Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
-
Xin Jiang
and Yanbing Ding
Abstract
This research aimed to evaluate the eradication efficacy, safety, and gastrointestinal symptom relief rates of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy in primary eradication patients in Yangzhou, China. It also investigated the possible factors influencing the success of different Helicobacter pylori eradication regimens. A single-center, prospective, open-label, randomized controlled study was performed from December 2020 and October 2021, in which 255 patients with H. pylori infection were assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to the three different groups. Our results showed that high-dose dual therapy (91.0%, 71/78) and resistance gene-based triple therapy (94.9%, 75/79) achieved eradication rates and compliance equivalent to those of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (85.3%, 64/75) in the per-protocol analysis, while high-dose dual therapy had lower rates of adverse events (11.5%, 9/78, P < 0.05), fewer side effects, and greater safety. Most patients’ gastrointestinal discomfort symptoms improved after eradication of H. pylori. Poor compliance (P < 0.05) and antibiotic resistance (P < 0.05) were risk factors for the efficacy of H. pylori eradication. Therefore, the appropriate regimen can be individualized for eradication therapy in clinical practice according to the patient’s resistance and tolerance to the drug.
1 Introduction
Helicobacter pylori is a gram-negative bacillus with a high infection rate and high pathogenicity. The prevalence of H. pylori infection in the Chinese population is nearly 50% [1], while it has slightly decreased in recent years, the rate is still high [2]. With the widespread use of antibiotics, the rate of antibiotic resistance in our population is also increasing [3]. At present, in the Chinese population, clarithromycin (resistance rate 20–40%), metronidazole (resistance rate 40–70%), and levofloxacin (resistance rate 20–40%) have high resistance rates, while the resistance rates of amoxicillin (0–5%), tetracycline (0–5%), and furazolidone (0–3%) are still low [4]. The eradication rate of standard triple therapy has been reduced to unacceptable levels (eradication rate <80%) as the therapy has been widely abandoned [5]. In the Maastricht V consensus report, it was proposed [6] that classical bismuth quadruple therapy is recommended as first-line eradication therapy in areas with high clarithromycin resistance (>15%). Since tetracycline is difficult to obtain in most parts of mainland China classical bismuth quadruple therapy cannot be widely used. Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy is recommended in the fifth national expert consensus on H. pylori infection in China [7], of which the most commonly used regimen with relatively fewer adverse reactions includes proton pump inhibitors (PPI) + amoxicillin + clarithromycin + bismuth. However, in our previous epidemiological survey, the resistance rate to clarithromycin reached 43.65% in the areas of Yangzhou, China. If such therapy was used, the eradication rate of H. pylori would inevitably be reduced and nearly half of the patients misused the antibiotics. The efficacy of clarithromycin-containing bismuth quadruple therapy has not been reported in adults in the areas of Yangzhou, China. In addition, there are many types of quadruple therapy drugs and patients have greater concerns about the occurrence of adverse drug events, which greatly affect medication compliance. Thus, we need to explore H. pylori eradication options that are more appropriate for the patients in the areas of Yangzhou, China.
When we analyzed the influential factors associated with H. pylori eradication failure, we found that antibiotic resistance was one of the most important causes of eradication failure [8]. As an infectious disease, H. pylori should theoretically be eradicated by selecting sensitive antibiotics based on susceptibility testing or local antibiotic resistance profiles. A study from Korea [9] aimed to evaluate the efficacy of drug susceptibility-based individualized therapy for first-line eradication of H. pylori in regions with high antibiotic resistance, with an intention-to-treat (ITT) eradication rate of 93.1% and a per-protocol (PP) eradication rate of 100.0%. Compared to sequential therapy, the eradication rate of drug susceptibility-based individualized therapy in the population was significantly higher. However, the difference in the antibiotic resistance spectrum in various regions, combined with the strict conditions of H. pylori culture and the low success rate of the sensitivity test, limits the selection of medication for H. pylori based on drug sensitivity tests [10]. With the rapid development of molecular biology techniques, antibiotic resistance in H. pylori can be obtained by genetic testing [11]. A multicenter prospective randomized controlled trial including 526 patients [12] was used to detect H. pylori infection and clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance by a molecular detection method of genotype HelicoDR test, and sensitive antibiotic eradication was selected according to its drug resistance results. The individualized eradication efficiency was higher than that of traditional triple therapy. This molecular biological detection method greatly solves the bottleneck associated with the limited use of drug sensitivity tests in clinical practice.
In our population, the rate of resistance to amoxicillin is very low, and amoxicillin is widely used in infectious diseases [13]. Through an in-depth study of the bactericidal mechanism of amoxicillin, it was found that the antibacterial effect of amoxicillin on H. pylori is pH-dependent [14]. When gastric acid is fully inhibited and the pH level in the stomach can continue to reach greater than 6, amoxicillin can fully exploit its bactericidal effect on H. pylori; more sufficient gastric acid secretion inhibition yields a greater antibacterial efficacy of amoxicillin. A randomized controlled study [15] from a large sample compared the eradication safety of high-dose dual therapy with that of bismuth quadruple therapy. Modified dual therapy at a high dose and high administration frequency was equally effective, safer, and less costly than bismuth-containing quadruple therapy.
Currently, there is a lack of data regarding the appropriate H. pylori eradication regimen in the areas of Yangzhou, China. The aim of this study is to determine whether high-dose dual therapy and resistance-based triple therapy are superior to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy in terms of eradication rates and incidence of adverse events, and to assess the factors that may affect the success of eradication.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
The study participants included those who took part in the screening program for upper gastrointestinal tumors in Yangshou Town, Hanjiang District, Yangzhou City between December 2020 and October 2021. All patients underwent H. pylori detection and gastroscopy. Patients were considered eligible for enrollment if they were 18–70 years old and had H. pylori infection. H. pylori infection was defined as both positive for H. pylori by 14C-UBT and successful detection of the H. pylori UreA gene. Patients with any one of the following criteria were excluded: (1) H. pylori negative by 14C-UBT, or H. pylori UreA was not detected; (2) previously received H. pylori eradication therapy; (3) had taken H2 receptor blockers, PPI, bismuth, antibiotics, or other drugs with antibacterial effects in the past 4 weeks; (4) allergies or have drug contraindications for PPI, bismuth, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, levofloxacin, furazolidone, or tetracycline drugs used in this study; (5) pregnant or lactating women; (6) history of malignant tumors or gastric surgery; (7) serious liver disease, kidney disease, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, lung disease, blood diseases, or other serious diseases affecting the evaluation of this study; and (8) unwilling or unable to sign the consent form.
This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Yangzhou University (2020-YKL11-10) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and the standards of Good Clinical Practice. Informed consent was obtained from each participant. This study was registered in the China Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2000040469).
2.2 Study design
This was a single-center, prospective, open-label, randomized controlled study. According to the order of presentation, patients who met the inclusion criteria were divided into an empirical bismuth quadruple therapy group, a high-dose dual therapy group, and a resistance gene-based triple therapy group at a ratio of 1:1:1 using a random number table. We collected general condition data, clinical data, and gastric mucosal tissue of the patients included in the study and performed gastroscopy, 14C-UBT, and H. pylori resistance gene detection. This was an open-label study in which both investigators and patients were aware of the eradication regimen; staff performing epidemiological investigations, gastroscopy, 14C-UBT, and H. pylori resistance gene testing were blinded to group assignment to avoid possible measurement bias.
All patients returned within 1 week after the end of the radical course of treatment, and the patients were asked about the adverse events during treatment to determine the incidence of these adverse events. The remaining drugs in the patients’ bodies were examined to assess medication compliance. After discontinuation for at least 1 month, all patients underwent a repeat 14C-UBT to assess H. pylori infection status and to determine whether eradication of H. pylori was successful.
2.3 Treatment regimens
The groups and intervention strategies of this study are shown in Figures 1 and 2, and patients who met the inclusion criteria were assigned to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy groups. Radical therapy for patients in the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy group (RACB regimen) was as follows: rabeprazole 20 mg, colloidal bismuth pectin 220 mg, amoxicillin 1,000 mg, and clarithromycin 500 mg all twice daily. Radical therapy for patients in the high-dose dual therapy group (RA regimen) was as follows: rabeprazole 20 mg and amoxicillin 750 mg four times daily. Lastly, radical therapy for patients in resistance gene-based triple therapy was as follows: if the patient was resistant to amoxicillin, rabeprazole 20 mg twice daily, furazolidone 100 mg twice daily, and tetracycline 500 mg three times daily (RFT regimen); if the patient was sensitive to amoxicillin and clarithromycin, rabeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1,000 mg, and clarithromycin 500 mg all twice daily (RAC regimen); if the patient was sensitive to amoxicillin and metronidazole, but was resistant to clarithromycin, rabeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1,000 mg twice daily, and metronidazole 400 mg three times daily (RAM regimen); if the patient was sensitive to amoxicillin and levofloxacin, but was resistant to clarithromycin and metronidazole, rabeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1,000 mg twice daily, and levofloxacin 500 mg once daily (RAL regimen); and if the patient was sensitive to amoxicillin, but was resistant to clarithromycin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin, rabeprazole 20 mg, amoxicillin 1,000 mg, and furazolidone 100 mg, all twice daily (RAF regimen).
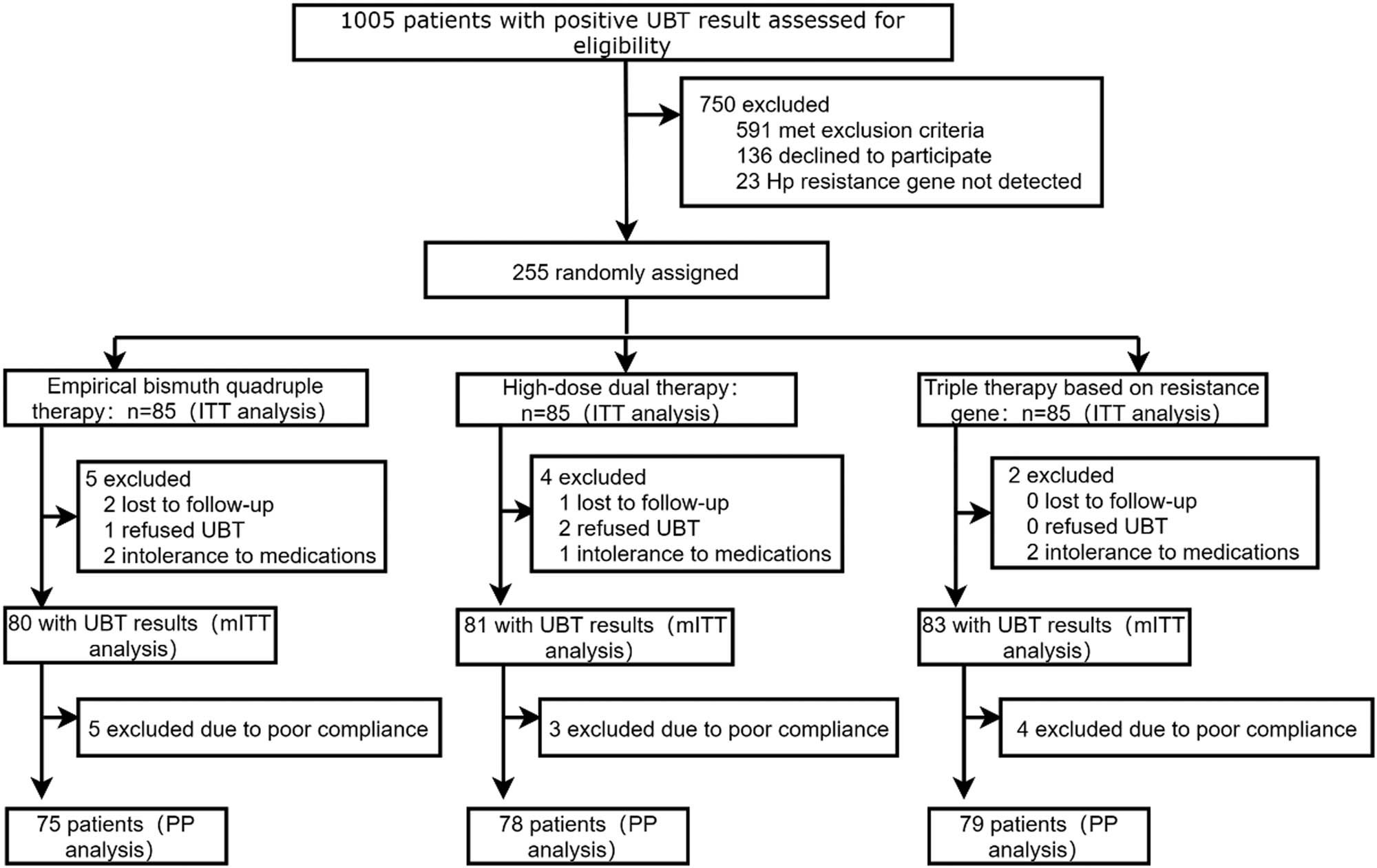
Study flowchart. ITT, intention-to-treat; mITT, modified intention-to-treat; PP, per-protocol.

Procedures for selecting sensitive antibiotic therapy based on H. pylori resistance gene test results. R, rabeprazole; A, amoxicillin; C, clarithromycin; M: metronidazole; L: levofloxacin; F: furazolidone; T, tetracycline.
The course of radical treatment in all three groups was 14 days, during which rabeprazole and colloidal bismuth pectin were administered half an hour before meals; amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, levofloxacin, furazolidone, and tetracycline were administered half an hour after meals; and the drugs that needed to be taken four times daily were taken at bedtime in addition to the three meal times.
2.4 H. pylori detection and resistance gene detection
All eligible participants underwent an upper endoscopy and 14C-UBT after entering the study. A gastric biopsy taken from the antrum was subjected to H. pylori UreA, vacA gene detection as well as resistance gene detection (Hangzhou Meilian Medical Laboratory Co., Ltd). Antibiotics targeted by the resistance genes included amoxicillin (PBP1), clarithromycin (23S rRNA), metronidazole (rdxA), and levofloxacin (gyrA).
14C-UBT was used to confirm the presence of H. pylori infection at least 4 weeks after treatment. The participants swallowed one 14C-urea capsule in a fasting state and sat quietly for 20 min. During this period, participants did not exercise, eat, or drink. After this period, the participants were instructed to gently blow air into a vial with a red indicator through a disposable plastic expiratory tube for 1–3 min. The red indicator disappeared and the vial cap was closed. Scintillation fluid was added first during the measurement, and the disintegrations per minute (DPM) value of the participant was measured for 3 min on the H. pylori tester to determine whether the participant was infected with H. pylori. If the DPM was ≥100, the patient was considered positive for H. pylori.
2.5 Safety and compliance
All participants were informed of medication-related matters, including drug type, dose, frequency, medication time, and possible adverse events, in-person before medication administration. Each participant was given a record sheet of adverse events during medication administration. The participants recorded their medication and adverse events every day. The investigator could be contacted by telephone at any time if the participant had obvious discomfort during medication. It was recommended that the drug should not be discontinued in cases of mild-to-moderate adverse events. We asked the participants to return 1–3 days after eradication for compliance assessment and to determine the incidence of adverse effects. After taking the drug on time for 2 weeks and stopping all drugs for at least 4 weeks, we instructed the participants to perform 14C-UBT to determine whether the eradication of H. pylori was successful. The definition of compliance was ≥80% of all study drugs taken as instructed; otherwise, the patient was considered to have poor compliance.
2.6 Statistical analysis
The main aim of this study was to compare empirical bismuth quadruple therapy with a control. During the pre-test, 20 patients in each group underwent H. pylori eradication, and the eradication rates were 75, 86, and 93% in the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy group, and resistance gene-based triple therapy, respectively. According to the purpose and design of this study, the hypothesis test type I error α was 0.05, type II error β was 0.2, and the sample size ratio of each group was 1:1:1, assuming the failure rate was 10–15%. It was determined that 85 patients were required in each group for the three radical treatment regimens.
All participants were included in the ITT analysis. The participants who had taken the drug at least once and had the reexamination result from the 14C-UBT were included in the mITT analysis. The participants with good compliance and reexamination results from the 14C-UBT were included in the PP analysis.
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS for Windows (version 21.0; IBM, Armonk, NY, USA). Two-sided P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant when comparing the three groups. Adjustment for multiple comparisons was made by setting a Bonferroni-corrected P level of 0.017. Categorical variables were described as percentages or frequencies, while continuous variables were described as mean ± standard deviation. The eradication rates and 95% CI were calculated. Intergroup differences were evaluated using Pearson chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and Student’s t test for continuous variables. Univariate analysis was performed to evaluate significant predictive variables for H. pylori eradication in participants with mITT analysis. A multiple logistic regression analysis was performed using variables with statistical significance in univariate analysis. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% CI for unsuccessful eradication were calculated according to the different variables.
3 Results
3.1 Characteristics of the participants
According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 255 participants were enrolled in this study from December 2020 to October 2021, and were assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy groups, with 85 patients in each group. Among the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, two patients were lost to follow-up, one patient refused to have reexamination of 14C-UBT, two patients were intolerant to adverse drug reactions and discontinued halfway, and finally, 80 patients were included in the mITT analysis; excluding five patients with poor compliance, a total of 75 patients were included in the PP analysis. Among the high-dose dual therapy, one patient was lost to follow-up, two patients refused to have reexamination of 14C-UBT, one patient was intolerant to adverse drug reactions and discontinued halfway, and finally, 81 patients were included in the mITT analysis; excluding three patients with poor compliance, a total of 78 patients were included in the PP analysis. Among the resistance gene-based triple therapy, two patients were intolerant to adverse drug reactions and discontinued halfway, and finally, 83 patients were included in the mITT analysis; excluding four patients with poor compliance, a total of 79 patients were included in the PP analysis. The baseline characteristics of participants collected in each group included: sex, age, body mass index, family population, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, smoking history, drinking history, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, dietary habits, family history of gastrointestinal cancer, previous history of dyspepsia, endoscopic diagnosis, pathological diagnosis, H. pylori virulence gene, antibiotic resistance, and antibiotic resistance pattern. Except for diastolic blood pressure, there were no significant differences in other baseline characteristics among the three groups in the ITT analysis population. Specific baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Comparison of baseline data between three therapy groups
| Baseline factors | Empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (n = 85) | High-dose dual therapy (n = 85) | Resistance gene-based triple therapy (n = 85) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n/N (%) | 0.119 | |||
| Male | 44/85(51.8%) | 31/85(36.5%) | 35/85(41.2%) | |
| Female | 41/85(48.2%) | 54/85(63.5%) | 50/85(58.8%) | |
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 54.42 ± 8.85 | 53.61 ± 8.59 | 53.51 ± 8.20 | 0.746 |
| BMI, mean ± SD, kg/m2 | 23.79 ± 2.65 | 24.49 ± 2.93 | 24.38 ± 3.08 | 0.239 |
| Family populations, n/N (%) | 0.182 | |||
| ≤3 | 45/85(52.9%) | 33/85(38.8%) | 39/85(45.9%) | |
| >3 | 40/85(47.1%) | 52/85(61.2%) | 46/85(54.1%) | |
| Systolic blood pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 131.22 ± 14.62 | 134.48 ± 11.81 | 131.13 ± 13.75 | 0.180 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mean ± SD, mmHg | 84.21 ± 7.23 | 87.06 ± 6.76 | 84.48 ± 7.74 | 0.020* |
| Smoking, n/N (%) | 28/85(32.9%) | 19/85(22.4%) | 30/85(35.3%) | 0.147 |
| Alcohol intake, n/N (%) | 34/85(40.0%) | 30/85(35.3%) | 25/85(29.4%) | 0.349 |
| Hypertension, n/N (%) | 20/85(23.5%) | 26/85(30.6%) | 21/85(24.7%) | 0.534 |
| Diabetes, n/N (%) | 3/85(3.5%) | 5/85(5.9%) | 3/85(3.5%) | 0.796 |
| Hyperlipemia, n/N (%) | 7/85(8.2%) | 8/85(9.4%) | 2/85(2.4%) | 0.142 |
| Dietary habits, n/N (%) | 0.467 | |||
| Regular diet | 76/85(89.4%) | 73/85(85.9%) | 78/85(91.8%) | |
| Irregular diet | 9/85(10.6%) | 12/85(14.1%) | 7/85(8.2%) | |
| Feeding rate, n/N (%) | 0.339 | |||
| Normal | 66/85(77.6%) | 69/85(81.2%) | 61/85(71.8%) | |
| Too fast or too slow | 19/85(22.4%) | 16/85(18.8%) | 24/85(28.2%) | |
| Food temperature, n/N (%) | 0.716 | |||
| Moderate | 76/85(89.4%) | 77/85(90.6%) | 79/85(92.9%) | |
| Too hot or too cold | 9/85(10.6%) | 8/85(9.4%) | 6/85(7.1%) | |
| Family history of gastrointestinal cancer, n/N (%) | 0.269 | |||
| Yes | 28/85(32.9%) | 31/85(36.5%) | 38/85(44.7%) | |
| No | 57/85(67.1%) | 54/85(63.5%) | 47/85(55.3%) | |
| Prior history of dyspepsia, n/N (%) | 0.606 | |||
| Yes | 26/85(30.6%) | 21/85(24.7%) | 21/85(24.7%) | |
| No | 59/85(69.4%) | 64/85(75.3%) | 64/85(75.3%) | |
| Endoscopic diagnosis, n/N (%) | 0.336 | |||
| Peptic ulcer | 13/85(15.3%) | 7/85(8.2%) | 9/85(10.6%) | |
| Nonpeptic ulcer | 72/85(84.7%) | 78/85(91.8%) | 76/85(89.4%) | |
| Pathological diagnosis, n/N (%) | 0.212 | |||
| Chronic superficial gastritis | 22/85(25.9%) | 28/85(32.9%) | 19/85(22.4%) | |
| Chronic atrophic gastritis | 43/85(50.6%) | 45/85(52.9%) | 40/85(47.1%) | |
| Intestinal metaplasia | 17/85(20.0%) | 11/85(12.9%) | 20/85(23.5%) | |
| Atypical hyperplasia | 3/85(3.5%) | 1/85(1.2%) | 6/85(7.1%) | |
| Vac A, n/N (%) | 0.539 | |||
| s1/m1 | 32/85(37.6%) | 32/85(37.6%) | 26/85(30.6%) | |
| s1/m2 | 53/85(62.4%) | 53/85(62.4%) | 59/85(69.4%) | |
| Antibiotic resistance, n/N (%) | ||||
| Amoxicillin resistance | 8/85(9.4%) | 7/85(8.2%) | 5/85(5.9%) | 0.684 |
| Clarithromycin resistance | 33/85(38.8%) | 42/85(49.4%) | 48/85(56.5%) | 0.068 |
| Levofloxacin resistance | 44/85(51.8%) | 32/85(37.6%) | 45/85(52.9%) | 0.063 |
| Metronidazole resistance | 29/85(34.1%) | 32/85(37.6%) | 37/85(43.5%) | 0.444 |
| Antibiotic resistance patterns, n/N (%) | ||||
| All sensitive | 20/85(23.5%) | 21/85(24.7%) | 12/85(14.1%) | 0.176 |
| Single resistance | 27/85(31.8%) | 21/85(24.7%) | 26/85(30.6%) | 0.554 |
| Double resistance | 27/85(31.8%) | 37/85(43.5%) | 33/85(38.8%) | 0.282 |
| Multidrug resistance | 11/85(12.9%) | 6/85(7.1%) | 14/85(16.5%) | 0.165 |
SD, standard deviation; BMI, body mass index; *P < 0.05.
3.2 Eradication rates
The primary outcome indicator of this study was to determine whether high-dose dual therapy and resistance gene-based triple therapy were superior to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy for H. pylori eradication. The eradication rate of resistance gene-based triple therapy was superior to that of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (90.6 vs 77.6%, respectively, with a rate difference of 13.0% in ITT analysis; 94.9 vs 85.3%, respectively, with a rate difference of 9.6% in PP analysis) (Table 2), but the difference was not statistically significant both in the ITT analysis and PP analysis (Figure 3). Moreover, the eradication rate of the high-dose dual therapy group was superior to that of the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy group (84.7 vs 77.6%, respectively, with a rate difference of 7.1% in the ITT analysis; 91.0 vs 85.3%, respectively, with a rate difference of 5.7% in the PP analysis) (Table 2), and also the difference was not statistically significant (Figure 3). We concluded that high-dose dual therapy and resistance gene-based triple therapy could achieve eradication rates equivalent to the efficacy of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy.
Comparison of eradication rates between three therapy groups
| Eradication rate | Empirical bismuth quadruple therapy | High-dose dual therapy | Resistance gene-based triple therapy | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n/N | 95% CI (%) | n/N | 95% CI (%) | n/N | 95% CI (%) | ||
| ITT analysis | 66/85(77.6%) | 67.7–85.2 | 72/85(84.7%) | 75.6–90.8 | 77/85(90.6%) | 82.5–95.2 | 0.067 |
| mITT analysis | 66/80(82.5%) | 72.7–89.3 | 72/81(88.9%) | 80.2–94.0 | 77/83(92.8%) | 85.1–96.6 | 0.124 |
| PP analysis | 64/75(85.3%) | 75.6–91.6 | 71/78(91.0%) | 82.6–95.6 | 75/79(94.9%) | 87.7–98.0 | 0.124 |
CI, confidence interval; ITT, intention-to-treat; mITT, modified intention-to-treat; PP, per-protocol.

Comparison of eradication rates between three therapy groups.
3.3 Compliance and adverse events
The compliance and incidence of adverse events among the groups are presented in Table 3. The compliance in both the high-dose dual therapy group and the resistance gene-based triple therapy group was comparable to that of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy. In terms of safety, in the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy group, two patients withdrew from the drug because of unbearable bitter taste, nausea, and dark stools; in the high-dose dual therapy group, one patient withdrew from the drug because of a rash with unbearable itching after eating seafood while taking the drug. In the resistance gene-based triple therapy group, one patient withdrew from the drug owing to dizziness and nausea after drinking alcohol while taking the drug, and one patient withdrew from the drug because of abdominal pain, diarrhea, and other gastrointestinal events. The other patients experienced mild or moderate adverse events and were not given specific treatment. There was a statistical difference in the incidence of adverse events between the three radical regimens (P = 0.009), mainly in symptoms such as bitter taste (P = 0.016), darkened stools (P < 0.001), and nausea (P = 0.039). The incidence of adverse events was significantly lower with the high-dose dual therapy than with the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (P = 0.002) and the incidence of adverse events with resistance gene-based triple therapy was equivalent to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (P = 0.272).
Comparison of safety and compliance between three therapy groups
| Safety and compliance | Empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (n = 75) | High-dose dual therapy (n = 78) | Resistance gene-based triple therapy (n = 79) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with adverse events | 24(32.0%)# | 9(11.5%)# | 19(24.1%) | 0.009* |
| Mild | 13(17.3%) | 6(7.7%) | 12(15.2%) | 0.181 |
| Moderate | 9(12.0%) | 2(2.6%) | 5(6.3%) | 0.068 |
| Severe | 2(2.7%) | 1(1.3%) | 2(2.5%) | 0.871 |
| Bitter taste | 14(18.7%)$ | 3(3.8%)$ | 10(12.7%) | 0.016* |
| Dark stools | 18(24.0)& | — | 2(2.5%)& | <0.001* |
| Nausea | 4(5.3%) | 3(3.8%) | 11(13.9%) | 0.039 |
| Diarrhea | 6(8.0%) | 5(6.4%) | 6(7.6%) | 0.925 |
| Constipation | 5(6.7%) | 1(1.3%) | 4(5.1%) | 0.224 |
| Abdominal pain/discomfort | 3(4.0%) | 2(2.6%) | 4(5.1%) | 0.774 |
| Asthenia | 2(2.7%) | 1(1.3%) | 2(2.5%) | 0.871 |
| Decreased appetite | 1(1.3%) | 1(1.3%) | 3(3.8%) | 0.624 |
| Rash | 3(4.0%) | 5(6.4%) | 2(2.5%) | 0.478 |
| Headache | 2(2.7%) | 1(1.3%) | 1(1.3%) | 0.695 |
| Dizziness | 1(1.3%) | 1(1.3%) | 2(2.5%) | 1.000 |
| Good compliance | 75/85(88.2%) | 78/85(91.8%) | 79/85(92.9%) | 0.537 |
-
# P = 0.002 for high-dose dual therapy versus empirical bismuth quadruple therapy; $ P = 0.004 for high-dose dual therapy versus empirical bismuth quadruple therapy; & P < 0.017 for resistance gene-based triple therapy versus empirical bismuth quadruple therapy; * P < 0.017.
3.4 Improvement of gastrointestinal symptoms after eradication therapy
The Global Overall Symptom questionnaires were given to participants before the H. pylori eradication therapy and after 1 month from the eradication therapy completed. The overall relief of gastrointestinal symptoms after eradication therapy was 81.3% (61/75) in patients treated with the empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, 89.7% (70/78) in patients treated with high-dose dual therapy, and 84.8% (67/79) in patients treated with the resistance gene-based triple therapy (Figure 4). Most patients’ discomfort symptoms improved after eradication of H. pylori, and there was no statistical difference between the three groups (P > 0.05).

Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after H. pylori eradication.
3.5 Risk factors for eradication failure
Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to investigate the risk factors for eradication failure. Univariate analysis (Table 4) showed poor compliance (40.0 vs 85.3%, P = 0.035), resistance to amoxicillin (50.0 vs 86.1%, P = 0.039), resistance to clarithromycin (61.3 vs 95.9%, P < 0.001), and multidrug resistance (45.5 vs 88.4%, P = 0.002) as risk factors for eradication failure in empirical bismuth quadruple therapy. Meanwhile poor compliance (33.3 vs 91.0%, P = 0.031) and resistance to amoxicillin (57.1 vs 91.9%, P = 0.027) were shown as risk factors for eradication failure in high-dose dual therapy; and poor compliance (50.0 vs 94.9%, P = 0.025) was shown as risk factors for eradication failure in resistance gene-based triple therapy. Multivariate analysis identified poor compliance (OR 13.607, 95% CI 1.249–148.187, P = 0.032) and resistance to clarithromycin (OR 12.582, 95% CI 1.925–82.245, P = 0.008) as independent predictors of eradication failure in empirical bismuth quadruple therapy. Meanwhile, multivariate analysis identified poor compliance (OR 33.500, 95% CI 2.479–452.762, P = 0.008) and resistance to amoxicillin (OR 12.562, 95% CI 2.066–76.391, P = 0.006) as independent predictors of eradication failure in high-dose dual therapy. We found no independent predictor of eradication failure in resistance gene-based triple therapy.
Univariate analysis showing factors affecting H. pylori eradication rates
| Influencing factors | Empirical bismuth quadruple therapy (n = 80) | High-dose dual therapy (n = 81) | Resistance gene-based triple therapy (n = 83) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eradication rate | P value | Eradication rate | P value | Eradication rate | P value | |
| Gender, n/N (%) | 0.331 | 0.838 | 1.000 | |||
| Male | 33/42(78.6%) | 25/29(86.2%) | 32/34(94.1%) | |||
| Female | 33/38(86.8%) | 47/52(90.4%) | 45/49(91.8%) | |||
| Age, years, n/N (%) | 0.652 | 0.275 | 0.483 | |||
| ≤50 | 20/23(87.0%) | 29/33(87.9%) | 33/36(91.7%) | |||
| 51–60 | 30/36(83.3%) | 27/32(84.4%) | 26/29(89.7%) | |||
| >60 | 16/21(76.2%) | 16/16(100.0%) | 18/18(100.0%) | |||
| BMI, kg/m2, n/N (%) | 0.563 | 0.268 | 0.645 | |||
| ≤22 | 16/19(84.2%) | 15/15(100.0%) | 13/15(86.7%) | |||
| 22–25 | 31/36(86.1%) | 27/30(90.0%) | 35/37(94.6%) | |||
| >25 | 19/25(76.0%) | 30/36(83.3%) | 29/31(93.5%) | |||
| Family populations, n/N (%) | 0.918 | 0.157 | 0.522 | |||
| ≤3 | 34/41(82.9%) | 30/31(96.8%) | 34/38(89.5%) | |||
| >3 | 32/39(82.1%) | 42/50(84.0%) | 43/45(95.6%) | |||
| Smoking, n/N (%) | 0.221 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||
| Yes | 19/26(73.1%) | 15/17(88.2%) | 27/29(93.1%) | |||
| No | 47/54(87.0%) | 57/64(89.1%) | 50/54(92.6%) | |||
| Alcohol intake, n/N (%) | 0.400 | 0.838 | 0.826 | |||
| Yes | 25/32(78.1%) | 25/29(86.2%) | 23/24(95.8%) | |||
| No | 41/48(85.4%) | 47/52(90.4%) | 54/59(91.5%) | |||
| Hypertension, n/N (%) | 1.000 | 0.644 | 0.986 | |||
| Yes | 16/19(84.2%) | 22/26(84.6%) | 20/21(95.2%) | |||
| No | 50/61(82.0%) | 50/55(90.9%) | 57/62(91.9%) | |||
| Diabetes, n/N (%) | 0.443 | 0.454 | 0.204 | |||
| Yes | 2/3(66.7%) | 4/5(80.0%) | 2/3(66.7%) | |||
| No | 64/77(83.1%) | 68/76(89.5%) | 75/80(93.8%) | |||
| Hyperlipemia, n/N (%) | 0.539 | 0.216 | 1.000 | |||
| Yes | 6/6(100.0%) | 6/8(75.0%) | 2/2(100.0%) | |||
| No | 60/74(81.1%) | 66/73(90.4%) | 75/81(92.6%) | |||
| Dietary habits, n/N (%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||
| Regular diet | 59/71(83.1%) | 61/69(88.4%) | 70/76(92.1%) | |||
| Irregular diet | 7/9(77.8%) | 11/12(91.7%) | 7/7(100.0%) | |||
| Feeding rate, n/N (%) | 1.000 | 0.879 | 1.000 | |||
| Normal | 51/62(82.3%) | 58/66(87.9%) | 56/60(93.3%) | |||
| Too fast or too slow | 15/18(83.3%) | 14/15(93.3%) | 21/23(91.3%) | |||
| Food temperature, n/N (%) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | |||
| Moderate | 59/71(83.1%) | 65/73(89.0%) | 71/77(92.2%) | |||
| Too hot or too cold | 7/9(77.8%) | 7/8(87.5%) | 6/6(100.0%) | |||
| Family history of gastrointestinal cancer, n/N (%) | 0.269 | 1.000 | 0.834 | |||
| Yes | 20/27(74.1%) | 27/30(90.0%) | 36/38(94.7%) | |||
| No | 46/53(86.8%) | 45/51(88.2%) | 41/45(91.1%) | |||
| Prior history of dyspepsia, n/N (%) | 0.847 | 0.893 | 1.000 | |||
| Yes | 19/24(79.2%) | 18/21(85.7%) | 19/20(95.0%) | |||
| No | 47/56(83.9%) | 54/60(90.0%) | 58/63(92.1%) | |||
| Endoscopic diagnosis, n/N (%) | 0.621 | 1.000 | 0.467 | |||
| Peptic ulcer | 11/12(91.7%) | 6/6(100.0%) | 7/8(87.5%) | |||
| Nonpeptic ulcer | 55/68(80.9%) | 66/75(88.0%) | 70/75(93.3%) | |||
| Pathological diagnosis, n/N (%) | 0.854 | 0.352 | 0.254 | |||
| Chronic superficial gastritis | 18/21(85.7%) | 22/26(84.6%) | 17/19(89.5%) | |||
| Chronic atrophic gastritis | 33/40(82.5%) | 41/44(93.2%) | 36/39(92.3%) | |||
| Intestinal metaplasia | 12/16(75.0%) | 8/10(80.0%) | 20/20(100.0%) | |||
| Atypical hyperplasia | 3/3(100.0%) | 1/1(100.0%) | 4/5(80.0%) | |||
| Compliance | 0.035*# | 0.031*$ | 0.025* | |||
| Good | 64/75(85.3%) | 71/78(91.0%) | 75/79(94.9%) | |||
| Poor | 2/5(40.0%) | 1/3(33.3%) | 2/4(50.0%) | |||
| Vac A | 0.287 | 0.443 | 0.443 | |||
| s1/m1 | 23/30(76.7%) | 26/31(83.9%) | 32/33(97.0%) | |||
| s1/m2 | 43/50(86.0%) | 46/50(92.0%) | 45/50(90.0%) | |||
| Amoxicillin resistance | 0.039* | 0.027*$ | ||||
| Yes | 4/8(50.0%) | 4/7(57.1%) | — | |||
| No | 62/72(86.1%) | 68/74(91.9%) | — | |||
| Clarithromycin resistance | <0.001*# | |||||
| Yes | 19/31(61.3%) | — | — | |||
| No | 47/49(95.9%) | — | — | |||
| Levofloxacin resistance | 0.118 | |||||
| Yes | 32/42(76.2%) | — | — | |||
| No | 34/38(89.5%) | — | — | |||
| Metronidazole resistance | 0.511 | |||||
| Yes | 25/29(86.2%) | — | — | |||
| No | 41/52(80.4%) | — | — | |||
| All sensitive | 0.289 | |||||
| Yes | 16/17(94.1%) | — | — | |||
| No | 50/63(79.4%) | — | — | |||
| Single resistance | 0.166 | |||||
| Yes | 25/27(92.6%) | — | — | |||
| No | 41/53(77.4%) | — | — | |||
| Multidrug resistance | 0.002* | |||||
| Yes | 5/11(45.5%) | — | — | |||
| No | 61/69(88.4%) | — | — | |||
BMI, body mass index; * P < 0.05; #Multivariate analysis identified poor compliance (OR 13.607, 95% CI 1.249–148.187, P = 0.032) and resistance to clarithromycin (OR 12.582, 95% CI 1.925–82.245, P = 0.008) as independent predictors of eradication failure in empirical bismuth quadruple therapy; $Multivariate analysis identified poor compliance (OR 33.500, 95% CI 2.479–452.762, P = 0.008) and resistance to amoxicillin (OR 12.562, 95% CI 2.066–76.391, P = 0.006) as independent predictors of eradication failure in high-dose dual therapy.
4 Discussion
H. pylori, an intragastric parasitic bacterium, has highly pathogenic characteristics [16–18]. China has a particularly high burden of H. pylori infections; the infection rate varies from region to region, and the prevalence of H. pylori infection in adults shows a decreasing trend in urban areas, which seems to be explained by differences in economic and social conditions [19,20]. However, in our previous epidemiological survey, we found that the infection rate of H. pylori in the areas of Yangzhou, China, reached 42.36% and belonged to areas with high infection rates. Recent surveillance reports on the trend of antimicrobial resistance in H. pylori have confirmed that the incidence of antibiotic resistance is increasing [4,21,22], resulting in a declining eradication rate, and that traditional triple therapy for H. pylori eradication is obsolete. Therefore, selection of an appropriate eradication therapy before the initial eradication of H. pylori is the focus of clinical attention. The consensus statement recommends [6,23,24] alternative first-line treatment options, including concomitant, sequential, mixed, and bismuth-containing quadruple therapy. Owing to the influence of clarithromycin and metronidazole resistance, non-bismuth quadruple therapy is not applicable in China. Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy is recommended as the first-line eradication regimen in the Fifth National Consensus Report on the Management of H. pylori infection in China [7]. It is also the most widely used radical regimen in clinical practice and can achieve a good eradication effect. However, there are many types of drugs for bismuth-containing quadruple therapy, and patients have greater concerns about the occurrence of adverse drug events which greatly affects medication compliance.
H. pylori is an infectious disease; theoretically, sensitive antibiotics should be selected for eradication therapy based on susceptibility testing or the local antibiotic resistance spectrum, which can avoid the abuse of antibiotics, reduce the types of drugs taken, and improve compliance [25,26]. However, the resistance rate of H. pylori to amoxicillin is still low, and high-dose dual therapy including PPI combined with amoxicillin has become an increasing concern in recent years. In a clinical study of dual therapy based on systematic review and meta-analysis, 12 randomized controlled studies were included, and the results showed that dual therapy with high-dose PPIs combined with amoxicillin, whether used for primary H. pylori eradication or salvage H. pylori eradication, could achieve better efficacy, with eradication rates of more than 90%, compared with various traditional radical therapies recommended by current mainstream clinical guidelines [27]. However, whether the above radical treatment options can achieve good results in rural areas of China has not been yet reported.
In this study, for the first time, we conducted a clinical study to determine whether high-dose dual therapy and resistance gene-based triple therapy were superior to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy for H. pylori eradication. The results showed that high-dose dual therapy and resistance gene-based triple therapy could achieve an eradication rate equivalent to empirical bismuth quadruple therapy. Due to the reduction in the types of drugs taken and precise radical cures, the adverse events of high-dose dual therapy were much lower than that of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, and the adverse events of resistance gene-based triple therapy were equivalent to that of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy.
Actually, Swedish scholar Unge et al. [28] first used a PPI and amoxicillin dual regimen to eradicate H. pylori as early as 1989, and since then many scholars have attempted different doses and frequencies of PPI and amoxicillin, but consistent and satisfactory eradication rates have remained difficult to obtain. With the deepening of the study on the kinetics and pharmacodynamics of amoxicillin and PPI, the mechanism of the dual regimen has been gradually elucidated. First, H. pylori strains are not susceptible to amoxicillin resistance because simultaneous mutations in multiple penicillin-binding protein-related genes cause marked resistance to amoxicillin [29]. Second, amoxicillin is a time-dependent antibiotic. The bactericidal effect mainly depends on the percentage of time when the plasma concentration is higher than the minimum inhibitory concentration. The same amoxicillin dose prolonged the percentage of time when divided into multiple doses. Multiple doses can also increase the local drug concentration in the gastric juice. Oral administration of four times per day can result in a better bactericidal effect [30,31]. Third, amoxicillin exerts a bactericidal effect by inhibiting the formation of bacterial cell walls and is effective only when bacteria multiply actively. H. pylori multiplies actively when the intragastric pH is >6.0; thus, amoxicillin has the best bactericidal effect at this pH [5]. In addition, amoxicillin is easily destroyed in an acidic environment, and adequate inhibition of gastric acid is the key to its effective sterilization. As potent antacids, most PPIs are metabolized by CYP2C19 enzymes. When CYP2C19 is a moderate or poor metabolizer, PPI has a better acid-inhibitory effect. When the CYP2C19 gene is an extensive metabolizer, PPI is rapidly metabolized by the body, with a decreased acid-inhibitory effect and decreased H. pylori eradication efficacy. Oral PPI can achieve satisfactory acid suppression in CYP2C19 fast, moderate, and poor metabolizers four times daily [30]. The PPI selected for this study was rabeprazole, which is mainly metabolized by non-enzymatic pathways and is less affected by CYP2C19, which can achieve effective acid suppression.
Antibiotic resistance is one of the most important reasons for the failure of H. pylori eradication. Our previous epidemiological survey found that the resistance rates to clarithromycin, metronidazole, and levofloxacin in the areas of Yangzhou were 41.0, 38.8, and 44.9%, respectively. The rapid increase in drug resistance may be related to the characteristics of antibiotics that can easily induce drug resistance and their widespread irrational use in mainland China. Therefore, it is essential to understand antibiotic resistance in patients before eradication therapy. This study collected complete antibiotic resistance information for each patient, which was very helpful for us to comprehensively and accurately assess the causes and risk factors of radical cure failure. Our univariate and multivariate analyses of the factors affecting H. pylori eradication failure revealed that antibiotic resistance is one of the most important risk factors. In the resistance gene-based triple therapy, we avoided the use of resistant antibiotics and chose sensitive antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori. The results showed that a high eradication rate was achieved despite the use of triple therapy, which indicates that it is necessary to select sensitive antibiotics to eradicate H. pylori based on resistance results in the areas of China with a high resistance rate. This not only achieves a good eradication effect but also avoids secondary resistance due to antibiotic abuse in rural areas.
We found that most patients were able to alleviate their gastrointestinal discomfort after H. pylori eradication. First, almost all patients with H. pylori infection have chronic active gastritis, with high acidity in the stomach and a high inflammatory reaction. PPI can increase the pH of the stomach and reverse damage to the gastric mucosa, thus relieving gastric discomfort [32]. Second, microbiota dysbiosis can also cause gastrointestinal discomfort. In a study on the effect of H. pylori infection on the gastrointestinal microbiota [33], it was found that the microbial diversity of H. pylori-infected patients was significantly lower than that of H. pylori-uninfected patients, leading to a disruption of the flora, while successful eradication of H. pylori resulted in a transient decrease in microbial diversity due to the use of antibiotics. However, in the long term it significantly increased the microbiota of H. pylori-positive patients. The hypogastric microbial richness and homogeneity of the intragastric environment in H. pylori-positive patients were similar to those in H. pylori-negative patients.
Two notable points were observed in this study. First, we collected comprehensive and complete pre-radical baseline data, including demographic data and clinical characteristics, as well as information on antibiotic resistance in all patients, which increased the reliability of our findings. Second, we chose to collect gastric mucosal samples for molecular biological detection of H. pylori virulence genes and drug resistance genes, avoiding the drawbacks of low positive rates and long durations of drug sensitivity test cultures, which cause an inability to routinely perform detection in clinical practice. This method greatly shortened the time of antibiotic resistance results, allowed patients to begin treatment as early as possible, and enabled more extensive individualized diagnosis and treatment in clinical practice.
This study had some limitations. First, it was a prospective, single-center study with a small sample size. Therefore, a multicenter study with a lager sample size is needed to verify the effectiveness of eradication efficacy. Second, we did not detect genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19 enzyme in patient blood samples. Although we selected rabeprazole, which is less affected by CYP2C19 enzymes, recent studies have shown that rabeprazole metabolism is also affected to some extent by the CYP2C19 genotype, which may have an impact on patients who choose high-dose dual therapy. At present, a potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB) has been selected for H. pylori eradication. It is a novel antacid with reversible and competitive inhibitory effects on H+, K+ ATPase-mediated gastric acid secretion. It is considered to have an antacid effect on PPI and has potential benefits for H. pylori eradication. A meta-analysis of 1,599 H. pylori-positive patients showed no significant difference in eradication rates between P-CAB-based therapy and conventional PPI therapy in clarithromycin-sensitive patients. However, P-CAB-based therapy was more effective than PPI-based regimens in clarithromycin-resistant patients [34]. Therefore, P-CAB is expected to be a strong first-line therapy for H. pylori eradication in the future.
5 Conclusions
In summary, in patients with the first-time eradication of H. pylori infection in the areas of Yangzhou, high-dose dual therapy and resistance gene-based triple therapy achieved eradication rates and compliance equivalent to those of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy. Meanwhile high-dose dual therapy had lower rates of adverse events, fewer side effects, and greater safety. Eradication of H. pylori improves gastrointestinal discomfort in most patients with the infection. Eradication failure is primarily related to antibiotic resistance and poor compliance. Therefore, the appropriate regimen can be individualized for eradication therapy in clinical practice according to the patient’s resistance and tolerance to the drug.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the study participants and research staff their contributions and commitment to the present study.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the Key Project for Social Development in Jiangsu Province (BE2019698), Strengthening Health Care via Science and Education Project and Clinical Medical Innovation Platform Foundation of Yangzhou (2018, YXZX20184, Gastroenterology), and Major public health projects in Yangzhou: Screening projects of early gastrointestinal diseases (2018).
-
Author contributions: Xin Jiang performed clinical study, statistical analysis, and manuscript preparation; Bin Deng and Qiang She enrolled participants, collected data; Yun Zhang performed laboratory study; Xin Jiang, Xuefeng Gao, Guangyao Li, and Guiqing Li performed the gathering of clinical data on efficacy, compliance, and adverse events; Yanbing Ding contributed to study conceptualization, study design, funding acquisition, and manuscript editing. All authors have read and approved the final draft of this article.
-
Conflict of interest: All the authors disclose no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Zamani M, Ebrahimtabar F, Zamani V, Miller WH, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Shokri-Shirvani J, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47:868–76. 10.1111/apt.14561.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Xie C, Lu NH. Review: clinical management of Helicobacter pylori infection in China. Helicobacter. 2015;20:1–10. 10.1111/hel.12178.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Savoldi A, Carrara E, Graham DY, Conti M, Tacconelli E. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a systematic review and meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:1372–82, e1317. 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.07.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Thung I, Aramin H, Vavinskaya V, Gupta S, Park JY, Crowe SE, et al. Review article: the global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016;43:514–33. 10.1111/apt.13497.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Graham DY, Fischbach L. Helicobacter pylori treatment in the era of increasing antibiotic resistance. Gut. 2010;59:1143–53. 10.1136/gut.2009.192757.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[6] Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’Morain CA, Gisbert JP, Kuipers EJ, Axon AT, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection – the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report. Gut. 2017;66:6–30. 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312288.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Liu WZ, Xie Y, Lu H, Cheng H, Zeng ZR, Zhou LY, et al. Fifth Chinese National Consensus Report on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter. 2018;23:e12475. 10.1111/hel.12475.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Zou Y, Qian X, Liu X, Song Y, Song C, Wu S, et al. The effect of antibiotic resistance on Helicobacter pylori eradication efficacy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter. 2020;25:e12714. 10.1111/hel.12714.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Lee JW, Kim N, Nam RH, Lee SM, Kwon YH, Sohn SD, et al. Favorable outcomes of culture-based Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in a region with high antimicrobial resistance. Helicobacter. 2019;24:e12561. 10.1111/hel.12561.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Gong YN, Li YM, Yang NM, Li HZ, Guo F, Lin L, et al. Centralized isolation of Helicobacter pylori from multiple centers and transport condition influences. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:944–52. 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.944.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Pohl D, Keller PM, Bordier V, Wagner K. Review of current diagnostic methods and advances in Helicobacter pylori diagnostics in the era of next generation sequencing. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:4629–60. 10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4629.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Delchier JC, Bastuji-Garin S, Raymond J, Megraud F, Amiot A, Cambau E, et al. Efficacy of a tailored PCR-guided triple therapy in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Med Mal Infect. 2020;50:492–9. 10.1016/j.medmal.2019.06.001.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Suzuki S, Esaki M, Kusano C, Ikehara H, Gotoda T. Development of Helicobacter pylori treatment: how do we manage antimicrobial resistance? World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25:1907–12. 10.3748/wjg.v25.i16.1907.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Furuta T, Graham DY. Pharmacologic aspects of eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2010;39:465–80. 10.1016/j.gtc.2010.08.007.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Yang J, Zhang Y, Fan L, Zhu YJ, Wang TY, Wang XW, et al. Eradication efficacy of modified dual therapy compared with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as a first-line treatment of Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114:437–45. 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000132.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Kato I, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric carcinoma among Japanese Americans in Hawaii. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1132–6. 10.1056/NEJM199110173251604.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Parsonnet J, Friedman GD, Vandersteen DP, Chang Y, Vogelman JH, Orentreich N, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:1127–31. 10.1056/NEJM199110173251603.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[18] International Agency for Research on Cancer and others. Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. Lyon. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1994;61:1–241.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Yu X, Yang X, Yang T, Dong Q, Wang L, Feng L. Decreasing prevalence of Helicobacter pylori according to birth cohorts in urban China. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017;28:94–7. 10.5152/tjg.2017.16557.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Wen X, Wen D, Yang Y, Chen Y, Wang G, Shan B. Urban–rural disparity in Helicobacter pylori infection-related upper gastrointestinal cancer in China and the decreasing trend in parallel with socioeconomic development and urbanization in an endemic area. Ann Glob Health. 2017;83:444–62. 10.1016/j.aogh.2017.09.004.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Kuo YT, Liou JM, El-Omar EM, Wu JY, Leow AHR, Goh KL, et al. Primary antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori in the Asia-Pacific region: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2:707–15. 10.1016/S2468-1253(17)30219-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Fischbach L, Evans EL. Meta-analysis: the effect of antibiotic resistance status on the efficacy of triple and quadruple first-line therapies for Helicobacter pylori. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;26:343–57. 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03386.x.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Fallone CA, Chiba N, van Zanten SV, Fischbach L, Gisbert JP, Hunt RH, et al. The Toronto consensus for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection in adults. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:51–69.e14. 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.04.006.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Chey WD, Leontiadis GI, Howden CW, Moss SF. ACG clinical guideline: treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:212–39. 10.1038/ajg.2016.563.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Wenzhen Y, Yumin L, Quanlin G, Kehu Y, Lei J, Donghai W, et al. Is antimicrobial susceptibility testing necessary before first-line treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection? Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Intern Med. 2010;49:1103–9. 10.2169/internalmedicine.49.3031.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Lopez-Gongora S, Puig I, Calvet X, Villoria A, Baylina M, Munoz N, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: susceptibility-guided versus empirical antibiotic treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2015;70:2447–55. 10.1093/jac/dkv155.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Gao CP, Zhang D, Zhang T, Wang JX, Han SX, Graham DY, et al. PPI-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter pylori infection: an update based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Helicobacter. 2020;25:e12692. 10.1111/hel.12692.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[28] Unge P, Gad A, Gnarpe H, Olsson J. Does omeprazole improve antimicrobial therapy directed towards gastric Campylobacter pylori in patients with antral gastritis? A pilot study. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1989;167:49–54. 10.3109/00365528909091311.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[29] Rimbara E, Noguchi N, Kawai T, Sasatsu M. Mutations in penicillin-binding proteins 1, 2 and 3 are responsible for amoxicillin resistance in Helicobacter pylori. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;61:995–8. 10.1093/jac/dkn051.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Sugimoto M, Shirai N, Nishino M, Kodaira C, Uotani T, Yamade M, et al. Rabeprazole 10 mg q.d.s. decreases 24-h intragastric acidity significantly more than rabeprazole 20 mg b.d. or 40 mg o.m., overcoming CYP2C19 genotype. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36:627–34. 10.1111/apt.12014.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Sahara S, Sugimoto M, Uotani T, Ichikawa H, Yamade M, Kagami T, et al. Potent gastric acid inhibition over 24 hours by 4-times daily dosing of esomeprazole 20 mg. Digestion. 2015;91:277–85. 10.1159/000381419.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Yamada S, Tomatsuri N, Kawakami T, Nakatsugawa Y, Nishimura T, Fujii H, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy ameliorates latent digestive symptoms in chronic atrophic gastritis. Digestion. 2018;97:333–9. 10.1159/000486618.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Guo Y, Zhang Y, Gerhard M, Gao JJ, Mejias-Luque R, Zhang L, et al. Effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastrointestinal microbiota: a population-based study in Linqu, a high-risk area of gastric cancer. Gut. 2020;69:1598–607. 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-319696.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Li M, Oshima T, Horikawa T, Tozawa K, Tomita T, Fukui H, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Vonoprazan, a potent acid blocker, is superior to proton-pump inhibitors for eradication of clarithromycin-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter. 2018;23:e12495. 10.1111/hel.12495.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing miR-210 inhibits neuronal inflammation and contribute to neurite outgrowth through modulating microglia polarization
- Current situation of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in a county hospital chest pain center during an epidemic of novel coronavirus pneumonia
- circ-IARS depletion inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by circ-IARS/miR-1252-5p/HDGF ceRNA pathway
- circRNA ITGA7 restrains growth and enhances radiosensitivity by up-regulating SMAD4 in colorectal carcinoma
- WDR79 promotes aerobic glycolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by the suppression of SIRT4
- Up-regulation of collagen type V alpha 2 (COL5A2) promotes malignant phenotypes in gastric cancer cell via inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT)
- Inhibition of TERC inhibits neural apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury through Akt activation and p-38 inhibition via the miR-34a-5p/XBP-1 axis
- 3D-printed polyether-ether-ketone/n-TiO2 composite enhances the cytocompatibility and osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells by downregulating miR-154-5p
- Propofol-mediated circ_0000735 downregulation restrains tumor growth by decreasing integrin-β1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer
- PVT1/miR-16/CCND1 axis regulates gastric cancer progression
- Silencing of circ_002136 sensitizes gastric cancer to paclitaxel by targeting the miR-16-5p/HMGA1 axis
- Short-term outcomes after simultaneous gastrectomy plus cholecystectomy in gastric cancer: A pooling up analysis
- SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
- Molecular mechanism by which the Notch signaling pathway regulates autophagy in a rat model of pulmonary fibrosis in pigeon breeder’s lung
- lncRNA TPT1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous-cell carcinomas by regulating the miR-26a/HMGA1 axis
- SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis
- Glycoprotein non-metastatic melanoma B interacts with epidermal growth factor receptor to regulate neural stem cell survival and differentiation
- Treatments for brain metastases from EGFR/ALK-negative/unselected NSCLC: A network meta-analysis
- Association of osteoporosis and skeletal muscle loss with serum type I collagen carboxyl-terminal peptide β glypeptide: A cross-sectional study in elder Chinese population
- circ_0000376 knockdown suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell tumor properties by the miR-545-3p/PDPK1 pathway
- Delivery in a vertical birth chair supported by freedom of movement during labor: A randomized control trial
- UBE2J1 knockdown promotes cell apoptosis in endometrial cancer via regulating PI3K/AKT and MDM2/p53 signaling
- Metabolic resuscitation therapy in critically ill patients with sepsis and septic shock: A pilot prospective randomized controlled trial
- Lycopene ameliorates locomotor activity and urinary frequency induced by pelvic venous congestion in rats
- UHRF1-induced connexin26 methylation is involved in hearing damage triggered by intermittent hypoxia in neonatal rats
- LINC00511 promotes melanoma progression by targeting miR-610/NUCB2
- Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of serum metabolomic characteristics in people with different vitamin D levels
- Role of Jumonji domain-containing protein D3 and its inhibitor GSK-J4 in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- circ_0014736 induces GPR4 to regulate the biological behaviors of human placental trophoblast cells through miR-942-5p in preeclampsia
- Monitoring of sirolimus in the whole blood samples from pediatric patients with lymphatic anomalies
- Effects of osteogenic growth peptide C-terminal pentapeptide and its analogue on bone remodeling in an osteoporosis rat model
- A novel autophagy-related long non-coding RNAs signature predicting progression-free interval and I-131 therapy benefits in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- WGCNA-based identification of potential targets and pathways in response to treatment in locally advanced breast cancer patients
- Radiomics model using preoperative computed tomography angiography images to differentiate new from old emboli of acute lower limb arterial embolism
- Dysregulated lncRNAs are involved in the progress of myocardial infarction by constructing regulatory networks
- Single-arm trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of baclofen in treatment of intractable hiccup caused by malignant tumor chemotherapy
- Genetic polymorphisms of MRPS30-DT and NINJ2 may influence lung cancer risk
- Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with KRAS-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis
- Pyroptosis-based risk score predicts prognosis and drug sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma
- Upregulation of lncRNA LANCL1-AS1 inhibits the progression of non-small-cell lung cancer via the miR-3680-3p/GMFG axis
- CircRANBP17 modulated KDM1A to regulate neuroblastoma progression by sponging miR-27b-3p
- Exosomal miR-93-5p regulated the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting ADAMTS9
- Downregulation of RBM17 enhances cisplatin sensitivity and inhibits cell invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer cells
- HDAC5-mediated PRAME regulates the proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway
- The association between sleep duration, quality, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study
- Myostatin silencing inhibits podocyte apoptosis in membranous nephropathy through Smad3/PKA/NOX4 signaling pathway
- A novel long noncoding RNA AC125257.1 facilitates colorectal cancer progression by targeting miR-133a-3p/CASC5 axis
- Impact of omicron wave and associated control measures in Shanghai on health management and psychosocial well-being of patients with chronic conditions
- Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of young patients aged ≤45 years old with non-small cell lung cancer
- TMT-based comprehensive proteomic profiling identifies serum prognostic signatures of acute myeloid leukemia
- The dose limits of teeth protection for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy based on the early oral health-related quality of life
- miR-30b-5p targeting GRIN2A inhibits hippocampal damage in epilepsy
- Long non-coding RNA AL137789.1 promoted malignant biological behaviors and immune escape of pancreatic carcinoma cells
- IRF6 and FGF1 polymorphisms in non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in the Polish population
- Comprehensive analysis of the role of SFXN family in breast cancer
- Efficacy of bronchoscopic intratumoral injection of endostar and cisplatin in lung squamous cell carcinoma patients underwent conventional chemoradiotherapy
- Silencing of long noncoding RNA MIAT inhibits the viability and proliferation of breast cancer cells by promoting miR-378a-5p expression
- AG1024, an IGF-1 receptor inhibitor, ameliorates renal injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy via the SOCS/JAK2/STAT pathway
- Downregulation of KIAA1199 alleviated the activation, proliferation, and migration of hepatic stellate cells by the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- Exendin-4 regulates the MAPK and WNT signaling pathways to alleviate the osteogenic inhibition of periodontal ligament stem cells in a high glucose environment
- Inhibition of glycolysis represses the growth and alleviates the endoplasmic reticulum stress of breast cancer cells by regulating TMTC3
- The function of lncRNA EMX2OS/miR-653-5p and its regulatory mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma
- Tectorigenin alleviates the apoptosis and inflammation in spinal cord injury cell model through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6
- Ultrasound examination supporting CT or MRI in the evaluation of cervical lymphadenopathy in patients with irradiation-treated head and neck cancer
- F-box and WD repeat domain containing 7 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by degrading delta-like ligand 1 to block Notch signaling pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0005615 enhances the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer by regulating the miR-665/NOTCH1 axis
- Long noncoding RNA Mhrt alleviates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy phenotypes by mediating the miR-765/Wnt family member 7B pathway
- Effect of miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis on atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation
- Cholesterol induces inflammation and reduces glucose utilization
- circ_0004904 regulates the trophoblast cell in preeclampsia via miR-19b-3p/ARRDC3 axis
- NECAB3 promotes the migration and invasion of liver cancer cells through HIF-1α/RIT1 signaling pathway
- The poor performance of cardiovascular risk scores in identifying patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies at high cardiovascular risk
- miR-2053 inhibits the growth of ovarian cancer cells by downregulating SOX4
- Nucleophosmin 1 associating with engulfment and cell motility protein 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell chemotaxis and metastasis
- α-Hederin regulates macrophage polarization to relieve sepsis-induced lung and liver injuries in mice
- Changes of microbiota level in urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis
- Identification of key enzalutamide-resistance-related genes in castration-resistant prostate cancer and verification of RAD51 functions
- Falls during oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy for gastrointestinal malignancies – (lessons learned from) a prospective study
- Outcomes of low-risk birth care during the Covid-19 pandemic: A cohort study from a tertiary care center in Lithuania
- Vitamin D protects intestines from liver cirrhosis-induced inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Integrated transcriptome analysis identifies APPL1/RPS6KB2/GALK1 as immune-related metastasis factors in breast cancer
- Genomic analysis of immunogenic cell death-related subtypes for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy outcomes in glioblastoma multiforme
- Circular RNA Circ_0038467 promotes the maturation of miRNA-203 to increase lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of chondrocytes
- An economic evaluation of fine-needle cytology as the primary diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of lymphadenopathy
- Midazolam impedes lung carcinoma cell proliferation and migration via EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of naringin against renal fibrosis
- PTPN12 down-regulated by miR-146b-3p gene affects the malignant progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- miR-141-3p accelerates ovarian cancer progression and promotes M2-like macrophage polarization by targeting the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway
- lncRNA OIP5-AS1 attenuates the osteoarthritis progression in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes
- Overexpression of LINC00607 inhibits cell growth and aggressiveness by regulating the miR-1289/EFNA5 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer
- Subjective well-being in informal caregivers during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Nrf2 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by inhibiting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission
- Unfolded protein response inhibits KAT2B/MLKL-mediated necroptosis of hepatocytes by promoting BMI1 level to ubiquitinate KAT2B
- Bladder cancer screening: The new selection and prediction model
- circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
- Prone position effect in intensive care patients with SARS-COV-2 pneumonia
- Clinical observation on the efficacy of Tongdu Tuina manipulation in the treatment of primary enuresis in children
- Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates cerebral I/R injury in rats via regulating VWF and autophagy-mediated SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway
- Knockdown of circ_0113656 assuages oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced vascular smooth muscle cell injury through the miR-188-3p/IGF2 pathway
- Low Ang-(1–7) and high des-Arg9 bradykinin serum levels are correlated with cardiovascular risk factors in patients with COVID-19
- Effect of maternal age and body mass index on induction of labor with oral misoprostol for premature rupture of membrane at term: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- Potential protective effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against COVID-19-associated acute kidney injury: A network-based pharmacological and molecular docking study
- Clinical significance of serum MBD3 detection in girls with central precocious puberty
- Clinical features of varicella-zoster virus caused neurological diseases detected by metagenomic next-generation sequencing
- Collagen treatment of complex anorectal fistula: 3 years follow-up
- LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through down-regulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424
- Efficacy analysis of empirical bismuth quadruple therapy, high-dose dual therapy, and resistance gene-based triple therapy as a first-line Helicobacter pylori eradication regimen – An open-label, randomized trial
- SMOC2 plays a role in heart failure via regulating TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway-mediated autophagy
- A prospective cohort study of the impact of chronic disease on fall injuries in middle-aged and older adults
- circRNA THBS1 silencing inhibits the malignant biological behavior of cervical cancer cells via the regulation of miR-543/HMGB2 axis
- hsa_circ_0000285 sponging miR-582-3p promotes neuroblastoma progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Long non-coding RNA GNAS-AS1 knockdown inhibits proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma cells via the microRNA-433-3p/Rab3A axis
- lncRNA UCA1 regulates miR-132/Lrrfip1 axis to promote vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation
- Twenty-four-color full spectrum flow cytometry panel for minimal residual disease detection in acute myeloid leukemia
- Hsa-miR-223-3p participates in the process of anthracycline-induced cardiomyocyte damage by regulating NFIA gene
- Anti-inflammatory effect of ApoE23 on Salmonella typhimurium-induced sepsis in mice
- Analysis of somatic mutations and key driving factors of cervical cancer progression
- Hsa_circ_0028007 regulates the progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the miR-1179/SQLE axis
- Variations in sexual function after laparoendoscopic single-site hysterectomy in women with benign gynecologic diseases
- Effects of pharmacological delay with roxadustat on multi-territory perforator flap survival in rats
- Analysis of heroin effects on calcium channels in rat cardiomyocytes based on transcriptomics and metabolomics
- Risk factors of recurrent bacterial vaginosis among women of reproductive age: A cross-sectional study
- Alkbh5 plays indispensable roles in maintaining self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells
- Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Correlation between microvessel maturity and ISUP grades assessed using contrast-enhanced transrectal ultrasonography in prostate cancer
- The protective effect of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in the nephrotoxicity induced by α-cypermethrin
- Norepinephrine alleviates cyclosporin A-induced nephrotoxicity by enhancing the expression of SFRP1
- Effect of RUNX1/FOXP3 axis on apoptosis of T and B lymphocytes and immunosuppression in sepsis
- The function of Foxp1 represses β-adrenergic receptor transcription in the occurrence and development of bladder cancer through STAT3 activity
- Risk model and validation of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection in patients with cerebrovascular disease in the ICU
- Calycosin protects against chronic prostatitis in rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway
- Pan-cancer analysis of the PDE4DIP gene with potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic values in multiple cancers including acute myeloid leukemia
- The safety and immunogenicity to inactivated COVID-19 vaccine in patients with hyperlipemia
- Circ-UBR4 regulates the proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced vascular smooth muscle cells via miR-515-5p/IGF2 axis
- Clinical characteristics of current COVID-19 rehabilitation outpatients in China
- Luteolin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats via regulating immune response, oxidative stress, and metabolic profiling
- miR-199a-5p inhibits aortic valve calcification by targeting ATF6 and GRP78 in valve interstitial cells
- The application of iliac fascia space block combined with esketamine intravenous general anesthesia in PFNA surgery of the elderly: A prospective, single-center, controlled trial
- Elevated blood acetoacetate levels reduce major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events risk in acute myocardial infarction
- The effects of progesterone on the healing of obstetric anal sphincter damage in female rats
- Identification of cuproptosis-related genes for predicting the development of prostate cancer
- Lumican silencing ameliorates β-glycerophosphate-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by attenuating the inhibition of APOB on KIF2C activity
- Targeting PTBP1 blocks glutamine metabolism to improve the cisplatin sensitivity of hepatocarcinoma cells through modulating the mRNA stability of glutaminase
- A single center prospective study: Influences of different hip flexion angles on the measurement of lumbar spine bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- Clinical analysis of AN69ST membrane continuous venous hemofiltration in the treatment of severe sepsis
- Antibiotics therapy combined with probiotics administered intravaginally for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Construction of a ceRNA network to reveal a vascular invasion associated prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma
- A pan-cancer analysis of STAT3 expression and genetic alterations in human tumors
- A prognostic signature based on seven T-cell-related cell clustering genes in bladder urothelial carcinoma
- Pepsin concentration in oral lavage fluid of rabbit reflux model constructed by dilating the lower esophageal sphincter
- The antihypertensive felodipine shows synergistic activity with immune checkpoint blockade and inhibits tumor growth via NFAT1 in LUSC
- Tanshinone IIA attenuates valvular interstitial cells’ calcification induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein via reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- AS-IV enhances the antitumor effects of propofol in NSCLC cells by inhibiting autophagy
- Establishment of two oxaliplatin-resistant gallbladder cancer cell lines and comprehensive analysis of dysregulated genes
- Trial protocol: Feasibility of neuromodulation with connectivity-guided intermittent theta-burst stimulation for improving cognition in multiple sclerosis
- LncRNA LINC00592 mediates the promoter methylation of WIF1 to promote the development of bladder cancer
- Factors associated with gastrointestinal dysmotility in critically ill patients
- Mechanisms by which spinal cord stimulation intervenes in atrial fibrillation: The involvement of the endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor/p75NTR pathways
- Analysis of two-gene signatures and related drugs in small-cell lung cancer by bioinformatics
- Silencing USP19 alleviates cigarette smoke extract-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in BEAS-2B cells by targeting FUNDC1
- Menstrual irregularities associated with COVID-19 vaccines among women in Saudi Arabia: A survey during 2022
- Ferroptosis involves in Schwann cell death in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- The effect of AQP4 on tau protein aggregation in neurodegeneration and persistent neuroinflammation after cerebral microinfarcts
- Activation of UBEC2 by transcription factor MYBL2 affects DNA damage and promotes gastric cancer progression and cisplatin resistance
- Analysis of clinical characteristics in proximal and distal reflux monitoring among patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Exosomal circ-0020887 and circ-0009590 as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and prediction of short-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes in STEMI patients
- Upregulated microRNA-429 confers endometrial stromal cell dysfunction by targeting HIF1AN and regulating the HIF1A/VEGF pathway
- Bibliometrics and knowledge map analysis of ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia
- Knockdown of NUPR1 inhibits angiogenesis in lung cancer through IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathways
- D-dimer trends predict COVID-19 patient’s prognosis: A retrospective chart review study
- WTAP affects intracranial aneurysm progression by regulating m6A methylation modification
- Using of endoscopic polypectomy in patients with diagnosed malignant colorectal polyp – The cross-sectional clinical study
- Anti-S100A4 antibody administration alleviates bronchial epithelial–mesenchymal transition in asthmatic mice
- Prognostic evaluation of system immune-inflammatory index and prognostic nutritional index in double expressor diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Prevalence and antibiogram of bacteria causing urinary tract infection among patients with chronic kidney disease
- Reactive oxygen species within the vaginal space: An additional promoter of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and uterine cervical cancer development?
- Identification of disulfidptosis-related genes and immune infiltration in lower-grade glioma
- A new technique for uterine-preserving pelvic organ prolapse surgery: Laparoscopic rectus abdominis hysteropexy for uterine prolapse by comparing with traditional techniques
- Self-isolation of an Italian long-term care facility during COVID-19 pandemic: A comparison study on care-related infectious episodes
- A comparative study on the overlapping effects of clinically applicable therapeutic interventions in patients with central nervous system damage
- Low intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy for chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Long-term follow-up
- The diagnostic accuracy of touch imprint cytology for sentinel lymph node metastases of breast cancer: An up-to-date meta-analysis of 4,073 patients
- Mortality associated with Sjögren’s syndrome in the United States in the 1999–2020 period: A multiple cause-of-death study
- CircMMP11 as a prognostic biomarker mediates miR-361-3p/HMGB1 axis to accelerate malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Analysis of the clinical characteristics and prognosis of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia (none APL) with PTPN11 mutations
- KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11
- Evaluation of placental oxygenation by near-infrared spectroscopy in relation to ultrasound maturation grade in physiological term pregnancies
- The role of ultrasonographic findings for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- Construction of immunogenic cell death-related molecular subtypes and prognostic signature in colorectal cancer
- Long-term prognostic value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin-I in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
- Establishing a novel Fanconi anemia signaling pathway-associated prognostic model and tumor clustering for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients
- Integrative bioinformatics analysis reveals STAT2 as a novel biomarker of inflammation-related cardiac dysfunction in atrial fibrillation
- Adipose-derived stem cells repair radiation-induced chronic lung injury via inhibiting TGF-β1/Smad 3 signaling pathway
- Real-world practice of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Results from a 2000–2016 cohort
- lncRNA LENGA sponges miR-378 to promote myocardial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation
- Diagnostic value of urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein and 24 h urine osmolality for recurrent calcium oxalate stones of the upper urinary tract: Cross-sectional study
- The value of color Doppler ultrasonography combined with serum tumor markers in differential diagnosis of gastric stromal tumor and gastric cancer
- The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 induces inflammation and EMT of lung epithelial cells and fibroblasts through the upregulation of GADD45A
- Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide plus in patients with connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: Efficacy and safety analysis
- MiR-1278 targets CALD1 and suppresses the progression of gastric cancer via the MAPK pathway
- Metabolomic analysis of serum short-chain fatty acid concentrations in a mouse of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease after dietary supplementation with branched-chain amino acids
- Cimifugin inhibits adipogenesis and TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 cells
- Predictors of gastrointestinal complaints in patients on metformin therapy
- Prescribing patterns in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and atrial fibrillation
- A retrospective analysis of the effect of latent tuberculosis infection on clinical pregnancy outcomes of in vitro fertilization–fresh embryo transferred in infertile women
- Appropriateness and clinical outcomes of short sustained low-efficiency dialysis: A national experience
- miR-29 regulates metabolism by inhibiting JNK-1 expression in non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NAFLD
- Clinical features and management of lymphoepithelial cyst
- Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
- ENPP1 ameliorates vascular calcification via inhibiting the osteogenic transformation of VSMCs and generating PPi
- Significance of monitoring the levels of thyroid hormone antibodies and glucose and lipid metabolism antibodies in patients suffer from type 2 diabetes
- The causal relationship between immune cells and different kidney diseases: A Mendelian randomization study
- Interleukin 33, soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, interleukin 27, and galectin 3 as predictors for outcome in patients admitted to intensive care units
- Identification of diagnostic immune-related gene biomarkers for predicting heart failure after acute myocardial infarction
- Long-term administration of probiotics prevents gastrointestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction in septic mice partly by upregulating the 5-HT degradation pathway
- miR-192 inhibits the activation of hepatic stellate cells by targeting Rictor
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of MR-pro ADM, procalcitonin, and copeptin in sepsis
- Review Articles
- Prenatal diagnosis of fetal defects and its implications on the delivery mode
- Electromagnetic fields exposure on fetal and childhood abnormalities: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Saddle pulmonary embolism in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review of case reports and case series
- Vitamin C and epigenetics: A short physiological overview
- Ebselen: A promising therapy protecting cardiomyocytes from excess iron in iron-overloaded thalassemia patients
- Aspirin versus LMWH for VTE prophylaxis after orthopedic surgery
- Mechanism of rhubarb in the treatment of hyperlipidemia: A recent review
- Surgical management and outcomes of traumatic global brachial plexus injury: A concise review and our center approach
- The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges
- METTL16 in human diseases: What should we do next?
- New insights into the prevention of ureteral stents encrustation
- VISTA as a prospective immune checkpoint in gynecological malignant tumors: A review of the literature
- Case Reports
- Mycobacterium xenopi infection of the kidney and lymph nodes: A case report
- Genetic mutation of SLC6A20 (c.1072T > C) in a family with nephrolithiasis: A case report
- Chronic hepatitis B complicated with secondary hemochromatosis was cured clinically: A case report
- Liver abscess complicated with multiple organ invasive infection caused by hematogenous disseminated hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report
- Urokinase-based lock solutions for catheter salvage: A case of an upcoming kidney transplant recipient
- Two case reports of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 3 caused by the hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α gene mutation
- Immune checkpoint inhibitor-related pancreatitis: What is known and what is not
- Does total hip arthroplasty result in intercostal nerve injury? A case report and literature review
- Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnosis of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by Tusanqi – Case report and literature review
- Synchronous triple primary gastrointestinal malignant tumors treated with laparoscopic surgery: A case report
- CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation combined with bone cement injection for the treatment of transverse metastases: A case report
- Malignant hyperthermia: Report on a successful rescue of a case with the highest temperature of 44.2°C
- Anesthetic management of fetal pulmonary valvuloplasty: A case report
- Rapid Communication
- Impact of COVID-19 lockdown on glycemic levels during pregnancy: A retrospective analysis
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Inhibition of miR-21 improves pulmonary vascular responses in bronchopulmonary dysplasia by targeting the DDAH1/ADMA/NO pathway”
- Erratum to: “Fer exacerbates renal fibrosis and can be targeted by miR-29c-3p”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “Study to compare the effect of casirivimab and imdevimab, remdesivir, and favipiravir on progression and multi-organ function of hospitalized COVID-19 patients”
- Retraction of “circ_0062491 alleviates periodontitis via the miR-142-5p/IGF1 axis”
- Retraction of “miR-223-3p alleviates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix deposition by targeting SP3 in endometrial epithelial cells”
- Retraction of “SLCO4A1-AS1 mediates pancreatic cancer development via miR-4673/KIF21B axis”
- Retraction of “circRNA_0001679/miR-338-3p/DUSP16 axis aggravates acute lung injury”
- Retraction of “lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 inhibits malignant phenotypes of gastric cancer cells”
- Special issue Linking Pathobiological Mechanisms to Clinical Application for cardiovascular diseases
- Effect of cardiac rehabilitation therapy on depressed patients with cardiac insufficiency after cardiac surgery
- Special issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part I
- FBLIM1 mRNA is a novel prognostic biomarker and is associated with immune infiltrates in glioma
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part III
- Development of a machine learning-based signature utilizing inflammatory response genes for predicting prognosis and immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer

