Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role and underlying mechanisms of colony-stimulating factor 2 (CSF2) in the progression of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC).
Methods
Transcriptomic and clinical data from The Cancer Genome Atlas were analyzed to assess the correlation between CSF2 expression, clinicopathological features, and patient prognosis. A neutrophil–tumor co-culture system was established to examine the effects of CSF2 on neutrophil polarization, tumor cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and autophagy. Protein expression was evaluated by flow cytometry, Western blot, and immunofluorescence. PD-L1 knockout and autophagy inhibitors (3-methyladenine and chloroquine) were used to explore regulatory mechanisms.
Results
CSF2 expression was significantly upregulated in KIRC tissues and was positively associated with advanced tumor stage and poor prognosis. In vitro, CSF2 promoted neutrophil polarization toward the tumor-supportive N2 phenotype and enhanced the proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells while inhibiting apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production. Additionally, CSF2 upregulated PD-L1 expression in tumor cells and activated autophagy by increasing LC-3, Beclin1, and ATG7 levels. These effects were reversed by PD-L1 knockout or treatment with the autophagy inhibitor 3-methyladenine.
Conclusion
CSF2 promotes KIRC progression through PD-L1–mediated neutrophil polarization and autophagy activation, representing a potential therapeutic target.
1 Introduction
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is one of the most prevalent tumors of the urinary system, accounting for approximately 3% of all adult malignancies and over 80% of kidney tumors, with kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) being the predominant histological subtype [1]. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), also known as CSF2, is a key growth factor in the hematopoietic system that enhances the body’s ability to kill tumor cells by regulating the function of antigen-presenting cells [2]. However, the expression levels and prognostic significance of CSF2 vary across solid malignancies and remain controversial [3,4]. Recent studies have identified CSF2 as a key gene associated with prognosis and immune regulation in KIRC. It was included in a nine-gene apoptosis-related prognostic signature with strong predictive power for overall survival [5]. Moreover, CSF2 was also part of an immune-related gene signature that predicted immunotherapeutic efficacy and reflected the tumor immune microenvironment, underscoring its value in personalized therapy [6]. Functional analyses further suggest that CSF2 inhibits tumor cell proliferation, infiltration, and migration, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target [7]. Studies have shown that elevated CSF2 levels in several malignancies have been associated with poor prognosis [8,9]. Chronic inflammation is a well-established driver of tumorigenesis and progression, influencing tumor development, invasion, metastasis, and therapy response [10,11]. Moreover, tumor-infiltrating neutrophils play a key role in renal cancer progression, lung metastasis, and angiogenesis [12]. Recent large-scale informatics studies have highlighted a global shift in oncological research focus toward immunotherapy, particularly neoadjuvant strategies, revealing emerging interest in biomarkers, tumor microenvironment, and immune checkpoint regulation as pivotal determinants of therapeutic outcomes [13].
The tumor microenvironment (TME) of RCC involves complex immune cell infiltration, including T cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, which together shape tumor progression and immune response. T cells exhibit stage-specific infiltration patterns, with CD4+ peaking in Stage 3 and CD8+ increasing through Stage 4, reflecting their dual role in surveillance and progression [14]. Tumor-associated macrophages, particularly M2-polarized subtypes, promote immunosuppression, angiogenesis, and invasion [15]. Neutrophils are increasingly recognized for their pro-tumor roles, with high neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios linked to poor prognosis and increased infiltration observed in tumors post-immunotherapy, suggesting a role in resistance [16,17]. Neutrophils and macrophages (particularly the M2 subtype) work synergistically in this environment, promoting an immunosuppressive milieu that aids tumor escape from immune surveillance [18]. Therefore, the TME in RCC is complex, involving various immune cells that both support tumor progression and pose challenges for immunotherapy. Neutrophils play a significant role in the TME of RCC, where their polarization into pro-tumor N2 phenotypes promotes tumor progression and immune suppression. In KIRC, neutrophils are recruited by chemokines such as CXCL2, which not only mediate their infiltration but also drive their polarization toward an immunosuppressive N2 phenotype, promoting angiogenesis, immune evasion, and tumor progression [19]. Moreover, interactions between neutrophils and M2 macrophages further amplify immunosuppression and support tumor growth [20]. These findings suggest that targeting neutrophil polarization could be a potential strategy to improve RCC treatment outcomes.
Studies suggest that programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), a key immune checkpoint protein, is involved in this process by regulating neutrophil polarization. For instance, neutrophil extracellular traps ejected by activated neutrophils exert immunosuppressive functions via programmed death 1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 [21]. Autophagy, a cellular process responsible for degrading and recycling cellular components, is intricately linked to neutrophil function and polarization. Autophagy in neutrophils regulates their survival, activation, and polarization. It plays a pivotal role in the N2 polarization of neutrophils by modulating inflammatory responses and metabolic pathways. Studies have shown that autophagy in neutrophils can enhance their survival and pro-tumor functions by facilitating the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are essential for their antimicrobial activity and polarization [22]. Additionally, autophagy-induced neutrophils contribute to cancer progression by increasing the secretion of inflammatory factors and promoting tumor cell migration [23]. Despite these findings, the specific role of CSF2 in modulating neutrophil polarization within the renal cancer microenvironment remains unclear. Building on these insights, we hypothesize that CSF2 may induce N2 polarization of neutrophils through the PD-L1 pathway, thereby driving tumor progression in RCC. By enhancing neutrophil polarization and promoting an immunosuppressive environment, CSF2 could potentially contribute to immune evasion and cancer progression. This study aims to investigate the role of CSF2 in neutrophil polarization in RCC, with the potential to uncover novel therapeutic targets. The significance of this research lies in its potential to elucidate key mechanisms of tumor progression and metastasis and to support the development of innovative immunotherapeutic strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Bioinformatic analysis
Transcriptomic data of KIRC were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA, https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov; 202208). RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data processed using the STAR pipeline were downloaded in fragments per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads (FPKM) format. FPKM values were converted to transcripts per million (TPM) for cross-sample normalization. The dataset comprised 613 tumors and 72 adjacent normal tissue samples. Clinical data were available for 537 patients, and clinical annotations were linked to all 613 RNA-seq samples. To ensure sample independence, nine duplicate RNA-seq samples from the same patients were excluded. Samples lacking clinical data or classified as technical duplicates were also removed to enhance the reliability of statistical inference. Gene expression data were log2-transformed [log2(TPM + 1)] to normalize distributions and reduce heteroscedasticity. CSF2 expression (ENSG00000164400.6) was extracted for downstream analysis. Comparisons between tumor and normal tissues were conducted using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test, implemented with the stats (v4.2.1) and car (v3.1-0) packages in R (v4.2.1). Data visualization was performed using ggplot2 (v3.4.4). Potential confounders, including sample duplication and missing clinical annotations, were rigorously addressed during data preprocessing.
2.2 Cell culture
Human renal cancer cell line 786-O (CL-0010) was procured from Wuhan Pricella Biotechnology Co., Ltd. 786-O renal cancer cell line is known for its resistance to chemotherapy and immunotherapy, making it suitable for investigating potential therapeutic strategies and understanding tumor progression and metastasis mechanisms [24]. Cells were cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (Cat. No.: D5796, Sigma-Aldrich), supplemented with 10% premium fetal bovine serum (FBS; Cat. No.: 16000044, Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Cat. No.: 15140122, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cultures were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2. Upon reaching 80% confluency, cells were harvested using 0.25% trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (Cat. No.: 25200056, Thermo Fisher Scientific) for subsequent experiments.
HL-60 cells (Cat. No.: CL-0110) were purchased from Wuhan Pricella Biotechnology Co., Ltd., and can be induced to differentiate into neutrophil-like cells. HL-60 cells are widely used as a model for neutrophil differentiation due to their ability to mimic neutrophil-like behavior upon differentiation, providing an efficient and reproducible system to study neutrophil functions [25,26]. HL-60 cells were cultured in Iscove's modified Dulbecco's medium (Procell, Wuhan, China, PM150510C) supplemented with 20% FBS and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Differentiation of HL-60 cells into neutrophil-like cells was achieved using a standard protocol involving 1.25% dimethyl sulfoxide (Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 days, as previously described [27]. Differentiation efficacy was assessed by flow cytometry using cluster of differentiation 11b (CD11b) as a neutrophil marker, achieving an 80% CD11b+ population [28]. After differentiation, neutrophil-like cells were co-cultured with 786-O cells at a 1:1 ratio in medium containing 20 ng/mL CSF2 (Peprotech, Cat No.: 300-03) for 5 days at 37°C and 5% CO2.
2.3 PD-L1 knockout
To investigate the role of PD-L1 in CSF2-mediated effects, PD-L1 knockout 786-O cells were generated using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology. Cells were transfected with a PD-L1-targeting CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-401626, sgRNA sequence: GCGAGCTAGCGAGATACT) using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cat No.: L3000008) following the manufacturer’s protocol. After 48 h, cells were selected with puromycin (2 μg/mL) for 7 days. Knockout efficiency was confirmed by Western blot using an anti-PD-L1 antibody (Abcam, Cat No.: ab213524). Knockout clones were expanded and used in subsequent co-culture and functional assays under the same conditions as the wild-type cells. To assess autophagy, co-culture cells were treated with 3-methyladenine (3-MA, 5 mM, Selleck, Cat No.: S2767) to inhibit early-stage autophagy [29] and chloroquine (CQ, 10 μM, Yeasen, Cat No.: 4608) for 24 h to inhibit late-stage autophagy [30]. Untreated cells served as the negative control group (Control).
2.4 Flow cytometry analysis
Flow cytometry analysis of CD11b, PD-L1, CD54, CD86, CD163, and CD206 were assessed on neutrophil-like HL-60 cells. Cells were collected from the culture medium and washed twice with PBS to remove residual medium. Subsequently, the cells were resuspended in PBS containing 0.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma-Aldrich, Cat No.: A9418) and adjusted to a concentration of 1 × 106 cells/mL. Cells were incubated separately with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated CD11b antibody (BioLegend, Cat No.: 101206), phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated PD-L1 antibody (BD Biosciences, Cat No.: 558065), APC-conjugated CD54 (BioLegend, Cat No.: 353108), FITC-conjugated CD86 (BioLegend, Cat No.: 305404), PE-conjugated CD163 (BioLegend, Cat No.: 333606), APC-conjugated CD206 (BioLegend, Cat No.: 321110) at 4°C in the dark for 30 min. For each staining condition, isotype control antibodies (FITC- or PE-conjugated, matched to the host species and subclass) were included to determine non-specific binding. Isotype-matched controls were included for each fluorochrome. For ROS detection, cells were incubated with 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA, Beyotime, Cat No.: S0033S) at a final concentration of 10 μM in serum-free medium. The cells were maintained at 37°C for 20 min in the dark with gentle agitation every 5 min. After incubation, cells were washed three times with serum-free medium to remove excess probe. The 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein fluorescence intensity was measured, reflecting intracellular ROS levels. Stained cells were analyzed using a BD FACSCalibur flow cytometer, acquiring at least 10,000 events per sample. Data analysis was performed using FlowJo software (v10, BD Biosciences).
2.5 Apoptosis detection by flow cytometry
Cells were harvested and centrifuged at 300 × g for 5 min at 4°C. For apoptosis detection, the cells were resuspended in 1× binding buffer (Cat No.: 556454, BD Biosciences) and stained with Annexin V-APC (Cat No.: 550474, BD Biosciences) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following incubation, the cells underwent a second centrifugation at 300 × g for 5 min at 4°C. Subsequently, the supernatant was discarded, and the cells were resuspended in binding buffer with the addition of propidium iodide (PI) solution (Cat No.: P4864, Sigma-Aldrich) to a final concentration of 5 µg/mL. The stained cells were then transferred to flow cytometry tubes and analyzed using a BD FACSCanto II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences). Data acquisition and analysis were conducted using FlowJo software, allowing the quantification of apoptotic cells by distinguishing Annexin V-positive/PI-negative (early apoptosis) from Annexin V-positive/PI-positive (late apoptosis) populations.
2.6 CCK-8 assay
During the co-culture period, cell proliferation was assessed daily using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Dojindo, Cat No.: CK04). On days 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 of culture, 10 µL of CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, followed by incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 2 h. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices, SpectraMax M5) to quantify cell proliferation.
2.7 Transwell assay
Cell migration was assessed using Transwell chambers (Corning, Cat No.: 3422). Serum-free medium (100 µL) was added to the upper chamber, and 150,000 cells in 100 µL were seeded. The lower chamber contained 600 µL of medium with 25% FBS as a chemoattractant. Subsequently, 100 µL of the cell suspension was added to each upper chamber. The plates were then incubated in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37°C for 24 h. Following incubation, the non-migrated cells were removed from the upper surface of the membrane using a cotton swab. The migrated cells on the lower surface were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (Cat No.: 158127, Sigma-Aldrich) for 15 min, stained with 0.1% crystal violet (Cat No.: C0775, Sigma-Aldrich) for 10 min, and washed three times with distilled water. The membranes were then carefully removed, mounted on slides, and imaged under a microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ti, Nikon Instruments Inc.) at 200× magnification to capture representative fields for analysis. The images were retained for quantification of cell migration.
2.8 Western blot
The protein concentrations were determined using the Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Protein Assay Kit (AP12L025, Shanghai Life-iLab Biotech Co., Ltd). Diluted protein standard solutions and BCA working solution were added to a 96-well microplate according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Absorbance values were measured at 562 nm using a microplate reader (Cat No.: 168-1000, Bio-Rad). A standard curve was constructed to calculate the protein concentrations of the samples. For Western blot analysis, equal amounts of protein (20 µg per lane) were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Cat No.: IPVH00010, Millipore). The membranes were blocked with 5% skim milk powder in Tris-buffered saline (TBS; 10 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4) at room temperature for 1 h with gentle shaking. After blocking, the membranes were washed three times with TBS containing 0.1% Tween-20 (TBST). The membranes were then incubated with PD-L1 (Abcam, ab213524, 1:1,000), TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) (Abcam, ab42121, 1:10,000), Prokineticin 2 (PK2, also known as Bv8) (Abcam, ab87360, 1:5,000), microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 (LC-3) (Abcam, ab192890, 1:2,000), Autophagy-related 7 (ATG7) (Abcam, ab52472, 1:100,000), Beclin 1 (Abcam, ab207612, 1:2,000) and GAPDH (Abcam, ab8245, 1:5,000) primary antibodies in TBST at 4°C overnight with gentle shaking. GAPDH was used as the internal loading control. The next day, the membranes were washed three times with TBST and incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (Abcam, ab6721, 1:10,000) at room temperature for 30 min with gentle shaking. Following three additional washes with TBST, the protein bands were detected using an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Cat No.: RPN2232, GE Healthcare) and imaged using a ChemiDoc MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad). Relative band intensities were normalized to GAPDH and quantified using ImageJ software (NIH, USA).
2.9 Immunofluorescence staining
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 20 min, followed by permeabilization with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat No.: T8787) for 10 min. The cells were then blocked with 1% BSA (Sigma-Aldrich, Cat No.: A2153) in PBS for 30 min to prevent nonspecific binding. Overnight incubation at 4°C was performed using a primary antibody against LC-3 (Abcam, Cat No.: ab192890) diluted at 1:200. The next day, cells were incubated with an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher, Cat No.: A11029) at a dilution of 1:500 for 1 h in the dark. Nuclei were stained for 15 min using 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Thermo Fisher, Cat No.: D1306). Finally, images were captured using a fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Eclipse Ti2) to analyze the formation of LC-3 puncta.
2.10 Statistical analysis
All experiments were independently conducted in triplicate. Data are presented as means ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test for comparisons between two groups, and one-way ANOVA for comparisons among three or more groups, with a significance threshold set at P < 0.05. Data processing and statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software (v 9.0, GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) and R software (v4.2.1). For the analysis of TCGA-KIRC RNA-seq and clinical data, gene expression values were transformed as log2(TPM + 1). Kruskal–Wallis tests were used to compare CSF2 expression across multiple pathological stages and T stages, while Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were applied for binary comparisons of N and M stages. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were constructed for overall survival analysis and compared using the log-rank test. R packages including ggplot2 (v3.4.4), stats (v4.2.1), and car (v3.1-0) were used for statistical testing and visualization.
-
Ethics approval: This study did not require ethical board approval because it did not perform human or animal trials.
-
Consent to participate: Not applicable.
-
Patient consent for publication: Not applicable for no human trials.
3 Results
3.1 High CSF2 expression correlates with disease progression and poor prognosis in KIRC
Analysis of KIRC data from TCGA revealed that CSF2 expression is significantly higher in KIRC tissues compared to adjacent normal tissues (Figure 1a). This differential expression suggests that CSF2 may play an active role in tumorigenesis or reflect alterations in the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, CSF2 expression increased progressively across pathological stages, with higher expression levels observed in advanced stages (Stage IV) compared to early stages (Stage I) (Figure 1b). This pattern implicates CSF2 in tumor progression, potentially by fostering inflammation or modulating immune responses that favor tumor growth and metastasis. Similarly, CSF2 expression increases with higher pathological T stages (T1–T4), with higher T stages showing significantly higher expression than lower T stages (Figure 1c). Since higher T stage reflects greater tumor size and invasion, this trend supports the idea that CSF2 may contribute to tumor aggressiveness, perhaps by influencing cell proliferation or extracellular matrix remodeling. Patients with lymph node metastasis (N1 stage) exhibited significantly higher CSF2 expression than those without nodal involvement (N0 stage) (Figure 1d), indicating a potential role for CSF2 in facilitating lymphatic dissemination. Additionally, CSF2 expression was significantly higher in patients with distant metastases (M1 stage) than in those without (M0 stage) (Figure 1e). Kaplan–Meier survival analysis further demonstrated that patients with high CSF2 expression had significantly shorter overall survival than those with low expression, supporting its prognostic relevance in KIRC (Figure 1f).
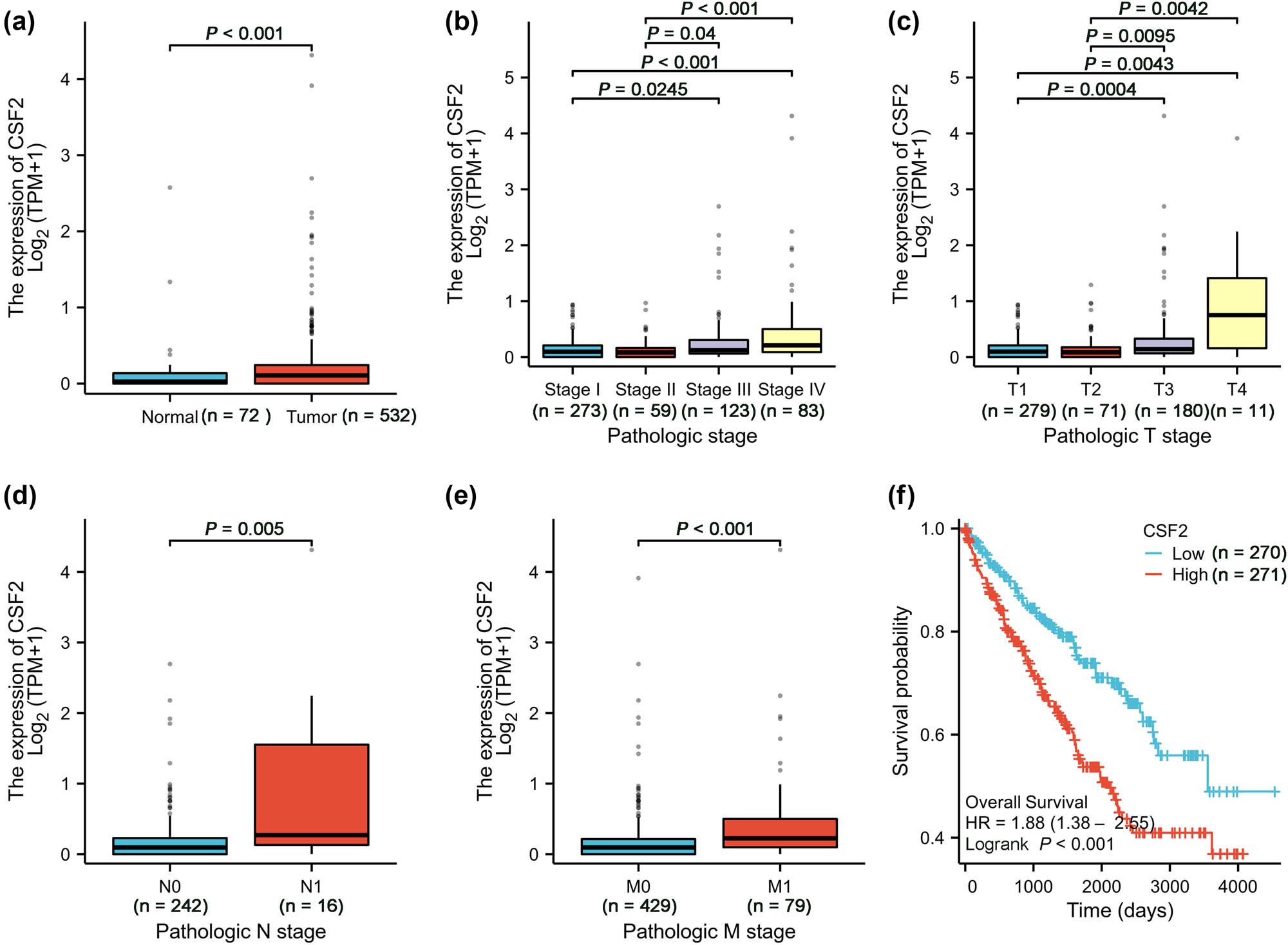
High CSF2 expression correlates with disease progression and poor prognosis in KIRC. (a) Comparison of CSF2 expression between normal and tumor tissues (Wilcoxon rank sum test). (b) CSF2 expression in different pathological stages (Stage I to Stage IV) (Kruskal–Wallis test). (c) CSF2 expression in different pathological T stages (T1 to T4) (Kruskal–Wallis test). (d) CSF2 expression in different pathological N stages (N0 and N1) (Wilcoxon rank sum test). (e) CSF2 expression in different pathological M stages (M0 and M1) (Wilcoxon rank sum test). (f) Overall survival comparison between high and low CSF2 expression groups (Log-rank test). KIRC: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.
3.2 CSF2 promotes N2 polarization of neutrophils and enhances proliferation and migration of co-cultured renal cancer cells
CSF2 treatment significantly increases CD11b expression in neutrophils compared to the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 2a). The proliferation rate of renal cancer cells co-cultured with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly higher over 5 days compared to the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 2b). The level of ROS in renal cancer cells co-cultured with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly lower than in the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 2c). Given that excessive ROS can induce tumor cell apoptosis, this reduction may reflect a protective effect provided by N2-polarized neutrophils, helping cancer cells evade oxidative stress [31]. The apoptosis rate of renal cancer cells co-cultured with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly lower than in the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 2d). This further supports the role of CSF2-induced neutrophils in creating a pro-survival microenvironment for renal cancer cells, possibly by secreting anti-apoptotic cytokines or modulating cell signaling pathways. The number of migrated renal cancer cells in co-culture with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly higher than in the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 2e). This implies that CSF2-activated neutrophils enhance tumor cell motility, potentially through remodeling of the extracellular matrix or secretion of chemotactic factors that facilitate metastasis.
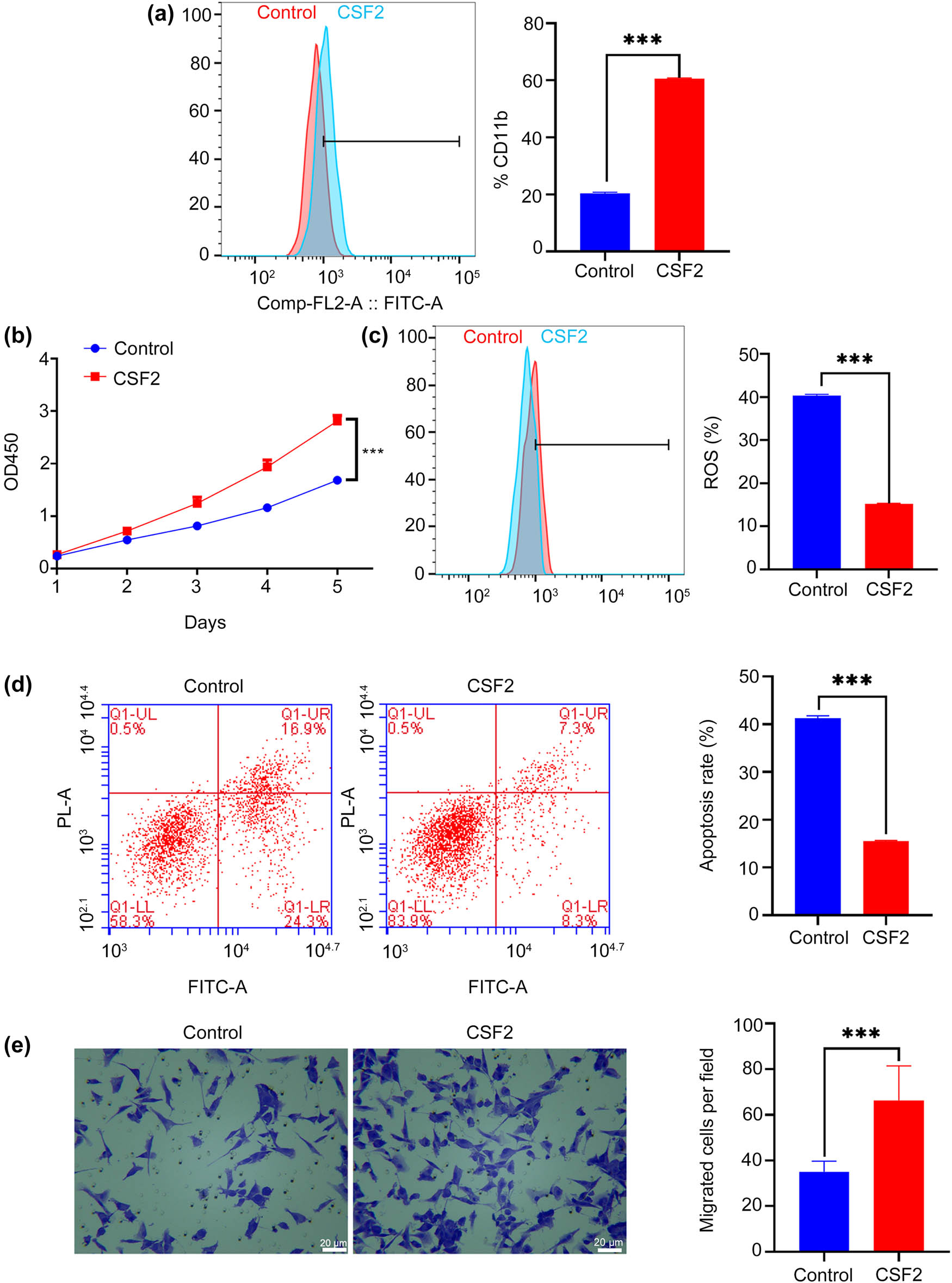
CSF2 promotes N2 polarization of neutrophils and enhances the proliferation and migration of co-cultured renal cancer cells. (a) Measurement of CD11b expression on neutrophils by flow cytometry. (b) Proliferation assay of renal cancer cells in co-culture with neutrophils. (c) Measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in renal cancer cells by flow cytometry. (d) Apoptosis assay of renal cancer cells in co-culture with neutrophils using flow cytometry. (e) Migration assay showing the number of migrated renal cancer cells in co-culture with neutrophils (200×); Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test. Compared with control group, *** P < 0.001.
3.3 CSF2-induced N2 polarization is partially mediated by tumor-derived PD-L1
To confirm the efficiency of PD-L1 knockout, Western blot analysis demonstrated that PD-L1 protein levels were almost undetectable in the PD-L1 knockout cells (Figure 3a). Flow cytometry revealed that CSF2 treatment increased N2 markers (CD163, CD206) and decreased N1 markers (CD54, CD86) in neutrophils (P < 0.001). The CD54 (high) neutrophils are a kind of reverse-transmigrated neutrophils characterized by proinflammatory phenotype [32] and CD163 and CD206 as markers of the immunosuppressive N2 phenotype [33]. when neutrophils were co-cultured with PD-L1 knockout renal cancer cells, the CSF2-induced shift toward the N2 phenotype was partially attenuated, with decreased CD163/CD206 expression and a partial recovery of CD54/CD86 levels compared to co-culture with wild-type tumor cells. In parallel, CSF2-treated neutrophils significantly reduced intracellular ROS levels in co-cultured renal cancer cells, indicating a shift toward a less oxidative, pro-survival microenvironment. Importantly, when co-cultured with PD-L1 knockout renal cancer cells, both N2 marker induction and ROS suppression were partially reversed, suggesting that tumor-derived PD-L1 is required for the full execution of the CSF2-induced immunosuppressive program in neutrophils (Figure 3b). These findings suggest a CSF2–PD-L1 axis that modulates neutrophil reprogramming and oxidative stress responses in favor of tumor survival.
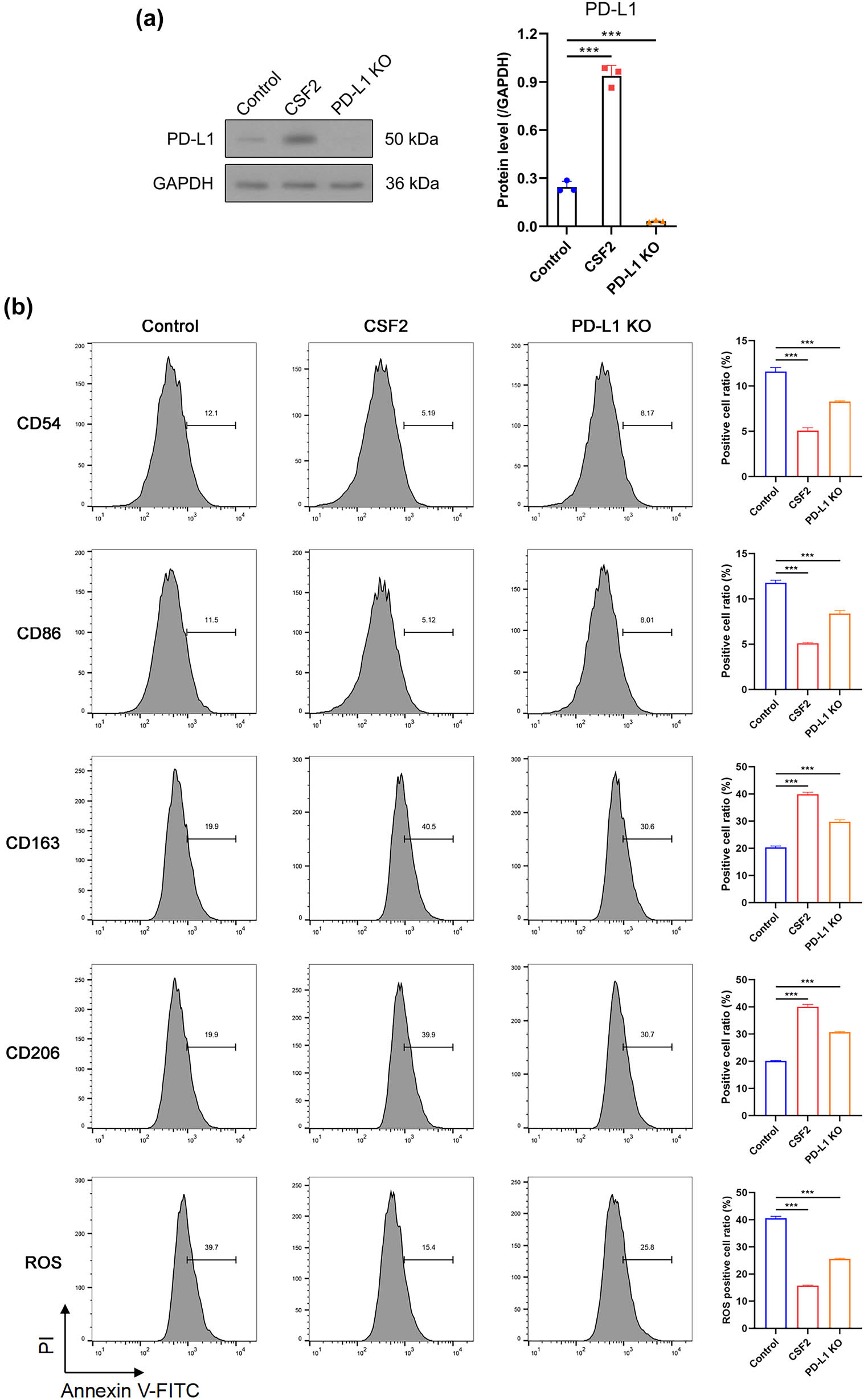
CSF2-induced N2 polarization is partially mediated by tumor-derived PD-L1. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 protein expression in renal cancer cells with or without CSF2 stimulation and PD-L1 knockout. (b) Flow cytometry analysis of neutrophil polarization markers (CD163, CD206, CD54, CD86) and intracellular ROS levels under CSF2 treatment and co-culture with PD-L1 knockout or control tumor cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA. Compared with control group, *** P < 0.001.
3.4 CSF2-treated neutrophils affect the PD-L1 pathway proteins in co-cultured renal cancer cells
Flow cytometry and Western blot analyses revealed that CSF2-treated neutrophils upregulated PD-L1 expression and downregulated TRAIL and Bv8 in co-cultured renal cancer cells (P < 0.001, Figure 4a and b). The protein levels of PD-L1 are significantly increased, while the levels of TRAIL and Bv8 are significantly decreased in renal cancer cells co-cultured with CSF2-treated neutrophils compared to the control group (P < 0.001, Figure 4b). This suggests that CSF2-primed neutrophils facilitate immune evasion by inducing PD-L1, while suppressing apoptotic and pro-angiogenic signaling pathways.
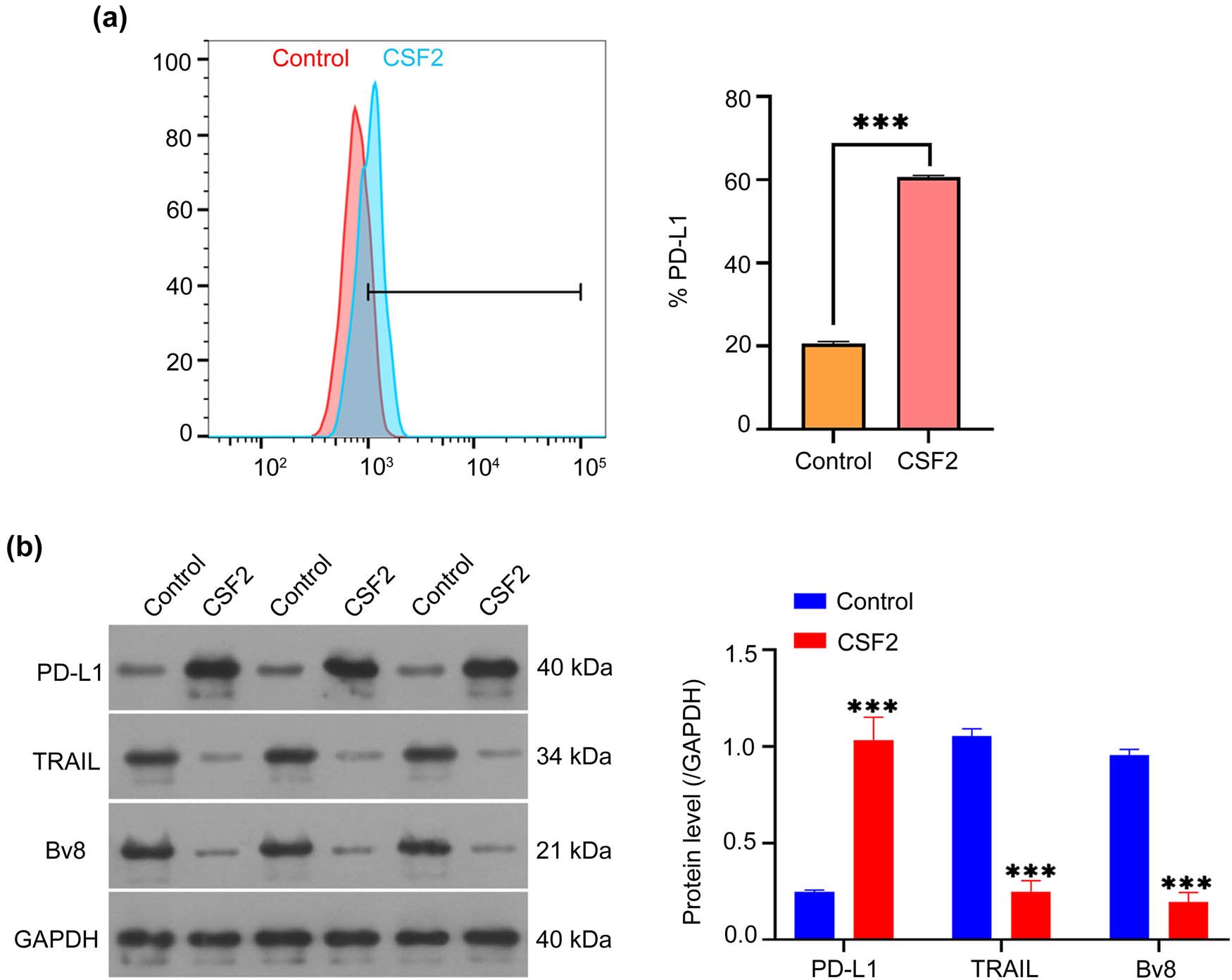
CSF2-treated neutrophils affect the PD-L1 pathway proteins in co-cultured renal cancer cells. (a) Measurement of PD-L1 expression on co-cultured renal cancer cells by flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test. Compared with the control group, *** P < 0.001. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1, TRAIL, and Bv8 protein levels in co-cultured renal cancer cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA. Compared with the control group, *** P < 0.001. PD-L1: Programmed death-ligand 1; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; Bv8: Prokineticin 2.
3.5 Autophagy activation by CSF2-treated neutrophils depends on PD-L1
Western blot analysis demonstrated that CSF2 treatment increased autophagy-related proteins LC-3 II/I, ATG7, and Beclin1 in co-cultured renal cancer cells (P < 0.001). PD-L1 knockout reversed autophagy induced by CSF2 treatment, and the expression of related proteins LC-3 II/I (P < 0.001), ATG7, and Beclin1 was significantly decreased (P < 0.05), suggesting that PD-L1 is involved in CSF2-mediated autophagy regulation (Figure 5a). Immunofluorescence confirmed increased LC-3 puncta formation, indicating enhanced autophagy (Figure 5b). These results suggest that PD-L1 mediates CSF2-driven autophagy, contributing to tumor cell survival and chemoresistance.
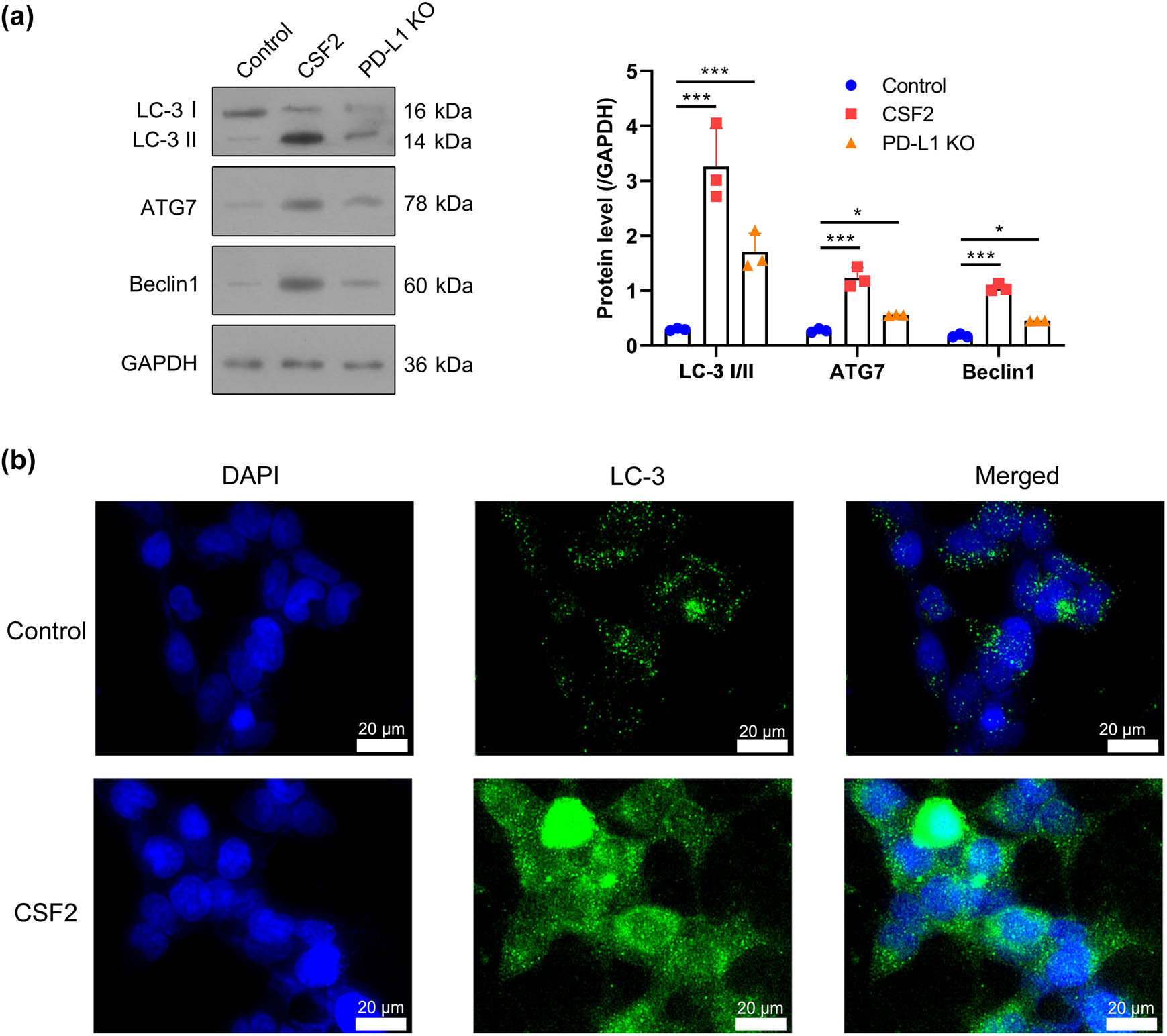
Autophagy activation by CSF2-treated neutrophils depends on PD-L1. (a) Western blot analysis of LC-3, ATG7, and Beclin1 protein levels in co-cultured renal cancer cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using one-way ANOVA. Compared with the control group, *** P < 0.001. (b) Immunofluorescence staining of LC-3 in renal cancer cells with DAPI as a nuclear counterstain. LC-3: Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3; ATG7: Autophagy-related 7; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
3.6 CSF2 promotes N2 polarization of neutrophils, and the migration-promoting effect on co-cultured renal cell carcinoma is reversed by 3-MA
CSF2 treatment significantly increases CD11b expression in neutrophils compared to the control group, and this effect is significantly reversed by 3-MA but not by CQ (P < 0.001, Figure 6a). The apoptosis rate of renal cancer cells co-cultured with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly lower than in the control group, but this effect is partially reversed by 3-MA (P < 0.001, Figure 6b). The number of migrated renal cancer cells in co-culture with CSF2-treated neutrophils is significantly higher than in the control group, and this migration-promoting effect is significantly reversed by 3-MA but not by CQ (P < 0.001, Figure 6c). These results indicate that CSF2-induced N2 polarization of neutrophils drives tumor progression through autophagy-dependent suppression of apoptosis and enhancement of migration, highlighting the critical role of autophagy in shaping an immunosuppressive niche for renal cancer metastasis. CSF2-treated neutrophils upregulate PD-L1 and suppress apoptosis-angiogenesis signaling in renal cancer cells.
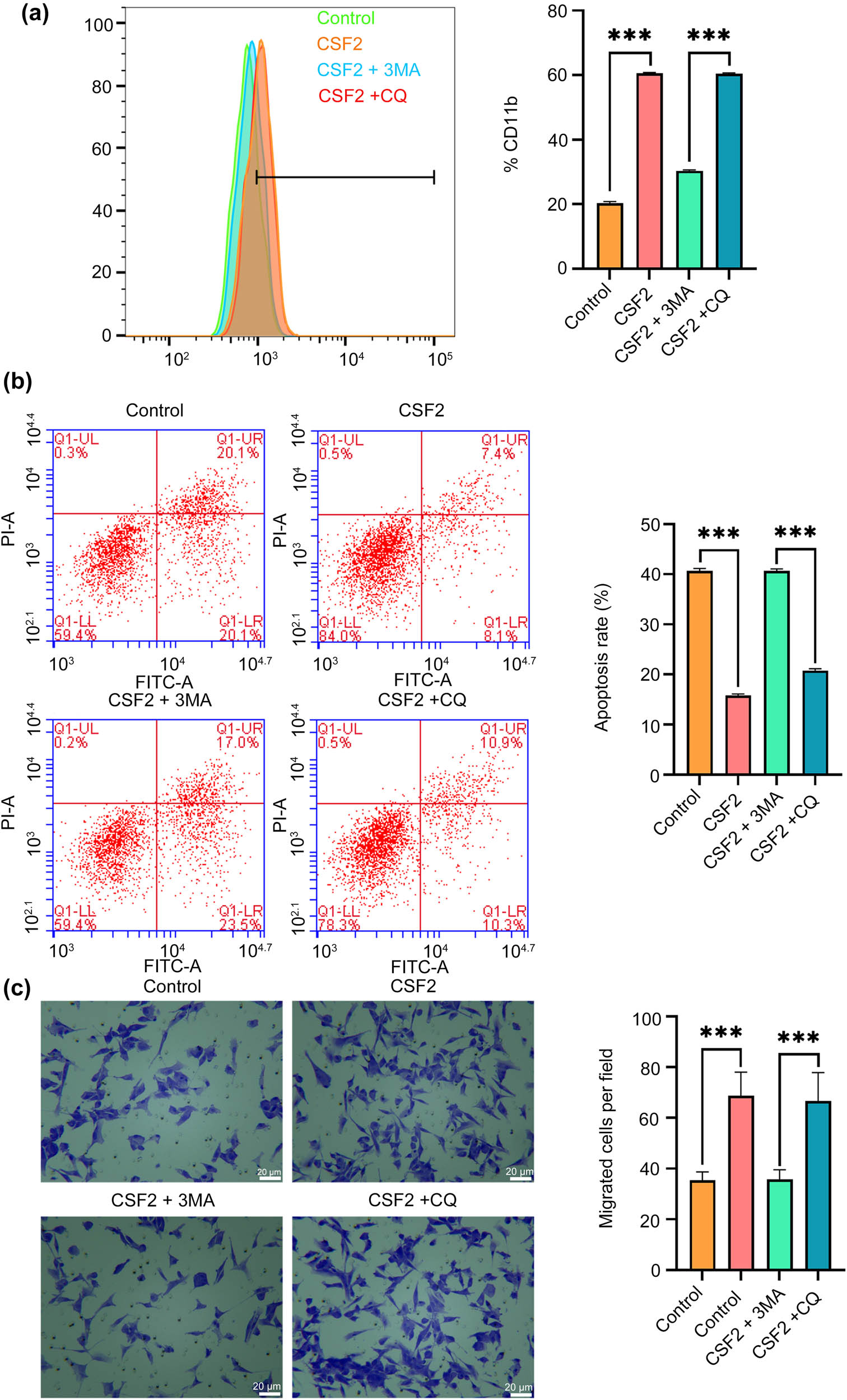
CSF2 promotes N2 polarization of neutrophils, and the migration-promoting effect on renal cell carcinoma is reversed by 3-MA. (a) Measurement of CD11b expression on neutrophils by flow cytometry. (b) Apoptosis assay of renal cancer cells in co-culture with neutrophils using flow cytometry. (c) Migration assay showing the number of migrated renal cancer cells in co-culture with neutrophils (200×). Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using Student’s t-test. Compared with the control group, *** P < 0.001. Cluster of differentiation 11b; 3-MA: 3-Methyladenine; CQ: Chloroquine.
4 Discussion
Renal cell carcinoma, a common malignant tumor of the urinary system, is difficult to detect early and is often treated surgically, but recurrence is unfortunately common [34]. Early-stage differentiation between benign and malignant renal masses is also challenging [35]. Once the disease progresses to advanced stages, systemic therapy becomes the mainstay of treatment. Nevertheless, existing immune and targeted therapies have not yielded optimal clinical outcomes, with drug resistance representing a major obstacle [36]. Although recent advancements involving probiotics, HIF-2α inhibitors, and stereotactic radiotherapy have shown promise in prolonging survival in advanced cases, the identification of novel therapeutic targets remains an urgent need [37]. Previous studies have shown that CSF2 can affect the progression of malignancy [3,38]. Initially discovered in 1977, CSF2 was identified for its role in stimulating colony formation in granulocytes and macrophages [39]. Since then, the immune function of CSF2 has been extensively studied, and its role in anti-tumor immunity is well-established in research and clinical applications [40]. However, its specific influence on the tumor microenvironment and the mechanisms through which it may promote tumor progression remain insufficiently elucidated. Building upon its reported pro-tumorigenic functions in gastric and colorectal cancers [41], this study selected CSF2 as a focal gene for investigation.
Recent studies have underscored the clinical relevance of CSF2 in KIRC, showing that its elevated expression is consistently associated with poor prognosis and an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. For instance, CSF2 was incorporated into a natural killer cell-related prognostic signature that stratifies KIRC patients by risk and predicts differential sensitivity to immune checkpoint inhibitors and chemotherapeutic agents, suggesting its potential utility in guiding personalized therapy [42]. Similarly, a lymphangiogenesis-related gene model including CSF2 was found to correlate with T-cell exhaustion and immunosuppressive cell infiltration, highlighting its role in shaping the immune microenvironment and informing immunotherapeutic response [43]. This study revealed that CSF2 expression was significantly higher in cancer tissues than in adjacent normal tissues and was positively correlated with Stage, Pathologic_T, Pathologic_N, and Pathologic_M, as well as being associated with poorer prognosis. This result is also in line with the findings of other scholars in breast cancer, head and neck cancer, bladder cancer, and other tumors [44]. These findings suggest that targeting CSF2 or its downstream pathways may enhance anti-tumor immunity and improve clinical outcomes in KIRC patients.
Previous studies have found that CSF2 facilitates tumor progression in malignancies such as bladder, prostate, and gastric cancers by promoting neovascularization within the tumor microenvironment [45–47]. This pro-angiogenic effect is frequently mediated by inflammatory immune cells [48], particularly neutrophils, which play a pivotal role in shaping the TME of tumors such as gastric cancer [49]. Neutrophils exhibit phenotypic plasticity, polarizing into either N1 (anti-tumorigenic) or N2 (pro-tumorigenic) subtypes. This study hypothesizes that CSF2 facilitates renal cancer progression through the polarization of neutrophils toward the tumor-promoting N2 phenotype.
Neutrophils interact closely with T cells to modulate immune responses in vivo [50]. For T cells, PD-1 is commonly involved in the immune function [51]. Upon binding to its ligand PD-L1, PD-1 can inhibit normal T-cell function and promote tumor growth, similar to the role of CSF2 [52]. During inflammatory responses, neutrophil-derived ROS can influence T-cell behavior [53]. ROS can also play an anti-tumor or tumor-promoting role [54]. Previous studies have found that luteolin can increase the content of ROS in glioblastoma, affect the function of endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, and then improve the level of tumor apoptosis [55]. Western blot analysis in this study revealed a significant upregulation of PD-L1 protein expression in CSF2-treated neutrophils. Flow cytometry further confirmed increased PD-L1 and decreased ROS levels, implying a tumor-suppressive role for ROS in renal cancer. The reduction in ROS also suggests a phenotypic shift from N1 to N2 neutrophils. Additional flow cytometry detected increased CD11b expression and reduced apoptosis in neutrophils following CSF2 treatment. Transwell assays indicated enhanced neutrophil migration. Immunoblotting for autophagy-related proteins – ATG7, Beclin1, and LC-3 – demonstrated that CSF2 significantly promoted autophagic activity. Notably, PD-L1 knockout reversed this effect, indicating that PD-L1 is a crucial mediator linking CSF2 signaling to autophagy induction. Combining CSF2 with autophagy inhibitors further revealed mechanistic insights: CSF2-enhanced migration was suppressed, and apoptosis was increased upon autophagy inhibition. Interestingly, 3-MA, an early-stage autophagy inhibitor, effectively blocked cell migration, whereas CQ, which targets late-stage autophagy, did not. This suggests that CSF2-driven migration relies on early autophagy events, and interruption at the initiation stage (via PI3K inhibition by 3-MA) more effectively disrupts pro-migratory signaling [29,30].
The recent advancements in AlphaFold, a deep learning-based model for protein structure prediction, have significantly transformed molecular biology and drug discovery. A recent scientometric analysis has quantitatively demonstrated the rapid growth and broad influence of AlphaFold-related research, identifying “structure prediction,” “artificial intelligence,” “drug discovery,” and “molecular dynamics” as core hotspots driving the field forward [56]. In this context, AlphaFold’s predictive capabilities may provide critical structural insights into proteins such as PD-L1, CSF2 receptor (CSF2R), and autophagy regulators (e.g., LC-3, Beclin1). For example, AlphaFold can identify key binding interfaces for drug development, model conformational changes upon ligand binding, and predict phosphorylation sites involved in protein function. Structural modeling of CSF2–CSF2R and PD-L1–autophagy protein interactions could greatly accelerate therapeutic design targeting the CSF2–PD-L1 axis in renal cancer.
However, this study has several important limitations that should be addressed in future research. First, the experiments are primarily based on in vitro cell models, lacking validation in animal models or clinical samples, making it difficult to directly translate the conclusions to clinical applications. The reliance on in vitro models also limits the ability to capture the complexity of the tumor microenvironment in vivo. Future studies should aim to incorporate animal models for in vivo validation and clinical samples to enhance the relevance and applicability of the results. Furthermore, the study lacks an in-depth exploration of the molecular mechanisms by which CSF2 modulates the tumor microenvironment, particularly its potential impact on other immune cells. While neutrophils were a focus, other immune components within the tumor microenvironment, such as T cells, macrophages, or dendritic cells, could play critical roles in the immune response [57]. Future research should consider investigating these additional immune cells to fully understand the interplay between CSF2, neutrophils, and other immune cells, and to identify potential therapeutic targets within the tumor microenvironment. Future research should also focus on increasing the sample size, incorporating animal models for in vivo validation, and further exploring the multi-cellular interactions and molecular mechanisms by which CSF2 regulates the tumor microenvironment, which may reveal new therapeutic targets.
In summary, this study confirmed that CSF2 induces N2 phenotype neutrophil polarization via the PD-L1 pathway, providing a new target and experimental basis for developing renal cancer therapies, which has significant clinical implications.
-
Funding information: This work was supported by the Key Project of Natural Science Research in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Province (No. 2023AH052009); Anhui Academic and Technical Leader Backup Candidate Project (No. 2020h213); the Key Project of Support Plan for Outstanding Young Talents in Colleges and Universities of Anhui Provincial Department of Education (No. gxyqzd2021117).
-
Author contributions: YS: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, writing – original draft. HSS: investigation, methodology, validation, supervision, writing – review & editing. YF: software, visualization, resources, writing – original draft. JFH: visualization, data curation, supervision, formal analysis. SX: funding acquisition, formal analysis, project administration, writing – review & editing.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
-
Data availability statement: The data involved in this study can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author via email.
References
[1] Incorvaia L, Madonia G, Corsini LR, Cucinella A, Brando C, Gagliardo C, et al. Challenges and advances for the treatment of renal cancer patients with brain metastases: From immunological background to upcoming clinical evidence on immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2021;163:103390. 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103390.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[2] Cox MJ, Manriquez Roman C, Tapper EE, Siegler EL, Chappell D, Durrant C, et al. GM-CSF disruption in CART cells modulates T cell activation and enhances CART cell anti-tumor activity. Leukemia. 2022;36(6):1635–45. 10.1038/s41375-022-01572-7.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[3] Rangsitratkul C, Lawson C, Bernier-Godon F, Niavarani S-R, Boudaud M, Rouleau S, et al. Intravesical immunotherapy with a GM-CSF armed oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus improves outcome in bladder cancer. Mol Ther - Oncol. 2022;24:507–21. 10.1016/j.omto.2022.01.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Luo Y, Li B, Li J, Zhang Y, Deng M, Hu C, et al. Coagulation Factor XIII subunit A is a biomarker for curative effects and prognosis in malignant solid tumors, especially non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:719085. 10.3389/fonc.2021.719085.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[5] Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhu B, Ma L, Xing Q. A novel nine apoptosis-related genes signature predicting overall survival for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and its associations with immune infiltration. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:567730. 10.3389/fmolb.2021.567730.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Gu J, Zhang X, Peng Z, Peng Z, Liao Z. A novel immune-related gene signature for predicting immunotherapy outcomes and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18922. 10.1038/s41598-023-45966-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Tu H, Hu Q, Ma Y, Huang J, Luo H, Jiang L, et al. Deciphering the tumour microenvironment of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Prognostic insights from programmed death genes using machine learning. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(13):e18524. 10.1111/jcmm.18524.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[8] Ansari KI, Bhan A, Saotome M, Tyagi A, De Kumar B, Chen C, et al. Autocrine GMCSF signaling contributes to growth of HER2+ breast leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Res. 2021;81(18):4723–35. 10.1158/0008-5472.can-21-0259.Search in Google Scholar
[9] Zhao X, Kong Y, Zhang L. Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy combined with stereotactic body radiation therapy and GM-CSF as salvage therapy in a PD-L1-negative patient with refractory metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review. Front Oncol. 2020;10:1625. 10.3389/fonc.2020.01625.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[10] Wang D, Li W, Albasha N, Griffin L, Chang H, Amaya L, et al. Long-term exposure to house dust mites accelerates lung cancer development in mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42(1):26. 10.1186/s13046-022-02587-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Fang L, Liu K, Liu C, Wang X, Ma W, Xu W, et al. Tumor accomplice: T cell exhaustion induced by chronic inflammation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:979116. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.979116.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[12] Kalaci E, Ürün Y. Nivolumab-induced immune-related neutropenia in a renal cell carcinoma patient. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2023;29(7):1797–801. 10.1177/10781552231186748.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[13] Guo SB, Hu LS, Huang WJ, Zhou ZZ, Luo HY, Tian XP. Comparative investigation of neoadjuvant immunotherapy versus adjuvant immunotherapy in perioperative patients with cancer: a global-scale, cross-sectional, and large-sample informatics study. Int J Surg. 2024;110(8):4660–71. 10.1097/js9.0000000000001479.Search in Google Scholar
[14] Hrizat AS, Lin R, Eberle-Singh J, O’neill R, Xia Y, Testa JR, et al. Tumor infiltrating T-cells and loss of expression of SWI/SNF genes in varying stages of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2025;266:155774. 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155774.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[15] Liu H, Lv Z, Zhang G, Yan Z, Bai S, Dong D, et al. Molecular understanding and clinical aspects of tumor-associated macrophages in the immunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43(1):242. 10.1186/s13046-024-03164-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Lou K, Cheng X. Prognostic value of the neutrophil‑to‑lymphocyte ratio in renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta‑analysis. Oncol Lett. 2025;29(5):231. 10.3892/ol.2025.14977.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Soupir AC, Hayes MT, Peak TC, Ospina O, Chakiryan NH, Berglund AE, et al. Increased spatial coupling of integrin and collagen IV in the immunoresistant clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma tumor microenvironment. Genome Biol. 2024;25(1):308. 10.1186/s13059-024-03435-z.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Zheng X, Tong T, Duan L, Ma Y, Lan Y, Shao Y, et al. VSIG4 induces the immunosuppressive microenvironment by promoting the infiltration of M2 macrophage and Tregs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;142(Pt A):113105. 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113105.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[19] Shen J, Wang R, Chen Y, Fang Z, Tang J, Yao J, et al. Prognostic significance and mechanisms of CXCL genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(16):7974–96. 10.18632/aging.204922.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Montemagno C, Jacquel A, Pandiani C, Rastoin O, Dawaliby R, Schmitt T, et al. Unveiling CXCR2 as a promising therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma: exploring the immunotherapeutic paradigm shift through its inhibition by RCT001. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43(1):86. 10.1186/s13046-024-02984-2.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Fang Q, Stehr AM, Naschberger E, Knopf J, Herrmann M, Stürzl M. No NETs no TIME: Crosstalk between neutrophil extracellular traps and the tumor immune microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1075260. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1075260.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] Liu J, Tao P, Su B, Zheng L, Lin Y, Zou X, et al. Interleukin-33 modulates NET formation via an autophagy-dependent manner to promote neutrophilic inflammation in cigarette smoke-exposure asthma. J Hazard Mater. 2025;487:137257. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137257.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[23] Zhang X, Shi H, Yuan X, Jiang P, Qian H, Xu W. Tumor-derived exosomes induce N2 polarization of neutrophils to promote gastric cancer cell migration. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):146. 10.1186/s12943-018-0898-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[24] Mao X, Huang W, Xue Q, Zhang X. Prognostic impact and immunotherapeutic implications of NETosis-related prognostic model in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024;150(5):278. 10.1007/s00432-024-05761-y.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[25] Hauert AB, Martinelli S, Marone C, Niggli V. Differentiated HL-60 cells are a valid model system for the analysis of human neutrophil migration and chemotaxis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2002;34(7):838–54. 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00010-9.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[26] Khachaturyan G, Holle AW, Ende K, Frey C, Schwederski HA, Eiseler T, et al. Temperature-sensitive migration dynamics in neutrophil-differentiated HL-60 cells. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7053. 10.1038/s41598-022-10858-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Bhakta SB, Lundgren SM, Sesti BN, Flores BA, Akdogan E, Collins SR, et al. Neutrophil-like cells derived from the HL-60 cell-line as a genetically-tractable model for neutrophil degranulation. PLoS One. 2024;19(2):e0297758. 10.1371/journal.pone.0297758.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Zhao J, Zhen N, Zhou Q, Lou J, Cui W, Zhang G, et al. NETs promote inflammatory injury by activating cGAS-STING pathway in acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5125. 10.3390/ijms24065125.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[29] Teper-Bamnolker P, Danieli R, Peled-Zehavi H, Belausov E, Abu-Abied M, Avin-Wittenberg T, et al. Vacuolar processing enzyme translocates to the vacuole through the autophagy pathway to induce programmed cell death. Autophagy. 2021;17(10):3109–23. 10.1080/15548627.2020.1856492.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[30] Ferreira PMP, Sousa RWR, Ferreira JRO, Militão GCG, Bezerra DP. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine in antitumor therapies based on autophagy-related mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 2021;168:105582. 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105582.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[31] Jiang T, Tang XY, Mao Y, Zhou YQ, Wang JJ, Li RM, et al. Matrix mechanics regulate the polarization state of bone marrow-derived neutrophils through the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway. Acta Biomater. 2023;168:159–73. 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.07.012.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[32] Yang L, Li H, Liu Y, Xie X, Zhang H, Niu H, et al. Increased circulating of CD54(high)CD181(low) neutrophils in myelodysplastic syndrome. Front Oncol. 2020;10:585216. 10.3389/fonc.2020.585216.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[33] Yang J, Xie Y, Xia Z, Ji S, Yang X, Yue D, et al. HucMSC-exo induced N2 polarization of neutrophils: Implications for angiogenesis and tissue restoration in wound healing. Int J Nanomed. 2024;19:3555–75. 10.2147/ijn.s458295.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[34] Song J, Liu YD, Su J, Yuan D, Sun F, Zhu J. Systematic analysis of alternative splicing signature unveils prognostic predictor for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):22753–64. 10.1002/jcp.28840.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[35] Bénard A, Podolska MJ, Czubayko F, Kutschick I, Klösch B, Jacobsen A, et al. Pleural resident macrophages and pleural IRA B cells promote efficient immunity against pneumonia by inducing early pleural space inflammation. Front Immunol. 2022;13:821480. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.821480.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[36] Cao Y, Wu Q, Lian S, Deng L. Lymphocytes infiltration and expression of PD-1 and PD-L1 in colorectal cancer between HIV-infected and Non-HIV-infected patients: A propensity score matched cohort study. Front Oncol. 2022;12:827596. 10.3389/fonc.2022.827596.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[37] Ren D, Cheng H, Wang X, Vishnoi M, Teh BS, Rostomily R, et al. Emerging treatment strategies for breast cancer brain metastasis: From translational therapeutics to real-world experience. Therap Adv Med Oncol. 2020;12:175883592093615. 10.1177/1758835920936151.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[38] Wagensveld LV, Walker C, Hahn K, Sanders J, Kruitwagen R, Aa MVD, et al. The prognostic value of tumor-stroma ratio and a newly developed computer-aided quantitative analysis of routine H&E slides in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023;rs.3.rs-3511087. 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3511087/v1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[39] Ruffolo LI, Jackson KM, Kuhlers PC, Dale BS, Figueroa Guilliani NM, Ullman NA, et al. GM-CSF drives myelopoiesis, recruitment and polarisation of tumour-associated macrophages in cholangiocarcinoma and systemic blockade facilitates antitumour immunity. Gut. 2022;71(7):1386–98. 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324109.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[40] Ding L, Dong HY, Zhou TR, Wang YH, Yan T, Li JC, et al. PD‐1/PD‐L1 inhibitors‐based treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: Mechanisms affecting efficacy and combination therapies. Cancer Med. 2021;10(18):6384–401. 10.1002/cam4.4190.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[41] Xin S, Sun X, Jin L, Li W, Liu X, Zhou L, et al. The prognostic signature and therapeutic value of phagocytic regulatory factors in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD). Front Genet. 2022;13:877278. 10.3389/fgene.2022.877278.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[42] Shi X, Yuan M, Yang Y, Wang N, Niu Y, Yang C, et al. Prognostic model for clear-cell renal cell carcinoma based on natural killer cell-related genes. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2023;21(3):e126–37. 10.1016/j.clgc.2022.11.009.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[43] Chen K, Gao M, Dong W, Liu H, Lin Y, Xie Y, et al. A novel lymphangiogenesis-related gene signature can predict prognosis and immunosuppressive microenvironment in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 2023;20(6):754–70. 10.7150/ijms.81078.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[44] Jin L, Sun Z, Liu H, Zhu X, Zhou Y, Fu B, et al. Inflammatory monocytes promote pre-engraftment syndrome and tocilizumab can therapeutically limit pathology in patients. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4137. 10.1038/s41467-021-24412-1.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[45] Chinnapaka S, Yang KS, Samadi Y, Epperly MW, Hou W, Greenberger JS, et al. Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells mitigate acute radiation syndrome by the rescue of damaged bone marrow cells from apoptosis. Stem Cell Transl Med. 2021;10(7):1095–114. 10.1002/sctm.20-0455.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[46] Ariafar A, Zareinejad M, Soltani M, Vahidi Y, Faghih Z. GM-CSF-producing lymphocytes in tumor-draining lymph nodes of patients with bladder cancer. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2021;32(1):1–7. 10.1684/ecn.2021.0462.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[47] Barqawi AB, Rodrigues Pessoa R, Crawford ED, Al-Musawi M, Macdermott T, O’donell C, et al. Boosting immune response with GM-CSF optimizes primary cryotherapy outcomes in the treatment of prostate cancer: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021;24(3):750–7. 10.1038/s41391-021-00321-8.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[48] Yin Z, Yu M, Ma T, Zhang C, Huang S, Karimzadeh MR, et al. Mechanisms underlying low-clinical responses to PD-1/PD-L1 blocking antibodies in immunotherapy of cancer: A key role of exosomal PD-L1. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(1):e001698. 10.1136/jitc-2020-001698.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[49] Ohms M, Möller S, Laskay T. An attempt to polarize human neutrophils toward N1 and N2 phenotypes in vitro. Front Immunol. 2020;11:532. 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00532.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[50] Shi YJ, Zhao QQ, Liu XS, Dong SH, E JF, Li X, et al. Toll‐like receptor 4 regulates spontaneous intestinal tumorigenesis by up‐regulating IL‐6 and GM‐CSF. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;24(1):385–97. 10.1111/jcmm.14742.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[51] Sammarco G, Varricchi G, Ferraro V, Ammendola M, De Fazio M, Altomare DF, et al. Mast cells, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human gastric cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(9):2106. 10.3390/ijms20092106.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[52] Hu P, Liu Q, Deng G, Zhang J, Liang N, Xie J, et al. Radiosensitivity nomogram based on circulating neutrophils in thoracic cancer. Future Oncol. 2019;15(7):727–37. 10.2217/fon-2018-0398.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[53] Kinouchi T, Uemura M, Wang C, Ishizuya Y, Yamamoto Y, Hayashi T, et al. Expression level of CXCL7 in peripheral blood cells is a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(12):2495–502. 10.1111/cas.13414.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[54] Nakamura K, Peng Y, Utsumi F, Tanaka H, Mizuno M, Toyokuni S, et al. Novel intraperitoneal treatment with non-thermal plasma-activated medium inhibits metastatic potential of ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6085. 10.1038/s41598-017-05620-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[55] Wang Q, Wang H, Jia Y, Pan H, Ding H. Luteolin induces apoptosis by ROS/ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in gliomablastoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;79(5):1031–41. 10.1007/s00280-017-3299-4.Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[56] Guo SB, Meng Y, Lin L, Zhou ZZ, Li HL, Tian XP, et al. Artificial intelligence alphafold model for molecular biology and drug discovery: A machine-learning-driven informatics investigation. Mol Cancer. 2024;23(1):223. 10.1186/s12943-024-02140-6.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[57] Yi M, Li T, Niu M, Mei Q, Zhao B, Chu Q, et al. Exploiting innate immunity for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):187. 10.1186/s12943-023-01885-w.Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- Luteolin alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuron injury by regulating NLRP3/IL-1β signaling
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Relationship of resting echocardiography combined with serum micronutrients to the severity of low-gradient severe aortic stenosis
- Effect of vibration on pain during subcutaneous heparin injection: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- The diagnostic performance of machine learning-based FFRCT for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
- Comparing biofeedback device vs diaphragmatic breathing for bloating relief: A randomized controlled trial
- Serum uric acid to albumin ratio and C-reactive protein as predictive biomarkers for chronic total occlusion and coronary collateral circulation quality
- Multiple organ scoring systems for predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients in the intensive care unit
- Single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis of the inner ear in gentamicin-treated mice via intraperitoneal injection
- Suppression of cathepsin B attenuates myocardial injury via limiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- Influence of sevoflurane combined with propofol anesthesia on the anesthesia effect and adverse reactions in children with acute appendicitis
- Identification of hub genes related to acute kidney injury caused by sevoflurane anesthesia and endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The value of diagnostic experience in O-RADS MRI score for ovarian-adnexal lesions
- Health education pathway for individuals with temporary enterostomies using patient journey mapping
- Serum TLR8 as a potential diagnostic biomarker of coronary heart disease
- Intraoperative temperature management and its effect on surgical outcomes in elderly patients undergoing lichtenstein unilateral inguinal hernia repair
- Immunohistochemical profiling and neuroepithelial heterogeneity in immature ovarian teratomas: a retrospective digital pathology-based study
- Associated risk factors and prevalence of human papillomavirus infection among females visiting tertiary care hospital: a cross-sectional study from Nepal
- Comparative evaluation of various disc elution methods for the detection of colistin-resistant gram-negative bacteria
- Effect of timing of cholecystectomy on weight loss after sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese individuals with cholelithiasis: a retrospective cohort study
- Causal association between ceramide levels and central precocious puberty: a mendelian randomization study
- Novel predictive model for colorectal liver metastases recurrence: a radiomics and clinical data approach
- Relationship between resident physicians’ perceived professional value and exposure to violence
- Multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes: a Mendelian randomization study of European ancestry
- Rapid pathogen identification in peritoneal dialysis effluent by MALDI-TOF MS following blood culture enrichment
- Comparison of open and percutaneous A1 pulley release in pediatric trigger thumb: a retrospective cohort study
- Impact of combined diaphragm-lung ultrasound assessment on postoperative respiratory function in patients under general anesthesia recovery
- Development and internal validation of a nomogram for predicting short-term prognosis in ICU patients with acute pyelonephritis
- The association between hypoxic burden and blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea
- Promotion of asthenozoospermia by C9orf72 through suppression of spermatogonia activity via fructose metabolism and mitophagy
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio in peripheral artery disease
- Research progress on autophagy and its roles in sepsis induced organ injury
- Neuronutrition in autism spectrum disorders
- Pumilio 2 in neural development, function, and specific neurological disorders
- Antibiotic prescribing patterns in general dental practice- a scoping review
- Clinical and medico-legal reflections on non-invasive prenatal testing
- Smartphone use and back pain: a narrative review of postural pathologies
- Targeting endothelial oxidative stress in hypertension
- Exploring links between acne and metabolic syndrome: a narrative review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Combined VAT and retroperitoneoscopy for pleural empyema due to nephro-pleuric fistula in xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
- A rare case of Opalski syndrome with a suspected multiple sclerosis etiology
- Newly diagnosed B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia demonstrating localized bone marrow infiltration exclusively in the lower extremities
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Repeat influenza incidence across two consecutive influenza seasons
- Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms

