Abstract
Liver cirrhosis affects the structures and physiological functions of the intestine. Our previous study revealed that liver injury inhibited 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D (25(OH)-VD). The aim of this study was to investigate the roles and mechanisms of vitamin D in liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal injury. The rat liver cirrhosis model was established through the administration of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) for 8 weeks. Hematoxylin–eosin staining was performed to unveil the intestinal injury induced by liver cirrhosis. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) analysis were used to determine the levels of 25(OH)-VD, vitamin D receptor, Cytochrome P450 24A1 (CYP24A1), and α-defensin 5 (DEFA5) in rat and human serum of liver cirrhosis. Furthermore, liver cirrhosis rats were treated with low-dose (500 IU/kg) and high-dose (2,000 IU/kg) vitamin D intraperitoneally. The expression levels of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway were evaluated by RT-PCR and Western blot. In conclusion, we determined the deficiency of vitamin D and down-regulation of DEFA5 and intestinal damage induced by liver cirrhosis. Moreover, vitamin D effectively inhibited liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Vitamin D might be a promising therapeutic strategy for future treatment of liver-induced intestinal injury.
1 Introduction
Cirrhosis is an advanced stage of liver fibrosis with the development of regenerative nodules of liver parenchyma separated by fibrotic septa with accompanying ascites, renal failure, hepatic encephalopathy, and variceal bleeding [1]. Besides, liver cirrhosis is divided into compensated and decompensated cirrhosis [2]. Patients with compensated cirrhosis may remain free of severe complications for several years, but decompensated cirrhosis has short overall survival [3]. Despite the advances in liver cirrhosis therapeutics, the treatments for cirrhosis still remain challenging. Liver transplantation is a primary intervention of cirrhosis, but the shortage of available donor organs severely restricted the applicability [4]. It has been reported that liver function is closely associated with intestinal barrier and microenvironment [5,6]. The liver–gut axis refers to the bidirectional relationship between the intestinal and the liver. The portal vein directly connects the liver to the intestinal and regulates the transfer of nutrients and microbial components along the liver–gut axis [7,8]. The damage of the intestinal barrier could be found in the animal liver failure model [6], revealing that liver failure may further facilitate the injury of intestinal biological functions.
Vitamin D is a class of fat-soluble vitamins that act a crucial role on intestinal absorption of calcium, phosphate, and other essential biological components [9]. Vitamin D receptor (VDR) is abundantly expressed in the distal ileum, where the Paneth cells are enriched [10]. Previous researches demonstrate that vitamin D is involved with intestinal immune system [11]. And the vitamin D deficiency could deteriorate the intestinal barrier function and dysbiosis [12]. Findings relating the relationship between the vitamin D and the innate defenses against bacterial pathogens have been reported [13]. 25(OH)VD3 could triggered a host-defense response in cattle by up-regulating plenty of β-defensins genes, which suggested that vitamin D acted crucial role in the protection of cattle from bacterial and viral pathogens [13]. In the present study, we found the deficiency of vitamin D and down-regulation of α-defensin 5 (DEFA5) in intestines induced by liver cirrhosis. Therefore, we reasoned that liver cirrhosis inhibited the 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D (25(OH)-VD) in intestines and, thereby, attenuating the secretion of DEFA5 and leading to sustained injury to the intestinal barrier.
Previous reports have demonstrated the protective roles of vitamin D in intestinal structures and biological functions. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of vitamin D on intestinal injury in cirrhosis remain unclear. TLR4 has been involved in the process of intestinal injury, inflammation, and oxidative stress [14]. Previous report indicated that the absence of TLR4 or TLR4-induced signaling attenuated local mucosal damage with significantly decreased cytokine and eicosanoid secretion including PGE2 production, thus promoting intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced damage [15]. Dysregulated intestinal TLR4 activation led to chronic inflammation and intestinal epithelial apoptosis in the setting of necrotizing enterocolitis, which is a key factor of death among preterm infants [16]. In this study, we revealed that vitamin D suppressed liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. The treatment of TLR4 agonist (GSK1795091) and ROS inducer (diallyl tetrasulfide) remarkably reversed the vitamin D-enhanced intestinal protection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals and clinical blood samples
A total of 30 adult male SD rats (200–220 g, 6 weeks old) were obtained from Shanghai Model Organisms Center. We have successfully constructed the liver cirrhosis model using male rats according to a previous report [17]. The same results are expected in female animals.
The clinical characteristics
| Liver cirrhosis group | Control group | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 49.81 ± 1.147, N = 74 | 35.09 ± 1.937, N = 35 |
| ALT (U/L) | 86.10 ± 16.74, N = 69 | 19.23 ± 2.102, N = 35 |
| ALP (U/L) | 157.4 ± 17.67, N = 69 | 61.89 ± 3.705, N = 35 |
| GGT (U/L) | 95.09 ± 18.38, N = 69 | 16.71 ± 1.635, N = 35 |
| TB (μmol/L) | 63.91 ± 14.90, N = 69 | 10.87 ± 0.7275, N = 35 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.477 ± 0.6853, N = 58 | 4.485 ± 0.2247, N = 35 |
| Crea (μmol/L) | 74.24 ± 9.463, N = 58 | 52.44 ± 1.637, N = 35 |
| HA (ng/mL) | 201.8 ± 22.57, N = 57 | N |
| LN (ng/mL) | 95.09 ± 7.023, N = 58 | N |
| PCIII (ng/mL) | 216.8 ± 41.96, N = 58 | N |
| IV-col (ng/mL) | 157.6 ± 21.95, N = 58 | N |
-
Ethics approval and consent to participate: All procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of Chengdu Public Health Clinical Center (Approval No: PJ-K2020-51-01, Chengdu, China). All of the blood samples were collected after written informed consent and the clinical characteristics are listed in Table 1.
2.2 Liver cirrhosis model and vitamin D therapy
Briefly, the rats were treated with CCl4 (Cat No. C07315202, Nanjing Reagent, China) by oral gavage at a dose of 2 mL/kg body weight twice a week for 8 weeks to generate a liver cirrhosis model. The cirrhosis rats were randomly divided into five groups (n = 5 per group). The low-dose vitamin D (VD-L) and high-dose vitamin D (VD-H) rats were injected daily of vitamin D injection (Zhejiang Xianju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Taizhou, China) intraperitoneally [18,19,20]. Besides, GSK1795091 (HY-111792; MedChemExpress, Princeton, NJ, USA) and diallyl tetrasulfide (Dat, ab143603; Abcam, Shanghai, China) were administered by tail vein injection to induce TLR4 and ROS levels, respectively. All rats were allowed free access to water and standard rat chow. Rats were anesthetized with isoflurane inhalation (induction dose of 5% and maintenance dose of 1.5%) and 3 mL of blood collected from the inferior vena cava in an EDTA tube, which was centrifuged at 1,500 rpm for 10 min to get the serum. After sacrificing the rats, the liver and ileum tissues of every rat were clipped and stored at −80℃ for the follow-up experiments.
Control group: Rats received oral administrations of the same volume of saline.
Cirrhosis group: Rats received CCl4 by oral gavage at a dose of 2 mL/kg for 8 weeks.
Cirrhosis + VD-L group: Rats received vitamin D (500 IU/kg) on the fourth week of CCl4 treatment.
Cirrhosis + VD-H group: Rats received vitamin D (2,000 IU/kg) on the fourth week of CCl4 treatment.
Cirrhosis + VD-H + GSK1795091 group: Rats received vitamin D (2,000 IU/kg) and GSK1795091 (20 mg/kg) on the fourth week of CCl4 treatment.
Cirrhosis + VD-H + Dat group: Rats received vitamin D (2,000 IU/kg) and Dat (25 mg/kg) on the fourth week of CCl4 treatment.
2.3 Liver function and histological evaluation
Liver function was assessed by the serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and albumin (ALB). The blood serum samples were obtained and subjected to analysis using an automatic biochemical analyzer (HITACHI 7600, Japan). Moreover, after being fixed with 10% formalin and embedded with paraffin, the liver tissues were cut into 4 µM slices for hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining and Masson staining analyses according to the methods described previously to evaluate the development of liver fibrosis [21]. In addition, the ileum tissues of each group were stained with HE to examine the effect of liver cirrhosis on the intestinal morphological structure. The sections were photographed under a light microscope (Olympus BX51, Japan).
2.4 Immunohistochemistry
The clinical ileum tissues were collected and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Then, the tissues were dehydrated, cleared, and paraffin-embedded. Four-micrometer paraffin sections were incubated with primary antibodies against ZO-1 (dilution ratio 1:1,000, ab221546; Abcam) at 4°C overnight, followed by incubation with goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase (dilution ratio 1:50, A0208; Beyotime, Shanghai, China) for 1 h at room temperature. Subsequently, the slides were stained with DAB and counterstained with hematoxylin for 30 s, followed by conventional treatments. Finally, photographs were photographed under observation by a light microscope (Olympus BX51, Japan).
2.5 Detection of the levels of 25(OH)VD3, VDR, CYP24A1, and DEFA5
Serum 25(OH)VD3 levels were analyzed through enzyme immunoassay using the 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D3 ELISA kit (Cat No. LS-F5643; LifeSpan Biosciences, USA). Serum VDR concentrations were detected using Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay Kit (Cat No. MBS022460; MyBioSource, USA). The levels of CYP24A1 were determined by Cytochrome P450 24A1 (CYP24A1) ELISA kit (Cat No. abx508211; Abbexa, USA). The Defensin 5 (Sandwich ELISA) kit (Cat No. LS-F33773; LifeSpan Biosciences) was applied to measure the levels of DEFA5 in human blood samples. The DEFA5 level of rat intestinal tissues was determined using the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis.
2.6 Measurement of inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress
The levels of inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, CXCL1, IL-1β and TNF-α, in the ileum tissues were determined with ELISA kits (Beyotime). And the catalog numbers were listed as follows: IL-6 (PI335), CXCL1 (PC175), IL-1β (PI303), and TNF-α (PT516). Besides, the oxidative stress markers were detected in the ileum tissues of the rats. Ileum samples were homogenized in lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, and 0.1% SDS, and the supernatants were used for the detection. The malondialdehyde (MDA) content and the activities of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) were measured using MDA, CAT, SOD, and GSH-Px ELISA kits ((Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. And the catalog numbers were listed as follows: MDA (A003-1-2), CAT (A007-2-1), SOD (A001-3-2), and GSH-Px (A005-1-2).
2.7 Western blot
The ileum tissues were lysed in RIPA buffer (Cat No. P0013C; Beyotime) and the total protein concentrations were detected through a BCA kit (Cat No. P0012S; Beyotime). Immunoblotting was carried out as previously reported. Proteins (50 μg/lane) were separated by 15% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels. After blocking the PVDF membrane (Cat No. IPVH00010; Millipore, USA), they were subsequently incubated overnight with primary antibodies against TLR4 (dilution ratio 1:1,000, AF7017; Affinity, China), MyD88 (dilution ratio 1:500, AF5192; Affinity), p-NF-kB (dilution ratio 1:1,000, ab194726; Abcam), NF-kB (dilution ratio 1:1,000, ab16502; Abcam), and GAPDH (dilution ratio 1:3,000, AF7021; Affinity). Then, the membranes were incubated with secondary HRP-conjugated antibodies (dilution ratio 1:3,000, S0001; Affinity) at room temperature for 2 h. The immunoreactive bands were then analyzed using the Western ECL reagent (Cat No. RPN2106V1, GE Healthcare, UK) according to the protocol of the manufacturer.
2.8 RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was isolated by TRIzol reagent (Cat No. 10296010; Invitrogen, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. cDNA was derived from 1 μg RNA using SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase (Cat No.18080044; Invitrogen). Quantitative PCR was performed with an SYBR-Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (Cat No. FSK-101; ToyoBo Life Sciences, Japan) in a CFX Real-Time System (Bio-Rad, Germany). The sequences of primers for DEFA5 were forward, ATCCACTCCTGCTCTCCCTC, and reverse, AGAAAGACACAAGGTACACAGAGT. The sequences of primers for TLR4 were forward, ACTGGGTGAGAAACGAGCTG, and reverse, GTCCACAGCAGAAACCCAGA. The primers for MyD88 were forward, GTTTGTGCTTCCGGGAACAC, and reverse, GCAAAGAGGCCTCCATTCCT. The primers for NF-kB were forward, ACGGTGGGATTGCATTCCAT, and reverse, GCCAAGTGCAAAGGTGTCTG. GAPDH was used as an internal control. The primers for GAPDH were forward, ATGCCATCACTGCCACTCA, and reverse, CCTGCTTCACCACCTTCTTG. The quantification of the relative gene levels was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [22].
2.9 Statistics analysis
All the experiments were repeated at least three times, and the data were represented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). p-Value was calculated by either a two-tailed unpaired Student’s test or one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukeys’s post hoc test. Statistical analysis was carried out by GraphPad prism 7.0 version (GraphPad Software, CA, USA). p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Liver cirrhosis affected the intestinal morphological structure
We established a liver cirrhosis rat model using CCl4 treatment for 8 weeks. The morphological changes were detected through HE and Masson staining. As shown in Figure 1a and b, the results showed that in the control group, the hepatic lobule structure was clear, and hepatic cords were arranged radially around the central veins. However, the liver samples of the cirrhosis group represented the destroyed hepatic lobular structure and remarkable interstitial collagen deposition. Moreover, the data of serum biochemical indicators in rats showed that the levels of ALT, AST, and ALP in rat serum were remarkably increased in the cirrhosis group while the ALB level was lowered compared with the control group (Figure 1c–f). The results indicated that liver cirrhosis rat models were constructed successfully. We next sought to investigate the influence of liver cirrhosis on the structure of intestines using HE staining. As shown in Figure 1g, the control group had normal intestinal morphology. However, the liver cirrhosis group indicated severe intestinal mucosal damage with wider villi spacing and inflammatory cell infiltrations. Furthermore, the result of ZO-1 staining showed a significantly decreased expression of ZO-1 in intestinal tissues of the cirrhosis group compared to the control group (Figure 1h). The results demonstrated that liver cirrhosis triggered gut injury and intestinal barrier disruption.

Liver cirrhosis affected the intestinal morphological structure. The rat liver cirrhosis model was established by CCl4 induction for 8 weeks. Histopathological characteristics in liver tissues with HE staining (a) and Masson Trichrome staining (b) (n = 5). Scale bar = 50 µm. Biochemical analysis of liver function between control and liver cirrhosis group: (c) ALT, (d) AST, (e) ALP, and (f) ALB (n = 5). (g) The histopathological changes in the intestines were evaluated by HE staining to investigate the impact of liver cirrhosis (n = 5). Scale bar = 50 µm. (h) Immunohistochemistry staining was applied to determine the expression of ZO-1. **p < 0.01 in 2-tailed t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
3.2 Liver cirrhosis reduced 25(OH)-VD and decreased the levels of DEFA5 in intestinal tissues
The intestinal epithelium is the main target tissue of the biologically active form of vitamin D-25(OH)-VD3, which regulates intestinal absorption of calcium, phosphate, and other biological effects [23]. 25(OH)-VD3 predominantly acts through the VDR, a nuclear, ligand-dependent transcription factor. 25(OH)-VD3 is inactivated through 24-hydroxylation by mitochondrial 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) to lose its normal physiological functions [24]. We measured the levels of 25(OH)-VD3, VDR, and CYP24A1 in the ileum of rats and the serum of liver cirrhosis patients. As shown in Figure 2a–f, the concentrations of 25(OH)-VD3 (Figure 2a and b) and VDR (Figure 2c and d) were remarkably attenuated in rat and human serum of liver cirrhosis, and in contrast, augmented levels of CYP24A1 (Figure 2e and f) were detected compared with the control group. Enteric defensins are antibacterial peptides secreted by Paneth cells in the small intestine. We further examined the levels of defensin 5 (DEFA5) in rat intestinal tissues using RT-PCR analysis and in human serum of liver cirrhosis using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The results revealed that a down-regulation of DEFA5 was determined in rat intestinal tissues (Figure 2g) and human serum of liver cirrhosis (Figure 2h). To summarize, we hypothesized that liver cirrhosis reduced hepatic 25(OH)-VD and inhibited the levels of DEFA5 in intestinal tissues.

Liver cirrhosis reduced 25(OH)-VD and decreased the levels of DEFA5 in intestinal tissues. The levels of 25(OH)-VD (a and b), VDR (c and d), and 24-hydroxylation by mitochondrial 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) (e and f) of rat and human serum of liver cirrhosis were measured through ELISA. (g and h) The concentrations of defensin 5 (DEFA5) in rat intestinal tissues and human serum of liver cirrhosis were detected using RT-PCR and ELISA, respectively. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 in 2-tailed t-test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
3.3 Vitamin D inhibited liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal pathological injury and inflammation
Based on the above results, we concluded that liver cirrhosis caused severe injury and suppressed the concentrations of 25(OH)VD3 in intestinal tissues. Vitamin D acts a crucial role in safeguarding the intestinal barrier and preventing gastrointestinal mucosal inflammation. Ileum tissues of each group were stained with HE and the results are shown in Figure 3a. The intestinal injury was observed in liver cirrhosis rats with inflammatory cell infiltration and wider villi spacing compared to the control group. Rats with low-dose or high-dose vitamin D administration exhibited improved intestinal integrity. However, the treatment of GSK1795091 and Dat effectively reversed the vitamin D-mediated intestinal repair. Moreover, we next measured the levels of the inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, CXCL1, IL-1β, and TNF-α, in the intestine to examine the role of liver cirrhosis on inflammatory response following vitamin D treatment. As shown in Figure 3b–e, the intestinal secretion levels of IL-6. CXCL1, IL-1β, and TNF-α were obviously increased in the liver cirrhosis group compared with the control group. And the treatment with low-dose or high-dose vitamin D significantly reduced inflammatory cytokine levels in the ileum tissues. Furthermore, the use of GSK1795091 and Dat obviously reversed the vitamin D-mediated inhibited inflammatory response. Hence, the intervention of vitamin D remarkably attenuated the secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by liver cirrhosis.
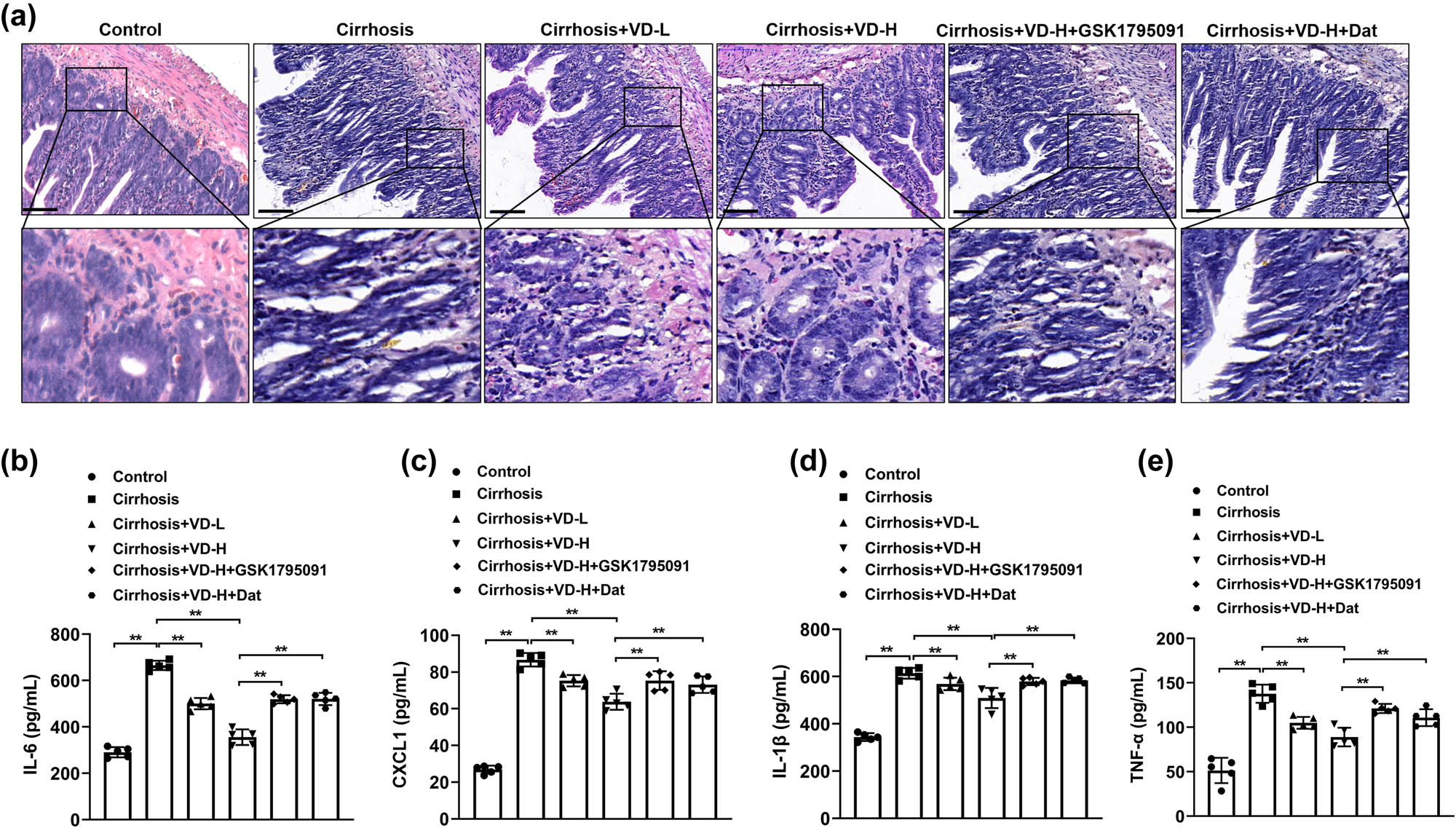
Vitamin D inhibited liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal pathological injury and inflammation. Vitamin D was intraperitoneally administered daily to 100 μL of vitamin D solution at different doses. The ileum tissues of each group were harvested for HE staining (a). n = 5, scale bar = 50 µm. VD-L: low-dose vitamin D group (500 IU/kg); VD-H: high-dose vitamin D group (2,000 IU/kg). The levels of inflammatory cytokines including IL-6 (b), IL-8 (c), IL-1β (d), and TNF-α (e) in the intestinal samples were determined by ELISA (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 in Tukey’s post hoc comparisons test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
3.4 Vitamin D treatment effectively suppressed oxidative stress activated by liver cirrhosis
It has been reported that the regulation of oxidative stress plays crucial roles in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis [25]. The changes in oxidative stress levels influence the microbial environment and the intestinal barrier integrity [26]. In our study, the oxidative damage was evaluated through the levels of CAT, GSH-Px, SOD, and MDA in intestinal tissues using ELISA kits. As shown in Figure 4a–d, the liver cirrhosis resulted in oxidative stress in the ileum tissues, reducing CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD and promoting MDA concentrations compared with the control group. In addition, the treatment of low-dose or high-dose vitamin D effectively inhibited oxidative stress by increasing CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD and attenuating MDA levels compared with the cirrhosis model group. However, the treatment of GSK1795091 and Dat effectively reversed the vitamin D-regulated oxidative stress. Taken together, liver cirrhosis may lead to oxidative stress in intestinal and the treatment of vitamin D significantly protects intestinal from oxidative stress-induced injury.

Vitamin D treatment effectively suppressed oxidative stress activated by liver cirrhosis. The levels of oxidative stress factors including CAT (a), GSH-Px (b), SOD (c), and MDA (d) in intestinal tissues were evaluated using ELISA kits (n = 5). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 in Tukey’s post hoc comparisons test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
3.5 The intervention of vitamin D inhibited TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling in the intestinal tissues of rats
The role of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in mediating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses has been reported previously [27]. Given the role of TLR4 activation and the downstream adapter MyD88 in activating the NF-κB signaling pathway, we investigated the influences of liver cirrhosis on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling in ileum tissues using RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. As shown in Figure 5a–h, the results showed that liver cirrhosis activated TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling in ileum samples of rats compared with the control group. Conversely, rats received low-dose or high-dose treatment of vitamin D exhibited decreased expression levels of TLR4, MyD88, and phospho-NF-κB p65 (p-NF-κB) in the ileum tissues compared with the liver cirrhosis model group. The treatment of GSK1795091 effectively reversed the vitamin D-mediated suppression of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway while Dat had no significant influence on this. These findings unveiled that vitamin D suppressed the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway activated by liver cirrhosis to facilitate intestinal damage repair.

The intervention of vitamin D inhibited TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling in the intestinal tissues of rats. (a–c) The mRNA expression of TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB was validated using RT-PCR analysis (n = 3). GAPDH mRNA was used to normalize the relative gene expression. (d–h) Western blot analysis was performed to determine the protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, NF-κB, and p-NF-κB of rat intestinal samples (n = 3). GAPDH protein was used as the internal reference. ns, no significant difference, **p < 0.01 in Tukey’s post hoc comparisons test. Data are presented as mean ± SD.
4 Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrated that liver cirrhosis caused the intestinal damage. The expressions of 25(OH)-D3 and VDR decreased while that of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [3] 24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) was increased in intestinal tissues of liver cirrhosis rats. Moreover, liver cirrhosis inhibited the levels of DEFA5 in either cirrhosis rats or clinical patients’ serum. The treatment of vitamin D effectively promoted the repair of intestinal injury by inhibiting the oxidative stress and inflammation. Mechanistically, vitamin D might promote the process of liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal damage repair by suppressing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Taken together, the results indicated that vitamin D intervention provides novel insight into the potential therapy of liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal damage.
Evidences have revealed that liver cirrhosis is associated with intestinal structures and functions, including the epithelial barrier dysfunction, the increased intestinal permeability, and inflammatory infiltration [28]. Induction of CD14 + Trem-1 + iNOS + intestinal macrophages in liver cirrhosis patients released IL-6, NO, and accelerated intestinal permeability [6]. Regulation of oxidative stress is crucial for the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis [29]. The alcohol, intestinal microbiota alterations, and intestinal inflammation of patients with liver cirrhosis may induce gut oxidative damage [5]. Moreover, systemic inflammation and oxidative stress factors induced in the liver could be transferred to the intestines through blood [30]. Previous researches reported that liver cirrhosis could cause significant intestinal oxidative stress and the enzyme xanthine oxidase in the mucosa and enterocyte mitochondria was the important source of free radicals [31]. Decompensated liver cirrhosis was related to the activation of intestinal oxidative stress, potentially resulting in intestinal damage and higher levels of systemic endotoxemia in the patients [32].
As generally known, vitamin D acts crucial roles not only in affecting intestinal epithelial integrity but also in regulating gut inflammatory responses and innate immune barrier functions [33,34]. Several studies have reported that vitamin D is involved in the progression of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) [35]. Vitamin D acts via the VDR to mediate gene transcription. Previous researches indicated that vitamin D suppressed Th17 and Th1 responses, increased Tregs, and promoted antimicrobial defensins release, which is mainly secreted by Paneth cells [12]. Moreover, the association between vitamin D and intestinal functions in cirrhosis has attracted the attention of numerous researchers. Wang et al. [36] found that vitamin D enhances gut barrier integrity in cirrhosis rats by increasing the heme oxygenase-1 expression. Active vitamin D3 treatment attenuated intestinal permeability, inhibited bacterial translocation, and enriched beneficial gut microbiota in cirrhosis rats [37]. In addition, it had been revealed that vitamin D levels were associated with liver cirrhosis severity and patients’ mortality [38].
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are transmembrane protein family receptors that play a key role in nonspecific or innate immune defense [39,40]. TLR4 is a key element in the TLR family. Previous reports revealed that the organism activated the innate immune responses after external stimulation and increased TLR4 level and triggered NF-κB through the MyD88-dependent pathway, which resulted in severe intestinal inflammation [41]. Furthermore, recent researches unveiled that the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway was involved in the regulation of oxidative stress injury [42]. Bacillus coagulans TL3 regulated the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signaling pathways in the cecal tissue of rats and regulated intestinal microflora to protect the intestine from inflammation and oxidative damage caused by LPS [43]. In this study, we found the activation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in intestinal tissues of liver cirrhosis rats while the treatment of vitamin D remarkably suppressed the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.
There are shortcomings in this study. A limitation of this work was the small sample size of animal experiments due to the limited time and financial support. In future research, we may investigate the changes in the intestinal flora composition induced by liver cirrhosis to further confirm the findings. Besides, we focused on the influences of liver cirrhosis on the intestines in this study. The livers treated with vitamin D are our further research direction and we think that there may be some interesting findings.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that vitamin D negatively regulated liver cirrhosis-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway, which revealed the practical implication for vitamin D supplementation as a strategy against cirrhosis-induced intestinal injury.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge our lab colleagues for their support in the work of this study.
-
Funding information: This work was financially supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2020YFS0485, 2018SZ0086), Chengdu Medical Research project (2021412), and Chengdu Science and Technology Program (2020-YF05-00034-SN).
-
Author contributions: PW conceived and designed the study. ML, YX, JL, XL, and DL collected data, analyzed data, and made the figures. ML and YX wrote the article, and PW was responsible for modification. All authors read and approved the version of the article submitted.
-
Conflict of interest: There is no conflict of interest to declare in this research.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Yeom SK, Lee CH, Cha SH, Park CM. Prediction of liver cirrhosis, using diagnostic imaging tools. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(17):2069–79. 10.4254/wjh.v7.i17.2069.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Garcia-Tsao G, Friedman S, Iredale J, Pinzani M. Now there are many (stages) where before there was one: In search of a pathophysiological classification of cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2010;51(4):1445–9. 10.1002/hep.23478.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Trebicka J, Fernandez J, Papp M, Caraceni P, Laleman W, Gambino C, et al. The predict study uncovers three clinical courses of acutely decompensated cirrhosis that have distinct pathophysiology. J Hepatol. 2020;73(4):842–54. 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.06.013.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Twu Y-C, Lee T-S, Lin Y-L, Hsu S-M, Wang Y-H, Liao C-Y, et al. Niemann-pick type C2 protein mediates hepatic stellate cells activation by regulating free cholesterol accumulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1122. 10.3390/ijms17071122.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Assimakopoulos SF, Tsamandas AC, Tsiaoussis GI, Karatza E, Zisimopoulos D, Maroulis I, et al. Intestinal mucosal proliferation, apoptosis and oxidative stress in patients with liver cirrhosis. Ann Hepatol. 2013;12(2):301–7. 10.1016/S1665-2681(19)31369-9.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Du Plessis J, Vanheel H, Janssen CEI, Roos L, Slavik T, Stivaktas PI, et al. Activated intestinal macrophages in patients with cirrhosis release NO and IL-6 that may disrupt intestinal barrier function. J Hepatol. 2013;58(6):1125–32. 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.01.038.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J Hepatol. 2020;72(3):558–77. 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.10.003.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Tripathi A, Debelius J, Brenner DA, Karin M, Loomba R, Schnabl B, et al. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;15(7):397–411. 10.1038/s41575-018-0011-z.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Stacchiotti V, Rezzi S, Eggersdorfer M, Galli F. Metabolic and functional interplay between gut microbiota and fat-soluble vitamins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(19):3211–32. 10.1080/10408398.2020.1793728.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Su D, Nie Y, Zhu A, Chen Z, Wu P, Zhang L, et al. Vitamin D signaling through induction of paneth cell defensins maintains gut microbiota and improves metabolic disorders and hepatic steatosis in animal models. Front Physiol. 2016;7:498. 10.3389/fphys.2016.00498.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Bancil AS, Poullis A. The Role of Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Healthc (Basel). 2015;3(2):338–50. 10.3390/healthcare3020338.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Malaguarnera L. Vitamin D and microbiota: Two sides of the same coin in the immunomodulatory aspects. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;79:106112. 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106112.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Merriman KE, Kweh MF, Powell JL, Lippolis JD, Nelson CD. Multiple β-defensin genes are upregulated by the vitamin D pathway in cattle. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;154:120–9. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.08.002.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Zhu Q, He G, Wang J, Wang Y, Chen W, Guo T. Down-regulation of toll-like receptor 4 alleviates intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury and acute lung injury in mice. Oncotarget. 2017;8(8):13678–89. 10.18632/oncotarget.14624.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Moses T, Wagner L, Fleming SD. TLR4-mediated Cox-2 expression increases intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced damage. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86(4):971–80. 10.1189/jlb.0708396.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Cho SX, Rudloff I, Lao JC, Pang MA, Goldberg R, Bui CB, et al. Characterization of the pathoimmunology of necrotizing enterocolitis reveals novel therapeutic opportunities. Nat Commun. 2020;11:5794. 10.1038/s41467-020-19400-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Giusto M, Barberi L, Di Sario F, Rizzuto E, Nicoletti C, Ascenzi F, et al. Skeletal muscle myopenia in mice model of bile duct ligation and carbon tetrachloride-induced liver cirrhosis. Physiol Rep. 2017;5(7):e13153. 10.14814/phy2.13153.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Vuillermot S, Luan W, Meyer U, Eyles D. Vitamin D treatment during pregnancy prevents autism-related phenotypes in a mouse model of maternal immune activation. Mol Autism. 2017;8:9. 10.1186/s13229-017-0125-0.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Tan X, Gao L, Cai X, Zhang M, Huang D, Dang D, et al. Vitamin D3 alleviates cognitive impairment through regulating inflammatory stress in db/db mice. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;9(9):4803–14. 10.1002/fsn3.2397.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Castillo EC, Hernandez-Cueto MA, Vega-Lopez MA, Lavalle C, Kouri JB, Ortiz-Navarrete V. Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation during the Induction and Progression of Osteoarthritis in a Rat Model. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2012;2012:156563. 10.1155/2012/156563.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Luo Y, Tian G, Zhuang Z, Chen J, You N, Zhuo L, et al. Berberine prevents non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-derived hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting inflammation and angiogenesis in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(5):2668–82.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Ish-Shalom S, Lichter A. Analysis of Fungal Gne Expression by Real Time Quantitative PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;638:103–14. 10.1007/978-1-60761-611-5_7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Fleet JC, Schoch RD. Molecular mechanisms for regulation of intestinal calcium absorption by vitamin D and other factors. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2010;47(4):181–95. 10.3109/10408363.2010.536429.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Xu Y, Hashizume T, Shuhart MC, Davis CL, Nelson WL, Sakaki T, et al. Intestinal and hepatic CYP3A4 catalyze hydroxylation of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3): implications for drug-induced osteomalacia. Mol Pharmacol. 2006;69(1):56–65. 10.1124/mol.105.017392.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Liu M, Sun T, Li N, Peng J, Fu D, Li W, et al. BRG1 attenuates colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis through autophagy-dependent oxidative stress sequestration. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4614. 10.1038/s41467-019-12573-z.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Chen Y, Yang B, Ross RP, Jin Y, Stanton C, Zhao J, et al. Orally administered CLA ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice via intestinal barrier improvement, oxidative stress reduction, and inflammatory cytokine and gut microbiota modulation. J Agric Food Chem. 2019;67(48):13282–98. 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b05744.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Bing X, Xuelei L, Wanwei D, Linlang L, Keyan C. EGCG maintains Th1/Th2 balance and mitigates ulcerative colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2017:3057268. 10.1155/2017/3057268.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Pijls KE, Jonkers DM, Elamin EE, Masclee AA, Koek GH. Intestinal epithelial barrier function in liver cirrhosis: an extensive review of the literature. Liver Int. 2013;33(10):1457–69. 10.1111/liv.12271.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Aceto GM, Catalano T, Curia MC. Molecular aspects of colorectal adenomas: the interplay among microenvironment, oxidative stress, and predisposition. BioMed Res Int. 2020;2020:1726309. 10.1155/2020/1726309.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Natarajan SK, Ramamoorthy P, Thomas S, Basivireddy J, Kang G, Ramachandran A, et al. Intestinal mucosal alterations in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis: Changes in glycosylation and luminal bacteria. Hepatology. 2006;43(4):837–46. 10.1002/hep.21097.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Ramachandran A, Prabhu R, Thomas S, Reddy JB, Pulimood A, Balasubramanian KA. Intestinal mucosal alterations in experimental cirrhosis in the rat: Role of oxygen free radicals. Hepatology. 2002;35(3):622–9. 10.1053/jhep.2002.31656.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Tsiaoussis GI, Assimakopoulos SF, Tsamandas AC, Triantos CK, Thomopoulos KC. Intestinal barrier dysfunction in cirrhosis: Current concepts in pathophysiology and clinical implications. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(17):2058–68. 10.4254/wjh.v7.i17.2058.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Fakhoury HMA, Kvietys PR, AlKattan W, Anouti FA, Elahi MA, Karras SN, et al. Vitamin D and intestinal homeostasis: Barrier, microbiota, and immune modulation. J Steroid Bioche Mol Biol. 2020;200:105663. 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105663.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Yamamoto EA, Jørgensen TN. Relationships Between Vitamin D, Gut Microbiome, and Systemic Autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2020;10:3141. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03141.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Battistini C, Ballan R, Herkenhoff ME, Saad SM, Sun J. Vitamin D modulates intestinal microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):362. 10.3390/ijms22010362.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Wang PF, Yao DH, Hu YY, Li Y. Vitamin D improves intestinal barrier function in cirrhosis rats by upregulating heme oxygenase-1 expression. Biomol Ther. 2019;27(2):222–30. 10.4062/biomolther.2018.052.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Lee PC, Hsieh YC, Huo TL, Yang UC, Lin CH, Li CP, et al. Active Vitamin D 3 treatment attenuated bacterial translocation via improving intestinal barriers in cirrhotic rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2021;65(3):e2000937. 10.1002/mnfr.202000937.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[38] Triantos C, Kalafateli M, Aggeletopoulou I, Diamantopoulou G, Spantidea PI, Michalaki M, et al. Vitamin D-related immunomodulation in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32(7):867–76. 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001597.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] López-López S, Romero de Ávila MJ, Hernández de León NC, Ruiz-Marcos F, Baladrón V, Nueda ML, et al. NOTCH4 Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Activated Macrophages by Interfering With Interferon-γ and TLR4 Signaling. Front Immunol. 2021;12:734966. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.734966.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] De Nardo D. Toll-like receptors: Activation, signalling and transcriptional modulation. Cytokine. 2015;74(2):181–9. 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.02.025.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Impellizzeri D, Fusco R, Genovese T, Cordaro M, D’Amico R, Trovato Salinaro A, et al. Coriolus versicolor downregulates TLR4/NF-κB signaling cascade in dinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-treated mice: A possible mechanism for the anti-colitis effect. Antioxidants. 2022;11(2):406. 10.3390/antiox11020406.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Du Z, Ma Z, Lai S, Ding Q, Hu Z, Yang W, et al. Atractylenolide i ameliorates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury via the TLR4/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:797499. 10.3389/fphar.2022.797499.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Wang Y, Lin J, Cheng Z, Wang T, Chen J, Long M. Bacillus coagulans TL3 inhibits LPS-induced caecum damage in rat by regulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and Nrf2 signal pathways and modulating intestinal microflora. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:5463290. 10.1155/2022/5463290.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer

