Abstract
Background: Health literacy (HL) and irrational beliefs about happiness significantly influence adults’ health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The purpose of this study was to examine whether irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL among adults.
Methods: A total of 686 adults (468 women and 218 men; mean age = 22.30 ± 6.83 years) completed self-report questionnaires, including the Health Literacy Scale-Short Form, the EUROHIS-QOL 8, and the Irrational Happiness Beliefs Scale. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling and bootstrapping methods.
Results: HL had both direct (β = 0.260, p < 0.01) and indirect effects on HRQoL. HL directly predicted irrational happiness (β = –0.369, p < 0.01), which in turn directly predicted HRQoL (β = –0.318, p < 0.01). Specifically, irrational happiness significantly mediated the relationship between HL and HRQoL (bootstrap coefficient = 0.117, 95% CI = 0.071–0.175).
Conclusion: These findings suggest that interventions aiming to enhance adults’ HRQoL should consider not only improving HL but also addressing irrational beliefs about happiness.
1 Introduction
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) refers to individuals’ subjective evaluations of how their physical, mental, emotional, and social health statuses affect their daily lives [1]. HRQoL is not confined merely to the presence or absence of medical conditions; it also encompasses how well individuals feel, their functionality, and their social participation [2]. In modern healthcare, the significance of HRQoL has increasingly been recognized, and it has become a widespread indicator for assessing the success of health interventions [3]. Psychological and social health emerge as determining factors of HRQoL, just as much as physical health does [4]. Research indicates that individuals with higher HRQoL not only tend to live longer but also exhibit greater satisfaction and happiness in their daily lives [5,6,7]. Therefore, HRQoL is an essential health indicator that allows for a more holistic consideration of individuals’ health statuses. A good HRQoL is critically important for the management of chronic diseases, healthy aging, and the enhancement of overall life satisfaction [8,9].
Health literacy (HL) refers to individuals’ abilities to acquire, understand, and use health-related information to make appropriate decisions [10]. Individuals with high HL participate more effectively in health systems and can better manage their own health conditions [11,12]. Studies have shown that HL improves individuals’ disease prevention behaviors, facilitates coping with chronic conditions, and enhances overall quality of life [12,13,14]. Particularly in situations where HL is low, individuals are more likely to misinterpret important health information, which can negatively impact health outcomes [15].
HL not only contributes to individuals’ physical and mental health but also plays a significant role in enhancing their HRQoL [16]. In this context, it has been observed that individuals with high HL not only experience better quality of life but also exhibit increased trust in healthcare services [17]. To better understand the relationship between HL and HRQoL, it is necessary to examine individuals’ emotional and cognitive processes. This is where the concept of irrational happiness comes into play, serving as a potential mediator that shapes the connection between the knowledge gained from HL and the quality of life.
1.1 The mediating role of irrational happiness
Irrational happiness is defined as the display of unrealistic optimism by individuals despite adverse health conditions or life challenges [18]. However, this type of happiness is considered a maladaptive trait rather than an adaptive one [19]; it may lead individuals to not take health-related threats seriously enough and to postpone appropriate health behaviors. While irrational happiness can enhance emotional comfort, such excessive optimism increases the likelihood of underestimating one’s health status and engaging in risky behaviors.
In this study, irrational happiness was found to function as a negative mediating mechanism in the relationship between HL and HRQoL. High HL enables individuals to assess health risks more accurately, whereas those with high levels of irrational happiness may tend to ignore or misinterpret this information. For example, excessive optimism might lead them to disregard health warnings and miss opportunities for early intervention [20]. Therefore, irrational happiness can prevent individuals from fully benefiting from their levels of HL, potentially creating a negative impact on HRQoL.
1.2 The present study
This study aims to examine the relationship between HL and HRQoL, and to investigate the mediating role of irrational happiness in this relationship. The literature has demonstrated that HL directly affects individuals’ health behaviors and health outcomes [11,12,14]. However, studies are limited regarding the role psychological factors, especially irrational happiness, play in the process by which individuals’ health knowledge translates into HRQoL. This research takes an important step toward deeply understanding the impact of irrational happiness on individuals’ quality of life. In line with this, we have developed the following hypotheses in our study:
Hypothesis 1: HL has a positive impact on HRQoL.
Hypothesis 2: Irrational happiness has a direct impact on HRQoL.
Hypothesis 3: Irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL.
2 Method
2.1 Participants
A total of 686 individuals aged between 18 and 56 participated in this study (mean age = 22.30, SD = 6.83). The sample consisted of 468 females (68.2%) and 218 males (31.8%). Based on socioeconomic status (SES), 73 participants (10.6%) were of low SES, 573 (83.5%) were of middle SES, and 40 (5.8%) were of high SES. In terms of educational attainment, 17 participants (2.5%) had completed high school, 627 participants (91.4%) held a bachelor’s degree, 27 participants (3.9%) had a master’s degree, and 15 participants (2.2%) held a doctoral degree. Data were collected in August and September 2024 from five different cities in Türkiye, representing small, medium, and large urban areas, using a convenience sampling method. The study was conducted in a digital environment. Approximately 56% of the participants reported having a chronic illness, while the remaining participants did not have an active illness at the time of the study. Regarding chronic health issues in the family, 411 participants (59.9%) reported having a family member with a chronic health problem, while 275 (40.1%) reported none. In the past 6 months, 87.5% of participants had visited a hospital at least once, and 20% had visited four times or more.
2.2 Measures
The Health Literacy Scale-Short Form (HLS-SF) was developed by Duong et al. [21] to measure individuals’ abilities to acquire, understand, evaluate, and apply health-related information. The Turkish adaptation and validity–reliability study of the scale have made it applicable to Turkish-speaking populations [22]. Studies have found the scale’s internal consistency reliability coefficient (Cronbach’s α) to be 0.856, and factor analyses have supported its structural validity [22].
The EUROHIS (WHOQOL-8.Tr) is an 8-item index measuring quality of life, constructed by selecting specific items from the World Health Organization Quality of Life Scale (WHOQOL). This scale aims to quickly and effectively assess individuals’ general quality of life and health status [23]. Studies on the psychometric properties of the Turkish version have demonstrated a high level of reliability, with an internal consistency reliability coefficient (Cronbach’s α) of 0.85. Structural validity analyses also support that the scale is a valid and reliable measurement tool within the Turkish population [23].
The Irrational Happiness Beliefs Scale (IHB) was developed to assess individuals’ irrational beliefs about happiness and their impact on subjective well-being [24]. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses confirmed that the IHB is unidimensional, consisting of three items with a high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.84). The scale showed significant positive correlations with measures of valuing happiness, negative affect, perceived stress, and irrational thinking. Conversely, it had significant negative correlations with satisfaction with life, subjective happiness, positive affect, psychological well-being, and rational thinking [24].
2.3 Data analysis
Initially, correlation analysis and descriptive statistics were conducted, followed by structural equation modeling (SEM). Adopting Kline’s [25] recommendations, a two-step SEM approach was employed. In the first step, we tested the measurement model to confirm whether the observed indicators effectively formed the latent variables and whether the relationships among these latent variables were valid. After validating the measurement model, we proceeded to test the hypothesized structural model. All analyses were performed using IBM SPSS 22 for descriptive statistics and correlation analyses and AMOS Graphics for SEM. Prior to SEM, the normality of the data was assessed via skewness and kurtosis values, which fell within acceptable ranges.
To evaluate the SEM results, we considered the goodness-of-fit indices recommended by Hu and Bentler [26], including chi-square (χ²) and degrees of freedom, as well as comparative fit index (CFI), normed fit index (NFI), Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), standardized root mean square residual (SRMR), root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) values. The critical thresholds were set as follows: a χ²/df ratio less than 5; CFI, NFI, and TLI values greater than 0.90; and SRMR and RMSEA values less than 0.80 [26]
In addition to SEM, we employed the increasingly popular bootstrapping procedure to provide additional evidence for the significance of mediation. Using bootstrapping with 10,000 resamples, we generated bootstrap estimates and confidence intervals (CIs). The absence of zero within these CIs indicates that the tested mediation effect is significant. All measurement scales demonstrated satisfactory reliability (Cronbach’s α > 0.70), further supporting the robustness of our analyses.
-
Ethical approval: The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Helsinki Declaration, and informed consent was obtained from all participants. Ethical approval for this research was obtained from the Yıldız Technical University Ethics Committee (ID = 2024-10/0335).
3 Results
Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics and Pearson correlations for the variables examined: HL, HRQoL, and irrational happiness. The Pearson correlation analysis revealed several significant relationships among the variables. HL was positively correlated with HRQoL (r = 0.329, p < 0.001), indicating that individuals with higher HL tend to report better quality of life related to their health. In contrast, HL was negatively associated with irrational happiness (r = −0.309, p < 0.001), suggesting that higher HL is linked to lower levels of irrational happiness. Additionally, HRQoL was negatively correlated with irrational happiness (r = −0.358, p < 0.001).
Relationships among variables and descriptive statistics
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. HL | — | ||
| 2. HRQoL | 0.329** | — | |
| 3. Irrational happiness | −0.309** | −0.358** | — |
| Mean | 34.62 | 27.27 | 9.74 |
| SD | 4.79 | 4.43 | 2.11 |
| Skewness | −0.229 | −0.530 | 0.865 |
| Kurtosis | 1.68 | 0.892 | 1.48 |
| Cronbach α | 0.789 | 0.816 | 0.702 |
** p < 0.001.
3.1 Measurement model
The measurement model consisted of three latent variables – HL, HRQoL, and irrational happiness – with a total of seven observed variables: two each for HL and HRQoL, and three for irrational happiness. The results indicated a good fit for the measurement model, χ²(11, N = 686) = 21.77, p < 0.001, χ²/df = 1.98; GFI = 0.991; NFI = 0.987; CFI = 0.994; TLI = 0.988; RFI = 0.975; TLI = 0.988; SRMR = 0.025; RMSEA = 0.038. Additionally, factor loadings ranged from 0.525 to 0.918, suggesting that the observed variables significantly represented the latent constructs.
3.2 Structural model
In the structural model, we tested whether irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL, including BMI, gender, and education level as control variables. The model with irrational happiness as a mediator demonstrated a good fit: χ²(26, N = 686) = 56.82, p < 0.001; χ²/df = 2.18; GFI = 0.984; NFI = 0.968; CFI = 0.982; TLI = 0.969; RFI = 0.945; SRMR = 0.034; RMSEA = 0.042. Results indicated that HL directly and positively predicted HRQoL (β = 0.262, p < 0.01). Conversely, HL directly and negatively predicted irrational happiness (β = −0.368, p < 0.01), which in turn directly and negatively predicted HRQoL (β = −0.319, p < 0.01). The bootstrapping analysis revealed that the indirect path coefficient was significant (bootstrap coefficient = 0.117, 95% CI = 0.072–0.172). Taking all these findings into account, it can be concluded that irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL. The path coefficients for this model are presented in Figure 1.
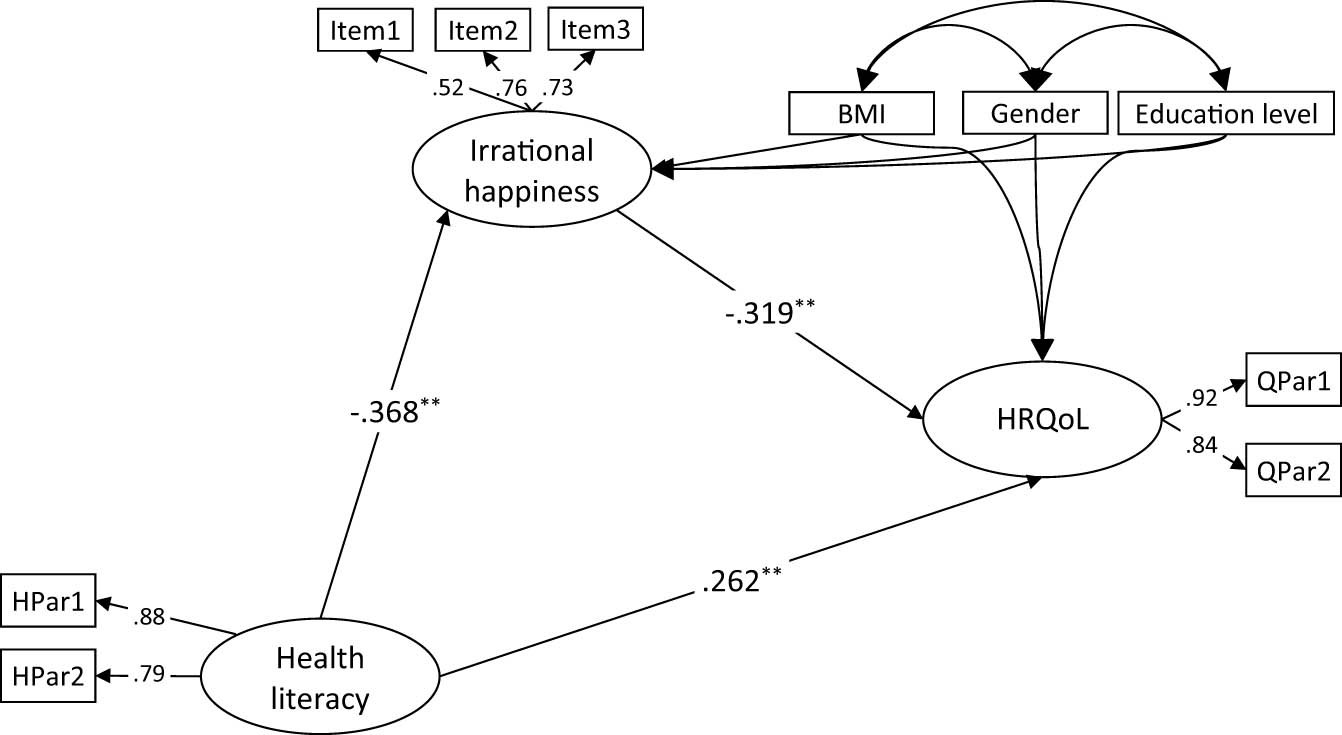
Standardized factor loadings for the structural model. Note. N = 686; ** p < 0.01.
4 Discussion
This study investigated whether irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL. Previous research aimed to identify and enhance the predictors of HRQoL when these variables were not considered together. According to the results of the study, the formulated hypotheses were confirmed and supported by structural equation modeling. The findings are discussed in detail below.
The first finding of the study indicates that HL has a positive effect on HRQoL. This result is consistent with findings in the literature that demonstrate a strong relationship between HL and individuals’ ability to manage their health conditions more effectively [10,17]. Individuals with high HL improve their treatment adherence and participate more actively in the healthcare system due to their capacity to understand and apply medical information [11,14]. This, in turn, enhances their physical and mental health levels, thereby increasing their HRQoL [3]. Research shows that individuals with high HL perform better not only in disease prevention and management processes but also in areas such as social participation and overall life satisfaction [12,13]. Consequently, these individuals can benefit more from the healthcare system by acting more consciously when accessing health services, leading to an improvement in their HRQoL.
In our study, Hypothesis 2, which proposed that irrational happiness has a direct negative effect on HRQoL, was confirmed. This finding indicates that irrational happiness does not always yield positive outcomes and that unrealistic optimism regarding individuals’ health conditions can produce negative effects. Specifically, irrational happiness is thought to increase the risk of underestimating the seriousness of health conditions and delaying necessary medical interventions. This finding aligns with previous research suggesting that emotions do not always facilitate making healthy decisions. For example, states of excessive optimism and irrational happiness can lead individuals to downplay their health problems, postpone seeking treatment, or ignore health-related risks [20]. Although irrational happiness may provide short-term emotional comfort, it can function as a cognitive bias that reduces HRQoL in the long term.
The findings support Hypothesis 3, demonstrating that irrational happiness mediates the relationship between HL and HRQoL. This result reveals that individuals with high HL experience lower levels of irrational happiness, which helps them make more balanced health decisions. High HL increases individuals’ access to and understanding of information about their health conditions, thereby reducing the use of defensive psychological mechanisms such as irrational happiness. This situation supports the notion that a lack of health knowledge can increase unrealistic optimism [27] and sustainably reduce individuals’ HRQoL [13,14,15]. In other words, a decrease in irrational happiness may lead individuals to misassess their health conditions and develop inappropriate health behaviors. Therefore, it can be stated that among individuals with high HL, irrational happiness may decrease, and by making more conscious and balanced choices in health decisions, they can positively influence their HRQoL levels.
5 Implications
This study has demonstrated that HL not only encompasses the capacity to acquire health-related information but also holds the potential to enhance individuals’ quality of life. The findings suggest that HL can reduce irrational happiness, thereby improving HRQoL. This is particularly significant for public health policies and health education programs. It is recommended that educational campaigns should not be limited to merely conveying information but should also consider psychological tendencies like irrational happiness to provide individuals with more realistic health perspectives. Additionally, health professionals and policymakers can offer guidance aimed at balancing individuals’ psychological well-being while providing accessible information platforms to improve HL. This approach will help patients develop an evidence-based yet realistic and sustainable quality of life strategy to improve long-term health outcomes.
6 Conclusion
This study has elucidated the relationship between HL and HRQoL, highlighting the mediating role of irrational happiness in this relationship. The findings indicate that HL directly enhances quality of life by increasing individuals’ access to health-related information and improving their decision-making abilities. At the same time, it has been observed that irrational happiness can lead to excessive optimism and underestimation of health conditions, which may negatively impact HRQoL. Consequently, enhancing HL is a critical tool to support individuals in making health decisions that are both realistic and balanced.
-
Funding information: This research received no external funding.
-
Author contributions: Conceptualization, A.H. and B.S; methodology, B.S; software, A.H. and B.S; validation, A.H. and B.S; investigation, A.H.; resources, A.H.; data curation, A.H.; writing – original draft preparation, A.H.; writing – review and editing, A.H. and B.S; project administration, A.H. and B.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The data are available from the corresponding author upon request. Please direct your requests to: atu-boy@hotmail.com.
References
[1] Karimi M, Brazier J. Health, health-related quality of life, and quality of life: What is the difference? Pharmacoeconomics. 2016;34:645–9.10.1007/s40273-016-0389-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Bakas T, McLennon SM, Carpenter JS, Buelow JM, Otte JL, Hanne KM, et al. Systematic review of health-related quality of life models. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2012;10:1–12.10.1186/1477-7525-10-134Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Haraldstad K, Wahl A, Andenæs R, Andersen JR, Andersen MH, Beisland E, et al. LIVSFORSK network. A systematic review of quality of life research in medicine and health sciences. Qual Life Res. 2019;28:2641–50.10.1007/s11136-019-02214-9Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Marker AM, Steele RG, Noser AE. Physical activity and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychol. 2018;37(10):893.10.1037/hea0000653Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Bożek A, Nowak PF, Blukacz M. The relationship between spirituality, health-related behavior, and psychological well-being. Front Psychol. 2020;11:1997.10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01997Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Marquez DX, Aguiñaga S, Vásquez PM, Conroy DE, Erickson KI, Hillman C, et al. A systematic review of physical activity and quality of life and well-being. Transl Behav Med. 2020;10(5):1098–109.10.1093/tbm/ibz198Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Sitlinger A, Zafar SY. Health-related quality of life: the impact on morbidity and mortality. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2018;27(4):675–84.10.1016/j.soc.2018.05.008Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Hajek A, König HH. The relation between personality, informal caregiving, life satisfaction and health-related quality of life: Evidence of a longitudinal study. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1249–56.10.1007/s11136-018-1787-6Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Wang SQ, Ying J, Zhang ML, Shi Y, Li Y, Xing ZJ, et al. Health-related life satisfaction and its influencing factors: A cross-sectional study in China. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2018;15(4):285–97.10.1111/jjns.12201Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Nutbeam D. The evolving concept of health literacy. Soc Sci Med. 2008;67(12):2072–8. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2008.09.050.Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Fleary SA, Joseph P, Pappagianopoulos JE. Adolescent health literacy and health behaviors: A systematic review. J Adolesc. 2018;62:116–27.10.1016/j.adolescence.2017.11.010Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Nutbeam D, Lloyd JE. Understanding and responding to health literacy as a social determinant of health. Annu Rev Public Health. 2021;42(1):159–73.10.1146/annurev-publhealth-090419-102529Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Ehmann AT, Groene O, Rieger MA, Siegel A. The relationship between health literacy, quality of life, and subjective health: Results of a cross-sectional study in a rural region in Germany. Int J Env Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1683.10.3390/ijerph17051683Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Magnani JW, Mujahid MS, Aronow HD, Cene CW, Dickson VV, Havranek E, et al. Health literacy and cardiovascular disease: fundamental relevance to primary and secondary prevention: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;138(2):e48–e74.10.1161/CIR.0000000000000579Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Lee MK, Oh J. Health-related quality of life in older adults: Its association with health literacy, self-efficacy, social support, and health-promoting behavior. Healthcare (Basel). 2020;8(4):407.10.3390/healthcare8040407Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Zheng M, Jin H, Shi N, Duan C, Wang D, Yu X, et al. The relationship between health literacy and quality of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2018;16:1–10.10.1186/s12955-018-1031-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Couture ÉM, Chouinard MC, Fortin M, Hudon C. The relationship between health literacy and quality of life among frequent users of health care services: a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2017;15:1–6.10.1186/s12955-017-0716-7Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Yıldırım M. Irrational happiness beliefs: conceptualization, measurement and its relationship with well-being, personality, coping strategies, and arousal. Doctoral dissertation, Leicester, England: University of Leicester; 2019.Suche in Google Scholar
[19] Yıldırım M, Maltby J. Examining irrational happiness beliefs within an adaptation-continuum model of personality and coping. J Ration-Emotive Cogn-Behav Ther. 2022;40(1):175–89.10.1007/s10942-021-00405-3Suche in Google Scholar
[20] Nezlek JB, Zebrowski BD. Implications of the dimensionality of unrealistic optimism for the study of perceived health risks. J Soc Clin Psychol. 2001;20(4):521–37.10.1521/jscp.20.4.521.22399Suche in Google Scholar
[21] Duong TV, Aringazina A, Kayupova G, Nurjanah, Pham TV, Pham KM, et al. Development and validation of a new short-form health literacy instrument (HLS-SF12) for the general public in six Asian countries. HLRP. 2019;3(2):90–102.10.3928/24748307-20190225-01Suche in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Karahan Yılmaz S, Eskici G. Validity and reliability study of the Turkish version of the health literacy scale-short form and digital healthy diet literacy scale. J Izmir Katip Celebi Univ Health Sci Fac. 2021;6(3):19–25.Suche in Google Scholar
[23] Eser E, Lağarlı T, Baydur H, Akkurt V, Akkus H, Arslan E, et al. Psychometric properties of the Turkish version of the EUROHIS (WHOQOL-8.Tr) in the Turkish population. Turk J Public Health. 2010;8(3):1–10.Suche in Google Scholar
[24] Yıldırım M, Maltby J. Irrational happiness beliefs scale: Development and initial validation. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2022;20:2277–90.10.1007/s11469-021-00513-2Suche in Google Scholar
[25] Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. 3rd edn. New York, NY: Guilford Press; 2011.Suche in Google Scholar
[26] Hu L, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct Equ Model. 1999;6(1):1–55.10.1080/10705519909540118Suche in Google Scholar
[27] Defeudis G, Mazzilli R, Scandurra C, Di Tommaso AM, Cimadomo D, Strollo R, et al. Diabetes and erectile dysfunction: The relationships with health literacy, treatment adherence, unrealistic optimism, and glycemic control. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2023;39(5):e3629.10.1002/dmrr.3629Suche in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Artikel in diesem Heft
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms


