Abstract
Purpose
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosic liver disease (MASLD) poses a global health challenge with limited therapeutic options. Hesperetin, a flavonoid extracted from citrus, exhibits multiple pharmacological properties, but its mechanisms in MASLD-associated lipid metabolism remain unclear. This study aimed to explore the mechanism of hesperetin for treating MASLD.
Methods
Network pharmacology identified the therapeutic targets for MASLD. Key targets were selected based on network topology analysis. Subsequently, Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathways and gene ontology enrichment were conducted. Molecular docking was performed to evaluate the binding affinity between hesperetin and the identified key targets. In vitro validation included lipid accumulation assays and verification of core target modulation via western blotting.
Results
Hesperetin significantly attenuated lipid accumulation in free fatty acid -induced HepG2 cells. Forty core targets of hesperetin for MASLD mitigation were identified. Notably, MYC, IL-6, IL1B, and PTGS2 had high network association values. KEGG analysis revealed predominant involvement in cancer-related pathways, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and JAK/STAT signaling. Biological processes included inflammatory response regulation and cytokine activity. Molecular docking confirmed strong hesperetin-IL-6 binding. Experimental data suggested that hesperetin may ameliorate lipid accumulation by modulating the IL-6-mediated STAT3-SOCS3 signaling pathway.
Conclusion
Hesperetin may ameliorate MASLD by targeting the IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 axis, underscoring its therapeutic potential.
1 Introduction
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), represents the initial stage for developing a malignant cascade characterized by the pathologic accumulation of lipids in hepatocytes [1]. The worldwide prevalence of MASLD exceeds 25%, with approximately 20% of the patients progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and cirrhosis, which eventually leads to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [2,3]. To date, limited reports have elucidated the mechanisms underlying MASLD pathology. Additionally, current treatment options are limited, relying predominantly on lifestyle modifications to attenuate disease progression. Fatty acid transport, synthesis, and β-oxidation processes in hepatocytes are influenced by the pathological conditions of MASLD, resulting in the incomplete breakdown and metabolism of excess fats, causing large amounts of fats. These phenomena trigger substantial fat accumulation in the hepatocytes, which ultimately leads to liver injury [4–6]. Consequently, strategies aimed at reducing hepatic lipid deposition represent a promising approach for the management of MASLD.
Flavonoids possess multiple medicinal properties, particularly decelerating cellular oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [7–10]. Hesperetin (3′, 5′, 7′-trihydroxy-4-methoxyflavone), a natural flavonoid derivative extracted from citrus, is derived from hesperidin through hydrolysis by human intestinal flora. Research indicates numerous therapeutic effects of hesperetin, including antidiabetic, antiviral, antitumor, and neuroprotective properties [11–14]. Studies have shown that hesperetin dose-dependently decreases the activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) [15]. Additionally, hesperetin treatment has been found to lower liver injury markers and improve NAFLD by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation [16]. Furthermore, hesperetin regulates hepatic lipid metabolism by influencing key signaling pathways, such as the PI3K-AKT-Nrf2 pathway [16]. However, the effects of hesperetin on MASLD-associated hepatic lipid accumulation and the underlying regulatory mechanisms have not been elucidated completely. Network pharmacology, a systems biology approach, integrates systems biology, bioinformatics, and topological analysis to comprehensively understand the complex mechanisms of small molecules and target proteins in human diseases from a holistic viewpoint [17–19].
In the present study, we investigated the efficacy of hesperetin in ameliorating abnormal lipid accumulation in MASLD via network pharmacology. Subsequently, we conducted a systematic analysis using several publicly accessible databases, enrichment tools, and bioinformatics resources, combined with comprehensive strategies such as molecular docking and in vitro experiments (Figure 1). Overall, this study provided new scientific support for the therapeutic potential and new drug development of hesperetin in MASLD prevention and treatment.
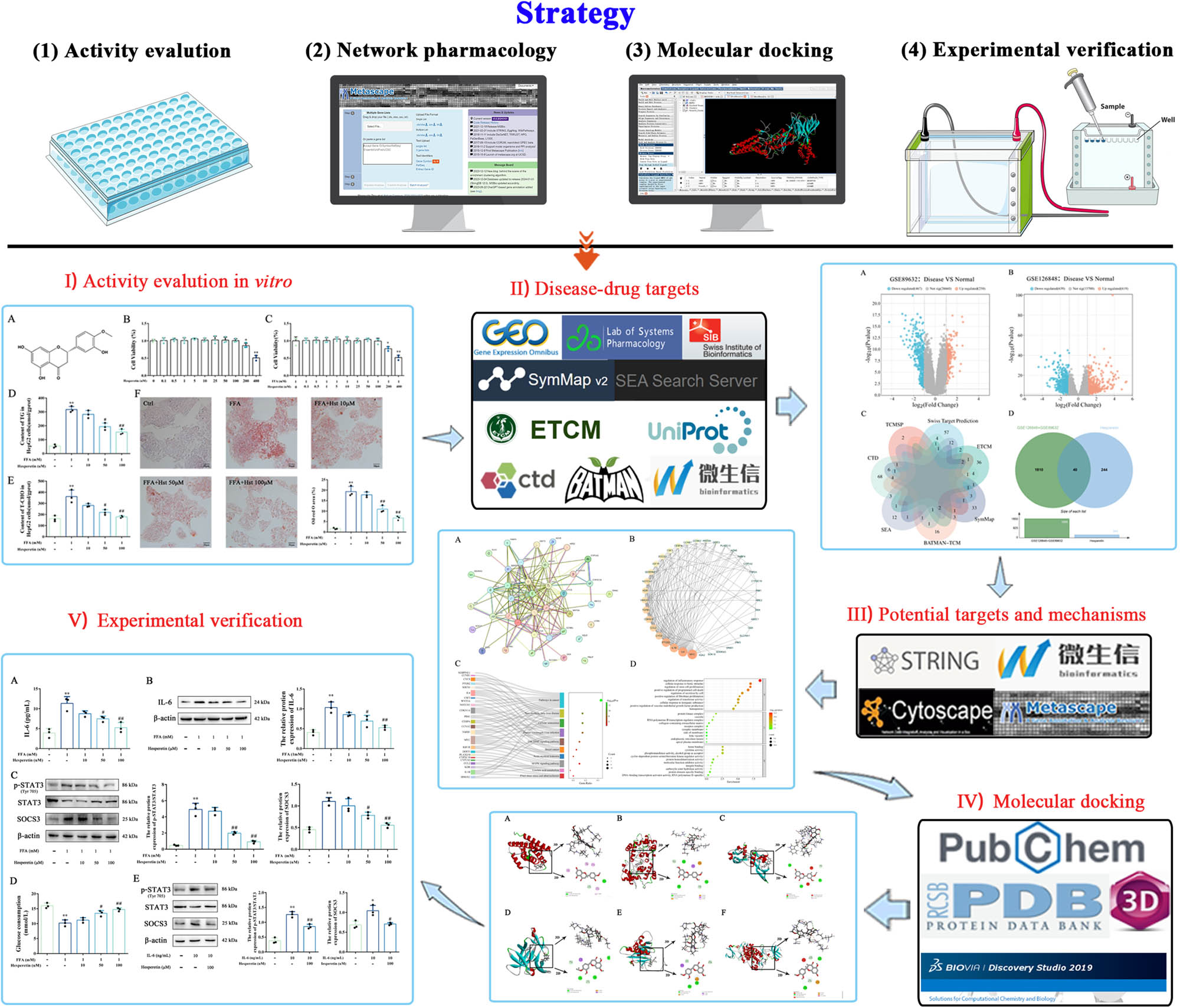
Whole framework of the potential mechanisms of hesperetin on MASLD.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Hesperetin (H107699) was purchased from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). NP-40 (P0013F) and 3-(4,5-dimethiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) (ST1537) were purchased from Beyotime (Nanjing, China). The primary antibodies against interleukin-6 (IL-6) (DF6087), p-JAK2 (AF3024), JAK2 (AF6022), p-STAT3 (AF3293), and STAT3 (AF6294) were purchased from Affinity Biosciences (OH, USA). The primary antibody against β-actin (PAC006) was purchased from Proteinbio (Nanjing, China). Phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (HY-K0021) was purchased from MCE (New Jersey, USA). Free fatty acid (FFA) was purchased from Kunchuang (Xi’an, China). Recombinant human IL-6 (P5138) was purchased from Beyotime (Nanjing, China).
2.2 Network pharmacology analysis
2.2.1 Data preparation
First putative hesperetin targets were screened from seven databases, namely the Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ETCM, http://www.tcmip.cn/ETCM/index.php/Home/), Bioinformatics Annotation Database for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine (BATMAN-TCM, http://bionet.ncpsb.org.cn/), Swiss Target Prediction Database (http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch), Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology (TCMSP, https://www.tcmsp-e.com/), Similarity Ensemble Approach Database (SEA, http://sea.bkslab.org), SymMap (http://www.symmap.org/), and Comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD, http://www.ctdbase.org). After that, using the Uniprot database (https://www.uniprot.org/) to obtain the normalization target gene for hesperetin by selecting “Homo sapiens.”
Then, the GSE89632 and GSE126848 datasets were retrieved from the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). To identify MASLD-related genes, the differently expressed genes among patients with MASLD and healthy individuals were identified using the interactive web tool GEO2R. This step helped us to screen for the genes with substantial differential expression, based on adj.P.Val < 0.05 & |log FC| > 1. Additionally, Venn diagrams are drawn to represent the plotted disease–drug sharing targets.
2.2.2 Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network
Gene symbols of hesperetin treatment targets for MSALD were imported into the STRING online database (version 11.5, https://www.string-db.org/). “Homo sapiens” was selected as the organism species, to obtain protein interactions among the targets. Subsequently, the PPI networks in tab-separated value format files were imported into Cytoscape 3.7.1. The network topology was analyzed using the network analyzer plug-in; topological features were calculated for each node.
2.2.3 Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway and gene ontology (GO) enrichment analyses
The intersecting targets underwent KEGG pathway and GO enrichment analyses using the Metascape platform (https://metascape.org/gp/index.html). The threshold value was set at P < 0.05.
2.2.4 Molecular docking
Molecular docking was performed using the LibDock module in Discovery Studio 2019 to evaluate the binding affinity between hesperetin and target proteins [20]. Prior to docking, the 2D structure of hesperetin was acquired in Spatial Data File format from the NCBI PubChem (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), and converted to 3D via the “Prepare Ligand” tool with default settings (adding hydrogen atoms, optimizing geometry using the CHARMm force field). Protein crystal structures of the potential targets (CEBPA, IL1B, IL-6, TGFB1, SOCS3, CYC3) were obtained from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) database (https://www.rcsb.org/). PDB IDs of CEBPA, IL1B, IL-6, TGFB1, SOCS3, and CYC3 were 6DC0, 1I1B, 4O9H, 4KV5, 2JZ3, and 3NWV, respectively. The protein structures were prepared by removing water molecules, co-crystallized ligands, and adding polar hydrogens, and optimizing hydrogen-bonding networks via the Prepare Protein tool. For the LibDock module, the docking site was defined as the active pocket of each target protein (radius: 10 Å around the co-crystallized ligand). Key parameters included Docking Preferences set to “High Quality,” Hotspot Spacing at 0.5 Å, Ligand Conformations set to 100 poses per run, and Minimization enabled for pose refinement. Binding interactions were analyzed using “Ligand–Protein Interaction” tool, categorizing hydrogen bonds, π–π stacking, and hydrophobic interactions. The highest-scoring pose for each target was chosen based on LibDockScore and structural, ensuring consistency with known functional domains.
2.3 Cell culture and treatment
HepG2 was kindly provided by Dr Wang Zeng from Nanjing Medical University. The cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin–streptomycin in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2. The cells were exposed to 1 mM FFA, comprising oleic acid (OA)/palmitic acid (PA) in a 2:1 ratio, consisting of 1% bovine serum albumin for 24 h to simulate the pathological state of MASLD. Subsequently, low (10 μM), medium (50 μM), and high (100 μM) doses of hesperetin (10, 50, and 100 μM) were added for 24 h.
2.4 Cell viability assay
HepG2 cells were incubated with hesperetin (0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM) for 24 h. Subsequently, cell viability was monitored using the MTT assay. The percentage of cell viability was computed relative to the absorbance intensity of the control cells.
2.5 Western blot
HepG2 cells were lysed with NP-40 lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) and total protein was isolated. Protein concentration was determined using bicinchoninic acid protein assay reagent (Beyotime, China). Total proteins (40 μg) were resolved on 8 or 10% sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gel and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween® 20 detergent (TBST) consisting of 5% skim milk powder for 1 h at room temperature. Furthermore, they were incubated overnight with special antibodies, including IL-6, p-STAT3, STAT3, SOCS3, and β-actin (1:1,000) at 4°C. After washing with TBST three times, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibodies (1:15,000) for 1 h at room temperature.
2.6 Cellular triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (T-CHO) measurement
TG and T-CHO values in the cell samples were detected by commercial detection kits (Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). After collecting the cells, appropriate amount of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was added. The cells were broken by ultrasonication under an ice-water bath. Subsequently, T-CHO and TG levels were detected directly. The absorbance was measured at 500 nm.
2.7 Detection of IL-6
Thelevel of inflammatory cytokines IL-6 in cell culture medium was determined using commercial human immunoassay enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (Neobioscience, Shenzhen, China), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.8 Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from FFA-induced HepG2 cells treated with hesperetin (100 μM) using TRIzol reagent (Vazyme Biotech Co. Ltd, Nanjing, China) and quantified. cDNA was synthesized by HiScript II Q RT SuperMix for qPCR (Vazyme Biotech Co. Ltd, Nanjing, China), and qPCR was carried out to amplify the target genes by AceQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix using specific primers (Thermo Fisher, Massachusetts, USA). All gene-specific mRNA expression values were compared to β-actin mRNA levels as a standard (Tongyong Biotech Co. Ltd, Anhui, China). The primer sequences for each gene are listed in Table S1.
2.9 Oil-red staining
Oil Red O stain was applied to assess lipid droplet formation in the HepG2 cells [21]. Briefly, HepG2 cells were washed with PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min. The cells were incubated with Oil Red O working solution for 30 min, briefly rinsed in 60% isopropanol, and counterstained with hematoxylin for 1 min. The images were acquired using a microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.10 Glucose consumption assay
HepG2 cells were inoculated in 96-well plates. Glucose uptake was assayed as described previously [20].
2.11 Statistical analysis
Data from the three independent experiments are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was conducted using GraphPad Prism software 6.0. P-values ≤0.05 indicated statistical significance.
3 Results
3.1 Hesperetin alleviated lipid accumulation in FFA-induced HepG2 cells
The anti-MASLD effects of hesperetin were assessed using the FFA-induced HepG2 cell model. The structural formula of hesperetin is shown in Figure 2a. First, the effects of different hesperetin concentrations on the activity of HepG2 cells were evaluated by an MTT assay. At concentrations <100 μM, hesperetin exhibited no significant effects on cell viability (Figure 2b). However, the cell viability was significantly inhibited as the concentration reached 200 or 400 μM. Additionally, we examined the effects of hesperetin on FFA-induced HepG2 cell viability. The cytotoxicity results suggested that hesperetin exerted no significant effect on FFA-induced HepG2 cell viability at concentrations <100 μM (Figure 2c). Thus, hesperetin concentrations of 10, 50, and 100 μM were selected for subsequent experiments. Hesperetin treatment significantly reduced the TG and T-CHO levels in FFA-induced HepG2 cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 2d and e). Oil Red O staining results revealed a dose-dependent decrease in intracellular lipid accumulation with hesperetin treatment, consistent with the TG and T-CHO level findings (Figure 2f). Collectively, the above results supported the potential of hesperetin to ameliorate hepatocyte lipid accumulation in MASLD. Nonetheless, further research is warranted to investigate the precise molecular mechanisms underlying this process.

Effects of hesperetin on lipid accumulation in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. (a) 2D structural formula of hesperetin. (b) Effects of different concentrations of hesperetin on cell viability in HepG2 cells. (c) Effects of different concentrations of hesperetin on cell viability in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. (d) Levels of TG in HepG2 cells. (e) Levels of T-CHO in HepG2 cells. (f) Oil Red O staining. Ctrl: HepG2 cells cultured in DMEM; FFA: HepG2 cells treated with FFA; FFA + Hst 10 μM: HepG2 cells treated with FFA + hesperetin 10 μM; FFA + Hst 50 μM: HepG2 cells treated with FFA + hesperetin 50 μM; FFA + Hst 100 μM: HepG2 cells treated with FFA + hesperetin 100 μM. The data represented as mean ± SD, n = 3. **P < 0.01, compared to Ctrl; # P < 0.05 or ## P < 0.01, compared to FFA.
3.2 Exploring hesperetin targets for the MASLD treatment by network pharmacology analysis
Figure 1 depicts the workflow for integrating network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation. Utilizing the GEO database, we obtained 1,850 genes associated with MASLD from the GSE89632 and GSE126848 datasets, following |log FC| > 1 and adj.P.Val < 0.05 screening criteria (Figure 3a and b). Subsequently, we retrieved 88, 54, 30, 8, 34, 95, and 60 targets of hesperetin targets from the Swiss target prediction, ETCM, BATMAN-TCM, TCMSP, SEA, CTD, and SymMap databases, respectively. Targets from these seven databases were merged and de-duplicated, resulting in 284 drug targets (Figure 3c). Ultimately, through further integration, we identified 40 overlapping targets corresponding to “Hesperetin-MASLD” (Figure 3d).

Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes and Venn diagrams of disease–drug intersection targets. (a) Differentially expressed genes in MASLD from GSE89632. (b) Differentially expressed genes in MASLD from GSE126848. (c) Venn diagram of hesperetin targets from different databases. (d) Venn diagram of the intersection of potential target genes of hesperetin and differentially expressed genes in the liver of patients with MASLD.
3.3 PPI analysis for targets of hesperetin against MASLD
We constructed a PPI network by importing 40 intersecting targets into the STRING database to explore the mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of hesperetin on MASLD (Figure 4a). Subsequently, the network was visualized using the Cytoscape 3.7.2 software and subjected to topological analysis (Figure 4b). The center network was based on three topological parameters as follows: betweenness centrality, degree value, and closeness centrality. Table 1 summarizes the topological parameter analysis structure. The leading ten targets were as follows: MYC (degree = 24), IL-6 (degree = 23), IL1B (degree = 21), PTGS2 (degree = 21), CYCS (degree = 17), CCL2 (degree = 16), TGFB1 (degree = 16), CDKN1A (degree = 16), HMOX1 (degree = 14), and KDR (degree = 14).

PPI network and enriched GO and KEGG analyses of potential target genes of hesperetin on MASLD. (a) The PPI network analyzed by STRING database. (b) The PPI network analyzed by Cytoscape 3.7.2. (c) KEGG pathway analysis by Sankey diagram. (d) GO functional analysis. The bubble chart shows the GO enrichment terms for BP, CC, and MF.
Degree value, betweenness centrality, and closeness centrality of key targets in the PPI network
| Gene name | Degree value | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| MYC | 24 | 0.227508 | 0.75 |
| IL-6 | 23 | 0.091871 | 0.734694 |
| IL1B | 21 | 0.082048 | 0.705882 |
| PTGS2 | 21 | 0.090734 | 0.705882 |
| CYCS | 17 | 0.084592 | 0.631579 |
| CCL2 | 16 | 0.06862 | 0.631579 |
| TGFB1 | 16 | 0.012414 | 0.642857 |
| CDKN1A | 16 | 0.026659 | 0.631579 |
| HMOX1 | 14 | 0.034351 | 0.610169 |
| KDR | 14 | 0.072083 | 0.610169 |
| NOTCH1 | 14 | 0.010395 | 0.62069 |
| SERPINE1 | 13 | 0.061264 | 0.590164 |
| SOCS3 | 12 | 0.033615 | 0.571429 |
| IGF1R | 12 | 0.051962 | 0.580645 |
| CSF3 | 11 | 0.012691 | 0.571429 |
| CEBPA | 11 | 0.014722 | 0.545455 |
| CCNB1 | 9 | 0.006468 | 0.537 |
| CCNA2 | 8 | 0.007113 | 0.529 |
| WNT5A | 7 | 0 | 0.522 |
| DDIT3 | 6 | 0.000894 | 0.48 |
| ACHE | 5 | 0 | 0.474 |
| FABP4 | 5 | 0.000353 | 0.474 |
| CYP1A2 | 5 | 0.005023 | 0.474 |
| PLA2G10 | 5 | 0.003396 | 0.468 |
| CYP2C19 | 4 | 0.004777 | 0.444 |
| TOP2A | 4 | 0.000787 | 0.456 |
| PIM1 | 3 | 0.000265 | 0.45 |
| NFE2 | 3 | 0.000198 | 0.468 |
| HCK | 3 | 0 | 0.439 |
| ABCC1 | 2 | 0.00335 | 0.456 |
| GCK | 2 | 0.000794 | 0.379 |
| SLC16A1 | 2 | 0.005343 | 0.444 |
| PIM3 | 2 | 0 | 0.444 |
| ADORA3 | 1 | 0 | 0.391 |
| DNM1 | 1 | 0 | 0.391 |
| SOX18 | 1 | 0 | 0.383 |
| KLK2 | 1 | 0 | 0.375 |
3.4 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses
We performed KEGG pathway analysis on 40 intersecting targets to explore the various mechanisms by which hesperetin action contributes to MASLD treatment. The KEGG analysis examined the pathways central to MASLD pathogenesis. Figure 4c depicts the leading ten enriched pathways with a false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05. Among these pathways, NAFLD, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway were highly enriched and met the FDR criteria. Table 2 summarizes the target genes enriched for each pathway.
KEGG pathways with TOP ten enrichment degree and related gene targets
| KEGG pathway | Log10(P) | Target count | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa05200: Pathways in cancer | −13.00 | 13 | CCNA2, CDKN1A, CEBPA, HMOX1, IGF1R, IL-6, MYC, NOTCH1, PIM1, PTGS2, TGFB1, WNT5A, CYCS |
| hsa04932: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | −8.89 | 7 | CEBPA, DDIT3, IL1B, IL-6, TGFB1, SOCS3, CYCS |
| hsa04218: Cellular senescence | −8.89 | 7 | CCNA2, CCNB1, CDKN1A, IL-6, MYC, SERPINE1, TGFB1 |
| hsa05163: Human cytomegalovirus infection | −7.77 | 7 | CDKN1A, IL1B, IL-6, MYC, PTGS2, CCL2, CYCS |
| hsa04630: JAK-STAT signaling pathway | −7.09 | 6 | CDKN1A, CSF3, IL-6, MYC, PIM1, SOCS3 |
| hsa05224: Breast cancer | −5.84 | 5 | CDKN1A, IGF1R, MYC, NOTCH1, WNT5A |
| hsa05221: Acute myeloid leukemia | −5.73 | 4 | CCNA2, CEBPA, MYC, PIM1 |
| hsa04010: MAPK signaling pathway | −5.58 | 6 | DDIT3, IGF1R, IL1B, KDR, MYC, TGFB1 |
| hsa00591: Linoleic acid metabolism | −5.07 | 3 | CYP1A2, CYP2C19, PLA2G10 |
| hsa05418: Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | −4.47 | 4 | HMOX1, IL1B, KDR, CCL2 |
Similar to KEGG analysis, we performed a GO enrichment analysis of the 40 intersecting targets; we analyzed biological processes (BP), cellular components (CC), and molecular functions (MF). The leading ten enriched BP, MF, and CC terms are presented as bubble charts (Figure 4d). The GO terms with high enrichment in BP consisted of the regulation of inflammatory response, cellular response to biotic stimulus, protein kinase complex, and cytokine activity.
3.5 Analyzing of molecular docking results
Based on the PPI network and KEGG pathway analyses, we selected relevant targets, namely IL-6, CYCS, TGFB1, IL1B, SOCS3, and CEPBA, enriched in the NAFLD pathway for molecular docking. Though DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (DDIT3) was annotated in the NAFLD pathway, it was excluded from molecular docking experiment because of its low network connectivity (degree = 6) and the lack of a resolved crystal structure, both of which prevented reliable docking analysis. For identifying the interactions, the “LibDock” module in Discovery Studio was used and clusters with the highest LibDockScore were selected (Table 3). Figure 5 presents the corresponding structures. Among these, IL-6 exhibited the highest LibDockScore (113.311), indicating strong binding affinity with hesperetin. This interaction was stabilized by conventional hydrogen bonds, carbon–hydrogen bonds, and pi-alkyl interactions, highlighting structural complementarity. The prioritization of IL-6 aligns with network pharmacology results (high degree value in PPI network, enrichment in NAFLD pathway, and JAK/STAT signaling pathway). As a central proinflammatory cytokine, IL-6 drives JAK/STAT3 signaling, which is dysregulated in MASLD to promote hepatic lipid accumulation and insulin resistance (IR) [22,23]. Other targets such as SOCS3 (LibDockScore = 112.091) showed favorable binding but were functionally linked to IL-6-mediated pathways, reinforcing IL-6 as the pivotal molecular hub. These results provide structural basis for hesperetin’s engagement with the IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 axis, bridging computational predictions with biological mechanisms. Thus, IL-6 might be a possible key target of hesperetin intervention in MASLD.
Binding energy and interactions of hesperetin with target proteins
| Targets | LibDockScore | Hydrogen bonds and other interacting residues |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | 113.311 | Ala130, Ala135, Asn132, Leu84, Leu133, Val85 |
| IL1B | 77.722 | Glu25, Leu80, Leu134, Phe133, Pro78, Thr79 |
| CYCS | 101.249 | Asp62, Arg91, Glu66, Glu66, Glu69, Lys88, Thr63 |
| TGFB1 | 96.276 | Arg25, Ile33, Lys26, Lys37, Phe24, Trp30 |
| SOCS3 | 112.091 | Lys104, Pro92, Pro96, Pro100, Ser94, Ser95 |
| CEBPA | 83.923 | Asp205, Asp228, His230, His243, Lys207, Lys210 |

Pattern diagram of molecular docking: (a) Hesperetin-IL-6, (b) hesperetin-CYCS, (c) hesperetin-TGFB1, (d) hesperetin-IL1B, (e) hesperetin-SOCS3, and (f) hesperetin-CEPBA.
3.6 Hesperetin mitigated hepatocyte lipid accumulation and IR by inhibiting IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 pathway in FFA-induced HepG2 cells
Network pharmacological analyses indicated that IL-6 ranked second in the PPI network and exhibited the highest binding affinity with hesperetin, positioning it as a pivotal node linking inflammation (KEGG: JAK-STAT signaling) and metabolic dysfunction (NAFLD pathway). This positioned IL-6 as a pivotal hub linking diverse pathological processes in MASLD. Therefore, we examined the effects of hesperetin on IL-6 secretion in FFA-induced HepG2 cells and the results showed that hesperetin attenuated the IL-6 release from FFA-stimulated HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 6a). Dysregulated IL-6-STAT3 signaling is directly associated with hepatic lipid accumulation and IR, core features of MASLD. SOCS3, a direct STAT3 target and negative regulator of insulin signaling, was also identified in the docking analysis (LibDockScore = 112.09). We thus further examined the changes in this signaling axis, and western blot results showed that hesperetin inhibited IL-6 protein expression (Figure 6b). Furthermore, p-STAT3 and SOCS3 expressions were significantly increased in FFA-induced HepG2 cells than in controls. However, p-STAT3 and SOCS3 expression decreased significantly after hesperetin treatment than after no-treatment (Figure 6c). Additionally, glucose consumption by FFA-induced HepG2 cells was significantly low. Compared with the low-dose group, the high-dose group demonstrated significant improvement in glucose consumption, suggesting that hesperetin reduced IR and promoted glucose uptake (Figure 6d).

Effects of hesperetin on IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 pathway in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. (a) IL-6 content in cell culture medium. (b) Relative protein levels of IL-6 in HepG2 cells. (c) Relative protein levels of p-STAT3/STAT3 and SOCS3 in HepG2 cells. (d) Glucose absorption in different groups. (e) Levels of IL-6 in HepG2 cells. (e) Relative protein levels of p-STAT3/STAT3 and SOCS3 in IL-6-induced HepG2 cells. The data represented as mean ± SD, n = 3. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to Ctrl; # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, compared to FFA.
To further validate the critical role of hesperetin in the IL-6-mediated STAT3-SOCS3 pathway, the IL-6-stimulated HepG2 cells was carried out. The results of western blot demonstrated that p-STAT3/STAT3 and SOCS3 levels were significantly elevated after IL-6 stimulation compared to the control. In contrast, the levels were significantly decreased after hesperetin treatment compared with IL-6 stimulation (Figure 6e).
3.7 Hesperetin regulates mRNA expression of key PPI network targets
To comprehensively assess the pharmacological network of hesperetin, we examined its effects on mRNA levels of genes enriched in the top five-degree values in the PPI network and in the KEGG “non-alcoholic fatty liver” pathway (MYC, IL-6, IL1B, PTGS2, CYCS, TGFB1, CEBPA, DDIT3, and SOCS3) in FFA-induced HepG2 cells using qRT-PCR (Figure S1). Compared to the FFA group, hesperetin (100 μM) significantly downregulated the mRNA expression of MYC, IL-6, IL1B, PTGS2, CYCS, DDIT3, and SOCS3. In contrast, other genes showed no significant changes, suggesting tissue-specific or compensatory regulatory mechanisms. These findings validate the predictions of network pharmacology and demonstrate that hesperetin engages a network of targets spanning inflammation, metabolism, and apoptosis, reinforcing its polypharmacological action in MASLD.
4 Discussion
MASLD is one of the most prevalent types of liver disease worldwide; it is characterized by abnormal lipids accumulation in the liver, which can eventually lead to cirrhosis and HCC [24]. No approved drugs are available for the treatment of MASLD. Lifestyle and dietary interventions remain the only recognized treatment options [25]. Hesperetin exerts therapeutic effects on numerous diseases as a natural product, characterized by multi-target and multi-pathway regulation; however, the exact mechanism by which it ameliorates hepatic abnormal lipid accumulation warrants further investigation [26–28]. In this study, we integrated network pharmacology, molecular docking, and in vitro experiments to explore the potential mechanism of hesperetin against MASLD.
Hesperetin, a flavonoid extracted from citrus species with high bioavailability, has been extensively evaluated for its wide range of pharmacological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetes, and anti-cancer properties [28,29]. Notably, its therapeutic potential is further supported by favorable pharmacokinetic profiles, as demonstrated in a clinical study involving six healthy volunteers who received 135 mg oral hesperetin. The results demonstrated that hesperetin was rapidly absorbed, with the plasma concentration peaking after 20 min; in addition, the area under the plasma concentration–time curve extrapolated to the time to infinity (AUC0−∞), the elimination half-life (t 1/2), and the maximum (C Max) were 4846.20 ± 1675.99 ng h/mL, 3.05 ± 0.91 h, and 825.78 ± 410.63 ng/mL, respectively [30]. Notably, findings from rodent models demonstrated preferential hepatic accumulation of hesperetin, with hepatic concentrations exceeding those in extrahepatic tissues (e.g., aorta and kidney) [31]. Collectively, these pharmacokinetic traits underscore hesperetin’s suitability for modulating liver-specific pathologies such as MASLD. Previous studies have shown that hesperetin attenuated OA or PA-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress; nonetheless, there are limited data on the in vitro hypolipidemic activity of hesperetin [16,32]. Therefore, we investigated the hypolipidemic activity of hesperetin in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. After determining the hesperetin dose, we investigated the effects of hesperetin on FFA-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Oil-red O staining results and biochemical indices reflected that hesperetin significantly reduced aberrant intracellular lipid accumulation in the model group. This finding indicated that hesperetin has the potential to improve hepatocyte lipid metabolism in MASLD.
Through network pharmacology analysis, we identified 40 putative hesperetin-MASLD targets. To explore the core targets, we constructed a PPI network expressing protein interactions by the STRING database and Cytoscape software; MYC, IL-6, IL1B, PTGS2, CYCS, CCL2, CDKN1, TGFB1, HMOX1, and KDR might be the possible core targets warranting attention. These targets are closely related to oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and lipid metabolism. For instance, MYC, with the highest degree value, plays a crucial role in hepatocyte apoptosis, liver fibrosis, and HCC in the MASLD mouse model [33,34]. IL-6 and IL1B are important promoters of the inflammatory response, which can accelerate the progression of MASLD. [35]. PTGS2, also termed cyclooxygenase 2, is expressed predominantly in inflammatory cells. It is substantially upregulated in chronic and acute inflammation, and, thus is a key target for several pharmacological inhibitors [20,36].
KEGG pathway and GO enrichment analyses provided further insights into the underlying mechanisms. GO enrichment analysis demonstrated that several BP are associated with the role of hesperetin in ameliorating MASLD. The regulation of inflammatory response, cellular response to biotic stimulus, regulation of stem cell proliferation, positive regulation of programmed cell death, and regulation of secretion were considerably enriched in BP. Additionally, the target genes were predominantly enriched in cytokine activity, phosphotransferase activity, and protein kinase complex, which demonstrated a potential relationship between hesperetin and the 40 MASLD targets. According to KEGG pathway analysis, significantly enriched pathways associated with MASLD encompassed cancer, NAFLD, cellular senescence, human cytomegalovirus infection, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway. The JAK-STAT pathway is central to cytokine-mediated inflammation and serves as a key bridge between immune responses and metabolic dysfunction in MASLD. Activation of JAK-STAT by pro-inflammatory cytokines promotes STAT3 phosphorylation, leading to the upregulation of inflammation-related genes like SOCS3, which in turn impairs insulin signaling and results in hepatic lipid accumulation [37]. Meanwhile, the NAFLD pathway, characterized by dysregulated lipid metabolism and oxidative stress, further exacerbates JAK-STAT activation through an inflammatory feedback loop [38]. The MAPK pathway, responsible for cellular stress and proliferation, interacts with the JAK-STAT and NAFLD pathways to modulate MASLD progression. The phosphorylation cascade of ERK1/2 and p38 within the MAPK axis enhances the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby amplifying JAK-STAT activation [39]. Our in vitro experiments demonstrated that hesperetin may disrupt this vicious cycle by inhibiting IL-6-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation, thereby attenuating inflammatory signaling in the JAK-STAT axis and lipid dysregulation in the NAFLD pathway. These results suggested that hesperetin may exert its therapeutic effects on MASLD through multi-pathway regulation.
To explore the binding mode and ability of hesperetin to potential MASLD targets, we selected core targets enriched in the NAFLD signaling pathway for molecular docking with hesperetin based on KEGG analysis results. Molecular docking analysis revealed that hesperetin exhibited stable binding interactions with potential MASLD targets, particularly demonstrating a high binding affinity with IL-6. While the PPI network and molecular docking identified multiple potential targets for hesperetin, our decision to focus on the IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 axis was based on three key factors aligning with the study’s mechanistic goals and clinical significance. First, IL-6 ranked second in the PPI network, followed only by MYC, and exhibited the highest binding affinity with hesperetin among all validated targets. Second, IL-6 as a pivotal node linking two hallmark pathways of MASLD: inflammation (JAK-STAT signaling) and metabolic dysfunction (NAFLD pathway). Lastly, SOCS3, a direct downstream target of STAT3, also demonstrated strong docking affinity with hesperetin, further emphasizing its significance as a crucial effector molecule. To validate this, we conducted in vitro experiments and found that hesperetin attenuated the IL-6 release from FFA-stimulated HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, western blot analysis showed that hesperetin treatment significantly decreased the expression of p-STAT3 and SOCS3 in FFA-induced HepG2 cells. Notably, hesperetin has demonstrated significant inhibitory effect on IL-6 in different disease models. Zhang et al. demonstrated that hesperetin significantly alleviated dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis symptoms and inhibited IL-6 expression both in vivo and in vitro [40]. Moreover, it exerted anti-neuroinflammatory effects by inhibiting microglia activation and downregulating the mRNA transcript levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6 [41]. Consistent with our findings, Dr Sun reported on the lipid-lowering ability of hesperetin and showed that hesperetin inhibited inflammatory responses in OA-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mice [16]. The JAK/STAT pathway plays a crucial role in lipid metabolism and inflammation [42,43]. Dysregulation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway leads to numerous diseases, including liver disease [44]. Cytokine-induced activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in the liver, notably by IL-6, triggers increased phosphorylation of STAT3, leading to IR and abnormal lipid accumulation [45]. Additionally, SOCS3 is closely related to IR development, as its overexpression in the liver leads to IR, while its inhibition enhances insulin sensitivity and ameliorates hepatic steatosis [46,47]. Cytokines upregulate SOCS3 transcription, primarily through STAT3 activation [48]. Taken together, hesperetin attenuated hepatocellular steatosis by inhibiting IL-6 expression and secretion, thereby blocking STAT3 phosphorylation and SOCS3 levels. While this focus on IL-6 enabled rigorous validation of a biologically plausible pathway, we recognize that other targets within the PPI network (such as MYC, IL1B, PTGS2) could also contribute to the effects of hesperetin. The validation of MYC, IL1B, and PTGS2 through qRT-PCR further supports the predictions of network pharmacology. The downregulation of IL1B and PTGS2 aligns with their roles in amplifying inflammatory cascades, reinforcing hesperetin’s pleiotropic anti-inflammatory action. In addition, while this study establishes an association between hesperetin and the modulation of IL-6-STAT3-SOCS3 signaling, further confirmation of causality is necessary. More genetic interventions such as IL-6 knockdown or SOCS3 overexpression in hepatocytes would enhance the mechanistic understanding. Without these additional experiments, the exact role of hesperetin in modulating this pathway remains to be further verified. Additionally, in vivo studies are needed to confirm the translational relevance of these findings.
This study also has several limitations that need to be addressed. First, challenges persist in the accuracy and reliability of retrieving data on compounds and disease targets from various databases due to their lack of comprehensiveness and currency. Moreover, it lacked in vivo and clinical experimental studies to directly validate the anti-MASLD effects of hesperetin and its associated pathways. Previous studies have demonstrated the hepatoprotective effects of hesperetin in OA-induced HepG2 cells and HFD-induced NAFLD rat models [16]. Furthermore, studies in different disease models have explored the biological effects of hesperetin on IL-6 gene expression and STAT3 phosphorylation signaling pathway [49,50]. However, in-depth in vivo and clinical studies are indispensable. Additionally, more research is required to determine the optimal dose of hesperetin for clinical treatment, as well as the potential effects of long-term hesperetin treatment on other organs and tissues.
5 Conclusion
In summary, we systematically explored the pharmacological mechanism by which hesperetin alleviated MASLD using a comprehensive strategy of network-based computational pharmacology, along with bioinformatics analysis. We identified 40 targets on MASLD for hesperetin treatment, of which IL-6 was a possible core therapeutic target. Furthermore, the in vitro validation experiments suggested that hesperetin may alleviate FFA-induced lipid accumulation partially through modulation of the IL-6-mediated STAT3-SOCS3 signaling pathway, warranting further mechanistic validation. Taken together, we hypothesized that hesperetin may be a potential therapeutic agent for MASLD.
Abbreviations
- ALT
-
alanine aminotransferase
- AST
-
aspartate aminotransferase
- BATMAN-TCM
-
Bioinformatics Annotation Database for Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- BP
-
biological processes
- CC
-
cellular components
- CTD
-
Comparative Toxicogenomics Database
- DDIT3
-
DNA damage-inducible transcript 3
- ETCM
-
Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- FDR
-
false discovery rate
- FFA
-
free fatty acid
- GEO
-
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GO
-
gene ontology
- HCC
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HFD
-
high-fat diet
- IL-6
-
interleukin-6
- IR
-
insulin resistance
- KEGG
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- MASLD
-
metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosic liver disease
- MF
-
molecular functions
- MTT
-
3-(4,5-dimethiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- NAFLD
-
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- OA
-
oleic acid
- PA
-
palmitic acid
- PBS
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PDB
-
Protein Data Bank
- PPI
-
protein–protein interaction
- SEA
-
Similarity Ensemble Approach Database
- T-CHO
-
total cholesterol
- TBST
-
Tris-buffered saline with 0.1% Tween® 20 detergent
- TCMSP
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology
- TG
-
triglyceride
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Bullet Edits Limited for the linguistic editing and proofreading of the manuscript. They also sincerely thank Prof. Jie Ren and her research team from School of Pharmacy, Changzhou University (Changzhou, Jiangsu, China) for providing experimental facilities and technical support.
-
Funding information: The work was supported by the Applied Basic Research of Changzhou Science and Technology Program (CJ20241113, CJ2023066, CJ20239014), the Advanced Training Program for Key Talents in Traditional Chinese Medicine of Jiangsu Province Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2022No.11).
-
Author contributions: L.-D.T. and H.Y. designed the study; Y.W., Y.L., and S.X. performed the experiments; Y.W. and S.X. analyzed the data; D.Z. edited the figures and tables; H.Y. wrote the paper; and L.-D.T. reviewed and edited the draft.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
[1] Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, Anstee QM, Targher G, Romero-Gomez M, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: an international expert consensus statement. J Hepatol. 2020;73(1):202–9.10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.045Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Younossi ZM, Loomba R, Anstee QM, Rinella ME, Bugianesi E, Marchesini G, et al. Diagnostic modalities for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and associated fibrosis. Hepatology. 2018;68(1):349–60.10.1002/hep.29721Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Friedman SL, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Rinella M, Sanyal AJ. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat Med. 2018;24(7):908–22.10.1038/s41591-018-0104-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Mato JM, Alonso C, Noureddin M, Lu SC. Biomarkers and subtypes of deranged lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(24):3009–20.10.3748/wjg.v25.i24.3009Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Barbier-Torres L, Fortner KA, Iruzubieta P, Delgado TC, Giddings E, Chen Y, et al. Silencing hepatic MCJ attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by increasing mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3360.10.1038/s41467-020-16991-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Yan T, Luo Y, Yan N, Hamada K, Zhao N, Xia Y, et al. Intestinal peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α-fatty acid-binding protein 1 axis modulates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2023;77(1):239–55.10.1002/hep.32538Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Yang T, Hu Y, Jiang W, Pang J, Zhou Y, Zhang H, et al. YY1 was indispensable for the alleviation of quercetin on diabetic nephropathy-associated tubulointerstitial inflammation. Phytomedicine. 2023;111:154659.10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154659Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Yang T, Wang Y, Cao X, Peng Y, Huang J, Chen L, et al. Targeting mTOR/YY1 signaling pathway by quercetin through CYP7A1-mediated cholesterol-to-bile acids conversion alleviated type 2 diabetes mellitus induced hepatic lipid accumulation. Phytomedicine. 2023;113:154703.10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154703Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[9] Yang H, Yang T, Heng C, Zhou Y, Jiang Z, Qian X, et al. Quercetin improves nonalcoholic fatty liver by ameliorating inflammation, oxidative stress, and lipid metabolism in db/db mice. Phytother Res. 2019;33(12):3140–52.10.1002/ptr.6486Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Shao Y, Hong R, Li B, Wang A, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al. Extraction technology, components analysis and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro of total flavonoids extract from Artemisia anomala S. Moore. Fitoterapia. 2023;170:105630.10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105630Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[11] Khezri MR, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M, Moloodsouri D. Hesperetin and the PI3K/AKT pathway: could their interaction play a role in the entry and replication of the SARS-CoV-2? J Food Biochem. 2022;46(9):e14212.10.1111/jfbc.14212Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Song C, Wang Z, Cao J, Dong Y, Chen Y. Hesperetin protects hippocampal neurons from the neurotoxicity of Aflatoxin B1 in mice. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2023;269:115782.10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115782Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Yang H, Wang Y, Xu S, Ren J, Tang L, Gong J, et al. Hesperetin, a promising treatment option for diabetes and related complications: a literature review. J Agric Food Chem. 2022;70(28):8582–92.10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03257Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[14] Hussain Y, Khan H, Efferth T, Alam W. Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress by hesperetin: focus on antitumor and cytoprotective effects. Phytomedicine. 2022;100:153985.10.1016/j.phymed.2022.153985Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Zareei S, Boojar MMA, Amanlou M. Inhibition of liver alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase by hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin: an in vitro and in silico study. Life Sci. 2017;178:49–55.10.1016/j.lfs.2017.04.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Li J, Wang T, Liu P, Yang F, Wang X, Zheng W, et al. Hesperetin ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and inflammation via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2-ARE pathway in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and a rat model of high-fat diet-induced NAFLD. Food Funct. 2021;12(9):3898–918.10.1039/D0FO02736GSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Cao ZH, Zhang Z, Yang Q, Fang XY, Bai HN, Li H, et al. Integrating network pharmacology and metabolomics to explore the potential mechanism of pinolenic acid against atherosclerosis. J Food Biochem. 2024;2024:14.10.1155/2024/9445763Search in Google Scholar
[18] Xu S, Tang L, Qian X, Wang Y, Gong J, Yang H, et al. Molecular mechanism of Ginkgo biloba in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental evaluations. J Food Biochem. 2022;46(12):e14419.10.1111/jfbc.14419Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Li P, Zhang J, Wu J, Ma J, Huang W, Gong J, et al. Integrating serum pharmacochemistry and network pharmacology to reveal the mechanism of chickpea in improving insulin resistance. Fitoterapia. 2024;172:105750.10.1016/j.fitote.2023.105750Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[20] Hu K, Sun YJ, Wang J, Wu SJ, Ren J, Su D, et al. Integrating network analysis and experimental validation to reveal the mechanism of pinocembrin in alleviating high glucose and free fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. J Funct Foods. 2023;110:105879.10.1016/j.jff.2023.105879Search in Google Scholar
[21] Yang H, Sun YJ, Zhang JL, Xu S, Tang LD, Gong JH, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates triglyceride accumulation through FXR deacetylation in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells. J Funct Foods. 2023;107:105679.10.1016/j.jff.2023.105679Search in Google Scholar
[22] Vida M, Gavito AL, Pavón FJ, Bautista D, Serrano A, Suarez J, et al. Chronic administration of recombinant IL-6 upregulates lipogenic enzyme expression and aggravates high-fat-diet-induced steatosis in IL-6-deficient mice. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(7):721–31.10.1242/dmm.019166Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Krizanac M, Mass Sanchez PB, Schröder SK, Weiskirchen R, Asimakopoulos A. Lipid-independent regulation of PLIN5 via IL-6 through the JAK/STAT3 axis in Hep3B Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(8):7219.10.3390/ijms24087219Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Chen K, Pan Y, Xiang X, Meng X, Yao D, Lin L, et al. The nonalcoholic fatty liver risk in prediction of unfavorable outcome after stroke: a nationwide registry analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2023;157:106692.10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106692Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Mitra S, Halder AK, Ghosh N, Mandal SC, Cordeiro M. Multi-model in silico characterization of 3-benzamidobenzoic acid derivatives as partial agonists of Farnesoid X receptor in the management of NAFLD. Comput Biol Med. 2023;157:106789.10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106789Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Salehi B, Cruz-Martins N, Butnariu M, Sarac I, Bagiu IC, Ezzat SM, et al. Hesperetin’s health potential: moving from preclinical to clinical evidence and bioavailability issues, to upcoming strategies to overcome current limitations. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(16):4449–64.10.1080/10408398.2021.1875979Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Evans JA, Mendonca P, Soliman KFA. Neuroprotective effects and therapeutic potential of the citrus flavonoid hesperetin in neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients. 2022;14(11):2228.10.3390/nu14112228Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Khan A, Ikram M, Hahm JR, Kim MO. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of citrus flavonoid hesperetin: special focus on neurological disorders. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(7):609.10.3390/antiox9070609Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Ferreira de Oliveira JMP, Santos C, Fernandes E. Therapeutic potential of hesperidin and its aglycone hesperetin: cell cycle regulation and apoptosis induction in cancer models. Phytomedicine. 2020;73:152887.10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152887Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[30] Kanaze FI, Bounartzi MI, Georgarakis M, Niopas I. Pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavanone aglycones hesperetin and naringenin after single oral administration in human subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2007;61(4):472–7.10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602543Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Takumi H, Mukai R, Ishiduka S, Kometani T, Terao J. Tissue distribution of hesperetin in rats after a dietary intake. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(8):1608–10.10.1271/bbb.110157Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Geng Y, Wu Z, Buist-Homan M, Blokzijl H, Moshage H. Hesperetin protects against palmitate-induced cellular toxicity via induction of GRP78 in hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;404:115183.10.1016/j.taap.2020.115183Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[33] Cheng W, Li M, Zhang L, Zhou C, Yu S, Peng X, et al. New roles of N6-methyladenosine methylation system regulating the occurrence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with N6-methyladenosine-modified MYC. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:973116.10.3389/fphar.2022.973116Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Porcu C, Antonucci L, Barbaro B, Illi B, Nasi S, Martini M, et al. Copper/MYC/CTR1 interplay: a dangerous relationship in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2018;9(10):9325–43.10.18632/oncotarget.24282Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Stojsavljević S, Gomerčić Palčić M, Virović Jukić L, Smirčić Duvnjak L, Duvnjak M. Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(48):18070–91.10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18070Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Ferrer MD, Busquets-Cortés C, Capó X, Tejada S, Tur JA, Pons A, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(18):3225–41.10.2174/0929867325666180514112124Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[37] McGillicuddy FC, Chiquoine EH, Hinkle CC, Kim RJ, Shah R, Roche HM, et al. Interferon gamma attenuates insulin signaling, lipid storage, and differentiation in human adipocytes via activation of the JAK/STAT pathway. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(46):31936–44.10.1074/jbc.M109.061655Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Yao Y, Luo ZP, Li HW, Wang SX, Wu YC, Hu Y, et al. P38γ modulates the lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2023;37(1):e22716.10.1096/fj.202200939RRSearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[39] Ito Y, Kanda M, Sasahara M, Tanaka C, Shimizu D, Umeda S, et al. Killer cell lectin-like receptor G2 facilitates aggressive phenotypes of gastric cancer cells via dual activation of the ERK1/2 and JAK/STAT pathways. Gastric Cancer. 2024;27(3):506–18.10.1007/s10120-024-01480-ySearch in Google Scholar PubMed
[40] Zhang J, Lei H, Hu X, Dong W. Hesperetin ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by maintaining the epithelial barrier via blocking RIPK3/MLKL necroptosis signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;873:172992.10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172992Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Jing S, Wang X, Zhang Z, Cao D, Huang K, Wang Y, et al. Hesperetin attenuates cognitive dysfunction via SIRT6/NLRP3 pathway in scopolamine-induced mice. Metab Brain Dis. 2023;38(7):2443–56.10.1007/s11011-023-01250-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(11):798–809.10.1038/nrc2734Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[43] Dodington DW, Desai HR, Woo M. JAK/STAT – emerging players in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2018;29(1):55–65.10.1016/j.tem.2017.11.001Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[44] Liu J, Wang F, Luo F. The role of JAK/STAT pathway in fibrotic diseases: molecular and cellular mechanisms. Biomolecules. 2023;13(1):119.10.3390/biom13010119Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Shi SY, Martin RG, Duncan RE, Choi D, Lu SY, Schroer SA, et al. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) protects against diet-induced steatohepatitis and glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(13):10277–88.10.1074/jbc.M111.317453Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Wójcik K, Jabłonowska E, Omulecka A, Piekarska A. Insulin resistance, adipokine profile and hepatic expression of SOCS-3 gene in chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(30):10449–56.10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10449Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Song H, Huang Q, Zhang Y, Shen X. Wheat germ peptide improves glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in HepG2 hepatocytes via regulating SOCS3/IRS1/Akt pathway. Nutr Res. 2023;120:135–44.10.1016/j.nutres.2023.10.005Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Rehman K, Akash MSH, Liaqat A, Kamal S, Qadir MI, Rasul A. Role of interleukin-6 in development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2017;27(3):229–36.10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2017019712Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Elhennawy MG, Abdelaleem EA, Zaki AA, Mohamed WR. Cinnamaldehyde and hesperetin attenuate TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis in rats through modulation of the JAk2/STAT3/SOCS3 pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35(5):e22730.10.1002/jbt.22730Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[50] Shirzad M, Heidarian E, Beshkar P, Gholami-Arjenaki M. Biological effects of hesperetin on interleukin-6/phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway signaling in prostate cancer PC3 cells. Pharmacogn Res. 2017;9(2):188–94.Search in Google Scholar
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms

