Abstract
Metastatic diseases of the spine are becoming increasingly common with an aging population and improvements in systemic cancer therapies. Microwave and vertebroplasty are the mainstay modalities for treating painful spine metastases. Most early spinal metastases predominantly attack the adnexa, but there are few reports on its treatment. This report presents a case of a 56-year-old female who had experienced severe thoracic back pain for several days and was diagnosed with a metastatic tumor of the right transverse process of T7. Percutaneous microwave ablation in combination with bone cement injection was used to treat the metastatic tumor under CT guidance. The postoperative pain on the Visual Analogue Scale was 1/10, without nerve or vessel damage and bone cement leakage during the operation.
1 Introduction
Spinal metastases are most common in bone metastasis, which is observed in 60–70% of patients with systemic cancer [1]. Invasion of the vertebral body and appendix by tumor tissue is frequent, which can lead to spinal cord compression, intractable pain, pathological fractures, and other problems [2]. However, most early spinal metastases predominantly attack the adnexa in clinical practice and there are few reports on the treatment of early adnexal metastases in the spine.
Pain alleviation and spinal stability are the main targets of treatment for spinal metastases [3,4]. Percutaneous vertebroplasty, which also enables percutaneous biopsy, has been demonstrated to be an economical and effective technique for reducing pain (usually in 74–100% of patients) and avoiding additional vertebral collapse in spinal metastases [5,6]. In recent years, image-guided percutaneous ablation techniques including radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation (MWA) have emerged as a viable therapeutic choice [7,8,9]. It can be carried out either alone or in conjunction with bone cement injection [10].
In this report, the author presents the use of MWA in combination with bone cement injection to percutaneously treat a case of early spinal metastases located on the transverse process.
2 Case presentation
A 56-year-old female, who had lung cancer and undergoing wedge resection of the upper left lung, presented with subacute onset, progressive, right thoracic back pain for several days. Her pain worsened at night and the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) was 8/10. A neurological exam showed normal motor function, normal sensation, and no abnormal reflexes. The patient had point tenderness over the T7 regions. Magnetic resonance imaging showed that the lesion was located at the right transverse process of T7. The vertebral body was not destroyed and the cervical spinal cord was not compressed (Figure 1). Bone scan showed diffuse increased uptake of the isotope at the level of the right transverse process of T7, without other abnormalities elsewhere in the skeleton (Figure 2).

Metastatic lung cancer of the right T7 transverse process (white arrows) showing enhancement after injection of gadolinium chelates.
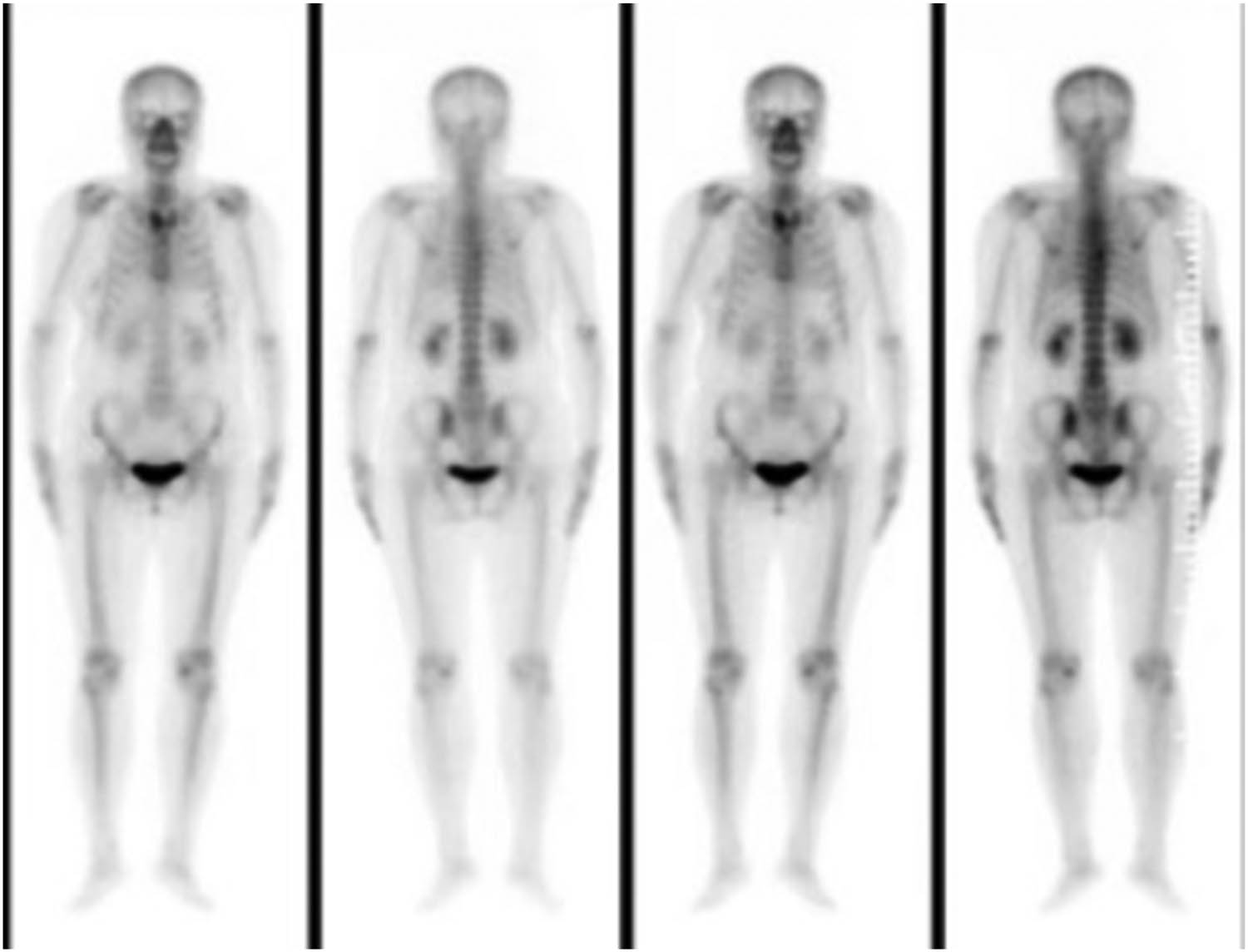
Bone scan showed diffuse increased uptake of the isotope at the level of the right transverse process of T7.
All procedures were performed using a Siemens Sensation 64 CT-scan (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) in the prone or supine position depending on the position of the lesion. The target lesion and needle path were located by non-enhanced helical CT acquisitions. Preoperative invasion range and destruction degree of adnexal tumor were determined and the injection route was planned according to X-ray, CT-scan, and MR (including enhanced) image data. After accurate marking of the skin and in strictly aseptic conditions, local subcutaneous injection of lidocaine 1% was performed at the defined skin entry point and an 11-gauge 15 cm co-axial needle (Dragon Crown Medical Co., LTD, China) was introduced step by step under CT-fluoroscopy (Figure 3a and b). After the needle was punctured into the right transverse process of T7 (adjusted during CT guidance), a 16G-gauge 20 cm MWA probe (ECO-100AL6, Nanjing Yigao Medical Technology Co., LTD, China) was advanced into the osseous lesions of T7’s right transverse process. Then connect the ablation needle to the ablation instrument (ECO-100A1, Nanjing Yigao Medical Technology Co., LTD, China), adjust the power to 70 W, and ablate twice for 2 min each time (Figure 4a). During the ablation process, the patient’s vital signs and the movement of the lower limbs were observed. After the ablation needle was withdrawn, the polymethylmethacrylate bone cement (PMMA, Heraeus Medical Ltd, German) was prepared in the appropriate ratio (powder (g)/liquid (mL) = 2:1) and was pushed with a cement-filled cannula (Dragon Crown Medical Co., LTD, China). The distribution of the bone cement is observed until it has diffused to the edge of the lesion (Figure 4b). After the bone cement has been filled, the cannulas were removed and the patient is returned to the ward for recovery.
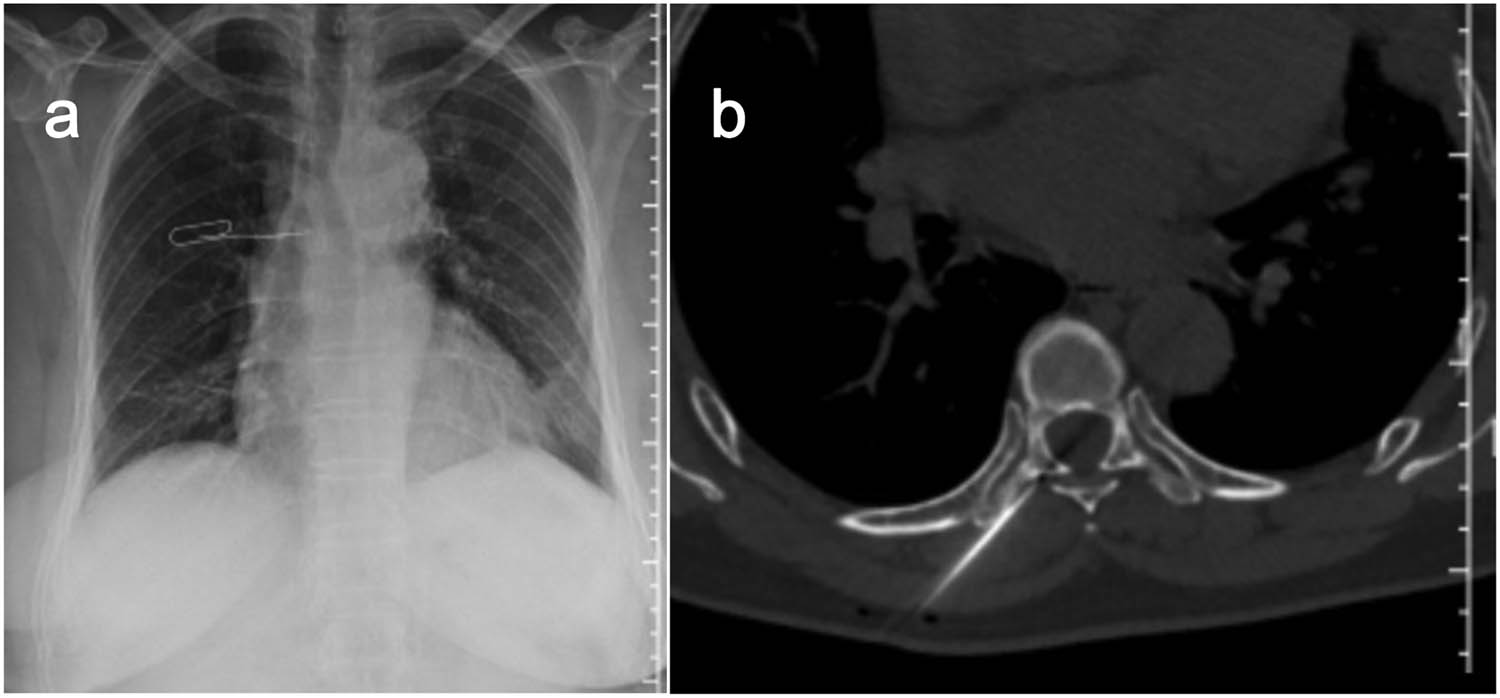
Localization is performed on the body surface by X-ray (a) and puncture is performed under CT guidance (b).
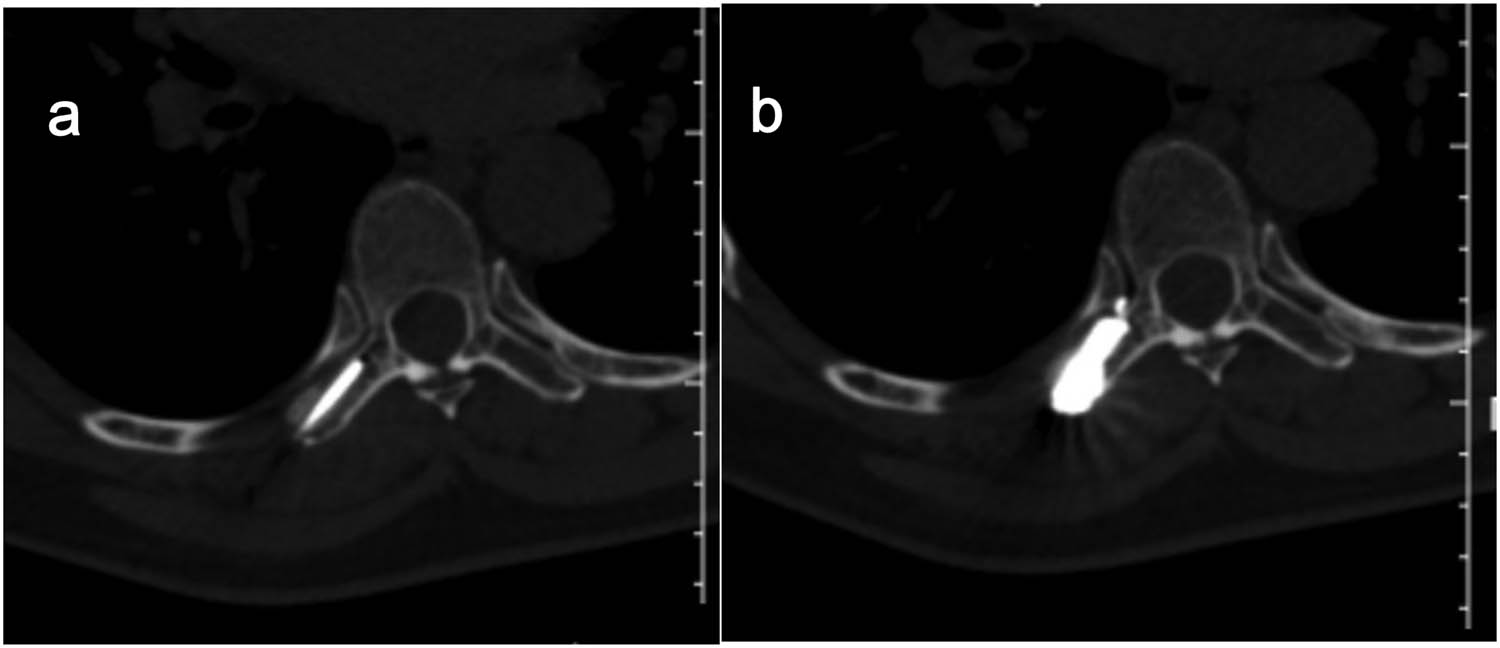
On control CT scan performed during MWA (a) and bone cement was injected into the lesion during the operation (b).
After the procedure, the patient felt painless and the VAS score was 1/10. No complications occurred during the operation. CT showed that the cement was well filled and no leaks at the right transverse process of T7 (Figure 5a). At the 6-month follow-up, the patient’s chest and back pain was relieved, and a repeat CT revealed no leakage of bone cement and no new destruction of bone (Figure 5b).
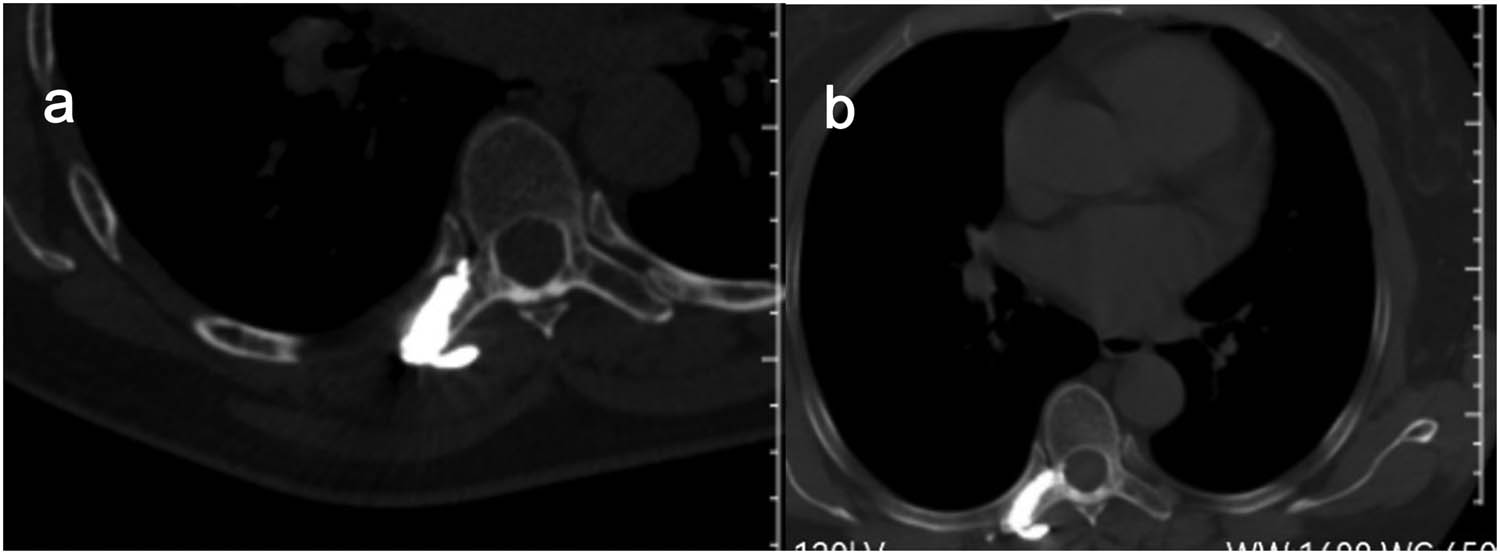
Postoperative CT showed intact cement filling and no leakage in the spinal canal (a) and follow-up after 6 months showed no displacement of the bone cement and no new bone destruction (b).
-
Ethical approval: All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee(s) and with the Helsinki Declaration. The Institutional Review Board of The Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical College approved the study protocol (approval document of biomedical ethics review committee of The Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical College, wyfy-2023-ky-146).
-
Informed consent: Written informed consent for publication was obtained from the patient.
3 Discussion
The survival time for patients with tumors has been vastly expanded due to advancements in technology for tumor treatment. Improving the quality of life is a clinical challenge for metastatic disease [4,11]. Palliative care is the major strategy for treating spinal metastases since it reduces suffering and enhances the quality of life. Medical treatment, surgical resection and reconstruction, local radiation, and local interventional treatment are examples of the available treatment modalities [12,13,14].
A better option for treating spinal metastatic tumors has emerged with the development of minimally invasive therapy. The primary technique of treatment for spinal metastases is vertebroplasty [6,15]. Bone cement is injected to restore the stability of the diseased vertebral body following percutaneous puncture of the puncture needle into the diseased vertebral body under fluoroscopic monitoring. The heat and self-toxicity generated during the hardening of the bone cement have the effect of killing tumor cells. The patient’s function improves and their pain is lessened after treatment [6]. However, there is a risk that the bone cement will leak during the injection and will not be able to completely enclose the tumor tissue, failing to obtain the intended results [16]. Electromagnetic waves include microwave, radiofrequency ablation, and laser interstitial thermal therapy [17]. By inserting the MWA needle into the patient’s tumor, the microwave electromagnetic radiation field’s heat induces an increase in tissue temperature, causes coagulation-type necrosis of tumor cells, inhibits tumor cell growth, and lessens the damage that tumor cells cause to the vertebral body, thereby reducing the patient’s pain and discomfort [8,9,10,18]. However, the strength of the bone cannot be increased by this treatment, and the spine’s stability is not significantly improved [19].
Spinal adnexal metastases cause microfractures within the adnexa causing irritation and injury to nerves inside and outside the adnexa, which is the most important factor in producing thoracolumbar back pain [20]. Direct invasion of nerve endings by the tumor tissue to damage and compress them is also a common cause of pain. In this article, we used MWA combined with bone cement for the treatment of transverse metastases. After the operation, the thoracolumbar back pain of the patient was rapidly relieved. In addition, MWA has a thermocoagulation effect, which can rapidly cause tumor coagulation and necrosis, vaporization, and facilitate the diffusion of bone cement to the marginal normal bone. It can play a thermocoagulation effect on the circumferential tumor. In addition, bone cement alone is cytotoxic and can cause necrosis of the surrounding tumor cells. The bone cement has to stabilize and support the effects on the vertebral attachments, and after injecting into the diseased vertebral attachments, it will fix the microscopic bone in a short period, block the loss of support of the diseased vertebral attachments due to the invasion of tumor cells [21], and reduce the stimulation of nerve roots and sinus vertebral nerves due to the instability of the spine [10,22,23]. Both of these factors can prevent further destruction of the spinal attachment and delay the infiltration of tumor cells into the vertebral body or vertebral canal while rapidly relieving the pain in the thoracic and lumbar back of patients.
Due to the spinal adnexa’s anatomical location, a CT-guided puncture is advised to guarantee the precision of the microwave needle placement. The major benefit of a CT scan is its ability to visualize the cross-section and pinpoint the target lesion with accuracy, guaranteeing that the ablation needle is inserted in the metastases’ center. To avoid the risk of intraoperative spinal cord and nerve injury, we shortened the ablation time and increased the ablation cycle with an RF power of 30 W. The ablation time was adjusted according to the location of the metastases. Two ablations of 2 min each are recommended for tumors located in the transverse process, spinous process, and articular process, and four ablations of 1 min each are recommended for tumors located in the vertebral plate and arch. In this article, the transverse process was ablated twice for a total of 2 min to lower the possibility of the intraoperative spinal cord and nerve damage. To prevent thermal injury to the surrounding normal tissues during the work of the ablation needle, it is crucial to verify that the water-cooling cycle is functioning properly before starting the microwave power output. Compared to the vertebral body, the vertebral adnexa which is smaller and situated closer to the spinal cord and nerve roots is vulnerable to bone cement leakage. In the process of making bone cement, we strictly follow the fixed ratio (powder (g)/liquid (mL) = 2:1) to ensure that the bone cement is in the “toothpaste apparatus” during the pushing process. Each injection should be between 0.3 and 0.5 mL and push injection process must be slow. To prevent bone cement from leaking, the needle’s tip should be placed away from the cortex of the damaged bone. In addition, careful observation and study of the preoperative imaging data are also essential to prevent leakage.
4 Limitations
This study has limitations, mostly intrinsic to the nature of case reports or case series. The poor financial situation of the patients and the short follow-up period, lack of a control group, and the single assessment index may not fully reflect the symptomatic improvement of the procedure. Future studies may need to include more cases and use better evaluation indicators.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, percutaneous MWA in combination with bone cement injection can enhance spinal stability, alleviate the pain of patients with spinal metastases, and maintain better long-term efficacy than single vertebroplasty treatment, which is worthy of clinical reference.
-
Funding information: This study was funded by the Start-up fund of Weifang Medical College (No. 041002) and the Teaching case base construction project for Professional degree postgraduates in Shandong Province (SDY-AL17060).
-
Author contributions: W.H.L. conceptualized the study and performed the operation, H.T.H. collected, wrote and revised the initial manuscript draft, H.J.T. reviewed the manuscript, and L.X. and X.G. provided critical feedback and edited subsequent revisions. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
[1] Bollen L, Dijkstra SPD, Bartels R, de Graeff A, Poelma DLH, Brouwer T, et al. Clinical management of spinal metastases – The Dutch national guideline. Eur J Cancer. 2018;104:81–90. 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.08.028.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Coleman RE. Clinical features of metastatic bone disease and risk of skeletal morbidity. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(20 Pt 2):6243–9s. 10.1158/1078-0432.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Tomasian A, Jennings JW. Vertebral metastases: minimally invasive percutaneous thermal ablation. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2020;23(4):100699. 10.1016/j.tvir.2020.100699.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Giammalva GR, Costanzo R, Paolini F, Benigno UE, Porzio M, Brunasso L, et al. Management of spinal bone metastases with radiofrequency ablation, vertebral reinforcement and transpedicular fixation: a retrospective single-center case series. Front Oncol. 2021;11:818760. 10.3389/fonc.2021.818760.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Xu S, Liu T, Zhang X, Liu H, Zhao Z, Xu L, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous vertebroplasty for the relief of osteoblastic spinal metastasis pain. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(1):727. 10.3892/etm.2021.10159.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Eleraky M, Papanastassiou I, Setzer M, Baaj AA, Tran ND, Vrionis FD. Balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of metastatic tumors of the upper thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;14(3):372–6. 10.3171/2010.11.SPINE09909.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Aubry S, Dubut J, Nueffer JP, Chaigneau L, Vidal C, Kastler B. Prospective 1-year follow-up pilot study of CT-guided microwave ablation in the treatment of bone and soft-tissue malignant tumours. Eur Radiol. 2017;27(4):1477–85. 10.1007/s00330-016-4528-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Kastler A, Alnassan H, Aubry S, Kastler B. Microwave thermal ablation of spinal metastatic bone tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(9):1470–5. 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.06.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Tomasian A, Jennings JW. Spine microwave ablation: safety and efficacy for treatment of vertebral metastases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022;43(3):E9–10. 10.3174/ajnr.A7439.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Khan MA, Deib G, Deldar B, Patel AM, Barr JS. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous microwave ablation and cementoplasty in the treatment of painful spinal metastases and myeloma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2018;39(7):1376–83. 10.3174/ajnr.A5680.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Ziu E, Viswanathan VK, Mesfin FB. Spinal metastasis. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Gillespie EF, Mathis NJ, Vaynrub M, Santos Martin E, Kotecha R, Panoff J, et al. Multidisciplinary treatment of non-spine bone metastases: results of a modified delphi consensus process. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022;35:76–83. 10.1016/j.ctro.2022.04.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Hayashi K, Tsuchiya H. The role of surgery in the treatment of metastatic bone tumor. Int J Clin Oncol. 2022;27(8):1238–46. 10.1007/s10147-022-02144-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] McCabe FJ, Jadaan MM, Byrne F, Devitt AT, McCabe JP. Spinal metastasis: the rise of minimally invasive surgery. Surgeon. 2022;20(5):328–33. 10.1016/j.surge.2021.08.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Gumusay O, Huppert LA, Behr SC, Rugo HS. The role of percutaneous vertebral augmentation in patients with metastatic breast cancer: literature review including report of two cases. Breast. 2022;63:149–56. 10.1016/j.breast.2022.03.016.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Wang L, Zhang C, Liang H, Huang T, Zhong W, Zhao Z, et al. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for spinal metastases: a retrospective study of risk factors and clinical outcomes. World J Surg Oncol. 2022;20(1):112. 10.1186/s12957-022-02583-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Cardia A, Cannizzaro D, Stefini R, Chibbaro S, Ganau M, Zaed I. The efficacy of laser interstitial thermal therapy in the management of spinal metastases: a systematic review of the literature. Neurol Sci. 2022;44(2):519–28. 10.1007/s10072-022-06432-x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Motaghi M, England RW, Nejad NH, Sankaran N, Patel AM, Khan MA. Assessing long-term locoregional control of spinal osseous metastases after microwave ablation. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;104:48–55. 10.1016/j.jocn.2022.07.025.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Pusceddu C, Sotgia B, Fele RM, Melis L. Treatment of bone metastases with microwave thermal ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24(2):229–33. 10.1016/j.jvir.2012.10.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Litak J, Czyżewski W, Szymoniuk M, Sakwa L, Pasierb B, Litak J, et al. Biological and clinical aspects of metastatic spinal tumors. Cancers. 2022;14(19):1–32. 10.3390/cancers14194599.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Urakawa H, Ando Y, Hase T, Kikumori T, Arai E, Maeda O, et al. Clinical value of serum bone resorption markers for predicting clinical outcomes after use of bone modifying agents in metastatic bone tumors: a prospective cohort study. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(12):3504–15. 10.1002/ijc.32836.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Chen L, Hou G, Zhang K, Li Z, Yang S, Qiu Y, et al. Percutaneous CT-guided microwave ablation combined with vertebral augmentation for treatment of painful spinal metastases. Am J Neuroradiol. 2022;43(3):501–6. 10.3174/ajnr.A7415.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Luna LP, Sankaran N, Ehresman J, Sciubba DM, Khan M. Successful percutaneous treatment of bone tumors using microwave ablation in combination with Zoledronic acid infused PMMA cementoplasty. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;76:219–25. 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.03.048.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer

