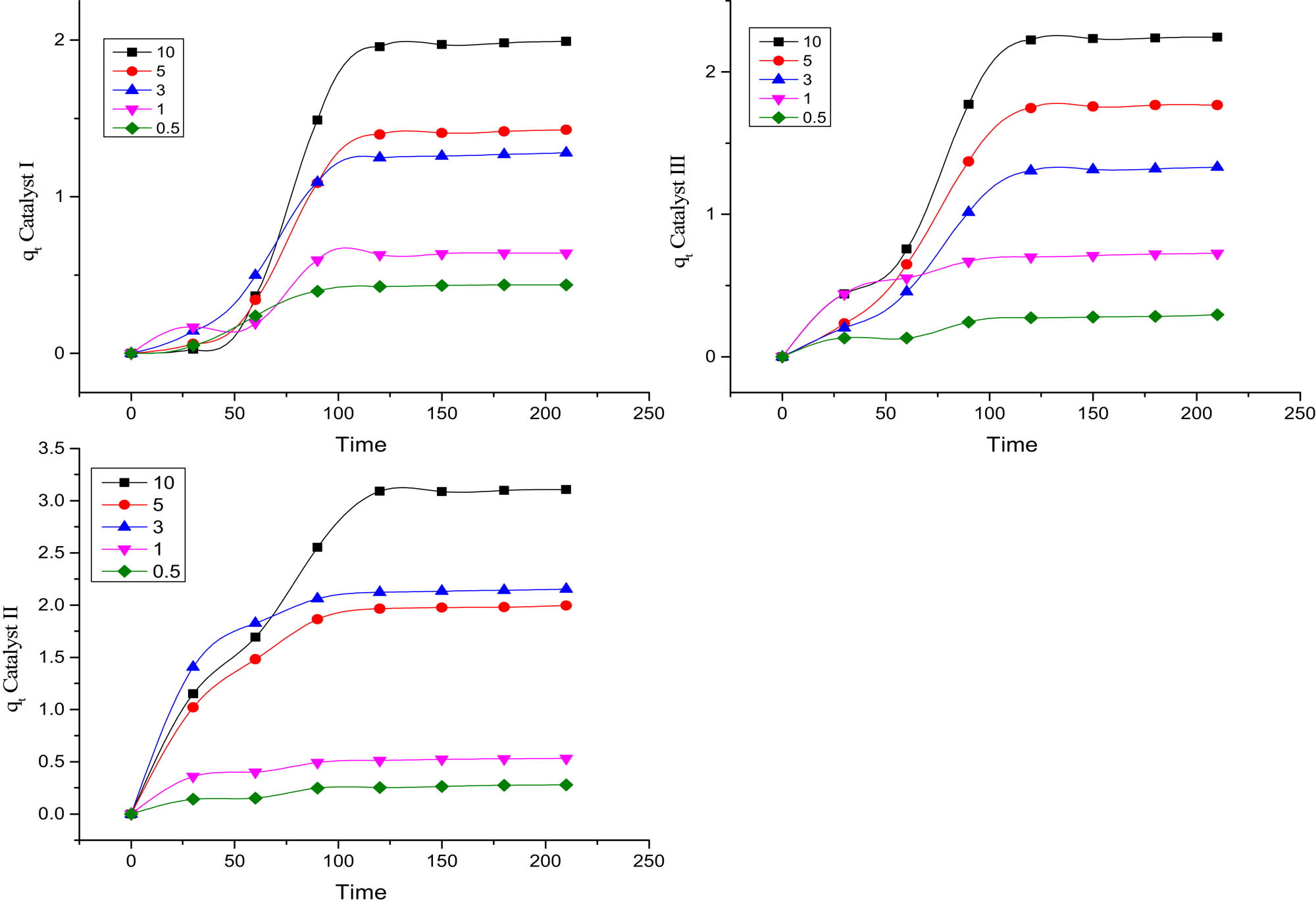
Initial concentration of MB (0.50/1.00/3.00/5.00/10.00 ppm) of catalysts I, II, and III q t (mg/g) vs time in minutes.
Moreover, here the experimental data fitted with a pseudo-second-order (Figures 8 and 9) adsorption model with regression (R 2) is ranged between 0.999 and 0.998.
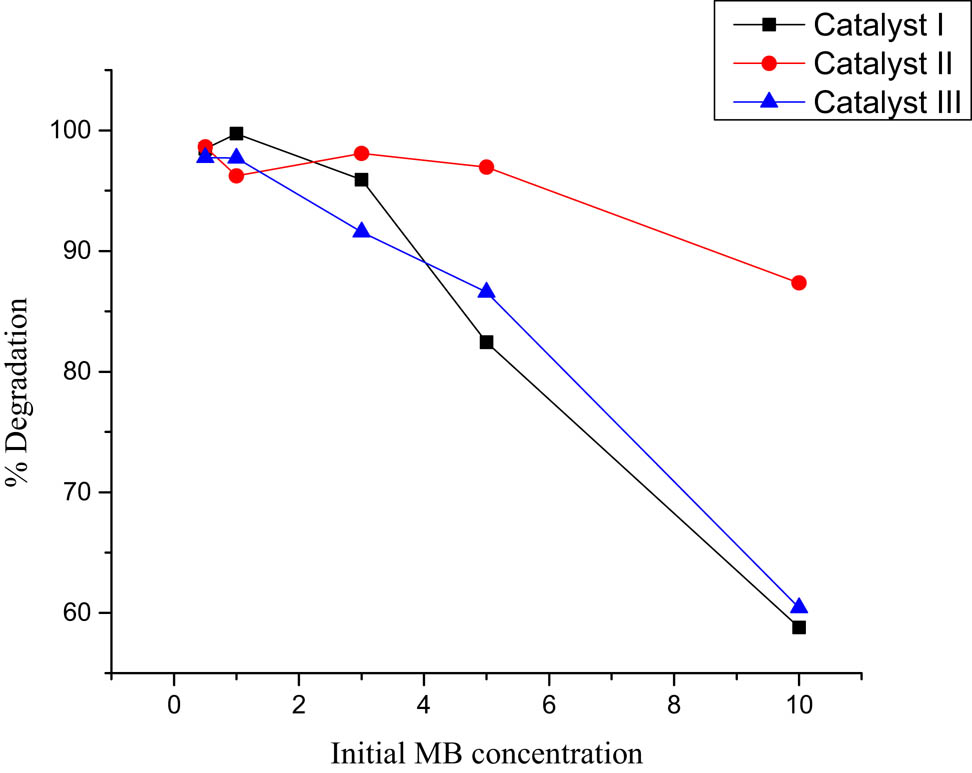
Degradation percentage of MB at different initial concentrations.
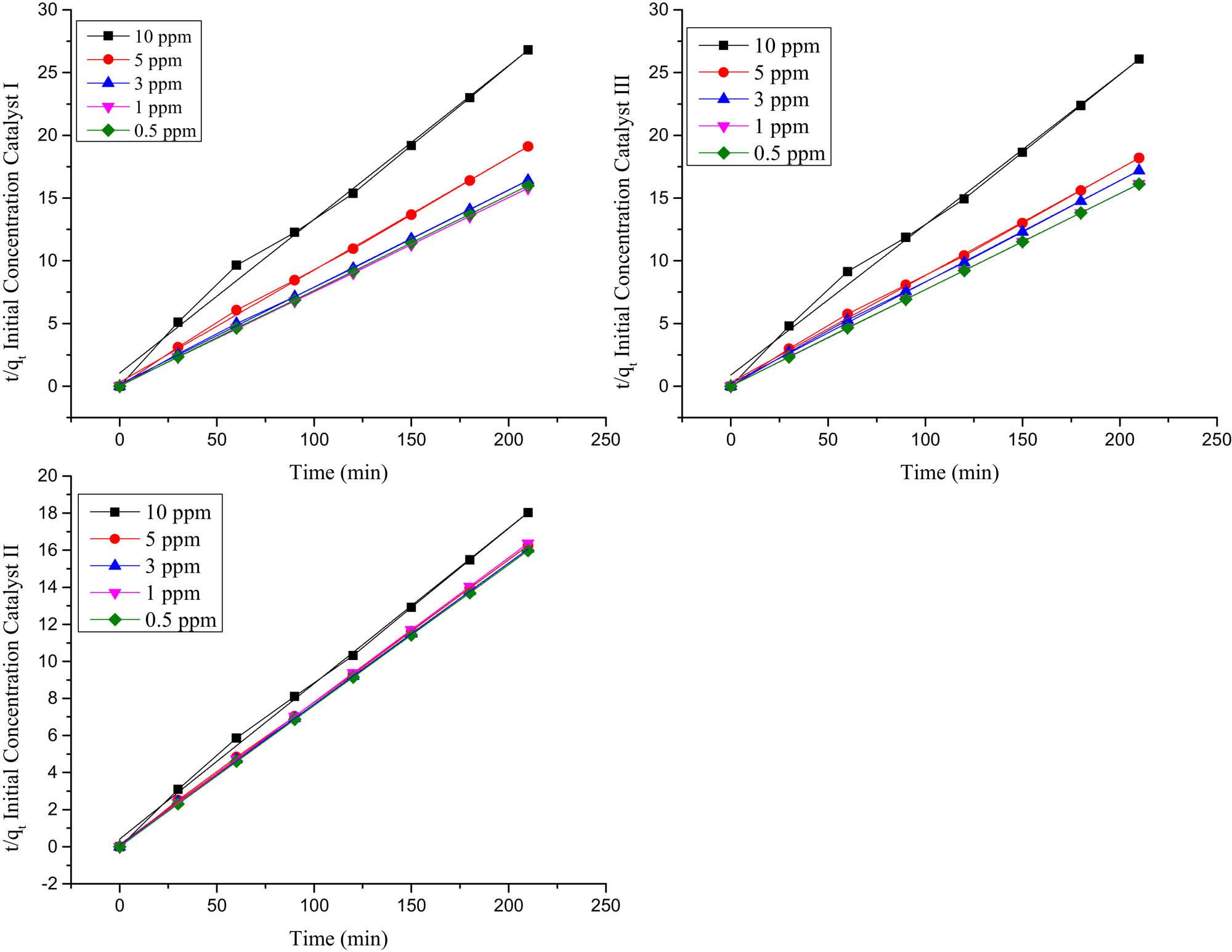
The applicability of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model to initial MB concentration for catalysts I, II, and III.
3.1.4 Degradation efficiency
The degradation efficiency in equation 2 of MB under the selected parameters is shown in Figure 10. The highest percentage degradation was found for catalyst I at an initial concentration of 1 ppm, but the highest percentage degradation for the parameters were for the catalyst II (50% of TiO2 : 50% of SiO2), here the GO works as both a photocatalyst and an adsorption material. The percentage removal ranged from 30 to 99%, where the pH was considered as the most significant parameter affecting the removal of the organic pollutant.
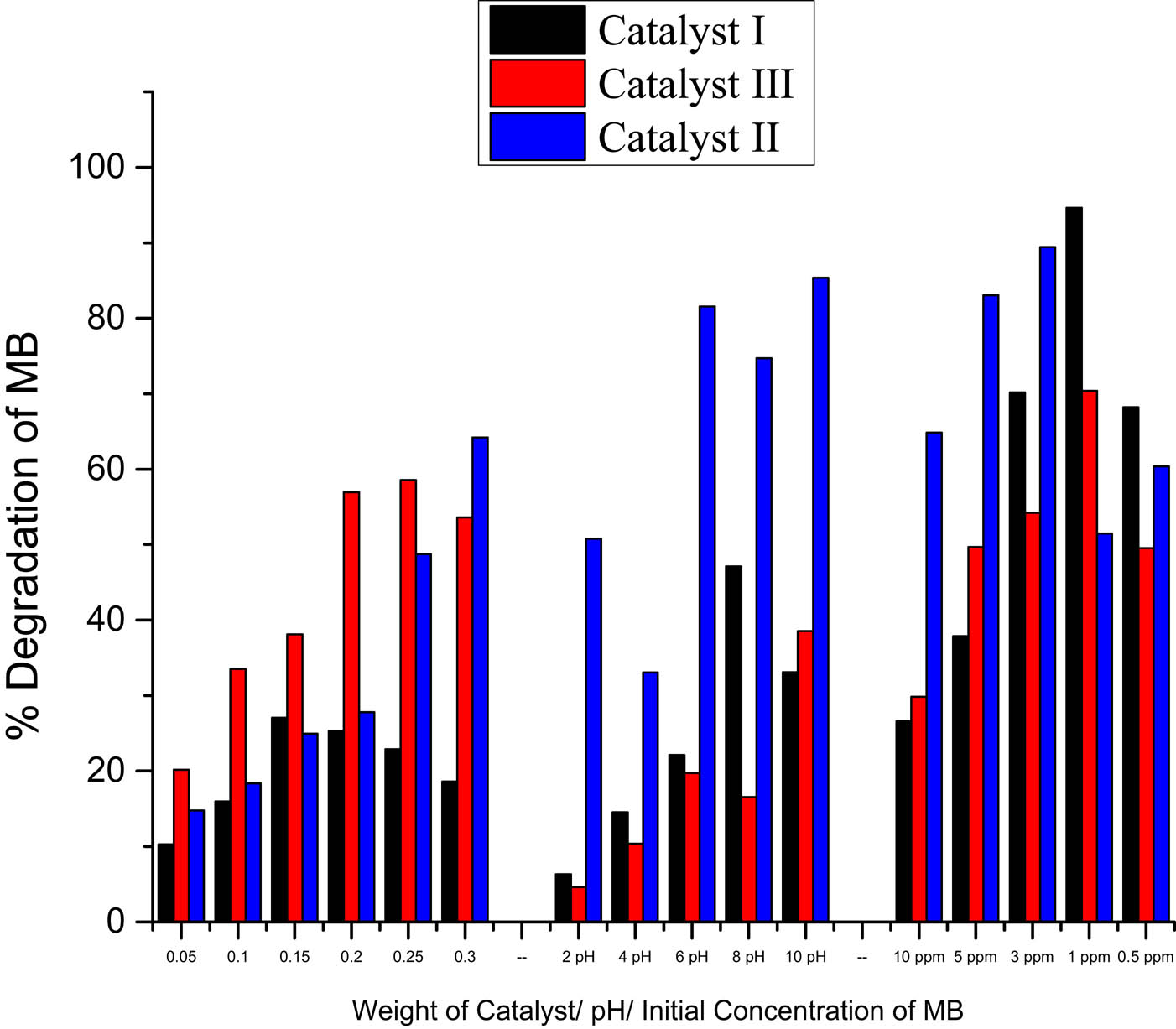
A comparison of the degradation efficiency for the three parameters.
3.2 Experiment design and descriptive analysis
SPSS 16.0 package was used for performing the experimental designs. FFD is used to evaluate the effect of the independent factors; weight, pH, and initial concentration on the response variable (qt ), qt represents the amount of MB dye onto catalyst at time t, qt (mg g−1) was calculated by mass balance relationship:
where C 0 is the initial MB concentration (mg L−1), C t is the concentration of MB at any time t, V is the volume of solution (L), and m is the mass catalyst (g).
Table 1 summarizes the results of ANOVA analysis under 23 FFD. Looking at the F and P-values at a significance level of 0.05, we see that the P-values are less than 0.05 for all factors under consideration; this indicates that there is significant evidence of the effect of each factor on the response variable (q t ). We can order the effect of the independent factor depending on the value of F as pH of solution > weight of catalyst > initial concentration of MB.
ANOVA table for 23 FFD
| Source | Mean square | F-value | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 4.044 | 11.746 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Weight | 2.966 | 8.615 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| pH | 5.794 | 16.827 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Concentration | 1.863 | 5.411 | 0.001 | Significant |
Table 2 shows the lower and upper limits for the weight of the factors of catalyst, pH of the solution, and concentration of MB in our experiment. In Tables 3–5, we computed the 95% confidence intervals for the q t under different levels of factor values, which are weight, pH, and concentration, respectively.
Lower and upper limits of parameters and their 95% confidence intervals in RSM design
| Parameter | Lower | Upper |
|---|---|---|
| Weight (g) | 0.05 | 0.3 |
| pH | 2 | 10 |
| Concentration (mg/L) | 0.5 | 10 |
95% confidence intervals for q t with respect to weight factor
| 95% confidence interval for the mean of q t | ||
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lower bound | Upper bound |
| 0.05 | 10.4146 | 12.5939 |
| 0.1 | 10.4077 | 12.6463 |
| 0.15 | 5.5870 | 6.9557 |
| 0.20 | 8.3495 | 10.8421 |
| 0.25 | 7.8545 | 10.8343 |
| 0.30 | 7.0887 | 10.4056 |
95% confidence intervals for q t with respect to pH factor
| 95% confidence interval for the mean of q t | ||
|---|---|---|
| pH | Lower bound | Upper bound |
| 2 | 9.8757 | 13.4034 |
| 4 | 8.5649 | 10.8542 |
| 6 | 6.4261 | 10.0417 |
| 8 | 6.4857 | 10.4860 |
| 10 | 4.2687 | 7.7523 |
95% confidence intervals for q t with respect to pH factor
| 95% confidence interval for the mean of q t | ||
|---|---|---|
| Concentration mg/L | Lower bound | Upper bound |
| 0.5 | 0.4411 | 0.6937 |
| 1 | 0.5488 | 1.0226 |
| 3 | 1.3069 | 2.5820 |
| 5 | 2.4935 | 4.4143 |
| 10 | 8.9588 | 9.8666 |
From Table 3, it is obvious that the shortest interval length for the mean q t is attained at weight 0.15 g. Therefore, statistically, we may recommend working with this level of weight to achieve better estimates and results for any future experiment in this field.
The same can be noted in Tables 4 and 5, where the shortest interval length is attained at pH = 7 and a concentration of 10 mg/L, respectively.
In our experiment, we used three levels of catalyst varied in the percentage of TiO2 pointed as (I) TiO2:GO (100%), (II) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (50%), and (III) TiO2:GO:SiO2 (25%). Table 6 summarizes all the descriptive results and confidence intervals for the mean q t under these catalyst levels.
Descriptive statistics and 95% confidence intervals for q t with respect to catalyst levels
| N | Mean | Std. deviation | Std. error | 95% confidence interval for mean | Minimum | Maximum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower bound | Upper bound | |||||||
| 100% (I) | 80 | 8.7885 | 4.45411 | 0.49798 | 7.7973 | 9.7797 | 0.05 | 14.84 |
| 25% (III) | 80 | 7.8881 | 4.13933 | 0.46279 | 6.9670 | 8.8093 | 0.45 | 14.53 |
| 50% (II) | 80 | 5.7678 | 3.94091 | 0.44061 | 4.8908 | 6.6448 | 0.27 | 12.49 |
To distinguish between these three levels of catalyst and depending on the real statistical analysis, we can say that 50% (II) level is recommended; the reason for that is the smallest standard error is obtained at this level which is 0.44061, and the smallest mean q t value is at 50% (II) level which equals to 5.7678. Finally, we can realize that the shortest interval length is at a 50% (II) level. Therefore, it supports our choice of 50% (II) as an optimal catalyst level among others. These results are consistent with the percentage degradation of the MB dye as shown in Figure 1. This result is consistent with the assumption that mixing the photocatalysts with the material helps to increase absorption, and has a significant effect by increasing the efficiency of photo-degradation. In addition, it affects the physical properties in terms of converting the material from a powder to a crystalline substance that is easy to handle and reuse.
3.3 RSM
RSM is a classic method used to optimize operational parameters so that its idea is to change one parameter while keeping the others constant. This technique saves time and effort to search for a local area of parameter space. In addition, there is a risk in which there may be only a local maximum. On the contrary, in some cases, RSM can define optimal operational conditions more quickly by modeling the empirical relationship between the dependent responses. RSM models contain a variety of mathematical and statistical equations that can connect the operational parameters and optimize the design of experiments. It is an advanced technique for fitting mathematical models to the observed experimental results. These mathematical models may include linear, quadratic, or polynomial equations, etc. The strategy of experimental design is used to obtain a suitable set of data that can be successfully used in an RSM [4].
Modeling is used to optimize the selected independent (explanatory) variables on the response variable, and for that reason RSM is performed using Minitab [19] package. RSM provides a background to study the parameters and their interaction effects on output responses, and then finally extracts a mathematical model that is useful in plotting the effect of parameters and their interactions. We divided our work into three parts: the first one at the catalyst I level, the second at catalyst II level, and the third at catalyst III level.
3.3.1 Part I
Table 7 shows the ANOVA results for assessing q t using RSM design under the catalyst I; it is clear that all factors have an effect on the response variable q t and we can order their effects depending on F-value as B > A > C. Therefore, the most effect on the response variable is because of the pH level and the lowest effect is because of the initial concentration of MB.
ANOVA table for RSM design with respect to catalyst I
| Source | Mean square | F-value | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 7.5136 | 17.56 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Linear | 14.3235 | 33.47 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A-weight | 15.7470 | 36.79 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| B-PH | 17.1173 | 40.00 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| C-concentration | 14.3071 | 33.43 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| Square | 0.1204 | 0.28 | 0.839 | Not significant |
| A 2 | 0.0233 | 0.05 | 0.816 | Not significant |
| B 2 | 0.1771 | 0.41 | 0.521 | Not significant |
| C 2 | 0.1468 | 0.34 | 0.559 | Not significant |
| Residual | 0.4280 | |||
| Lack-of-fit | 1.4424 | 4.19 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Pure error | 0.3443 |
The model F-value of 17.56 implies that the model is significant. The “lack of-fit F-value” of 4.19 implies that the lack of fit is significant with a pure error of 0.3443.
The reliability of a model can be checked by determining the R 2 coefficient. In this study, R 2 is 0.812 for the nonlinear model, implying that 81.2% of response variability is obtained by a nonlinear regression model.
From Table 7, we conclude that the linear model is a better fit than the quadratic model, this appears from the F-values of A2 ,B2, and C2 with small values (Not significant). The interaction between factors can t be estimated using RSM, in this case, we used a nonlinear regression model, and the regression equation is given by equation. The interaction between factors cannot be estimated using RSM; in this case, we used a nonlinear regression model, and the regression equation is given by equation (3).
The regression model equation reduces to
where
From equation (3), the model under 100% indicates a strong effect of weight, followed by pH level with a weak effect of concentration. It also appears that the interaction effect between some factors are strong such as weight with pH and weight with initial concentration, whereas a weak interaction effect is obtained between pH and initial concentration factors.
Figure 11 illustrates the q t response surface and contour plots as a function of the weight versus pH, weight versus initial concentration, and pH versus initial concentration. Similar to the above result in equation (3), there is a noticeable change in the trend of q t variation at low and high levels of the parameters weight versus pH and weight versus initial concentration. It can be noticed from the response surface plot of weight versus pH that q t attains its maximum value at the minimum level of weights and maximum level of pH. This result is clear from the contour plot as well. Similar argument can be obtained for other response surface and contour plots. This means there is a significant interaction between the two parameters.
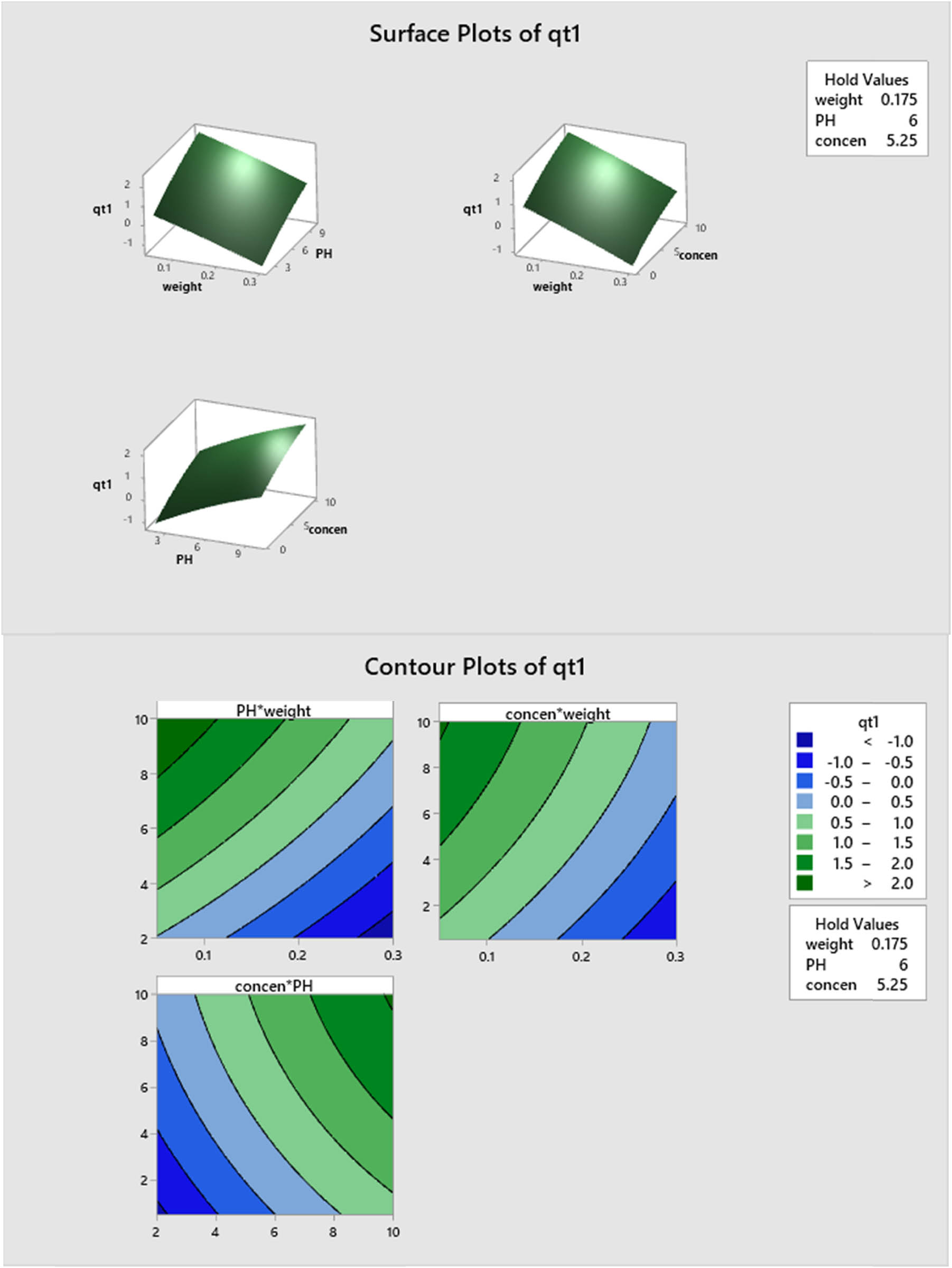
Plots of response surface and contours of the q t efficiency percentage as a function of the explanatory factors on q t (mg/g) amount at 100%.
3.3.2 Part II
Table 8 shows the ANOVA results for assessing q t using RSM design under catalyst III. All factors have an effect on the response variable q t and their order of effect depending on F-value is C > B > A. Therefore, the most effect on the response variable is because of concentration and the lowest effect is because of weight.
ANOVA table for RSM design with respect to catalyst II
| Source | Mean square | F-value | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 12.5169 | 15.11 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Linear | 13.5031 | 16.30 | 0.000 | Significant |
| A-weight | 4.2662 | 5.15 | 0.025 | Significant |
| B-PH | 13.1227 | 15.84 | 0.000 | Significant |
| C-concentration | 26.9062 | 32.47 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Square | 7.9685 | 9.62 | 0.000 | Significant |
| A 2 | 5.7109 | 6.89 | 0.010 | Significant |
| B 2 | 11.1160 | 13.42 | 0.000 | Significant |
| C 2 | 0.2946 | 0.36 | 0.552 | Not significant |
| Residual | 0.8286 | |||
| Lack-of-fit | 4.3498 | 8.08 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Pure error | 0.5381 |
The model F-value of 15.11 indicates that the model is significant. In addition, the lack of-fit F-value of 4.3498 implies that the lack of fit is significant with a pure error of 0.5381.
The reliability of a model can be checked by determining the R 2 coefficient. In this study, R 2 is 0.979 for the nonlinear model, implying that 97.9% of response variability is obtained by a regression model.
From Table 8, we may conclude that the linear and quadratic models are both significant and can be used to model q t value. The F-values of A 2 and B 2 indicated a significant effect of these quadratic forms on q t , whereas C 2 is not significant in this model. Moreover, the interaction between the factors cannot be estimated using RSM, and so we used a nonlinear regression model; the regression equation, in this case, is given by equation (4).
From equation (2), the model under catalyst III indicates a strong effect of weight, followed by initial concentration and weak effect of pH level. It also appears that the interaction effect between some factors is strong such as weight with pH and weight with initial concentration, whereas a weak interaction effect is obtained between pH and initial concentration factors.
Figure 12 shows the q t response surface and contour plots as a function of weight versus pH, weight versus initial concentration, and pH versus initial concentration. Similar to the above result in equation (4), there is a clear change in the trend of q t variation at low and high levels of the weight versus pH and weight versus initial concentration. From the response surface plot of weight versus pH, it can be concluded that q t attains its maximum value at the maximum level of pH and a minimum level of weight. This result is clear from the contour plot as well. Similar argument can be obtained for other response surface and contour plots. Therefore, there is a significant interaction between these two parameters.
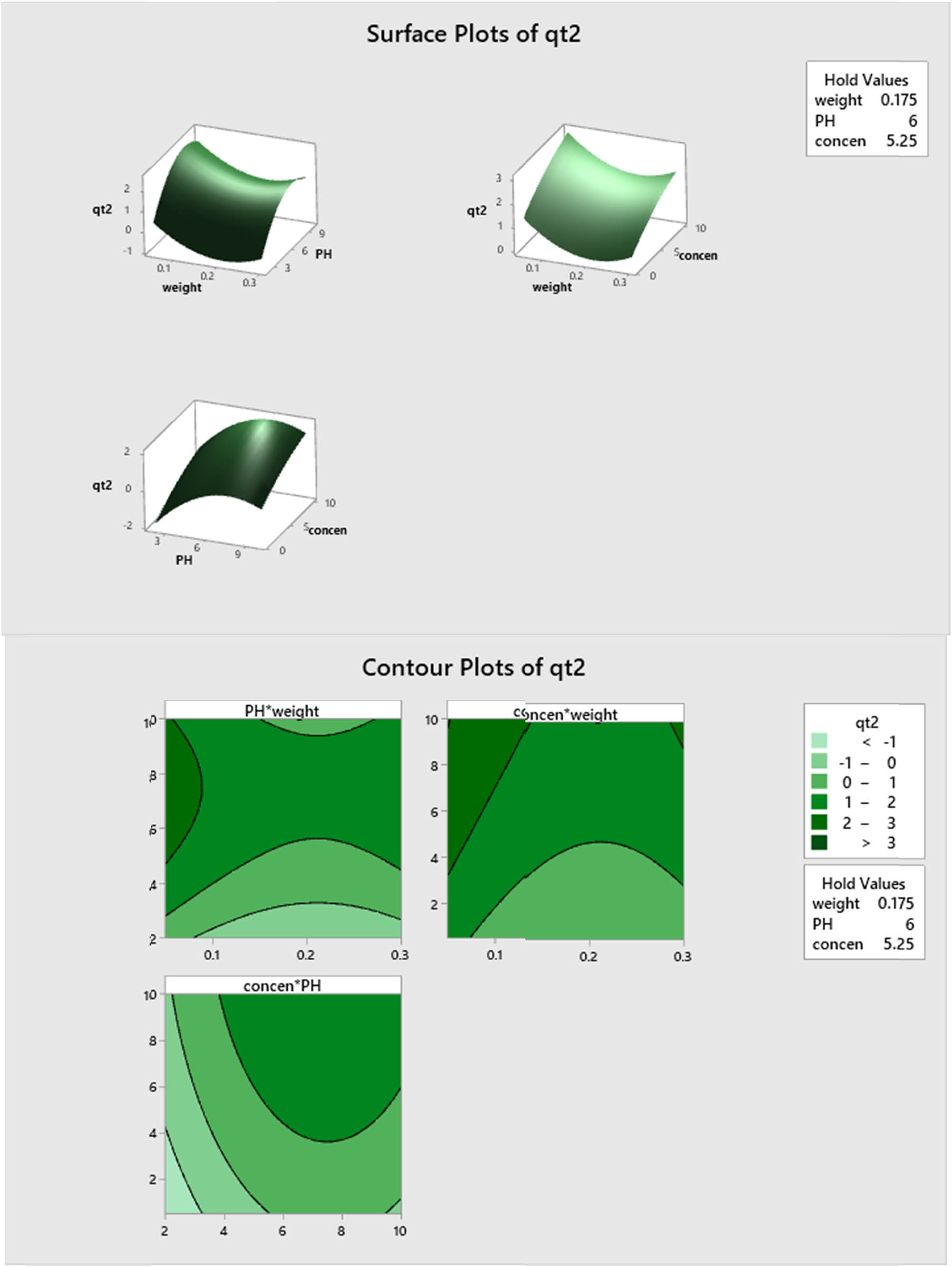
Plots of response surface and contours for q t efficiency percentage as a function of the explanatory factors on q t (mg/g) amount at 25%.
3.3.3 Part III
Table 9 shows the ANOVA results for assessing q t using RSM design under catalyst II. All factors have an effect on the response variable q t and their order of effect depending on F-value are C > A > B. Therefore, the most effect on the response variable is because of the initial concentration and the lowest effect is because of the pH level.
ANOVA table for RSM design with respect to catalyst III
| Source | Mean square | F-value | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 9.1813 | 8.47 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Linear | 13.6073 | 12.55 | 0.000 | Significant |
| A-weight | 4.3632 | 4.02 | 0.047 | Significant |
| B-PH | 0.2535 | 0.23 | 0.630 | Significant |
| C-concentration | 37.8847 | 34.95 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Square | 2.7771 | 2.56 | 0.059 | Not significant |
| A 2 | 0.0296 | 0.03 | 0.869 | Not significant |
| B 2 | 3.1003 | 2.86 | 0.094 | Not significant |
| C 2 | 5.1156 | 4.72 | 0.032 | Significant |
| Residual | 1.0841 | |||
| Lack-of-fit | 7.2873 | 12.73 | 0.000 | Significant |
| Pure error | 0.5725 |
The F-value of the model is 8.47, which indicates that the model is significant. The lack-of-fit F-value of 12.73 implies that the lack of fit is significant with a pure error of 0.5725.
The reliability of a model can be examined by determining the value of R 2. In this study, R 2 is 0.968 for the nonlinear model, implying that 96.8% of response inconsistency is obtained by the regression model.
From Table 9, we may conclude that the linear model is significant, whereas the quadratic models are not significant. The F-values of A 2 and B 2 indicated a nonsignificant effect of these quadratic forms on q t , whereas C 2 is the only significant factor in this model. Moreover, the interaction between the factors cannot be estimated using RSM, and so we used a nonlinear regression model; the regression equation, in this case, is given by equation (5).
In equation (5), the model under catalyst II indicates a strong effect of weight, followed by pH, and then the initial concentration. It also appears that the interaction effect between some factors is strong such as weight with pH and weight with initial concentration, whereas a weak interaction effect is obtained between pH and initial concentration factors.
Figure 13 represents q t response surface and contour plots as a function of the weight versus pH, weight versus initial concentration, and pH versus initial concentration. Similar to the above result in equation (5), there is a clear change in the trend of q t variation at low and high levels of the parameters weight versus pH. From the response surface plot of weight versus pH, it can be concluded that q t attains its maximum value at the maximum level of pH and a minimum level of weight. This result is clear from the contour plot as well. Similar argument can be obtained for other response surface and contour plots. This leads to a considerable interaction between these two parameters.
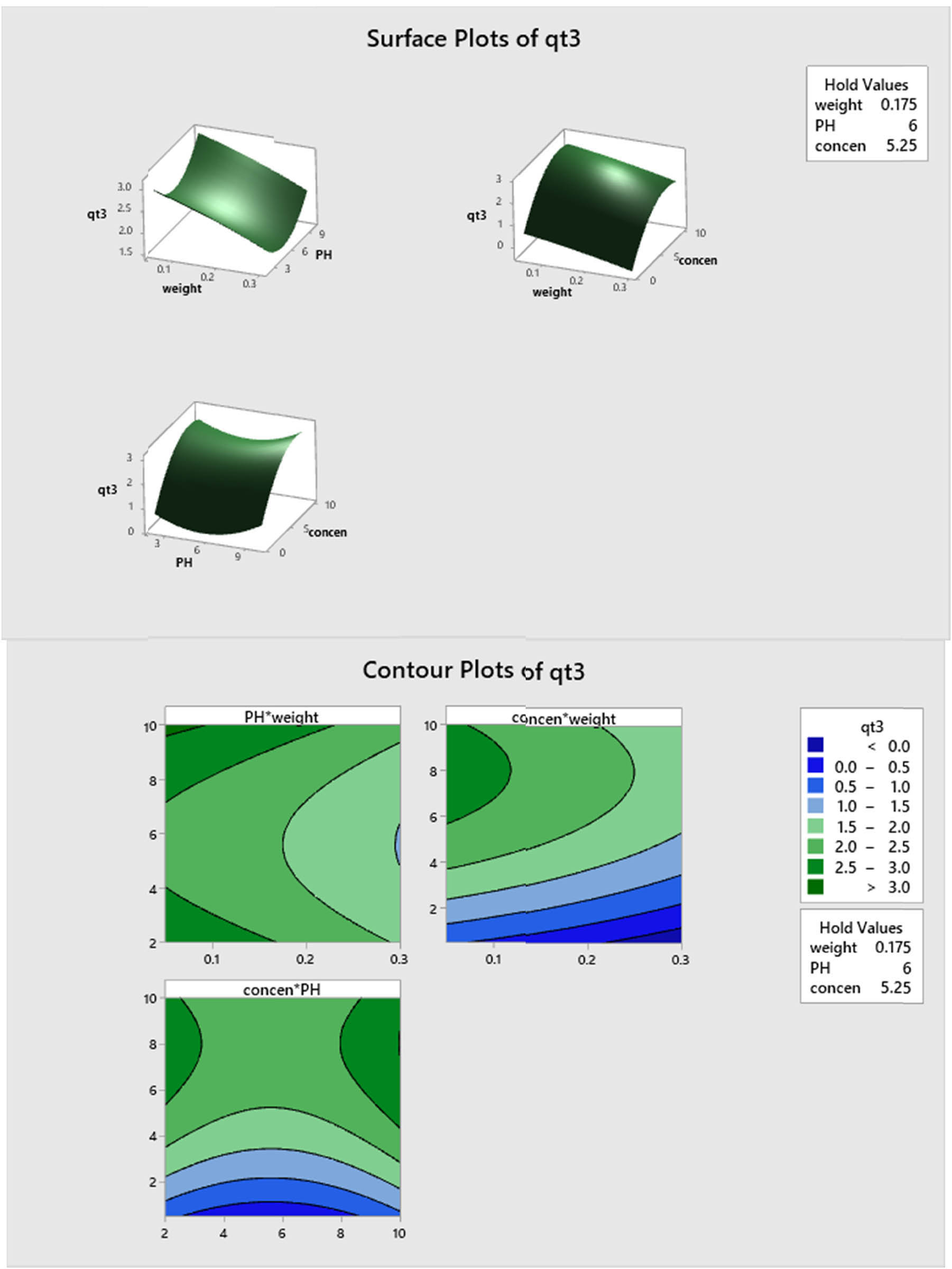
Plots of response surface and contour for q t efficiency percentage as a function of the explanatory factors on q t (mg/g) amount at 50%.
4 Conclusions and recommendations
The results gave an inference of the importance of the pH of wastewater in promoting the removal of pollutants, bearing in mind that the optimum pH varies with different chemicals. Therefore, consideration should be given in the future to modification and/or synthesis of novel photocatalysis applied to a wide range of pH.
Further investigation can be performed on the recycling and stability of catalyst as a future point of research work. The recycling process is influenced by manufactured materials as it has good packing and crystal shape.
Acknowledgment
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project grant number IFT20158.
-
Funding information: This research work was funded by the Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia through the project grant number IFT20158.
-
Author contributions: Hanan Haj Ahmad: writing – review and editing. Waed Alahmad: writing – original draft.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
[1] Dabrowski W, Karolinczak B, Malinowski P, Boruszko D. Modeling of pollutants removal in subsurface vertical flow and horizontal flow constructed wetlands. Water (Switzerland). 2019;11:180. 10.3390/w11010180.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Sen TK, Thi MT, Afroze S, Phan C, Ang M. Removal of anionic surfactant sodium dodecyl sulphate from aqueous solution by adsorption onto pine cone biomass of pinus radiate: Equilibrium, thermodynamic, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Desalin Water Treat. 2012;45(1–3):263–75.10.1080/19443994.2012.692036Search in Google Scholar
[3] Anfar Z, Ait Ahsaine H, Zbair M, Amedlous A, Ait El Fakir A, Jada A, et al. Recent trends on numerical investigations of response surface methodology for pollutants adsorption onto activated carbon materials: A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol [Internet]. 2020;50(10):1043–84. 10.1080/10643389.2019.1642835 Search in Google Scholar
[4] Ateia M, Alalm MG, Awfa D, Johnson MS, Yoshimura C. Modeling the degradation and disinfection of water pollutants by photocatalysts and composites: A critical review. Sci Total Environ [Internet]. 2020;698:134197. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134197 Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Cheng X, Yu X, Xing Z, Yang L. Synthesis and characterization of N-doped TiO2 and its enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Arab J Chem [Internet]. 2016;9:S1706–11. 10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.04.052 Search in Google Scholar
[6] Kannaiyan D, Kochuveedu ST, Jang YH, Jang YJ, Lee JY, Lee J, et al. Enhanced photophysical properties of nanopatterned titania nanodots/nanowires upon hybridization with silica via block copolymer templated sol–gel process. Polymers (Basel). 2010;2(4):490–504.10.3390/polym2040490Search in Google Scholar
[7] Yaqoob AA, Parveen T, Umar K. Role of nanomaterials in the treatment of. Water. 2020;12(495):1–30.10.3390/w12020495Search in Google Scholar
[8] Chong MN, Jin B, Chow CWK, Saint C. Recent developments in photocatalytic water treatment technology: A review. Water Res [Internet]. 2010;44(10):2997–3027. 10.1016/j.watres.2010.02.039 Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Kim J, Kim JJ, Lee SJ. Efficient removal of indoor particulate matter using water microdroplets generated by a MHz-frequency ultrasonic atomizer. Build Environ [Internet]. 2020;175(January):106797. 10.1016/j.buildenv.2020.106797 Search in Google Scholar
[10] Dao NTM, Nguyen TA, Nguyen VA, Terashima M, Goel R, Yasui H. A mathematical model of a nitrifying expanded-bed reactor for the pretreatment of drinking water. Biochem Eng J [Internet]. 2020;158(March):107561. 10.1016/j.bej.2020.107561 Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sargolzaei J, Hedayati Moghaddam A, Nouri A, Shayegan J. Modeling the removal of phenol dyes using a photocatalytic reactor with SnO2/Fe3O4 nanoparticles by intelligent system. J Dispers Sci Technol. 2015;36(4):540–8.10.1080/01932691.2014.916222Search in Google Scholar
[12] Dehghan A, Dehghani MH, Nabizadeh R, Ramezanian N, Alimohammadi M, Najafpoor AA. Adsorption and visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride from aqueous solutions using 3D hierarchical mesoporous BiOI: Synthesis and characterization, process optimization, adsorption and degradation modeling. Chem Eng Res Des [Internet]. 2018;129:217–30. 10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.003 Search in Google Scholar
[13] Udrea ML, Ion R. Modelling of methylene blue dye adsorption on beech and fir wood sawdust as adsorbent support materials. J Sci Arts. 2019;3(3):675–87.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Alahmad W, Alshammari H, Aldosari O, Alsomadi R. Treatment of simulated wastewater spiked with phenols using TiO2/GO/SiO2 under environmental conditions. Fresenius Environ Bull. 2018;27(12B):9922.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Cenens J, Schoonheydt RA. Visible spectroscopy of methylene blue on hectorite, Laponite B, and barasym in aqueous suspension. Clays Clay Miner. 1988;36(3):214–24.10.1346/CCMN.1988.0360302Search in Google Scholar
[16] Dinh VP, Huynh TDT, Le HM, Nguyen VD, Dao VA, Hung NQ, et al. Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of methylene blue and chromium(iii) from aqueous solution onto pomelo fruit peel. RSC Adv. 2019;9(44):25847–60.10.1039/C9RA04296BSearch in Google Scholar
[17] Houas A, Lachheb H, Ksibi M, Elaloui E, Guillard C, Herrmann JM. Photocatalytic degradation pathway of methylene blue in water. Appl Catal B Environ. 2001;31(2):145–57.10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00276-9Search in Google Scholar
[18] Siahpoosh ZH, Soleimani M. Photocatalytic degradation of azo anionic dye (RR120) in ZnO-Ghezeljeh nanoclay composite catalyst/UV-C system: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Process Saf Environ Prot [Internet]. 2017;111:180–93. 10.1016/j.psep.2017.07.009 Search in Google Scholar
[19] Abdellah MH, Nosier SA, El-Shazly AH, Mubarak AA. Photocatalytic decolorization of methylene blue using TiO2/UV system enhanced by air sparging. Alexandria Eng J [Internet]. 2018;57(4):3727–35. 10.1016/j.aej.2018.07.018 Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Hanan Haj Ahmad and Waed Alahmad, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation

