Abstract
Background
Sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is a complex neurological complication of sepsis involving activation of microglia in the central nervous system (CNS), blood–brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction, neurotransmitter dysfunction, impaired brain metabolism, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Neuroinflammation is a critical component of the pathogenesis. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway, as a key intracellular signaling pathway, plays a crucial role in regulating neuroinflammation, maintaining the integrity of the BBB, and promoting neuronal cell survival.
Objective
This review aims to summarize the role of the PI3K/Akt pathway in SAE-associated neuroinflammation and highlights potential therapeutic targets and strategies for its management.
Methods
We systematically reviewed recent basic and clinical studies on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in neuroinflammation associated with SAE, as well as the development of pathway-specific agonists and inhibitors.
Results
The PI3K/Akt pathway serves as a crucial intracellular signaling axis involved in the regulation of neuroinflammatory processes. Accumulating evidence indicates that targeted modulation of this pathway may alleviate neuroinflammation associated with SAE and enhance neurological recovery.
Conclusion
Targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway represents a promising therapeutic approach for SAE. Advances in the development of specific agonists and inhibitors provide new opportunities for clinical translation and drug discovery in neuroinflammatory conditions.
1 Introduction
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) caused by infection, characterized by dysregulation of the body’s immune response to infection. It is one of the key causes of death in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit [1]. Among these, sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE) is one of the most common complications of sepsis, with an incidence rate as high as 70% [2], which significantly increases the morbidity and mortality rate and diminishes the quality of life of the patients [3,4]. The pathogenesis of SAE is complex and multifactorial, with contributing key factors including activation of microglia in the central nervous system (CNS), blood–brain barrier (BBB) dysfunction, brain edema, neurotransmitter dysfunction, impaired brain metabolism, and mitochondrial dysfunction [5–8]. Additional mechanisms, such as the accumulation of amyloid-β and tau proteins, activation of the complement system, and direct neuronal injury, may also contribute to the development of SAE [9]. Overall, SAE results from the synergistic effects of multiple factors, rather than a single cause. Among these, neuroinflammation has been shown to play a crucial role throughout the SAE process and is closely associated with prognosis.
Neuroinflammation is an immune response activated by microglia and astrocytes in the CNS, usually occurring in response to CNS injury, infection, toxin stimulation, or autoimmunity [9]. Systemic inflammation induced by sepsis is mediated by the excessive release of proinflammatory cytokines – such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) – which increases the permeability of the BBB, thereby facilitating inflammatory factors to enter the brain and trigger an inflammatory response in the CNS. The sustained inflammatory response disrupts the BBB and facilitates the infiltration of peripheral immune cells. This exacerbates CNS injury, leading to neuronal damage [10,11], demyelination [12], impaired regeneration [13], and synaptic dysfunction.
Among the numerous molecular pathways implicated in neuroinflammation, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway has been extensively studied for its involvement in various physiological processes within the CNS, including cell survival, autophagy, neurogenesis, neuronal proliferation and differentiation, synaptic plasticity, anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidative stress, and neural repair [9,14]. Recently, several studies have confirmed that this pathway is closely related to the development of neurological diseases and plays an important role in modulating various pathological changes [15–17].
Based on the roles of neuroinflammation and PI3K/Akt pathway activation in the pathogenesis of SAE, this article aims to elucidate their specific roles and interrelationships in SAE development. The following sections will comprehensively describe the neuroinflammation triggered by sepsis, the underlying mechanisms of the PI3K/Akt pathway, its role in SAE, and the potential treatment of SAE through targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway.
2 Sepsis-induced neuroinflammation
The presence of neuroinflammation in SAE has been clearly demonstrated [18,19]. Autopsy studies of patients who died from sepsis revealed significantly increased expression of markers associated with acute neuroinflammation, suggesting that neuroinflammation may play a critical role in the progression of SAE [20]. While infection does not occur directly in the brain, peripheral inflammatory signals can trigger widespread neuroinflammation through both neuronal and humoral pathways [21]. Neuroinflammation is initiated by multiple biological mechanisms, including immune responses, oxidative stress, the release of inflammatory mediators, and damage to the BBB. Although neuroinflammation can initially have a protective effect, prolonged or excessive inflammation can result in neural tissue damage.
Neuroinflammatory responses can be classified into two categories: secondary inflammatory responses induced by peripheral immune cells and primary inflammatory responses triggered by resident immune cells. Initially, during sepsis, pathogens or their associated toxins – such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) – stimulate the host immune system, leading to an exaggerated inflammatory response and the subsequent development of SIRS. These peripheral inflammatory signals affect the CNS through two main pathways: humoral and neuronal. Through the humoral pathway, elevated circulating pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) enter the brain via the disrupted BBB and directly activate CNS inflammation. In a septic environment, the intense secretion of inflammatory factors and chemokines recruits peripheral immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, to the brain, thereby exacerbating neuronal damage [22,23]. Neuroinflammation can also be amplified through neurotransmission, with the vagus nerve upregulating pro-inflammatory gene expression by transmitting signals to the nucleus tractus solitarius of the medulla oblongata [24]. This central-peripheral inflammation cascade amplifies the inflammatory response. In sepsis, microglia become hyperactivated, releasing large amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) and chemokines (MCP-1). Overactivated microglia induce apoptosis and synaptic damage in neurons, stimulate reactive oxygen species (ROS) production [25], and further trigger oxidative stress and inflammatory cascades. Astrocytes are also activated [26], and synergize with microglia to exacerbate the inflammatory response. This includes breaking down matrix components in the BBB, leading to barrier disruption, and secreting large quantities of inflammatory factors (IL-6), which promote the spread of inflammation. Cytokines and chemokines also disrupt the integrity of the BBB by affecting the expression of tight junction proteins (Claudin, Occludin) [22,23,27]. The sepsis-induced immune response produces an abundance of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β), which bind to specific receptors and activate apoptotic signaling pathways such as Fas and Caspase [28,29]. This activation ultimately leads to neuronal and glial cell death, causing further damage to the nervous system. Additionally, activated inflammatory mediators and immune cells generate ROS and reactive nitrogen species, leading to increased oxidative damage [30,31]. These free radicals damage cell membranes, proteins, and DNA, which further contribute to neuronal dysfunction, apoptosis, and long-term neurological impairment. Sepsis-induced oxidative stress also disrupts mitochondrial function, compromising the cellular energy supply. Mitochondrial damage exacerbates neuronal apoptosis and creates a vicious cycle by releasing cytokines and activating neuroinflammatory pathways [32].
3 PI3K/Akt pathway and its role in brain tissue
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway consists of two main components: phosphatidylinositol 3 (PI3K) and its downstream serine/threonine protein kinase B (PKB, also known as Akt). PI3K is a class of intracellular lipid kinases, classified into types I, II, or III based on substrate specificity and sequence homology [33,34]. Akt is a proto-oncogene product that, upon activation, modulates a variety of downstream signaling molecules, including mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) [35] and glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3) [36], among others.
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is a central intracellular regulatory network involved in diverse biological processes, including cell survival, proliferation, metabolism, protein synthesis, immune regulation, and stress responses. By promoting proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis, and enhancing cell survival, this pathway plays a critical role in tumorigenesis and has emerged as a prominent target for cancer therapy [37–39]. Akt, a key effector of the PI3K/Akt pathway, regulates glucose and lipid metabolism, as well as cell differentiation and growth [40], and holds therapeutic potential for diabetes and metabolic disorders. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway also plays a critical role in bone and joint diseases, such as osteoarthritis [41], and in erythroid hematopoiesis [40], suggesting its potential as a novel therapeutic target. In neurological disorders, the PI3K/Akt pathway regulates neuronal survival, mitigates inflammation, preserves BBB integrity, and exerts neuroprotective effects in conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases [42,43]. Thus, the PI3K/Akt pathway holds broad clinical potential across various diseases, including cancer, metabolic disorders, neurological conditions, and osteoarticular diseases.
In normal brain tissues, the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway plays a crucial role in neuronal survival, synaptic plasticity, energy metabolism, BBB integrity, and neurodevelopment [44]. The activation of this pathway depends on upstream ligands such as derived brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and mediates multiple regulatory effects on neuronal anti-apoptosis, resistance to oxidative stress, synaptic plasticity, and energy metabolism through downstream targets including mTOR, GSK-3β, and cAMP response element-binding protein 2 [45]. For example, Akt inhibits the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by phosphorylating pro-apoptotic proteins such as BAD and Caspase-9, thereby preventing premature neuronal apoptosis and contributing to the maintenance of the functional integrity of brain tissue [46]. Akt exerts antioxidant effects by activating the Nrf2 pathway and scavenging ROS [47]. It also activates mTOR-dependent protein synthesis to support dendritic spine formation and long-term potentiation (LTP) [47], and promotes the membrane translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 to enhance neuronal glucose uptake. In addition, Akt plays a key role in stabilizing the intracerebral microenvironment by maintaining the expression of endothelial tight junction proteins, such as Zonula Cccludens-1 (ZO-1), at the BBB [48].
However, in the pathological state of SAE, the systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress lead to inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, released during sepsis indirectly suppress the activity of the PI3K catalytic subunit p110 via activation of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway [25]. Simultaneously, excessive ROS promote the conversion of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) by activating the lipid phosphatase PTEN, a negative regulator of PI3K, thereby impairing Akt membrane localization and phosphorylation [49]. Mitochondrial dysfunction further exacerbates energy metabolism disorders and reduces the efficiency of Akt activation [25]. Akt inactivation results in the dephosphorylation of BAD, which in turn activates Bax/Bak-mediated mitochondrial cytochrome c release and triggers the caspase cascade, ultimately enhancing neuronal apoptosis. Additionally, GSK-3β disinhibition leads to Tau protein hyperphosphorylation, promoting the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and downregulating the expression of synapse-associated proteins such as PSD-95, contributing to synaptic damage [50]. Decreased Akt activity in endothelial cells also compromises tight junction integrity, aggravating brain edema and neuroinflammation.
In summary, the PI3K/Akt pathway plays a critical role in maintaining CNS homeostasis under normal conditions. However, in SAE, its expression and activity are markedly altered, resulting in the loss of its original protective functions and, in some cases, contributing to disease progression. Comparing the dynamic changes of this pathway between physiological and pathological states may help elucidate its role in SAE pathogenesis and provide a theoretical foundation for targeted therapeutic interventions. (Figure 1).
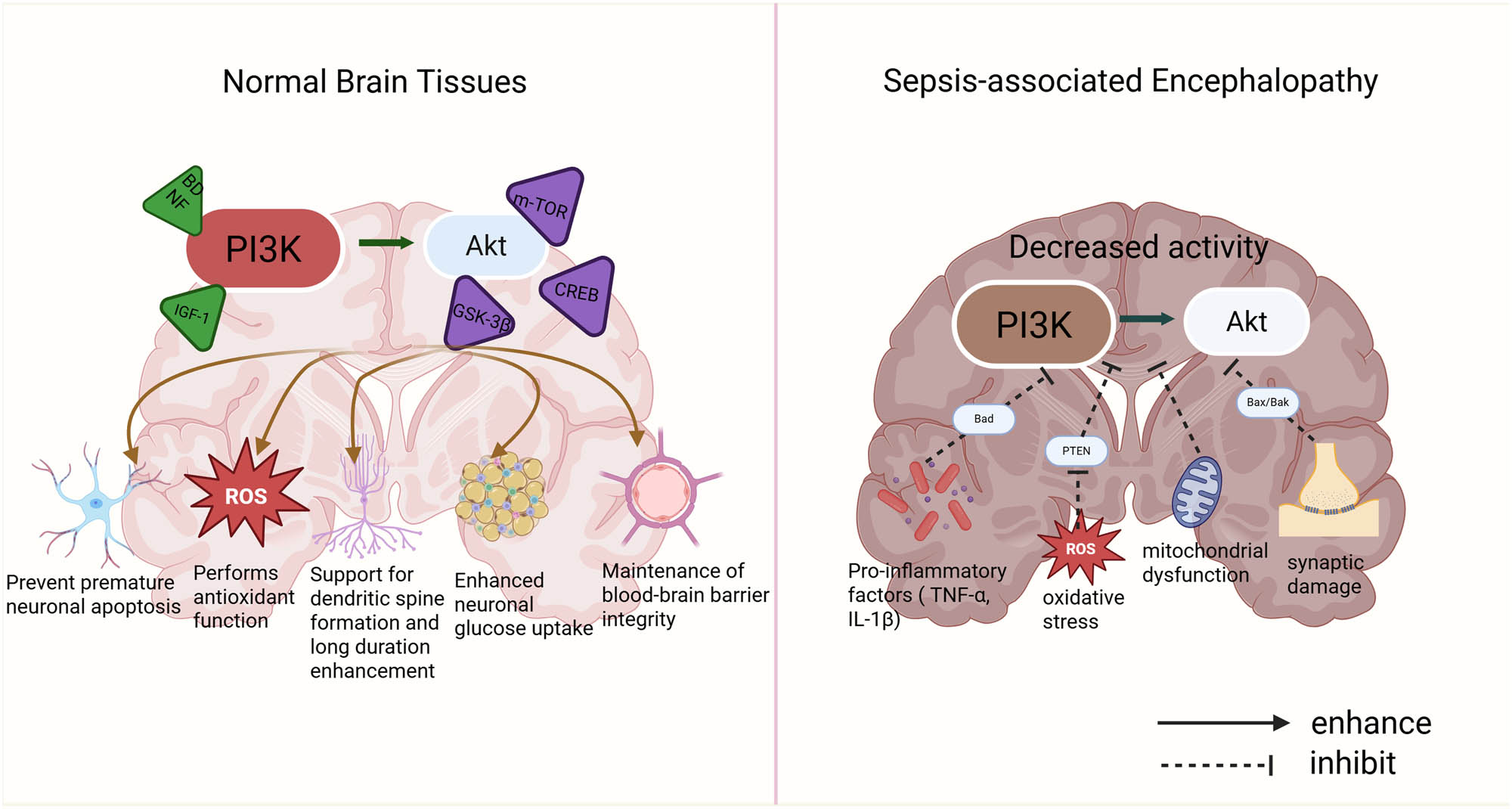
Differences in PI3K/Akt pathway in normal brain tissue and SAE conditions. ROS: reactive oxygen species.
4 PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in SAE
As discussed previously, sepsis-induced neuroinflammation is a core pathogenic mechanism of SAE. Within the pathophysiological framework of SAE, the PI3K/Akt pathway plays a dual regulatory role in both CNS injury and neuroprotection. It does so by modulating the expression of neuroinflammatory factors, regulating microglial activation, maintaining the integrity of the BBB, and controlling neuronal apoptosis. The PI3K/Akt pathway is a classical signaling cascade that regulates neuronal survival and neurogenesis, making it a crucial player in the progression and potential treatment of SAE [40,51]. In the CLP mouse model, protein expression levels of PI3K and Akt in hippocampal tissues were significantly decreased [52–54], whereas activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway attenuated SAE-related damage [52–57].
4.1 Regulation of inflammatory factors
The PI3K/Akt pathway suppresses the excessive release of pro-inflammatory cytokines during sepsis through multiple mechanisms. First, it initiates a negative feedback regulatory loop that significantly reduces the overexpression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 [58–60]. Second, the pathway upregulates the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators, such as IL-10, which subsequently inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine production via paracrine signaling [58]. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits the activation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB, further modulating inflammation [61]. It also contributes to the regulation of the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance [62], thereby attenuating the inflammatory cascade. Clinical studies have confirmed that pharmacological agents like dexmedetomidine [63] and metformin [64] can activate the PI3K/Akt pathway, inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine release and improving sepsis-associated brain and lung injury.
4.2 Regulation of microglia polarization
The PI3K/Akt signaling pathway plays a crucial role in regulating microglia polarization. It modulates microglial M1/M2 polarization by influencing multiple signaling pathways [65], including NF-κB [66] and chemokine receptor CXCR7 [67], which promote the transformation of microglia to the M2 phenotype and enhance their anti-inflammatory properties. M2-polarized microglia secrete anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and TGF-β [68], thereby reducing the neuroinflammatory response. Agents like tretinoin and curcumin have been demonstrated to inhibit the activation of pro-inflammatory M1 microglia while promoting the anti-inflammatory properties of M2 microglia, presumably via activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway [69]. Furthermore, the PI3K/Akt pathway indirectly regulates microglial inflammation by modulating the neuron-derived BDNF-PI3K/Akt signaling axis [70,71]. Akt increases the secretion of BDNF from neurons by enhancing vesicular transport, which in turn strengthens the inhibitory effect of neurons on microglial inflammation. Compounds like pineoside [72] and paeoniflorin [72] regulate the BDNF-PI3K/Akt axis, achieving a balanced regulation of microglia M1/M2 polarization and alleviating neuroinflammatory disorders such as SAE.
4.3 Maintenance of BBB integrity
The PI3K/Akt pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the BBB. Akt regulates the expression of tight junction proteins, such as Claudin, Occludin, and ZO-1, through the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby preserving BBB structural integrity [73,74]. Chen et al. [75] demonstrated in an in vitro BBB model that activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway enhances the transcription and translation of tight junction proteins, resulting in decreased permeability of endothelial cell monolayers. Wang et al. [76] found that in a murine model of sepsis treatment with a PI3K-selective agonist significantly increased the expression of tight junction proteins in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits the TNF-α- and IL-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases, thereby reducing extracellular matrix degradation and protecting the BBB structure [77]. Zhi et al. [78] observed that selective PI3K agonist treatment significantly reduced levels of S100β and neuron-specific enolase in the cerebrospinal fluid of sepsis patients, along with other markers of BBB damage, and improved neurocognitive function scores. Gong et al. [79] reported that combined administration of a PI3K agonist and an anti-inflammatory agent significantly reduced the morbidity and mortality of patients with SAE, and the levels of tight junction protein degradation products, such as Occludin and Claudin-5 fragments, were notably lower in the peripheral blood of treated patients. This suggests that the combination regimen may exert neuroprotective effects by preserving BBB integrity.
4.4 Regulation of neuronal apoptosis
Neuronal apoptosis is a key pathological feature in sepsis-induced neuroinflammation, with its regulatory mechanisms linked to the PI3K/Akt pathway. First, the PI3K/Akt pathway inhibits neuronal apoptosis by regulating several downstream effector molecules. Activated Akt effectively blocks Bad-induced apoptosis by phosphorylating Bad at the Ser136 site, preventing its binding to Bcl-2. Additionally, the pathway upregulates the nuclear translocation of the antioxidant-related transcription factor Nrf2, which increases the expression of superoxide dismutase and catalase, thereby reducing oxidative stress-induced neuronal injury. Puerarin has been shown to reduce neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress through the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway [80]. Furthermore, the PI3K/Akt pathway promotes neural repair and regeneration. Akt-mTOR signaling enhances myelin sheath growth and stability during development by driving cap-dependent translation to facilitate myelin formation [81]. It has also been demonstrated that resveratrol can activate PI3K/Akt signaling to promote axonal regeneration and neurological recovery. Additionally, the PI3K/Akt pathway may play a role in regulating synaptic plasticity by modulating the reorganization of post-synaptic proteins, such as PSD-95 [82], and influences synaptic transmission efficiency as well as LTP [83]. Moreover, novel PI3K agonists have shown promising neuroprotective effects in animal models, providing new intervention targets for the treatment of SAE [84].
4.5 Discovery of new molecules
In recent years, several novel molecules have been identified as regulators of the PI3K/Akt pathway, with significant effects on the development and progression of SAE. Protein kinase N2 (PKN2), in particular, exerts a broad range of regulatory effects on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway through mechanisms such as direct phosphorylation, modulation of membrane localization, and catalytic activity. PKN2 can directly phosphorylate the p85 regulatory subunit of PI3K [85], inducing a conformational change that alters its interactions with other signaling molecules. Furthermore, PKN2 affects the membrane localization of PI3K, thereby modulating its enzymatic activity [85]. Wang et al. [86] demonstrated that PKN2 overexpression activated the mTOR pathway in PC12 cells, reducing H2O2-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis. Additionally, PKN2 modulates Akt activity by phosphorylating its Ser473 site [87], a key step in regulating the function of Akt within the PI3K/Akt pathway. By phosphorylating Akt at this critical site, PKN2 influences the activity and substrate specificity of Akt, thereby affecting downstream signaling processes. In addition, PKN2 may play a role in regulating the integrity of the BBB [88]. Bai et al. [89] found that H2 alleviates septic brain injury by activating PKN2 phosphorylation, which is associated with the PI3K pathway. While PKN2 exerts a broad range of regulatory effects on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, there are currently fewer studies focusing on its role in septic encephalopathy. This presents an opportunity for future, more in-depth research. PTEN, as a negative regulator of the PI3K/Akt pathway, inhibits AKT activation by dephosphorylating PIP3 and converting it to PIP2 [90]. This action helps maintain normal neuronal function and survival, protecting against neuronal injury caused by dysregulated signaling. Furthermore, the signaling between PTEN-induced kinase 1 (PINK1) and the Parkin pathway is crucial in SAE. High expression of PINK1 can activate mitochondrial autophagy through up-regulation of Parkin, which reduces inflammatory responses, preventing neuroinflammation and alleviating cognitive impairments in SAE mice. In the absence of PINK1, there is a suppression of Ca2+ transients in the hippocampus, leading to elevated intracellular Ca2+ levels, which exacerbate sepsis-induced cognitive dysfunction in mice, highlighting the vital role of PINK1 in maintaining neuronal stability [91]. Girdin can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, promote neuronal survival, and prevent apoptosis by regulating the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby alleviating neuroinflammation [92,93]. Phosphorylated Girdin enhances the activity of intracellular anti-apoptotic factors, such as Bcl-2 and mTOR, which reduce programmed cell death [94]. Additionally, Girdin regulates microglial activation, as overactivation of microglia exacerbates the neuroinflammatory response. Rheb (Ras homolog enriched in brain), a small GTP-binding protein, plays a key role in the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway by directly activating mTOR, which is crucial for neuroprotection. In an LPS-induced neuroinflammation model, upregulation of Rheb was linked to astrocyte proliferation and neuronal apoptosis [95]. The Rheb-mTOR signaling pathway contributes to neuroinflammation-induced astrocyte activation and neuronal apoptosis through cell cycle activation [96]. Moreover, specific overexpression of Rheb in retinal ganglion cells significantly reduced cell death and effectively induced axonal regeneration [97], suggesting that Rheb promotes neural repair, potentially alleviating sepsis-induced neuroinflammation. Additionally, BAG3 is involved in regulating Akt downstream targets like mTORC1, affecting cellular autophagy processes. BAG3 forms a complex with CHIP (C-terminus of Hsc70 interacting protein) [98], which facilitates the ubiquitination and degradation of key inhibitors negatively regulating PI3K/Akt signaling, such as phosphatase and Tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN), thereby positively regulating this pathway. Bcl-2-associated athanogene 3 (BAG3) also plays a protective role in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), and studies have shown that sevelamer sodium can attenuate AKI in a rat sepsis model through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway, with BAG3 involved in this protective mechanism. Although there are currently fewer studies directly examining these molecules in SAE, they play critical roles in the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which is integral to SAE pathogenesis. Future research should focus on how these molecules specifically contribute to SAE and whether they can be targeted for effective therapeutic interventions, potentially offering more effective treatments for patients with SAE (Figure 2).
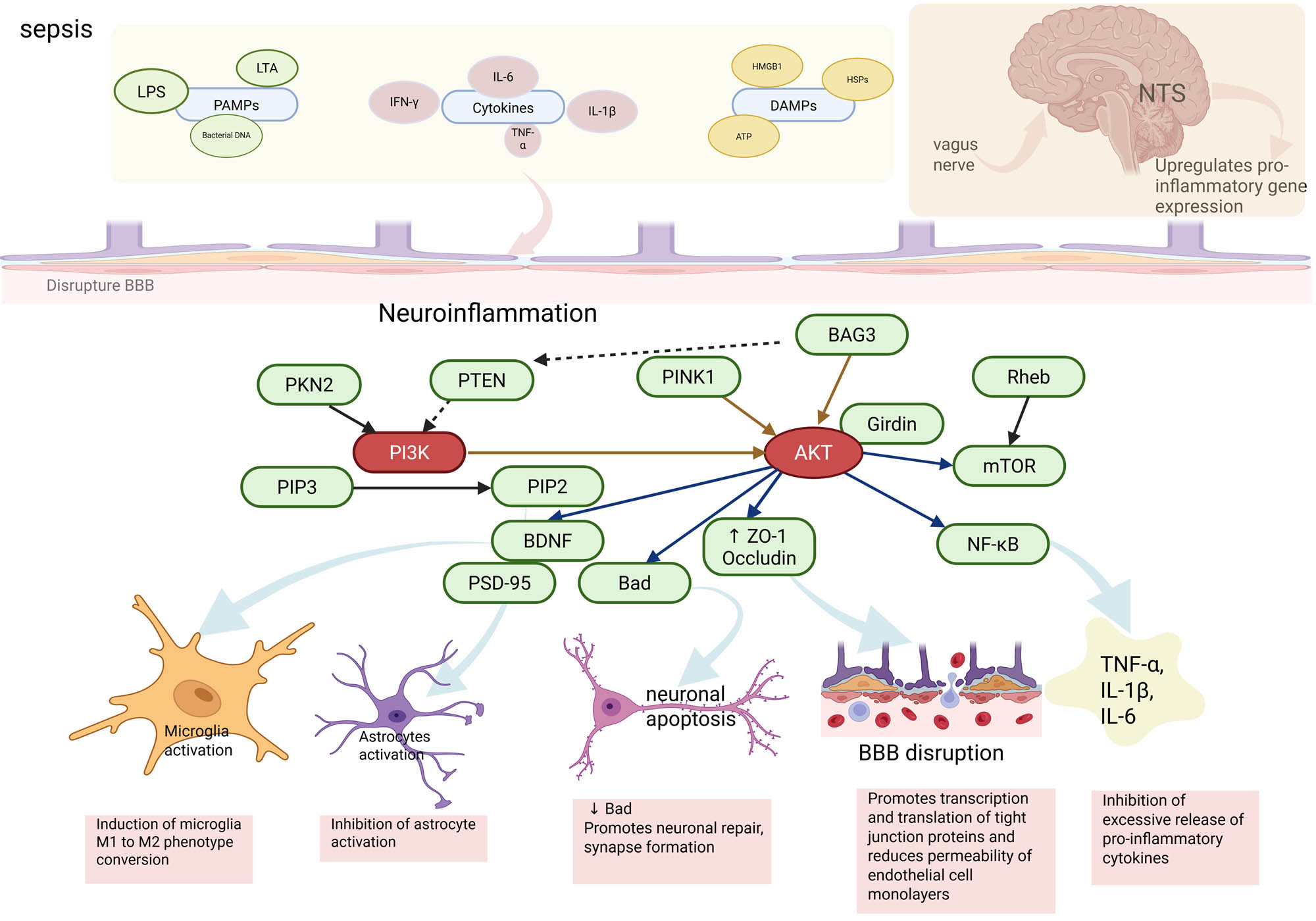
Inflammatory signaling regulates SAE through the PI3K/Akt pathway. PAMPs: pathogen-associated molecular patterns; DAMPS: damage-associated molecular patterns; LTA: lipoteichoic acid; NTS: nucleus tractus solitarius; BBB: blood–brain barrier.
5 Therapeutic potential of PI3K/Akt pathway modulators
IGF-1 attenuates the inflammatory response and ameliorates SAE by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Treatment with recombinant human IGF-1 significantly reduced serum levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in patients with SAE, while also improving the Glasgow Coma Score (GCS), strengthening BBB integrity, reducing neuroinflammation, and enhancing cognitive function [99,100]. BDNF activates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway through the TrkB receptor, upregulates the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and promotes the expression of synaptic plasticity-associated proteins (PSD95) [101,102]. BDNF has been shown to significantly ameliorate memory deficits in a mouse model of sepsis and reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the CNS. Several studies have shown that various naturally active compounds exert neuroprotective effects by modulating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Curcumin significantly increased the level of phosphorylated Akt in neurons (the p-Akt/Akt ratio increased 2.1-fold), promoting the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 and enhancing cellular resistance to oxidative stress [103]. Resveratrol significantly reduced the volume of cerebral infarcts and neurological damage scores in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion rats, significantly lowering levels of myeloperoxidase, TNF-α, and upregulating p-Akt expression. The use of Akt inhibitors blocked the effects of resveratrol. Resveratrol was also shown to reduce neuronal apoptosis, as evidenced by an increase in the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and a decrease in the number of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells [104]. Additionally, quercetin and rhodiola rosea glycosides synergistically activate PI3K/Akt downstream targets, significantly reducing pro-inflammatory factors and improving cognitive function [105,106]. Oleanolic acid [107] and dihydromyricetin (DHM) [108] inhibit oxidative stress through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby exerting neuroprotective effects. Based on their role in other neuroinflammatory diseases, these natural compounds may have important therapeutic potential in SAE. In cases of overactivated PI3K/Akt signaling, the PI3K-selective inhibitor LY294002 exerts a bidirectional modulatory effect, reducing inflammatory responses and neurotoxicity [104,109]. However, the targets of PI3K inhibitors need to be carefully selected to avoid inhibiting neuroprotective effects.
Several PI3K inhibitors have been developed for tumor therapy, such as PI-103, BKM120, and GDC-0941 [110,111]. These inhibitors block tumor cell proliferation and survival by targeting key nodes of the PI3K/Akt pathway, including PI3K, Akt, and mTOR. Some PI3K inhibitors have been approved for the treatment of specific hematologic malignancies. For example, Linperlisib, the first highly selective PI3Kδ inhibitor marketed in China, has been approved for the treatment of relapsed and/or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL), demonstrating significant clinical efficacy and good tolerability [112]. In addition, Duvelisib [113], a dual PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ inhibitor, has also been approved by the FDA for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), and FL who have received at least two prior therapies. Although these drugs have shown effectiveness in treating specific types of hematologic malignancies, their potential application in neuroinflammatory and neurological disorders requires further research and exploration. Although most compounds targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway – such as estrogen [114], resveratrol, curcumin [115], GDC-0941, duvelisib, and leniolisib [112] – have already entered clinical trials for other diseases (oncology, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases), their clinical application in sepsis, especially SAE, remains largely unexplored or is still in its infancy. This suggests that, in the future, compounds with established clinical safety profiles could be prioritized for translational research in SAE, particularly through the use of animal models to verify their target specificity and neuroprotective efficacy (Table 1).
Major research models, mechanisms, and key findings of PI3K/Akt pathway agonists and inhibitors associated with SAEs
| Compound | Mechanisms | Model | Key findings | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant human IGF-1 | Activates PI3K/Akt pathway to reduce inflammation | C57BL/6 mice; sepsis induced by intratracheal instillation of P. aeruginosa (PA103 strain) | Decrease in serum IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 levels; increase in GCS score; enhancement of BBB function; decrease in neuroinflammation and improvement in cognitive ability | [99,100] |
| BDNF | Activates the PI3K/Akt pathway via TrkB receptors | SCID-Beige mice; NB xenograft model for metastasis | Improvement of memory deficits and reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines in CNS | [101,102] |
| Estrogen | Activates PI3k/Akt, upregulates Bcl-2, and downregulates Bax and Caspase-3,8 | VSC4.1 motor neuron cells | Antiapoptotic | [116] |
| Curcumin | Increases phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and promotes Nrf2 nuclear translocation | C57BL/6 mice; LPS-induced sepsis model; HL-1 cardiomyocytes; LPS stimulation | Enhanced antioxidant stress response and 2.1-fold increase in p-Akt/Akt ratio, promoting neuroprotection | [103] |
| Resveratrol | Increases p-Akt expression and inhibits oxidative stress | SD rats; MCAO-induced cerebral I/R injury model | Reduced cerebral infarct volume, improved neurologic scores, decreased MPO, TNF-α, increased p-Akt, and decreased apoptosis | [117] |
| Quercetin | Activates PI3K/Akt pathway, anti-inflammatory effects | C57BL/6 mice; G. parasuis-induced encephalitis model; mouse brain endothelial cells; G. parasuis stimulation | Significantly reduced inflammatory cytokines and improved cognitive function | [105,106] |
| Oleanolic acid | Activates PI3K/Akt pathway to inhibit oxidative stress and neuroinflammation | Rats; methylmercury-induced ALS model | Reduces oxidative stress and neuroinflammation | [107] |
| DHM | Activates the PI3K/Akt pathway to reduce oxidative stress | C57BL/6 mice; MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model; MES23.5 cells; MPP⁺ stimulation | Reduces oxidative stress and neuroinflammation and provides neuroprotection | [108] |
| PI-103 series | PI3K inhibitor targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis | Human tumor xenograft models (glioblastoma, breast cancer, leukemia, prostate cancer, etc.) | Inhibits tumor cell proliferation and survival by targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | [110,111] |
| BKM120 series | PI3K inhibitor targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway | Human tumor xenograft models (glioblastoma, breast cancer, leukemia, prostate cancer, etc.) | Inhibits tumor cell growth and survival by blocking PI3K/Akt signaling | [110,111] |
| GDC-0941 | PI3K inhibitor targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway | Human tumor xenograft models (glioblastoma, breast cancer, leukemia, prostate cancer, etc.) | Inhibits tumor growth, metastasis, and survival in preclinical models by blocking PI3K/Akt signaling | [110,111] |
| Imperius | Highly selective PI3Kδ inhibitor | Refractory/relapsed FL | Approved for FL treatment in China; demonstrated significant clinical efficacy and tolerability | [112] |
| Duvelisib | Dual PI3Kδ/PI3Kγ inhibitor | Refractory CLL and FL | FDA approved for the treatment of CLL, SLL, and FL; effective in patients with relapsed/refractory disease | [113] |
| LY294002 | PI3K inhibitor targeting the PI3K pathway | Rat astrocyte; LPS-induced astrocyte culture model used | Inhibits the PI3K/Akt pathway; shows bidirectional regulation in overactive pathways, reducing inflammation and neurotoxicity | [104,109] |
6 Conclusion
Neuroinflammation is a key contributor to the pathogenesis of SAE, leading to CNS injury and adversely affecting cognitive function and patient survival. The underlying mechanisms primarily involve the activation of microglia and astrocytes, the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, disruption of the BBB structure, increased oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Among the numerous signaling pathways implicated in SAE, the PI3K/Akt pathway has emerged as a central regulator. This pathway plays a pivotal role in modulating neuroinflammatory responses, preserving BBB integrity, and promoting neuronal survival. Several studies have demonstrated that activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by specific compounds can attenuate inflammation and neuronal damage, thereby alleviating SAE-related symptoms. However, the majority of these findings remain at the preclinical stage, and no PI3K/Akt-targeted agents have yet demonstrated clinical efficacy in SAE treatment.
As mentioned above, the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway plays a key role in regulating neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and BBB function, and holds great promise for clinical application. Activation of this pathway can reduce brain tissue damage and improve cognitive function, making it applicable to a variety of neurological diseases, including SAE. In addition, the PI3K/Akt pathway is closely related to immune system homeostasis. Moderate activation of this pathway can inhibit excessive immune responses and reduce systemic inflammation, which is particularly important in SAE, a condition characterized by a pathological “inflammatory storm.” Currently, several drugs targeting this pathway have entered clinical trials for oncology and metabolic diseases and have demonstrated favorable safety profiles. As a potential therapeutic target, the PI3K/Akt pathway is expected to offer a novel intervention strategy for diseases such as SAE in the future.
Despite these advances, several critical knowledge gaps remain. The PI3K family comprises multiple isoforms – PI3Kα, PI3Kγ, and PI3Kδ – each with distinct cellular distribution and functions. For example, PI3Kγ, as a central driver of microglial inflammatory responses, promotes M1-type polarization through the activation of chemokine receptors (the CXCL12–CXCR4 axis), thereby inducing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the infiltration of peripheral immune cells into the brain [118]. PI3Kα, on the one hand, maintains neuronal metabolism and anti-apoptotic functions via the Akt/mTOR pathway [119]; on the other hand, its overactivation may exacerbate mitochondrial autophagy disorders due to oxidative stress [120]. Current research on the roles of these isoforms in SAE is limited, fragmented, and lacks systematic comparison and precise localization. Moreover, most studies have been conducted in acute animal models or in vitro systems, and their clinical relevance and translational potential remain to be validated. Notably, the PI3K/Akt pathway is intricately linked with multiple other signaling cascades – including MAPK, JAK/STAT, NF-κB, mTOR, and NLRP3 – which can induce diverse, and sometimes opposing, biological outcomes. This complexity makes it challenging to predict the net effect of pathway activation or inhibition in the inflammatory milieu of SAE.
Future studies should aim to delineate the cell-type-specific and stage-specific roles of individual PI3K isoforms during SAE progression and evaluate their potential as therapeutic targets in terms of efficacy and safety. Additionally, integrating single-cell transcriptomics and multi-omics approaches may provide insights into the dynamic crosstalk between the PI3K/Akt pathway and other signaling networks. On this basis, the development of selective, brain-targeted PI3K modulators, and the investigation of combination therapies – such as anti-inflammatory agents paired with BBB-protective compounds – may accelerate the translation of preclinical findings into clinically viable interventions for SAE.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Dr. Beibei Dong, Dr. Yuanyuan Bai, and Dr. Xiuhu An for their meticulous guidance and valuable suggestions during the preparation of this review. We also appreciate the support and assistance provided by our team members in data collection and discussions. Additionally, we acknowledge the Department of Anesthesiology at Tianjin Medical University General Hospital for providing excellent research conditions and support for this study.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: Both authors contributed to the conception, design, writing, and revision of the manuscript. Yang Guo was responsible for the conceptualization, literature review, drafting, and preparation of the initial manuscript. Yonghao Yu provided guidance on the study design, critically revised the manuscript, and oversaw the finalization process. The corresponding author had full access to all study data and took responsibility for the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Both authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: This review article does not contain any new experimental data. All data referenced are derived from previously published studies.
References
[1] Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM, Antonelli M, Ferrer R, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43(3):304–77. 10.1007/s00134-017-4683-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Czempik PF, Pluta MP, Krzych ŁJ. Sepsis-associated brain dysfunction: a review of current literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(16):5852. 10.3390/ijerph17165852.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Pan S, Lv Z, Wang R, Shu H, Yuan S, Yu Y, et al. Sepsis-induced brain dysfunction: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:1328729. 10.1155/2022/1328729.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Pu Y, Zhao L, Xi Y, Xia Y, Qian Y. The protective effects of mirtazapine against lipopolysaccharide (lps)-induced brain vascular hyperpermeability. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):3680–93. 10.1080/21655979.2021.2024962.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Zhou Y, Bai L, Tang W, Yang W, Sun L. Research progress in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e33458.10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33458Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Hong Y, Chen P, Gao J, Lin Y, Chen L, Shang X. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt A):110800. 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110800.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[7] Wang X, Wen X, Yuan S, Zhang J. Gut–brain axis in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Neurobiol Dis. 2024;195:106499. 10.1016/j.nbd.2024.106499.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Xin Y, Tian M, Deng S, Li J, Yang M, Gao J, et al. The key drivers of brain injury by systemic inflammatory responses after sepsis: microglia and neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(3):1369–90.10.1007/s12035-022-03148-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Long LH, Cao WY, Xu Y, Xiang YY. Research progress on the role of microglia in sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024;76(2):289–300.Search in Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Qin C, Huang J, Tang X, Liu C, Huang K, et al. The role of astrocytes in oxidative stress of central nervous system: a mixed blessing. Cell Proliferation. 2020;53(3):e12781.10.1111/cpr.12781Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Yang QQ, Zhou JW. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: symphony of glial cells. Glia. 2019;67(6):1017–35. 10.1002/glia.23571.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[12] Leitner GR, Wenzel TJ, Marshall N, Gates EJ, Klegeris A. Targeting toll-like receptor 4 to modulate neuroinflammation in central nervous system disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23(10):865–82. 10.1080/14728222.2019.1676416.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Yong HYF, Rawji KS, Ghorbani S, Xue M, Yong VW. The benefits of neuroinflammation for the repair of the injured central nervous system. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16(6):540–6.10.1038/s41423-019-0223-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Matsuda S, Ikeda Y, Murakami M, Nakagawa Y, Tsuji A, Kitagishi Y. Roles of PI3K/AKT/GSK3 pathway involved in psychiatric illnesses. Diseases. 2019;7(1):22.10.3390/diseases7010022Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Ji Y, Wang D, Zhang B, Lu H. Bergenin ameliorates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease by activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;72(3):823–33. 10.3233/jad-190870.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[16] Abdel Rasheed NO, Ibrahim WW. Telmisartan neuroprotective effects in 3-nitropropionic acid huntington’s disease model in rats: cross talk between PPAR-γ and PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Life Sci. 2022;297:120480. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120480.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[17] Yoon JH, Lee N, Youn K, Jo MR, Kim HR, Lee DS, et al. Dieckol ameliorates aβ production via PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β regulated app processing in sweapp n2a cell. Mar Drugs. 2021;19(3):152.10.3390/md19030152Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Yin XY, Tang XH, Wang SX, Zhao YC, Jia M, Yang JJ, et al. Hmgb1 mediates synaptic loss and cognitive impairment in an animal model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):69.10.1186/s12974-023-02756-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Zhang Y, Chen S, Tian W, Zhu H, Li W, Dai W, et al. Emerging trends and hot spots in sepsis-associated encephalopathy research from 2001 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:817351.10.3389/fmed.2022.817351Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Singer BH, Dickson RP, Denstaedt SJ, Newstead MW, Kim K, Falkowski NR, et al. Bacterial dissemination to the brain in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(6):747–56.10.1164/rccm.201708-1559OCSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Ren C, Yao RQ, Zhang H, Feng YW, Yao YM. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy: a vicious cycle of immunosuppression. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):14.10.1186/s12974-020-1701-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Huang X, Hussain B, Chang J. Peripheral inflammation and blood–brain barrier disruption: effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27(1):36–47.10.1111/cns.13569Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Galea I. The blood–brain barrier in systemic infection and inflammation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(11):2489–501.10.1038/s41423-021-00757-xSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Namgung U, Kim KJ, Jo BG, Park JM. Vagus nerve stimulation modulates hippocampal inflammation caused by continuous stress in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):33.10.1186/s12974-022-02396-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Moraes CA, Zaverucha-do-Valle C, Fleurance R, Sharshar T, Bozza FA, d’Avila JC. Neuroinflammation in sepsis: molecular pathways of microglia activation. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14(5):416.10.3390/ph14050416Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Danielski LG, Giustina AD, Gava FF, Barichello T, Petronilho F. The many faces of astrocytes in the septic brain. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(12):7229–35. 10.1007/s12035-022-03027-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[27] Rempe RG, Hartz AMS, Bauer B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood–brain barrier: versatile breakers and makers. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(9):1481–507.10.1177/0271678X16655551Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Greene C, Connolly R, Brennan D, Laffan A, O'Keeffe E, Zaporojan L, et al. Blood-brain barrier disruption and sustained systemic inflammation in individuals with long covid-associated cognitive impairment. Nat Neurosci. 2024;27(3):421–32.10.1038/s41593-024-01576-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Han Y, Qiu L, Wu H, Song Z, Ke P, Wu X. Focus on the cgas-sting signaling pathway in sepsis and its inflammatory regulatory effects. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:3629–39.10.2147/JIR.S465978Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Olufunmilayo EO, Gerke-Duncan MB, Holsinger RMD. Oxidative stress and antioxidants in neurodegenerative disorders. Antioxidants. 2023;12(2):517.10.3390/antiox12020517Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[31] Geloso MC, Zupo L, Corvino V. Crosstalk between peripheral inflammation and brain: focus on the responses of microglia and astrocytes to peripheral challenge. Neurochem Int. 2024;180:105872. 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105872.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Zhang J, Chen S, Hu X, Huang L, Loh P, Yuan X, et al. The role of the peripheral system dysfunction in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1337994.10.3389/fmicb.2024.1337994Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Sharma A, Mehan S. Targeting PI3K-AKT/mTOR signaling in the prevention of autism. Neurochem Int. 2021;147:105067. 10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105067.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[34] Cianciulli A, Porro C, Calvello R, Trotta T, Lofrumento DD, Panaro MA. Microglia mediated neuroinflammation: focus on PI3K modulation. Biomolecules. 2020;10(1):137.10.3390/biom10010137Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Peng Y, Wang Y, Zhou C, Mei W, Zeng C. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and its role in cancer therapeutics: are we making headway? Front Oncol. 2022;12:819128.10.3389/fonc.2022.819128Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Guerau-de-Arellano M, Piedra-Quintero ZL, Tsichlis PN. AKT isoforms in the immune system. Front Immunol. 2022;13:990874.10.3389/fimmu.2022.990874Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep. 2020;47(6):4587–629.10.1007/s11033-020-05435-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Miricescu D, Totan A, Stanescu II S, Badoiu SC, Stefani C, Greabu M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer: from molecular landscape to clinical aspects. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1):173.10.3390/ijms22010173Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Rascio F, Spadaccino F, Rocchetti MT, Castellano G, Stallone G, Netti GS, et al. The pathogenic role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer onset and drug resistance: an updated review. Cancers. 2021;13(16):3949.10.3390/cancers13163949Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, Akhavan-Niaki H. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway: erythropoiesis and beyond. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(3):2373–85. 10.1002/jcp.27262.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[41] Sun K, Luo J, Guo J, Yao X, Jing X, Guo F. The Pi3k/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(4):400–9. 10.1016/j.joca.2020.02.027.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[42] Zhao B, Yin Q, Fei Y, Zhu J, Qiu Y, Fang W, et al. Research progress of mechanisms for tight junction damage on blood–brain barrier inflammation. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(6):1579–90. 10.1080/13813455.2020.1784952.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Zou P, Yang F, Ding Y, Zhang D, Liu Y, Zhang J, et al. Lipopolysaccharide downregulates the expression of zo-1 protein through the akt pathway. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):774.10.1186/s12879-022-07752-1Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Zheng T, Jiang T, Ma H, Zhu Y, Wang M. Targeting PI3K/AKT in cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury alleviation: from signaling networks to targeted therapy. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(10):7930–49. 10.1007/s12035-024-04039-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[45] Liu T, Li X, Zhou X, Chen W, Wen A, Liu M, et al. Pi3k/akt signaling and neuroprotection in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Neural Regener Res. 2025;20(10):2758–75.10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00568Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] He X, Li Y, Deng B, Lin A, Zhang G, Ma M, et al. The PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in inflammation, cell death and glial scar formation after traumatic spinal cord injury: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Proliferation. 2022;55(9):e13275.10.1111/cpr.13275Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[47] Aliyari M, Ghoflchi S, Hashemy SI, Hashemi SF, Reihani A, Hosseini H. The PI3K/AKT pathway: a target for curcumin’s therapeutic effects. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025;24(1):52.10.1007/s40200-025-01563-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[48] Lee DC, Choi H, Oh JM, Lee J, Lee J, Lee HY, et al. Urban particulate matter regulates tight junction proteins by inducing oxidative stress via the AKT signal pathway in human nasal epithelial cells. Toxicol Lett. 2020;333:33–41. 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.07.017.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[49] Zhao S, Chen F, Yin Q, Wang D, Han W, Zhang Y. Reactive oxygen species interact with NLRP3 inflammasomes and are involved in the inflammation of sepsis: from mechanism to treatment of progression. Front Physiol. 2020;11:571810.10.3389/fphys.2020.571810Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Rekha A, Afzal M, Babu MA, Menon SV, Nathiya D, Supriya S, et al. Gsk-3β dysregulation in aging: implications for Tau pathology and Alzheimer’s disease progression. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2025;133:104005. 10.1016/j.mcn.2025.104005.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[51] Liu Q, Telezhkin V, Jiang W, Gu Y, Wang Y, Hong W, et al. Electric field stimulation boosts neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells for spinal cord injury treatment via pi3k/akt/gsk-3β/β-catenin activation. Cell Biosci. 2023;13(1):4.10.1186/s13578-023-00954-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Zhang Z, Wang L, Li F, Qian X, Hong Z, Wu L, et al. Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell on sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice by regulating pi3k/akt pathway. J Integr Neurosci. 2022;21(1):38. 10.31083/j.jin2101038.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Yang M, He Y, Xin Y, Jiang J, Tian M, Tan J, et al. Identification of biomarkers and therapeutic targets related to sepsis-associated encephalopathy in rats by quantitative proteomics. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):4.10.1186/s12864-022-09101-7Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Lin SP, Zhu L, Shi H, Ye S, Li Q, Yin X, et al. Puerarin prevents sepsis-associated encephalopathy by regulating the akt1 pathway in microglia. Phytomedicine. 2023;121:155119. 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155119.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[55] Gu M, Mei XL, Zhao YN. Sepsis and cerebral dysfunction: BBB damage, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy as key mediators and the potential therapeutic approaches. Neurotox Res. 2021;39(2):489–503. 10.1007/s12640-020-00270-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Yin L, Chen X, Ji H, Gao S. Dexmedetomidine protects against sepsis‑associated encephalopathy through HSP90/AKT signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(5):4731–40. 10.3892/mmr.2019.10718.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[57] Kawakami M, Hattori M, Ohashi W, Fujimori T, Hattori K, Takebe M, et al. Role of g protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in oxidative and nitrosative stress-related neurohistopathological changes in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Neurochem. 2018;145(6):474–88. 10.1111/jnc.14329.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[58] Pan T, Sun S, Chen Y, Tian R, Chen E, Tan R, et al. Immune effects of PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α-regulated glycolysis in polymorphonuclear neutrophils during sepsis. Crit Care. 2022;26(1):29.10.1186/s13054-022-03893-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[59] Wan P, Tan X, Xiang Y, Tong H, Yu M. PI3K/AKT and cd40l signaling regulate platelet activation and endothelial cell damage in sepsis. Inflammation. 2018;41(5):1815–24. 10.1007/s10753-018-0824-5.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[60] Zhang L, Li B, Li W, Jiang J, Chen W, Yang H, et al. Mir-107 attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial injury by targeting pten and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Tissues Organs. 2023;212(6):523–34. 10.1159/000525476.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[61] Sun LJ, Qiao W, Xiao YJ, Cui L, Wang X, Ren WD. Naringin mitigates myocardial strain and the inflammatory response in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction through regulation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;75:105782. 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105782.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[62] Hassan D, Menges CW, Testa JR, Bellacosa A. AKT kinases as therapeutic targets. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43(1):313.10.1186/s13046-024-03207-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[63] Wang N, Wang M. Dexmedetomidine suppresses sevoflurane anesthesia-induced neuroinflammation through activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019;19(1):134.10.1186/s12871-019-0808-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[64] Tang G, Yang H, Chen J, Shi M, Ge L, Ge X, et al. Metformin ameliorates sepsis-induced brain injury by inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):97977–89.10.18632/oncotarget.20105Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[65] Li L, Jiang W, Yu B, Liang H, Mao S, Hu X, et al. Quercetin improves cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by promoting microglia/macrophages m2 polarization via regulating PI3K/AKT/NF-κb signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;168:115653. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115653.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[66] Tian Y, Liu B, Li Y, Zhang Y, Shao J, Wu P, et al. Activation of rarα receptor attenuates neuroinflammation after sah via promoting m1-to-m2 phenotypic polarization of microglia and regulating MAFB/MSR1/PI3K-AKT/NF-κb pathway. Front Immunol. 2022;13:839796.10.3389/fimmu.2022.839796Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[67] Li T, Liu T, Chen X, Li L, Feng M, Zhang Y, et al. Microglia induce the transformation of a1/a2 reactive astrocytes via the CXCR7/PI3K/AKT pathway in chronic post-surgical pain. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):211.10.1186/s12974-020-01891-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[68] Chu E, Mychasiuk R, Hibbs ML, Semple BD. Dysregulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in microglia: shaping chronic neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):276.10.1186/s12974-021-02325-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[69] Yu Y, Shen Q, Lai Y, Park SY, Ou X, Lin D, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in microglial cells. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:386.10.3389/fphar.2018.00386Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[70] Liu B, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Liu M, Zhang C, Zhao Y, et al. Ω-3 dpa protected neurons from neuroinflammation by balancing microglia m1/m2 polarizations through inhibiting Nf-κb/mapk p38 signaling and activating neuron-BDNF-PI3K/AKT pathways. Mar Drugs. 2021;19(11):587.10.3390/md19110587Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[71] Saw G, Krishna K, Gupta N, Soong TW, Mallilankaraman K, Sajikumar S, et al. Epigenetic regulation of microglial phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway involved in long-term potentiation and synaptic plasticity in rats. Glia. 2020;68(3):656–69.10.1002/glia.23748Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[72] Lu R, Zhang L, Wang H, Li M, Feng W, Zheng X. Echinacoside exerts antidepressant-like effects through enhancing BDNF-CREB pathway and inhibiting neuroinflammation via regulating microglia m1/m2 polarization and jak1/stat3 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:993483.10.3389/fphar.2022.993483Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[73] Ye ZY, Xing HY, Wang B, Liu M, Lv PY. Dl-3-n-butylphthalide protects the blood–brain barrier against ischemia/hypoxia injury via upregulation of tight junction proteins. Chin Med J. 2019;132(11):1344–53.10.1097/CM9.0000000000000232Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[74] Zhao X, Zeng H, Lei L, Tong X, Yang L, Yang Y, et al. Tight junctions and their regulation by non-coding rnas. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(3):712–27.10.7150/ijbs.45885Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[75] Chen J, Zhang X, Liu X, Zhang C, Shang W, Xue J, et al. Ginsenoside rg1 promotes cerebral angiogenesis via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in ischemic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;856:172418. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172418.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[76] Wang HJ, Ran HF, Yin Y, Xu XG, Jiang BX, Yu SQ, et al. Catalpol improves impaired neurovascular unit in ischemic stroke rats via enhancing VEGF-PI3K/AKT and VEGF-MEK1/2/ERK1/2 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(7):1670–85.10.1038/s41401-021-00803-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[77] Nan W, He Y, Wang S, Zhang Y. Molecular mechanism of ve-cadherin in regulating endothelial cell behaviour during angiogenesis. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1234104.10.3389/fphys.2023.1234104Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[78] Zhi M, Huang J, Jin X. Clinical value of serum neuron-specific enolase in sepsis-associated encephalopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev. 2024;13(1):191.10.1186/s13643-024-02583-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[79] Gong Z, Lao D, Wu Y, Li T, Lv S, Mo X, et al. Inhibiting PI3K/AKT- signaling pathway improves neurobehavior changes in anti-nmdar encephalitis mice by ameliorating blood–brain barrier disruption and neuronal damage. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023;43(7):3623–37.10.1007/s10571-023-01371-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[80] Zhang Q, Yao M, Qi J, Song R, Wang L, Li J, et al. Puerarin inhibited oxidative stress and alleviated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through PI3K/AKT/NRF2 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1134380.10.3389/fphar.2023.1134380Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[81] Fedder-Semmes KN, Appel B. The AKT-mTOR pathway drives myelin sheath growth by regulating cap-dependent translation. J Neurosci. 2021;41(41):8532–44.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0783-21.2021Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[82] Yoshii A, Constantine-Paton M. Postsynaptic localization of psd-95 is regulated by all three pathways downstream of trkb signaling. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2014;6:6.10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00006Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[83] Udoh UG, Bruno JR, Osborn PO, Pratt KG. Serotonin strengthens a developing glutamatergic synapse through a pi3k-dependent mechanism. J Neurosci. 2024;44(6):e1260232023.10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1260-23.2023Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[84] Gong GQ, Bilanges B, Allsop B, Masson GR, Roberton V, Askwith T, et al. A small-molecule pi3kα activator for cardioprotection and neuroregeneration. Nature. 2023;618(7963):159–68.10.1038/s41586-023-05972-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[85] Wallroth A, Koch PA, Marat AL, Krause E, Haucke V. Protein kinase n controls a lysosomal lipid switch to facilitate nutrient signalling via mtorc1. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(9):1093–101. 10.1038/s41556-019-0377-3.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[86] Wang L, Zhang L. Protein kinase N2 reduces hydrogen peroxide-induced damage and apoptosis in pc12 cells by antioxidative stress and activation of the mtor pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2483669.10.1155/2022/2483669Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[87] Baffi TR, Lordén G, Wozniak JM, Feichtner A, Yeung W, Kornev AP, et al. Mtorc2 controls the activity of PKC and AKT by phosphorylating a conserved tor interaction motif. Sci Signal. 2021;14(678):eabe4509.10.1126/scisignal.abe4509Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[88] Gao Q, Hernandes MS. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and blood–brain barrier dysfunction. Inflammation. 2021;44(6):2143–50.10.1007/s10753-021-01501-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[89] Bai Y, Li L, Dong B, Ma W, Chen H, Yu Y. Phosphorylation-mediated pi3k-art signalling pathway as a therapeutic mechanism in the hydrogen-induced alleviation of brain injury in septic mice. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26(22):5713–27.10.1111/jcmm.17568Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[90] Liu A, Zhu Y, Chen W, Merlino G, Yu Y. Pten dual lipid- and protein-phosphatase function in tumor progression. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(15):3666.10.3390/cancers14153666Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[91] Li C, Yu T, Li W, Gong L, Shi J, Liu H, et al. Pink1 deficiency with Ca(2+) changes in the hippocampus exacerbates septic encephalopathy in mice. Chem Biol Interact. 2023;374:110413. 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110413.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[92] Liu L, Zhang J, Han Y, Liu D. The mechanism of girdin in degenerative brain disease caused by high glucose stimulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:892897.10.3389/fendo.2022.892897Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[93] Enomoto A, Ping J. Takahashi MGirdin, a novel actin-binding protein, and its family of proteins possess versatile functions in the akt and wnt signaling pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1086:169–84. 10.1196/annals.1377.016.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[94] Hu JT, Li Y, Yu B, Gao GJ, Zhou T, Li S. Girdin/giv is upregulated by cyclic tension, propagates mechanical signal transduction, and is required for the cellular proliferation and migration of mg-63 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(2):493–9. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.165.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[95] Cao M, Tan X, Jin W, Zheng H, Xu W, Rui Y, et al. Upregulation of ras homolog enriched in the brain (rheb) in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation. Neurochem Int. 2013;62(4):406–17. 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.01.025.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[96] Deng L, Chen L, Zhao L, Xu Y, Peng X, Wang X, et al. Ubiquitination of rheb governs growth factor-induced mtorc1 activation. Cell Res. 2019;29(2):136–50.10.1038/s41422-018-0120-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[97] Jiang J, Zhang L, Zou J, Liu J, Yang J, Jiang Q, et al. Phosphorylated s6k1 and 4e-bp1 play different roles in constitutively active rheb-mediated retinal ganglion cell survival and axon regeneration after optic nerve injury. Neural Regener Res. 2023;18(11):2526–34.10.4103/1673-5374.371372Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[98] Brenner CM, Choudhary M, McCormick MG, Cheung D, Landesberg GP, Wang JF, et al. Bag3: nature’s quintessential multi-functional protein functions as a ubiquitous intra-cellular glue. Cells. 2023;12(6):937.10.3390/cells12060937Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[99] Ashare A, Nymon AB, Doerschug KC, Morrison JM, Monick MM, Hunninghake GW. Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves survival in sepsis via enhanced hepatic bacterial clearance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178(2):149–57.10.1164/rccm.200709-1400OCSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[100] Xu L, Zhang W, Sun R, Liu J, Hong J, Li Q, et al. Igf-1 may predict the severity and outcome of patients with sepsis and be associated with microrna-1 level changes. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):797–804.10.3892/etm.2017.4553Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[101] Jin W. Regulation of BDNF-TRKB signaling and potential therapeutic strategies for parkinson’s disease. J Clin Med. 2020;9(1):257.10.3390/jcm9010257Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[102] Hua Z, Gu X, Dong Y, Tan F, Liu Z, Thiele CJ, et al. PI3K and MAPK pathways mediate the BDNF/TRKB-increased metastasis in neuroblastoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(12):16227–36.10.1007/s13277-016-5433-zSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[103] Hou D, Liao H, Hao S, Liu R, Huang H, Duan C. Curcumin simultaneously improves mitochondrial dynamics and myocardial cell bioenergy after sepsis via the sirt1-drp1/pgc-1α pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(7):e28501.10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28501Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[104] Owjfard M, Rahimian Z, Karimi F, Borhani-Haghighi A, Mallahzadeh A. A comprehensive review on the neuroprotective potential of resveratrol in ischemic stroke. Heliyon. 2024;10(14):e34121.10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34121Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[105] Sun P, Yang Y, Yang L, Qian Y, Liang M, Chen H, et al. Quercetin protects blood–brain barrier integrity via the PI3K/AKT/ERK signaling pathway in a mouse model of meningitis induced by glaesserella parasuis. Biomolecules. 2024;14(6):696.10.3390/biom14060696Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[106] Zhang B, Wang Y, Li H, Xiong R, Zhao Z, Chu X, et al. Neuroprotective effects of salidroside through PI3K/AKT pathway activation in Alzheimer’s disease models. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2016;10:1335–43.10.2147/DDDT.S99958Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[107] Sharma R, Mehan S, Khan Z, Das Gupta G, Narula AS. Therapeutic potential of oleanolic acid in modulation of pi3k/akt/mtor/stat-3/gsk-3β signaling pathways and neuroprotection against methylmercury-induced neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int. 2024;180:105876. 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105876.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[108] Ren ZX, Zhao YF, Cao T, Zhen XC. Dihydromyricetin protects neurons in an mptp-induced model of Parkinson’s disease by suppressing glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37(10):1315–24.10.1038/aps.2016.42Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[109] Xiao CL, Yin WC, Zhong YC, Luo JQ, Liu LL, Liu WY, et al. The role of PI3K/AKT signalling pathway in spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;156:113881. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113881.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[110] Khezri MR, Jafari R, Yousefi K, Zolbanin NM. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer: molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic interventions. Exp Mol Pathol. 2022;127:104787. 10.1016/j.yexmp.2022.104787.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[111] He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS, Xu WW, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):425.10.1038/s41392-021-00828-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[112] Bird ST, Tian F, Flowers N, Przepiorka D, Wang R, Jung TH, et al. Idelalisib for treatment of relapsed follicular lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a comparison of treatment outcomes in clinical trial participants vs medicare beneficiaries. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6(2):248–54.10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3994Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[113] Blair HA. Duvelisib: first global approval. Drugs. 2018;78(17):1847–53. 10.1007/s40265-018-1013-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[114] Rusquec P, Blonz C, Frenel JS, Campone M. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in estrogen-receptor positive her2 negative advanced breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020;12:1758835920940939.10.1177/1758835920940939Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[115] Hedayati N, Safari MH, Milasi YE, Kahkesh S, Farahani N, Khoshnazar SM, et al. Modulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway by resveratrol in cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunity. Discover Oncol. 2025;16(1):669.10.1007/s12672-025-02471-wSearch in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[116] Bai Y, Mi W, Meng X, Dong B, Jiang Y, Lu Y, et al. Hydrogen alleviated cognitive impairment and blood‒brain barrier damage in sepsis-associated encephalopathy by regulating abc efflux transporters in a pparα-dependent manner. BMC Neurosci. 2023;24(1):37.10.1186/s12868-023-00795-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[117] Chen JY. Research progress on the mechanisms of resveratrol in the prevention and treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Adv Clin Med. 2024;14(3):228–33.10.12677/ACM.2024.143689Search in Google Scholar
[118] Wright B, King S, Suphioglu C. The importance of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(21):11638.10.3390/ijms252111638Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[119] Fakhri S, Iranpanah A, Gravandi MM, Moradi SZ, Ranjbari M, Majnooni MB, et al. Natural products attenuate PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway: a promising strategy in regulating neurodegeneration. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153664. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153664.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[120] Wiegman CH, Li F, Ryffel B, Togbe D, Chung KF. Oxidative stress in ozone-induced chronic lung inflammation and emphysema: a facet of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1957.10.3389/fimmu.2020.01957Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms

