Abstract
Objective
This study investigates the association between serum SLC31A1, a copper death-promoting factor, and clinicopathological features/prognosis in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC).
Methods
A cohort of 250 PTC patients was stratified into good (n = 205) and poor (n = 45) prognosis groups. Clinicopathological parameters (age, sex, tumor diameter, differentiation, TNM stage, thyroid exocapsular invasion, lymph node metastasis) and serum SLC31A1 levels (measured via ELISA) were analyzed. Patients were further categorized into high/low SLC31A1 expression groups based on median values. Prognostic correlations were evaluated using Kaplan–Meier survival analysis, Cox regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve assessment.
Results
Elevated serum SLC31A1 levels were significantly associated with poor prognosis, advanced TNM stages (III/IV), poor differentiation, thyroid exocapsular invasion, and lymph node metastasis. Multivariate Cox analysis identified high SLC31A1 as an independent predictor of poor prognosis (HR = 1.235, 95% CI 1.158–1.317). ROC analysis demonstrated strong predictive accuracy for SLC31A1 in prognosis assessment (AUC = 0.859).
Conclusion
High serum SLC31A1 expression correlates with aggressive clinicopathological features and independently predicts adverse outcomes in PTC patients, suggesting its potential as a prognostic biomarker for clinical stratification.
1 Introduction
Standing as the most frequently diagnosed thyroid malignancies, the incidence of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is climbing globally at an annual increase rate of 6% [1]. While PTC generally has a good prognosis, relapse and metastasis still occur in some patients [2,3], so finding new biomarkers as well as therapeutic targets is crucial to improve patient prognosis. Advances in molecular biology have led researchers to explore further mechanisms about the metastasis of PTC, aiming to uncover new diagnostic indicators and therapeutic approaches.
As a trace element necessary for body, copper plays a critical role in various biological functions, including antioxidant defense, iron homeostasis, and cell respiration [4]. However, abnormal intracellular copper levels have been linked to multiple pathological conditions, especially cancer [5,6]. Copper death (Cuproptosis) is a newly identified novel form of cell death, which leads to an increase in intracellular oxidative stress through the accumulation of copper ions, ultimately triggering cell death [7]. This newly discovered cell death mechanism has shown promising implications in cancer biology, suggesting potential therapeutic applications in oncology [8,9].
SLC31A1 is an important copper transporter that affects the absorption of dietary copper in cell membranes [10]. Research studies have shown that SLC31A1 is abnormally expressed in various cancer types, with significant implications for patient outcomes and survival rates [11,12]. For example, SLC31A1 is elevated expression in breast cancer samples and predicts poor prognosis [13,14]. Furthermore, glioma patients exhibit heightened SLC31A1 expression levels, which inversely correlate with key survival metrics including overall survival (OS), progression-free survival, and disease-specific survival. Laboratory investigations have demonstrated that SLC31A1 enhances glioma cell proliferation and migratory capabilities [15]. The role of SLC31A1 in PTC has not been specifically reported. At present, only a few studies on gene chips have reported the role of copper cell death in thyroid cancer [16–18]. However, none of these studies addressed copper-related gene expression patterns and their clinical relevance in thyroid cancer. Furthermore, the specific role of SLC31A1 and its relationship with clinicopathological features still need to be further explored in PTC.
This investigation aimed to analyze serum SLC31A1 expression in PTC patients and explore the correlation between it and clinicopathological indicators. At the same time, the effect of SLC31A1 expression level on patient prognosis was evaluated to provide a new perspective for understanding the role of copper death pathway in thyroid papillary carcinoma and explore potential diagnosis and treatment strategies, thereby advancing both our fundamental understanding of PTC biology and the development of targeted treatment strategies.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research object
This study analyzes patients who underwent thyroid surgery at our hospital from January 2017 to August 2021. Among 288 pathologically confirmed PTC cases, 30 individuals did not meet the inclusion criteria and 8 were excluded due to incomplete data, and 250 patients with PTC were finally included as research objects. Participants were divided into good prognosis group (n = 205) and poor prognosis group (n = 45). All subjects provided written informed consent after being thoroughly informed about the study objectives. This research protocol was approved by our hospital’s Ethics Committee in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki principles.
2.2 Inclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria include: (1) age ≥ 18-years old; (2) first unilateral thyroidectomy or total thyroidectomy; (3) complete clinical data; (4) thyroid ultrasound examination was performed before surgery, and PTC was confirmed by pathology after surgery; and (5) the patient or his family is informed and signs the consent form.
2.3 Exclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria include: (1) patients with thyroid disease or taking thyroid-related drugs within the past 3 months; (2) combined with malignant tumors in other parts or serious damage to the heart, brain, liver, kidney, and other vital organs; (3) those who received any antitumor therapy before admission; (4) pregnant or lactating women; and (5) incomplete clinical data.
2.4 Collect data
Baseline clinical and pathological data such as age, sex, tumor diameter, degree of differentiation (high, medium, low, and undifferentiated), lesions (single, multiple), TNM stage (stage I–II, stage III–ⅠV), thyroid exocapsular invasion, and lymph node metastasis were collected. About 5 mL of fasting elbow venous blood was drawn from each participants during morning admission and natural agglutination at room temperature for 30 min in the collection tube. After blood coagulation, the upper serum was collected and frozen at −80°C for later use after centrifugation at 2,000 rpm for 20 min.
2.5 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Serum SLC31A1 levels were determined according to ELISA kit instructions. Among them, the SLC31A1 ELISA kit (ABIN6970338) was purchased from antibodies online. All operations were performed in strict accordance with the instructions. Detection range was 0.781–50 ng/mL.
2.6 Follow-up and prognosis assessment
Post-discharge follow-up was conducted at 6-month intervals for a period of 3 years, through both outpatient visits and telephone consultations, with the final follow-up date set as August 2024. The 3-year disease-free survival (DFS) rate was calculated for all patients. Poor prognosis was defined as the occurrence of disease recurrence, metastasis, or death during the follow-up period.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis and mapping were performed using GraphPad Prism 8.01 Software (GraphPad Software Inc., USA) and SPSS 21.0 statistical software (SPSS, Inc., USA). Data normality was assessed using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Normally distributed continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared using independent-samples t-tests. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages, with comparisons made using chi-square tests. Survival analysis was conducted using Kaplan–Meier curves, with differences assessed by the log-rank test. Prognostic factors were identified through Cox regression analysis. The predictive value of serum SLC31A1 for poor prognosis was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. All statistical tests were two-tailed, with P < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
-
Informed consent: All patients involved signed the informed consent form.
-
Ethical approval: This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki principles.
3 Results
3.1 Clinical baseline characteristics of the enrolled population
This study included 250 patients with PTC as research objects, and divided them into good (n = 205) and poor (n = 45) prognosis groups based on clinical outcome. Comparative analysis of baselines characteristics (Table 1) revealed no significant differences between two groups in age, gender, BMI, and tumor diameter (all P > 0.05). However, significant differences were observed in tumor differentiation degree, lesion status, TNM stage, thyroid extracapsular invasion, and lymph node metastasis (all P < 0.05).
Clinical baseline data
| Good prognosis group (n = 205) | Poor prognosis group (n = 45) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52.55 ± 7.88 | 52.91 ± 8.29 | 0.784 |
| Gender ( n , %) | |||
| Female | 151 (73.66%) | 31 (68.89%) | 0.579 |
| Male | 54 (26.34%) | 14 (31.11%) | |
| Tumor diameter (cm) | |||
| <2 | 75 (36.59%) | 15 (33.33%) | 0.734 |
| ≥2 | 130 (63.41%) | 30 (66.67%) | |
| Degree of differentiation ( n , %) | |||
| High and medium differentiation | 138 (67.32%) | 19 (42.22%) | 0.002 |
| Low, undifferentiated | 67 (32.68%) | 26 (57.78%) | |
| Lesion status ( n , %) | |||
| Single | 120 (58.54%) | 18 (40.00%) | 0.031 |
| Multiple | 85 (41.46%) | 27 (60.00%) | |
| TNM staging ( n , %) | |||
| Stage I–II | 128 (62.44%) | 20 (44.44%) | 0.030 |
| Stage III–IV | 77 (37.56%) | 25 (55.56%) | |
| Thyroid exocapsular invasion ( n , %) | |||
| Yes | 65 (31.71%) | 24 (53.33%) | 0.010 |
| No | 140 (68.29%) | 21 (46.67%) | |
| Lymph node metastasis ( n , %) | |||
| Yes | 60 (29.27%) | 24 (53.33%) | 0.003 |
| No | 145 (70.73%) | 21 (46.67%) |
P < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference.
3.2 Serum SLC31A1 levels were significantly higher in patients with poor prognosis
While SLC31A1 dysregulation has been documented in various malignancies and linked to patient outcomes [11,12], its role in PTC remains largely unexplored. Therefore, we detected the serum SLC31A1 level of PTC patients by ELISA kit, and the results revealed significantly elevated serum SLC31A1 levels in patients with poor prognosis compared to those with good prognosis (P < 0.001) (Figure 1), suggesting a potential association between SLC31A1 expression and PTC progression.
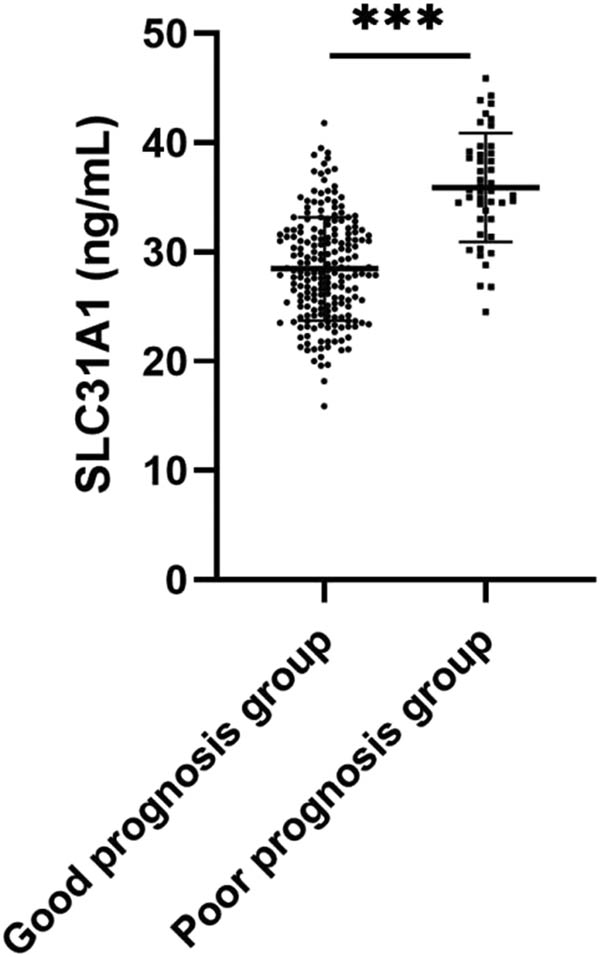
Comparison of serum SLC31A1 levels between good and poor prognosis groups. Serum SLC31A1 levels were determined by ELISA. *** indicates P < 0.001.
3.3 Relationship between serum SLC31A1 level and clinicopathological indexes and prognosis in PTC
To investigate association between serum SLC31A1 levels and clinicopathological indicators, PTC patients were stratified into low (n = 125) and high (n = 205) expression groups based on the median value of serum SLC31A1 value in PTC patients (29.65). Comparative analysis showed no significant differences in age, gender, tumor diameter, and lesion status (all P > 0.05) (Table 2). However, results demonstrated high proportions of lower differentiation, advanced TNM stage, and higher percentages of thyroid extranuclear invasion, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis (P < 0.05). These results indicate that the serum SLC31A1 level in PTC patients is related to differentiation degree, TNM stage, thyroid extranuclear invasion, lymph node metastasis, and prognosis.
Relationship between serum SLC31A1 level and clinicopathological indexes and prognosis in PTC
| Low SLC31A1 (N = 125) | High SLC31A1 (N = 125) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 52.04 ± 7.71 | 53.19 ± 8.16 | 0.252 |
| Gender ( n , %) | |||
| Female | 90 (72.00%) | 92 (73.60%) | 0.887 |
| Male | 35 (28.00%) | 33 (26.40%) | |
| Tumor diameter (cm) | |||
| <2 | 44 (35.20%) | 46 (36.80%) | 0.895 |
| ≥2 | 81 (64.80%) | 79 (63.20%) | |
| Degree of differentiation ( n , %) | |||
| High and medium differentiation | 90 (72.00%) | 67 (53.60%) | 0.004 |
| Low, undifferentiated | 35 (28.00%) | 58 (46.40%) | |
| Lesion status ( n , %) | |||
| Single | 75 (60.00%) | 63 (50.40%) | 0.162 |
| Multiple | 50 (40.00%) | 62 (49.60%) | |
| TNM staging ( n , %) | |||
| Stage I–II | 83 (66.40%) | 65 (52.00%) | 0.029 |
| Stage III–IV | 42 (33.60%) | 60 (48.00%) | |
| Thyroid exocapsular invasion ( n , %) | |||
| Yes | 36 (28.80%) | 53 (42.40%) | 0.034 |
| No | 89 (71.20%) | 72 (57.60%) | |
| Lymph node metastasis ( n , %) | |||
| Yes | 30 (24.00%) | 54 (43.20%) | 0.002 |
| No | 95 (76.00%) | 71 (56.80%) | |
| Prognosis ( n , %) | |||
| Good prognosis | 121 (96.80%) | 84 (67.20%) | <0.001 |
| Poor prognosis | 4 (3.20%) | 41 (32.80%) |
P < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference.
3.4 Elevated SLC31A1 expression predicts poor prognosis in PTC
Kaplan–Meier analysis with log-rank test revealed significantly reduced DFS in patients with high SLC31A1 expression compared to those with low expression (P < 0.0001) (Figure 2), suggesting that elevated SLC31A1 levels are associated with adverse outcomes in PTC.
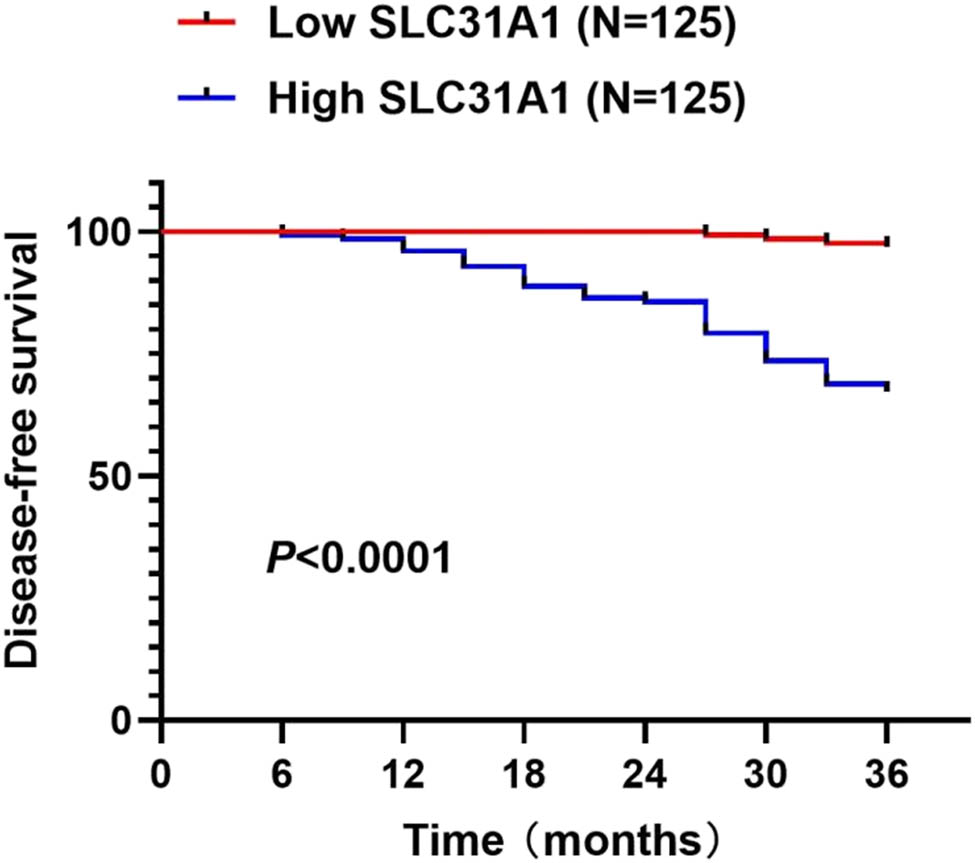
DFS according to SLC31A1 expression levels in PTC.
3.5 Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors in PTC
Follow-up time was taken as the time variable, and the prognosis of PTC patients was the dependent variable (good = 0, poor = 1). Age, sex, tumor diameter, degree of differentiation, lesions, TNM stage, thyroid extranuclear invasion, lymph node metastasis, and serum SLC31A1 level of the enrolled population in Table 1 were included as independent variables. Univariate analysis showed that the degree of differentiation, lesion status, TNM stage, thyroid epidural invasion, lymph node metastasis, and serum SLC31A1 level were significantly prognostic factors (all P < 0.05, Table 3). Subsequent multivariate analysis revealed that poor differentiation, advanced TNM stage, lymph node involvement, and elevated serum SLC31A1 levels were independent predictors of poor prognosis in PTC patients (all P < 0.05, Table 3).
Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors in PTC
| Variable | Univariable | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | |
| Age (years) | 1.006 (0.969–1.044) | 0.763 | — | — |
| Gender (n, %) | 1.231 (0.655–2.314) | 0.519 | — | — |
| Tumor diameter (cm) | 1.118 (0.602–2.078) | 0.724 | — | — |
| Degree of differentiation (n, %) | 2.627 (1.454–4.748) | 0.001 | 1.935 (1.051–3.562) | 0.034 |
| Lesion condition (n, %) | 1.991 (1.097–3.615) | 0.024 | 1.433 (0.763–2.690) | 0.263 |
| TNM staging (n, %) | 1.923 (1.068–3.463) | 0.029 | 1.869 (1.022–3.418) | 0.042 |
| Thyroid exocapsular invasion (n, %) | 2.202 (1.226–3.956) | 0.008 | 1.163 (0.630–2.148) | 0.629 |
| Lymph node metastasis (n, %) | 2.498 (1.391–4.489) | 0.002 | 1.882 (1.039–3.410) | 0.037 |
| SLC31A1 (ng/mL) | 1.266 (1.197–1.340) | 0.000 | 1.235 (1.158–1.317) | 0.000 |
P < 0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference.
3.6 Prognostic value of serum SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Based on the above results, ROC curve analysis was performed to further assess the prognostic value of serum SLC31A1 in PTC patients. The results showed that the area under ROC curve of serum SLC31A1 level in predicting poor prognosis of PTC patients was 0.859, the sensitivity was 77.78%, and the specificity was 82.44% (Figure 3). These results indicated demonstrating the robust predictive value of serum SLC31A1 for PTC outcomes.
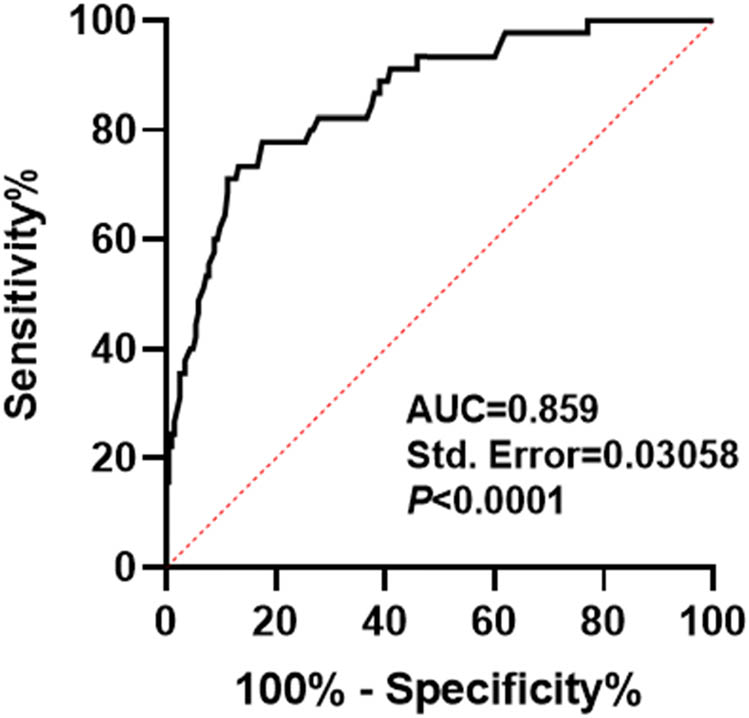
Value analysis of serum SLC31A1 in predicting poor prognosis of PTC patients.
4 Discussion
Although PTC is generally considered an inert tumor with a relatively low disease-specific mortality rate, the incidence of local recurrence and distant metastasis is still high, which has a significant impact on patient survival [19,20]. Therefore, the identification of biomarkers related to clinicopathological features and prognosis is of vital significance for optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient prognosis.
SLC31A1 is a major copper transporter, and its high expression may lead to the increase of intracellular copper ion levels, which may affect multiple biological processes, including oxidative stress, DNA damage repair, and apoptosis [11,21]. The elevated intracellular copper ion level caused by high SLC31A1 expression may promote the development of PTC through several mechanisms. First, copper ions can trigger oxidative stress by generating excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to DNA damage and cell death [22]. Second, copper ions can also activate a variety of signaling pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and NF-κB [23,24]. In addition, copper ions can inhibit apoptosis by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins, thus promoting the survival of tumor cells [25].
SLC31A1 has reportedly as a potential biomarker for cancer therapy and has been associated with chemical resistance in specific cancer types [26,27]. Studies have shown that SLC31A1 is significantly upregulated in multiple malignancies, correlating with decreased OS [11]. Our findings of elevated SLC31A1 expression in PTC patients with poor prognosis align with these observations, suggesting its potential utility as a prognostic indicator in PTC.
Analysis of clinicopathological features revealed that elevated SLC31A1 expression significantly correlated with poor differentiation, advanced TNM stage, extrathyroidal extension, and lymph node involvement, suggesting its role in tumor aggressiveness and metastatic potential. These findings suggest that SLC31A1 may influence prognosis by promoting the aggressiveness and metastasis of cancer cells in PTC. Survival analysis demonstrated reduced DFS in patients with high SLC31A1 expression. Multivariate Cox regression confirmed SLC31A1 as an independent prognostic factor, consistent with previous findings of its potential utility as a prognostic biomarker across multiple malignancies [11].
The high expression of SLC31A1 not only indicates a poor prognosis in PTC, but its copper transport function also suggests potential therapeutic value. Although this study did not involve therapeutic validation, multiple preclinical studies across cancer types have provided theoretical support for SLC31A1-targeted strategies. For example, in osteosarcoma, silencing SLC31A1 via siRNA reverses cisplatin resistance by reducing copper ion uptake [27]. Zinc ions can indirectly inhibit copper transport function by competitively binding to the copper ion-binding domain of SLC31A1. This ion competition mechanism has been verified in enterocytes [28]. In addition, ROS-responsive nanoparticles loaded with elesclomol and copper ions can serve as a targeted drug delivery system, enabling specific release of the drugs at SLC31A1 highly expressed tumor sites. This approach enhances antitumor effects by synergistically inducing copper death and immunogenic cell death [9], providing a technical reference for the precise treatment of PTC. Although the aforementioned studies have not been directly validated in PTC, the SLC31A1-dependent copper metabolism mechanism has revealed cross-cancer commonality. Subsequent research may focus on the following directions: in PTC cell lines (such as TPC-1, K1), SLC31A1 perform knockdown or overexpression to detect intracellular copper ion concentration, ROS levels, phosphorylation status of signaling pathways, and expression of apoptosis-related proteins (such as Bcl-2, Bax); reverse phenotypes using copper chelators (such as tetrathiomolybdate) to confirm copper metabolism dependency; construct SLC31A1-overexpressing xenograft tumor models in nude mice, and use combined SLC31A1 inhibitors with copper carriers like elesclomol to observe changes in tumor growth, metastasis, and apoptotic markers (such as Cleaved caspase-3); use immunoprecipitation to screen SLC31A1-interacting proteins (such as ATP7A) to clarify copper transport mechanisms, and employ RNA-seq technology to mine downstream antioxidant stress genes and epithelial–mesenchymal transition-related pathways. The above research will provide key experimental evidence for the transformation of SLC31A1 from a prognostic marker to a therapeutic target, promoting the development of individualized treatments for PTC.
ROC analysis demonstrated the robust prognostic utility of serum SLC31A1 in PTC. This finding provides clinicians with a new biomarker to help identify high-risk patients early and treat them accordingly. However, it is important to note that the predictive power of a single biomarker is limited, and future studies may consider combining other biomarkers or clinical indicators to improve the accuracy of predictions.
The detection of serum SLC31A1 holds multidimensional application potential in the clinical management of PTC. Specifically, serum SLC31A1 levels could serve as a non-invasive biomarker for postoperative risk stratification, allowing clinicians to identify high-risk patients (e.g., those with advanced TNM stage or poor differentiation) who may benefit from intensified surveillance or adjuvant therapies. Additionally, serial monitoring of SLC31A1 levels could aid in early detection of recurrence by reflecting tumor burden changes, complementing traditional imaging techniques. For treatment selection, high SLC31A1 expression may predict sensitivity to copper-targeted therapies (e.g., elesclomol) or inform combination strategies with other molecularly targeted agents (e.g., BRAF inhibitors in V600E-mutated tumors). Furthermore, integrating SLC31A1 into existing prognostic models (such as MACIS or AMES) could enhance their accuracy in predicting long-term outcomes. While these applications require validation in larger, multicenter cohorts, this study provides a foundational rationale for exploring SLC31A1 as a tool to guide personalized management of PTC patients.
In summary, the high expression of SLC31A1 in thyroid papillary carcinoma is associated to poor clinicopathological features and prognosis, and SLC31A1 may become a potential therapeutic target for PTC. Although this study provides important information about SLC31A1 in PTC, there are some limitations. The single-center design and relatively small sample size may limit result generalizability. Additionally, this study only discussed the relationship between the expression of SLC31A1 and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis, without further exploring its specific molecular mechanism. Future studies could further validate the mechanism of action of SLC31A1 in PTC through in vitro experiments and animal models, and explore its possibility as a potential therapeutic target.
-
Funding information: Authors state no funding involved.
-
Author contributions: C.H. submitted ethics approval, collected the data, and started the original draft of the manuscript. R.L. and T.Z. were the supervising investigators; they prepared the original elements of the protocol and supervised the data collection. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
-
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
-
Data availability statement: The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
[1] Wei X, Wang X, Xiong J, Li C, Liao Y, Zhu Y, et al. Risk and prognostic factors for BRAFV600E mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma. BioMed Res Int. 2022;2022:9959649.10.1155/2022/9959649Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[2] Lam AK. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: current position in epidemiology, genomics, and classification. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2022;2534:1–15.10.1007/978-1-0716-2505-7_1Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[3] Abdullah MI, Junit SM, Ng KL, Jayapalan JJ, Karikalan B, Hashim OH. Papillary thyroid cancer: genetic alterations and molecular biomarker investigations. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(3):450–60.10.7150/ijms.29935Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[4] Myint ZW, Oo TH, Thein KZ, Tun AM, Saeed H. Copper deficiency anemia: review article. Ann Hematol. 2018;97(9):1527–34.10.1007/s00277-018-3407-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[5] Ge EJ, Bush AI, Casini A, Cobine PA, Cross JR, DeNicola GM, et al. Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(2):102–13.10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[6] Tsang T, Posimo JM, Gudiel AA, Cicchini M, Feldser DM, Brady DC. Copper is an essential regulator of the autophagic kinases ULK1/2 to drive lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(4):412–24.10.1038/s41556-020-0481-4Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[7] Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang J, Yang Y, Fleishman JS, Wang Y, et al. Cuproptosis: a novel therapeutic target for overcoming cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat Rev Comment Antimicrob Anticancer Chemother. 2024;72:101018.10.1016/j.drup.2023.101018Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[8] Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, et al. Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):174.10.1186/s13045-022-01392-3Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[9] Guo B, Yang F, Zhang L, Zhao Q, Wang W, Yin L, et al. Cuproptosis induced by ROS responsive nanoparticles with elesclomol and copper combined with αPD-L1 for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Adv Mater Deerfield Beach Fla. 2023;35(22):e2212267.10.1002/adma.202212267Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[10] Qi Y, Yao Q, Li X, Li X, Zhang W, Qu P. Cuproptosis-related gene SLC31A1: Prognosis values and potential biological functions in cancer. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):17790.10.1038/s41598-023-44681-8Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[11] Mi J, Luo J, Zeng H, Zhang H, Jamil M, Abdel-Maksoud MA, et al. Elucidating cuproptosis-related gene SLC31A1 diagnostic and prognostic values in cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2023;15(10):6026–41.Search in Google Scholar
[12] Kong FS, Ren CY, Jia R, Zhou Y, Chen JH, Ma Y. Systematic pan-cancer analysis identifies SLC31A1 as a biomarker in multiple tumor types. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):61.10.1186/s12920-023-01489-9Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[13] Li L, Li L, Sun Q. High expression of cuproptosis-related SLC31A1 gene in relation to unfavorable outcome and deregulated immune cell infiltration in breast cancer: an analysis based on public databases. BMC Bioinf. 2022;23(1):350.10.1186/s12859-022-04894-6Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[14] Wu JH, Cheng TC, Zhu B, Gao HY, Zheng L, Chen WX. Identification of cuproptosis-related gene SLC31A1 and upstream LncRNA-miRNA regulatory axis in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18390.10.1038/s41598-023-45761-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[15] Wang J, Li S, Guo Y, Zhao C, Chen Y, Ning W, et al. Cuproptosis-related gene SLC31A1 expression correlates with the prognosis and tumor immune microenvironment in glioma. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(3):279.10.1007/s10142-023-01210-0Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[16] Wang L, Yao B, Yang J, Tian Z, He J. Construction of a novel cuproptosis-related gene signature for predicting prognosis and estimating tumor immune microenvironment status in papillary thyroid carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):1131.10.1186/s12885-022-10175-5Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[17] Huang J, Shi J, Wu P, Sun W, Zhang D, Wang Z, et al. Identification of a novel cuproptosis-related gene signature and integrative analyses in thyroid cancer. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):2014.10.3390/jcm12052014Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[18] Shi Y, Sheng P, Guo M, Chen K, Zhou H, Wu M, et al. Cuproptosis-related lncRNAs predict prognosis and immune response of thyroid carcinoma. Front Genet. 2023;14:1100909.10.3389/fgene.2023.1100909Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[19] Ywata de Carvalho A, Kohler HF, Gomes CC, Vartanian JG, Kowalski LP. Predictive factors for recurrence of papillary thyroid carcinoma: analysis of 4,085 patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital Organo Uff Della Soc Ital Otorinolaringol E Chir Cerv-facc. 2021;41(3):236–42.10.14639/0392-100X-N1412Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[20] Xu S, Huang H, Huang Y, Qian J, Wang X, Xu Z, et al. Comparison of lobectomy vs total thyroidectomy for intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma with lymph node metastasis. JAMA Surg. 2023;158(1):73–9.10.1001/jamasurg.2022.5781Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[21] Kong R, Sun G. Targeting copper metabolism: a promising strategy for cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1203447.10.3389/fphar.2023.1203447Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[22] He H, Zou Z, Wang B, Xu G, Chen C, Qin X, et al. Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and cell death via copper ion-mediated P38 MAPK activation in vascular endothelial cells. Int J Nanomed. 2020;15:3291–302.10.2147/IJN.S241157Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[23] Eckers A, Reimann K, Klotz LO. Nickel and copper ion-induced stress signaling in human hepatoma cells: analysis of phosphoinositide 3′-kinase/Akt signaling. Biometals Int J Role Met Ions Biol Biochem Med. 2009;22(2):307–16.10.1007/s10534-008-9167-2Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[24] Persichini T, Percario Z, Mazzon E, Colasanti M, Cuzzocrea S, Musci G. Copper activates the NF-kappaB pathway in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2006;8(9–10):1897–904.10.1089/ars.2006.8.1897Search in Google Scholar PubMed
[25] Gao L, Zhang A. Copper-instigated modulatory cell mortality mechanisms and progress in oncological treatment investigations. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1236063.10.3389/fimmu.2023.1236063Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[26] Wu G, Peng H, Tang M, Yang M, Wang J, Hu Y, et al. ZNF711 down-regulation promotes CISPLATIN resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer via interacting with JHDM2A and suppressing SLC31A1 expression. EBioMedicine. 2021;71:103558.10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103558Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[27] Cheng C, Ding Q, Zhang Z, Wang S, Zhong B, Huang X, et al. PTBP1 modulates osteosarcoma chemoresistance to cisplatin by regulating the expression of the copper transporter SLC31A1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9):5274–89.10.1111/jcmm.15183Search in Google Scholar PubMed PubMed Central
[28] Li Y, Ma J, Wang R, Luo Y, Zheng S, Wang X. Zinc transporter 1 functions in copper uptake and cuproptosis. Cell Metab. 2024;36(9):2118–29.e6.10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.009Search in Google Scholar PubMed
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- 10.1515/med-2025-1198
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms
Articles in the same Issue
- Research Articles
- Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro testing of the rutin effects on triple-negative breast cancer
- Impact of diabetes on long-term survival in elderly liver cancer patients: A retrospective study
- Knockdown of CCNB1 alleviates high glucose-triggered trophoblast dysfunction during gestational diabetes via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Risk factors for severe adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients
- Analysis of the effect of ALA-PDT on macrophages in footpad model of mice infected with Fonsecaea monophora based on single-cell sequencing
- Development and validation of headspace gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector method for the determination of ethanol in the vitreous humor
- CMSP exerts anti-tumor effects on small cell lung cancer cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis
- Predictive value of plasma sB7-H3 and YKL-40 in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Antiangiogenic potential of Elaeagnus umbellata extracts and molecular docking study by targeting VEGFR-2 pathway
- Comparison of the effectiveness of nurse-led preoperative counseling and postoperative follow-up care vs standard care for patients with gastric cancer
- Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis
- Adhered macrophages as an additional marker of cardiomyocyte injury in biopsies of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy
- Association between statin administration and outcome in patients with sepsis: A retrospective study
- Exploration of the association between estimated glucose disposal rate and osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults: An analysis of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
- A comparative analysis of the binary and multiclass classified chest X-ray images of pneumonia and COVID-19 with ML and DL models
- Lysophosphatidic acid 2 alleviates deep vein thrombosis via protective endothelial barrier function
- Transcription factor A, mitochondrial promotes lymph node metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
- Serum PM20D1 levels are associated with nutritional status and inflammatory factors in gastric cancer patients undergoing early enteral nutrition
- Hydromorphone reduced the incidence of emergence agitation after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea: A randomized, double-blind study
- Vitamin D replacement therapy may regulate sleep habits in patients with restless leg syndrome
- The first-line antihypertensive nitrendipine potentiated the therapeutic effect of oxaliplatin by downregulating CACNA1D in colorectal cancer
- Health literacy and health-related quality of life: The mediating role of irrational happiness
- Modulatory effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on bone cell dynamics in osteoporosis
- Mechanism research on inhibition of gastric cancer in vitro by the extract of Pinellia ternata based on network pharmacology and cellular metabolomics
- Examination of the causal role of immune cells in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Clinical analysis of ten cases of HIV infection combined with acute leukemia
- Investigating the cardioprotective potential of quercetin against tacrolimus-induced cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats: A mechanistic insights
- Clinical observation of probiotics combined with mesalazine and Yiyi Baitouweng Decoction retention enema in treating mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis
- Diagnostic value of ratio of blood inflammation to coagulation markers in periprosthetic joint infection
- Sex-specific associations of sex hormone binding globulin and risk of bladder cancer
- Core muscle strength and stability-oriented breathing training reduces inter-recti distance in postpartum women
- The ERAS nursing care strategy for patients undergoing transsphenoidal endoscopic pituitary tumor resection: A randomized blinded controlled trial
- The serum IL-17A levels in patients with traumatic bowel rupture post-surgery and its predictive value for patient prognosis
- Impact of Kolb’s experiential learning theory-based nursing on caregiver burden and psychological state of caregivers of dementia patients
- Analysis of serum NLR combined with intraoperative margin condition to predict the prognosis of cervical HSIL patients undergoing LEEP surgery
- Commiphora gileadensis ameliorate infertility and erectile dysfunction in diabetic male mice
- The correlation between epithelial–mesenchymal transition classification and MMP2 expression of circulating tumor cells and prognosis of advanced or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Tetrahydropalmatine improves mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells of atherosclerosis in vitro by inhibiting Ras homolog gene family A/Rho-associated protein kinase-1 signaling pathway
- A cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum oxidative stress levels and arteriovenous fistula maturation in maintenance dialysis patients
- A comparative analysis of the impact of repeated administration of flavan 3-ol on brown, subcutaneous, and visceral adipose tissue
- Identifying early screening factors for depression in middle-aged and older adults: A cohort study
- Perform tumor-specific survival analysis for Merkel cell carcinoma patients undergoing surgical resection based on the SEER database by constructing a nomogram chart
- Unveiling the role of CXCL10 in pancreatic cancer progression: A novel prognostic indicator
- High-dose preoperative intraperitoneal erythropoietin and intravenous methylprednisolone in acute traumatic spinal cord injuries following decompression surgeries
- RAB39B: A novel biomarker for acute myeloid leukemia identified via multi-omics and functional validation
- Impact of peripheral conditioning on reperfusion injury following primary percutaneous coronary intervention in diabetic and non-diabetic STEMI patients
- Clinical efficacy of azacitidine in the treatment of middle- and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome in middle-aged and elderly patients: A retrospective study
- The effect of ambulatory blood pressure load on mitral regurgitation in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients
- Expression and clinical significance of ITGA3 in breast cancer
- Single-nucleus RNA sequencing reveals ARHGAP28 expression of podocytes as a biomarker in human diabetic nephropathy
- rSIG combined with NLR in the prognostic assessment of patients with multiple injuries
- Toxic metals and metalloids in collagen supplements of fish and jellyfish origin: Risk assessment for daily intake
- Exploring causal relationship between 41 inflammatory cytokines and marginal zone lymphoma: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Gender beliefs and legitimization of dating violence in adolescents
- Effect of serum IL-6, CRP, and MMP-9 levels on the efficacy of modified preperitoneal Kugel repair in patients with inguinal hernia
- Effect of smoking and smoking cessation on hematological parameters in polycythemic patients
- Pathogen surveillance and risk factors for pulmonary infection in patients with lung cancer: A retrospective single-center study
- Necroptosis of hippocampal neurons in paclitaxel chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment mediates microglial activation via TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway
- Celastrol suppresses neovascularization in rat aortic vascular endothelial cells stimulated by inflammatory tenocytes via modulating the NLRP3 pathway
- Cord-lamina angle and foraminal diameter as key predictors of C5 palsy after anterior cervical decompression and fusion surgery
- GATA1: A key biomarker for predicting the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Influencing factors of false lumen thrombosis in type B aortic dissection: A single-center retrospective study
- MZB1 regulates the immune microenvironment and inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration
- Integrating experimental and network pharmacology to explore the pharmacological mechanisms of Dioscin against glioblastoma
- Trends in research on preterm birth in twin pregnancy based on bibliometrics
- Four-week IgE/baseline IgE ratio combined with tryptase predicts clinical outcome in omalizumab-treated children with moderate-to-severe asthma
- Single-cell transcriptomic analysis identifies a stress response Schwann cell subtype
- Acute pancreatitis risk in the diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease: A critical focus
- Effect of subclinical esketamine on NLRP3 and cognitive dysfunction in elderly ischemic stroke patients
- Interleukin-37 mediates the anti-oral tumor activity in oral cancer through STAT3
- CA199 and CEA expression levels, and minimally invasive postoperative prognosis analysis in esophageal squamous carcinoma patients
- Efficacy of a novel drainage catheter in the treatment of CSF leak after posterior spine surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- Comprehensive biomedicine assessment of Apteranthes tuberculata extracts: Phytochemical analysis and multifaceted pharmacological evaluation in animal models
- Relation of time in range to severity of coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Dopamine attenuates ethanol-induced neuronal apoptosis by stimulating electrical activity in the developing rat retina
- Correlation between albumin levels during the third trimester and the risk of postpartum levator ani muscle rupture
- Factors associated with maternal attention and distraction during breastfeeding and childcare: A cross-sectional study in the west of Iran
- Mechanisms of hesperetin in treating metabolic dysfunction-associated steatosis liver disease via network pharmacology and in vitro experiments
- The law on oncological oblivion in the Italian and European context: How to best uphold the cancer patients’ rights to privacy and self-determination?
- The prognostic value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and prognostic nutritional index for survival in patients with colorectal cancer
- Factors affecting the measurements of peripheral oxygen saturation values in healthy young adults
- Comparison and correlations between findings of hysteroscopy and vaginal color Doppler ultrasonography for detection of uterine abnormalities in patients with recurrent implantation failure
- The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital
- Causal relationship between asthma and ankylosing spondylitis: A bidirectional two-sample univariable and multivariable Mendelian randomization study
- Correlations of health literacy with individuals’ understanding and use of medications in Southern Taiwan
- Correlation of serum calprotectin with outcome of acute cerebral infarction
- Comparison of computed tomography and guided bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Curdione protects vascular endothelial cells and atherosclerosis via the regulation of DNMT1-mediated ERBB4 promoter methylation
- The identification of novel missense variant in ChAT gene in a patient with gestational diabetes denotes plausible genetic association
- Molecular genotyping of multi-system rare blood types in foreign blood donors based on DNA sequencing and its clinical significance
- Exploring the role of succinyl carnitine in the association between CD39⁺ CD4⁺ T cell and ulcerative colitis: A Mendelian randomization study
- Dexmedetomidine suppresses microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via the mmu-miRNA-125/TRAF6 signaling axis
- Analysis of serum metabolomics in patients with different types of chronic heart failure
- Diagnostic value of hematological parameters in the early diagnosis of acute cholecystitis
- Pachymaran alleviates fat accumulation, hepatocyte degeneration, and injury in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Decrease in CD4 and CD8 lymphocytes are predictors of severe clinical picture and unfavorable outcome of the disease in patients with COVID-19
- METTL3 blocked the progression of diabetic retinopathy through m6A-modified SOX2
- The predictive significance of anti-RO-52 antibody in patients with interstitial pneumonia after treatment of malignant tumors
- Exploring cerebrospinal fluid metabolites, cognitive function, and brain atrophy: Insights from Mendelian randomization
- Development and validation of potential molecular subtypes and signatures of ocular sarcoidosis based on autophagy-related gene analysis
- Widespread venous thrombosis: Unveiling a complex case of Behçet’s disease with a literature perspective
- Uterine fibroid embolization: An analysis of clinical outcomes and impact on patients’ quality of life
- Discovery of lipid metabolism-related diagnostic biomarkers and construction of diagnostic model in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head
- Serum-derived exomiR-188-3p is a promising novel biomarker for early-stage ovarian cancer
- Enhancing chronic back pain management: A comparative study of ultrasound–MRI fusion guidance for paravertebral nerve block
- Peptide CCAT1-70aa promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and invasion via the MAPK/ERK pathway
- Electroacupuncture-induced reduction of myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury via FTO-dependent m6A methylation modulation
- Hemorrhoids and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Cell-free adipose extract inhibits hypertrophic scar formation through collagen remodeling and antiangiogenesis
- HALP score in Demodex blepharitis: A case–control study
- Assessment of SOX2 performance as a marker for circulating cancer stem-like cells (CCSCs) identification in advanced breast cancer patients using CytoTrack system
- Risk and prognosis for brain metastasis in primary metastatic cervical cancer patients: A population-based study
- Comparison of the two intestinal anastomosis methods in pediatric patients
- Factors influencing hematological toxicity and adverse effects of perioperative hyperthermic intraperitoneal vs intraperitoneal chemotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer
- Endotoxin tolerance inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages of septic mice by restoring autophagic flux through TRIM26
- Lateral transperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy: A single-centre experience of 21 procedures
- Petunidin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced retinal microglia inflammatory response in diabetic retinopathy by targeting OGT/NF-κB/LCN2 axis
- Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as biomarkers for diagnosing and assessing the severity of acute cholecystitis
- Factors determining the number of sessions in successful extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy patients
- Development of a nomogram for predicting cancer-specific survival in patients with renal pelvic cancer following surgery
- Inhibition of ATG7 promotes orthodontic tooth movement by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio under compression force
- A machine learning-based prognostic model integrating mRNA stemness index, hypoxia, and glycolysis‑related biomarkers for colorectal cancer
- Glutathione attenuates sepsis-associated encephalopathy via dual modulation of NF-κB and PKA/CREB pathways
- FAHD1 prevents neuronal ferroptosis by modulating R-loop and the cGAS–STING pathway
- Association of placenta weight and morphology with term low birth weight: A case–control study
- Investigation of the pathogenic variants induced Sjogren’s syndrome in Turkish population
- Nucleotide metabolic abnormalities in post-COVID-19 condition and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and their association with endocrine dysfunction
- TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling in high-altitude pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role and mechanisms via macrophage M2 polarization
- Ultrasound-guided unilateral versus bilateral erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia of patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy
- Profiling gut microbiome dynamics in subacute thyroiditis: Implications for pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment
- Delta neutrophil index, CRP/albumin ratio, procalcitonin, immature granulocytes, and HALP score in acute appendicitis: Best performing biomarker?
- Anticancer activity mechanism of novelly synthesized and characterized benzofuran ring-linked 3-nitrophenyl chalcone derivative on colon cancer cells
- H2valdien3 arrests the cell cycle and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer
- Prognostic relevance of PRSS2 and its immune correlates in papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Association of SGLT2 inhibition with psychiatric disorders: A Mendelian randomization study
- Motivational interviewing for alcohol use reduction in Thai patients
- 10.1515/med-2025-1198
- Polyphyllin II inhibits thyroid cancer cell growth by simultaneously inhibiting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation
- Relationship between the expression of copper death promoting factor SLC31A1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma and clinicopathological indicators and prognosis
- CSF2 polarized neutrophils and invaded renal cancer cells in vitro influence
- Proton pump inhibitors-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic literature analysis of case reports
- The current status and influence factors of research ability among community nurses: A sequential qualitative–quantitative study
- OKAIN: A comprehensive oncology knowledge base for the interpretation of clinically actionable alterations
- The relationship between serum CA50, CA242, and SAA levels and clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
- Identification and external validation of a prognostic signature based on hypoxia–glycolysis-related genes for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma
- Engineered RBC-derived nanovesicles functionalized with tumor-targeting ligands: A comparative study on breast cancer targeting efficiency and biocompatibility
- Review Articles
- The effects of enhanced external counter-pulsation on post-acute sequelae of COVID-19: A narrative review
- Diabetes-related cognitive impairment: Mechanisms, symptoms, and treatments
- Microscopic changes and gross morphology of placenta in women affected by gestational diabetes mellitus in dietary treatment: A systematic review
- Review of mechanisms and frontier applications in IL-17A-induced hypertension
- Research progress on the correlation between islet amyloid peptides and type 2 diabetes mellitus
- The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- The application of augmented reality in robotic general surgery: A mini-review
- The effect of Greek mountain tea extract and wheat germ extract on peripheral blood flow and eicosanoid metabolism in mammals
- Neurogasobiology of migraine: Carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and nitric oxide as emerging pathophysiological trinacrium relevant to nociception regulation
- Plant polyphenols, terpenes, and terpenoids in oral health
- Laboratory medicine between technological innovation, rights safeguarding, and patient safety: A bioethical perspective
- End-of-life in cancer patients: Medicolegal implications and ethical challenges in Europe
- The maternal factors during pregnancy for intrauterine growth retardation: An umbrella review
- Intra-abdominal hypertension/abdominal compartment syndrome of pediatric patients in critical care settings
- PI3K/Akt pathway and neuroinflammation in sepsis-associated encephalopathy
- Screening of Group B Streptococcus in pregnancy: A systematic review for the laboratory detection
- Giant borderline ovarian tumours – review of the literature
- Leveraging artificial intelligence for collaborative care planning: Innovations and impacts in shared decision-making – A systematic review
- Cholera epidemiology analysis through the experience of the 1973 Naples epidemic
- Risk factors of frailty/sarcopenia in community older adults: Meta-analysis
- Supplement strategies for infertility in overweight women: Evidence and legal insights
- Scurvy, a not obsolete disorder: Clinical report in eight young children and literature review
- A meta-analysis of the effects of DBS on cognitive function in patients with advanced PD
- Protective role of selenium in sepsis: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies
- Strategies for hyperkalemia management in dialysis patients: A systematic review
- Case Reports
- Delayed graft function after renal transplantation
- Semaglutide treatment for type 2 diabetes in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia: A case report and review of the literature
- Diverse electrophysiological demyelinating features in a late-onset glycogen storage disease type IIIa case
- Giant right atrial hemangioma presenting with ascites: A case report
- Laser excision of a large granular cell tumor of the vocal cord with subglottic extension: A case report
- EsoFLIP-assisted dilation for dysphagia in systemic sclerosis: Highlighting the role of multimodal esophageal evaluation
- Molecular hydrogen-rhodiola as an adjuvant therapy for ischemic stroke in internal carotid artery occlusion: A case report
- Coronary artery anomalies: A case of the “malignant” left coronary artery and its surgical management
- Rapid Communication
- Biological properties of valve materials using RGD and EC
-
A single oral administration of flavanols enhances short
-term memory in mice along with increased brain-derived neurotrophic factor - Letter to the Editor
- Role of enhanced external counterpulsation in long COVID
- Expression of Concern
- Expression of concern “A ceRNA network mediated by LINC00475 in papillary thyroid carcinoma”
- Expression of concern “Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates spinal cord injury through the miR-301a/KLF7 axis to activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway”
- Expression of concern “circ_0020123 promotes cell proliferation and migration in lung adenocarcinoma via PDZD8”
- Corrigendum
- Corrigendum to “Empagliflozin improves aortic injury in obese mice by regulating fatty acid metabolism”
- Corrigendum to “Comparing the therapeutic efficacy of endoscopic minimally invasive surgery and traditional surgery for early-stage breast cancer: A meta-analysis”
- Corrigendum to “The progress of autoimmune hepatitis research and future challenges”
- Retraction
- Retraction of “miR-654-5p promotes gastric cancer progression via the GPRIN1/NF-κB pathway”
- Retraction of: “LncRNA CASC15 inhibition relieves renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through downregulating SP-A by sponging to miR-424”
- Retraction of: “SCARA5 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via inactivating the STAT3 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways”
- Special Issue Advancements in oncology: bridging clinical and experimental research - Part II
- Unveiling novel biomarkers for platinum chemoresistance in ovarian cancer
- Lathyrol affects the expression of AR and PSA and inhibits the malignant behavior of RCC cells
- The era of increasing cancer survivorship: Trends in fertility preservation, medico-legal implications, and ethical challenges
- Bone scintigraphy and positron emission tomography in the early diagnosis of MRONJ
- Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer
- Special Issue Computational Intelligence Methodologies Meets Recurrent Cancers - Part IV
- Exploration of mRNA-modifying METTL3 oncogene as momentous prognostic biomarker responsible for colorectal cancer development
- Special Issue The evolving saga of RNAs from bench to bedside - Part III
- Interaction and verification of ferroptosis-related RNAs Rela and Stat3 in promoting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
- The mRNA MOXD1: Link to oxidative stress and prognostic significance in gastric cancer
- Special Issue Exploring the biological mechanism of human diseases based on MultiOmics Technology - Part II
- Dynamic changes in lactate-related genes in microglia and their role in immune cell interactions after ischemic stroke
- A prognostic model correlated with fatty acid metabolism in Ewing’s sarcoma based on bioinformatics analysis
- Red cell distribution width predicts early kidney injury: A NHANES cross-sectional study
- Special Issue Diabetes mellitus: pathophysiology, complications & treatment
- Nutritional risk assessment and nutritional support in children with congenital diabetes during surgery
- Correlation of the differential expressions of RANK, RANKL, and OPG with obesity in the elderly population in Xinjiang
- A discussion on the application of fluorescence micro-optical sectioning tomography in the research of cognitive dysfunction in diabetes
- A review of brain research on T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction
- Metformin and estrogen modulation in LABC with T2DM: A 36-month randomized trial
- Special Issue Innovative Biomarker Discovery and Precision Medicine in Cancer Diagnostics
- CircASH1L-mediated tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer: PI3K/AKT pathway mechanisms

