Abstract
In many plastic applications, improvement of the flame retardancy is a very significant topic. Polypropylene (PP) is used in many applications such as housing industry due to its cost performance efficiency. Enhancement of flame retardancy properties of PP is necessary in many applications. In this study, the investigation focuses on the synergistic effect of mica mineral and IFR in enhancing the flame retardancy properties of PP in order to achieve cost competitive solution, so as to provide that different/various ratios of IFR and mica mineral were added into PP to compose 30 wt% of the total mass of the polymeric compounds. The synergistic effect of mica mineral with IFR in PP was investigated by limiting oxygen index (LOI), glow wire test (GWT), UL-94 test, thermal gravimetric analyses (TGA), and mechanical tests. The results from LOI, UL 94, and GWT tests indicated that mica added to PP/IFR compound has a synergistic flame retardancy effects with the IFR system. When the content of mica was 6 wt%, LOI value of PP compound reaches to 34.9% and becomes V-0 rating (3.2 mm) in UL 94 flammability tests and compounds pass GWT tests both at 750 and 850°C.
1 Introduction
Polypropylene (PP) is the most widely used commodity thermoplastic polymer in many different commercial applications, compatible with many processing techniques. In addition, it is known as one of the fastest growing classes of commodity thermoplastics, with a market share growth of 6–7%. Its strong growth rate is based on moderate cost and favourable properties. PP is useful for many applications such as fibres, films, filaments, and injection molding parts for automobiles, rigid packaging, appliances, medical equipment, food packaging, and consumer products. Due to its poor flame retardancy property, its usage field is also limited. For example, LOI value of PP is around 18% and so flame retardancy properties of PP must be improved by the use of flame retardants for applications in the construction, automotive, appliances, and electronics industries [1].
Fire is a unique destructive force of nature and known as a physical and chemical phenomenon. The interaction between the flame, its fuel, and the surrounding can be strongly nonlinear, and quantitative estimation of the process involved is often complex. The burning process and the processes of interest in an enclosure fire mainly involve mass fluxes and heat fluxes to and from the fuel and the surroundings [2].
Flame retardant materials are used to increase flame retardancy properties of materials. Intumescent flame retardants (IFR) have been improved as alternatives for the halogenated flame retardants because these flame retardants, upon heating, promote the formation of char which provides insulation from heat and oxidative degradation. IFR has been improved which can be incorporated in a thermoplastic prior to molding. Phosphoric acid, phosphorus oxide, pentaerythritol (PER), and melamine are used for intumescent system [3]. Ammonium polyphosphate (APP), PER, and melamine system form a well-known intumescent flame retardant, which was first used in fire retardant intumescent coatings. It is mainly combined of inorganic acid sources (e.g. ammonium polyphosphate, etc.), carbonifics (e.g. pentaerythritol, sorbitol, etc.), and spumifics (e.g. melamine, etc.). Acid sources are also known as dehydrating agents. When they are exposed to heat, acid source starts to release acid to the system. Carbonifics are carbon-rich materials as char formers. This acid source reacts with carbonifics to create char layer on the surface of burning material. Spumifics are known as blowing agents; they generate gases in intumesent system during combustion process. Finally, char foam is generated in the system. Char foam acts as a barrier to eliminate heat transfer to the surface of burning material. Char foam also reduces dripping of molten plastic. Intumescent system is used in thermoplastics to provide lower flame retardant efficiency, lower thermal stability, and lower water resistance compared with halogenated flame retardants [4]. Competitive market conditions have been leading researchers to find cost competitive solutions for IFR systems and one of the most known is usage of synergistic materials like clay, talc, calcium carbonate, etc. [5].
Mica belongs to a group of aluminosilicate minerals characterized by a layered structure which can be cleaved to give thin, flexible sheets. Muscovite and phlogopite are the most common and commercially available classes of mica. It is chemically inert and thermally stable up to 600°C where dehydroxylation takes place. It can be used as flame retardant extender and char promoter [6].
Agglomeration of mica emerged after increasing the amount of mica from 5 to 40% in PP composites. However, particle distribution was good and the particles were spherical in shape. Coupling agents prevented reagglomeration of the particles and formed strong bonds between the matrix and the mica, leading to improved mechanical properties of the composite [7]. Crystalline structure of clay minerals appears to affect the synergy with APP/PER. The presence of the tetrahedral SiO4 sheets on both sides of the interlayer space, as in the mica structure, or in the Pal, seems to lead to a greater synergistic action. Particle size (D (V, 0.5) (μm)) of mica is 210.69 µm [5]. Sheng and coworkers studied on interaction mechanism of APP mixed with muscovite. Thermal Gravimetric (TG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) were used for microstructural analysis. APP started to decompose at 295°C. The main thermal decomposition products are polyphosphoric acid and NH4H2PO4 at 300°C. The decomposition product of APP, polyphosphoric acid, can interact with muscovite chemically and produce Al2O3·2SiO2, α-SiO2, and phosphates (AlPO4 and K5P3O10) compounds during 400–800°C [8].
Synergistic compositions have significant effect on plastic materials to reduce filler content in formulations and also to improve flammability properties. Particularly, mineral filler such as huntite&hydromagnesite is used as traditional halogen-free flame retardant, but needs to be added with a high loading level (up to 60 wt%) to achieve the required flame retardancy effect in plastic material. However, poor mechanical properties and processability of final compounds are obtained in high level content of minerals [9].
The objective of this study is to work the synergistic effects of mica mineral with IFR system in PP using the UL 94 flammability test, limiting oxygen index (LOI), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and glow wire flammability test (GWFT). Physical and mechanical properties of the compounds have also been tested. Compounds have been produced in twin-screw extrusion and testing sample preparation has been completed in injection molding machine. Final formulation will be used in appliance industry such as bottom side of refrigerator and electronic card holder of washing machine.
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials
The PP homopolymer of PP 578 L was used with melt flow index (MFI) 25 g/10 min at 230°C/2.16 kg and density 0.905 g/cm3. This material is supplied by Sabic (Netherlands). The IFR (Intumescent flame retardant) compound consisting of APP and synergist (JLS PNP2D) was supplied by JLS (China). Mica mineral was supplied by Mikron’s Company (Turkey). The main compositions and properties of IFR PNP2D and mica mineral were given in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. All chemicals were used without further purification and the raw materials used in the experiment were not chemically treated before experiment.
Main compositions and basic properties of IFR PNP2D
| Appearance and compositions | Basic properties |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White, free-flowing powder |
| Phosphorus content (%) | 21 ± 1 |
| Nitrogen content (%) | 18 ± 1 |
| Average particle size (µm) | Approx. 15 |
| Moisture content (%) | 0.50 |
| Density at 25°C (g/cm3) | Approx. 1.8 |
| Thermal decomposition (°C) | ≥250 |
Properties of mica mineral
| Properties | Results |
|---|---|
| Average particle size (d 50) (µm) | 19.52 |
| D97 (µm) | 78.55 |
| D2 (µm) | 8.35 |
2.2 Preparation of flame retardant PP formulations
Prior to mixing and getting the mica dried, the sample was heated first to 100°C for 4 h and cooled slowly then to room temperature under vacuum for 10 h. PP, mica mineral, and IFR were compounded in twin-screw extrusion at the different loading levels to obtain seven different polymeric composite samples. IFR and mica mineral were added to PP to compose 30 wt% of the total mass of the polymeric compounds. Mica was added with mass fractions 2, 4, 6, 8, and 15 wt%. Additionally, 30 wt% mica reinforced PP compound was prepared to see flame retardancy performance of mica without IFR system indicated in Table 3. Compounds were extruded by a co-rotating twin-screw extruder at a temperature profile of 180, 180, 180, 185, 190, 190, and 195°C, and cutting into pellets using a granulator. In this study, in order to form well-mixed compound intermeshing, co-rotating twin-screw extruder was used; Coperion ZSK 26Mc with three Brabender feeders, with the screw diameter 25.5 mm and L/D ratio 44:1 (shaft length/screw diameter). Arburg 370 S 800–150 injection machine was used to produce specimens according to ISO 20753:2018 standard [10].
Experimental design of mica and IFR-filled polypropylene compounds
| No | Samples name | PP (wt%) | Mica mineral (wt%) | IFR (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Neat PP | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | PP70/IFR30/M0 | 70 | 0 | 30 |
| 3 | PP70/IFR28/M2 | 70 | 2 | 28 |
| 4 | PP70/IFR26/M4 | 70 | 4 | 26 |
| 5 | PP70/IFR24/M6 | 70 | 6 | 24 |
| 6 | PP70/IFR22/M8 | 70 | 8 | 22 |
| 7 | PP70/IFR15/M15 | 70 | 15 | 15 |
| 8 | PP70/IFR0/M30 | 70 | 30 | 0 |
PP: polypropylene, IFR: intumescent flame retardant, M: mica mineral with loading level (wt%).
2.3 Analysis of sample
2.3.1 Density measurement
Density values were measured with Mettler Toledo density test equipment according to the procedure explained in ISO 1183-1 Plastics-methods for determining the density of non-cellular plastics-Part 1: Immersion method [11].
2.3.2 Determination of MFI
MFI or melt flow rate (MFR) was measured by using Zwick testing machine according to ISO 1133 test standard. The testing device is basically an extrusion plastometer operating at a fixed temperature. Test temperature and weight is set to 230°C and 2.16 kg, respectively.
where S is the reference time in second, i.e. 600 s; M is the average mass of the cut-offs, in grams; and t is the cut-off time interval, i.e. 30 s [12].
2.3.3 Mechanical properties – tensile testing
Test specimens were held in a heat-controlled room at a temperature of 23 ± 2°C and 50% humidity for at least 24 h to prevent the specimens from the post-crystallization or physical ageing effects.
Tensile properties of polymeric compounds were investigated by using Zwick-Z020 testing equipment according to ISO 527-1/2 1A plastics-determination of tensile properties-Part 2: Test conditions for molding and extrusion plastics. [13]. At least five specimens were tested for each compounds.
2.3.4 Izod notched impact testing
Izod notched impact strength of specimens was determined by Zwick-HIT-50 P test equipment according to ISO 180/A plastics-determination of Izod impact strength [14].
2.3.5 TGA
TGA performed on a Q500 thermal gravimetric analyser. Samples weighting about 20.0 mg were heated from room temperature to 900°C at a heating rate of 20°C/min in a dynamic nitrogen atmosphere. The nitrogen flow rate was 50 mL/min.
2.3.6 LOI
This test was carried out by using LOI test apparatus (Fire Testing Technology) equipped with test chimney, specimen holders, gas measurement and control devices, flame igniter, timing device, fume extraction system, and gas supplies according to ASTM D2863-10 standard [15].
2.3.7 GWFT
Glow wire test (GWT) was carried out by using PTL Glow-wire test apparatus to determine the fire resistance. This test method measures and describes the resistance of materials, products, or assemblies to heat and flame under controlled conditions, but does not by itself incorporate all factors required for fire hazard or fire risk assessment of the materials, products, or assemblies under actual fire conditions. PTL GWT apparatus is equipped with glow wire, thermocouple, temperature indicator, supply circuit, text fixture, indicator board, and test chamber [16].
2.3.8 UL 94 flammability testing-vertical
Rate of burning and time of burning of self-supporting plastics in a vertical position were measured by using CEAST flammability tester. The CEAST flammability tester is equipped with test chamber, text fixture, laboratory burner, gas supply, wire gauze, timing device, and flexible specimen support fixture [17]. UL 94 flammability test results are categorized by burning ratings V-0, V-1, or V-2 depending on the total burning time and dripping behaviours as described in the standard. The best flame retardancy property of plastic materials classified as V-0 rating.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Density results
Density test results showed a steady increase with increasing mica loading level. Mica and IFR have higher density of 2.83 and 1.8 g/cm3, respectively, than that of PP, which is 0.906 g/cm3. Therefore, the incorporation of mica and IFR into the PP matrix resulted in processing composites with higher density results (Figure 1) as obeying the rule mixture. On the other hand, even though total FR ratios were constant due to higher density of mica, increased mica content increased the density of compounds slightly.
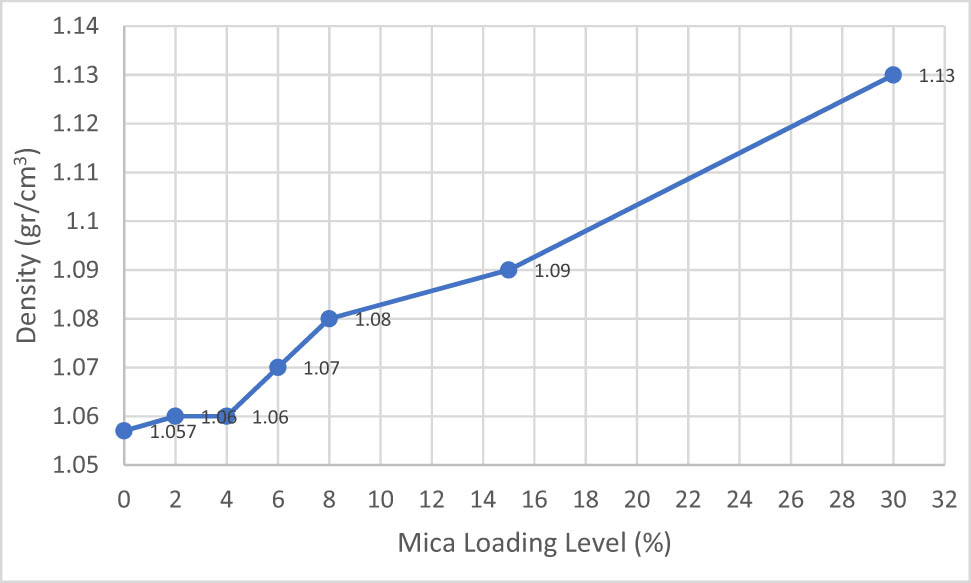
Density graph of neat PPs, IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
3.2 MFI test results
MFI value decreased when IFR was added to PP compound from 22.35 to 14.88 g/10 min at 230°C and 2.16 kg loading. When mica mineral was incorporated to PP with IFR, MFI values started to increase around 15.3%. At 8% IFR loading level, MFI values decreased from 19.35 g/10 min to 17.64 g/10 min because the addition of filler content into the PP/IFR compounds will improve flexibility of compound due to plastic deformation owing to stress concentration. The MFI test results were given in Figure 2.
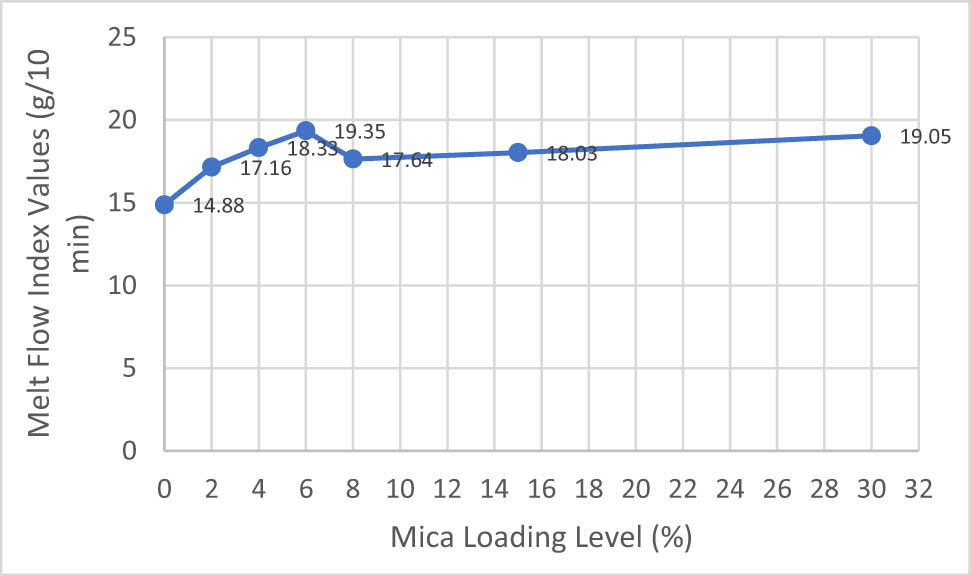
MFI graph of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
3.3 Mechanical properties tensile test results
The mechanical properties of PP and its flame retardant compounds with different loading of mica mineral are indicated in Figures 3–6. The addition of IFR by high amount into PP material reduces the tensile strength and elongation at yield point values due to effect of mineral like reinforcing effect. Increasing the amount of mica mineral content in PP compounds increases elastic modulus. Tensile strength value of PP homopolymer decreased when IFR and mica mineral were added to system. No selective difference is observed on tensile strength values of only IFR and IFR/mica-filled PP compounds. PP70/IFR0/M30 showed better tensile strength properties compared to IFR/mica-filled PP compounds at different loading levels each other which might be related with higher particle size with aspect ratio as explained in Verbeek study [7]. Strain value of neat PP homopolymer decreased with increasing amounts of mica mineral content in PP/IFR/Mica compounds. No selective difference is observed on tensile strain values of 30% IFR and 30% mica mineral in PP compounds. In addition to them, when the mica content is less than 8%, the tensile strength values decrease, and it reaches up to at mica content of 8%, and then it started to increase with increase of the mica content in the PP compound. This shows that tensile strength values of the compound improved because of high filler concentration. It is generally believed that the polymer matrix around the inclusions can produce plastic deformation thanks to stress concentration. Liang, Li, and Feng observed that elastic modules nonlinearly increased when the amount of IFR content in PP compound increases. IFR material has stiffening effect on the final compound. This effect is related to the movement of the big chains of the matrix material that is blocked by IFR particles. Stiffness of filled PP compounds can be improved by adding IFR content to the PP compound. However, increasing IFR content leads to a decreased tensile strength of PP compound. It is related to interfacial adhesion between inorganic materials and polymer matrix. If interfacial adhesion improves, tensile yield strength values can start to increase [18].
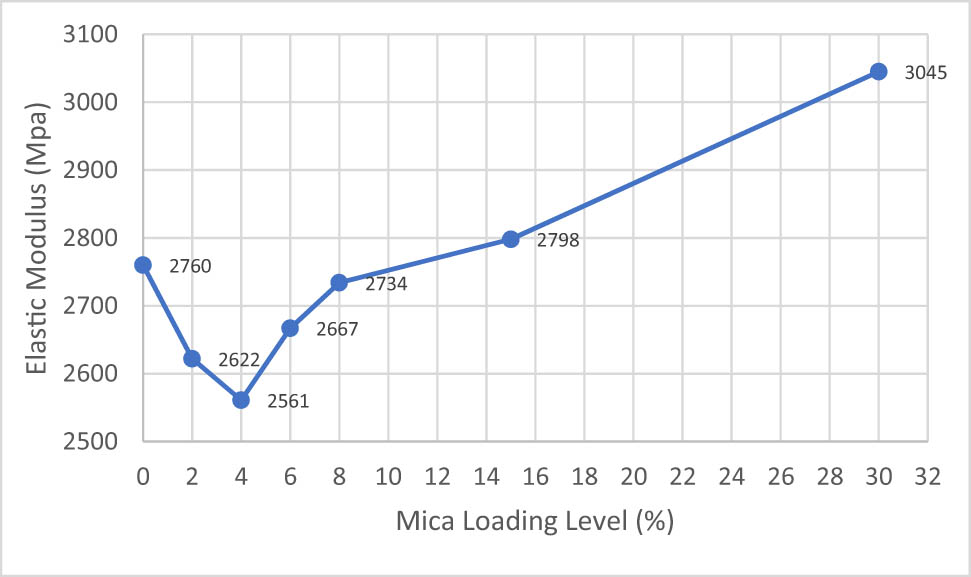
Elastic modulus results of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
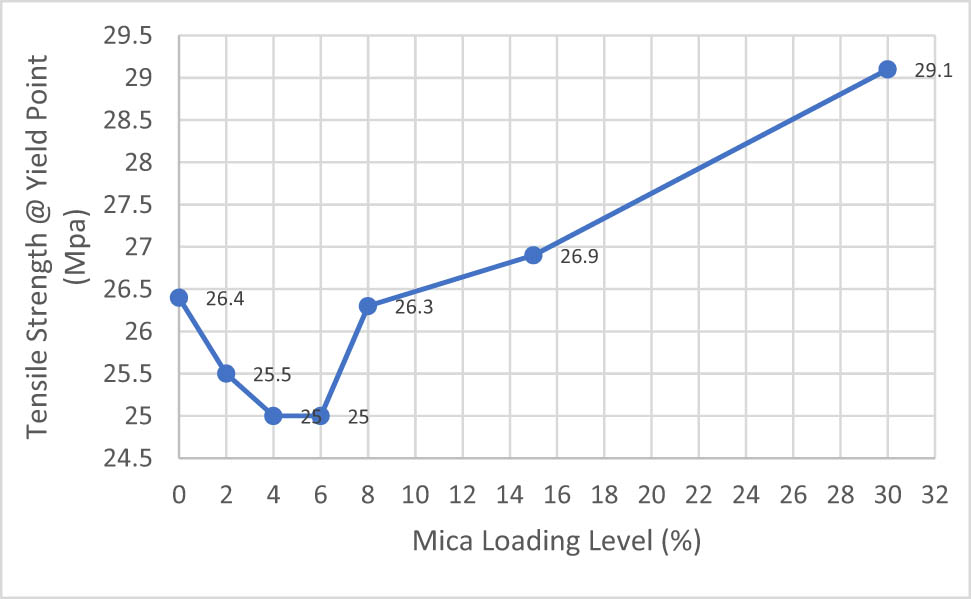
Tensile strength at yield point results of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
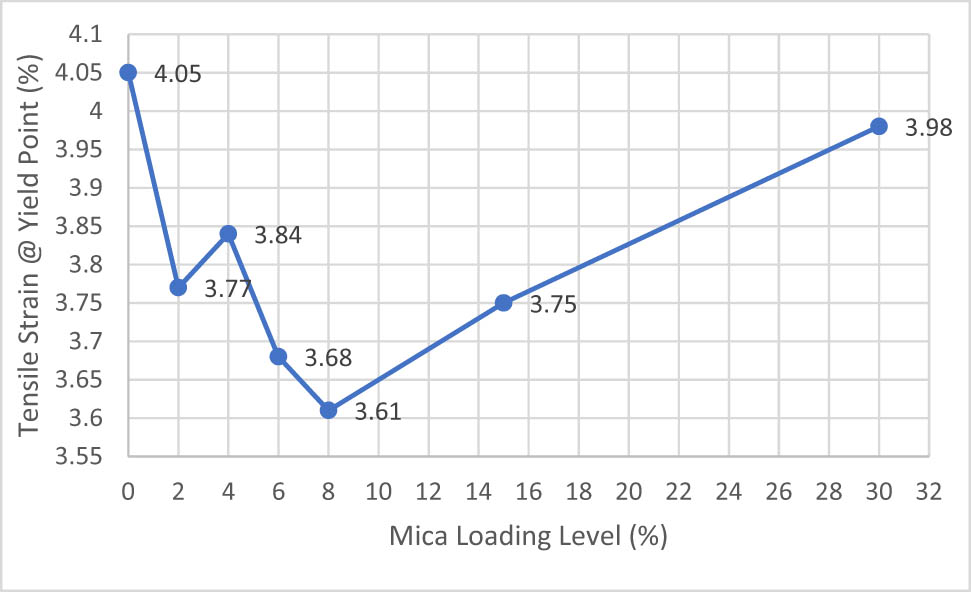
Tensile strain at yield point results of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
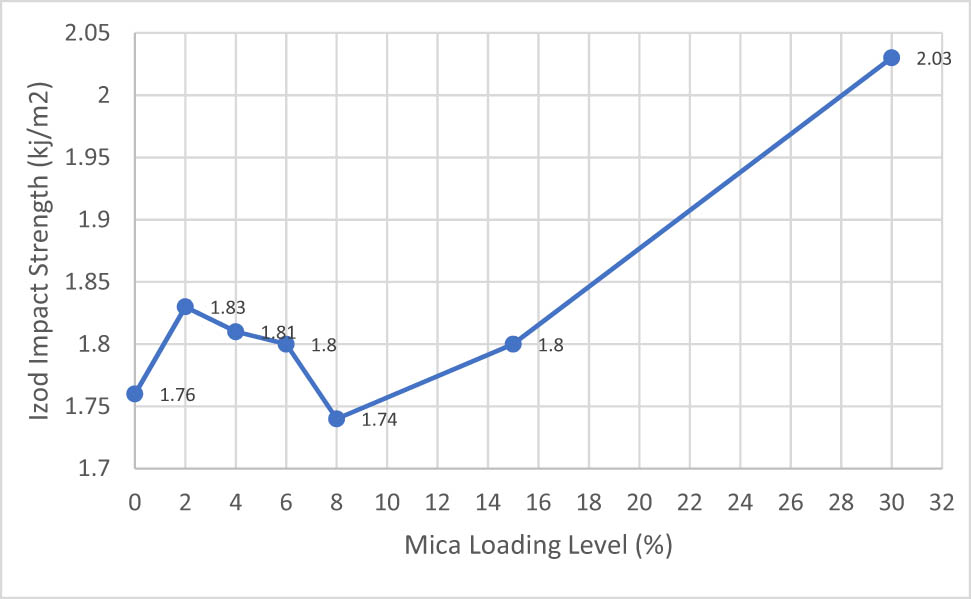
Izod impact test results of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds.
Tensile properties of filled PP compounds depend on interaction between polymer and fillers. The reduction in elongation at yield and break point may be the formation of some voids due to debonding of mica from polymer structure upon failure. Mica has good shape stability, high elasticity, high shear and compressive strength, perfect cleavability, and incompressibility in terms of mechanical properties. According to literature, when mica is added to polymer matrix, some physical properties of polymer matrix as mechanical strength, modulus, and heat distortion temperature can be improved. The size, shape, and distribution of mica particles in the polymer compound have effect on mechanical properties of final compound. Interfacial adhesion is affected from these properties directly. Liang and Yang have compounded with high density polyethylene and surface-treated mica in twin-screw extrusion. When they added surface-treated mica to HDPE during compounding, they observed that tensile strength of the compounds increases slightly with an increase of weight fraction of the particles. As they explained that the interfacial adhesion between the filler and matrix for compounds has impact on tensile strength especially, so after the surface of mica particles is treated by a silane-coupling agent, the interfacial adhesion between mica and HDPE matrix is improved [19].
3.4 Izod notched impact results
Izod impact strength values of neat PPs and IFR-filled PP compounds were listed in Figure 6. The Izod impact strength value of PP homopolymer is around 3.22 kJ/m2. Different loading levels of IFR and mica mineral in PP compounds showed negative effect on Izod impact strength (Figure 6). No selective difference is observed on Izod impact values at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 15% mica loading level in PP compounds. The reduction of Izod impact strength with IFR and mica addition into PP could be explained by the restriction of chain mobility.
3.5 TGA
TGA is an effective method to observe the decomposition behaviours and to calculate char residue. The TGA curves of neat PP and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds were shown in Figures 7–14. PP began to decompose at 250°C and was consumed completely at 500°C. It can be observed that the initial degradation temperature increased from 250°C in PP to between 260–270°C in PP compounds. According to literature, mica presented a mass loss around to 700°C related to dehydroxylations process [7]. Addition of mica gave minimal effect on TGA curves. However, char residue was increased from 8.46 to 10.25, 11.55, 15.74, 20.88, and 28.42% at 2, 4, 6, 8, 15, and 30% mica content, respectively. It is obvious that the char residue increased by the increasing loading of mica.
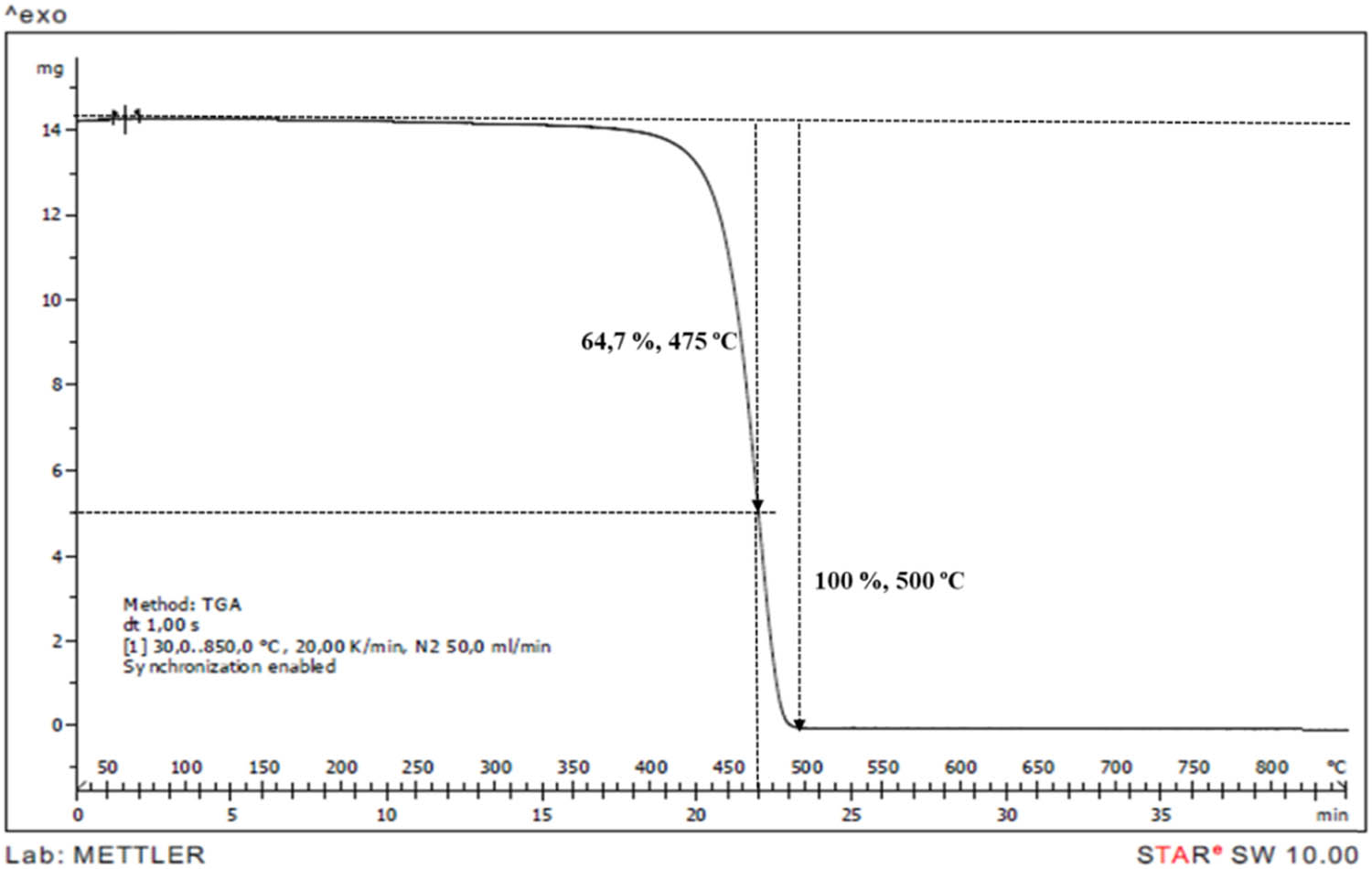
TGA thermogram of neat polypropylene.
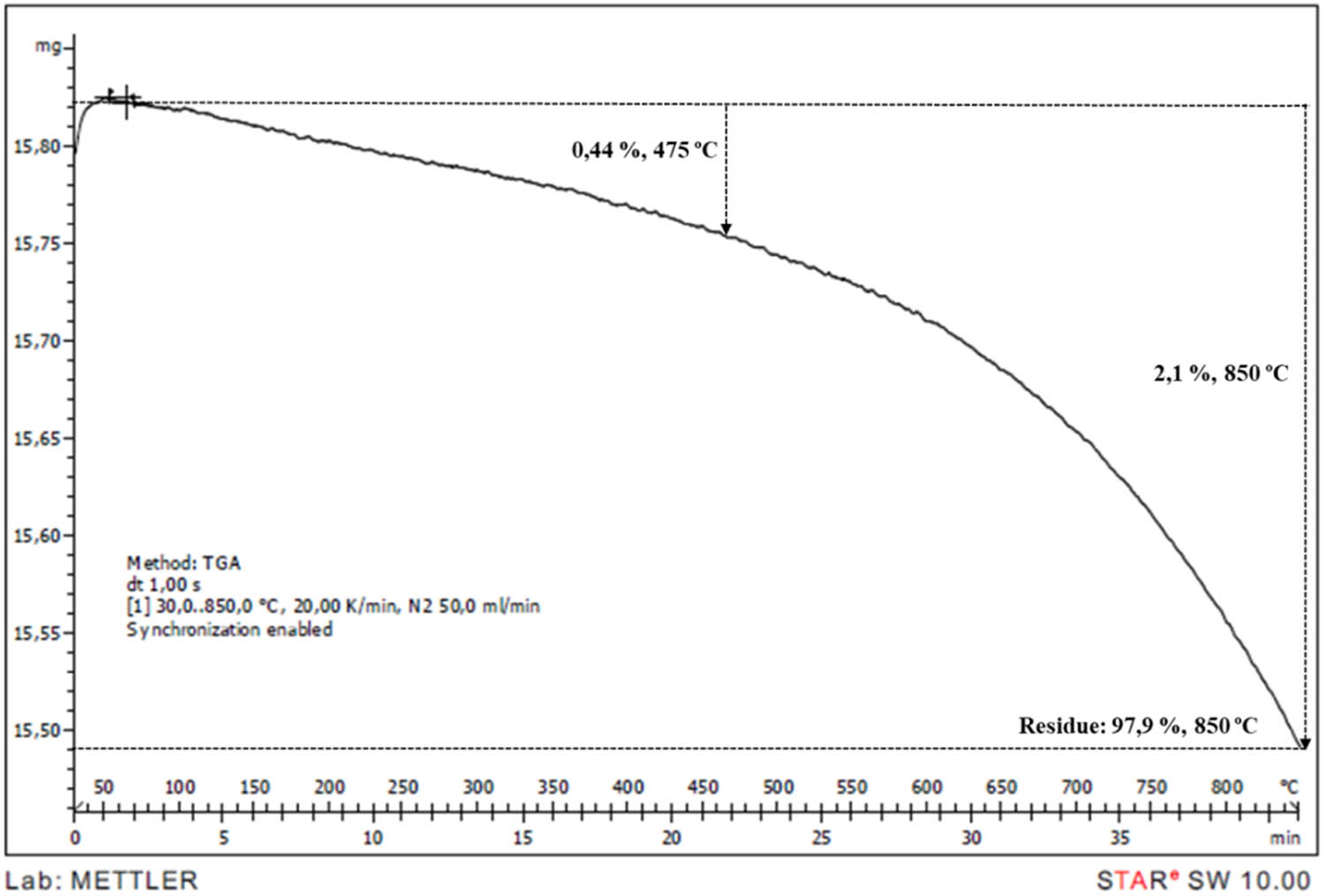
TGA thermogram of pure mica mineral.
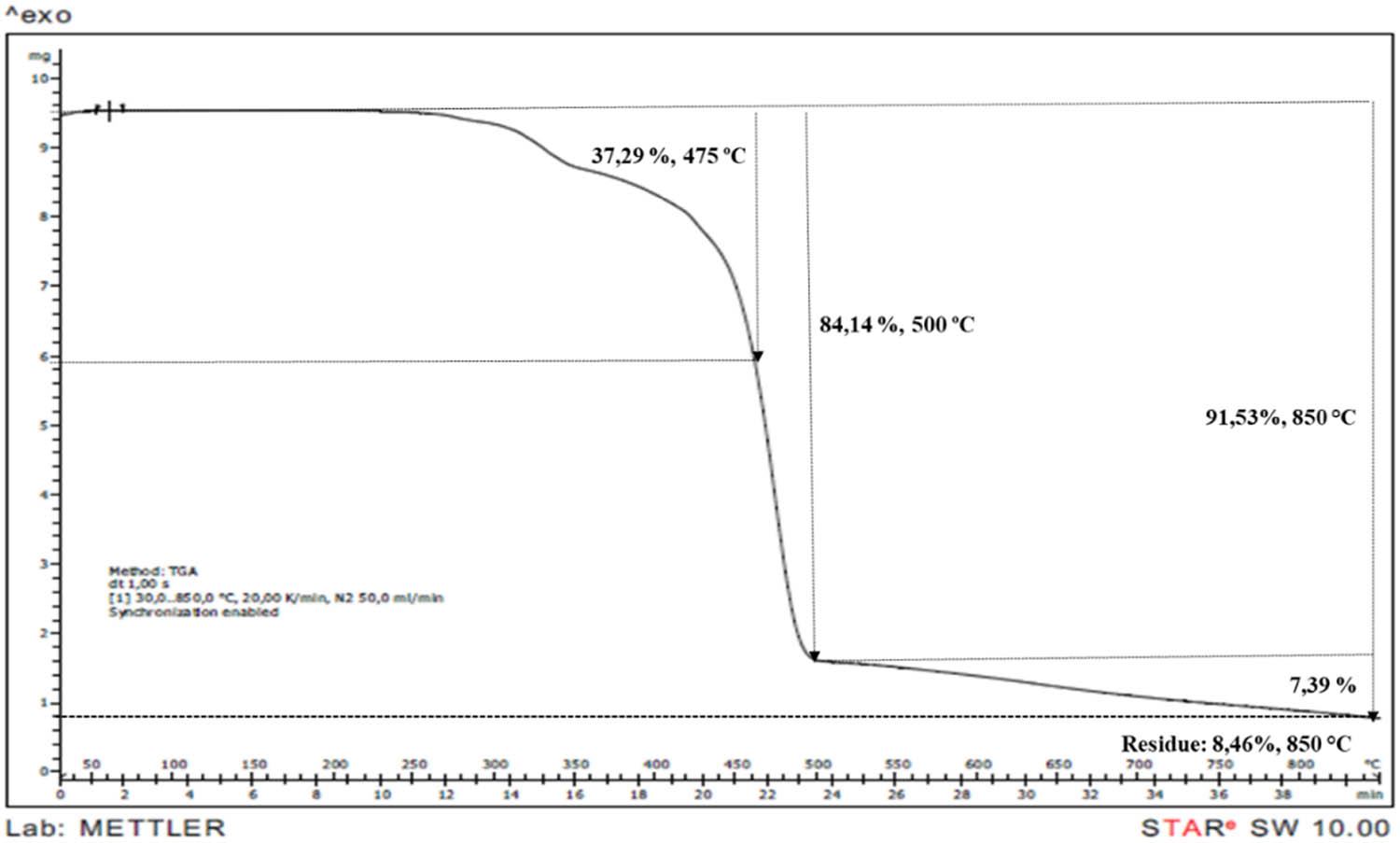
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR30/M0 sample.
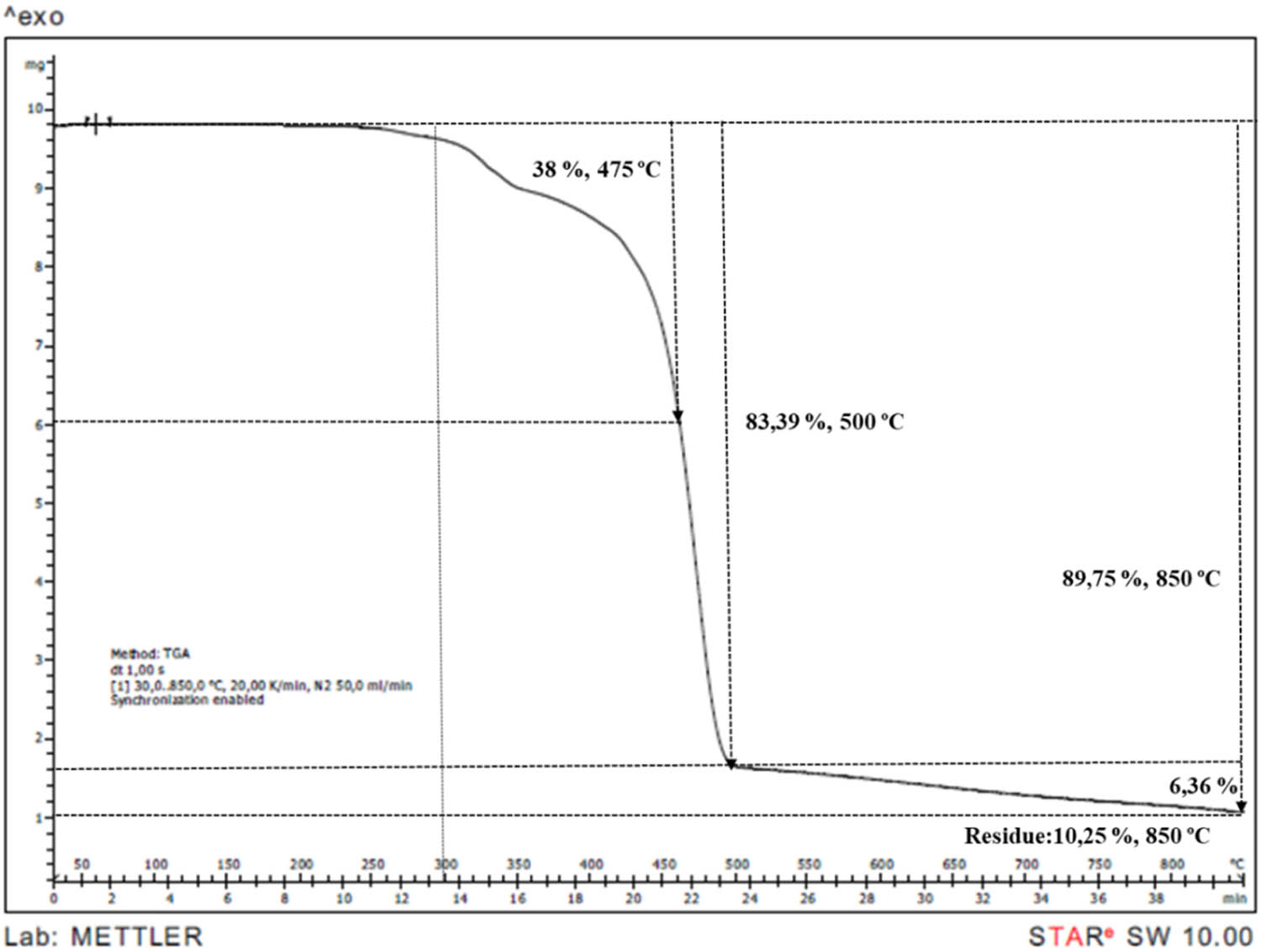
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR28/M2 sample.
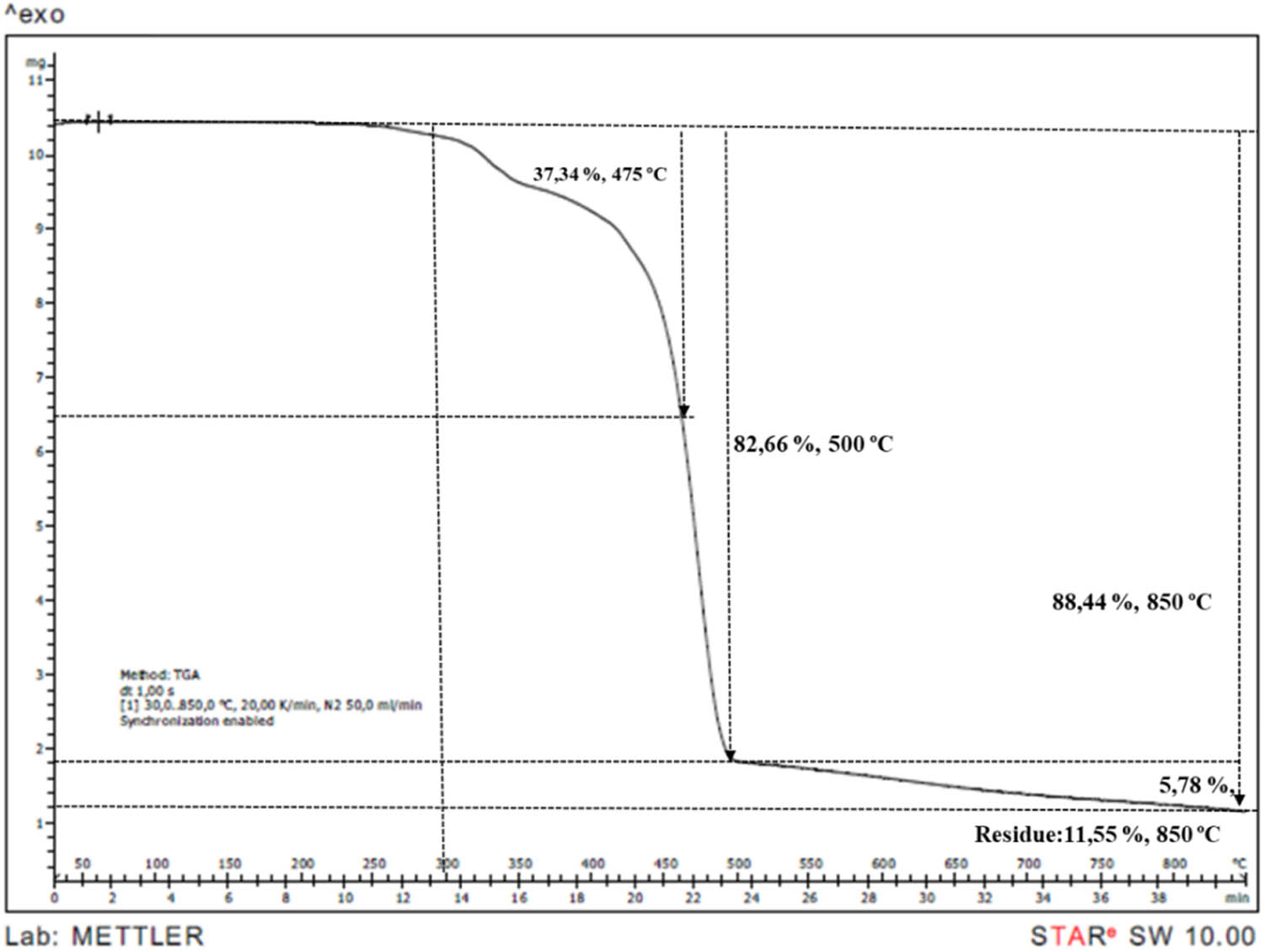
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR26/M4 sample.
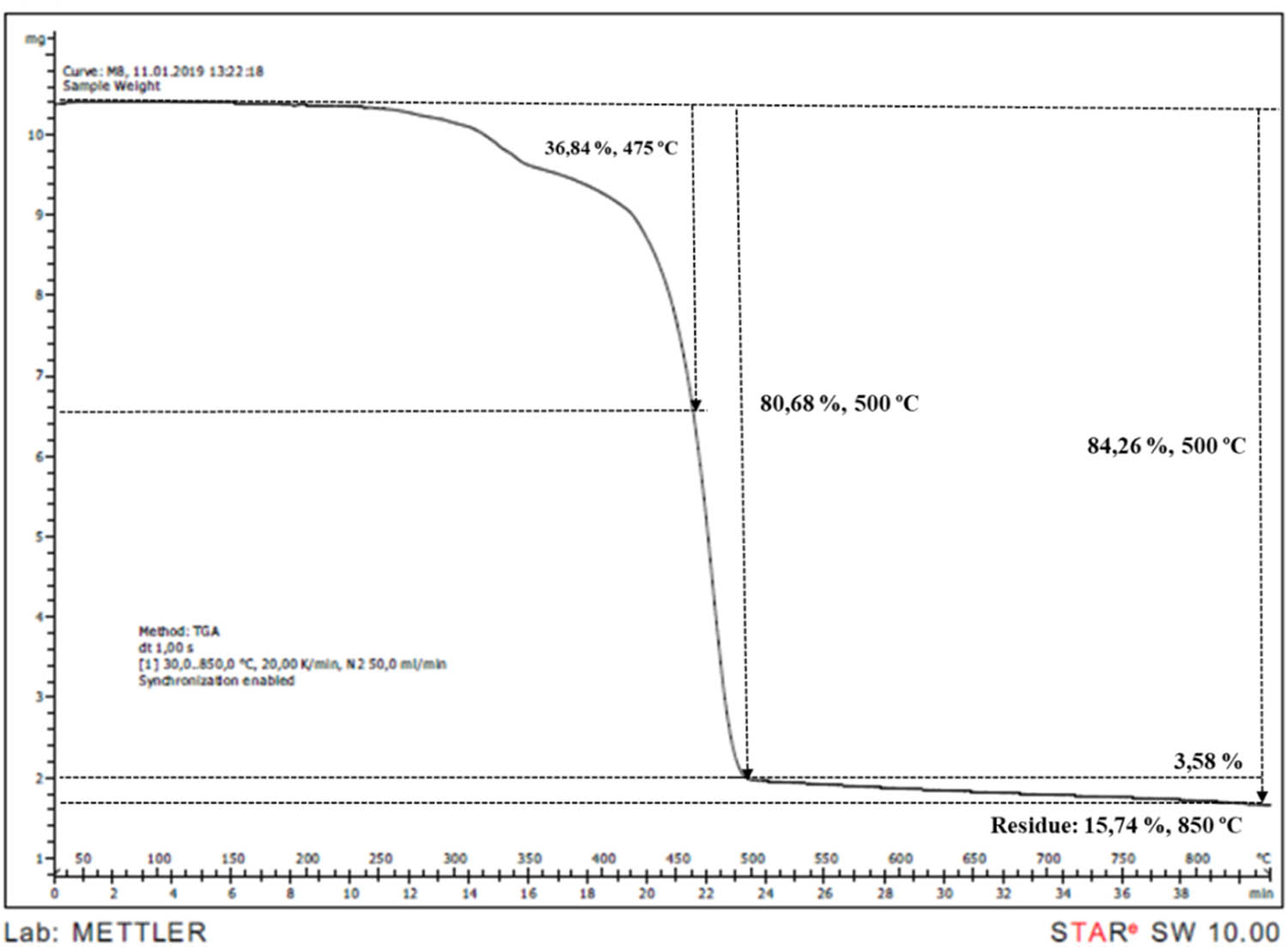
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR22/M8 sample.
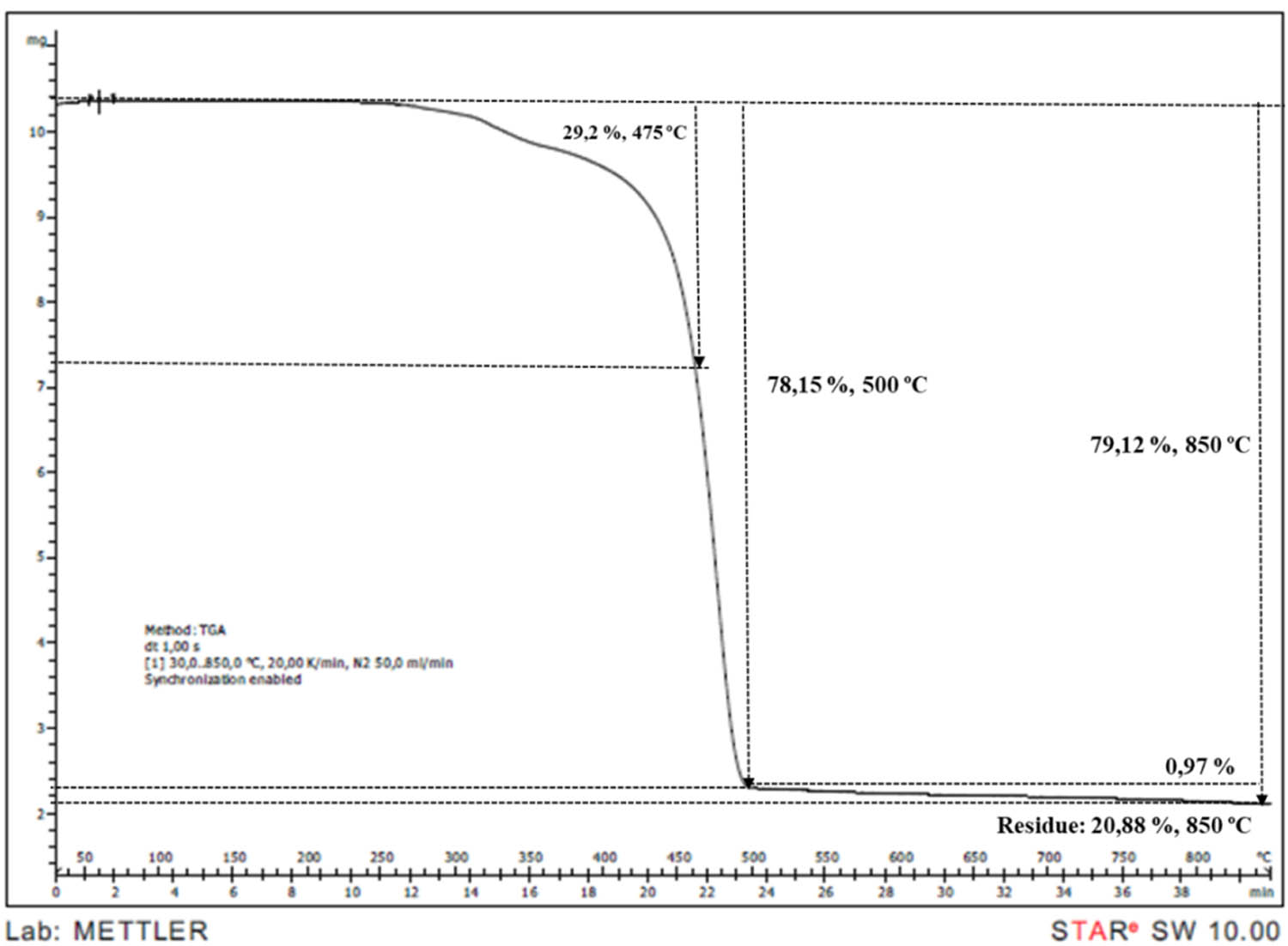
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR15/M15 sample.
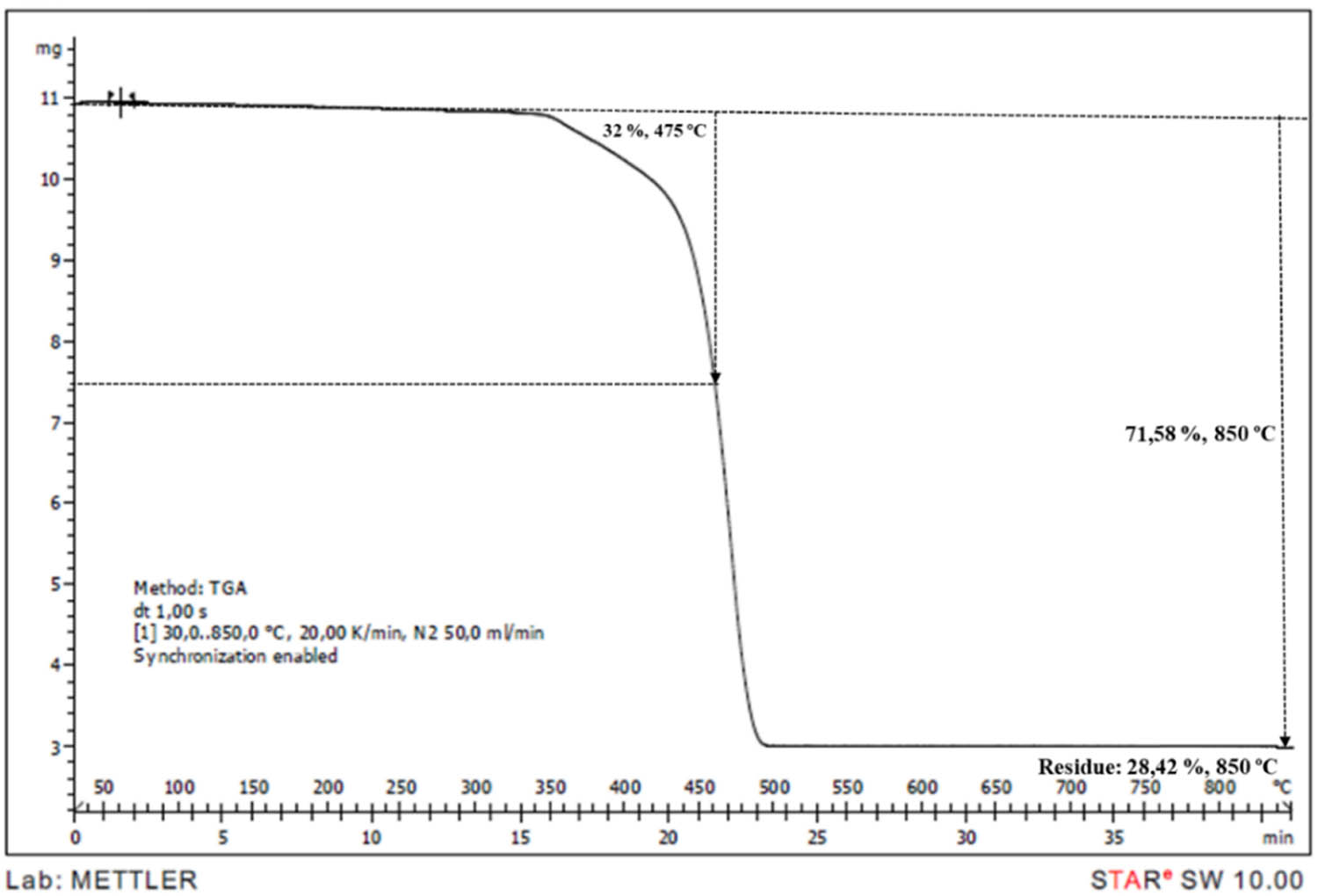
TGA thermogram of PP/IFR0/M30 sample.
3.6 Flame retardancy properties
Flame retardancy properties of PP composites were investigated by LOI, glow wire flammability temperature (GWT), and UL 94 vertical flammability test methods.
3.6.1 LOI
The LOI test method determines the minimum concentration of oxygen in a flowing mixture of oxygen and nitrogen that supports combustion of neat PP, IFR-filled PP, and IFR and mica-filled PP compounds. LOI value of neat PP is around 18.2%. The LOI values of the samples containing both IFR and mica were lower than that of sample containing only IFR, and the LOI of the sample containing 2% mica reached a maximal value of 37.5%. The results indicated that the replacement of IFR with mica at a reasonable amount level can improve the flame retardancy properties of PP matrix. However, PP compounds with increasing mica content levels decrease the LOI values. The main reason for this phenomenon may be that, during the combustion process, higher concentration of filler like mica makes the char too rigid and brittle so LOI values start to decrease when mica content increased in PP compound. Huang and Chen observed the same effect in their work with sepiolite and IFR [20]. The LOI results of neat PPs, IFR, mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds are presented in Figure 15.
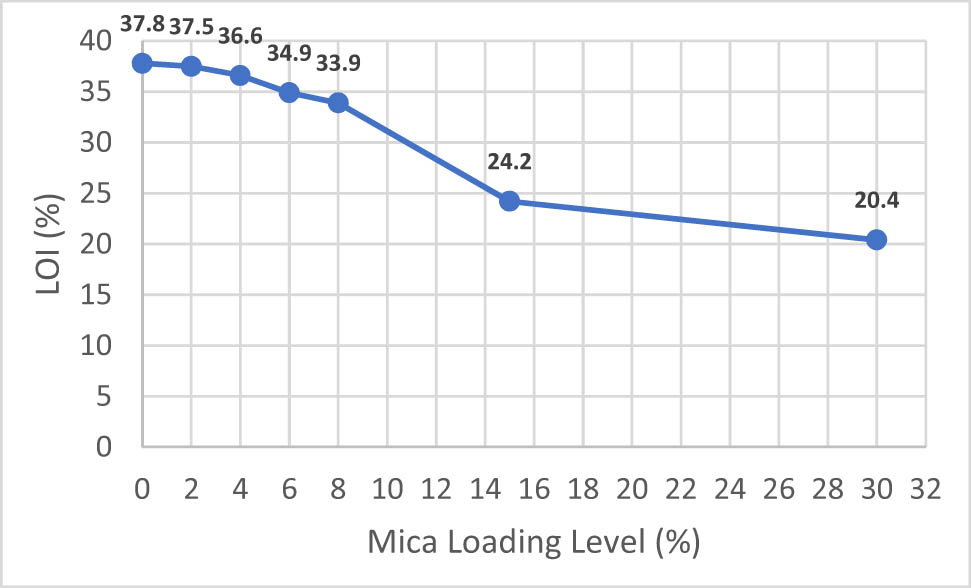
LOI (%) test results.
3.6.2 GWFT
GWT test results provide a way of comparing the ability of materials to extinguish flames and their ability not to produce particles capable of spreading fire. GWT results are given in Table 4.
Glow wire test results of neat PPs, IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds
| Samples | Glow wire temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| 750 | 850 | |
| PP70/IFR30/M0 | There is no flame and no glowing | There is no flame and no glowing |
| PP70/IFR28/M2 | There is no flame and no glowing | There is no flame and no glowing |
| PP70/IFR26/M4 | There is no flame and no glowing | Ignition time is 1 s. Burning time is less than 20 s after removal of the glow wire and the cotton does not ignite |
| PP70/IFR24/M6 | There is no flame and no glowing | Ignition time is 4 s. Burning time is less than 20 s after removal of the glow wire and the cotton does not ignite |
| PP70/IFR22/M8 | There is no flame and no glowing | Ignition time is 2 s. Burning time is less than 30 s after removal of the glow wire and the cotton does not ignite |
| PP70/IFR15/M15 | Ignition time is 15 s. Failed | Failed |
| PP70/IFR0/M30 | Failed | Failed |
The effects of IFR and mica mineral on flame retardancy properties of polymeric composites were investigated. The tests were done at temperatures of 750 and 850°C. IFR decreased burning time of PP compounds significantly. The GWT results indicated that the replacement of IFR with mica at a reasonable amount level (2, 4, 6, and 8 wt%) can improve the flame retardancy properties of PP matrix due to dehydration and better char forming. When mica loading level increased to 15 wt% in PP compounds, flame retardancy properties of PP matrix decreased due to affecting the continuity of IFR system as explained by Huang et al. [20]. According to test results, PP70/IFR0/M30 sample didn’t pass both 750 and 850°C. PP70/IFR0/M30 sample showed that only mica is not effective on flame retardancy on PP matrix.
3.6.3 UL 94 flammability test (Vertical)
The small scale ignition and flame spread of plastic materials are determined by using UL 94 test. The test results are categorized by flammability ratings V0, V1, or V2 in UL 94 vertical flammability test. The highest flame retardant rating is V-0.
V-0: Burning stops within 10 s after two applications of 10 s, each of a flame to a test bar. NO flaming drips are allowed.
V-1: Burning stops within 60 s after two applications of 10 s, each of a flame to a test bar. NO flaming drips are allowed.
V-2: Burning stops within 60 s after two applications of 10 s, each of a flame to a test bar. Flaming drips are allowed.
Horizontal burning (HB): Slow HB on a 3 mm thick specimen with a burning rate is less than 3″/min or stops burning before the 5″ mark. H-B rated materials are considered “self-extinguishing.”
UL-94 test results of the PP/IFR compounds versus mica loading level are given in Table 5. From the Table 5, when the loading level of mica was kept in between 2 and 8 wt% in IFR, samples of the PP/IFR compounds can pass the V-0 rating. Nevertheless, increasing loading level to 15%, it is classified as HB. According to these results, suitable amount of mica can cause the synergistic effect in the PP/IFR/Mica compounds more sufficient.
UL 94 vertical test results of IFR, Mica, and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds
| Samples | UL 94 test-vertical | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | Dripping | Flame rating | |
| PP70/IFR30/M0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | No | V0 |
| PP70/IFR28/M2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | No | V0 |
| PP70/IFR26/M4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | No | V0 |
| PP70/IFR24/M6 | 1 | 7 | 0 | No | V0 |
| PP70/IFR22/M8 | 2 | 6 | 0 | No | V0 |
| PP70/IFR15/M15 | Horizontal burning (HB) | ||||
| PP70/IFR0/M30 | Horizontal burning (HB) | ||||
T1: The burning time with flame of samples after the first ignition.
T2: The burning time with flame of samples after the second ignition.
T3: The burning time without flame of samples after the second ignition.
4 Conclusion
IFR and mica were compounded with PP material in twin-screw extrusion to increase flame retardancy properties of PP. The LOI, UL 94, and GWT results indicated that mica had a significant effect on flame retardancy and LOI value which can reach to 37.5% with loading level of 2 wt% mica at the total amount of flame retardant additives kept constant at 30 wt%. Additionally, the PP/IFR compounds passed UL 94 V0 rating at both 750 and 850°C GWTs and with 2–8 wt% mica loading. According to TGA analyses, the results showed that mica improved the thermal stability of PP/IFR compounds and also promoted the formation of char layer. When mica mineral was added to PP without IFR system, it has no effect on flame retardancy properties of PP. In terms of mechanical properties, increasing the amount of mica mineral content in PP compounds increases the elastic modulus. Tensile strength value of PP homopolymer decreased when IFR and mica mineral were added to the system. No selective difference is observed on tensile strength values of only IFR and IFR/Mica-filled PP compounds. As a result, 30 wt% IFR PP compound and PP70/IFR28/M2, PP70/IFR26/M4, PP70/IFR24/M6 samples have similar properties in terms of mechanical and flame retardancy properties. Therefore, mica content can be used up to 6 wt% in PP compound with IFR material.
-
Funding information: The authors received no external funding.
-
Author contributions: All authors contributed to this work.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
-
Data availability statement: All data generated during this study are included in this published article.
References
[1] Maier C, Calafut T. Polypropylene: the definitive user’s guide and databook. Norwich, NY: Plastics Design Library; 1998. p. 27–50. ISBN 9781884207587.10.1016/B978-188420758-7.50008-4Search in Google Scholar
[2] Troitzsch J. Plastics flammability handbook: principles, regulations, testing, and approval. Munich: Hanser Publications; 2004. p. 3–150. ISBN 9781569903568.10.3139/9783446436695Search in Google Scholar
[3] Url-1. http://www.cefic-efra.org (accessed at 02.12.2011).10.1016/S0969-4765(11)70136-9Search in Google Scholar
[4] Wilkie CA, Morgan AB. Fire retardancy of polymeric materials. Boca Raton, FL, USA: RC Press Taylor & Francis Group; 2010. p. 1–15. ISBN 978-1-4200-8399-6.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Ribeiro S, Cescon L, Riberio R. Effect of clay minerals structure on the polymer flame retardancy intumescent process. Appl Clay Sci. 2018;161:301–9.10.1016/j.clay.2018.04.037Search in Google Scholar
[6] Rothon RN. Particulate fillers for polymers. Shrewsbury: Rapra Technology Ltd.; 2002. Vol. 9. p. 10–7. ISBN 9781847350329.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Verbeek J, Christopher M. Mica reinforced polypropylene composites. Polym Compos. 2012;121:800. 10.1002/9783527645213.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Sheng H, Fei C, Junguo L, Qiang S, Lianmeng Z. Influencing mechanism and interaction of muscovite on thermal decomposition of ammonium polyphosphate. J Wuhan Univ Technol Mater Sci Ed. 2016;31:334–9. 10.1007/s11595-016-1372-1.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Zakut M. Effects of Huntite/hydromagnesite on capacity of flame retardancy, mechanical and physical properties of polypropylene. Msc thesis. Istanbul, Turkey: Istanbul Technical University; 2012.Search in Google Scholar
[10] ISO 20753. Plastics – test specimens. Geneva, Switzerland: British Standard/ European Standard/International Organization for Standardization; 2018.Search in Google Scholar
[11] ISO 1183. Methods for determining density of non-cellular plastics. Geneva, Switzerland: British Standard/European Standard/International Organization for Standardization; 1999.Search in Google Scholar
[12] ISO 1133. Determination of the melt flow rate of thermoplastics. Geneva, Switzerland: British Standard/European Standard/International Organization for Standardization; 2005.Search in Google Scholar
[13] ISO 527. Determination of tensile properties. Geneva, Switzerland: British Standard/ European Standard/International Organization for Standardization; 1993.Search in Google Scholar
[14] ISO 180. Plastics, determination of izod impact strength of rigid materials. Geneva, Switzerland: British Standard/European Standard/International Organization for Standardization; 2000.Search in Google Scholar
[15] ASTM D2863. Standard test method for measuring the minimum oxygen concentration to support candle-like combustion of plastics (Oxygen index). United State: ASTM Internatıonal; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[16] ASTM D6194. Standard test method for glow wire ignition of materials. United State: ASTM Internatıonal; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[17] ASTM D3801. Standard test method for measuring the comparative burning characteristics of solid plastics in a verticel position. United State: ASTM Internatıonal; 2010.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Liang J, Li F, Feng J. Mechanical properties and morphology of intumescent flame retardant filled polypropylene composites. Polym Adv Technol. 2015 Mar 1;121:800. 10.1002/pat.3262.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Liang J, Jang Q. Mechanical, thermal and flow properties of HDPE-mica composites. J Thermoplast Comp Mater. 2012 Sep;5:371. 10.1177/08927057074592.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Huang N, Chen ZJ, Wang JQ, Wie P. Synergistic effects of sepiolite on intumescent flame retardant polypropylene. Exp Polym Lett. 2010;4:743–52. 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2010.90.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Merve Kahraman et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation

