Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
-
Lei Huang
and Shunyi Lu
Abstract
Large segmental bone defects are commonly operated with autologous bone grafting, which has limited bone sources and poses additional surgical risks. In this study, we fabricated poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)/β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) composite membranes by electrostatic spinning and further promoted osteogenesis by regulating the release of β-TCP in the hope of replacing autologous bone grafts in the clinical practice. The addition of β-TCP improved the mechanical strength of PLGA by 2.55 times. Moreover, β-TCP could accelerate the degradation of PLGA and neutralize the negative effects of acidification of the microenvironment caused by PLGA degradation. In vitro experiments revealed that PLGA/TCP10 membranes are biocompatible and the released β-TCP can modulate the activity of osteoblasts by enhancing the calcium ions concentration in the damaged area and regulating the pH of the local microenvironment. Simultaneously, an increase in β-TCP can moderate the lactate content of the local microenvironment, synergistically enhancing osteogenesis by promoting the tube-forming effect of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Therefore, it is potential to utilize PLGA/TCP bioactive membranes to modulate the microenvironment at the site of bone defects to promote bone regeneration.
1 Introduction
Although natural bone tissue has the ability to self-repair small defects, severe bone defects due to trauma, tumor resection, and congenital malformations mostly require clinical intervention [1,2]. Autologous bone grafting is a common surgical procedure used in practice, but has obvious limitations due to deficiencies in donor resources and the risk of secondary injuries [3,4]. Previous studies have explored various methods to prepare bone repair membranes, with reports showing fibrous membranes made using electrostatic spinning being popular in the biomedical field due to their high porosity, drug loading properties, and biomimetic topology [5,6]. In the recent decades, bone repair membranes are commonly prepared by 3D printing, Hot-Press compression molding, and electrostatic spinning [7–9]. Fibrous membranes prepared though electrostatic spinning was reported to have high porosity, drug-loading properties and biomimetic topology, and is widely studied in the biomedical field [10,11]. Bioactive bone membranes are supposed to have several criteria including biocompatibility, osteoinductive activity, and space maintenance capacity, further promoting bone regeneration and rebuilding bone microenvironment [12,13]. Additionally, bioactivity can be considered a desirable feature of bone regeneration membrane in order to initiate and enhance bone formation [14]. Hence, artificial bone graft substitute is considered as an alternative to autologous/allograft. It is of great significance to develop a biocompatible and osteoinductive activity bone membrane for the clinical treatment of bone defects.
Poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) has been approved by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical therapeutic use as a copolymer with controlled biodegradability and good biocompatibility [15]. It has been widely used for drug delivery due to the slow-releasing properties of the structure [16]. Jadidi et al. [17] showed encapsulating vancomycin into a PLGA coating for slow release significantly improved the cellular activity of the scaffold. Meanwhile, the lactic acid released from PLGA degradation can be metabolized by the body and promotes angiogenesis [18]. Study has indicated that PLGA microspheres are beneficial to implant in situ pore formation and bone ingrowth in bone defect areas [15]. β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) is an absorbable calcium-phosphate salt that is susceptible to new bone replacement and is widely applied in bone repair because of its good osteoconductive capacity. Due to its similarity to bone minerals in terms of crystallinity and chemical composition, β-TCP has been favored by researchers for its excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability [19]. Incidentally, studies also demonstrated that PLGA can combine well with β-TCP to prepare various complexes to facilitate bone regeneration [20,21].
In this study, we intended to prepare PLGA/β-TCP composite membranes by electrostatic spinning to control the release of β-TCP. The mechanical and thermal properties as well as the in vitro osteogenic and angiogenic abilities of the composite membranes were then evaluated. The pore formation with the addition of PLGA in β-TCP promoted the growth of new bone and vascularization property. Our results reveal that PLGA/β-TCP composite membranes can be the next generation of bone regenerative material.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Preparation of PLGA/β-TCP bioactive membrane
600 mg PLGA (lactic acid, LA:glycolic acid, GA = 70:30, M w = 105, DaiGang, China) was added to 4 mL of tetrahydrofuran/N,N-dimethylformamide (v/v = 3:1) mixed solution and stirred magnetically at room temperature for 24 h. Then, 6, 30, and 60 mg β-TCP (Sigma, USA) were added to the PLGA solution and stirred for another 3 h before sonication for 1 h. The solution was sonicated at an operating voltage of 22 kV, operating distance of 15 cm, and a feed rate of 1 mL/h. Samples were named PLGA, PLGA/TCP1, PLGA/TCP5, PLGA/TCP10 according to different β-TCP concentrations.
2.2 Membrane characterization
2.2.1 Surface morphology
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM, S-4800, Hitachi, Japan) was used to analyze the surface morphological characteristics of the membrane specimens. Elemental analysis was conducted by energy dispersive spectroscopy, and mapping of both calcium and phosphorus. β-TCP particles were analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM, Hitachi, H-800, Japan).
2.2.2 Chemical phase composition
The bioactive membrane specimens were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku D/Max2550, Cu Karadiation, Japan).
2.2.3 Differential scanning calorimetry analysis
The thermal properties of the samples were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC2910, USA). The test conditions were: 3–5 mg samples were heated from 25 to 200°C at 10°C/min to eliminate thermal history, held at 200°C for 2 min, then cooled to 0°C at 10°C/min held at 0°C for 2 min, then heated to 220°C at 10°C/min.
2.2.4 Thermogravimetric analysis
The thermal stability of the specimens was tested by a thermogravimetric analyzer (TG209F1-GC 7820A, China), where 3–5 mg of specimens would be heated from 30 to 600°C in nitrogen at a rate of 10°C/min.
2.2.5 Degradation characteristics
The degradation characteristics of the samples were performed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). For each group of three parallel samples (30 mm × 10 mm × 1 mm), they were submersed in 10 mL of PBS and placed in a shaker (37°C, 80 rpm). The pH of the soaking solution was measured with a pH meter (Mettler Toledo, China) for the corresponding days and change in mass was measured.
2.2.6 Ion release
The pH changes and ion release of the samples were performed in PBS. For each group of three parallel samples (30 mm × 10 mm × 1 mm), they were soaked in 10 mL of PBS and placed in a shaker (37°C, 80 rpm). The collected soaking solution was measured with an inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-AES, PerkinElmer Optima 2000, USA) for Ca2+ concentration.
2.2.7 Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of the composite film were determined by a universal mechanical testing machine (SANS CMT 2503, USA), which was tested in room temperature at a stretching speed of 10 mm/min.
2.3 In vitro osteogenesis assay
2.3.1 Cell culture
Protocol of animal experimentation in the study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Suzhou University (Suzhou, China). Four-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats (SD rats) were purchased from Shanghai JASJ Laboratory Animal Co. Primary bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) were derived from the femur and tibia of the SD rats in accordance with the published methodology [15]. BMSCs were cultivated in α-MEM medium (Gibco, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum, (BI, USA) and 1% penicillin and streptomycin (Sigma, USA). Cells of the second to fourth generation were used for subsequent experiments. All material samples were sterilized by ethylene oxide and isolated samples (10 mm × 3 mm) were immersed in α-MEM at 37°C for 24 h to retrieve the material extracts following ISO 10993.
-
Ethical approval: The research related to animal use has been complied with all the relevant national regulations and institutional policies for the care and use of animals, and has been approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Suzhou University.
2.3.2 Cell proliferation and adhesion
To perform live/dead staining assays, BMSCs were processed with material extract for 1/3/5/7 days and then exchanged for a Calcein-AM/PI double staining kit (Beyotime, China) for 30 min according to the instruction manual. Observation and photography were carried out with an inverted fluorescent microscope (Olympus, IX71, Japan).
Cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay of BMSCs was conducted with the density of 5 × 104 cells/well seeded in a 24-well culture plate. After 1, 3, and 5 days of incubation with material extract, the medium was substituted with α-MEM medium containing 10% CCK-8 solution (Beyotime, China). The plates were then cultured at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 30 min, and the absorbance on the plates was recorded at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Epoch, BioTek Instruments, Inc.).
2.3.3 Osteogenic differentiation
To study osteogenic differentiation, osteogenic induction medium (OIM) was made of α-MEM containing 0.05 mM vitamin C (Sigma, USA), 10 mM β-glycerophosphate (Sigma, USA), and 10 nM dexamethasone (Sigma, USA). BMSCs were prepared in 12-well plates along with extracts in a cell culture incubator at 1 × 105 cells/well. The medium was substituted with OIM upon reaching cell density confluency of 70–80%. BMSCs culture were exchanged for OIM every 3 days to evaluate osteogenic differentiation with alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining, ALP activity was recorded after 14 days of culture and Alizarin Red S (ARS) staining after 21 days.
A BCIP/NBT solution (Beyotime, China) was utilized to determine ALP expression. After 14 days of incubation, BMSCs were washed three times with PBS and then processed with 10% neutral formalin for 15 min. Samples were stained according to the protocol and washed with PBS before observation with an optical microscope (Olympus, IX71, Japan). After 14 days of incubation, ALP activity was examined using an ALP assay kit (Beyotime, China). BMSCs were lysed with RIPA lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) and then centrifuged for 20 min at 3,000 rpm to detect ALP activity. Total cell protein was quantified in parallel with the BCA protein assay kit (Beyotime, China). Activity of ALP was identified after absorbance measurements at 405 nm on a microplate reader (Epoch, BioTek Instruments, Inc.)
ARS staining assay was performed to assess mineralization (Beyotime, China). Following 21 days of culture, calcium deposition was assessed with 0.5% Alizarin Red workup and observed by optical microscopy according to the instruction manual (Olympus, IX71, Japan).
2.4 In vitro angiogenesis assay
2.4.1 Cell culture
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were acquired from the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences cell bank and were utilized to estimate the influence of β-TCP on angiogenesis in vitro.
2.4.2 Tube formation assay
Twenty-four-well plates were pre-treated initially with polymerized Matrigel (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Cells were then seeded onto the Matrigel surface at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well and incubated in the extract for 12 h. Microscopic images were taken at random and ImageJ with the Angiogenesis Analyzer plug-in (NIH, Bethesda, MD) was used to quantify the tubular network (number of primary nodes and total segment length).
2.4.3 Transwell assay
The invasion capacity of HUVECs was assayed by the transwell assay. HUVECs were placed on the top layer of a transwell cell culture chamber (Costar, Cambridge, MA, USA). After the transwell chamber was capped with 50 μL of Matrigel (BD, Biosciences, USA), the membrane extract was placed underneath the cell permeable membrane for 12 h of incubation. The upper chamber was then washed twice with HUVECs to exclude non-invasive cells. HUVECs that had migrated through the membrane were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Beyotime, China) for 15 min and then colored with 0.4% crystal violet stain (Amresco, USA) for 20 min. Several microscopic areas were randomly selected for analysis.
2.4.4 Angiogenesis-related gene levels
After 3 days in culture, HUVECs were harvested and reverse transcribed to cDNA and RT-PCR was performed to check the gene expression levels of Willebrand Factor (vWF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), CD31, and β-actin as a control reference. Sequence information used in the study is presented in Table 1.
Primer sequences of each angiogenesis-related gene
| Gene | Direction | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| VEGF | Forward | TTCAAGCCATCCTGTGTGCC |
| Reverse | CACCAACGTACACGCTCCAG | |
| vWF | Forward | CCGATGCAGCCTTTTCGGA |
| Reverse | TCCCCAAGATACACGGAGAGG | |
| CD31 | Forward | AACAGTGTTGACATGAAGAGCC |
| Reverse | TGTAAAACAGCACGTCATCCTT | |
| β-actin | Forward | ATGTTCCAGTATGACTCCACTCAC |
| Reverse | GAAGACACCAGTAGACTCCACGAC |
2.5 Statistical analysis
At least three independent replicates were used for each experiment and continuous variables were represented as mean value ± standard deviation. One-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) were used to compare different treatment interventions in SPSS 20.0. The level of significant difference was set at p* < 0.05 and p** < 0.01.
3 Results
3.1 Chemical phase and thermal properties of the active membranes
As shown in Figure 1a, all groups of samples exhibited a broad peak at 2θ = 22°. PLGA is an amorphous polymer and the intensity of this peak with concentration of β-TCP content increases, indicating that β-TCP was well dispersed within the PLGA films in this concentration range. Loading of β-TCP in the PLGA membrane is shown in Figure 1b and c. The incorporation of β-TCP caused a decrease in the thermal decomposition temperature and glass transition temperature of PLGA, but the effect on thermal performance was slight. The decrease in thermal stability may be due to the agglomeration of β-TCP particles. The regularity of ion release also remained largely constant in the composite membrane. Concentration of calcium ions released best was in first 24 h and reached a stable value after 2 weeks, depending on the amount of β-TCP (Figure 1d). The addition of β-TCP not only accelerated the degradation of PLGA, but also neutralized the negative side effects of acidification of the microenvironment caused by PLGA degradation (Figure 1e and f).

Chemical phase and thermal properties of the active membranes. (a) XRD of the membrane. (b) DSC. (c) TGA. (d) Ca2+ release concentration. (e) Weight loss and (f) pH vibration of PBS after samples soaking. Data are presented as the mean value ± SD; n = 3.
3.2 Mechanical properties of bioactive membrane
Mechanical properties of the electrospinning membrane increased continuously with the increase in β-TCP content, from the initial 3.05 ± 0.10 MPa (PLGA) to 7.79 ± 0.135 MPa (PLGA/TCP10). The tensile strength of PLGA/TCP5 film increased by 134% compared to the pure PLGA film, but the β-TCP content increased from 5 to 10 wt%, mechanical properties only improved by 9% (Figure 2a and b). The tensile modulus displayed the same trend in Figure 2c.
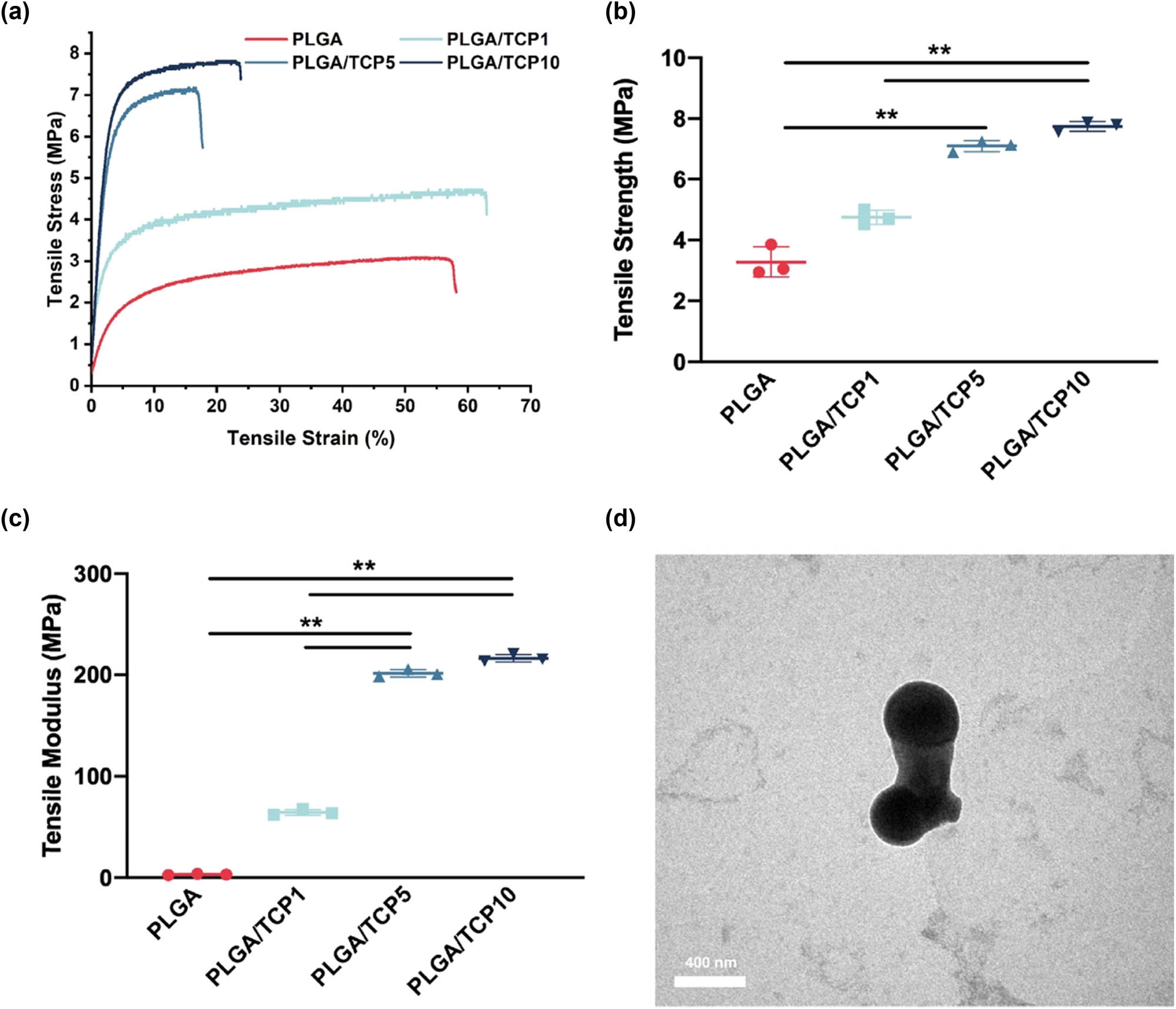
The mechanical properties of PLGA/β-TCP bioactive membrane. (a) Tensile stress–tensile strain of PLGA/β-TCP bioactive membrane, (b) tensile stress, and (c) tensile modulus. (d) Microscopic morphology of β-TCP. Data are presented as the mean value ± SD; n = 3; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
3.3 Microscopic morphology and elemental distribution of the membranes
The microscopic morphology of the composite film can be clearly observed from Figure 3. Meanwhile, the roughly 400 nm of β-TCP was observed by the TEM (Figure 2d). The addition of β-TCP did not have much effect on the diameter of the PLGA fibers, which remained in the range of 1–20 μm. As shown in the elemental distribution diagram, β-TCP is well dispersed in the PLGA fibers. The dense membrane structure has the potential to act as a physical barrier at the wound site [22].
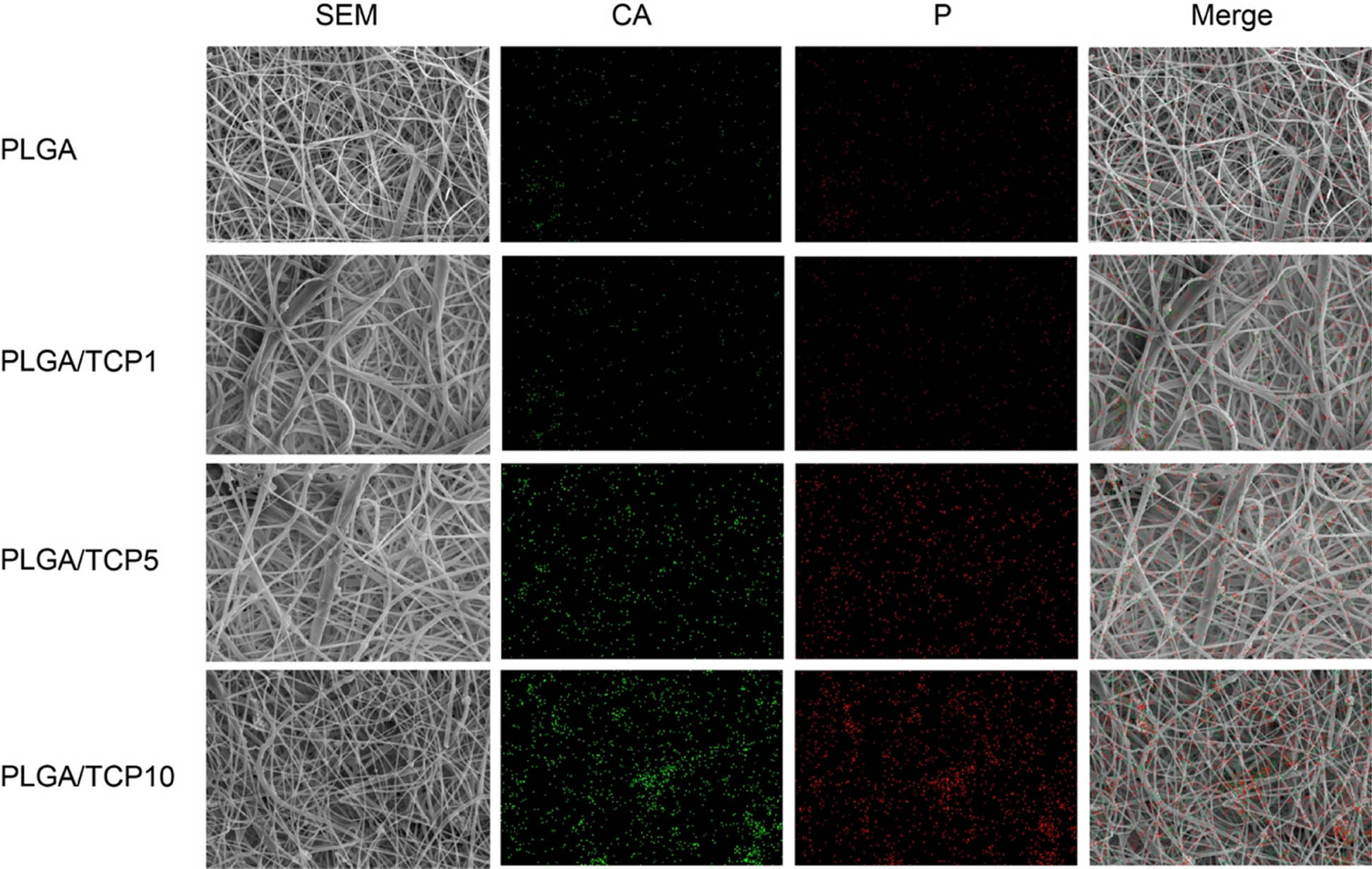
Microscopic morphology and elemental distribution of the membranes. First column: SEM of the membrane; second column: elemental distribution of calcium; third column: elemental distribution of phosphorus; fourth column: elemental distribution on the membrane.
3.4 Effect of PLGA/TCP on proliferation and adhesion of BMSCs
Cell viability is a primary parameter for analyzing the biocompatibility of a bio-scaffold as it directly affects both cell proliferation and differentiation directly. We cultivated BMSCs with PLGA/TCP extracts. Live/dead cell staining revealed that the scaffold did not hinder cell proliferation and almost no dead cells were detected during the observation (Figure 4a and b). Cell viability was measured in parallel using the CCK-8 assay to facilitate assessment. As shown in Figure 4c, the OD values increased with incubation time, but there was no statistical difference between the three groups, demonstrating that BMSCs proliferated well in the infiltrates of the material in each group. Additionally, we co-cultured cells with the surface of the material and detected the cytotoxic effect of materials on both BMSCs and HUVECs by using live/dead staining and CCK-8 assays after 1, 4, and 7 days. The results also showed that the bioactive membranes had no cytotoxic effect after co-culturing cells on the surface of the materials (Figures S2 and S3). In summary, PLGA/TCP was non-cytotoxic and promoted cell adhesion and proliferation.
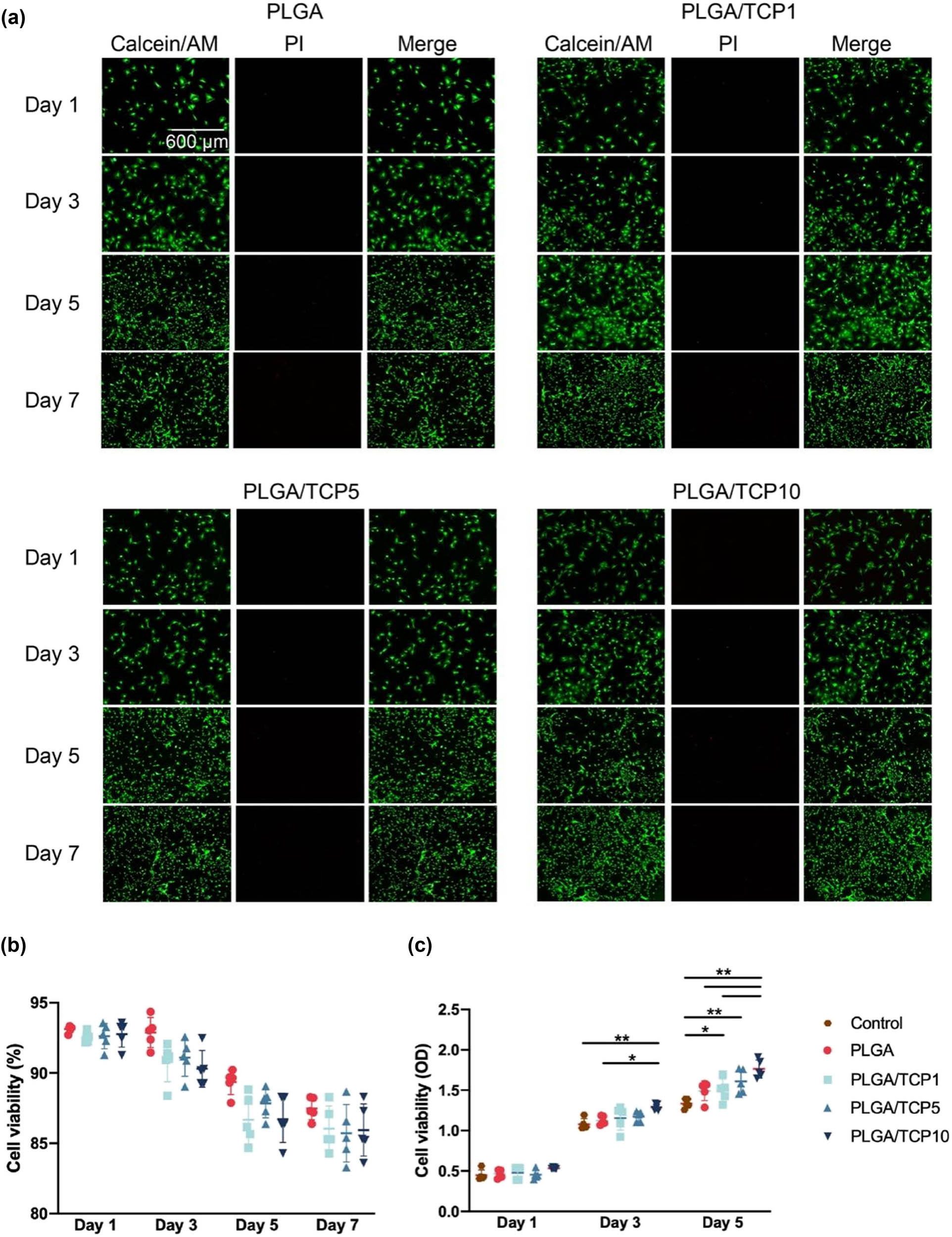
Proliferation and cell adhesion of BMSCs treated with extracts. (a) Live/dead staining results of BMSCs. (b) Cell viability according to the live/dead assays. (c) CCK-8 analysis of BMSCs. Data are presented as mean value ± SD; n = 3; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
3.5 Effect of PLGA/TCP on osteogenic differentiation capacity of BMSCs
To verify the subsequent effect of PLGA/TCP on osteogenesis in the local microenvironment, we combined the material extract with OIM to culture BMSCs. Figure 5a and b illustrate the outcome of ALP staining and ALP activity of BMSCs after 14 days of culture. ALP staining revealed an increased amount of ALP-positive cells in the PLGA/TCP scaffold group compared to the PLGA group, as well as an increase in positive cells with the increase in β-TCP content, indicating that β-TCP significantly enhance osteogenic differentiation. The PLGA/TCP1 group showed an increase (approximately 1.65-fold) ALP activity compared to the PLGA group as well as PLGA/TCP5 (approximately 2.26-fold), while the PLGA/TCP10 group exhibited the highest increase in ALP activity over 14 days (approximately 2.93-fold), as shown in Figure 5b. Formation and deposition of calcium salt nodules regarded as a marker of osteoblast maturation. We examined calcified nodules with alizarin red staining to identify the long-term effects of β-TCP in promoting bone formation [15]. ARS staining resulting from culturing BMSCs after 21 days is shown in Figure 5c. An increased amounts of calcified nodules was observed in the PLGA/TCP10 group, while the PLGA group had the lowest number of calcified nodules. This shows that PLGA/TCP10 extract accelerated and enhanced the mineralization process in osteoblasts, confirming that PLGA/TCP10 promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs.
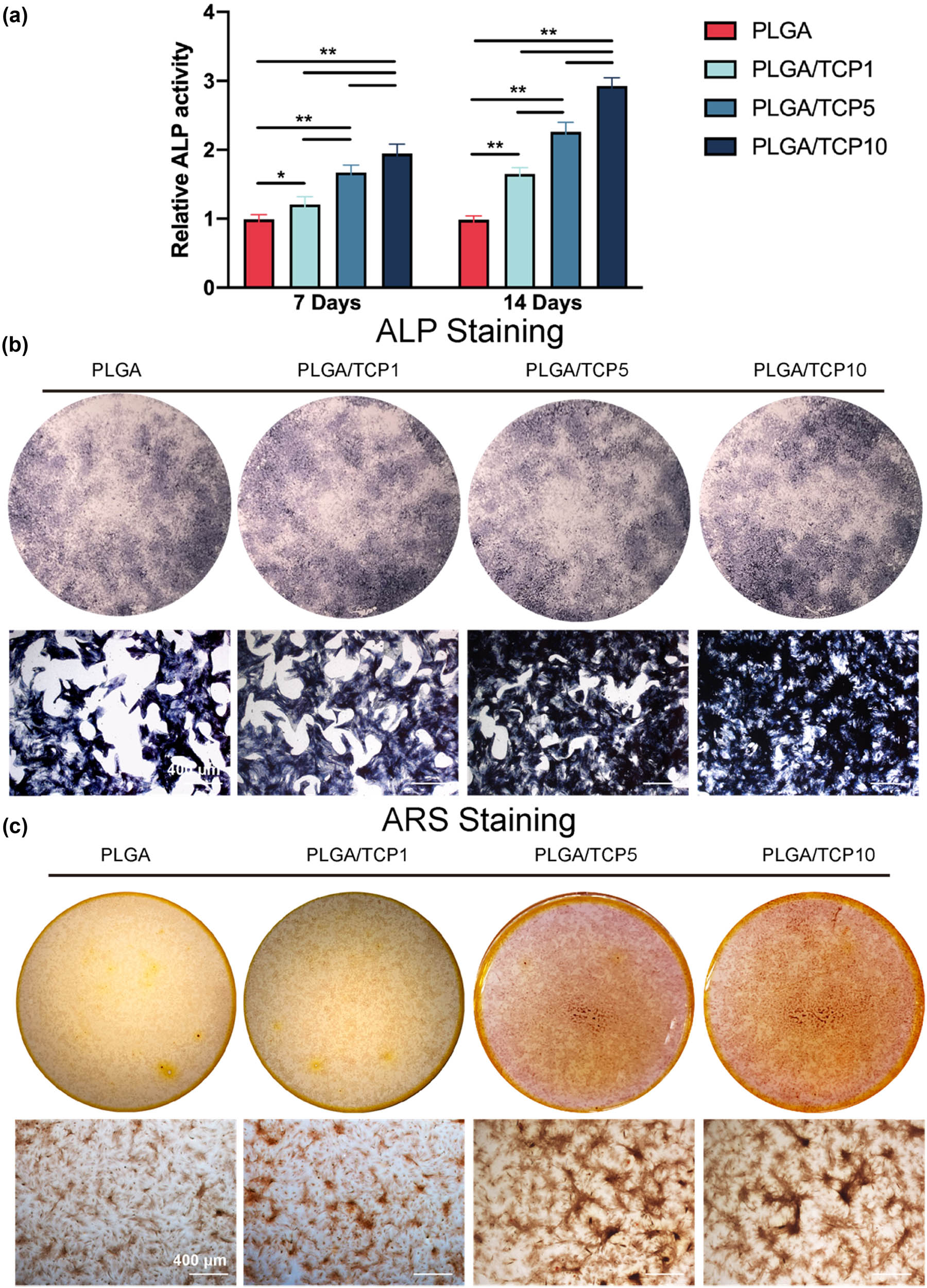
Osteogenic effect on BMSCs treated with extracts. (a) Quantification of ALP activity of BMSCs for 7 and 14 days. (b) ALP staining of BMSCs for 14 days. (c) ARS staining of BMSCs for 21 days. Data are presented as mean value ± SD; n = 3; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
3.6 Effect of PLGA/TCP on angiogenic capacity of HUVECs
As shown in Figure 6a, our results displayed that HUVECs in the PLGA/TCP10 group had the best angiogenic capacity. The angiogenic capacity of HUVECs was assessed by ImageJ, by quantifying the number of grids and primary nodes in the tube formation test and thus reflecting the angiogenic capacity of HUVECs, with more primary nodes and total segment length detected in the PLGA/TCP10 group (Figure 6b). Transwell assay was also used to evaluate the effect of PLGA/TCP on the migratory capacity of HUVECs. Results revealed that the crystal violet stain of migrating cells was significantly higher in the PLGA/TCP10 group compared to the other groups (Figure 6c and d). We performed qRT-PCR analysis to validate the angiogenic effect at the gene expression level after 3 days of incubation in the extracts. Compared to cells in the PLGA group, HUVECs in the PLGA/TCP10 group exhibited approximately 3.31-fold vWF expression, 2.96-fold VEGF expression and 3.08-fold CD31 expression (Figure 6e). These results suggest that PLGA/TCP has a positive effect on the angiogenic capacity of HUVECs.
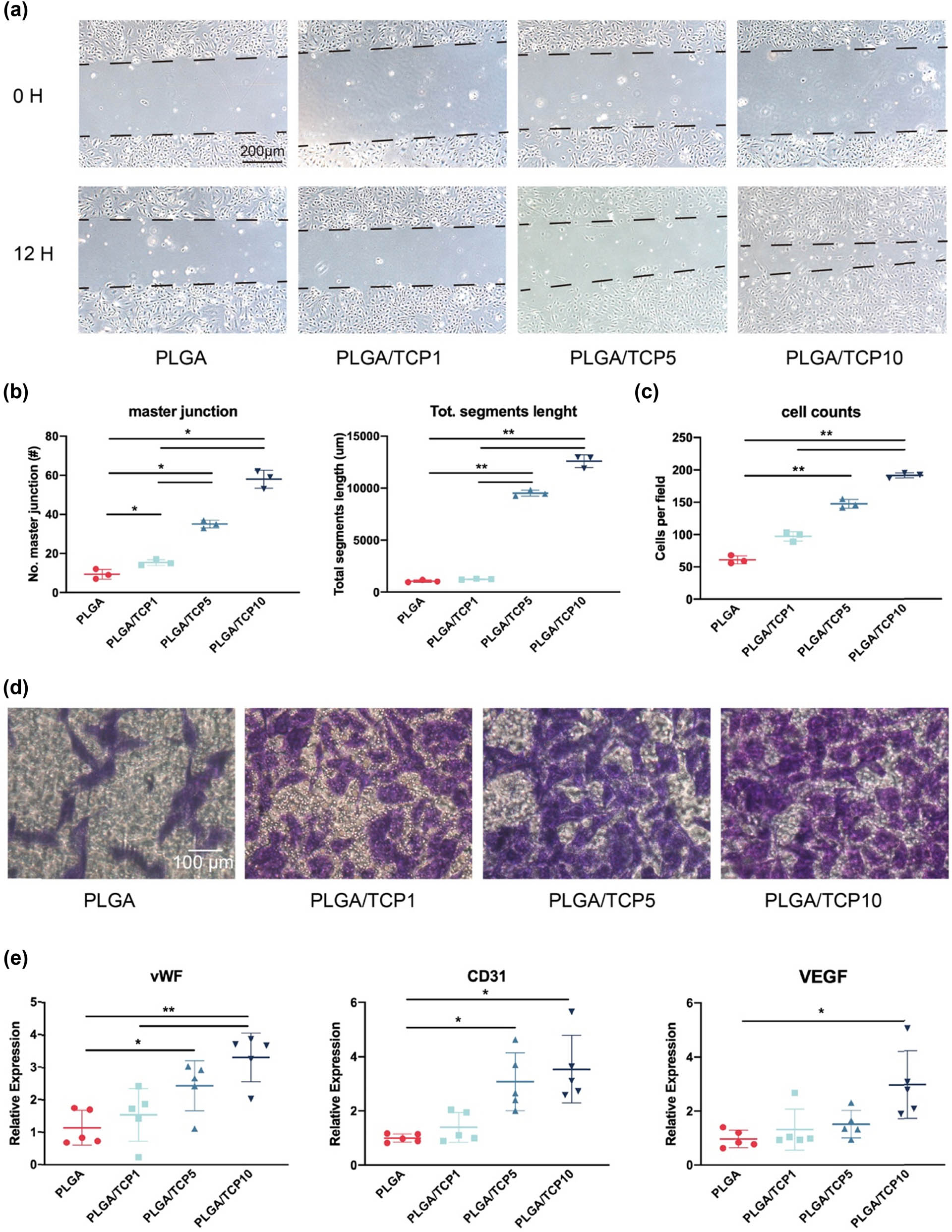
Angiogenic effect of HUVECs treated with extracts. (a) Tube formation assay of HUVECs cells. (b) Number of master junction and total segment length calculated with ImageJ. (c) Quantitative analysis of the Transwell assay. (d) Transwell assay of HUVECs cells. (e) Angiogenesis related gene expression of HUVECs cultured in extracts for 3 days. Data are presented as mean value ± SD; n = 3; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01.
4 Discussion
Due to population aging, traffic accident, or sports injury, bone defects and comminuted fracture remain as common clinical challenges [23,24]. The clinical gold standard for the reconstruction of bone defects is autologous bone grafting. However, its application is restricted by the low availability of bone grafts and donor-site morbidity [1,15,23]. Therefore, there is an increasing clinical demand for biomaterials for the treatment of bone defects. β-TCP is favored by researchers because of its excellent biocompatibility, good osteogenic activity, and can be combined with other materials to improve its biomechanical properties and osteogenic capacity [25]. Although the mechanical strength of β-TCP is slightly lower, its biodegradation rate is faster, which facilitates the growth of new bone around the implanted β-TCP base scaffold, and thus, β-TCP can be combined with other materials to improve its biomechanical properties and osteogenic ability [26]. However, the biomedical application of β-TCP is limited due to its inherent brittleness, non-degradability, and non-plastic ability [25,27]. PLGA, authorized by the US FDA, is frequently used to regulate the degradation rate of implants to meet clinical needs [28]. It was reported that the strength of calcium phosphate cement could be enhanced by adding PLGA medical sutures to form connected pores after polymer fiber degradation [29]. Studies also revealed that PLGA nanofibers can greatly improve the toughness and accelerate the degradation of calcium phosphate by using high aspect ratio and controllable degradation of PLGA [15]. PLGA degradation produces GA and LA, which could be metabolized and absorbed by the human body [15]. Previous studies have showed that the acidic products due to PLGA degradation lower the pH of the local environment, producing a local inflammatory response [30]. Simultaneously, the release of β-TCP is able to neutralize the local production of acid to some extent, overcoming the potential negative effects caused by excessive acidity and regulating the microenvironment for osteogenic repair [31]. Moreover, a high level of LA can make the local microenvironment become weakly acidic, which can facilitate the degradation of β-TCP [32,33]. In this study, we found that the viscosity of the bioactive membrane will be too large and the particles are easy to agglomerate when the TCP concentration exceeds 10%. It is difficult to prepare the electrospinning so that we prepared bioactive membrane with three concentrations of PLGA/TCP1, PLGA/TCP5, and PLGA/TCP10 for subsequent experiments in this study. Our results also showed that Ca2+ release was greater in the PLGA/TCP10 group than in the other groups, which led to an osteogenic environment during material degradation, thus greatly improving osseointegration and the growth of new bone towards the defect area.
As good biocompatibility is the prerequisite for the application of biomaterials in tissue repair [1], in this study, CCK-8 and live/dead staining assay were applied to evaluated cell viability. In addition, after cells were co-cultured with the surface of the material, it was still observed that both BMSCs and HUVECs could proliferate well and cell viability was not inhibited. Cell survival rate of live/dead assay and CCK-8 analysis showed that BMSCs proliferated well in all groups, demonstrating that PLGA/TCP membranes were non-cytotoxic for cell viability and proliferation. For osteogenic capacity, ALP staining and ALP activity assay were performed to measure the osteogenic capacity of BMSCs after osteogenic induction. ALP is a primary marker reflecting osteoblast differentiation and early bone mineral formation on biomaterials in vitro [34]. The results of ALP activity on the days 7 and 14 showed that osteogenic differentiation capacity of BMSCs was significantly increased after adding various membranes’ extracts, and PLGA/TCP10 group had the best osteogenic differentiation capacity in BMSCs. Moreover, the results of ALP staining on the day 14 and ARS staining on the day 21 also showed that the mineralization deposition gradually increased and PLGA/TCP10 group had the most mineralized nodules, suggesting that PLGA/TCP10 had the best effect of osteogenic differentiation capacity on BMSCs.
Bone tissue is a vascularized connective tissue, which primarily deliver oxygen, nutrients, hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors to bone cells and such neovascularization is indispensable for proper bone regeneration and remodeling [35–37]. Furthermore, it is reported that LA promotes vascular growth, which is also important for bone regeneration [38]. A recent study has revealed that the vascularization of bone defects is conducive to the recruitment of more BMSCs. Hence, the establishment of a vascular network at the bone defect area is favorable for bone formation [39]. Currently, the influence of PLGA/TCP on the angiogenic capability of HUVECs was also investigated by tube formation tests. The degradation of PLGA releases lactic acid, leading to localized accumulation of lactic acid in the osteogenic region. Moderate levels of lactic acid promote the angiogenic effect of HUVECs, but an overly acidic microenvironment impedes angiogenesis [40]. Regulation of the microenvironmental pH by β-TCP allows for a relatively neutral osteogenic zone, promoting angiogenesis in vitro. In the present study, the invasion and angiogenesis ability of HUVECs were assessed by tube formation and Transwell assay. As shown in the results, PLGA/TCP10 membrane had the best angiogenic capacity effect on HUVECs. The number of master junctions and total segment length were used to quantify the tube formation capacity by Image J, and the results also confirmed this tendency. Similar trends were also observed in the transwell assay, where the PLGA/TCP10 had the best invasive capacity of HUVECs. qRT-PCR results also revealed that the PLGA/TCP10 group had the best positive effect on angiogenic capacity in HUVECs. As angiogenesis is closely associated with osteogenesis, taken together, the results of this study demonstrated that PLGA/TCP10 membrane could improve the angiogenesis ability of HUVECs and synergistically promote bone regeneration.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we developed a PLGA/β-TCP compound membrane through electrostatic spinning aiming to control the release of β-TCP, to modulate the activity of osteoblasts and vascular endothelial cells. This biodegradable bioactive repair membrane possesses good mechanical and thermochemical properties, offering certain biological functions and is capable of facilitating osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Our results show that PLGA/β-TCP composite membranes further support the potential of PLGA and β-TCP as biomaterials.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation BoXi Cultivation Program Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University (BXQN2023013).
-
Author contributions: Lei Huang and Zhuorun Song designed the study, performed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. Jiayi Wang, Mengxuan Bian, and Jiapeng Zou analyzed the data. Jun Ge and Shunyi Lu made the final version of figures and prepared the manuscript for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Hu Z, Lu J, Zhang T, Liang H, Yuan H, Su D, et al. Piezoresistive MXene/Silk fibroin nanocomposite hydrogel for accelerating bone regeneration by re-establishing electrical microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2023;22:1–17.Search in Google Scholar
[2] Iantomasi T, Romagnoli C, Palmini G, Donati S, Falsetti I, Miglietta F, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoporosis: molecular mechanisms involved and the relationship with microRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(4):3772.Search in Google Scholar
[3] Jawahier PA, Waaijer L, d’Ailly PN, Schep NWL. Masquelet procedure for the treatment of intra-articular defects of the wrist. J Wrist Surg. 2023;12(6):543–8.Search in Google Scholar
[4] von Hertzberg-Boelch S, Luedemann M, Rudert M, Steinert A. PMMA bone cement: Antibiotic elution and mechanical properties in the context of clinical use. Biomedicines. 2022;10(8):1830.Search in Google Scholar
[5] Cao S, Zhao Y, Hu Y, Zou L, Chen J. New perspectives: In-situ tissue engineering for bone repair scaffold. Compos Part B: Eng. 2020;202:108445.Search in Google Scholar
[6] Koons GL, Diba M, Mikos AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5(8):584–603.Search in Google Scholar
[7] Guirguis D, Tucker C, Beuth J. Accelerating process development for 3D printing of new metal alloys. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):582.Search in Google Scholar
[8] Siraj S, Al-Marzouqi AH, Iqbal MZ, Ahmed W. Impact of micro silica filler particle size on mechanical properties of polymeric based composite material. Polym (Basel). 2022;14(22):4830.Search in Google Scholar
[9] He C, Lv Q, Liu Z, Long S, Li H, Xiao Y, et al. Random and aligned electrostatically spun PLLA nanofibrous membranes enhance bone repair in mouse femur midshaft defects. J Biomater Appl. 2023;37(9):1582–92.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Fu Y, Huang S, Feng Z, Huang L, Zhang X, Lin H, et al. MXene-functionalized ferroelectric nanocomposite membranes with modulating surface potential enhance bone regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(2):900–17.Search in Google Scholar
[11] Lin J, He Y, He Y, Feng Y, Wang X, Yuan L, et al. Janus functional electrospun polyurethane fibrous membranes for periodontal tissue regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(38):9223–36.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Wu S, Luo S, Cen Z, Li Q, Li L, Li W, et al. All-in-one porous membrane enables full protection in guided bone regeneration. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):119.Search in Google Scholar
[13] Zhu Y, Zhou J, Dai B, Liu W, Wang J, Li Q, et al. A bilayer membrane doped with struvite nanowires for guided bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(18):e2201679.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Niu X, Wang L, Xu M, Qin M, Zhao L, Wei Y, et al. Electrospun polyamide-6/chitosan nanofibers reinforced nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-6 composite bilayered membranes for guided bone regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;260:117769.Search in Google Scholar
[15] Cai P, Lu S, Yu J, Xiao L, Wang J, Liang H, et al. Injectable nanofiber-reinforced bone cement with controlled biodegradability for minimally-invasive bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2023;21:267–83.Search in Google Scholar
[16] Ruirui Z, He J, Xu X, Li S, Peng H, Deng Z, et al. PLGA-based drug delivery system for combined therapy of cancer: research progress. Mater Res Express. 2021;8(12):122002.Search in Google Scholar
[17] Jadidi A, Salahinejad E, Sharifi E, Tayebi L. Drug-delivery Ca-Mg silicate scaffolds encapsulated in PLGA. Int J Pharmaceutics. 2020;589:119855.Search in Google Scholar
[18] Bazgir M, Saeinasab M, Zhang W, Zhang X, Min Tsui K, Maasoumi Sarvestani A, et al. Investigation of cell adhesion and cell viability of the endothelial and fibroblast cells on electrospun PCL, PLGA and coaxial scaffolds for production of tissue engineered blood vessel. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):282.Search in Google Scholar
[19] Bohner M, Santoni BLG, Döbelin N. β-tricalcium phosphate for bone substitution: Synthesis and properties. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:23–41.Search in Google Scholar
[20] Zhou Y, Hu J, Li B, Xia J, Zhang T, Xiong Z. Towards the clinical translation of 3D PLGA/β-TCP/Mg composite scaffold for cranial bone regeneration. Mater (Basel). 2024;2:17.Search in Google Scholar
[21] Hatt LP, van der Heide D, Armiento AR, Stoddart MJ. β-TCP from 3D-printed composite scaffolds acts as an effective phosphate source during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1258161.Search in Google Scholar
[22] Qiao F, Lv Y. Hybrid cell membrane-functionalized matrixes for modulating inflammatory microenvironment and improving bone defect repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;e2203047.Search in Google Scholar
[23] Huang L, Lu S, Bian M, Wang J, Yu J, Ge J, et al. Punicalagin attenuates TNF-α-induced oxidative damage and promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2023;430(1):113717.Search in Google Scholar
[24] Zheng S, Zhou C, Yang H, Li J, Feng Z, Liao L, et al. Melatonin accelerates osteoporotic bone defect repair by promoting osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:826660.Search in Google Scholar
[25] Deyneko DV, Lebedev VN, Barbaro K, Titkov VV, Lazoryak BI, Fadeeva IV, et al. Antimicrobial and cell-friendly properties of cobalt and nickel-doped tricalcium phosphate ceramics. Biomim (Basel). 2023;9(1):14.Search in Google Scholar
[26] Sudo Y, Nishida Y, Nakashima H, Arai T, Takatsu T. Clinical outcomes of a novel unidirectional porous β-tricalcium phosphate filling in distal radius fracture with volar locking plate fixation: secondary publication of the Japanese version. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;60(1):1.Search in Google Scholar
[27] Umrath F, Schmitt LF, Kliesch SM, Schille C, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Gurewitsch E, et al. Mechanical and functional improvement of β-TCP scaffolds for use in bone tissue engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(8):427.Search in Google Scholar
[28] Paul PS, Patel T, Cho JY, Yarahmady A, Khalili A, Semenchenko V, et al. Native PLGA nanoparticles attenuate Aβ-seed induced Tau aggregation under in vitro conditions: potential implication in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):144.Search in Google Scholar
[29] Hatt LP, Wirth S, Ristaniemi A, Ciric DJ, Thompson K, Eglin D, et al. Micro-porous PLGA/β-TCP/TPU scaffolds prepared by solvent-based 3D printing for bone tissue engineering purposes. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad084.Search in Google Scholar
[30] Li Z, Li G, Xu J, Li C, Han S, Zhang C, et al. Hydrogel transformed from nanoparticles for prevention of tissue injury and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Adv Mater. 2022;34(16):e2109178.Search in Google Scholar
[31] Lin Z, Chen Z, Chen Y, Yang N, Shi J, Tang Z, et al. Hydrogenated silicene nanosheet functionalized scaffold enables immuno-bone remodeling. Exploration (Beijing). 2023;3(4):20220149.Search in Google Scholar
[32] Wang X, Li X, Gu N, Shao Y, Guo Y, Deng Y, et al. pH-responsive, self-sculptured Mg/PLGA composite microfibers for accelerated revascularization and soft tissue regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2024;158:213767.Search in Google Scholar
[33] Cao H, Li L, Li L, Meng X, Liu Y, Cheng W, et al. New use for old drug: Local delivery of puerarin facilitates critical-size defect repair in rats by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. J Orthop Transl. 2022;36:52–63.Search in Google Scholar
[34] Liu X, Chen M, Luo J, Zhao H, Zhou X, Gu Q, et al. Immunopolarization-regulated 3D printed-electrospun fibrous scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;276:121037.Search in Google Scholar
[35] Wang J, Zhang L, Wang L, Tang J, Wang W, Xu Y, et al. Ligand-selective targeting of macrophage hydrogel elicits bone immune-stem cell endogenous self-healing program to promote bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;e2303851.Search in Google Scholar
[36] Kong L, Li J, Bai Y, Xu S, Zhang L, Chen W, et al. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase enhances the dentin-pulp complex regeneration mediated by crosstalk between vascular endothelial cells and dental pulp stem cells. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):61.Search in Google Scholar
[37] Diomede F, Marconi GD, Fonticoli L, Pizzicanella J, Merciaro I, Bramanti P, et al. Functional relationship between osteogenesis and angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242.Search in Google Scholar
[38] Hu F, Huang K, Zhang H, Hu W, Tong S, Xu H. IGF-PLGA microspheres promote angiogenesis and accelerate skin flap repair and healing by inhibiting oxidative stress and regulating the Ang 1/Tie 2 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2024;193:106687.Search in Google Scholar
[39] Cheng D, Ding R, Jin X, Lu Y, Bao W, Zhao Y, et al. Strontium ion-functionalized nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite microspheres promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(16):19951–65.Search in Google Scholar
[40] Ding J, Liu Y, Liu Z, Tan J, Xu W, Huang G, et al. Glutathione-responsive organosilica hybrid nanosystems for targeted dual-starvation therapy in luminal breast cancer. Mol Pharm. 2023;21(2):745–59.Search in Google Scholar
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?
Articles in the same Issue
- Biomedical Sciences
- Constitutive and evoked release of ATP in adult mouse olfactory epithelium
- LARP1 knockdown inhibits cultured gastric carcinoma cell cycle progression and metastatic behavior
- PEGylated porcine–human recombinant uricase: A novel fusion protein with improved efficacy and safety for the treatment of hyperuricemia and renal complications
- Research progress on ocular complications caused by type 2 diabetes mellitus and the function of tears and blepharons
- The role and mechanism of esketamine in preventing and treating remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia based on the NMDA receptor–CaMKII pathway
- Brucella infection combined with Nocardia infection: A case report and literature review
- Detection of serum interleukin-18 level and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis and its clinical significance
- Ang-1, Ang-2, and Tie2 are diagnostic biomarkers for Henoch-Schönlein purpura and pediatric-onset systemic lupus erythematous
- PTTG1 induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and promotes aerobic glycolysis by regulating c-myc
- Role of serum B-cell-activating factor and interleukin-17 as biomarkers in the classification of interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features
- Effectiveness and safety of a mumps containing vaccine in preventing laboratory-confirmed mumps cases from 2002 to 2017: A meta-analysis
- Low levels of sex hormone-binding globulin predict an increased breast cancer risk and its underlying molecular mechanisms
- A case of Trousseau syndrome: Screening, detection and complication
- Application of the integrated airway humidification device enhances the humidification effect of the rabbit tracheotomy model
- Preparation of Cu2+/TA/HAP composite coating with anti-bacterial and osteogenic potential on 3D-printed porous Ti alloy scaffolds for orthopedic applications
- Aquaporin-8 promotes human dermal fibroblasts to counteract hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage: A novel target for management of skin aging
- Current research and evidence gaps on placental development in iron deficiency anemia
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2910829 in PDE4D is related to stroke susceptibility in Chinese populations: The results of a meta-analysis
- Pheochromocytoma-induced myocardial infarction: A case report
- Kaempferol regulates apoptosis and migration of neural stem cells to attenuate cerebral infarction by O‐GlcNAcylation of β-catenin
- Sirtuin 5 regulates acute myeloid leukemia cell viability and apoptosis by succinylation modification of glycine decarboxylase
- Apigenin 7-glucoside impedes hypoxia-induced malignant phenotypes of cervical cancer cells in a p16-dependent manner
- KAT2A changes the function of endometrial stromal cells via regulating the succinylation of ENO1
- Current state of research on copper complexes in the treatment of breast cancer
- Exploring antioxidant strategies in the pathogenesis of ALS
- Helicobacter pylori causes gastric dysbacteriosis in chronic gastritis patients
- IL-33/soluble ST2 axis is associated with radiation-induced cardiac injury
- The predictive value of serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic surgery
- Carrying SNP rs17506395 (T > G) in TP63 gene and CCR5Δ32 mutation associated with the occurrence of breast cancer in Burkina Faso
- P2X7 receptor: A receptor closely linked with sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: Is there sufficient evidence?
- Identification of KDM4C as a gene conferring drug resistance in multiple myeloma
- Microbial perspective on the skin–gut axis and atopic dermatitis
- Thymosin α1 combined with XELOX improves immune function and reduces serum tumor markers in colorectal cancer patients after radical surgery
- Highly specific vaginal microbiome signature for gynecological cancers
- Sample size estimation for AQP4-IgG seropositive optic neuritis: Retinal damage detection by optical coherence tomography
- The effects of SDF-1 combined application with VEGF on femoral distraction osteogenesis in rats
- Fabrication and characterization of gold nanoparticles using alginate: In vitro and in vivo assessment of its administration effects with swimming exercise on diabetic rats
- Mitigating digestive disorders: Action mechanisms of Mediterranean herbal active compounds
- Distribution of CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 gene polymorphisms in Han and Uygur populations with breast cancer in Xinjiang, China
- VSP-2 attenuates secretion of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in BV2 cells by mediating the PPARγ/NF-κB signaling pathway
- Factors influencing spontaneous hypothermia after emergency trauma and the construction of a predictive model
- Long-term administration of morphine specifically alters the level of protein expression in different brain regions and affects the redox state
- Application of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the etiological diagnosis of peritoneal dialysis-associated peritonitis
- Clinical diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of neurodyspepsia syndrome using intelligent medicine
- Case report: Successful bronchoscopic interventional treatment of endobronchial leiomyomas
- Preliminary investigation into the genetic etiology of short stature in children through whole exon sequencing of the core family
- Cystic adenomyoma of the uterus: Case report and literature review
- Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a drug delivery mechanism
- Dynamic changes in autophagy activity in different degrees of pulmonary fibrosis in mice
- Vitamin D deficiency and inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes: Big data insights
- Lactate-induced IGF1R protein lactylation promotes proliferation and metabolic reprogramming of lung cancer cells
- Meta-analysis on the efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to treat malignant lymphoma
- Mitochondrial DNA drives neuroinflammation through the cGAS-IFN signaling pathway in the spinal cord of neuropathic pain mice
- Application value of artificial intelligence algorithm-based magnetic resonance multi-sequence imaging in staging diagnosis of cervical cancer
- Embedded monitoring system and teaching of artificial intelligence online drug component recognition
- Investigation into the association of FNDC1 and ADAMTS12 gene expression with plumage coloration in Muscovy ducks
- Yak meat content in feed and its impact on the growth of rats
- A rare case of Richter transformation with breast involvement: A case report and literature review
- First report of Nocardia wallacei infection in an immunocompetent patient in Zhejiang province
- Rhodococcus equi and Brucella pulmonary mass in immunocompetent: A case report and literature review
- Downregulation of RIP3 ameliorates the left ventricular mechanics and function after myocardial infarction via modulating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway
- Evaluation of the role of some non-enzymatic antioxidants among Iraqi patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The role of Phafin proteins in cell signaling pathways and diseases
- Ten-year anemia as initial manifestation of Castleman disease in the abdominal cavity: A case report
- Coexistence of hereditary spherocytosis with SPTB P.Trp1150 gene variant and Gilbert syndrome: A case report and literature review
- Utilization of convolutional neural networks to analyze microscopic images for high-throughput screening of mesenchymal stem cells
- Exploratory evaluation supported by experimental and modeling approaches of Inula viscosa root extract as a potent corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in a 1 M HCl solution
- Imaging manifestations of ductal adenoma of the breast: A case report
- Gut microbiota and sleep: Interaction mechanisms and therapeutic prospects
- Isomangiferin promotes the migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
- Prognostic value and microenvironmental crosstalk of exosome-related signatures in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer
- Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers for male severe sepsis
- Knockdown of Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits growth and glycolysis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- The expression and biological role of complement C1s in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- A novel GNAS mutation in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a with articular flexion deformity: A case report
- Predictive value of serum magnesium levels for prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy
- HSPB1 alleviates acute-on-chronic liver failure via the P53/Bax pathway
- IgG4-related disease complicated by PLA2R-associated membranous nephropathy: A case report
- Baculovirus-mediated endostatin and angiostatin activation of autophagy through the AMPK/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metformin mitigates osteoarthritis progression by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and enhancing chondrocyte autophagy
- Evaluation of the activity of antimicrobial peptides against bacterial vaginosis
- Atypical presentation of γ/δ mycosis fungoides with an unusual phenotype and SOCS1 mutation
- Analysis of the microecological mechanism of diabetic kidney disease based on the theory of “gut–kidney axis”: A systematic review
- Omega-3 fatty acids prevent gestational diabetes mellitus via modulation of lipid metabolism
- Refractory hypertension complicated with Turner syndrome: A case report
- Interaction of ncRNAs and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway: Implications for osteosarcoma
- Association of low attenuation area scores with pulmonary function and clinical prognosis in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Long non-coding RNAs in bone formation: Key regulators and therapeutic prospects
- The deubiquitinating enzyme USP35 regulates the stability of NRF2 protein
- Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as potential diagnostic markers for rebleeding in patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding
- G protein-coupled receptor 1 participating in the mechanism of mediating gestational diabetes mellitus by phosphorylating the AKT pathway
- LL37-mtDNA regulates viability, apoptosis, inflammation, and autophagy in lipopolysaccharide-treated RLE-6TN cells by targeting Hsp90aa1
- The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin: A focused review
- Chemical composition’s effect on Solanum nigrum Linn.’s antioxidant capacity and erythrocyte protection: Bioactive components and molecular docking analysis
- Knockdown of HCK promotes HREC cell viability and inner blood–retinal barrier integrity by regulating the AMPK signaling pathway
- The role of rapamycin in the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in mitophagy in podocytes
- Laryngeal non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature
- Clinical value of macrogenome next-generation sequencing on infections
- Overview of dendritic cells and related pathways in autoimmune uveitis
- TAK-242 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy via inhibiting pyroptosis and TLR4/CaMKII/NLRP3 pathway
- Hypomethylation in promoters of PGC-1α involved in exercise-driven skeletal muscular alterations in old age
- Profile and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of bacteria isolated from effluents of Kolladiba and Debark hospitals
- The expression and clinical significance of syncytin-1 in serum exosomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- A histomorphometric study to evaluate the therapeutic effects of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on the kidneys infected with Plasmodium chabaudi
- PGRMC1 and PAQR4 are promising molecular targets for a rare subtype of ovarian cancer
- Analysis of MDA, SOD, TAOC, MNCV, SNCV, and TSS scores in patients with diabetes peripheral neuropathy
- SLIT3 deficiency promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by modulating UBE2C/WNT signaling
- The relationship between TMCO1 and CALR in the pathological characteristics of prostate cancer and its effect on the metastasis of prostate cancer cells
- Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a potential target for enhancing the chemosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- PHB2 alleviates retinal pigment epithelium cell fibrosis by suppressing the AGE–RAGE pathway
- Anti-γ-aminobutyric acid-B receptor autoimmune encephalitis with syncope as the initial symptom: Case report and literature review
- Comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of Lonicera japonica cv. Damaohua
- Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells regulate glutathione metabolism depending on the ERK–Nrf2–HO-1 signal pathway to repair phosphoramide mustard-induced ovarian cancer cells
- Electroacupuncture on GB acupoints improves osteoporosis via the estradiol–PI3K–Akt signaling pathway
- Renalase protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy
- Review: Dicranostigma leptopodum: A peculiar plant of Papaveraceae
- Combination effect of flavonoids attenuates lung cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the STAT3 and FAK signaling pathway
- Renal microangiopathy and immune complex glomerulonephritis induced by anti-tumour agents: A case report
- Correlation analysis of AVPR1a and AVPR2 with abnormal water and sodium and potassium metabolism in rats
- Gastrointestinal health anti-diarrheal mixture relieves spleen deficiency-induced diarrhea through regulating gut microbiota
- Myriad factors and pathways influencing tumor radiotherapy resistance
- Exploring the effects of culture conditions on Yapsin (YPS) gene expression in Nakaseomyces glabratus
- Screening of prognostic core genes based on cell–cell interaction in the peripheral blood of patients with sepsis
- Coagulation factor II thrombin receptor as a promising biomarker in breast cancer management
- Ileocecal mucinous carcinoma misdiagnosed as incarcerated hernia: A case report
- Methyltransferase like 13 promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells through targeting PI3K/ATK signaling pathway
- The debate between electricity and heat, efficacy and safety of irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver cancer: A meta-analysis
- ZAG promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting lipid synthesis
- Baicalein inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitigates placental inflammation and oxidative stress in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Impact of SWCNT-conjugated senna leaf extract on breast cancer cells: A potential apoptotic therapeutic strategy
- MFAP5 inhibits the malignant progression of endometrial cancer cells in vitro
- Major ozonated autohemotherapy promoted functional recovery following spinal cord injury in adult rats via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
- Axodendritic targeting of TAU and MAP2 and microtubule polarization in iPSC-derived versus SH-SY5Y-derived human neurons
- Differential expression of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and Toll-like receptor/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathways in experimental obesity Wistar rat model
- The therapeutic potential of targeting Oncostatin M and the interleukin-6 family in retinal diseases: A comprehensive review
- BA inhibits LPS-stimulated inflammatory response and apoptosis in human middle ear epithelial cells by regulating the Nf-Kb/Iκbα axis
- Role of circRMRP and circRPL27 in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Investigating the role of hyperexpressed HCN1 in inducing myocardial infarction through activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
- Characterization of phenolic compounds and evaluation of anti-diabetic potential in Cannabis sativa L. seeds: In vivo, in vitro, and in silico studies
- Quantitative immunohistochemistry analysis of breast Ki67 based on artificial intelligence
- Ecology and Environmental Science
- Screening of different growth conditions of Bacillus subtilis isolated from membrane-less microbial fuel cell toward antimicrobial activity profiling
- Degradation of a mixture of 13 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by commercial effective microorganisms
- Evaluation of the impact of two citrus plants on the variation of Panonychus citri (Acari: Tetranychidae) and beneficial phytoseiid mites
- Prediction of present and future distribution areas of Juniperus drupacea Labill and determination of ethnobotany properties in Antalya Province, Türkiye
- Population genetics of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the northwest Pacific Ocean via GBS sequencing
- A comparative analysis of dendrometric, macromorphological, and micromorphological characteristics of Pistacia atlantica subsp. atlantica and Pistacia terebinthus in the middle Atlas region of Morocco
- Macrofungal sporocarp community in the lichen Scots pine forests
- Assessing the proximate compositions of indigenous forage species in Yemen’s pastoral rangelands
- Food Science
- Gut microbiota changes associated with low-carbohydrate diet intervention for obesity
- Reexamination of Aspergillus cristatus phylogeny in dark tea: Characteristics of the mitochondrial genome
- Differences in the flavonoid composition of the leaves, fruits, and branches of mulberry are distinguished based on a plant metabolomics approach
- Investigating the impact of wet rendering (solventless method) on PUFA-rich oil from catfish (Clarias magur) viscera
- Non-linear associations between cardiovascular metabolic indices and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in the US population (2017–2020)
- Knockdown of USP7 alleviates atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice by regulating EZH2 expression
- Utility of dairy microbiome as a tool for authentication and traceability
- Agriculture
- Enhancing faba bean (Vicia faba L.) productivity through establishing the area-specific fertilizer rate recommendation in southwest Ethiopia
- Impact of novel herbicide based on synthetic auxins and ALS inhibitor on weed control
- Perspectives of pteridophytes microbiome for bioremediation in agricultural applications
- Fertilizer application parameters for drip-irrigated peanut based on the fertilizer effect function established from a “3414” field trial
- Improving the productivity and profitability of maize (Zea mays L.) using optimum blended inorganic fertilization
- Application of leaf multispectral analyzer in comparison to hyperspectral device to assess the diversity of spectral reflectance indices in wheat genotypes
- Animal Sciences
- Knockdown of ANP32E inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth and glycolysis by regulating the AKT/mTOR pathway
- Development of a detection chip for major pathogenic drug-resistant genes and drug targets in bovine respiratory system diseases
- Exploration of the genetic influence of MYOT and MB genes on the plumage coloration of Muscovy ducks
- Transcriptome analysis of adipose tissue in grazing cattle: Identifying key regulators of fat metabolism
- Comparison of nutritional value of the wild and cultivated spiny loaches at three growth stages
- Transcriptomic analysis of liver immune response in Chinese spiny frog (Quasipaa spinosa) infected with Proteus mirabilis
- Disruption of BCAA degradation is a critical characteristic of diabetic cardiomyopathy revealed by integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis
- Plant Sciences
- Effect of long-term in-row branch covering on soil microorganisms in pear orchards
- Photosynthetic physiological characteristics, growth performance, and element concentrations reveal the calcicole–calcifuge behaviors of three Camellia species
- Transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of NaHCO3 promoting tobacco leaf maturation
- Bioinformatics, expression analysis, and functional verification of allene oxide synthase gene HvnAOS1 and HvnAOS2 in qingke
- Water, nitrogen, and phosphorus coupling improves gray jujube fruit quality and yield
- Improving grape fruit quality through soil conditioner: Insights from RNA-seq analysis of Cabernet Sauvignon roots
- Role of Embinin in the reabsorption of nucleus pulposus in lumbar disc herniation: Promotion of nucleus pulposus neovascularization and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells
- Revealing the effects of amino acid, organic acid, and phytohormones on the germination of tomato seeds under salinity stress
- Combined effects of nitrogen fertilizer and biochar on the growth, yield, and quality of pepper
- Comprehensive phytochemical and toxicological analysis of Chenopodium ambrosioides (L.) fractions
- Impact of “3414” fertilization on the yield and quality of greenhouse tomatoes
- Exploring the coupling mode of water and fertilizer for improving growth, fruit quality, and yield of the pear in the arid region
- Metagenomic analysis of endophytic bacteria in seed potato (Solanum tuberosum)
- Antibacterial, antifungal, and phytochemical properties of Salsola kali ethanolic extract
- Exploring the hepatoprotective properties of citronellol: In vitro and in silico studies on ethanol-induced damage in HepG2 cells
- Enhanced osmotic dehydration of watermelon rind using honey–sucrose solutions: A study on pre-treatment efficacy and mass transfer kinetics
- Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on photosynthetic traits of 53 cowpea varieties under NaCl stress
- Comparative transcriptome analysis of maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings in response to copper stress
- An optimization method for measuring the stomata in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) under multiple abiotic stresses
- Fosinopril inhibits Ang II-induced VSMC proliferation, phenotype transformation, migration, and oxidative stress through the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway
- Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salsola imbricata methanolic extract and its phytochemical characterization
- Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Absorbable calcium and phosphorus bioactive membranes promote bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenic differentiation for bone regeneration
- New advances in protein engineering for industrial applications: Key takeaways
- An overview of the production and use of Bacillus thuringiensis toxin
- Research progress of nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Bioelectrochemical biosensors for water quality assessment and wastewater monitoring
- PEI/MMNs@LNA-542 nanoparticles alleviate ICU-acquired weakness through targeted autophagy inhibition and mitochondrial protection
- Unleashing of cytotoxic effects of thymoquinone-bovine serum albumin nanoparticles on A549 lung cancer cells
- Erratum
- Erratum to “Investigating the association between dietary patterns and glycemic control among children and adolescents with T1DM”
- Erratum to “Activation of hypermethylated P2RY1 mitigates gastric cancer by promoting apoptosis and inhibiting proliferation”
- Retraction
- Retraction to “MiR-223-3p regulates cell viability, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting RHOB”
- Retraction to “A data mining technique for detecting malignant mesothelioma cancer using multiple regression analysis”
- Special Issue on Advances in Neurodegenerative Disease Research and Treatment
- Transplantation of human neural stem cell prevents symptomatic motor behavior disability in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease
- Special Issue on Multi-omics
- Inflammasome complex genes with clinical relevance suggest potential as therapeutic targets for anti-tumor drugs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
- Gastroesophageal varices in primary biliary cholangitis with anti-centromere antibody positivity: Early onset?

