Abstract
In order to decrease the difficulty in trace mercury determination, an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis cells was proposed in this article. The adsorption process was characterized by optical microscopy and SEM. The adsorption mechanism was analyzed by IR. The adsorption performance was studied by measuring the concentration of supernate and calculating the adsorption efficiency. When adsorbing Hg2+, Bacillus subtilis cells gathered and their structure turned coarse. The IR results illustrated that functional groups bound with Hg for complexation during adsorption. Bacillus subtilis completed adsorption for trace Hg2+ in 15 min. The adsorption efficiency was maintained above 80% under low Hg2+ concentrations (<200 µg/L). The proposed study illustrates that Bacillus subtilis cells are highly efficient and easily obtained material for the adsorption of trace mercury, which shows potential to be further used in the pretreatment of trace Hg2+ detection.
1 Introduction
Heavy metal ions are serious pollutants to water environment, which have a critical influence on both aquatic organisms and human beings. Among the heavy metal ions, mercury ion is one of the most toxic ions. Mercury can be absorbed by human body through food chain or drinking water. Due to the difficulty in metabolism by the body, the absorbed mercury ions accumulate continuously [1]. The accumulated mercury ions can cause neuro turbulence and chronic poisoning, leading to the damage of organs and even death [2]. The famous Minamata disease is the result of excessive intake of mercury polluted food and water. Because of mercury ions’ extensive toxicity, the water environment quality standard for mercury ions is critical. In China, the standard limit for Hg2+ in surface water is two orders of magnitude lower than that of Cr6+ and Pb2+, and is three orders of magnitude lower than that of Cu2+ and Zn2+. Thus, sensitive, accurate, fast and convenient detection techniques for mercury are urgently needed [3].
A large number of analysis methods have been employed and studied for the determination of Hg2+, including cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry [4,5], colorimetric methods [6], fluorescence spectrometry [7], inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry [8,9], electrochemical analysis [10,11,12], etc. These techniques have high sensitivity, good selectivity and low detection limit. However, they also show certain limitations, such as the high cost of instruments, the complexity of sample preparation and the complicated test procedures.
To overcome the shortcoming of a single detection technique, the combination of pre-concentration technique with detection technique shows potential in precise determination. Duan et al. [13] coupled solid phase extraction with cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry for Hg determination, which made the established method concise and suitable for routine analysis. Seibert et al. [14] proposed a method for Hg determination using a flow injection system coupled to an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) instrument. The pre-concentration process included the on-line complexation with DDTP, sorption of the Hg complexes and the elution with methanol. The pre-concentration procedure and the analytical conditions can be optimized for the highest sensitivity.
In Hg pre-concentration process, sorption material determines the sensitivity and the selectivity of the method [15]. Various sorption materials have been proposed, including carbon-based materials [16], polymers [17], ionic liquid [18], biosorbents [19], etc. Among the adsorbents, biosorbents attract much attention owing to their numerous functional groups, good yield, small size and low cost [20,21]. Fungus, bacteria, algae and yeast are commonly used biological materials.
Bacterial biosorbents are widely distributed in the environment with a huge variety. They are cost-effective, easily cultivated and environmentally friendly. Besides, bacterial biosorbents also show high adsorption capacity and low toxicity [22,23,24,25]. Cain et al. [26] studied the biosorption of Hg2+ by two strains of cyanobacteria. Both of them showed excellent adsorption performance. Singh et al. [27] investigated the potential of Brevundimonas species IITISM22 to remove mercury. Live biomass of bacterial cells was used and the removal performance was measured. Deniz and Karabulut [28] used a coastal seaweed community composed of Chaetomorpha sp., Polysiphonia sp., Ulva sp. and Cystoseira sp. species as natural biosorbent material for the bioremediation of zinc-containing synthetic wastewater. Ibrahim [29] examined four species of red seaweeds to remove Co(ii), Cd(ii), Cr(iii) and Pb(ii) ions from aqueous solution. Galaxaura oblongata biomass was relatively more efficient to remove metal ions with mean biosorption efficiency of 84%.
Since Hg2+ detection is of great significance and microorganisms are good adsorption materials, it is meaningful to study biosorbents and their adsorption performance to low concentration of Hg2+. In this article, an adsorption method of mercury ions based on Bacillus subtilis was proposed. The adsorption process was characterized by microscopy and SEM. The adsorption mechanism was analyzed based on IR measurements. The adsorption time was optimized and the adsorption performance was tested.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Reagents and apparatus
Bacillus subtilis (No. 1.88) was obtained from the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The standard solution of Hg2+ (100 mg/L) was purchased from China National Research Centre for Certified Reference Material. NaCl, peptone and beef extract were of analytical grade and were used without further purification. Deionized water with the resistivity of 18 MΩ was used throughout the experiment. All the experiments were performed at 25°C without special illustration.
The optical microscopy images were carried out by Olympus BX51 using a 100× Olympus objective. SEM analysis was carried out using S-4800 field emission scanning electron microscope produced by Hitachi (Tokyo, Japan). FT-IR was measured using Spectrum One (PerkinElemer, USA) with diamond ATR accessory. ICP-MS (PerkinElmer ELAN DRC) was used for mercury determination at concentrations lower than 100 ppb. Heavy metal ion solutions with other concentrations were tested by Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) (PerkinElmer Optima 8300).
2.2 Preparation of Bacillus subtilis cells and Hg2+ solutions
B. subtilis cells were used for adsorption. The specific cultivation process of B. subtilis was introduced in ref. [30]. Cells in stationary phase were harvested by centrifuging at 6,000 rpm for 20 min. The cells were added to Hg2+ solutions at the concentration of 0.66 g/L (dry weight).
The standard solution of Hg2+ was diluted to 1–250 µg/L by deionized water. To increase the ion concentration of diluted solutions, NaCl was added at the concentration of 5 g/L, which was exactly the NaCl concentration of microbe’s culture medium. The prepared Hg2+ solutions were poured into conical flasks for subsequent adsorption.
2.3 Adsorption experiment
To observe B. subtilis cells’ response to Hg2+, the centrifuged cells of 0.66 g/L were added into 100 mL, 100 µg/L Hg2+ solution. The mixture was put into a rotating shaker at 150 rpm and 37°C. At each adsorption time (0, 15, 30, 45, 90 and 180 min), 6 mL of the mixture was taken out. The taken mixture was separated by 0.45 mm filter membrane. The filtrate was sent for Hg2+ concentration measurement. The cells on the filter membrane were obtained by washing the filter membrane with deionized water. The collected cells were observed by optical microscopy and SEM. The IR spectrum of the cells before and after adsorption of 15 min for 100 µg/L Hg2+ solution was measured.
For optimization of adsorption time, the adsorption time was subdivided to 0, 3, 7, 11 and 15 min. The adsorption efficiencies at different adsorption time were calculated. The adsorption efficiency
where C 0 is the Hg2+ concentration of solution measured before adsorption. C 1 is the Hg2+ concentration of filtrate measured after adsorption.
To study the adsorption performance, the adsorption efficiencies of cells to solutions with different Hg2+ concentrations were recorded. The parameters of the adsorption experiment are shown in Table 1.
The adsorption experimental parameters
| Item | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Quantity of microorganisms | 0.66 g/L |
| pH | 6 |
| Temperature | 37°C |
| Rotation speed | 150 rpm |
| Base solution | 5 g/L NaCl |
| Separation method after adsorption | 0.45 µm filter membrane |
| Adsorption time (min) | 0, 3, 7, 11, 15, 30, 45, 60, 90 and 180 |
| Concentration of treated Hg2+ solution (µg/L) | 1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 150, 200 and 250 |
3 Results and discussion
3.1 The morphological characteristics of B. subtilis
Microscope (1,000×) was used to observe the morphological characteristics of B. subtilis cells before and after Hg2+ adsorption. B. subtilis cells without adsorption were used as the control group. Cells that adsorbed Hg2+ (100 µg/L) were used as experimental group. The adsorption time was set as 15, 30, 45, 90 and 180 min. Figure 1 shows the microscopic results. Without contacting Hg2+ solution, cells were plump, bacilliform and well-distributed in the observed area (Figure 1(a)). After contacting Hg2+ solution, cells aggregated together. Bacilliform single cells could only be seen at the edge of the aggregates. The volume of the cells was smaller than that in control group. When the adsorption time extended, the aggregation extent was enhanced and the number of cells contained in the aggregates increased (Figure 1(b)–(f)). The microscopic results indicate that Bacillus subtilis cells can respond to Hg2+ solution, which makes the following study applicable.
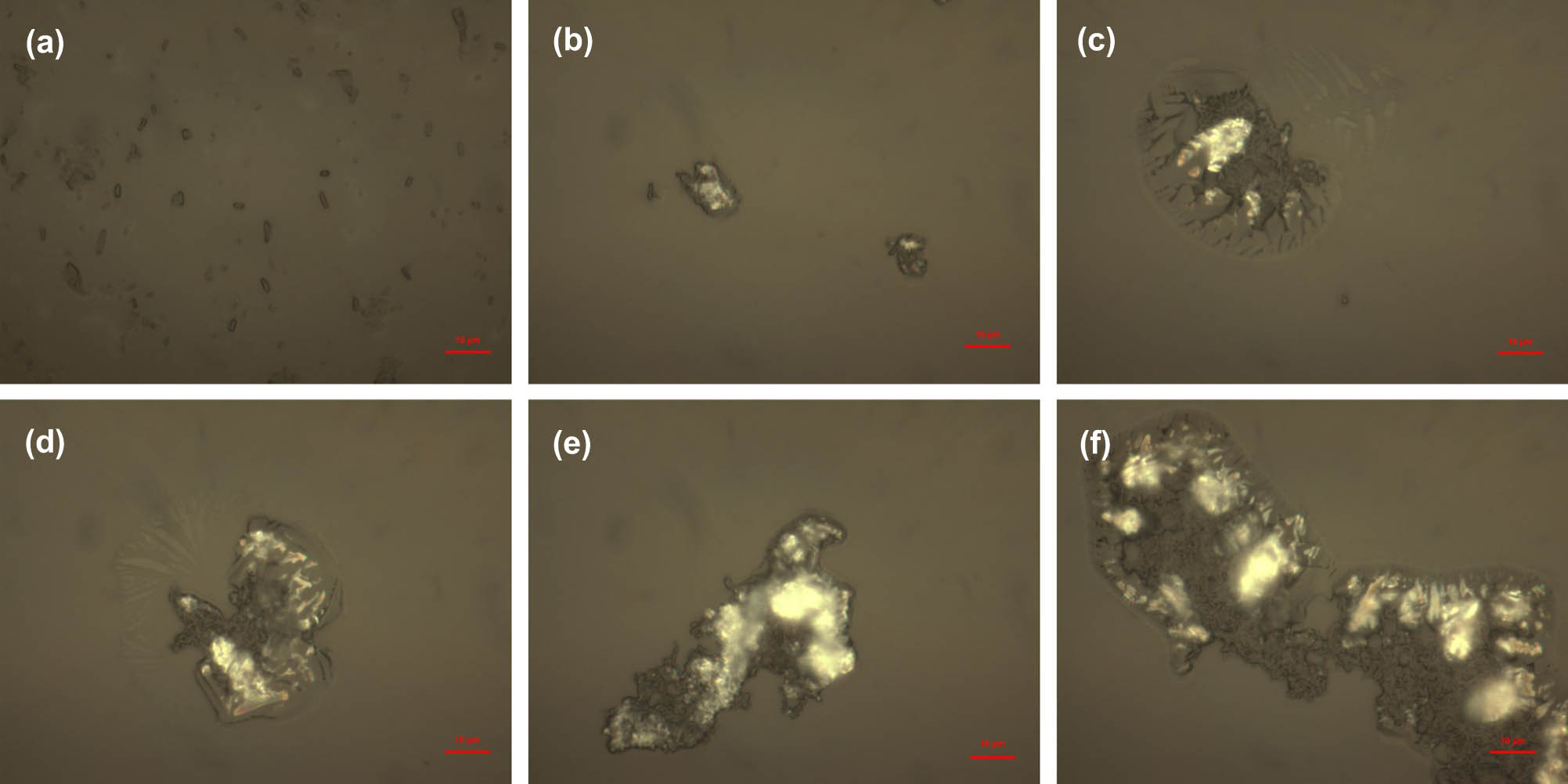
Microscopic images of B. subtilis after different adsorption time, including control group (a), 15 min (b), 30 min (c), 45 min (d), 90 min (e) and 180 min (f).
To further compare the cells’ morphology before and after Hg2+ adsorption, SEM was used for more detailed characterization. The SEM images are shown in Figure 2. The B. subtilis cells without adsorption had a regular edge with a plump spatial structure (Figure 2(a)). The cells were uniformly distributed. After 15 min immersion of the cells in Hg2+ solution, the cells aggregated and the edges of the cells were blurry (Figure 2(b)). The spatial structure was lost and the structure tended to be flat and coarse. When the immersion lasted for 90 min, the cells’ aggregation became more serious. Most cells were in piles, losing their spatial structure. Only a few cells’ edges in the margin of the aggregates could be distinguished. The SEM results illustrate that trace Hg2+ solution can cause microbes’ response and that the responses are enhanced along with the adsorption time.

SEM images of B. subtilis cells after different adsorption time, including control group (a), 15 min (b) and 90 min (c and d).
3.2 The IR characterization of B. subtilis cells
Infrared spectrum analysis can obtain the information of functional groups and chemical bonds, which plays an important role in studying the structure of organics. Besides, the variation in the functional groups can be identified by spectra comparison. The IR spectrum of B. subtilis cells before and after 15 min’s adsorption for 100 µg/L Hg2+ solution are shown in Figure 3. The IR absorption bands and possible corresponding groups are displayed in Table 2.
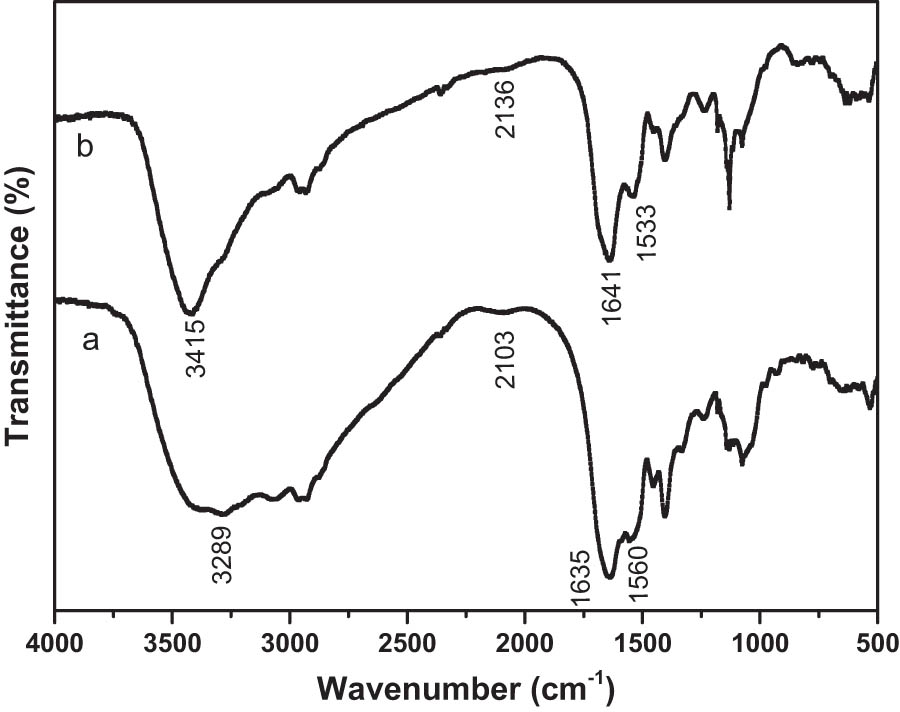
IR spectra of B. subtilis cells before (a) and after (b) adsorption for 100 µg/L Hg2+ solution.
IR absorption bands and possible corresponding groups
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional group |
|---|---|
| 3,289 | –OH |
| 2,103 | –SH |
| 1,635 | –COO and –C═O |
| 1,560 | –NH |
As seen from the IR test results of raw cells before Hg2+ adsorption (Figure 3(a) and Table 2), large amounts of functional groups such as carboxyl, amino and hydroxyl existed in B. subtilis cells, which was in accordance with previous report [31]. After Hg2+ adsorption, the peaks of the spectrum showed some shifts. The peak at 3,289 cm−1 representing the stretching of –OH groups shifted to 3,415 cm−1. It indicated the improved bond length between Hg and bacterial surface. The peak at 1,635 cm−1 corresponding to –COO− vibration shifted to 1,641 cm−1, indicating the functional groups participated in the adsorption. Before adsorption, the peaks in –SH and –NH2 were 2,103 and 1,560 cm−1. After adsorption, the peaks shifted to 2,136 and 1,533 cm−1, respectively. The peak shifts indicated that the functional groups participated in adsorption and bound with Hg. Thus, during adsorption, complexation was considered as the main mechanism. The IR results were similar to previous studies [32,33].
3.3 Optimization of adsorption parameters
Many factors can influence the adsorption capacity of microorganisms, including microbial factors, heavy metal factors and environmental factors. The microbial factors mainly include metabolic capacity, physiological status and existing status. The heavy metal factors mainly include the species, concentration and valence of heavy metal ions. The environmental factors mainly contain pH, temperature and adsorption time. In this study, the adsorption target was Hg2+ and the solution concentration to be treated was at µg/L level. Thus, the heavy metal factors could be ignored. To avoid the influence caused by microbial factors for the adsorption, critical microbial conditions (37°C, 150 rpm, 5 g/L NaCl base solution, and microbes’ concentration of 0.66 g/L) were controlled during the adsorption process. The parameters were in accordance with those used in microbial cultivation process, which better improved the applicability of microorganisms to adsorption environment. Therefore, the optimization of adsorption parameters focused on the selection of adsorption time.
Adsorption time is one of the most important parameters affecting the adsorption capacity. With the increase in adsorption time, the complete sorption phenomenon is completed mainly in two steps [27]. The first step is the quick adsorption period, achieving rapid binding of metal ion to the biosorbent’s surface. The main adsorption mechanism is surface adsorption process, relying on the ion exchange and complexation by the functional groups on the cells’ surface. This period can be completed in a short time and the adsorption proportion can reach about 70%. The second step is the slow adsorption period. Slow intracellular diffusion is observed. Microbes consume energy to transmit heavy metal into the cell, which usually needs several hours. The above conclusion is applicable to the removal of heavy metal ions. To study the adsorption process of low concentration Hg2+, the influence of adsorption time was studied in this article.
The adsorption efficiencies corresponding to different adsorption time were tested and the response curve is shown in Figure 4. In the first 15 min, the adsorption efficiency increased sharply and reached 92.96%. After 15 min, although the adsorption time increased, the adsorption efficiency remained the same as that of 15 min. This adsorption process was different from the reported two-step process. It could be explained by the Hg2+ concentration of trace level. Functional groups on the surface of B. subtilis cells were enough for trace concentration adsorption, through which the achieved adsorption efficiency could be above 90% in 15 min. Under this circumstance, there was no need for the second stage and the adsorption could be completed quickly and efficiently. In the subsequent experiments, 15 min was used as the adsorption time.

The optimization of adsorption time by the adsorption efficiency.
3.4 The performance of adsorption
Adsorption efficiency is a significant characteristic for evaluating adsorption performance. The higher the adsorption efficiency is, the better the performance of adsorption is. Considering the subsequent accurate detection, another important requirement is that the adsorption efficiency should be stable. Only with stable adsorption efficiency, a trace Hg2+ concentration can uniquely correspond to a high Hg2+ concentration after pre-concentration. This uniqueness guarantees the accuracy of the subsequent detection. Thus, the adsorption efficiency of solutions with different Hg2+ concentrations was studied and the result is shown in Figure 5. Hg2+ solutions of 1–250 µg/L were prepared for adsorption. After 15 min adsorption, 0.45 µm filter membrane was used for the separation of the cells and the supernate. The Hg2+ concentration of the supernate was measured and the adsorption efficiency was calculated. As seen from Figure 5, the adsorption efficiency decreased with the increase of Hg2+ concentration. When the Hg2+ concentration was lower than 200 µg/L, the adsorption efficiency remained above 80% and the efficiency differences between different Hg2+ concentrations were small. However, when the Hg2+ concentration was higher than 250 µg/L, the adsorption efficiency dropped obviously, indicating that the functional sites on cell surface were not enough for Hg2+. Therefore, under the experimental conditions used in this article, effective adsorption can be achieved for Hg2+ solution with the concentration lower than 200 µg/L, which satisfies the requirement of trace Hg2+ adsorption.
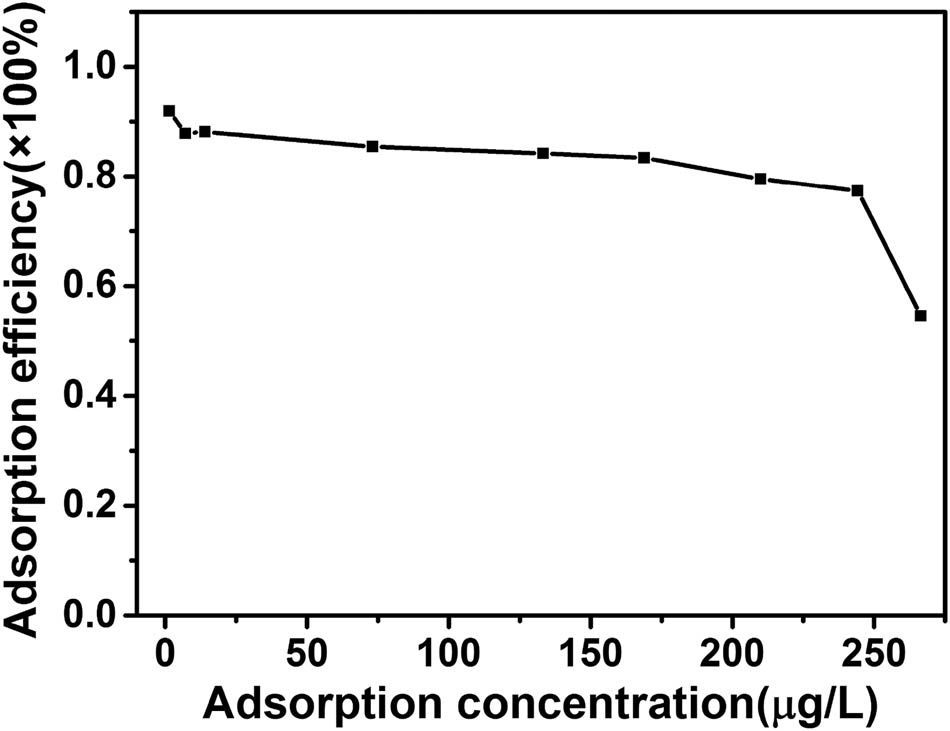
The adsorption efficiency response curve to different Hg2+ concentrations.
4 Conclusion
Mercury is extremely toxic and its standard limit is at a trace level. Since Hg2+ detection is of great importance and microorganisms are good adsorption materials, it is meaningful to study biosorbents and their adsorption performance to low concentration of Hg2+. Thus, an adsorption method of trace mercury based on B. subtilis was proposed in this article. The adsorption process was characterized. The adsorption mechanism was analyzed and the adsorption performance was studied. B. subtilis cells gathered and their structure turned coarse after Hg2+ adsorption. The IR test illustrated that complexation of functional groups with Hg2+ was the main adsorption mechanism. The adsorption for trace Hg2+ could be completed in 15 min. The adsorption efficiency can be maintained above 80% for solutions with low Hg2+ concentrations (<200 µg/L). The proposed research provides an adsorption means for trace Hg2+, which is promising in the coupling with the detection method for accurate and sensitive detection of trace Hg2+.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61901476).
-
Author contributions: Y.L. – investigation, methodology and formal analysis; S.X. – conceptualization and supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the article.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
-
Data availability statement: The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
References
[1] Kumar N, Hu Y, Singh S, Mizaikoff B. Emerging biosensor platforms for the assessment of water-borne pathogens. Analyst. 2018;143:359–73.10.1039/C7AN00983FSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Kumari S, Jamwal R, Mishra N, Singh DK. Recent developments in environmental mercury bioremediation and its toxicity: a review. environ. nanotechnol. Monit Manage. 2020;13:100503.10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100283Search in Google Scholar
[3] Suherman AL, Tanner EE, Compton RG. Recent developments in inorganic Hg2+ detection by voltammetry. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 2017;94:161–72.10.1016/j.trac.2017.07.020Search in Google Scholar
[4] López Guerrero MM, Siles Cordero MT, Vereda Alonso E, García de Torres A, Cano Pavón JM. Cold vapour generation electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry and solid phase extraction based on a new nanosorbent for sensitive Hg determination in environmental samples (sea water and river water). Microchem J. 2017;132:274–9.10.1016/j.microc.2017.02.012Search in Google Scholar
[5] Kamyabi MA, Aghaei A. A simple and selective approach for determination of trace Hg(II) using electromembrane extraction followed by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta, Part B. 2017;128:17–21.10.1016/j.sab.2016.12.007Search in Google Scholar
[6] Zhang H, Ren Q, Mohd S, Yang C, Li J, Pei Y, et al. Early-warning and semi-quantitative colorimetric detection of Hg(II) with lysine-bis-Schiff base cellulose membranes designed by simple interfacial covalent bonding. Sens Actuators, B. 2021;346:130435.10.1016/j.snb.2021.130435Search in Google Scholar
[7] Hu J, Wang D, Dai L, Shen G, Qiu J. Application of fluorescent biosensors in the detection of Hg(II) based on T-Hg(II)-T base pairs. Microchem J. 2020;159:105562.10.1016/j.microc.2020.105562Search in Google Scholar
[8] Chen Y, He M, Chen B, Hu B. Thiol-grafted magnetic polymer for preconcentration of Cd, Hg, Pb from environmental water followed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry detection. Spectrochim Acta, Part B. 2021;177:106071.10.1016/j.sab.2021.106071Search in Google Scholar
[9] Saint’Pierre TD, Rocha RCC, Duyck CB. Determination of Hg in water associate to crude oil production by electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchem J. 2013;109(7):41–5.10.1016/j.microc.2012.05.005Search in Google Scholar
[10] Niu B, Yao B, Zhu M, Guo H, Ying S, Chen Z. Carbon paste electrode modified with fern leave-like MIL-47(as) for electrochemical simultaneous detection of Pb(ii), Cu(ii) and Hg(ii). J Electroanal Chem. 2021;886:115121.10.1016/j.jelechem.2021.115121Search in Google Scholar
[11] Sengupta P, Pramanik K, Sarkar P. Simultaneous detection of trace Pb(ii), Cd(ii) and Hg(ii) by anodic stripping analyses with glassy carbon electrode modified by solid phase synthesized iron-aluminate nano particles. Sens Actuators, B. 2021;329:129052.10.1016/j.snb.2020.129052Search in Google Scholar
[12] Bansoda BK, Kumarb T, Thakurc R, Ranac S, Singh I. A review on various electrochemical techniques for heavy metal ions detection with different sensing platforms. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:443–55.10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.031Search in Google Scholar
[13] Duan T, Song X, Xu J, Guo P, Chen H, Li H. Determination of Hg(ii) in waters by on-line preconcentration using Cyanex 923 as a sorbent – cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta, Part B. 2006;61:1069–73.10.1016/j.sab.2006.09.005Search in Google Scholar
[14] Seibert EL, Dressler VL, Pozebon D, Curtius AJ. Determination of Hg in seawater by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after on-line pre-concentration. Spectrochim Acta, Part B. 2001;56:1963–71.10.1016/S0584-8547(01)00334-2Search in Google Scholar
[15] Llompart M, Celeiro M, Garcia-Jares C, Dagnac T. Environmental applications of solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2019;112:1–12.10.1016/j.trac.2018.12.020Search in Google Scholar
[16] Duval B, Gredilla A, Vallejuelo SFO, Tessier E, Amouroux D, Diego A. A simple determination of trace mercury concentrations in natural waters using dispersive micro-solid phase extraction preconcentration based on functionalized graphene nanosheets. Microchem J. 2020;154:104549.10.1016/j.microc.2019.104549Search in Google Scholar
[17] Jia X, Zhao J, Ren H, Wang J, Hong Z, Zhang X. Zwitterion-functionalized polymer microspheres-based solid phase extraction method on-line combined with HPLC-ICP-MS for mercury speciation. Talanta. 2019;196:592–9.10.1016/j.talanta.2019.01.013Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Li Z, Xia S, Wang J, Bian C, Tong J. Determination of trace mercury in water based on N-octylpyridiniumionic liquids preconcentration and stripping voltammetry. J Hazard Mater. 2016;301:206–13.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.061Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Ozdemir S, Kılınç E, Sen F, Soylak M. Development of Armillae mellea immobilized nanodiamond for the preconcentrations of Cr(iii), Hg(ii) and Zn(ii). Anal Biochem. 2021;617:114122.10.1016/j.ab.2021.114122Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Vijayaraghavan K, Yun YS. Bacterial biosorbents and biosorption. Biotechnol Adv. 2008;26:266–91.10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.02.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Kamyabi MA, Kazemi D, Bikas R, Soleymani-Bonoti F. Investigation of the Hg(ii) biosorption from wastewater by using garlic plant and differential pulse voltammetry. Anal Biochem. 2021;627:114263.10.1016/j.ab.2021.114263Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Qin H, Hu T, Zhai Y, Lu N, Aliyeva J. The improved methods of heavy metals removal by biosorbents: a review. Environ Pollut. 2020;258:1–16.10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113777Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Beni AA, Esmaeili A. Biosorption, an efficient method for removing heavy metals from industrial effluents: a review. Environ Technol Innovat. 2020;17:100503.10.1016/j.eti.2019.100503Search in Google Scholar
[24] Gabr RM, Hassan SHA, Shoreit AAM. Biosorption of lead and nickel by living and non-living cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, ASU 6a. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad. 2008;62(2):195–203.10.1016/j.ibiod.2008.01.008Search in Google Scholar
[25] Javaid A, Bajwa R, Shafique U, Anwar J. Removal of heavy metals by adsorption on Pleurotus ostreatus. Biomass Bioenergy. 2011;35(5):1675–82.10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.12.035Search in Google Scholar
[26] Cain A, Vannela R, Woo LK. Cyanobacteria as a biosorbent for mercuric ion. Bioresour Technol . 2008;99:6578–86.10.1016/j.biortech.2007.11.034Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Singh S, Kumar V, Gupta P, Ray M, Kumar A. The synergy of mercury biosorption through Brevundimonas sp. IITISM22: kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamic modeling. J Hazard Mater. 2021;415:125653.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125653Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Deniza F, Karabulut A. Biosorption of heavy metal ions by chemically modified biomass of coastal seaweed community: studies on phycoremediation system modeling and design. Ecol Eng. 2017;106:101–8.10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.05.024Search in Google Scholar
[29] Ibrahim WM. Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by red macroalgae. J Hazard Mater. 2011;192:1827–35.10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.019Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Li Y, Sun J, Wang J, Bian C, Tong J, Li Y, et al. A single-layer structured microbial sensor for fast detection of biochemical oxygen demand. Biochem Eng J. 2016;112:219–25.10.1016/j.bej.2016.04.021Search in Google Scholar
[31] Bai J, Yao H, Fan F, Lin M, Zhang L, Ding H, et al. Biosorption of uranium by chemically modified Rhodotorula glutinis. J Environ Radioact. 2010;101(11):969–73.10.1016/j.jenvrad.2010.07.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Rezaei H. Biosorption of chromium by using Spirulina sp. Arab J Chem. 2016;9(6):846–53.10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.11.008Search in Google Scholar
[33] Long J, Li H, Jiang D, Luo D, Chen Y, Xia J, et al. Biosorption of strontium(ii) from aqueous solutions by Bacillus cereus isolated from strontium hyperaccumulator Andropogon gayanus. Process Saf Environ Prot. 2017;111:23–30.10.1016/j.psep.2017.06.010Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Yijin Li and Shanhong Xia, published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation

