Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
-
Mohammed Hawash
, Nidal Jaradat
Abstract
The current study aimed to design and synthesize a novel series of fluorophenyl-isoxazole-carboxamide derivatives and evaluate their antiproliferative activities. Anticancer activities of the novel compounds were evaluated by MTS assay against four cancer cell lines, including liver (Hep3B, HepG2), cervical (HeLa), and breast (MCF-7), and α-fetoprotein tumor marker, cell cycle analysis, and annexin V tests. Chemo-informatics analysis showed that all synthesized derivatives 2a–2f obeyed Lipinski’s rule. Compound 2f was the most potent compound against Hep3B and Hep-G2 cancer cell lines with IC50 values of 5.76 and 34.64 µg/mL, respectively. Moreover, compounds 2a–2c and 2e showed potent inhibitory activity against Hep3B with an IC50 value range of 7.66–11.60 µg/mL. Hep3B secretions of α-fetoprotein (α-FP) results showed that compound 2f reduced the secretion of Hep3B to 168.33 ng/mL and compound 2d reduced the secretion to value approximately 598.33 ng/mL, in comparison with untreated cells’ value of 1116.67 ng/mL. Furthermore, cell cycle analysis showed that the 2f compound induced arrest in the G2-M phase in 6.73% of the total cells and that was lower than the activity of the positive control doxorubicin (7.4%). Moreover, 2b and 2f compounds reduced the necrosis rate of Hep3B to 4-folds and shifted the cells to apoptosis.
1 Introduction
Cancer is a disease that has spread in recent decades, and it is one of the main reasons for mortality and death worldwide [1,2,3]. In 2016, about 17.2 million new cases of cancer and 8.9 million deaths were registered around the world. From 2006 to 2016, there was an increase in cancer cases of about 28% [4]. However, in 2018, the number of deaths was estimated at 9.6 million, and according to the World Health Organization (WHO), the distribution of the most common cancers was as follows: breast (2.09 million), lung (2.09 million), colorectal (1.80 million), prostate (1.28 million), and skin cancer (1.04 million) [3].
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fourth most common type of cancer, was one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths in 2020. Approximately 80% of cases found in Asia and the African regions arise due to hepatitis B, C, and chronic alcohol use. The early stage of HCC is asymptomatic and the patients are diagnosed in the advanced stages. Surgical therapy was associated with postoperative complications and a high risk of recurrence. Radio-frequency ablation, microwave ablation, radioembolization, molecular targeted therapies, and chemotherapy remain the alternative ways of treatment [5,6].
Cancer occurs due to the abnormal and uncontrolled proliferation of living cells and damage of the genes that regulate the cell cycle [7]. The cancer therapy protocols include surgery, radiation, immunotherapy, gene therapy, and chemotherapy. Nowadays, chemotherapy is an effective way to stop and eliminate cancer growth. New methods of treatment depend on mechanisms involved in cancer progression [3,8].
Chemotherapy has been widely used, particularly against various cancer types [9]. However, many agents were extracts from plants with various pharmacological activities [10,11] and some of them with cytotoxic activity [12]. One of the most extracted compounds, the Combretastatin, was isolated from the African Combretum caffrum plant and it was successfully modified to find new analogs with potent anticancer activity. In recent years, fosbretabulin (combretastatin A-4 phosphate) (Figure 1) was approved by the FDA and utilized for the treatment of thyroid cancer [13,14].
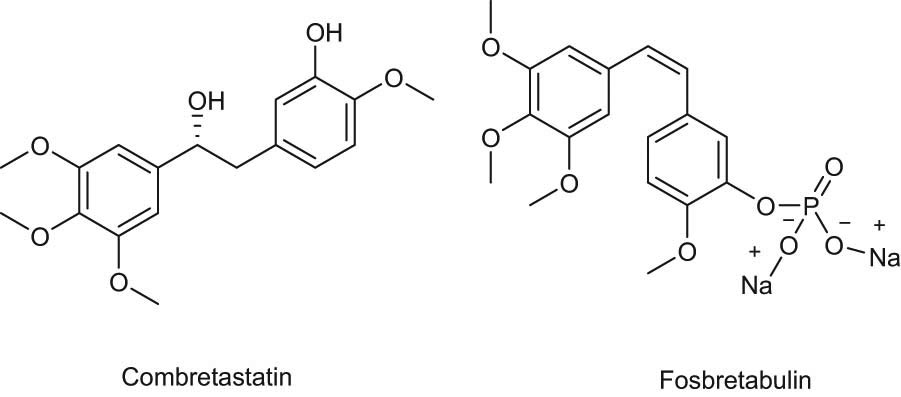
Combretastatin, CA-4P (fosbretabulin) structures.
Many types of research attempt to combine or hybridize various chemical moieties to develop new anticancer agents [15,16]. Many compounds that have halogen-aryl with heterocyclic-carboxamide as a linker with methoxyphenyl were synthesized and evaluated as anticancer agents (st.1, Figure 2), and many other compounds were synthesized, which combined the heterocyclic-carboxamide with the methoxyphenyl moiety (st.2, and st.3; Figure 2) [17]. However, heterocyclic compounds that contain nitrogen with oxygen atoms have diverse medical and biological activities. One of these molecules is the isoxazole ring, which has various biological activities such as anticancer, antituberculosis, insecticidal, antibacterial, and antifungal [5]. Many researchers have focused on this heterocycle (isoxazole) and have synthesized compounds with anticancer activity (st.4, and st.5; Figure 2) [17,18,19,20].
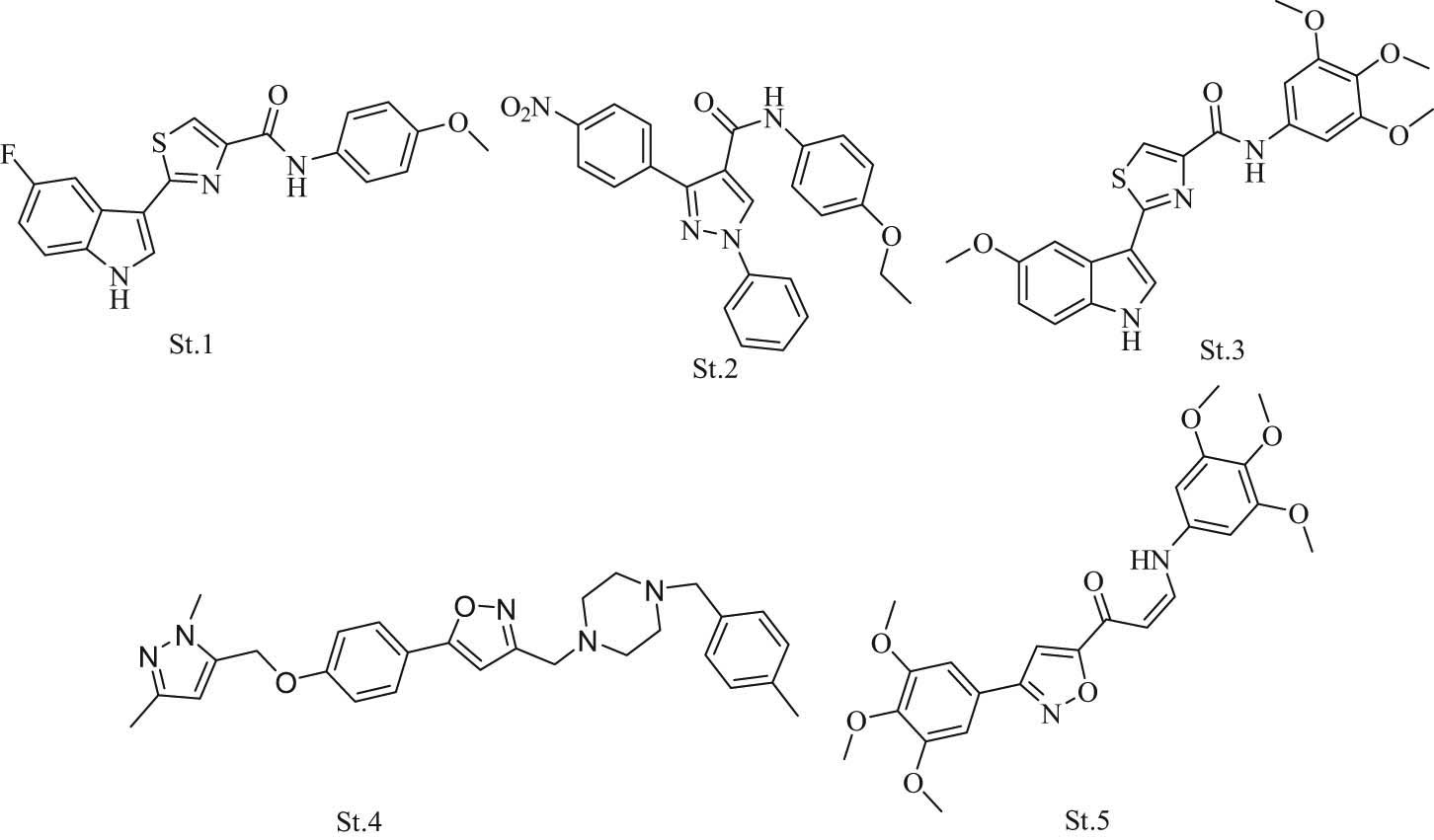
Compounds with fluoro-aryl, heterocyclic-amide, methoxy phenyl, and isoxazole with anticancer activities.
Regarding the mentioned data, the current study aims to synthesize novel fluorophenyl-isoxazole-carboxamide analogs with different substituents and evaluate their anticancer activity on various cancer cell lines including, HeLa, MCF-7, HepG2, and HepB3, utilizing different anticancer tests (α-fetoprotein, cell cycle analysis, and apoptosis/necrosis).
2 Experimental
2.1 Materials and chemical methods
2.1.1 Chemical reagents and instruments
All the used chemical reagents were purchased from Alfa Aesar (Massachusetts, United States) and Sigma-Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany). SMP-II digital melting point apparatus was used without correction to determine the melting points of the synthesized compounds. Proton and carbon nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded in DMSO-d6 and were performed on a Bruker 300 MHz-Avance III High-Performance Digital FT-NMR spectrometer at the Doping and Narcotics Analysis Laboratory in the Faculty of Pharmacy, Anadolu University, Turkey. Tetramethylsilane (TMS) was used as an internal standard. All chemical shifts were recorded as δ (ppm). High-resolution mass spectrometer data (HRMS) were collected using a Waters LCT Premier XE Mass Spectrometer (high sensitivity orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight instrument) using ESI (positive proton) method; the instrument is coupled to an ACQUITY Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography system (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) at Pharmacy Faculty, of Gazi University, Ankara-Turkey.
2.2 Synthesis
2.2.1 The general synthesis procedure of fluoro-isoxazole-carboxamide derivatives (2a–2f)
15 mL of dichloromethane (DCM) and 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxylic acid (1) (1.5 mmol) were added and dissolved, and then 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP; 0.3 mmol) and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylamino propyl) carbodiimide (EDC; 1.8 mmol) were added and were allowed to stir under argon gas in room temperature (25°C) for 30–60 min. The aniline derivative (1.8 mmol) was added and the mixture was allowed to stir for 24–72 h. During the stirring of the reaction, the TLC was used to monitor the reaction process. The reaction mixture was dried under vacuumed pressure. Recrystallization and flash chromatography were used to purify the final product [21].
2.2.1.1 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-N-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)isoxazole-4-carboxamide (2a)
This product was purified by column chromatography n-hexane:ethyl acetate (1:4) solvent system. Solid product, M.P. 156–158°C. Yield 77%; ESI-MS: 387.1365 (100), 388.1396 (20). For C20H19FN2O5. IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1,699 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 10.42 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.74 (2H, t, J = 7.35 Hz, Ar-H), 7.36 (2H, t, J = 9 Hz, Ar-H), 7.01 (2H, s, Ar-H), 3.73 (6H, s, O-CH3), 3.61 (3H, s, O-CH3), 2.57 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 170.51 (Carbonyl carbone), 165.23, 161.96, 160.15, 159.83, 153.21, 135.17, 130.65, 130.54, 116.61, 116.32, 97.82 (aromatic carbone), 60.55 & 56.16 (methoxy carbone), 12.47 (alphatic carbone).
2.2.1.2 N-(4-(tert-Butyl)phenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide (2b)
This product was purified by column chromatography DCM:ethyl acetate solvent system (3:2). Solid product, M.P. 169–171°C. Yield 66%; ESI-MS: 353.1665 (100), 354.1721 (20). For C20H21FN2O2. IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1699.19 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 10.41 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.72–7.77 (2H, m, Ar-H), 7.54 (2H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar-H), 7.31–7.37 (4H, m, Ar-H), 2.56 (3H, s, CH3), 1.25 (9H, s, –C–(CH3)3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 170.43 (carbonyl carbone), 165.20, 161.92, 160.12, 159.77, 146.96, 139.41, 136.45, 130.59, 130.47, 125.91, 124.98, 119.91, 116.58, 116.29, 113.71 (aromatic carbone), 31.61 & 12.39 (alphatic carbone).
2.2.1.3 N-(4-Chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide (2c)
This product was purified by column chromatography n-hexane:ethyl acetate solvent system (3:2). Solid product, M.P. 202−204°C. Yield 82%; ESI-MS: 391.0850 (100), 393.0853 (33). For C19H16ClFN2O4. IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1,716 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 9.30 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.83 (1H, s, Ar-H), 7.75 (2H, t, J = 7 Hz, Ar-H), 7.39 (2H, t, J = 9 Hz, Ar-H), 7.15 (1H, s, Ar-H), 3.78 (3H, s, O-CH3), 3.66 (3H, s, O-CH3), 2.65 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 165.35 (carbonyl carbone), 159.90, 148.53, 131.31, 131.99, 126.44, 124.81, 116.86, 116.61, 116.32, 113.81, 112.81, 112.86, 108.18 (aromatic carbone), 55.93 (methoxy carbone), 12.79 (alphatic carbone).
2.2.1.4 N-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide (2d)
This product was purified by column chromatography DCM:ethyl acetate solvent system (3:2) and then by recrystallization acetone:water system. Solid product, M.P. 135–137°C, Yield 91%; ESI-MS: 357.1251 (100), 358.1292 (20). For C19H17FN2O4. IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1699.16 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 10.42 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.73 (2H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar-H), 7.35 (2H, t, J = 9 Hz, Ar-H), 6.86 (2H, d, J = 1.8 Hz, Ar-H), 6.28 (1H, t, J = 2.1 Hz, Ar-H), 3.71 (6H, s, O-CH3), 2.56 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 170.60 (carbonyl carbone), 165.24, 161.96, 160.97, 159.84, 140.64, 130.64, 130.53, 124.98, 116.62, 116.33, 113.67, 98.74, 96.43 (aromatic carbone), 55.62 & 55.59 (methoxy carbone), 12.47 (alphatic carbone).
2.2.1.5 N-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide (2e)
This product was purified by column chromatography DCM:ethyl acetate solvent system (2.5:2.5). Solid product, M.P. 171–172.5°C. Yield 90%; ESI-MS: 357.1252 (100), 358.1289 (20). For C19H17FN2O4. IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1,683 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 10.33 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.75 (2H, t, J = 7 Hz, Ar-H), 7.31–7.38 (3H, m, Ar-H), 7.13 (1H, dd, J = 8.7, 2.4 Hz, Ar-H), 6.91 (1H, d, J = 8.7 Hz, Ar-H), 3.72 (6H, s, O-CH3), 2.57 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 170.39 (carbonyl carbone), 165.22, 159.88, 159.82, 148.96, 145.89, 132.54, 130.65, 130.53, 116.59, 116.30, 112.37, 112.13, 105.10 (aromatic carbone), 56.14, 55.82 (methoxy carbone), 12.45 (alphatic carbone).
2.2.1.6 3-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-N-phenylisoxazole-4-carboxamide (2f)
This product was purified by column chromatography DCM:ethyl acetate solvent system (3.5:1.5). Solid product, M.P. 149−150.5°C. Yield 89%; IR (FTIR/FTNIR-ATR): 1,684 cm−1 amide carbonyl (C═O). 1H NMR (DMSO-d6) δ: 10.47 (1H, s, amide NH), 7.73−7.77 (2H, m, Ar-H), 7.62 (2H, d, J = 7.5 Hz, Ar-H), 7.32−7.38 (4H, m, Ar-H), 7.11 (1H, t, J = 7.2 Hz, Ar-H), 2.58 (3H, s, CH3). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6) δ ppm: 170.55 (carbonyl carbone), 165.21, 161.94, 160.92, 159.82, 139.01, 130.63, 130.52, 129.29, 124.96, 124.57, 120.20, 116.58, 116.29, 113.67, 99.97 (aromatic carbone), 12.44 (alphatic carbone).
2.3 Chemo-informatics properties of synthesized compounds
Regarding the basis of Lipinski’s rule of five (RO5) and chemo-informatics properties, the synthesized compounds were evaluated and multiple online servers were employed, such as Molsoft (http://www.molsoft.com/) and Molinspiration (http://www.molinspiration.com/), to predict the bioactivity score and molecular properties of newly designed compounds.
2.4 Biological methods
Cell culture, MTS assay, apoptosis, α-fetoprotein, cell cycle, and flow cytometry.
HCC (Hep3B and HepG2), cervical adenocarcinoma (HeLa), and breast carcinoma (MCF7) were used as cancer cell lines which were cultured in RPMI-1640 media and accomplished with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% l-glutamine, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin antibiotics. Then, the cells were matured in a moist atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C. In a 96-well plate, the cells were seeded at 2.6 × 104 cells/well. After 72 h, the cells were confluent and media was changed and then the cells were incubated with various concentrations (500, 100, 50, 10, and 1 µg/mL) of the evaluated compounds (2a–2f) for 24 h. The viability of cells was assessed by Cell Tilter 96® Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation (MTS) Assay regarding the manufacturer’s procedures (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI). However, at the end of the treatment, about 20 μL/100 μL of MTS solution/media was added to each well, and for 2 h, they were incubated at 37°C. Finally, the absorbance was measured at 490 nm [22].
DMEM was applied to culture Hep3B, using a serum of 10% fetal bovine and we detect tumor activity by using α-FP (α-fetoprotein) as a marker. We indicate Hep3B cell by smearing HBsAg on its surface (Water et al., 1998). Hep3B was incubated with each compound in 10 µl/mL for 24 h. After that, a commercially obtainable ELISA kit from R & D Systems, Inc., USA, was used to assess the level of α-FP in the medium, then harvested, and trypsinized the Hep3B cells (0.05% trypsin/0.53 Mm EDTA); after that, was washed and finally analyzed for cell cycle and apoptosis by the mechanism of flow cytometry.
After Hep3B cells were harvested, they were adjusted to 106/mL buffer (in saline containing 1% albumin: the biological industries, Israel) for 10 min to found out their purity, which has staining properties, considering they were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. After that, for 20 min, cells were permeabilized with 0.1% saponin in PBS, then, for 30 min, stained using antihuman HBsAg monoclonal antibody (R&D system, USA), all at room temperature. After that, according to manufacture direction, we made apoptosis and viability measurements, by staining fragmented DNA using propidium-iodide PI, while annexin V-conjugated to FITC to stain phosphatidylserine (R&D systems, Minneapolis, Mn) [23].
Annexin-V (+) and propidium-iodide (−) define apoptosis, while annexin-V (−) and propidium-iodide (−) indicate the presence of viable cell. In each experimental test, unstained controls were used, such as FMO and IgG isotypes. Propidium-iodide was utilized to analyze the cell cycle by quantitation of the contents of DNA. Seventy percent of cold ethanol at 40 C was added to fixed Hep3B for 30 min at least, then the cell was washed 2 times using PBS. Finally, discard the supernatant after Rotate at 2,000 rpm. To make sure that DNA was exclusively stained, we treated the cells with ribonuclease (50 mcg of 100 mcg/mL RNase), and then 5 mcL of 50 mcg propidium-iodide/100 mL was applied to stain them; after that flow cytometer was used as an analyzer (Becton-Dickinson LSR 11, Immunofluorometry systems, Mountain View, CA).
According to the manufacturer’s procedures, the apoptosis and viability analyses were done, and the used staining was the phosphatidylserine staining by annexin V-conjugated to FITC and propidium-iodide staining of DNA fragments (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). Viable cells were specified as negative for both annexin-V and propidium-iodide (−), while the apoptosis was specified as negative for propidium-iodide (−) and as positive for annexin-V (+). In each experimental tuning, unstained controls were used, such as those mentioned before (FMO and IgG isotype) [24].
Cell cycle test was processed by using propidium-iodide to quantitate the DNA contents. The Hep3B cells were settled in cold 70% of ethanol for at least 30 min at 4°C and then the cells were washed twice in PBS. Spin at 2,000 rpm and the supernatant was discarded. To be sure that just DNA is stained, the treatment with ribonuclease (50 μL of 100 μg/mL RNase) was performed on the cells, and then stained with 5 μL of 50 μg of propidium-iodide/100 mL, and by the flow cytometer (Becton-Dickinson LSR II, Immunofluorometry systems, Mountain View, CA), was measured [24].
Hep3B, HeLa, and MCF7 cancer cell lines were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium and supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 1% l-glutamine, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C. The cells were seeded at 2.6 × 104 cells/well in a 96-well plate. After 72 h, the cells were confluent; the medium was changed and cells were incubated with various concentrations (500, 100, 50, 10, and 1 µg/mL) of the synthesized compounds for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed with the Cell Tilter 96® Aqueous One Solution Cell Proliferation (MTS) assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI). Briefly, at the end of the treatment, 20 μL of MTS solution per 100 μL of the medium was added to each well and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The absorbance was measured at 490 nm [25].
-
Ethical approval: The conducted research is not related to either human or animal use.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Chemistry
The synthesis of novel fluorophenyl-isoxazole-carboxamide derivatives (2a–2f) was outlined in Scheme 1. The coupling reaction to form the fluorophenyl-isoxazole-carboxamide compounds 2a–2f was afforded by using EDCI and DMAP as activating agent and covalent nucleophilic catalysts, respectively. After the coupling step, they were reacted with the aniline derivatives [26], EDCI (1-ethyl-3-(30-dimethylamino)carbodiimide, and are usually used for peptide or amide coupling, and there is no need for additional amine. The carbodiimide reacts with the COOH (carboxylic acid) to form the anhydride mixed with O-acylisourea; the produced intermediate directly reacts with the aniline or amine derivatives to produce the desired final amide product as well as urea as side-product [27]. The synthesis of these derivatives was confirmed HRMS, the ppm values for all compounds were less than 2.8, the difference between the calculated mass and the founded mass for all compounds was less than 0.0011 g/mol, for example, compound 2a’s calculated mass was 387.1356 g/mol in comparison with founded mass 387.1265 g/mol. Further, they were purified by column chromatography using different solvent systems (n-hexane: ethyl acetate, and dichloromethane: ethyl acetate). The 1H-NMR peaks confirmed the synthesis of these products. A singlet peak of one proton for N–H amide in the range of 9.30−10.47 ppm was observed in each compound. Multiple signals in the aromatic region were observed, and singlet peaks integrated for 3 protons were observed around 2.60 ppm which refers to the methyl group on the isoxazole ring. The 13C-NMR spectrum showed a C signal of carbonyl around 170.5 ppm, and at 12.5 ppm, the signal of aliphatic carbon methyl.
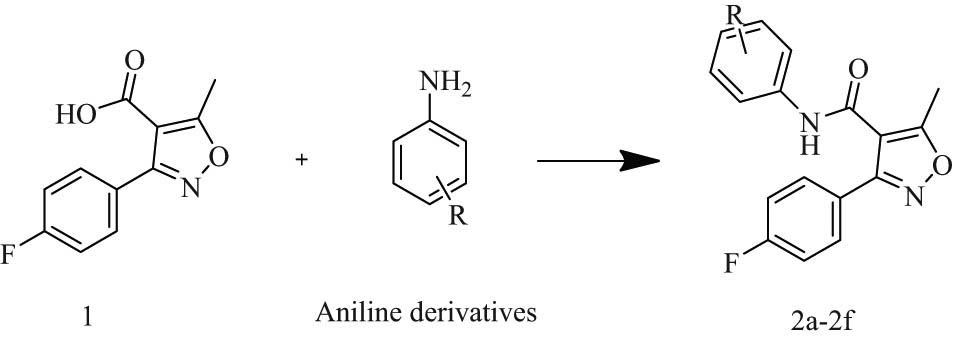
1+ aniline derivatives stirred in 16 mL DCM, then DMAP and EDC were added under inert gas and stirred for 24–48 h.
3.2 LO5 and chemo-informatics properties of synthesized compounds (2a–2f)
The predicted chemo-informatic characteristics were processed by computational tools. Results showed that synthesized compounds 2a–2f have excellent predicted values regarding the molecular weight (g/mol), hydrogen bond acceptor and donor (HBA & HBD, respectively), partition coefficient (log P), the polar surface area (PSA; A2), and molar volume (M.V.; A3). Moreover, the RO5 analysis depicted that almost all synthesized compounds, 2a–2f, obey this rule and possess excellent values regarding the standard values (Table 1) [28]. Our predicted data showed that all synthesized compounds were within the standard range, which showed their good oral bioavailability character. However, drug score parameter was used to evaluate the synthesized compounds according to their hydrogen bonding properties, molecule size, hydrophobicity, flexibility, and electronic distribution and the results showed that all the synthesized structures showed excellent drug score values (0.45–0.95), which represents its better drug-likeness behavior and may be assumed as drug candidate agents against their targets. The overall predicted values of all synthesized compounds are listed in Table 1.
Chemo-informatics properties of synthesized compounds 2a–2f
| Properties | 2a | 2b | 2c | 2d | 2e | 2f | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M.Wt (g/mol) | 386.13 | 352.16 | 390.08 | 356.12 | 356.12 | 296.10 | <500 |
| HBA | 7 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | <10 |
| HBD | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | <5 |
| log P | 2.84 | 5.08 | 3.89 | 3.54 | 2.87 | 3.15 | <5 |
| PSA (A2) | 68.27 | 45.29 | 59.85 | 60.38 | 60.55 | 45.29 | <89 |
| nrotb | 6 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | <10 |
| Drug score | 0.95 | 0.67 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 0.46 | 0.85 | 0.0−2.0 |
3.3 Biological evaluations
3.3.1 Cytotoxic evaluation of the compounds 2a–2f
The MTS test was utilized on MCF-7, HeLa, Hep3B, and HepG2 cancer cell lines to assess the cytotoxicity of the produced new compounds. As shown in Table 2, five concentrations were used (500, 100, 50, 10, and 1 µg/mL). Based on the results shown in Table 2, the compound 2f showed the most potent activity on Hep3B and HepG2 cancer cell lines, with IC50 values of 5.76 and 34.64 µg/mL, respectively, while compounds 2a−2c and 2e showed IC50 values below 11.6 µg/mL against the Hep3B cancer cell line. However, compounds 2b−2e showed moderate activities against HepG2 with IC50 values in the range of 38.8−48.5 µg/mL. In contrast, our synthesized compounds showed weak or negligible activities against HeLa and MCF7 cancer cell lines with IC50 values over 51 µg/mL. Previously, our research group was synthesized in a similar series of chlorophenyl isoxazole derivatives, and the halogen (Cl) was on the ortho position on the phenyl ring; the most active compound was 3-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-5-methylisoxazole-4-carboxamide against Hep3B with IC50 value of 23 µg/mL [21]. However, in this current series, the same compound with fluorophenyl showed better activities against Hep3B with IC50 7.66 µg/mL, as well as almost all of these new series compounds were more potent than the previous work.
IC50 of fluorophenyl-isoxazole-carboxamide compounds and doxorubicin on different cancer cells (Hep3B, HepG2, Hela, and MCF-7)

|
IC50 (µg/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | R group | Hep 3B | HepG2 | HeLa | MCF-7 |
| 2a |

|
11.6 ± 1.4 | >100 | 59.48 ± 2.1 | >100 |
| 2b |

|
9.58 ± 1.2 | 41.53 ± 2.3 | >100 | >100 |
| 2c |

|
8.54 ± 1.7 | 38.85 ± 2.6 | 61.99 ± 2.7 | 81.96 ± 3.1 |
| 2d |

|
89.12 ± 3.6 | 48.50 ± 3.5 | >100 | >100 |
| 2e |

|
7.66 ± 1.2 | 44.98 ± 2.1 | >100 | >100 |
| 2f |

|
5.76 ± 1.1 | 34.64 ± 2.4 | 90.12 ± 2.3 | >100 |
| DOX | 1.21 ± 1.0 | 1.59 ± 0.9 | 0.84 ± 1.1 | 3.19 ± 1.3 | |
Note: P value ≤0.05.
3.3.2 Alpha-fetoprotein results
According to the results of the MTS test and because the synthesized compounds showed potent activities against Hep3B, the inhibitory effects on cell proliferation were used and medium levels of α-FP were evaluated. Actually, all synthesized compounds, except the 2d compound, showed a reduction of secretion with values below 598 ng/mL. The compound 2f was the most active compound in the MTS assay and decreased the Hep3B secretions of α-FP to 168.33 ng/mL in comparison with untreated cells with a value of 1116.67 ng/mL. The results showed that the 2f compound has anticancer activity on the Hep3B cancer cell line (Figure 3).
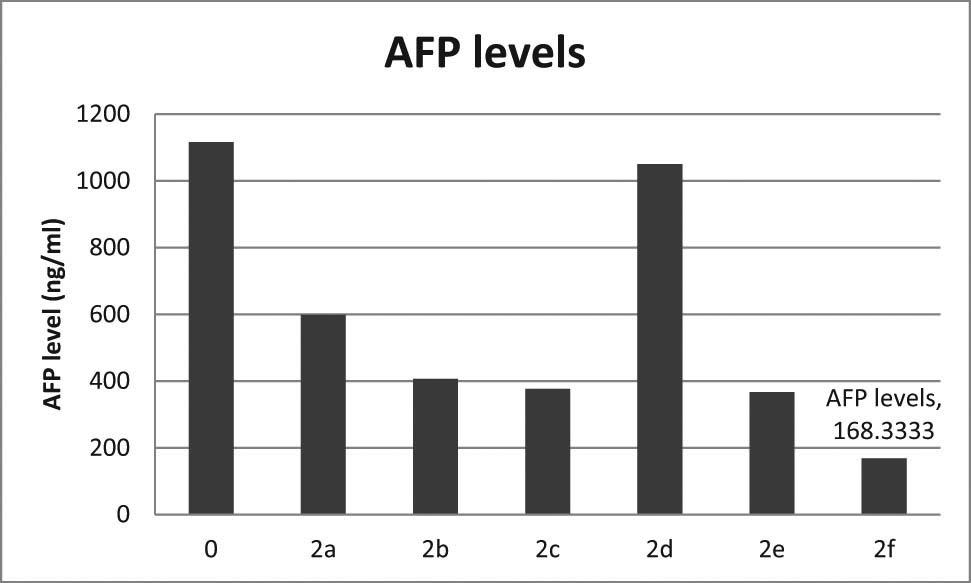
Cell proliferation of the synthesized compound 2a–2f and untreated cells (control).
3.3.3 Cell cycle analysis of Hep3B cells
The flow cytometry analysis was used to verify the ability of 2f and other active compounds (2b, 2c, and 2e) in changing the behaviors for each phase in the cell cycle of Hep3B cell lines. These changes of the normal disturbances in the cell cycle phases were investigated using the boiled solution of the active derivatives to induce cell cycle progression, and they were compared with positive control anticancer drug doxorubicin (Dox). The data in Figure 4 show a similar proportion of cells in the G1 phase following treatment with 2f compound as compared with DOX. The 2f compound showed also similar behaviors as the DOX in reducing proportions of cell percentages in the S, as well as the G2-M phase (P < 0.05). These data showed significant changes in cell cycle parameters in different phases, especially in S and the G2/M phase (mitosis state); these results indicate a significant delay in the mitotic phase and can confirm the potent anticancer activity of the 2f compound.
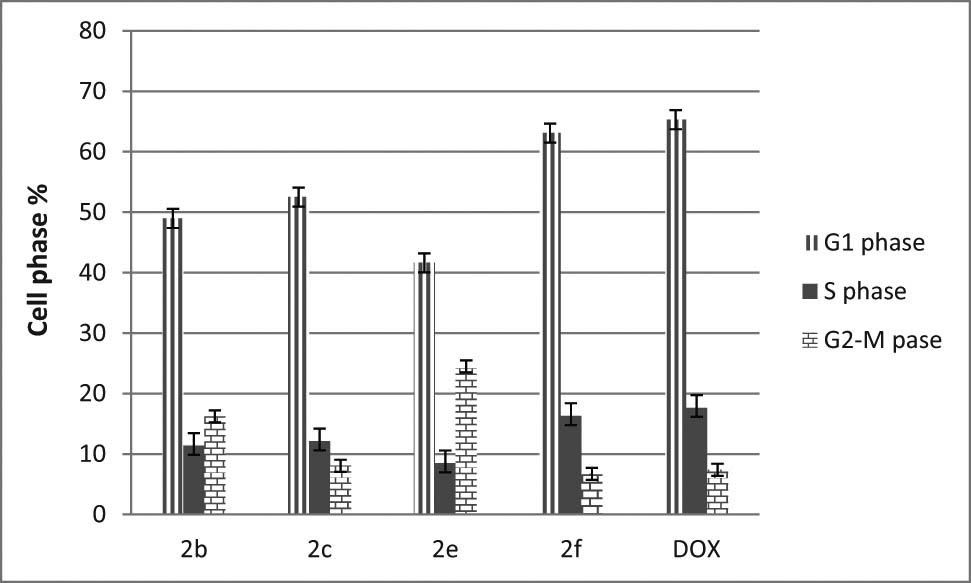
Cell cycle analysis of Hep3B cells after treatment with the synthesized compounds and DOX.
3.3.4 Apoptosis versus necrosis test
The next step of the current study was to determine whether the synthesized compounds induced programmed cell death (apoptosis) and necrosis. Apoptosis was defined as AnnexivV+/PI−, while late apoptotic or necrotic cells were defined as AnnexivV+/PI+. Figure 5 illustrates that Hep3B untreated cells possess a baseline apoptotic cell population of 43.0%, while 2b, 2e, and 2f compounds reduced apoptosis to 8.3, 14.53, and 10.6%, respectively. An annexin-V+/PI+ fraction from 2b, 2e, and 2f compounds significantly increased apoptosis/necrosis cells to 69.67, 67.66, and 66.33%, respectively, as compared with 28.83% in untreated cells. These findings support the 2f compound’s potent anticancer properties by increasing the necrotic activity of annexin-V+/PI+ in the Hep3B cell line, thereby hastening their death.
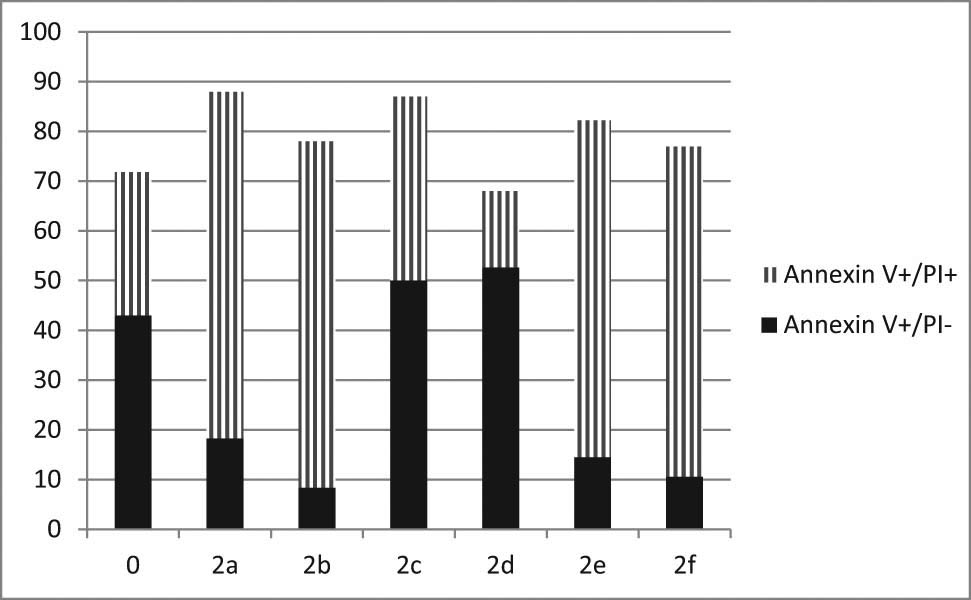
Necrosis versus apoptosis of the synthesized compounds.
4 Conclusion
The synthesized fluoro-isoxazole-carboxamide derivatives showed anticancer activity on the hepatocellular cancer cell lines. Five compounds showed potent activity against the Hep3B cancer cell line, with IC50 values close to the positive control Dox. The most potent compound 2f demonstrated potent anticancer activity in different in vitro tests. The MTS assay showed potent activity against Hep3B, with IC50 around 5 µg/mL, moderate activity against HepG2, with IC50 values around 35 µg/mL, and weak activity against HeLa, with IC50 values around 90 µg/mL. The α-FP tumor marker analysis of 2f derivative decreased the Hep3B secretions to 168 ng/mL compared with 1,116 ng/mL in the negative control (untreated cells), indicating less proliferation and tumorigenicity of Hep3B. For further evaluation of the molecular effects of the novel synthesized compounds, the 2f compound induces cell cycle arrest in the mitotic phase (G2/M) and is similar to Dox positive control values. In future projects, further analogs and derivatives based on the lead compound 2f will be designed and synthesized as promising anticancer agents. More in vivo research is needed to confirm the efficacy and create appropriate pharmaceutical dosage forms for the most active substances.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank An-Najah National University and Anadolu University for their support in chemical analysis.
-
Funding information: Not applicable.
-
Author contributions: M. H designed the compounds and their synthesis. S.I., S.I., & A.A. performed the chemical synthesis. S.L. & T.S. characterized the compounds. M.H., N.J., & M.A. contributed to the writing of the manuscript. M.H., J.A., & A.M. designed the biological experiments. J.A. & A.M. performed the experiments for biological evaluation of the compounds on cancer cells. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Sekhon R, Bhatla N. Gynecological cancer update. Asian J Oncol. 2016;2(2):61.10.4103/2454-6798.197372Search in Google Scholar
[2] Didkowska J, Wojciechowska U, Mańczuk M, Łobaszewski J. Lung cancer epidemiology: contemporary and future challenges worldwide. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4(8):1–11.10.21037/atm.2016.03.11Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Hawash M. Highlights on specific biological targets; cyclin-dependent kinases, epidermal growth factor receptors, ras protein, and cancer stem cells in anticancer drug development. Drug Res. 2019;69(09):471–8.10.1055/a-0898-7347Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH, Alam T, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Allen C, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(11):1553–68.10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2706Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Kumar KA, Jayaroopa P. Isoxazoles: molecules with potential medicinal properties. Int J Pharm Chem Biol Sci. 2013;3:294–304.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Vilchez V, Turcios L, Marti F, Gedaly R. Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(2):823.10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.823Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Sherr CJ. Cancer cell cycles. Science. 1996;274(5293):1672–7.10.1126/science.274.5293.1672Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Sysak A, Obmińska-Mrukowicz B. Isoxazole ring as a useful scaffold in a search for new therapeutic agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2017;137:292–309.10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.06.002Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Huang C-Y, Ju D-T, Chang C-F, Reddy PM, Velmurugan BK. A review on the effects of current chemotherapy drugs and natural agents in treating non–small cell lung cancer. Biomedicine. 2017;7(4):12–23.10.1051/bmdcn/2017070423Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Jaradat N, Zaid A, Hussein F, Zaqzouq M, Aljammal H, Ayesh O. Anti-lipase potential of the organic and aqueous extracts of ten traditional edible and medicinal plants in Palestine; a comparison study with orlistat. Medicines. 2017;4(4):89.10.3390/medicines4040089Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Jaradat N, Hawash M, Dass G. Phytochemical analysis, in-vitro anti-proliferative, anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-obesity activities of Rumex rothschildianus Aarons. extracts. BMC Compl Med Ther. 2021;21(1):1–11.10.1186/s12906-021-03282-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Jaradat NA, Al-lahham S, Zaid AN, Hussein F, Issa L, Abualhasan MN, et al. Carlina curetum plant phytoconstituents, enzymes inhibitory and cytotoxic activity on cervical epithelial carcinoma and colon cancer cell lines. Eur J Integr Med. 2019;30:100933.10.1016/j.eujim.2019.100933Search in Google Scholar
[13] Abma E, Daminet S, Smets P, Ni Y, de Rooster H. Combretastatin A4-phosphate and its potential in veterinary oncology. Vet Comp Oncol. 2017;15(1):184–93.10.1111/vco.12150Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Nathan P, Zweifel M, Padhani AR, Koh DM, Ng M, Collins DJ, et al. Phase I trial of combretastatin A4 phosphate (CA4P) in combination with bevacizumab in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(12):1–12.10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3376Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Kamal A, Reddy VS, Shaik AB, Kumar GB, Vishnuvardhan MV, Polepalli S, et al. Synthesis of (Z)-(arylamino)-pyrazolyl/isoxazolyl-2-propenones as tubulin targeting anticancer agents and apoptotic inducers. Org Biomol Chem. 2015;13(11):3416–31.10.1039/C4OB02449DSearch in Google Scholar
[16] Kamal A, Shaik AB, Jain N, Kishor C, Nagabhushana A, Supriya B, et al. Design and synthesis of pyrazole-oxindole conjugates targeting tubulin polymerization as new anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2015;92:501–13.10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.10.077Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Hawash M, Baytas S. Antiproliferative activities of some biologically important scaffold. FABAD J Pharm Sci. 2017;43(1):59–77.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Yong J-P, Lu C-Z, Wu X. Potential anticancer agents. I. synthesis of isoxazole moiety containing quinazoline derivatives and preliminarily in vitro anticancer activity. Anti Cancer Agents Medi Chem Anti Cancer Agents. 2015;15(1):131–6.10.2174/1871520614666140812105445Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Kumar RN, Dev GJ, Ravikumar N, Swaroop DK, Debanjan B, Bharath G, et al. Synthesis of novel triazole/isoxazole functionalized 7-(trifluoromethyl) pyrido [2, 3-d] pyrimidine derivatives as promising anticancer and antibacterial agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016;26(12):2927–30.10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.038Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Shahinshavali S, Sreenivasulu R, Guttikonda V, Kolli D, Rao M. Synthesis and anticancer activity of amide derivatives of 1, 2-isoxazole combined 1, 2, 4-thiadiazole. Russ J Gen Chem. 2019;89(2):324–9.10.1134/S1070363219020257Search in Google Scholar
[21] Eid AM, Hawash M, Amer J, Jarrar A, Qadri S, Alnimer I, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel isoxazole-amide analogues as anticancer and antioxidant agents. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:633297.10.1155/2021/6633297Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Shi M, Ho K, Keating A, Shoichet MS. Doxorubicin‐conjugated immuno‐nanoparticles for intracellular anticancer drug delivery. Adv Funct Mater. 2009;19(11):1689–96.10.1002/adfm.200801271Search in Google Scholar
[23] Hawash M, Qneibi M, Jaradat N, Abualhasan M, Amer J, Amer EH, et al. The impact of filtered water-pipe smoke on healthy versus cancer cells and their neurodegenerative role on AMPA receptor. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2021;1–9. 10.1080/01480545.2021.1935397.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Waters J, Bailey C, Love C, Thomas H. A study of the antigenicity and immunogenicity of a new hepatitis B vaccine using a panel of monoclonal antibodies. J Med Virol. 1998;54(1):1–6.10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199801)54:1<1::AID-JMV1>3.0.CO;2-BSearch in Google Scholar
[25] Hawash M, Eid AM, Jaradat N, Abualhasan M, Amer J, Naser Zaid A, et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of benzodioxole derivatives as potential anticancer and antioxidant agents. Heterocycl Commun. 2020;26(1):157–67.10.1515/hc-2020-0105Search in Google Scholar
[26] Biava M, Battilocchio C, Poce G, Alfonso S, Consalvi S, Di Capua A, et al. Enhancing the pharmacodynamic profile of a class of selective COX-2 inhibiting nitric oxide donors. Bioorg Med Chem J. 2014;22(2):772–86.10.1016/j.bmc.2013.12.008Search in Google Scholar
[27] Montalbetti, CAGN, Falque, V, Amide. bond formation and peptide coupling. Tetrahedron. 2005;61(46):10827–52.10.1016/j.tet.2005.08.031Search in Google Scholar
[28] Jadhav PB, Yadav AR, Gore MG. Concept of drug likeness in pharmaceutical research. Int J Pharm Biol Sci. 2015;6:142–54.Search in Google Scholar
© 2021 Mohammed Hawash et al., published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation
Articles in the same Issue
- Regular Articles
- Qualitative and semi-quantitative assessment of anthocyanins in Tibetan hulless barley from different geographical locations by UPLC-QTOF-MS and their antioxidant capacities
- Effect of sodium chloride on the expression of genes involved in the salt tolerance of Bacillus sp. strain “SX4” isolated from salinized greenhouse soil
- GC-MS analysis of mango stem bark extracts (Mangifera indica L.), Haden variety. Possible contribution of volatile compounds to its health effects
- Influence of nanoscale-modified apatite-type calcium phosphates on the biofilm formation by pathogenic microorganisms
- Removal of paracetamol from aqueous solution by containment composites
- Investigating a human pesticide intoxication incident: The importance of robust analytical approaches
- Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by chloroform fraction of Juniperus phoenicea and chemical constituents analysis
- Recovery of γ-Fe2O3 from copper ore tailings by magnetization roasting and magnetic separation
- Effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties of blueberry anthocyanins
- Modeling the removal of methylene blue dye using a graphene oxide/TiO2/SiO2 nanocomposite under sunlight irradiation by intelligent system
- Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Cinnamomum cassia essential oil and its application in food preservation
- Full spectrum and genetic algorithm-selected spectrum-based chemometric methods for simultaneous determination of azilsartan medoxomil, chlorthalidone, and azilsartan: Development, validation, and application on commercial dosage form
- Evaluation of the performance of immunoblot and immunodot techniques used to identify autoantibodies in patients with autoimmune diseases
- Computational studies by molecular docking of some antiviral drugs with COVID-19 receptors are an approach to medication for COVID-19
- Synthesis of amides and esters containing furan rings under microwave-assisted conditions
- Simultaneous removal efficiency of H2S and CO2 by high-gravity rotating packed bed: Experiments and simulation
- Design, synthesis, and biological activities of novel thiophene, pyrimidine, pyrazole, pyridine, coumarin and isoxazole: Dydrogesterone derivatives as antitumor agents
- Content and composition analysis of polysaccharides from Blaps rynchopetera and its macrophage phagocytic activity
- A new series of 2,4-thiazolidinediones endowed with potent aldose reductase inhibitory activity
- Assessing encapsulation of curcumin in cocoliposome: In vitro study
- Rare norisodinosterol derivatives from Xenia umbellata: Isolation and anti-proliferative activity
- Comparative study of antioxidant and anticancer activities and HPTLC quantification of rutin in white radish (Raphanus sativus L.) leaves and root extracts grown in Saudi Arabia
- Comparison of adsorption properties of commercial silica and rice husk ash (RHA) silica: A study by NIR spectroscopy
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) as a high-capacity material for next-generation sodium-ion capacitors
- Aroma components of tobacco powder from different producing areas based on gas chromatography ion mobility spectrometry
- The effects of salinity on changes in characteristics of soils collected in a saline region of the Mekong Delta, Vietnam
- Synthesis, properties, and activity of MoVTeNbO catalysts modified by zirconia-pillared clays in oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane
- Synthesis and crystal structure of N,N′-bis(4-chlorophenyl)thiourea N,N-dimethylformamide
- Quantitative analysis of volatile compounds of four Chinese traditional liquors by SPME-GC-MS and determination of total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities
- A novel separation method of the valuable components for activated clay production wastewater
- On ve-degree- and ev-degree-based topological properties of crystallographic structure of cuprite Cu2O
- Antihyperglycemic effect and phytochemical investigation of Rubia cordifolia (Indian Madder) leaves extract
- Microsphere molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for diazepam analysis using itaconic acid as a monomer in propanol
- A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species
- Machine vision-based driving and feedback scheme for digital microfluidics system
- Study on the application of a steam-foam drive profile modification technology for heavy oil reservoir development
- Ni–Ru-containing mixed oxide-based composites as precursors for ethanol steam reforming catalysts: Effect of the synthesis methods on the structural and catalytic properties
- Preparation of composite soybean straw-based materials by LDHs modifying as a solid sorbent for removal of Pb(ii) from water samples
- Synthesis and spectral characterizations of vanadyl(ii) and chromium(iii) mixed ligand complexes containing metformin drug and glycine amino acid
- In vitro evaluation of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic activity isolated from local pickled leaf mustard from Wuwei in Anhui as substitutes for chemical synthetic additives
- Utilization and simulation of innovative new binuclear Co(ii), Ni(ii), Cu(ii), and Zn(ii) diimine Schiff base complexes in sterilization and coronavirus resistance (Covid-19)
- Phosphorylation of Pit-1 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 at serine 126 is associated with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in prolactinomas
- Molecularly imprinted membrane for transport of urea, creatinine, and vitamin B12 as a hemodialysis candidate membrane
- Optimization of Murrayafoline A ethanol extraction process from the roots of Glycosmis stenocarpa, and evaluation of its Tumorigenesis inhibition activity on Hep-G2 cells
- Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode
- Synthesis, chemo-informatics, and anticancer evaluation of fluorophenyl-isoxazole derivatives
- In vitro and in vivo investigation of polypharmacology of propolis extract as anticancer, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and chemical properties
- Topological indices of bipolar fuzzy incidence graph
- Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2–ZnO catalyst and its catalytic synthesis of rosin glycol ester
- Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe3+ and treatment of Hepatitis B
- Investigation of bovine serum albumin aggregation upon exposure to silver(i) and copper(ii) metal ions using Zetasizer
- Discoloration of methylene blue at neutral pH by heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reactions using crystalline and amorphous iron oxides
- Optimized extraction of polyphenols from leaves of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) grown in Lam Dong province, Vietnam, and evaluation of their antioxidant capacity
- Synthesis of novel thiourea-/urea-benzimidazole derivatives as anticancer agents
- Potency and selectivity indices of Myristica fragrans Houtt. mace chloroform extract against non-clinical and clinical human pathogens
- Simple modifications of nicotinic, isonicotinic, and 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acids toward new weapons against plant diseases
- Synthesis, optical and structural characterisation of ZnS nanoparticles derived from Zn(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Presence of short and cyclic peptides in Acacia and Ziziphus honeys may potentiate their medicinal values
- The role of vitamin D deficiency and elevated inflammatory biomarkers as risk factors for the progression of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Quantitative structure–activity relationship study on prolonged anticonvulsant activity of terpene derivatives in pentylenetetrazole test
- GADD45B induced the enhancing of cell viability and proliferation in radiotherapy and increased the radioresistance of HONE1 cells
- Cannabis sativa L. chemical compositions as potential plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidinesynthase enzyme inhibitors: An in silico study for drug development
- Dynamics of λ-cyhalothrin disappearance and expression of selected P450 genes in bees depending on the ambient temperature
- Identification of synthetic cannabinoid methyl 2-{[1-(cyclohexylmethyl)-1H-indol-3-yl] formamido}-3-methylbutanoate using modern mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques
- Study on the speciation of arsenic in the genuine medicinal material honeysuckle
- Two Cu(ii)-based coordination polymers: Crystal structures and treatment activity on periodontitis
- Conversion of furfuryl alcohol to ethyl levulinate in the presence of mesoporous aluminosilicate catalyst
- Review Articles
- Hsien Wu and his major contributions to the chemical era of immunology
- Overview of the major classes of new psychoactive substances, psychoactive effects, analytical determination and conformational analysis of selected illegal drugs
- An overview of persistent organic pollutants along the coastal environment of Kuwait
- Mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced protection in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2: Everything we know so far – A comprehensive review
- Challenge of diabetes mellitus and researchers’ contributions to its control
- Advances in the design and application of transition metal oxide-based supercapacitors
- Color and composition of beauty products formulated with lemongrass essential oil: Cosmetics formulation with lemongrass essential oil
- The structural chemistry of zinc(ii) and nickel(ii) dithiocarbamate complexes
- Bioprospecting for antituberculosis natural products – A review
- Recent progress in direct urea fuel cell
- Rapid Communications
- A comparative morphological study of titanium dioxide surface layer dental implants
- Changes in the antioxidative properties of honeys during their fermentation
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Corrosion study of copper in aqueous sulfuric acid solution in the presence of (2E,5E)-2,5-dibenzylidenecyclopentanone and (2E,5E)-bis[(4-dimethylamino)benzylidene]cyclopentanone: Experimental and theoretical study”
- Erratum to “Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “A nitric oxide-releasing prodrug promotes apoptosis in human renal carcinoma cells: Involvement of reactive oxygen species”
- Special Issue on 3rd IC3PE 2020
- Visible light-responsive photocatalyst of SnO2/rGO prepared using Pometia pinnata leaf extract
- Antihyperglycemic activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urb. leaf ethanol extract SNEDDS in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Selection of oil extraction process from Chlorella species of microalgae by using multi-criteria decision analysis technique for biodiesel production
- Special Issue on the 14th Joint Conference of Chemistry (14JCC)
- Synthesis and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of isatin-pyrrole derivatives against HepG2 cell line
- CO2 gas separation using mixed matrix membranes based on polyethersulfone/MIL-100(Al)
- Effect of synthesis and activation methods on the character of CoMo/ultrastable Y-zeolite catalysts
- Special Issue on Electrochemical Amplified Sensors
- Enhancement of graphene oxide through β-cyclodextrin composite to sensitive analysis of an antidepressant: Sulpiride
- Investigation of the spectroelectrochemical behavior of quercetin isolated from Zanthoxylum bungeanum
- An electrochemical sensor for high sensitive determination of lysozyme based on the aptamer competition approach
- An improved non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor amplified with CuO nanostructures for sensitive determination of uric acid
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 2020
- Fast discrimination of avocado oil for different extracted methods using headspace-gas chromatography-ion mobility spectroscopy with PCA based on volatile organic compounds
- Effect of alkali bases on the synthesis of ZnO quantum dots
- Quality evaluation of Cabernet Sauvignon wines in different vintages by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2019)
- Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, thermal modification, and application
- Electrochemical determination of atenolol and propranolol using a carbon paste sensor modified with natural ilmenite
- Special Issue on the Conference of Energy, Fuels, Environment 2020
- Assessment of the mercury contamination of landfilled and recovered foundry waste – a case study
- Primary energy consumption in selected EU Countries compared to global trends
- Modified TDAE petroleum plasticiser
- Use of glycerol waste in lactic acid bacteria metabolism for the production of lactic acid: State of the art in Poland
- Topical Issue on Applications of Mathematics in Chemistry
- Theoretical study of energy, inertia and nullity of phenylene and anthracene
- Banhatti, revan and hyper-indices of silicon carbide Si2C3-III[n,m]
- Topical Issue on Agriculture
- Occurrence of mycotoxins in selected agricultural and commercial products available in eastern Poland
- Special Issue on Ethnobotanical, Phytochemical and Biological Investigation of Medicinal Plants
- Acute and repeated dose 60-day oral toxicity assessment of chemically characterized Berberis hispanica Boiss. and Reut in Wistar rats
- Phytochemical profile, in vitro antioxidant, and anti-protein denaturation activities of Curcuma longa L. rhizome and leaves
- Antiplasmodial potential of Eucalyptus obliqua leaf methanolic extract against Plasmodium vivax: An in vitro study
- Prunus padus L. bark as a functional promoting component in functional herbal infusions – cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial effects
- Molecular and docking studies of tetramethoxy hydroxyflavone compound from Artemisia absinthium against carcinogens found in cigarette smoke
- Special Issue on the Joint Science Congress of Materials and Polymers (ISCMP 2020)
- Preparation of cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.) essential oil loaded poly(lactic acid) nanofibers
- Influence of mica mineral on flame retardancy and mechanical properties of intumescent flame retardant polypropylene composites
- Production and characterization of thermoplastic elastomer foams based on the styrene–ethylene–butylene–styrene (SEBS) rubber and thermoplastic material
- Special Issue on Applied Chemistry in Agriculture and Food Science
- Impact of essential oils on the development of pathogens of the Fusarium genus and germination parameters of selected crops
- Yield, volume, quality, and reduction of biotic stress influenced by titanium application in oilseed rape, winter wheat, and maize cultivations
- Influence of potato variety on polyphenol profile composition and glycoalcaloid contents of potato juice
- Carryover effect of direct-fed microbial supplementation and early weaning on the growth performance and carcass characteristics of growing Najdi lambs
- Special Issue on Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (ABB 2021)
- The electrochemical redox mechanism and antioxidant activity of polyphenolic compounds based on inlaid multi-walled carbon nanotubes-modified graphite electrode
- Study of an adsorption method for trace mercury based on Bacillus subtilis
- Special Issue on The 1st Malaysia International Conference on Nanotechnology & Catalysis (MICNC2021)
- Mitigating membrane biofouling in biofuel cell system – A review
- Mechanical properties of polymeric biomaterials: Modified ePTFE using gamma irradiation

