Abstract
The widespread utilization of traditional chemical pesticides has given rise to numerous negative impacts, leading to a surge in interest in exploring environmentally friendly alternatives. Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), a bacterium renowned for its insecticidal properties, produces Cry proteins during its lifecycle. These proteins have distinct advantages over traditional chemical pesticides, including higher environmental safety, broader insecticidal spectra, and lower pesticide residues. Consequently, the discovery and application of Bt hold immense significance in plant disease and pest management, as well as in plant protection. Currently, Bt preparations occupy a prominent position as the world’s largest and most widely used biopesticides. This article comprehensively reviews the fundamental aspects, insecticidal mechanisms, practical applications, and fermentation technologies related to Bt.
1 Introduction
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a Gram-positive bacterium known for its ability to produce spores and parasporal crystals. In 1901, the Japanese scientist Shigetane Ishiwatari isolated this rod-shaped bacterium from the larvae of Bombyx mori [1]. A decade later, in 1915, Berliner isolated the bacterium from the Mediterranean flour moth, an insect that had infested a flour mill in Thüringen, Germany, hence the official name Bacillus thuringiensis [2].
The earliest commercial production began in France in 1938 under the name Sporeine [3]. Subsequently, Hannay confirmed that these crystals were, in fact, toxic protein crystals responsible for the mass mortality of the Mediterranean flour moth [4]. By the early 1980s, Gonzalez et al. [5] revealed that the genes coding for crystal proteins were localized on transmissible plasmids. Over the past century, the classification of Bt has become increasingly clear and precise. Researchers have conducted extensive analysis on its structure, effective components, and insecticidal mechanisms, laying a solid foundation for its extensive application in agriculture, forestry, and pest control [6].
Today, Bt preparations are globally recognized as one of the most widely used biopesticides. Their environmental safety, broad insecticidal spectrum, and minimal pesticide residues make them an attractive alternative to traditional chemical pesticides.
2 Overview of Bt
2.1 Morphological characteristics of Bt
Bt is widely distributed in nature. Currently, tens of thousands of Bt strains have been isolated and preserved globally, originating from various sources such as soil [7], animals [8], plant surfaces [9], and feces [10]. The vegetative cells of Bt exhibit a rod-shaped morphology with blunt ends. When cultivated for a certain period, the vegetative cells transform into thicker sporangiums, which are larger than the vegetative cells. Subsequently, the sporangium ruptures, releasing oval-shaped spores along with parasporal crystal proteins. These crystal proteins can have various shapes, including obtuse rhombus, square, ellipsoid, and irregular forms.
2.2 Taxonomic status of Bt
In the ninth edition of Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, Bt is listed as one of the species in group 18 of the second category, with the characteristic of forming one or more accessory spore crystal proteins, while forming spores allows it to be distinguished from other Bacillus strains. Bt, Bacillus cereus (Bc), and Bacillus anthracis are closely related and belong to the Bc group. Despite the high similarity in their genome sequences, there are significant differences in the composition of their spores, which affect their survival abilities [11]. There is a particularly close evolutionary relationship between Bt and Bc, to the extent that 16S rDNA sequences alone cannot distinguish between the two species. However, more advanced techniques such as average nucleotide identity analysis and ribosomal multilocus sequence typing can successfully separate Bc and Bt into two distinct branches on the evolutionary tree [12]. This demonstrates the complexity and subtle differences within the Bacillus strains group, requiring sophisticated molecular techniques for accurate classification and identification.
3 Physicochemical properties of Bt
3.1 Insecticidal crystal proteins (ICPs)
ICPs, also known as δ-endotoxins, produced by Bt are environmentally friendly active proteins. These proteins remain inactive in the acidic environment of the vertebrates’ gastrointestinal tract but become lethal to insects under the alkaline conditions found in their midguts [13]. Extensive research has revealed that the insecticidal process of ICPs follows a specific sequence of events. First, the parasporal crystals are lysed within the insect’s body. This lysis is followed by enzymatic activation, where the disulfide bonds within the ICPs are cleaved under alkaline conditions, releasing the protoxin. This protoxin is then further activated by trypsin enzymes, transforming it into an active toxin protein. Subsequently, the activated toxin protein binds to receptors on the midgut epithelial cell membrane. The toxic component of the protein, alpha-helix, inserts into the cytoplasmic membrane, creating holes or foci. This disrupts the membrane potential and leads to imbalances in cell permeability. As a result, the midgut undergoes necrosis, and there is damage to the peritoneal membrane and midgut epithelium. Finally, alkaline substances from the midgut enter the insect’s blood cavity, causing paralysis and eventually death [14]. The insecticidal mechanism of Bt is depicted in Figure 1.

Insecticidal mechanism of parasporal crystals.
3.2 Insecticidal characteristics and existing problems of Bt
Bt, as a microbial pesticide, has been widely used due to its unique insecticidal properties since its discovery. Overall, Bt preparations are considered safe and reliable as they can specifically target and eliminate harmful insects without harming animals and plants. In addition, it reduces the usage rate of chemical pesticides, and it is in line with the strategy of sustainable development of agricultural economy for it is harmless to the environment. Nevertheless, the widespread application of Bt inevitably poses some potential safety concerns. Certain Bt strains produce thuringiensin, also known as β-exotoxin, during their growth process. This exotoxin, secreted outside the cells, exhibits a broad insecticidal spectrum but is toxic to mammals, posing a potential safety hazard in agricultural applications [15].
Repeated application of insecticides to a specific insect population results in the survival of unaffected individuals who subsequently transmit their genetic traits to the subsequent generation. Over time, an increasing number of insect populations develop resistance to these insecticides. Unfortunately, insects have developed resistance to most widely used synthetic chemical insecticides. In 1979, the United Nations Environment Programme declared insecticide resistance as “one of the most serious environmental problems in the world.”
Research studies indicate that the mechanisms of Bt resistance primarily arise from four aspects: alteration in the activation process of Bt toxin [16], chelation of Bt toxin with glycolipids and lipases, enhancement of the immune mechanisms of pests [17], and reduction or alteration in the binding of Bt toxin to midgut receptors [18]. The resistance mechanism of insects to Bt toxin is shown in Figure 2. Bt resistance can lead to poor crop quality, increased pesticide production costs, and the emergence of secondary pests due to the large quantities of pesticides used to eliminate the target pest.
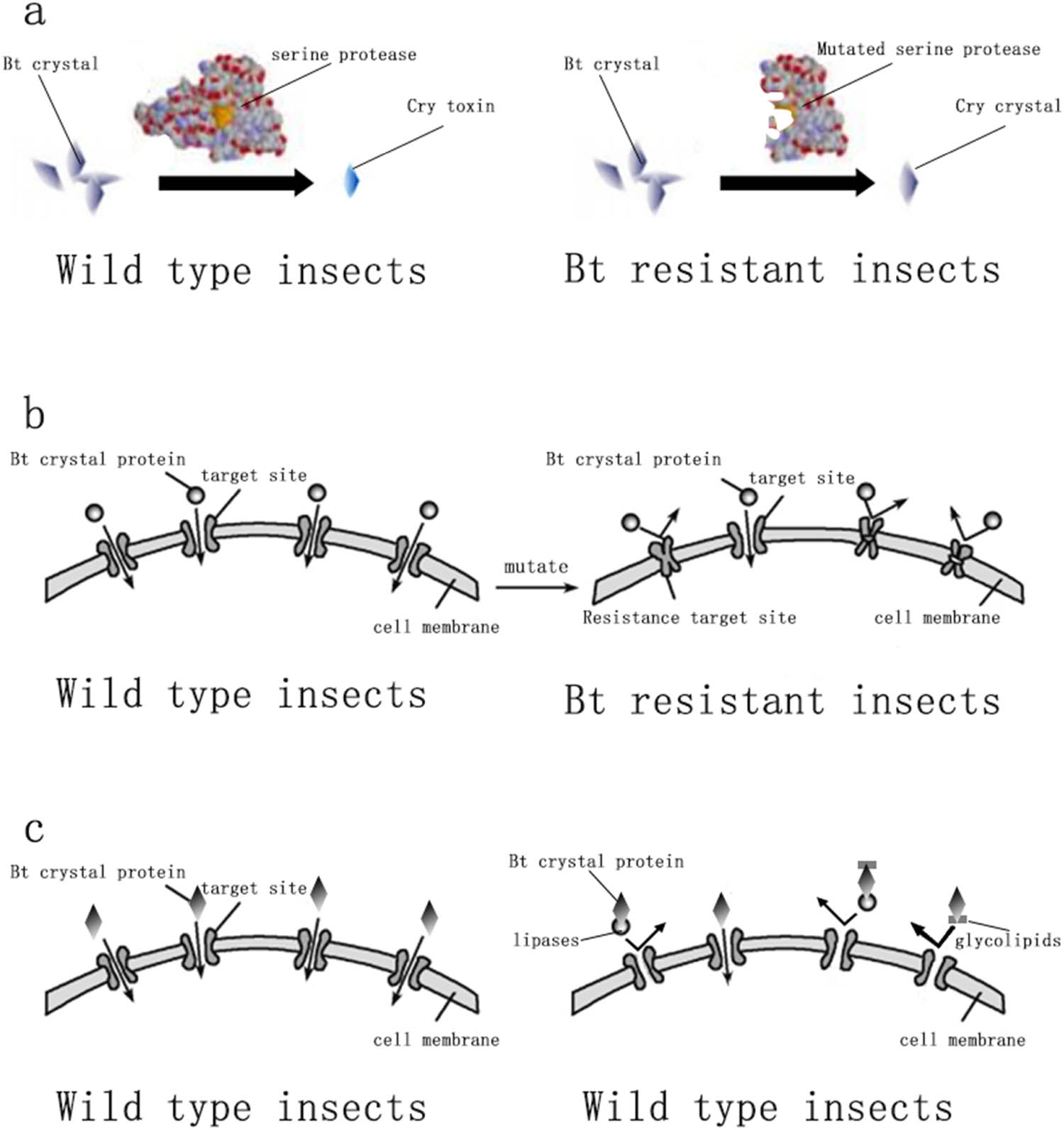
Bt resistance mechanism of insects. (a) Alteration in the activation process of Bt toxin. (b) Reduction or alteration in the binding of Bt toxin to midgut receptors. (c) Chelation of the Bt toxin with glycolipids and lipases.
In conclusion, despite the significant insecticidal effect and environmental friendliness of Bt, its application must take into account safety concerns, particularly the emergence of insect resistance. Therefore, continuous research and improvements are necessary to ensure the long-term effectiveness and safety of Bt in agricultural production. Additionally, exploring integrated pest management strategies, combining biological, physical, and chemical control methods, is essential to achieve effective pest control while minimizing the impact on the environment and ecosystems.
4 Selection of Bt
In practical applications, biopesticides derived from Bt exhibit limitations, including a short persistent period and poor insecticidal efficacy. Hence, the future direction aims to enhance the toxicity and stability of Bt as an insecticide. Currently, numerous scholars have explored strategies and methods for optimizing the insecticidal activity of Bt. These include isolating and screening high-potency strains, genetically enhancing insecticidal crystals, utilizing genetic engineering to improve insecticidal genes, and increasing mutation rates through mutagenic agents, among others [19,20,21,22]. Gebremariam et al. [23] isolated 31 strains of Bt from 70 soil samples. However, only 20 strains (64.5%) proved virulent against the greater wax moth, with a maximum mortality rate of 95%. In another study, Barkad et al. [24] cloned the lon gene into a multi-copy vector, incorporating its original promoter and transcriptional terminator, and expressed it in B. thuringiensis serovar israelensis ATCC 35646. The results indicated efficient transcription and translation of the recombinant lon gene, leading to an improvement in the yield of intracellular toxins in the strain. Furthermore, the LC50 value of the cry1Ac-cry9Aa toxin decreased to 0.725 ng/cm2, lower than that of the control group. Additionally, Zhu et al. [25] identified a high-yield mutant strain of Bt, named BtX023PN, derived from the wild Bt X023. This strain was mutated using atmospheric and room temperature plasma and nitrosoguanidine. The virulence of BtX023PN against Plutella xylostella and Mythimna seperata increased by 2.33 and 2.13 times, respectively. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and SDS-PAGE analysis revealed a 61% increase in the production of Cry1Ac protein.
Although many insecticidal genes of Bt were sequenced, it is still necessary to study their toxicity mechanism and actual insecticidal effect. Based on the optimization of Bt, it is also necessary to investigate the protein expression level, stability of insecticidal effect, genetic stability, and production technology. At the genome level, based on high-throughput sequencing technology and sequence similarity alignment technology, all potential insecticidal protein gene profiles of newly discovered strains were quickly predicted and analyzed at the DNA level; at the proteomics level, high-throughput and high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry can identify all potential insecticidal proteins produced by the strain at the whole proteome level. With the rapid progress of genome and proteome technology and data analysis, the analysis and identification of the complete spectrum of ICP genes in Bt have become the most convenient way. Based on the many advanced and efficient methods mentioned above, it is believed that Bt can overcome its obstacles and better benefit the humanity.
5 Research on Bt insecticides
5.1 Insecticidal toxin
The classification of Bt crystal toxins reveals the existence of 73 families and 6 groups of endotoxin proteins [26]. Each strain produces distinct types of toxins, which are either proteins or small molecules released outside the cell or stored within it. The toxins primarily include δ-endotoxins, exotoxins, hemolysins, enterotoxins, and vegetative insecticidal proteins (Vip’s). Notably, δ-endotoxins varying in molecular weight serve as the primary toxins for pest control. Also known as parasporal crystals, these toxins encompass the Cry protein and the Cyt protein. When ingested by larvae of Lepidoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera, δ-endotoxins activate and decompose into small units of approximately 60 kDa, forming pores on the cell membrane, disrupting the osmotic pressure balance, leading to the lysis of midgut epithelial cells, and ultimately causing insect death [22]. Furthermore, some studies suggest that certain endotoxins eliminate pests by disrupting the function of intestinal cell mitochondria [27]. The Cry protein, with a molecular weight ranging from 72 to 134 kDa, is encoded by a single gene designated as “Cry.” This gene is further categorized into CryӀ, CryⅡ, CryⅢ, and CryⅣ. Specifically, the CryӀ gene exhibits insecticidal effects against Lepidoptera insects, while CryⅡ targets both Lepidoptera and Diptera. On the other hand, CryⅢ and CryⅣ are specific to Coleoptera and Diptera, respectively. Additionally, the Cyt protein demonstrates insecticidal activity against Diptera insects [28,29,30].
The research on the structure and function of δ-endotoxins has now been relatively in-depth. The three-dimensional structure of the substance is shown in Figure 3, with three structural domains. Notably, domains I and II are intricately linked to its specific insecticidal activity [31]. Further investigations have revealed that domain II is the region where the protein primarily functions. Through mutagenesis experiments targeting several crucial residues within this region, it was discovered that these residues significantly impact the larvicidal activity of δ-endotoxin [32]. It can be seen that this area is very important.
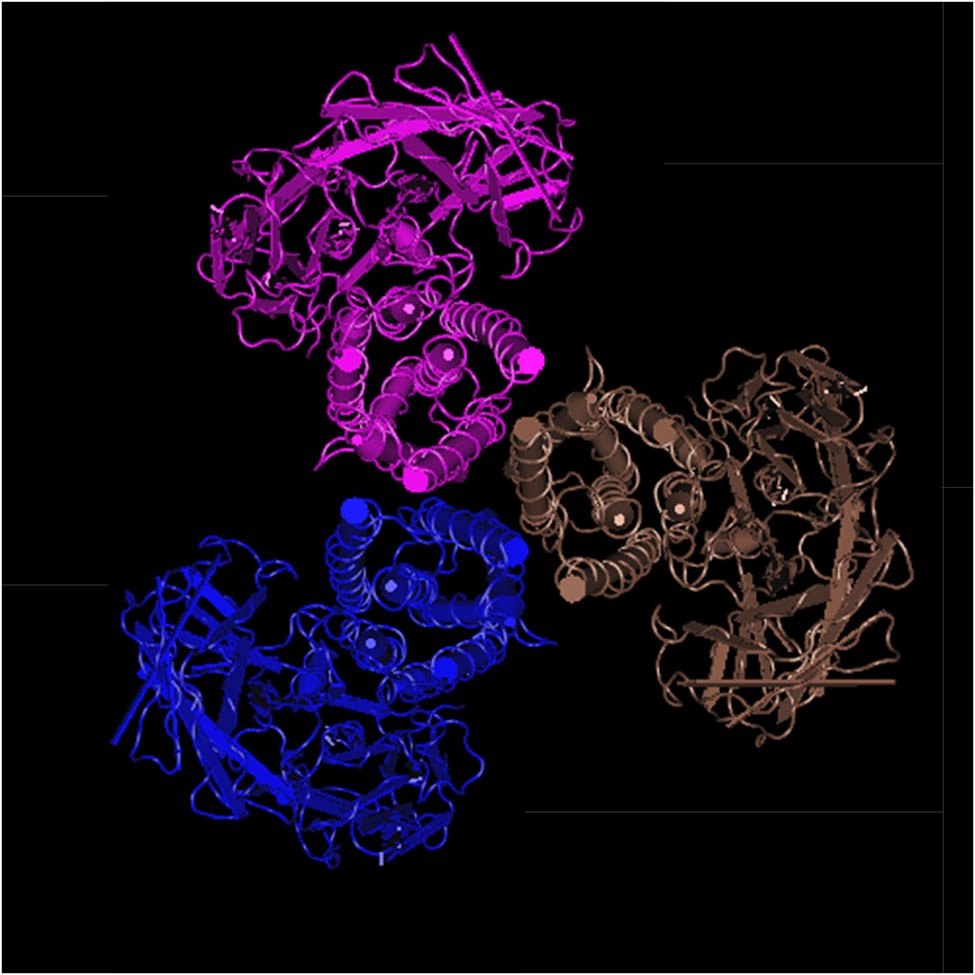
Three-dimensional structure of Cry1B.867.
5.2 Classification of ICPs
In 1998, Crickmore et al. [33] proposed a novel classification system for ICPs. This system employed an evolutionary tree algorithm to categorize and name the proteins into four distinct levels. Proteins with amino acid sequence homology below 45% were designated as the first level and represented by Arabic numerals. Proteins exhibiting homology between 45 and 78% fell into the second level and were represented by capital letters. Proteins with homology ranging from 78 to 95% were classified as the third level and designated with lowercase English letters. Finally, proteins with homology exceeding 95% comprised the fourth level and were represented by Arabic numerals. This comprehensive classification framework provides a useful tool for understanding and comparing the ICPs, facilitating further research and applications in biological pest control.
6 Application of Bt in agriculture and forestry
Bt overcomes the shortcomings of chemical pesticides, such as low safety, challenges in properly disposing of residues, significant environmental pollution, and the tendency to cause abnormal coloration in vegetables and fruits. Currently, Bt has emerged as the microbial insecticide with the largest production both domestically and internationally. It represents the most commercially successful and widely utilized microbial insecticide for controlling agricultural and forestry pests [34].
Bt is the largest and most widely used live microbial pesticide in China, and it is also an indispensable biological insecticide in many green and organic food production processes, accounting for over 10% of the total microbial pesticide market share [35]. These Bt biological insecticides are extensively utilized in the management of agricultural pests, forest and fruit tree pests, storage pests, as well as medical pests due to their outstanding economic, social, and ecological benefits. At present, the annual production of China’s Bt industry is about 30,000 tons (16,000 IU/µl), and the sales revenue in 2017 was about 100 million yuan [36]. This is sufficient to demonstrate the important role of Bt biopesticides in China’s agriculture and environmental protection work.
6.1 Bt formulation is directly used for pest control
Mazigo et al. [37] conducted a study in the Kilangali village, South Central Tanzania, where they utilized high-specific toxin-producing bacteria and Bt as biological larvicides in rice farmers. The findings revealed that over half (56.6%) of the participants reported a notable decrease in mosquito density within their households, while a quarter (26.6%) observed a reduction in the mosquito population on their farms. Notably, 93.3% of the participants reported that these measures effectively reduced the risk of malaria within their families. Eski et al. [38] carried out the insecticidal performance of 21 strains of Bacillus, especially Agelastica alni (Coleoptera: Chrysoptera), in order to develop an effective biopesticide. It was found that the Bacillus thuringiensis var.tenebrionis-xd3 (Btt-Xd3) was the best. To optimize the toxin protein and spore production of Xd3, the study determined the optimal growth conditions: a nutrient broth medium with salt, a pH of 7, and a temperature of 30°C. Under laboratory conditions, the lethal concentration 50 (LC50) of Btt-Xd3 against the target larvae was found to be 1.5 × 104 c.f.u./ml. Consequently, a new biological pesticide, Btt-xd3, was developed from B. thuringiensis (Xd3), holding promise as a biological control agent against Coleoptera pests. Furthermore, Liu et al. [39] isolated a Bt strain, X023 (Btx023), from the Hunan Province, China, exhibiting high insecticidal activity. The study explored the effect of adding metals (Cu, Fe, Mg, and Mn) to the growth medium on the formation of spores and ICPs. Bioassays revealed that the wild strain Btx023 demonstrated significant insecticidal activity against P. xylostella. Notably, the addition of 1 × 10−5 M Cu2+ significantly enhanced the expression of cry1Ac and vip3Aa genes, leading to an increase in insecticidal activity. qRT-PCR and proteomic analysis further revealed that the upregulated proteins were involved in amino acid synthesis, the glyoxylate pathway, oxidative phosphorylation, and polyphosphorylation, among others. Copper ions appeared to play a crucial role in regulating these processes, which provided abundant raw materials for ICP synthesis.
6.2 Research on Bt genetically modified crops
The Bt gene has emerged as the most widely utilized transgenic insecticidal gene, attributed to its product, the Bt toxin protein, which boasts remarkable insecticidal effects, safety, and efficiency. Common Bt genetically modified crops, including tomatoes, corn, and cotton, have revolutionized agriculture. Canada pioneered in the commercialization of Bt genetically modified corn in 1996, which has since become widely cultivated in North America, significantly mitigating losses caused by corn pests [40]. China followed suit the next year, promoting this genetically modified corn to its farmers [41]. Since then, Bt genetically modified crops have gained global acceptance, leading to the development of numerous insect-resistant plant varieties. Statistics reveal that over 200 million ha of arable land worldwide are now planted with Bt genetically modified crops [42].
Coleoptera insects, renowned for causing severe damage to crops, pose a significant threat to crop yield and quality, thus making them a critical target for pest control efforts [43]. By the end of 2018, researchers had isolated and cloned a total of 850 Bt genes globally. Among these genes, Cry1Ba, Cry3, Cry7, Cry8, Cry18, Cry23, Cry34, Cry37, and Cry43 have demonstrated a remarkable impact on most Coleoptera insects [44].
Pests, diseases, and weeds collectively cause significant losses to global food production. Statistics indicate that pests are responsible for 14% of annual food production losses, while diseases account for 10% and weeds contribute 11%. The economic toll of these harmful organisms is staggering, amounting to an annual loss of 120 billion yuan worldwide [45]. These organisms have become a critical biological factor hindering agricultural production. The application of Bt offers a promising solution, effectively reducing crop and forestry diseases and pests, ultimately benefiting the humanity.
7 Application of Bt in anticancer drugs
Cancer, a severe threat to human life, remains a challenging research area globally [46]. In recent years, certain bacterial proteins have garnered significant attention for their antitumor properties, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa azurin [47] and Corynebacterium diphtheriae toxin [48], among these, proteins derived from non-insecticidal and non-hemolytic strains of Bt have demonstrated killing effects on various human cancer cells [49]. These proteins, specifically cytotoxic to human cancer cells, are known as “parasporins.” Parasporins (PSs), a class of bacterial proteins, can be categorized into six types: PS1, PS2, PS3, PS4, PS5, and PS6 [50]. Each type recognizes and eliminates cancer cells through distinct mechanisms. For instance, PS1 elevates Ca2+ levels and triggers apoptosis in multiple cancer cell types. PS2 functions as a cytolysin, targeting the plasma membrane of specific cancer cells. On the other hand, PS3 and PS6 act as pore-forming toxins, dissolving the plasma membrane of cancer cells. PS4 induces cancer cell death through a non-apoptotic pathway. The diverse mechanisms employed by PSs suggest that they may target different molecules and activate various signaling pathways in cancer cells [51]. The discovery of new PSs from Bt strains with specific cytotoxicity to human cancer cells has garnered increasing attention. For example, PS2 from Bt, a member of aerolysin-type β pore-forming toxins, has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for cancer treatment due to its strong and selective cytotoxicity against human cancer cells without affecting normal cells [52]. For another example, Moazamian et al. [50] conducted a study in Iran, during which they isolated a total of 88 Bt strains. When the non-hemolytic crystal proteins of these isolates were treated with proteinase K, five strains belonging to three different biotypes of B. thuringiensis – namely, thuringiensis, kurstaki, and sotto – were identified to exhibit distinct cytotoxic effects against HCT-116 colon cancer cells and CCRF-CEM blood cancer cells. This finding suggests that the isolated Bt strains possess specific and different cytotoxicity toward human colon cancer and blood cancer cells.
The discovery of these strains with specific cytotoxicity is significant as it opens up new possibilities for the development of targeted anticancer therapeutics. The distinct cytotoxic mechanisms employed by these B. thuringiensis strains may offer novel approaches for the treatment of cancer. Future research on these strains could lead to the identification of novel bioactive components and the elucidation of their underlying mechanisms of action, potentially leading to the development of more effective and targeted anticancer drugs.
8 Function and application of Bt in environmental pollution control
8.1 Advantages of Bt in bioremediation
Bioremediation, a controlled or spontaneous process involving microorganisms, particularly stands out as a reliable environmental protection technology for water treatment. Its simplicity in operation, low investment requirements, minimal environmental interference, and absence of secondary pollution make it an increasingly popular choice for water environment treatment [53]. Among the various microorganisms capable of bioremediation, Bt has garnered significant attention [54]. Numerous studies have demonstrated the ability of Bt strains to effectively remove organic pollutants from both water and soil environments. These pollutants include, but are not limited to, petroleum hydrocarbons, pentachlorophenol, hexavalent chromium-contaminated wastewater, and organophosphorus pesticides [56,57,58]. Compared to other bacteria, Bt offers several distinct advantages. First, it is environmentally friendly and poses high safety standards, making it a suitable candidate for bioremediation applications. Second, the cost of using Bt is relatively low, which is a crucial factor in large-scale industrial applications. Finally, Bt is easy to cultivate and scale up for industrial fermentation, ensuring a consistent supply for bioremediation efforts. Despite its promising potential, there have been relatively few reports on the use of Bt for pollutant removal. This may be due to a lack of awareness or insufficient research in this area. However, given the established benefits of Bt in bioremediation and the increasing demand for sustainable and cost-effective water treatment solutions, it is anticipated that more research will be conducted in this direction in the future.
8.2 Pollutants degraded by Bt
Muñoz-Martínez et al. [59] isolated a strain of Bt from soil collected at a composting plant located northeast of Mexico City. This bacterium demonstrated remarkable potential in degrading bendiocarb, a commonly used insecticide. The study was conducted in a biofilm reactor, where the Bt strain was immobilized using fragments of volcanic rock, known as tezontle, as a support material. Operated on a continuous basis, this system achieved degradation rates exceeding 90% for the insecticide, displaying high removal efficiency. The utilization of Bt in this manner offers several advantages. First, the bacterium’s natural ability to degrade organic pollutants, including insecticides, makes it an ideal candidate for bioremediation applications. Second, the use of tezontle as a support material not only provides a stable environment for bacterial growth but also enhances the bioremediation process by increasing the surface area available for microbial attachment and degradation. This study demonstrates the potential of Bt in bioremediation, particularly in the degradation of insecticides. Its effectiveness in removing bendiocarb from water sources, combined with the ease of operation and low cost of the biofilm reactor system, makes it a promising technology for practical applications in water environment treatment. Future research could focus on optimizing the reactor conditions, exploring the degradation mechanisms of Bt, and extending its application to other types of pollutants.
In order to explore the effects and potential mechanisms of heavy metal-tolerant bacteria and biochar (BC) on reducing heavy metal accumulation in vegetables, Li et al. [60] tested Bt HC-2. The ability of BC and BC + HC-2 to fix Cd and Pb in culture medium was studied, and their effects on the dry weight and Cd of radish in metal-contaminated soil under field conditions were also investigated. The impact of Pb absorption and its potential mechanisms was also studied. These treatments significantly increased the dry weight of radish roots (18.4–22.8%) and leaves (37.8–39.9%) and decreased Cd (28–94%) and Pb (22–63%) contents in the radish roots compared with that of the control. Treatment with HC-2, BC, and BC + HC-2 also significantly increased the pH, organic matter content, NH4+ content, and NH4+/NO3− ratio of rhizosphere soils and decreased the DTPA-extractable Cd (37–58%) and Pb (26–42%) contents in rhizosphere soils of radish. Furthermore, BC + HC-2 had higher ability than the other two treatments to protect radish against Cd and Pb toxicity and increased the radish biomass. Therefore, Bt HC-2 combined with BC can ensure vegetable safety in situ for the bioremediation of heavy metal-polluted farmlands.
9 Research on the excavation method of toxin proteins from Bt
Since the discovery in the early twentieth century that Bt can effectively kill pests, it has become an important issue to explore and utilize the efficient ICP of Bt in agricultural production and forestry pest control. From the early isolation of bacterial strains, followed by spraying pesticides rich in insecticidal proteins, to using molecular biology techniques to transform plants into expressing specific insecticidal proteins, humans have been continuously improving the accuracy of using ICPs in Bt. Therefore, continuously exploring new and usable genetic resources of Bt ICPs is a very important topic.
The rapid development of molecular biology technology in the 1980s and 1990s provided a technical foundation for the expression of Bt insecticidal proteins in target crops. The Bt toxin protein gene was first expressed in cotton in 1990 [61] and then successfully constructed and expressed in potatoes in 1995 [62]. The cloning and identification of insecticidal protein genes have become an important aspect of the development of Bt resources.
With the advent of high-throughput sequencing technology, the cost and time required for microbial genome sequencing have been significantly reduced. This remarkable progress has facilitated the exponential growth of genomic data, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of various microorganisms, including Bacillus thuringiensis. As of April 11, 2024, the NCBI website alone has published whole-genome sequencing data for 27 strains of Bt. These genomes have been annotated multiple times, resulting in 88 genome assembly and annotation reports, as well as 584 plasmid annotation reports (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene). This makes it possible to high-throughput explore Bt toxin protein genes based on genomic data and mass spectrometry technology.
At the genomic level, high-throughput sequencing technology, coupled with sequence similarity alignment techniques, enables rapid prediction and analysis of all potential insecticidal protein gene maps of newly discovered Bt strains. This approach allows researchers to identify regions of the genome encoding insecticidal proteins, thereby facilitating the discovery of novel toxins or toxin variants; at the proteomic level, high-throughput and high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry techniques can identify all potential insecticidal proteins produced by strains at the entire proteomic level. The rapid development of genome and proteome technology, combined with data analysis capabilities, is the most effective method for the full spectrum analysis and identification of ICP genes in Bt. This approach holds promise for the discovery of new insecticidal proteins, which could potentially lead to the development of more effective and environmentally friendly pest control strategies.
9.1 Exploration and identification methods of insecticidal proteins based on DNA libraries
In the 1980s, genetic technology and molecular biology underwent rapid advancements, leading to a shift in the way researchers explored Bt insecticidal proteins. At that time, Escherichia coli was predominantly utilized to establish DNA libraries of these insecticidal proteins [63]. Subsequently, toxicological experiments were conducted on various pests to assess their insecticidal effects.
The core approach for discovering the insecticidal potential of Bt involved cloning the insecticidal protein gene onto suitable vectors [64]. This cloning process allowed researchers to determine the gene sequence encoding the insecticidal protein through gene sequencing technology. In 1983, Wong’s research group made a significant breakthrough by cloning and sequencing the gene regulatory sequence of ICPs, along with the DNA sequence encoding 333 amino acids at the N-terminus, which accounts for one fourth of the total length of ICPs [65].
Rabha and his colleagues [66] sequenced the entire genome of the Bacillus thuringiensis BA04 strain, isolated from soil samples in the Kashiranga National Park in Assam, Northeast India. This extensive sequencing effort aimed to understand the gene composition and identify genes responsible for producing insecticidal proteins, including virulence factors. They achieved great results: a total of 6,111 genes were discovered, including two new crystal protein coding genes (MH753632.1 and MH75363.1). These genes hold significant potential for developing insect-resistant genetically modified crops, thus contributing to sustainable agriculture. Additionally, this strain could be harnessed for the production of effective biopesticides, offering a natural and environmentally friendly approach to pest management.
9.2 Discovery methods based on a high-throughput genome sequencing technology
In recent years, the advent of high-throughput sequencing technology has revolutionized the exploration of Cry genes. This powerful tool enables the large-scale parallel sequencing of millions of DNA molecules, generating vast amounts of data at a reduced cost. This rapid and comprehensive analysis of the transcriptome and genome of Bt offers unprecedented insights, enabling researchers to solve problems that once took years to tackle.
Currently, researchers have developed a sophisticated high-throughput system designed to identify novel crystal protein genes (Cry) in Bt strains [67]. This innovative approach incorporates three distinct prediction methods: BLAST, Hidden Markov model, and support vector machine. These methods work in tandem to accurately predict Cry toxin genes within the genome. The performance of the system has been validated, demonstrating its remarkable speed, sensitivity, and specificity. With an average speed of 1.02 Mb/min for protein and open reading frames and 1.80 Mb/min for nucleotide sequences, it processes data swiftly, enabling the rapid analysis of large genomes.
With the decreasing cost of high-throughput genome sequencing technology, the publication of genomic data for Bt strains in public databases is growing exponentially. As the field of genomics continues to expand, researchers are poised to unlock even more secrets of Bt, leading to the development of more effective and sustainable biopesticides.
10 Synergism of insecticidal activity of Bt
Although Bt-based biopesticides are currently among the most effective and widely used biopesticides, their insecticidal activity and stability in practical applications often require enhancement through the use of synergists. These synergists, which are commonly employed to boost the performance of biopesticides, include a range of additives such as chemical additives, chemical insecticides, biological insecticides, and other enhancers [68].
The research conducted by Konecka et al. [69] has revealed a significant synergistic effect between the Cry toxin and carvacrol. When the bacterial toxin comprised 0.1 or 0.05% of the mixture, the combination was most effective in reducing the number of first instar and third instar Spodoptera exigua pests. The utilization of these mixtures led to a remarkable increase in insect mortality, exceeding the expected mortality by approximately 1.9 times. Furthermore, Akhanaev et al. [68] evaluated the effectiveness of a commercially available insecticide, Lepidocide, which is based on Bt var. kurstaki and Lymantria dispar multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus (LdMNPV). The study also investigated the enhanced efficacy of these components when combined with an optical brightener for controlling L. dispar larvae. The results demonstrated that most combinations of Lepidocide and LdMNPV, containing 5 mg/mL optical brightener, exhibited synergistic effects. These mixtures were highly effective in reducing the number of second instar larvae. Additionally, Soares Figueiredo et al. [70] were interested in understanding how combinatorial proteins interact with pests and whether combinatorial proteins contribute to resistance control and management. This work demonstrated the toxicity of Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry1Ca, Cry1Ea, Cry2Aa, Cry2Ab, Vip3Aa, and Vip3Ca in single and combined assays against S. frugiperda neonatal larvae. All protein mixtures had synergistic action in the control of the larvae. The Vip3Aa + Cry1Ab mixture had the highest toxicity, in the following sequential order: Vip3Aa + Cry2Ab, Cry1Ab + Cry2Ab + Vip3Aa, Cry1Ea + Cry1Ca, Cry1Ab + Cry2Ab, Vip3Ca + Cry1Ea, and Vip3Ca + Cry1Ca. Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry2Ab, and Vip3Aa were bound to more than one site on the brush border membrane vesicles of S. frugiperda. The Cry1Ab and Cry1Ac proteins share their binding sites, while Cry1Ab does not share its binding site with those of Cry2Aa and Cry2Ab proteins. The Vip3Aa protein does not share receptors with the tested Cry1 and Cry2. The results suggest that a combination of these tested proteins may increase the toxicity against S. frugiperda neonates.
The selection of appropriate synergists is crucial to ensure compatibility with the biopesticide and to minimize any potential negative impacts on the environment or non-target organisms. Researchers are continuously exploring new synergistic options and optimizing their use to enhance the performance of Bt biopesticides, making them even more effective and sustainable tools for pest management.
11 Existing problems and prospects
Bt preparation, as a new microbial pesticide, is environment-friendly, has no effect to soil microorganisms, and can maintain the ecosystem balance. Moreover, its protein toxin is harmless to humans and other animals, has high safety, and is in line with the values of sustainable development and the inevitable trend of pesticide development in the future. However, there are still many problems to be solved for the large-scale application of Bt preparation.
The resistance of pests can be inherited stably.
Short insecticidal spectrum: in general, a strain can only be effective to its specific sensitive insects, and a single preparation cannot control multiple pests at the same time, so the insecticidal activity has limitations.
Poor quick response, short duration, and unstable control effect: compared with traditional chemical pesticides, Bt preparation needs more time to exert its activity.
The insecticidal effect is easily affected by the weather and environment: Bt preparation itself is a microbial insecticide, and the growth, reproduction, and activity of microorganisms are affected by many factors. For example, the most suitable growth temperature of Bt is 24–32°C, so its effect is poor when the temperature is lower than 15°C; the residual period of the preparation will be greatly reduced by the scouring of rainwater; meanwhile, the sporocystic insecticidal protein is easily inactivated after ultraviolet irradiation, etc.
In view of the above problems, a promising optimization direction is to select new high-efficiency Bt strains, reduce the cost of Bt fermentation, and improve the level of Bt fermentation. According to the mechanism of Bt preparation, it has become a research hotspot to reasonably unearth high-efficiency, stable, and environment-friendly synergistic substances, develop complex Bt preparation, and make up for the original defects. In addition, by constructing new strains through genetic engineering technology, we can obtain transgenic strains with a wider insecticidal spectrum and a high level of expression of ICPs.
On the basis of these studies, we can combine transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabonomics in the future to explore Bt more comprehensively. We believe that the development of quick acting, long-lasting, and broad-spectrum microbial agents will gradually reduce the use of or even completely replace the chemical pesticides in the near future.
12 Conclusions
To summarize, this article provides a comprehensive overview of the recent research achievements regarding the use of Bt in pest control. The key topics include its distinct features, the underlying mechanisms of action, application techniques, and synergism. Despite being the most extensively studied and applied biological insecticide, there are still challenges that urgently need to be addressed.
With technological advancements, Bt remains a prominent research focus in the realm of pest control, promising broader application prospects in the future. However, the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms and principles related to Bt, particularly its long-term safety for human health and the ecological environment, remains elusive. Therefore, further elucidating the molecular mechanisms and principles associated with Bt, as well as enhancing its safety evaluation system, is crucial not only for safeguarding the sustainable development of this biological insecticide but also for promoting the establishment of novel pest control strategies and fostering green agricultural practices.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding was involved.
-
Author contributions: K.L.: manuscript writing, investigation; M.C.: manuscript revising; J.S.: literature search and organization; T.M.: manuscript writing, revising, and editing.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
[1] Karabörklü S, Azizoglu U, Azizoglu ZB. Recombinant entomopathogenic agents: a review of biotechnological approaches to pest insect control. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;34(1):14.10.1007/s11274-017-2397-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Valtierra-de-Luis D, Villanueva M, Berry C, Caballero P. Potential for Bacillus thuringiensis and other bacterial toxins as biological control agents to combat dipteran pests of medical and agronomic importance. Toxins (Basel). 2020 Dec;12(12):773.10.3390/toxins12120773Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Roh JY, Choi JY, Li MS, Jin BR, Je YH. Bacillus thuringiensis as a specific, safe, and effective tool for insect pest control. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Apr;17(4):547–59.Search in Google Scholar
[4] Hannay CL. The dissociation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Nov;13(11):1566–8.10.1139/m67-206Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] González Jr JM, Brown BJ, Carlton BC. Transfer of Bacillus thuringiensis plasmids coding for delta-endotoxin among strains of B. thuringiensis and B. cereus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982 Nov;79(22):6951–5.10.1073/pnas.79.22.6951Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Baranek J, Pluskota M, Rusin M, Konecka E, Kaznowski A, Wiland-Szymanska J. Insecticidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis strains isolated from tropical greenhouses towards Cydia pomonella and Spodoptera exigua larvae. BioControl: J Int Organ Biol Control. 2023;68:39–48.10.1007/s10526-022-10173-3Search in Google Scholar
[7] Saibu S, Nsa IY, Odunsi AA, Akinyemi NM, Oyetibo GO, Adebusoye SA. Draft genome sequence of Bacillus thuringiensis SS2, from dibenzofuran-contaminated soil, reveals putative aromatic compound degradation genes. Microbiol Resour Announce. 2023 May;12(5):e0019823.10.1128/mra.00198-23Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Santos EN, Menezes LP, Dolabella SS, Santini A, Severino P, Capasso R, et al. Bacillus thuringiensis: From biopesticides to anticancer agents. Biochimie. 2022 Jan;192:83–90.10.1016/j.biochi.2021.10.003Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Espinoza-Vergara G, García-Suárez R, Verduzco-Rosas LA, Cando-Narvaez A, Ibarra JE. Bacillus thuringiensis: a natural endophytic bacterium found in wild plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2023 May;99(6):fiad043.10.1093/femsec/fiad043Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Gothandaraman R, Venkatasamy B, Thangavel T, Eswaran K, Subbarayalu M. Molecular characterization and toxicity evaluation of indigenous Bacillus thuringiensis isolates against key lepidopteran insect pests. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2022;32(1):1–11.10.1186/s41938-022-00639-ySearch in Google Scholar
[11] Srinivasan VB, Angrasan M, Chandel N, Rajamohan G. Genome sequence and comparative analysis of Bacillus cereus BC04, reveals genetic diversity and alterations for antimicrobial resistance. Funct Integr Genomics. 2018;18(4):477–87.10.1007/s10142-018-0600-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Zhou H, Zhang J, Shao Y, Wang J, Xu W, Liu Y, et al. Development of a high resolution melting method based on a novel molecular target for discrimination between Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Food Res Int. 2022;151:110845.10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110845Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Rajan V. An alkaline foregut protects herbivores from latex in forage, but increases their susceptibility to Bt endotoxin. Life (Basel). 2023 Nov;13(11):2195.10.3390/life13112195Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Tetreau G, Andreeva EA, Banneville AS, De Zitter E, Colletier JP. How does bacillus thuringiensis crystallize such a large diversity of toxins? Toxins (Basel). 2021;13(7):443.10.3390/toxins13070443Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Sauka DH, Peralta C, Pérez MP, Molla A, Fernandez-Göbel T, Ocampo F, et al. Bacillus thuringiensis Bt_UNVM-84, a Novel Strain Showing Insecticidal Activity against Anthonomus grandis Boheman (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Toxins (Basel). 2023 Dec;16(1):4.10.3390/toxins16010004Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Khalil H, Moussa S, Zein HS, Ahmed DS, Shaurub ESH, Elarabi NI. Alterations in the expression of certain midgut genes of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae and midgut histopathology in response to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C toxin. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2021;31(1):1–9.10.1186/s41938-021-00370-0Search in Google Scholar
[17] Caccia S, Astarita F, Barra E, Lelio ID, Varricchio P, Pennacchio F. Enhancement of Bacillus thuringiensis toxicity by feeding Spodoptera littoralis larvae with bacteria expressing immune suppressive dsRNA. J Pest Sci. 2020;93:303–14.10.1007/s10340-019-01140-6Search in Google Scholar
[18] Liu L, Xu P, Liu K, Wei W, Chang Z, Cheng D. Advances in receptor-mediated resistance mechanisms of Lepidopteran insects to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 May;38(5):1809–23.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Hemthanon T, Promdonkoy B, Boonserm P. Screening and characterization of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates for high production of Vip3A and Cry proteins and high thermostability to control Spodoptera spp. J Invertebr Pathol. 2023 Nov;201:108020.10.1016/j.jip.2023.108020Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Razzaq A, Ali A, Zafar MM, Nawaz A, Xiaoying D, Pengtao L, et al. Pyramiding of cry toxins and methanol producing genes to increase insect resistance in cotton. GM Crop Food. 2021 Jan;12(1):382–95.10.1080/21645698.2021.1944013Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Soonsanga S, Rungrod A, Phaonakrop N, Roytrakul S, Promdonkoy B. Proteomic analysis and promoter modification of bacillus thuringiensis to improve insecticidal Vip3A protein production. Mol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;64(1):100–7.10.1007/s12033-021-00401-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[22] Naing ZL, Soe ET, Zhang C, Niu L, Tang J, Ding Z, et al. Cadherin is a binding protein but not a functional receptor of bacillus thuringiensis Cry2Ab in helicoverpa armigera. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jul;89(7):e0062523.10.1128/aem.00625-23Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Gebremariam A, Chekol Y, Assefa F. Isolation, characterization, and bio-insecticidal efficiency of Ethiopian isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis against Galleria mellonella L. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and tomato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Genn.) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2021;31:1–12.10.1186/s41938-021-00375-9Search in Google Scholar
[24] Barkad MA, Bayraktar A, Doruk T, Tunca S. Effect of lon protease overexpression on endotoxin production and stress resistance in Bacillus thuringiensis. Curr Microbiol. 2021;12:3483–93.10.1007/s00284-021-02610-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Zhu Z, Chen W, Zhou H, Cheng H, Luo S, Zhou K, et al. ARTP and NTG compound mutations improved Cry protein production and virulence of Bacillus thuringiensis X023. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(11):4211–21.10.1007/s00253-022-11983-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Rashki M, Maleki M, Torkzadeh-Mahani M, Shakeri S, Nezhad PS. Isolation of Iranian Bacillus thuringiensis strains and characterization of lepidopteran-active cry genes. Egypt J Biol Pest Control. 2021;31(1):1–10.10.1186/s41938-021-00432-3Search in Google Scholar
[27] Jain D, Saharan V, Pareek S. Current status of Bacillus thuringiensis: insecticidal crystal proteins and transgenic crops. Advances in plant breeding strategies: Agronomic, abiotic and biotic stress traits. Berlin, Germany: Springer International Publishing; 2016. p. 657–98.10.1007/978-3-319-22518-0_18Search in Google Scholar
[28] Arsov A, Gerginova M, Paunova-Krasteva T, Petrov K, Petrova P. Multiple cry genes in bacillus thuringiensis strain BTG suggest a broad-spectrum insecticidal activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul;24(13):11137.10.3390/ijms241311137Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Singh D, Thayil SM, Sohal SK, Kesavan AK Exploration of insecticidal potential of Cry protein purified from Bacillus thuringiensis VIID1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Mar;174:362–9.10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.143Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Domínguez-Arrizabalaga M, Villanueva M, Escriche B, Ancín-Azpilicueta C, Caballero P. Insecticidal activity of bacillus thuringiensis proteins against coleopteran pests. Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun;12(7):430.10.3390/toxins12070430Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Wang Y, Wang J, Fu X, Nageotte JR, Jerga A. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Da_7 and Cry1B.868 protein interactions with novel receptors allow control of resistant fall armyworms, Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith). Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019;85(16):e00579-19.10.1128/AEM.00579-19Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[32] Paul S, Das S. Natural insecticidal proteins, the promising bio-control compounds for future crop protection. Nucleus. 2021;64:7–20.10.1007/s13237-020-00316-1Search in Google Scholar
[33] Crickmore N, Zeigler DR, Feitelson J, Schnepf E, Van Rie J, Lereclus D, et al. Revision of the nomenclature for the bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 1998;62(3):807–13.10.1128/MMBR.62.3.807-813.1998Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Sanahuja G, Banakar R, Twyman RM, Capell T, Christou P. Bacillus thuringiensis: A century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021;9:283–300.10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00595.xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[35] Zhao YX. Biological pesticides usher in a new situation of accelerating development. Farmers Dly. 2023;7:1–12.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Li L, Chen Z, Yu Z. Mass production, application and market development of bacillus thuringiensis biopesticides in China. Bacillus thuringiensis Lysinibacillus sphaericus. Berlin, Germany: Springer International Publishing; vol. 12. 2017. p. 185–212.10.1007/978-3-319-56678-8_12Search in Google Scholar
[37] Mazigo HD, Massawe IS, Rumisha SF, Kweka EJ, Mboera LEG. Rice farmers’ perceptions and acceptability in the use of a combination of biolarvicide (Bacillus thuringiensis var. israeliensis) and fertilizers application for malaria control and increase rice productivity in a rural district of central Tanzania. Malar J. 2019;18(1):71.10.1186/s12936-019-2697-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Eski A, Demir İ, Sezen K, Demirbağ Z. A new biopesticide from a local Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis (Xd3) against alder leaf beetle (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017;33(5):95.10.1007/s11274-017-2263-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Liu Z, Xie J, Deng Z, Wang M, Dang D, Luo S, et al. Enhancing the insecticidal activity of new Bacillus thuringiensis X023 by copper ions. Microb Cell Fact. 2020;19(1):1–10.10.1186/s12934-020-01452-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Fisher KE, Flexner JL, Mason CE. Plant preferences of z-phero’mone race ostrinia nubilalis (lepidoptera: crambidae) based on leaf tissue consumption rates. J Econ Entomol. 2020 Jun;113(3):1563–7.10.1093/jee/toaa047Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Liang J, Yang X, Jiao Y, Wang D, Zhao Q, Sun Y, et al. The evolution of Chinas regulation of agricultural biotechnology. aBIOTECH. 2022 Dec;3(4):237–49.10.1007/s42994-022-00086-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Tilgam J, Kumar K, Jayaswal D, Choudhury S, Kumar A, Jayaswall K, et al. Success of microbial genes based transgenic crops: Bt and beyond Bt. Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Dec;48(12):8111–22.10.1007/s11033-021-06760-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Mi L, Gu Z, Li Y, Xu W, Shu C, Zhang J, et al. Enterobacter Strain IPPBiotE33 Displays a Synergistic Effect with Bacillus thuringiensis Bt185. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep;24(18):14193.10.3390/ijms241814193Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Cui Z, Huang N, He P, Xu W, Hu J, Cui S. Progress in the application of Bacillus thuringiensis in pest control. Mod Flour Milling Ind. 2023;37(01):13–8.Search in Google Scholar
[45] Niederhuber M. Insecticidal plants: The tech and safety of GM Bt crops. http://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2015/insecticidal-plants/, 2015 Aug.Search in Google Scholar
[46] Liu M, Yan Q, Peng B, Cai Y, Zeng S, Xu Z, et al. Use of cucurbitacins for lung cancer research and therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021;88:1–14.10.1007/s00280-021-04265-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Sharma P, Kaur S, Chadha BS, Kaur R, Kaur M, Kaur S. Anticancer and antimicrobial potential of enterocin 12a from Enterococcus faecium. BMC Microbiol. 2021;21(1):39.10.1186/s12866-021-02086-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Yaghoubi A, Khazaei M, Avan A, Hasanian SM, Soleimanpour S. The bacterial instrument as a promising therapy for colon cancer. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2020;35:595–606.10.1007/s00384-020-03535-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Grace JJ, Ramani G, Shenbagarathai R. Enhancement of Purified Human Colon Cancer-Specific Parasporal Toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis-LDC-501. Curr Microbiol. 2019;77:104–14.10.1007/s00284-019-01800-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Moazamian E, Bahador N, Azarpira N, Rasouli M. Anti-cancer Parasporin Toxins of New Bacillus thuringiensis Against Human Colon (HCT-116) and Blood (CCRF-CEM) Cancer Cell Lines. Curr Microbiol. 2018;75:1090–8.10.1007/s00284-018-1479-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Aldeewan A, Zhang Y, Li S. Bacillus thuringiensis parasporins functions on cancer cells. Int J Pure Appl Biosci. 2014;2(4):67–74.Search in Google Scholar
[52] Chankamngoen W, Janvilisri T, Promdonkoy B, Boonserm P. In vitro analysis of the anticancer activity of Lysinibacillus sphaericus binary toxin in human cancer cell lines. 3 Biotech. 2020;10(8):1–9.10.1007/s13205-020-02361-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[53] Wu CY, Zhong ZC, Wu XP, Chen YJ, Shu CC. A comprehensive study on flocculation of anionic dyes using the bioflocculant produced by Bacillus thuringiensis: Kinetics, affecting factors, and perspectives. Water Environ Res. 2023 May;95(5):e10868.10.1002/wer.10868Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[54] Wu S, Zhong J, Lei Q, Song H, Chen SF, Wahla AQ, et al. New roles for Bacillus thuringiensis in the removal of environmental pollutants. Environ Res. 2023 Nov;236(Pt 1):116699.10.1016/j.envres.2023.116699Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Marchlewicz A, Guzik U, Hupert-Kocurek K, Nowak A, Wilczyńska S, Wojcieszyńska D. Toxicity and biodegradation of ibuprofen by Bacillus thuringiensis B1 2015b. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017;24(8):7572–84.10.1007/s11356-017-8372-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[56] Surhio MA, Talpur FN, Nizamani SM, Talpur MK, Amin F, Khaskheli AA, et al. Effective bioremediation of endocrine-disrupting phthalate esters, mediated by bacillus strains. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017;228(10):386.10.1007/s11270-017-3567-2Search in Google Scholar
[57] Suresh G, Balasubramanian B, Ravichandran N, Ramesh B, Kamyab H, Velmurugan H, et al. Bioremediation of hexavalent chromium-contaminated wastewater by Bacillus thuringiensis and Staphylococcus capitis isolated from tannery sediment. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. 2021;11:383–91.10.1007/s13399-020-01259-ySearch in Google Scholar
[58] Xu K, Hasi Q, Mu X, Xiao C, Zhang Y, Jiang X, et al. Lipophilic, nanocellulose based macroporous sponge loaded with mixed microorganisms for efficient elimination of petroleum hydrocarbon pollution in water. Cellulose. 2022;29(11):6161–79.10.1007/s10570-022-04653-zSearch in Google Scholar
[59] Muñoz-Martínez S, Ahuatzi-Chacón D, Santoyo-Tepole F. Biodegradation of the insecticide bendiocarb by bacillus thuringiensis in a packed biofilm reactor. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2021;57(S1):S46–53.10.1134/S0003683821100070Search in Google Scholar
[60] Li Z, Wang P, Yue X, Wang J, Ren B, Qu L, et al. Effects of Bacillus thuringiensis HC-2 combined with biochar on the growth and Cd and Pb accumulation of radish in a heavy metal-contaminated farmland under field conditions. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Sep;16(19):3676.10.3390/ijerph16193676Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[61] Perlak FJ, Deaton RW, Armstrong TA, Fuchs RL, Sims SR, Greenplate JT, et al. Insect resistant cotton plants. Biotechnology (N Y). 1990 Oct;8(10):939–43.10.1038/nbt1090-939Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Adang MJ, Brody MS, Cardineau G, Eagan N, Roush RT, Shewmaker CK, et al. The reconstruction and expression of a Bacillus thuringiensis cryIIIA gene in protoplasts and potato plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;21(6):1131–45.10.1007/BF00023609Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[63] Doss VA, Kumar KA, Jayakumar R, Sekar V. Cloning and expression of the vegetative insecticidal protein (vip3V) gene of Bacillus thuringiensis in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif. 2002 Oct;26(1):82–8.10.1016/S1046-5928(02)00515-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[64] Dutta TK, Mandal A, Kundu A, Phani V, Mathur C, Veeresh A, et al. RNAi-mediated knockdown of gut receptor-like genes prohibitin and α-amylase altered the susceptibility of Galleria mellonella to Cry1AcF toxin. BMC Genomics. 2022;23(1):1–14.10.1186/s12864-022-08843-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Wong HC, Schnepf HE, Whiteley HR. Transcriptional and translational start sites for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb;258(3):1960–7.10.1016/S0021-9258(18)33082-5Search in Google Scholar
[66] Rabha M, Das D, Konwar T, Acharjee S, Sarmah BK. Whole genome sequencing of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from Assam soil. BMC Microbiol. 2023 Mar;23(1):91.10.1186/s12866-023-02821-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Ye W, Zhu L, Liu Y, Crickmore N, Peng D, Ruan L, et al. Mining new crystal protein genes from Bacillus thuringiensis on the basis of mixed plasmid-enriched genome sequencing and a computational pipeline. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Jul;78(14):4795–801.10.1128/AEM.00340-12Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Akhanaev Y, Pavlushin S, Polenogova O, Klementeva T, Lebedeva D, Okhlopkova O, et al. The effect of mixtures of Bacillus thuringiensis-based insecticide and multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus of Lymantria dispar L. in combination with an optical brightener on L. dispar larvae. BioControl. 2022;67(3):331–43.10.1007/s10526-022-10137-7Search in Google Scholar
[69] Konecka E, Kaznowski A, Grzesiek W, Nowicki P, Czarniewska E, Baranek J. Synergistic interaction between carvacrol and Bacillus thuringiensis crystalline proteins against Cydia pomonella and Spodoptera exigua. BioControl. 2020;65(4):447–60.10.1007/s10526-020-10011-4Search in Google Scholar
[70] Soares Figueiredo C, Nunes Lemes AR, Sebastião I, Desidério JA. Synergism of the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1, Cry2, and Vip3 Proteins in Spodoptera frugiperda Control. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;188:798–809.10.1007/s12010-019-02952-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?

