Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
-
Rong Liu
and Zhen Jiang
Abstract
Our purpose was to devise a radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography (CTA) images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism. 57 patients (95 regions of interest; training set: n = 57; internal validation set: n = 38) with femoral popliteal acute lower limb arterial embolism confirmed by pathology and with preoperative CTA images were retrospectively analyzed. We selected the best prediction model according to the model performance tested by area under the curve (AUC) analysis across 1,000 iterations of prediction from three most common machine learning methods: support vector machine, feed-forward neural network (FNN), and random forest, through several steps of feature selection. Then, the selected best model was also validated in an external validation dataset (n = 24). The established radiomics signature had good predictive efficacy. FNN exhibited the best model performance on the training and validation groups: its AUC value was 0.960 (95% CI, 0.899–1). The accuracy of this model was 89.5%, and its sensitivity and specificity were 0.938 and 0.864, respectively. The AUC of external validation dataset was 0.793. Our radiomics model based on preoperative CTA images is valuable. The radiomics approach of preoperative CTA to differentiate new emboli from old is feasible.
1 Introduction
Acute limb ischemia (ALI) refers to the abrupt stenosis or occlusion of the lower extremity arteries due to various causes, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the limbs and circulatory disorders. Because ALI progresses rapidly, early screening and timely and correct treatment are vital in saving patients’ lives and limbs. Acute arterial embolization and acute thrombosis are two common causes of ALI. Acute lower extremity arterial embolization (ALEAE) refers to acute ischemic lesions in limbs and tissues caused by blood being pushed to the distal arteries and obstructing arterial blood flow after the heart or near-end artery wall embolus is detached. Emboli originate from the heart, and most of the older ones are left atrial thromboses with reduced systolic capacity and blood retention. The clinical manifestations of the two causes are similar, but the clinical treatments for different causes differ [1]. Because old emboli may be found at the heads of whole emboli in acute arterial embolization, the fundamental problem cannot be solved only by thrombolytic therapy, and the removal of emboli is imperative for patients. However, acute thrombosis is caused by lower extremity atherosclerosis. Luminal stenosis leads to thrombolysis in some patients. The effects are not good because if arterial embolization is mistakenly used to remove emboli, then patients may require repeated stenting. This is a waste of money, time, and trust. In other words, if we can find the old emboli at the head, to some extent, we can select the appropriate treatment.
The diagnosis of both ALE and ALI is mainly based on digital subtraction angiography (DSA). However, DSA has some limitations in practical application [2]. First, DSA is an invasive examination. Second, it is closely related to the operator’s experience. If the operator cannot complete the diagnosis after a single contrast injection, the amount of contrast agent and radiation the patient receives increase dramatically.
In clinical practice, noninvasive imaging modalities play an important role in the diagnosis of ALI [3]. However, the age of thrombosis is still a dilemma for medical imaging specialists. Although, venous duplex ultrasonography, combining color flow Doppler imaging with compression ultrasonography, which is the current gold standard first-line investigation for imaging deep vein thrombosis, is unable to differentiate between acute and chronic thrombi [4]. Some studies have also used magnetic resonance imaging for lower extremity thrombosis in older adults, but its clinical application has been greatly reduced by its long scanning time, insensitivity to calcification, and metal limitations. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a kind of examination of acute lower extremity arterial ischemia [5]. It is noninvasive, rapid, and also shows other abdominal and pelvic lesions [6]. Preoperative lower extremity CTA can help to determine the best surgical approach and devise the best surgical plan, so it is unfortunate that it cannot perform thrombosis aging more accurately.
Recently, the emerging field of radiomics has expanded its use and improved the understanding of medical imaging. Radiomics is the process of extracting quantitative features from radiological images via high-throughput analysis and selecting features to build a signature for a complete tumor characterization [7,8,9].
The core task of radiomics is to automatically analyze image feature data to obtain valuable information for disease diagnosis, prognosis, and prediction. The process of radiomics can be divided into several parts: acquiring high-quality, standardized images, and determining tumor regions using a segmentation algorithm or clinical expert sketching; extracting large numbers of image features from the tumor region and selecting the most effective features; and establishing a prediction model by analyzing the selected features and results through machine learning. The research methods of radiomics can obtain useful information from images and have great potential to improve the value of diagnosis and prognosis.
To date, few studies have applied radiomics to the prediction of lower extremity arterial thrombosis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism of femoral popliteal artery by preoperative CTA-based radiomics model.
2 Materials and methods
The workflow of this research is presented in Figure 1.
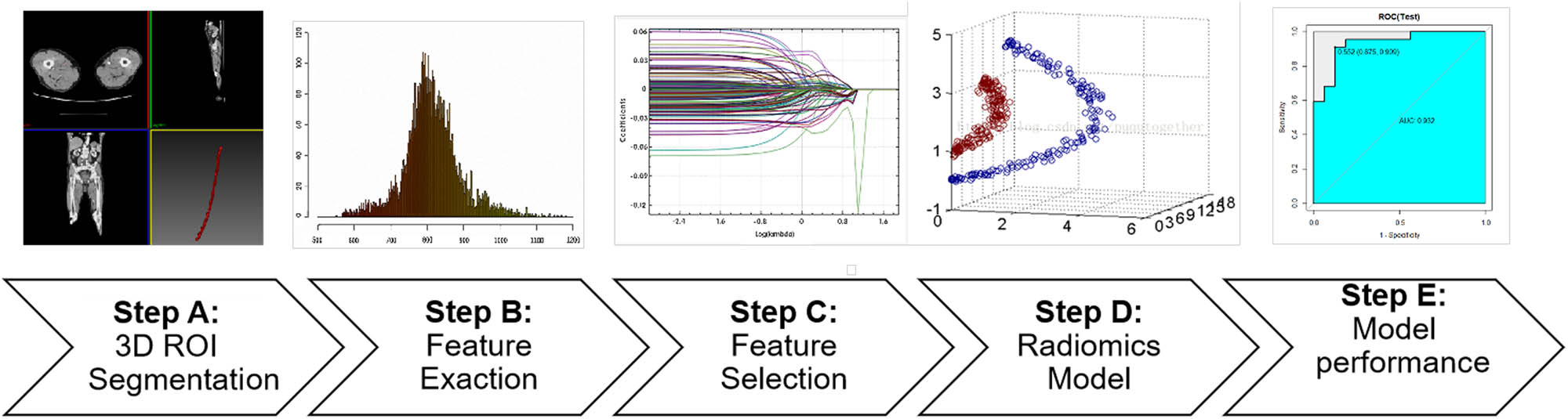
Research workflow. A: Three-dimensional (3D) ROIs were segmented from CTA images; B and C: Quantitative imaging texture features were extracted and selected to construct the radiomics model; D: Three different radiomics models were constructed; E: ROC curve analysis was used to evaluate the performance of the model.
2.1 Patients population
This retrospective study was approved by the ethical review board of our hospital (IRB number: JD-HG-2021-32). Informed consent was obtained from all patients. Fifty-seven patients with acute arterial embolism in our hospital were enrolled in the study between January 2015 and December 2017, including 45 male and 12 female adults aged from 40 to 88 years, with an average age of 73.52 years. In total, 95 ROIs were detected in these patients, including old emboli (50) and new thromboses (45).
The inclusion criteria were:
Clinical manifestations of acute onset, manifested by varying degrees of sudden limb pain, followed by numbness, paleness, cyanosis, dyskinesia, cold limbs, arterial pulse weakening, or disappearance of symptoms;
Gross specimen showing that the thrombosis head was sclerotic and the tail thrombosis was soft; pathological diagnosis showing that the head thromboses was white and the tail thromboses was red;
Embolus taken immediately after CTA examination of the lower extremities at DSA.
The exclusion criteria included:
Artifacts in images;
Unclear popliteal artery lumen;
Images could not be matched;
Nephrotic syndrome.
Figure 2 shows the details of patient selection.

Flow diagram of patient selection.
2.2 CT imaging
Before therapy, all patients received conventional CT scans using the GE 64-layer LightSpeed VCT scanner. The scan ranged from the lower abdominal aorta to the sole of the foot. The patient assumed the advanced scanning position of the supine foot, and the foot was fixed to the inversion. The scan conditions were tube voltage 120 kV, tube current 260 mA, and pitch 0.8. The contrast agent was 370 mgI/mL, which was injected into the cubital vein at 4 mL/s, and the amount was 100 mL. After the injection, it was diluted with 30 mL of normal saline. The scan was performed using the contrast agent to track the prep smart technique, and a region of interest (ROI) was placed at the level of the abdominal aorta. The field value was 150 HU, and the delay was 10 s after the trigger. Blood vessel volume data were transmitted from CT scans to a GE ADW4.6 stand-alone workstation for volume rendering, maximum intensity projection, curved planar reconstruction, multiplanar reconstruction, and multi planar reformation. CT scan images were exported in DICOM format.
2.3 Fogarty balloon catheter thrombectomy
The anesthesia method was 2% lidocaine local anesthesia, and longitudinal incision of the upper part of the femoral artery was performed. After the artery was exposed, systemic intravenous heparinization was achieved with 5,000 units of heparin, and a longitudinal incision was made in the anterior wall of the artery. After the catheter was inserted into the blood vessel, the balloon was dilated. It was then slowly withdrawn, removing the emboli and secondary thromboses. A sign of successful thrombectomy is a violent jet of blood near the heart with turbulent blood flow to the distal end. Angiography indicates smooth blood flow with no filling defect.
2.4 ROI and texture extraction
Lesions were outlined as ROIs, and feature extraction was performed using the Artificial Intelligence Kit software package (version 3.1.0, GE Healthcare (Shanghai, China) Co., Ltd). All data are sketched on the CTA axis map. The thrombosis lesions corresponding to the head and tail of the general specimen are selected, and the ROI is placed along the contour of the lesion. The calcified blood vessel region of the pixel threshold is elucidated to further adjust the ROI, and then the respective image ensemble feature values within the ROI are extracted. ROI outlining of the thrombosis was performed by an experienced imaging specialist and examined by another imaging specialist. Then, ROIs from multiple levels of the same lesion were merged into a three-dimensional (3D) ROI. Figure 3 shows an example of the delineated 3D ROI. Radiomics features were extracted from the axial CTA images. The computer-derived features, including first-order statistics, gradient-based histogram features, second-order Haralick textures, and form factor parameters, were calculated based on the voxels in the delineated ROI. The extracted radiomics features include: (1) gray histogram: kurtosis, skewness, mean, variance, and percentile (10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 90%); (2) Gray level co-occurrence matrix: contrast, angular second order, correlation, and entropy; (3) gray run length matrix: long run enhancement, short run enhancement, fractional run, and run length non-uniformity measure; (4) form factor parameters: sphericity, surface area, compactness, and volume; (5) Haralick features: Haralick correlation, angular second moment, contrast, Haralick entropy, variance, sum average, sum entropy, and inverse difference moment; (6) gray level size zone matrix: small and large zone emphasis, gray-level nonuniformity, zone percentage, and gray-level variance.

Example of 3D ROI segmentation. Male patient aged 65 years with thrombosis in the right lower extremity deep vein. (a) CTA imaging. (b and c) Image segmentation performed on CTA images. (d) 3D ROI segmentation.
2.5 Feature selection and radiomics model
Despite the fact that 396 features were exacted through texture analysis, not all of them would be useful for differential diagnosis. We adopted a series of dimensionality reduction methods to avoid overfitting and feature selection methods to identify the optimal features to include in the radiomics model. ANOVAs and Mann–Whitney U tests were first used to delete less useful features, and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) method was also performed to explore which features correlated best with histopathology. The LASSO method is a kind of compressed estimation that refines the model by constructing a penalty function, which first determined the hyper-parameter λ using 10-fold cross validation, and the optimized λ corresponding to the minimized binomial deviation was selected and used to compress some coefficients and set some coefficients to zero. Finally, 34 of the most useful predictive biomarkers with non-zero coefficients were investigated to construct the radiomics prediction model.
To distinguish the difference between new and old thromboses, the 95 ROIs from 57 patients were randomly divided into two groups: 60% of the ROIs were assigned to the training set (n = 57), and the rest were assigned to the internal validation set (n = 38). The training set was used to establish the predictive radiomics model, and the internal validation set was used to evaluate the model’s performance. Besides, the external validation dataset was also prepared to evaluate the model’s performance to validate the model’s generalization.
For model construction, we used three of the most common machine learning methods available and selected the best prediction model according to performance through iterative verification.
Support vector machine (SVM) is a common discrimination method in machine learning. It is a supervised learning method that is commonly used for pattern recognition, classification, and regression analysis. The SVM method maps the sample space into a high-dimensional feature space that can even have infinite dimensions (Hilbert space) through a nonlinear mapping (p), transforming the problem of nonlinear separability in the original sample space into the feature space. In our SVM model, we used the radial basis function (RBF) to convert the data so that the original could not be separated into linear functions. RBF is a real-valued function that only depends on the distance from a specific point. In SVM, the coefficient C is the cost function’s penalty coefficient, and higher values are associated with less error tolerance. To increase accuracy, we set the coefficient C to 1,000.
In recent years, deep learning has been widely employed in various fields, especially for automatic lesion segmentation. Deep learning is a series of new structures and methods that can be evolved by multi-layer ANNs with additional layers. The back-propagation (BP) algorithm is the most important part of feedforward neural networks (FNN). It is a supervised learning algorithm that is often used to train multilayer perception networks, and it is defined by the activation function used by each artificial neuron (i.e., node) being micro. Multilayer FNNs have one input layer, one or more hidden layers in the middle, and one output layer. In our model, we used the BP method with ten layers, with each layer being equivalent to a single-layer FNN. This network construction forms dimensional hyperplanes, which helps to achieve more complex classification of input patterns.
Random forest (RF) is a new, highly flexible machine learning algorithm that has a wide range of applications. It integrates multiple basic decision tree units by ensemble learning, and it is an ensemble learning method.
Intuitively, each decision tree is a classifier (assuming the classification problem is now addressed). Thus, for an input sample, N trees will have N classification results. RF integrates all of the classification voting results and assigns the most voted category as the final output. This article used 500 trees, and the number of variables attempted at each split was 5. We created an RF model because it has state-of-the-art accuracy among current algorithms and gives estimates of which variables are important in the classification.
3 Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using R (version 3.4.7, http://www.Rproject.org). Two-tailed testing was used in all statistical analyses, with the level of statistical significance determined as p < 0.05. Before model construction, two-step preprocessing was performed on the data obtained from texture analysis: first, the missing data were replaced with medians to eliminate their impact on the final results. Second, to reduce the effects of dataset size on the results, standardization was performed.
To test the radiomics model’s performance, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used, and the area under curve (AUC) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was analyzed. Each model was iterated 1,000 times, and the model with the best AUC was selected. The DeLong’s test was used to determine the significance of AUC differences among the three classifiers.
4 Results
4.1 General information
Two site datasets were included in the study, one site contained 57 patients, 95 total ROIs were delineated: 45 were new arterial thromboses (47%), and 50 were old arterial emboli (53%). The second site consisted of 21 patients, 24 ROIs were delineated: 14 were new arterial thromboses (58%), and 10 were old arterial emboli (42%).
4.2 Feature selection
Figure 4 shows the two feature selection steps and the number of remaining features in each step.

Feature extraction.
The features after feature exaction are listed in Table 1.
Radiomics: predictive factors
| Feature type | Feature name |
|---|---|
| Gradient-based histogram features | Percentile (10%, 15%) |
| Relative deviation | |
| Texture parameters | Correlation (offset 4, 7) |
| Cluster shade | |
| Cluster prominence | |
| GLCM | GLCM energy (angles 0°, 90°, 135°) |
| GLCM entropy (angles 0°, 90°) | |
| Inverse difference moment | Inverse difference moment (offset 1, 7) |
| RLM | Run length nonuniformity (all directions, offset 1, 4, 7) |
| Short run emphasis | |
| Long run emphasis | |
| Long run high-grey level emphasis | |
| Low grey-level run emphasis | |
| Form factor parameters | Surface area |
| Compactness (1, 2) | |
| Volume CC | |
| Volume MM | |
| Sphericity | |
| Spherical disproportion |
Through feature selection, we found six different types of image features that can influence the model construction: gradient-based histogram features (3), texture parameters (4), GLCM (5), Inverse difference moment (2), RLM (13), and form factor parameters (7).
4.3 Model performance
Table 2 shows the sample distribution of the training and internal validation datasets. As shown in Table 3 and Figures 5–7, all three models had high performance to distinguish the new emboli from old, but the BP model was the best one, in which the AUC value and 95% CI were 0.960 and (0.899–1), respectively. Compared to the other two models, p values of the DeLong’s test were both less than 0.05. The BP model was also validated in an external validation dataset, and the AUC was 0.793 (95%CI: 0.601–0.985) (Figure 8).
ROI distribution
| Total | New thrombus | Old thrombus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data | 95 | 45 | 50 |
| Training set | 57 | 27 | 30 |
| Validation set | 38 | 18 | 20 |
| External validation | 24 | 14 | 10 |
Comparison between SVM, BP, and RF
| SVM model | RF model | BP model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation | Internal | Internal | Internal | External |
| AUC | 0.770 | 0.932 | 0.960 | 0.793 |
| 95% CI | 0.633–0.907 | 0.853–1.000 | 0.899–1 | 0.601–0.985 |
| Accuracy | 0.763 | 0.842 | 0.895 | 0.792 |
| Sensitivity | 0.813 | 0.875 | 0.938 | 0.643 |
| Specificity | 0.727 | 0.812 | 0.864 | 1.000 |

ROC curve of BP model in internal validation dataset.

ROC curve of RF model.

ROC curve of SVM model.

ROC curve of BP model in the external validation dataset.
5 Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that used preoperative CTA to differentiate new emboli from old. ALI is approximately five times more prevalent in the lower extremities than the upper extremities [10], so we studied only patients with femoral popliteal artery embolism. Perioperative morbidity and mortality after ALI are also high, ranging from 20–40% [11]. The sudden interruption of the blood supply to the lower extremity arteries and insufficient time to establish collateral blood circulation may lead to serious blood supply insufficiency. Ischemic symptoms occur more quickly, and the degree of ischemia is more serious. Thus, the importance of early diagnosis and clinical treatment are obvious. The age of patients in this study was in the range of 40–88 years, and most of them were older adults. Based on our experience, DSA thrombectomy was more suitable for this kind of patients than traditional surgical thrombectomy after definite diagnosis of CTA before operation. In addition, for some patients with both arterial thromboses and lower extremity atherosclerosis, or patients with a long duration of arterial thrombectomy or thrombolysis is less effective, and balloon dilatation and stent treatment are required. Thus, preoperative CTA to distinguish new emboli from old can provide useful guidance for treatment.
Previous research reported used duplex scanning to differentiate embolic from thrombotic acute arterial occlusion [12]. In their study, the clinical data were not sufficient to differentiate the embolic from thrombotic occlusion. The acuteness of presentation was not clinically or statistically different between embolic and thrombotic groups. The site of occlusion, state of the arterial wall (healthy or affected by atherosclerosis), and the presence of calcification or collaterals were not sufficient to differentiate embolic from thrombotic occlusion. Just the arterial diameters at the site of occlusion were useful. Thus, we hypothesized whether radiomics could be used to differentiate. Radiomics methods have been widely spread because they can transform medical images into high-dimensional quantitative textural features and use the optimal features to guide clinical decision making [13]. Most previous radiomics studies focused on tumors. Compared with simple subjective qualitative features based on tumor lesions, quantitative image features can describe tumor heterogeneity more comprehensively and quantitatively. Such quantitative features have been used in many medical imaging applications to assist with disease diagnosis and treatment, and they can compensate for the shortcomings of traditional qualitative diagnosis [14,15,16,17,18]. The results show that the various imaging features extracted from CT images can reflect the tumor’s potential biological characteristics and heterogeneity, which can be used to predict the postoperative prognosis and evaluate curative effects on patients [21,22]. Recently, several studies reported that the value on atherosclerosis and thrombus radiomics features derived from NCCT and CTA are more predictive of recanalization [23,24].
In this study, we devised a radiomics method to distinguish new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism. Although radiomics has been widely applied, radiomics methods differ, and their repeatability is poor. Because SVM, RF, and ANN have been recognized as three major methods in supervised machine learning, we used them to construct three radiomics models and chose the one with the best predictions throughout 1,000 iterations. In this study, we extracted 34 predictive factors based on angiographic features of preoperative CT images. We found that the relationships between the uniformity of the gray distribution in the ROI, the degree of texture of grooves, and three-dimensional shape are the main discriminant factors of lower limb acute arterial embolism. The FNN radiomics prediction model had the largest area under the ROC curve: 0.960 (0.899–1). When the models were trained with the validation dataset, they retained high performance in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and AUC for achieving the correct diagnosis. Thus, the results indicate that the radiomics approach of using preoperative CTA images to differentiate new emboli from old is feasible and can effectively help with clinical preoperative diagnosis and evaluation.
6 Limitation
First, it was a single-center retrospective study with potential bias; second, texture features were extracted from manually segmented data, and it was difficult to exclude small blood vessels within the thromboses, which may affect the accuracy of some features; third, all patients with arterial embolism but no arterial thrombosis were selected. In our next study, we will select patients with arterial thrombosis for validation.
7 Conclusion
In conclusion, despite the fact that CT-based radiomics methods cannot be expected to replace pathological diagnosis, as a noninvasive approach, the radiomics prediction model based on angiographic labeling of preoperative CTA images is valuable for distinguishing the new femoral emboli from old. This noninvasive method can provide individualized preoperative predictors for clinicians and patients. In addition, the method performs radiomics analysis on existing images without additional cost and thus has the potential for extensive clinical use.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
-
Funding information: This study is supported by Jiangsu senile Health Research Project (LKM2023016) and “Image Medical Star” Project of Suzhou Medical Association (2022YX-M05).
-
Author contributions: R.L. and Z.J. contributed to the overall concept and study design. W.Z., D.S., and G.F. did the data collection and X.L. did data processing and analysis. R.L. and C.L. drafted the first draft of the manuscript. J.Y. provided external validation data and outlined the ROI. W.C. provided financial support. All authors critically reviewed and revised the manuscript to confirm accuracy. All authors gave final approval on the final draft for submission.
-
Conflict of interest: None.
-
Data availability statement: The analyzed datasets generated during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wallace A, Pershad Y, Saini A, Alzubaidi S, Naidu S, Knuttinen G, et al. Computed tomography angiography evaluation of acute limb ischemia. Vasa. 2019;48(1):57–64. 10.1024/0301-1526/a000759. Epub 2018 Oct 30.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Dakhil B, Lacal P, Abdesselam AB, Couffinhal JC, Gordienco A, Bagan P. Evaluation of balloon catheter-guided intraarterial thrombolysis for acute peripheralarterial occlusion. Ann Vasc surg. 2013;27(6):781–4. 10.1016/j.avsg.2012.11.011.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Qian WL, Zhou DJ, Jiang Y, Feng C, Chen Q, Wang H, et al. Ultra-low radiation dose CT angiography of the lower extremity using the iterative model reconstruction (IMR) algorithm. Clin Radiol. 2018;73(11):985.e13–9. 10.1016/j.crad.2018.08.001. Epub 2018 Sep 6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[4] Dharmarajah B, Sounderajah V, Rowland SP, Leen EL, Davies AH. Aging techniques for deep vein thrombosis: A systematic review. Phlebology. 2015;30(2):77–84. 10.1177/0268355514528691. Epub 2014 Mar 25.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Oweis Y, Viets Z, Shetty AS. Role of lower extremity run-off CT angiography in the evaluation of acute vascular disease. Abdom Radiol. 2017;42(4):1028–45. 10.1007/s00261-016-0907-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Preuß A, Elgeti T, Hamm B, Werncke T. Extravascular incidental findings in run-off CT angiography in patients with acute limb ischaemia: incidence and clinical relevance. Clin Radiol. 2015;70(6):622–9. 10.1016/j.crad.2015.02.014. Epub 2015 Mar 24.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Jiang Y, Chen C, Xie J, Wang W, Zha X, Lv W, et al. Radiomics signature of computed tomography imaging for prediction of survival and chemotherapeutic benefits in gastric cancer. EBio Med. 2018;36:171–82. 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 14.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Ren J, Tian J, Yuan Y, Dong D, Li X, Shi Y, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging based radiomics signature for the preoperative discrimination of stage I-II and III-IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2018;106:1–6. 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Bibault JE, Giraud P, Housset M, Durdux C, Taieb J, Berger A, et al. Deep Learning and Radiomics predict complete response after neo-adjuvant chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):12611. 10.1038/s41598-018-30657-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Davis FM, Albright J, Gallagher KA, Gurm HS, Koenig GC, Schreiber T, et al. Early outcomes following endovascular, open surgical, and hybrid revascularization for lower extremity acute limb ischemia. Ann Vasc Surg. 2018;51:106–12. 10.1016/j.avsg.2017.12.025. Epub 2018 Mar 5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Baril DT, Ghosh K, Rosen AB. Trends in the incidence, treatment, and outcomes of acute lower extremity ischemia in the United States Medicare population. J Vasc Surg. 2014;60(3):669–77.e2. 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.03.244. Epub 2014 Apr 24.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Elmahdy MF, Ghareeb Mahdy S, Baligh Ewiss E, Said K, Kassem HH, Ammar W. Value of duplex scanning in differentiating embolic from thrombotic arterial occlusion in acute limb ischemia. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2010;11(4):223–6. 10.1016/j.carrev.2009.09.001.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology. 2016;278(2):563–77. 10.1148/radiol.2015151169. Epub 2015 Nov 18.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Liang C, Huang Y, He L, Chen X, Ma Z, Dong D, et al. The development and validation of a CT-based radiomics signature for the preoperative discrimination of stage I-II and stage III-IV colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(21):31401–12. 10.18632/oncotarget.8919.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Huang YQ, Liang CH, He L, Tian J, Liang CS, Chen X, et al. Development and validation of a radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(18):2157–64. 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.9128. Epub 2016 May 2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Aerts HJ, Velazquez ER, Leijenaar RT, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using aquantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4006. 10.1038/ncomms5006.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Huang Y, Liu Z, He L, Chen X, Pan D, Ma Z, et al. Radiomics signature: A potential biomarker for the prediction of disease-free survival in early-stage (I or II) non-small cell lung cancer. Radiology. 2016;281(3):947–57. 10.1148/radiol.2016152234. Epub 2016 Jun 27.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, et al. Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(9):1234–48. 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010. Epub 2012 Aug 13.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Zhang Y, Oikonomou A, Wong A, Haider MA, Khalvati F. Radiomics-based prognosis analysis for non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46349. 10.1038/srep46349.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] van Timmeren JE, Leijenaar RTH, van Elmpt W, Reymen B, Oberije C, Monshouwer R, et al. Survival prediction of non-small cell lung cancer patients using radiomics analyses of cone-beam CT images. Radiother Oncol. 2017;123(3):363–9. 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.04.016. Epub 2017 May 12.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[21] Coroller TP, Grossmann P, Hou Y, Rios Velazquez E, Leijenaar RT, Hermann G, et al. CT-based radiomic signature predicts distant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Radiother Oncol. 2015;114(3):345–50. 10.1016/j.radonc.2015.02.015. Epub 2015 Mar 4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Li Q, Kim J, Balagurunathan Y, Liu Y, Latifi K, Stringfield O, et al. Imaging features from pretreatment CT scans are associated with clinical outcomes in nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. Med Phys. 2017;44(8):4341–9. 10.1002/mp.12309. Epub 2017 Jun 24.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Kolossváry M, De Cecco CN, Feuchtner G, Maurovich-Horvat P. Advanced atherosclerosis imaging by CT: Radiomics, machine learning and deep learning. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2019;13(5):274–80. 10.1016/j.jcct.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 Apr 21.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Qiu W, Kuang H, Nair J, Assis Z, Najm M, McDougall C, et al. Radiomics-based intracranial thrombus features on CT and CTA predict recanalization with intravenous alteplase in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40(1):39–44. 10.3174/ajnr.A5918. Epub 2018 Dec 20.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer

